Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Site and Data
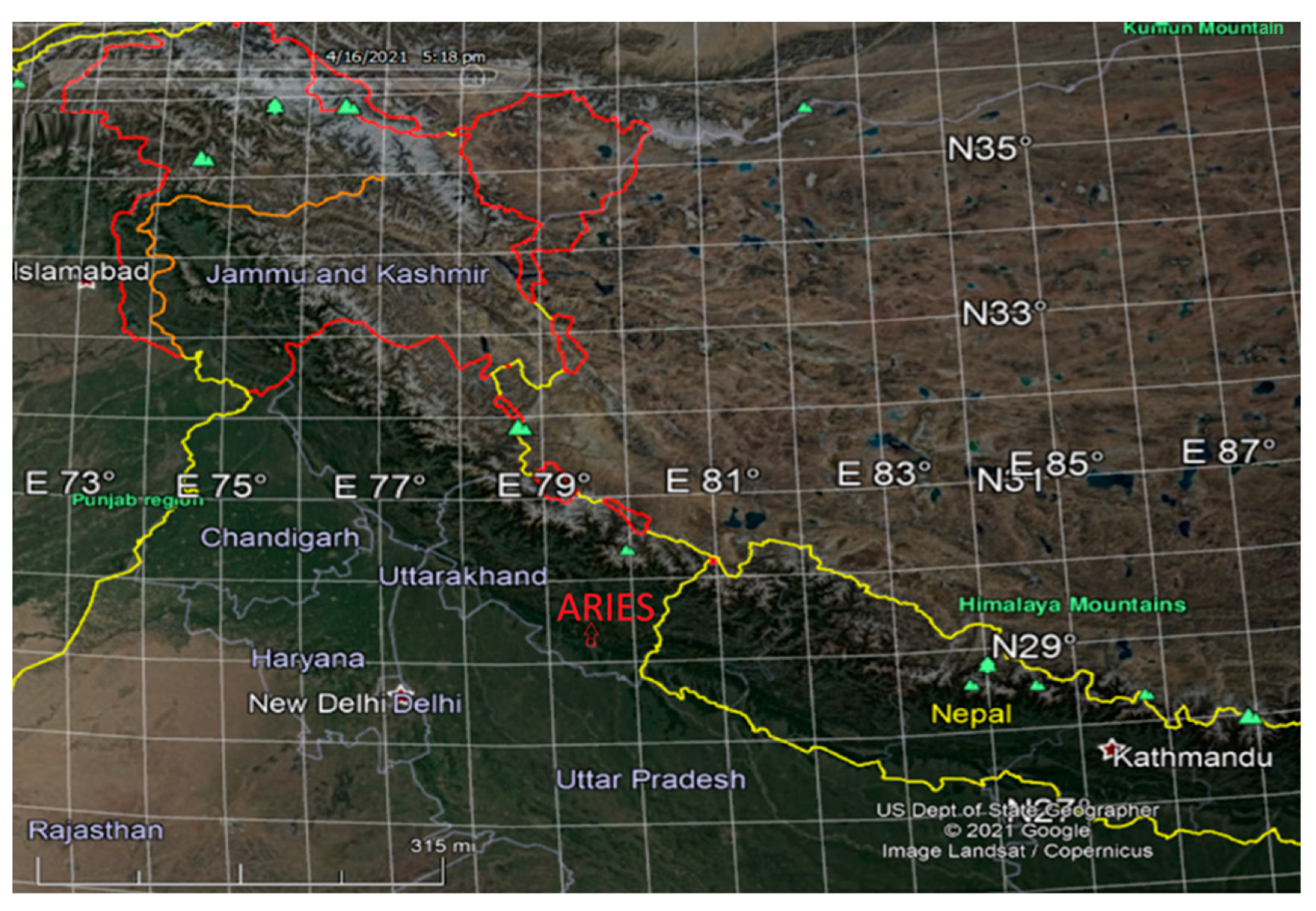
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Data Used
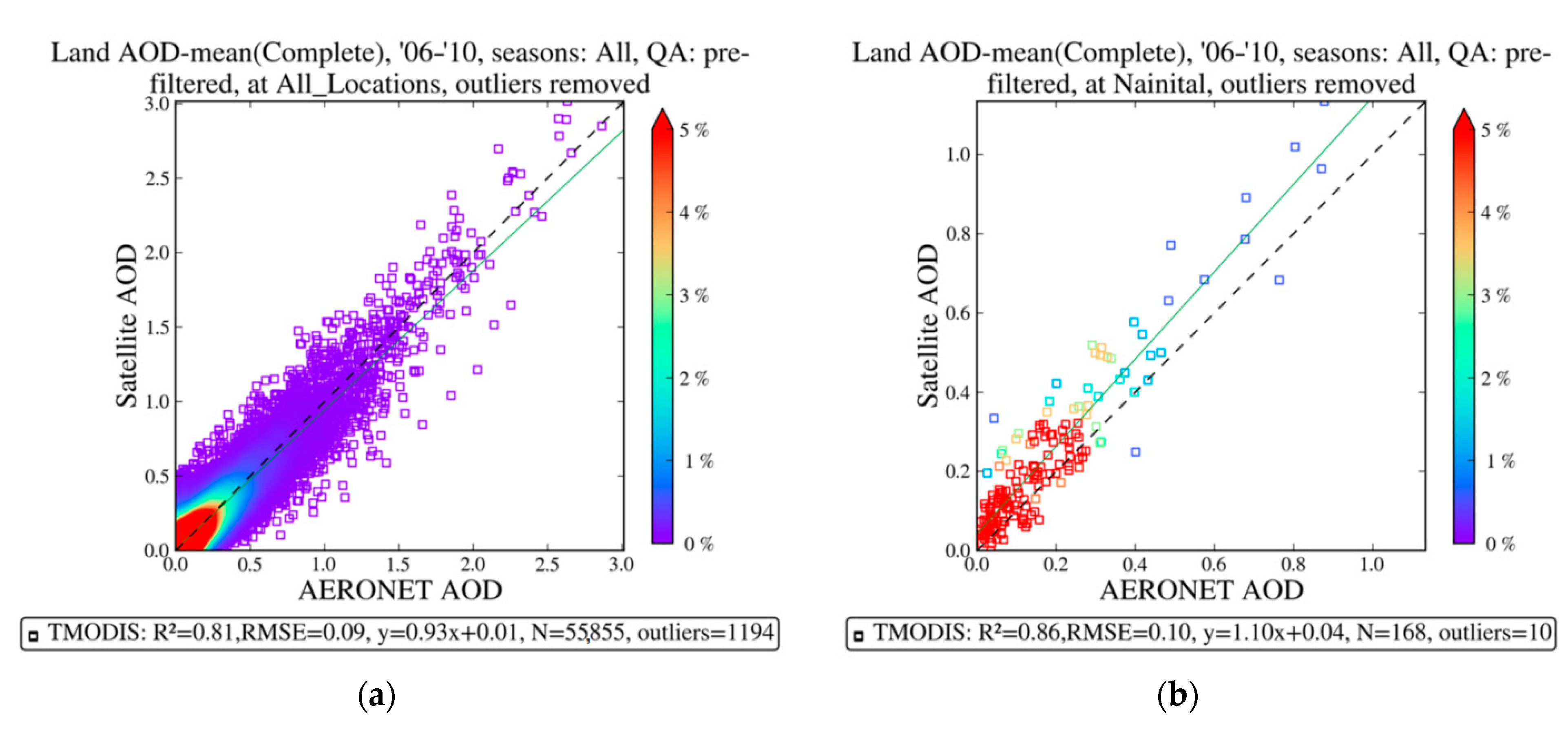
2.2.1. AERONET Sun Photometer
2.2.2. Model Forecasts
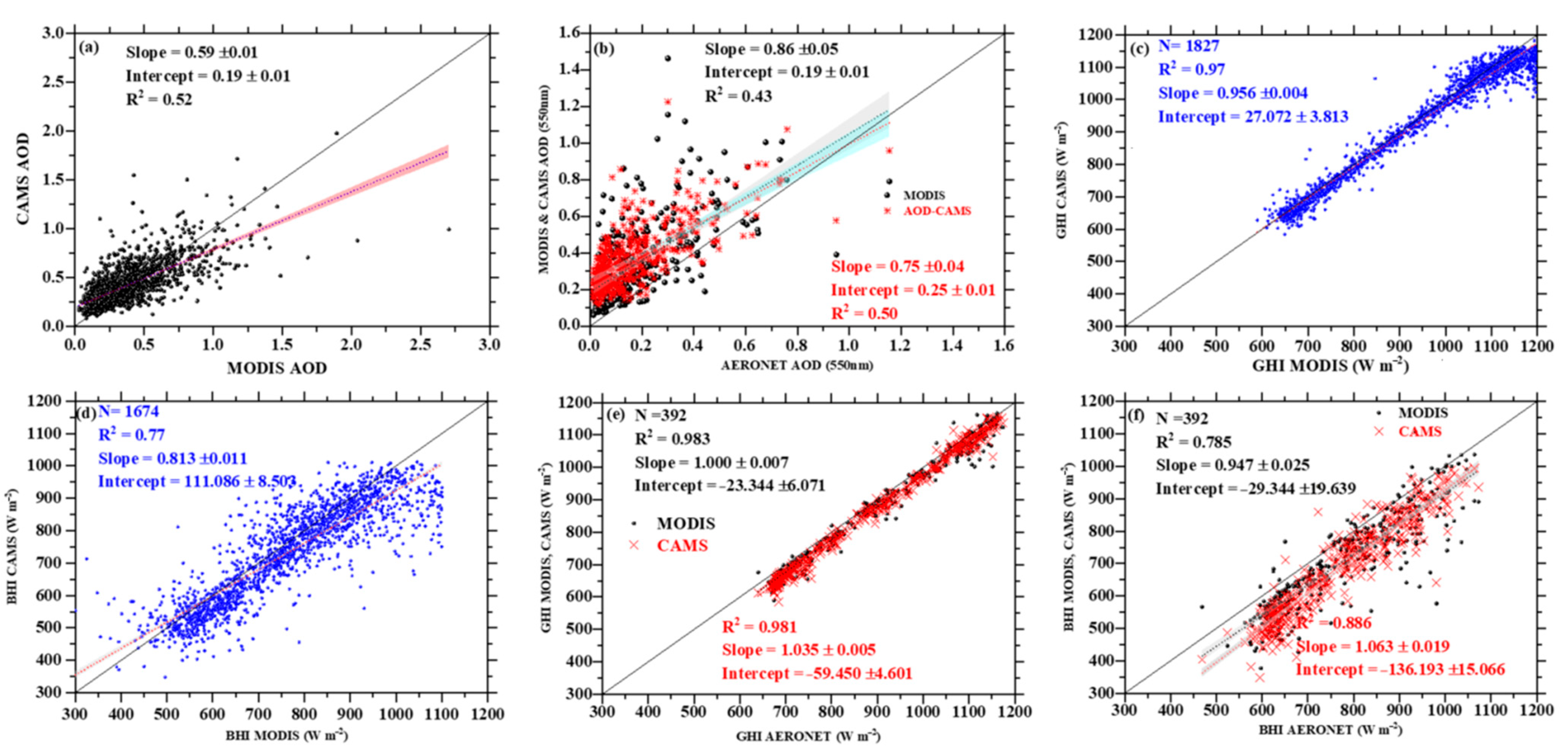
2.2.3. Satellite Observations
3. Methodology
3.1. Radiative Transfer Model
3.2. Financial Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
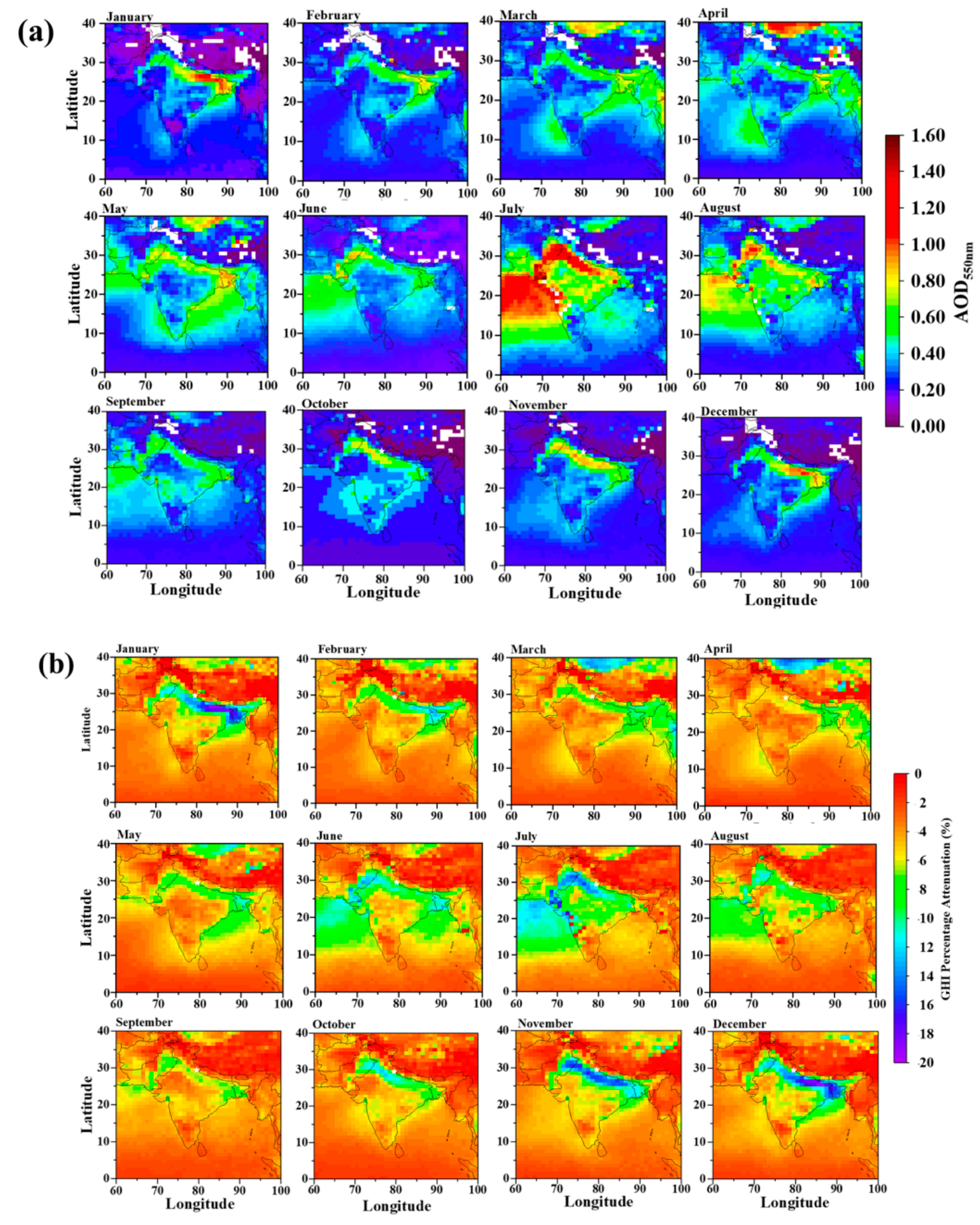
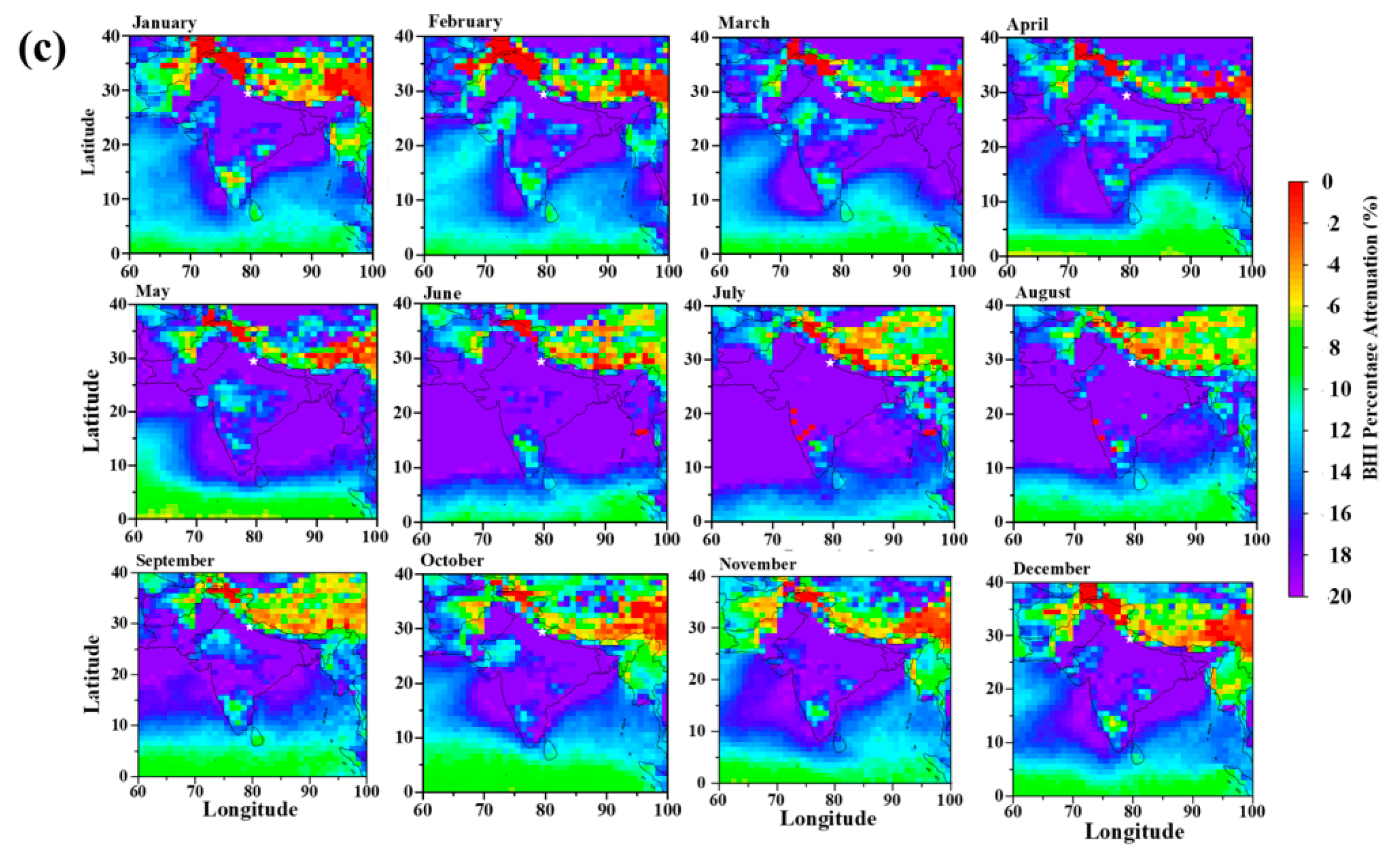
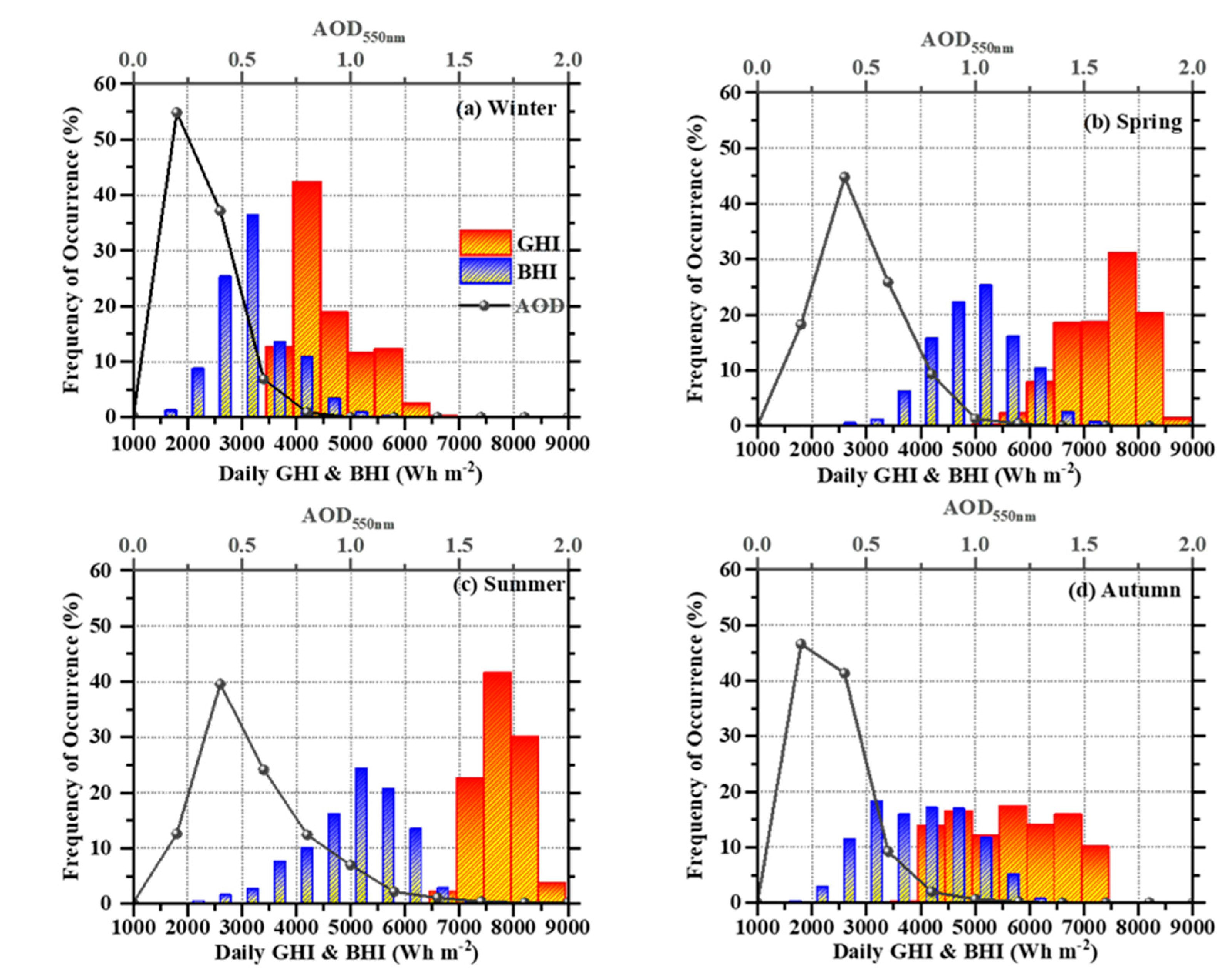
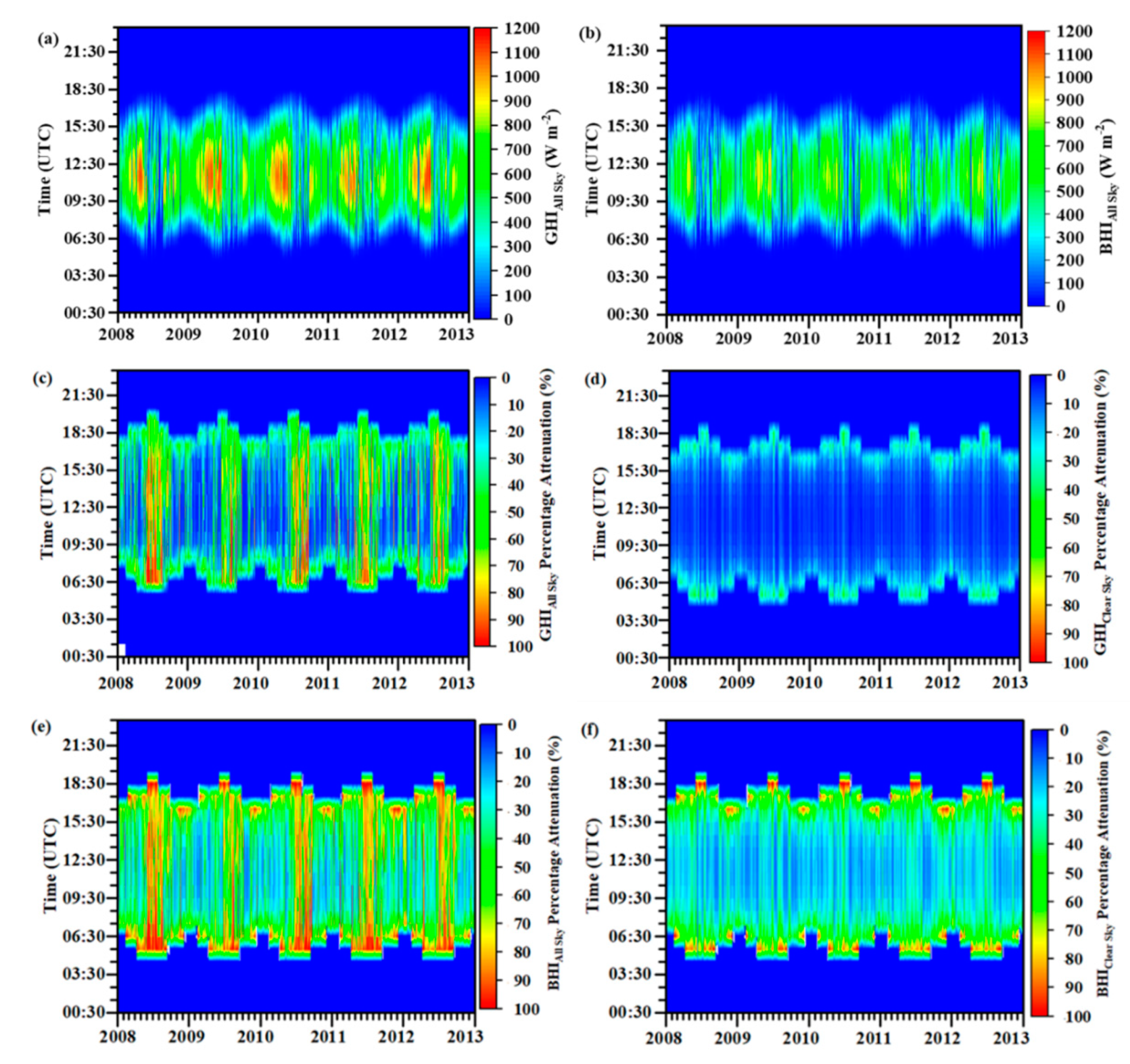
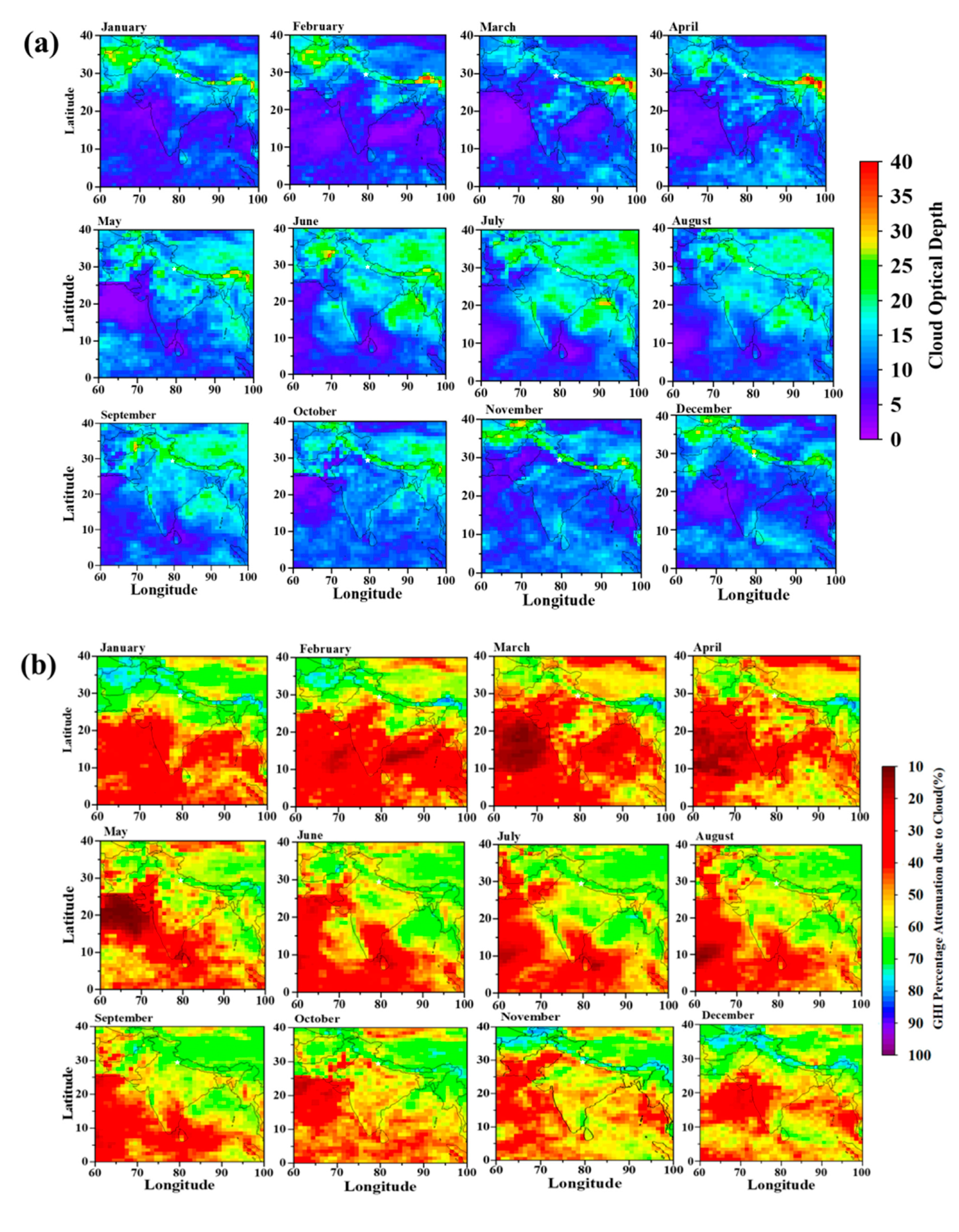
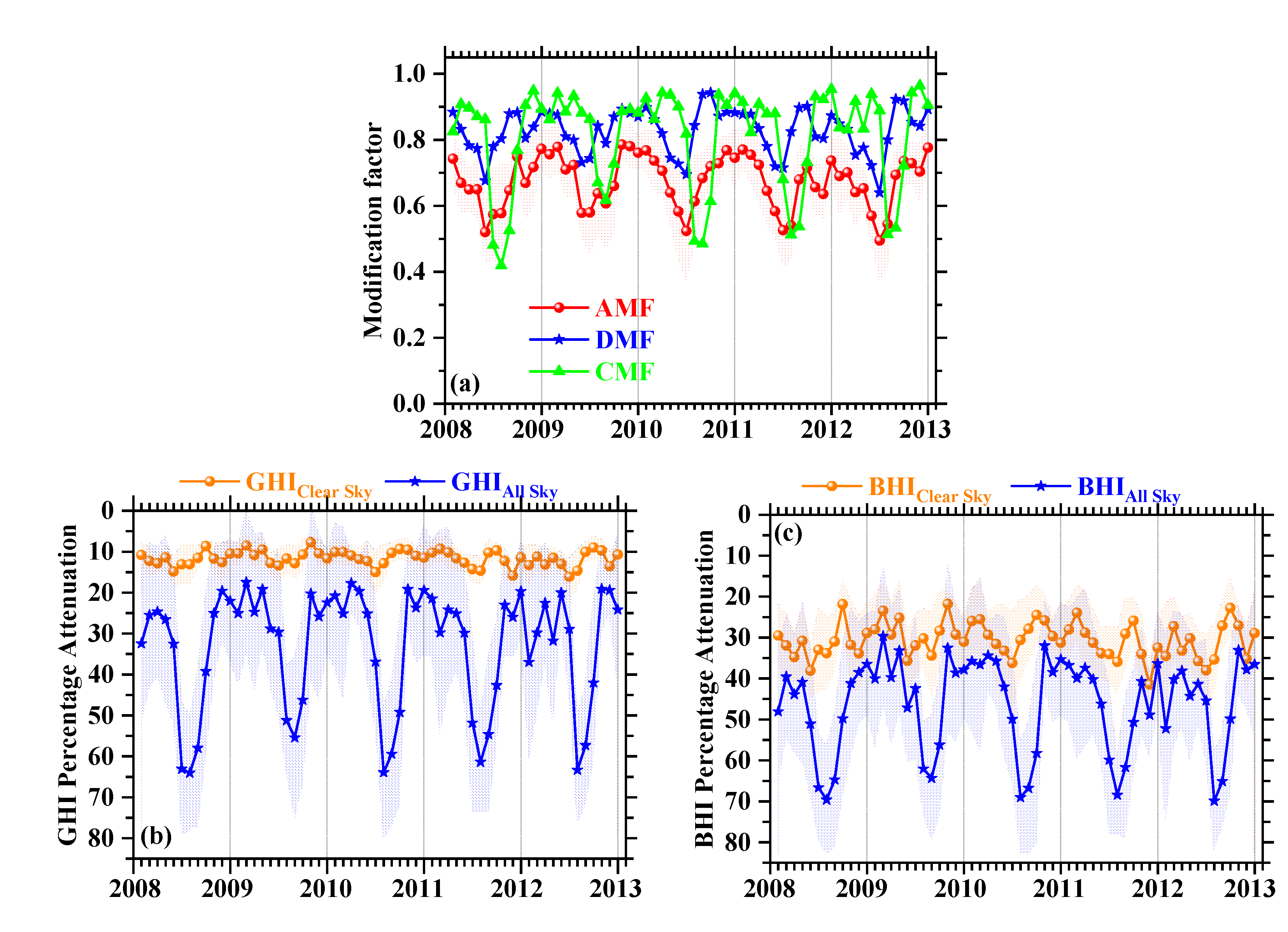
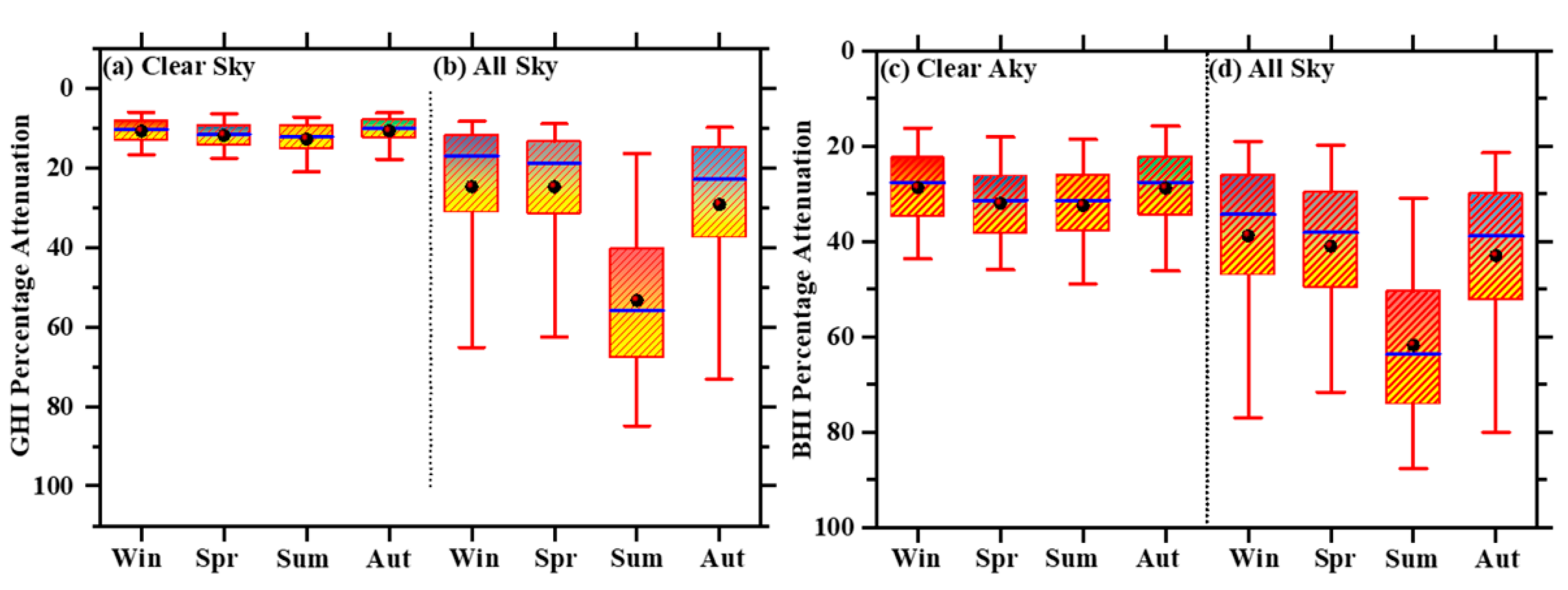
4.1. Clear-Sky Effect on Solar Energy
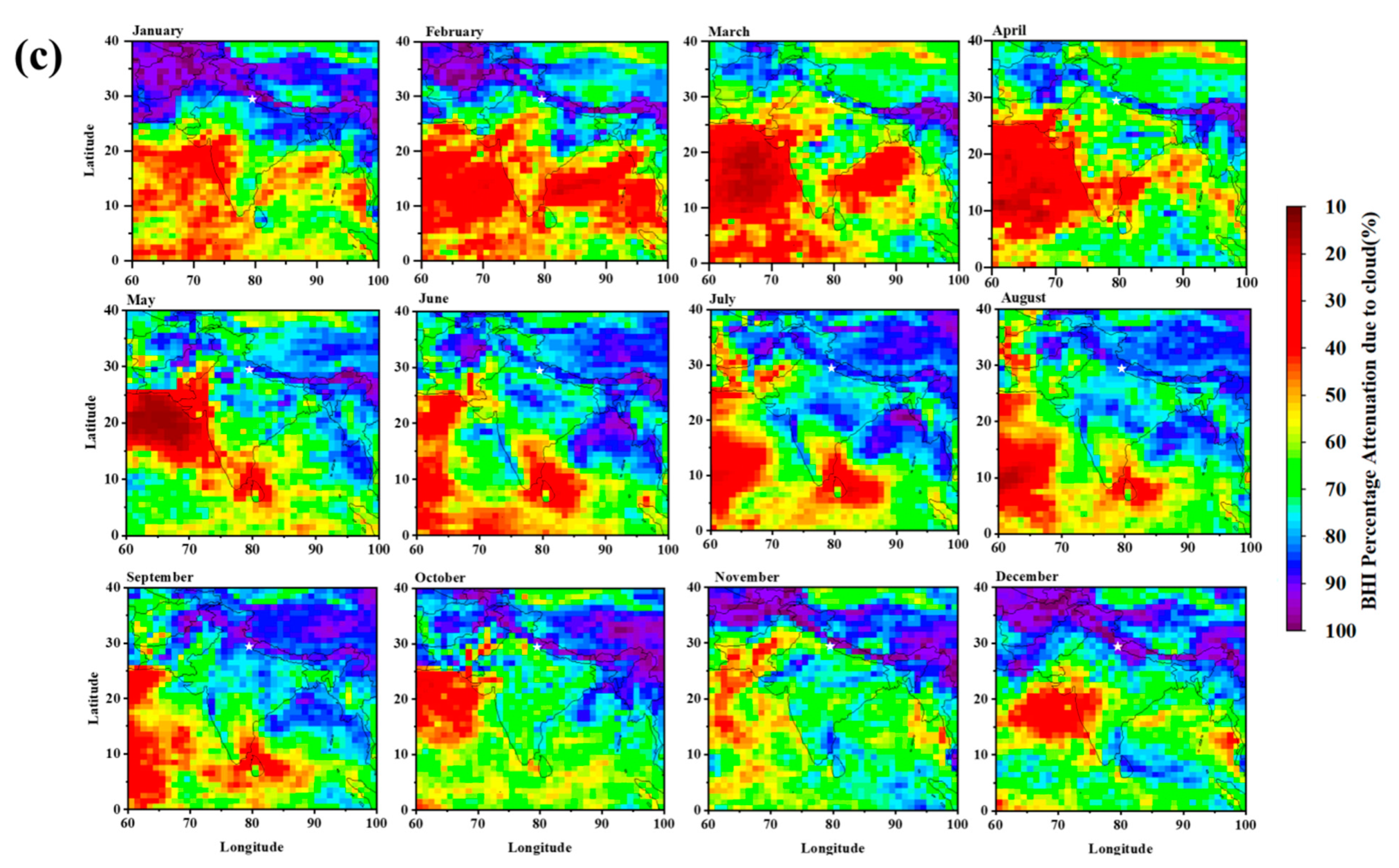
4.2. All-Sky Effect on Solar Energy
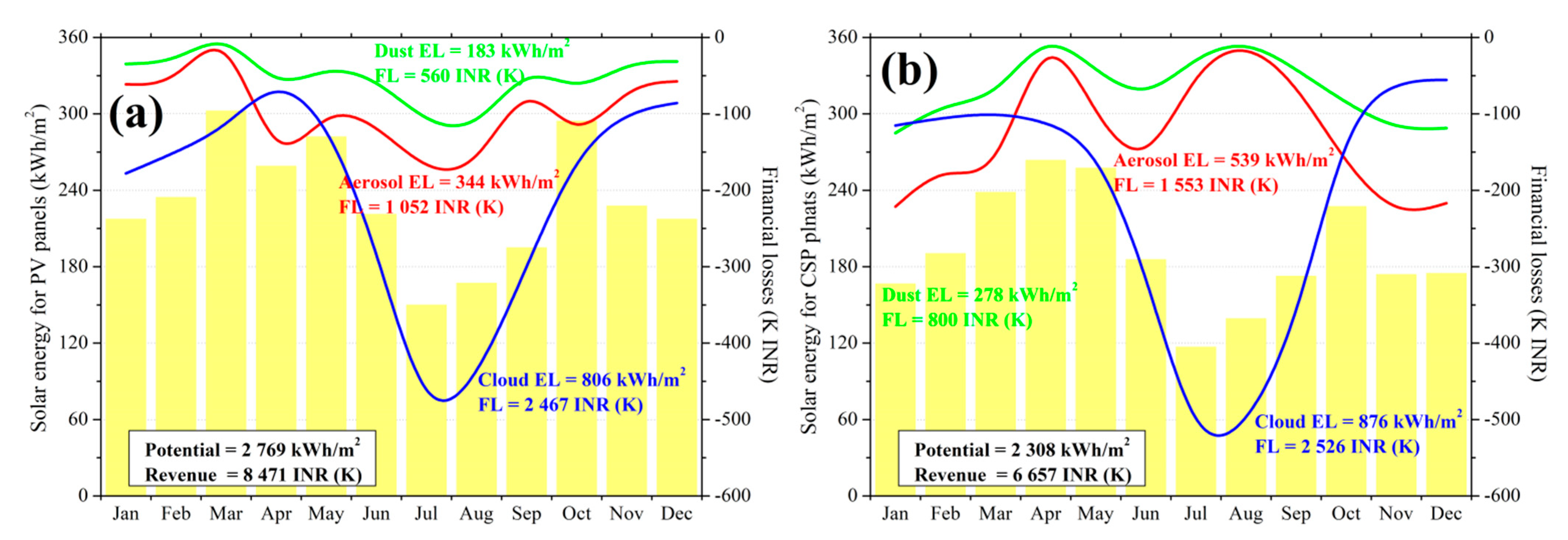
4.3. Economic Impact
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Seasons | Aerosol Optical Depth at 550 nm | AMF ± SD | DMF ± SD | CMF ± SD | |||
| MODIS Mean ± SD | CAMS AOD Mean ± SD | CAMS Dust Mean ± SD | Aeronet AOD Mean ± SD | ||||
| Winter | 0.25 ± 0.16 | 0.30 ± 0.12 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.23 | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 0.89 ± 0.15 |
| Spring | 0.46 ± 0.23 | 0.47 ± 0.18 | 0.28 ± 0.11 | 0.36 ± 0.22 | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.64 ± 0.11 | 0.90 ± 0.12 |
| Summer | 0.55 ± 0.34 | 0.55 ± 0.27 | 0.23 ± 0.18 | 0.35 ± 0.17 | 0.60 ± 0.14 | 0.60 ± 0.14 | 0.60 ± 0.24 |
| Autumn | 0.27 ± 0.20 | 0.34 ± 0.15 | 0.15 ± 0.07 | 0.38 ± 0.23 | 0.72 ± 0.09 | 0.72 ± 0.09 | 0.85 ± 0.18 |
| Global horizontal Irradiance (KWh m−2) | Beam horizontal Irradiance (KWh m−2) | ||||||
| All Sky ± SD | Clear Sky ± SD | Clean Sky ± SD | All Sky ± SD | Clear sky ± SD | Clean Sky ± SD | ||
| Winter | 222.84 ± 74.26 | 267.80 ± 43.11 | 287.58 ± 43.38 | 176.96 ± 64.43 | 208.67 ± 40.75 | 278.67 ± 35.31 | |
| Spring | 281.49 ± 78.71 | 311.46 ± 58.57 | 337.83 ± 56.26 | 253.20 ± 79.66 | 293.61 ± 51.49 | 325.24 ± 55.84 | |
| Summer | 179.06 ± 90.33 | 313.91 ± 59.99 | 364.81 ± 49.01 | 146.99 ± 84.20 | 304.86 ± 54.97 | 321.17 ± 61.22 | |
| Autumn | 239.67 ± 87.64 | 299.13 ± 68.79 | 316.77 ± 74.60 | 191.79 ± 72.82 | 253.95 ± 68.20 | 307.43 ± 71.28 | |
References
- Ellabban, O.; Abu-Rub, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Renewable energy resources: Current status, future prospects and their enabling technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Saygin, D.; Wagner, N.; Ghosh, A.; Chawla, K. Renewable Energy Prospects for India, a Working Paper Based on REmap; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strat. Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarli, M.S.; Salvarli, H. For sustainable development: Future trends in renewable energy and enabling technologies, Renewable Energy-Resources, Challenges and Applications. IntechOpen 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.C.R.; Majid, M.A. Renewable energy for sustainable development in India: Current status, future prospects, challenges, employment, and investment opportunities. Sustain. Soc. 2020, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Otani, K.; Takashima, T.; Xue, Y. Solar spectral influence on the performance of photovoltaic (PV) modules under fine weather and cloudy weather conditions. Prog. Photovolt. 2013, 21, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Norris, J.R.; Wild, M. Evaluation of multi decadal variability in CMIP5 surface solar radiation and inferred underestimation of aerosol direct effects over Europe, China, Japan, and India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6311–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirnberger, D.; Blackburn, G.; Muller, B.; Reise, C. On the impact of solar spectral irradiance on the yield of different PV technologies. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 132, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Bais, A. Solar energy prediction and verification using operational model forecasts and ground-based solar measurements. Energy 2015, 93, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Peng, W.; Wagner, F.; Mauzerall, D.L. Climate, air quality and human health benefits of various solar photovoltaic deployment scenarios in China in 2030. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M. An Introduction to Solar Radiation; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; ISBN 978-0-12-373750-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielicki, B.; Cess, R.D.; King, M.D.; Randall, D.A.; Harrison, E.F. Mission to planet Earth: Role of clouds and radiation in climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 2125–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, Climate, and the Hydrological Cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, S.; Girolamo, L.D. A climatology of aerosol optical and microphysical properties over the Indian subcontinent from 9 years (2000–2008) of Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) data. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moorthy, K.K.; Babu, S.S.; Manoj, M.R.; Satheesh, S.K. Buildup of aerosols over the Indian region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Srivastava, M.K.; Devara, P.C.S. Scattering and absorption properties of near-surface aerosol over Gangetic–Himalayan region: The role of boundary-layer dynamics and long-range transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1555–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Francis, D.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Rashki, A.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, S.; Liakakou, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.L. The role of the Intertropical Discontinuity region and the heat low in dust emission and transport over the Thar desert, India: A Premonsoon case study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13197–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Jia, S.; Sarkar, S. Black carbon aerosol in India: A comprehensive review of current status and future prospects. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupakheti, D.; Kang, S.; Rupakheti, M.; Cong, Z.; Panday, A.; Holben, B. Identification of absorbing aerosol types at a site in the northern edge of Indo-Gangetic Plain and a polluted valley in the foothills of the central Himalayas. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupakheti, D.; Kang, S.; Rupakheti, M. Two heavy haze events over Lumbini in southern Nepal: Enhanced aerosol radiative forcing and heating rates. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 236, 117658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Hsu, N.C.; Lau, K.-M. Premonsoon aerosol characterization and radiative effects over the Indo-Gangetic Plains: Implications for regional climate warming. J. Geophy. Res. 2010, 115, D17208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, Z.L.; Škerlak, B.; Kim, S.W.; Lauer, A.; Mues, A.; Rupakheti, M.; Kang, S. Atmospheric brown clouds reach the Tibetan Plateau by crossing the Himalayas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6007–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, W.K.M.; Sang, J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.M.; Koster, R.D.; Yasunari, T.J. Impacts of snow darkening deposition of light-absorbing aerosols on hydroclimate of Eurasia during boreal spring and summer. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 8441–8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Giorgi, F.; Giuliani, G. Investigating the relative responses of regional monsoon dynamics to snow darkening and direct radiative effects of dust and carbonaceous aerosols over the Indian subcontinent. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kharol, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.; Badrinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Wild, M. Molti-decadal variation of the net downward shortwave radiation over south Asia: The solar dimming effect. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013 the Physical Science Basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report 20 of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K. Long-term changes in surface solar radiation and their effects on air temperature in the Shanghai region. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3385–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Raptis, P.I.; Marinou, E.; Proestakis, E.; Solomos, S.; Gerasopoulos, E.; et al. Dust Impact on Surface Solar Irradiance Assessed with Model Simulations, Satellite Observations and Ground-Based Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, Y. Clear-sky surface soalr radiation and the radiative effects of aerosol and water vapour based on simultanions and satellite observations over Northern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wagner, F.; Peng, W.; Yang, J.; Mauzerall, D.L. Reduction of solar photovoltaic resources due to air pollution in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11867–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Sinha, P.R.; Vinoj, V.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Tripathi, S.N.; Misra, A.; Sharma, M.; Singh, R.P. Aerosol Properties and Radiative Forcing over Kanpur during Severe Aerosol Loading Conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Barth, M.C.; Madronich, S.; Naja, M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Pfister, G.G.; Knote, C.; Brasseur, G.P.; Ojha, N.; Sarangi, T. Effects of dust aerosols on tropospheric chemistry during a typical pre-monsoon season dust storm in northern India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6813–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Barth, M.C.; Pfister, G.G.; Naja, M.; Brasseur, G.P. WRF-Chem simulations of a typical pre-monsoon dust storm in northern India: Influences on aerosol optical properties and radiation budget. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2431–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, R.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Srivastava, M.K.; Singh, A.K. Meteorological, atmospheric and climatic perturbations during major dust storms over Indo-Gangetic Basin. Aeo. Res. 2015, 17, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Sun, S. The effects of economic growth, urbanization and industrialization on fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11452–11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anser, M.K.; Alharthi, M.; Aziz, B.; Wasim, S. Impact of urbanization, economic growth, and population size on residential carbon emissions in the SAARC countries. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commercial Real Estate India. India 2030 Exploring the Future; Commercial Real Estate India: New Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, M.; Awasthi, N.; Singh, L. Electrical Power Scenario in Uttarakhand. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2017, 8, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Uttarakhand. Renewable Energy. Available online: https://investuttarakhand.com/themes/backend/uploads/IP_UK_Renewable%20Energy%20SectorProfile-2019-05-21.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Sagar, R.; Kumar, B.; Dumka, U.C.; Moorthy, K.K.; Pant, P. Characteristics of aerosol spectral optical depths over Manora Peak: A high-altitude station in the central Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D06207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumka, U.C.; Moorthy, K.K.; Kumar, R.; Hegde, P.; Sagar, R.; Pant, P.; Singh, N.; Babu, S.S. Characteristics of aerosol black carbon mass concentration over a high altitude location in the central Himalayas from multi-year measurements. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Bhattu, D.; Tripathi, S.N.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Madhavan, B.L. Seasonal inhomogeneity in cloud precursors over Gangetic Himalayan region during GVAX campaign. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Sheoran, R. Identification of key aerosol types and mixing states in the central Indian Himalayas during the GVAX campaign: The role of particle size in aerosol classification. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 761, 143188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Sagar, R.; Pant, P. Short-period modulations in aerosol optical depths over the central Himalayas: Role of mesoscale processes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarangi, T.; Naja, M.; Ojha, N.; Kumar, R.; Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S.; Kumar, A.; Sagar, R.; Chandola, H.C. First simultaneous measurements of ozone, CO and NOy at a high altitude regional representative site in the central Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1592–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Dumka, U.C.; Naja, M.; Singh, N.; Phanikumar, D.V. ARIES, Nainital: A strategically important location for climate change studies in the Central Gangetic Himalayan region. Curr. Sci. 2015, 109, 703–715. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanre, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET data base. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.; Sinyuk, A.; Pinker, R.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Chatenet, B.; Li, Z.; Singh, R.P.; Tripathi, S.N.; et al. Climatological aspects of the optical properties of fine/coarse mode aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D19205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Tripathi, S.N.; Eck, T.F.; Newcomb, W.W.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Mattoo, S.; Wang, S.-H.; et al. Aerosol properties over the Indo-Gangetic Plain: A mesoscale perspective from the TIGERZ experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D18203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Tripathi, S.N.; Misra, A.; Giles, D.M.; Eck, T.F.; Sagar, R.; Holben, B.N. Latitudinal variation of aerosol properties from Indo-Gangetic Plain to Central Himalayan foothills during TIGERZ campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4750–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinyuk, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Giles, D.M.; Slutsker, I.; Korkin, S.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Sorokin, M.; Lyapustin, A. The AERONET Version 3 aerosol retrieval algorithm, associated uncertainties and comparisons to Version 2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3375–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmospheric Monitoring Service, Copernicus. Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/data (accessed on 16 November 2019).
- Schroedter-Homscheidt, M.; Hoyer-klick, C.; Killius, N.; Lefèvre, M. User’s Guide to the CAMS Radiation Service: Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service; German Aerospace Center: Cologne, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, S.N.; Dey, S.; Tare, V.; Satheesh, S.K.; Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S. Enhanced layer of black carbon in a north Indian industrial city. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethva, H.; Satheesh, S.K.; Srinivasan, J. Seasonal variability of aerosols over Indo-Gangetic basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D21204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Météo-France. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document for Cloud Products (CMa-PGE01 v3.2, CT-PGE02 v2.2 & CTTH-PGE03 v2.2); Technical Report SAF/NWC/CDOP/MFL/SCI/ATBD/01; Météo-France: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. Technical note: The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations—Description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emde, C.; Buras-Schnell, R.; Kylling, A.; Mayer, B.; Gasteiger, J.; Hamann, U.; Kylling, J.; Richter, B.; Pause, C.; Dowling, T.; et al. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations (version 2.0.1). Geosci. Model. Dev. 2016, 9, 1647–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Raptis, P.I.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kiranoudis, C.; Bais, A.F. Assessment of surface solar irradiance derived from real-time modelling techniques and verification with ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricchiazzi, P.; Yang, S.; Gautier, C.; Sowle, D. SBDART: A research and software tool for plane-parallel radiative transfer in the Earth’s atmosphere. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Ackerman, T.P.; Mather, J.H.; Clothiaux, E.E. The K-Distribution Method and Correlated-k Approximation for a Shortwave Radiative Transfer Model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1999, 62, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettle, E.P. Models of Aerosols, Clouds, and Precipitation for Atmospheric Propagation Studies. In Proceedings of the Atmospheric Propagation in the UV, Visible, IR and MM Wave Region and Related Systems Aspects, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–13 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; El-Askary, H.; Taylor, M.; Gkikas, A.; Proestakis, E.; Kontoes, C.; El-Khayat, M.M. Earth-Observation-Based Estimation and Forecasting of Particulate Matter Impact on Solar Energy in Egypt. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoom, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Kashyap, Y.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, A. Rooftop Photovoltaic Energy Production Management in India Using Earth-Observation Data and Modeling Techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercom India. Available online: https://mercomindia.com/uttarakhand-generic-tariff-rooftop-solar/ (accessed on 7 June 2021).
- Panjwani, M.K.; Narejo, G.B. Effect of humidity on the efficiency of solar cell (photovoltaic). Int. J. Eng. Res. Gen. Sci. 2014, 2, 499–503. [Google Scholar]
- Gwandu, B.; Creasey, D.J. Humidity: A factor in the appropriate positioning of a photovoltaic power station. Renew. Energy 1995, 6, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Payra, S.; Gautam, R.; Prakash, D.; Soni, M.; Holben, B.; Bell, S. Dust events and their influence on aerosol optical properties over Jaipur in Northwestern India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7327–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabat, P.; Somot, S.; Mallet, M.; Sevault, F.; Driouech, F.; Meloni, D.; Di Sarra, A.; Di Biagio, C.; Formenti, P.; Sicard, M.; et al. Dust aerosol radiative effects during summer 2012 simulated with a coupled regional aerosol-atmosphere-ocean model over the Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3303–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalil, S.A.; Shaffie, A.M. Evaluation of transposition models of solar irradiance over Egypt. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Jeong, S.; Park, H.; Park, C.-F. The effect of particulate matter on solar photovoltaic power generation over the Republic of Korea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 084004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.H.; Ghoroi, C.; Dixit, D.; Schauer, J.J.; Shindell, D.T. Large reductions in solar energy production due to dust and particulate air pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, I.M.; Karthik, S.; Liu, H.; Buonassisi, T.; Nobre, A. Urban haze and photovoltaics Energy. Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos, A.M.; Amonov, M.O.; Shafer, M.M.; Devi, J.J.; Gupta, T.; Tripathi, S.N.; Rana, K.S.; McKenzie, M.; Bergin, M.H.; Schauer, J.J. Source apportionment of carbonaceous fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in two contrasting cities across the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vreeland, H.; Schauer, J.J.; Russell, A.G.; Marshall, J.D.; Fushimi, A.; Jain, G.; Sethuraman, K.; Verma, V.; Tripathi, S.N.; Bergin, M.H. Chemical characterization and toxicity of particulate matter emissions from roadside trash combustion in urban India. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Di Girolamo, L.; van Donkelaar, A.; Tripathi, S.N.; Gupta, T.; Mohan, M. Variability of outdoor fine particulate (PM2.5) concentration in the Indian Subcontinent: A remote sensing approach. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, M.; Ichoku, C.; Leptoukh, G. Multi-sensor Aerosol Products Sampling System (MAPSS). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.; Kaufman, Y.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoom, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Bansal, A.; Kazadzis, S. Solar Energy Estimations in India Using Remote Sensing Technologies and Validation with Sun Photometers in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2014, Report 2015. Available online: http://www.irena.org/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2015/IRENA_RE_Power_Costs_2014_report.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2018).
- Haney, J.; Burstein, A. PV System Operations and Maintenance Fundamentals. Solar America Board for Codes and Standards Report 2013. Available online: http://www.solarabcs.org/about/publications/reports/operationsmaintenance/pdfs/SolarABCs-35-2013.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumka, U.C.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Ningombam, S.S.; Masoom, A. Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163248
Dumka UC, Kosmopoulos PG, Ningombam SS, Masoom A. Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163248
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumka, Umesh Chandra, Panagiotis G. Kosmopoulos, Shantikumar S. Ningombam, and Akriti Masoom. 2021. "Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163248
APA StyleDumka, U. C., Kosmopoulos, P. G., Ningombam, S. S., & Masoom, A. (2021). Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163248









