Twice Is Nice: The Benefits of Two Ground Measures for Evaluating the Accuracy of Satellite-Based Sustainability Estimates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Correlation between Ground Measures
2.2. Derivation of Correction Equation
2.3. Simulations
2.4. Application to Crop Yields
2.5. Application to Household Consumption
3. Results
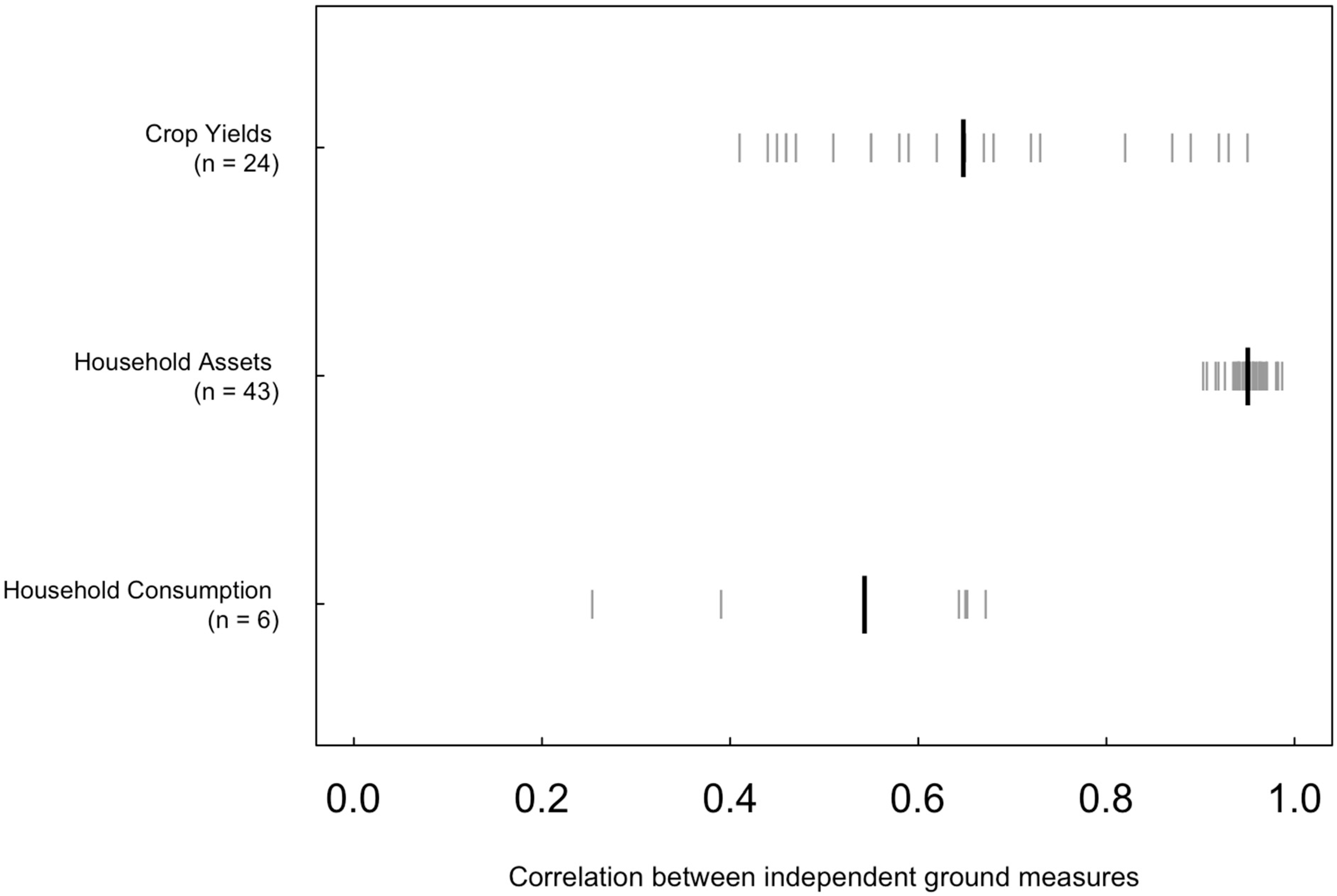
3.1. Correlations between Ground Measures
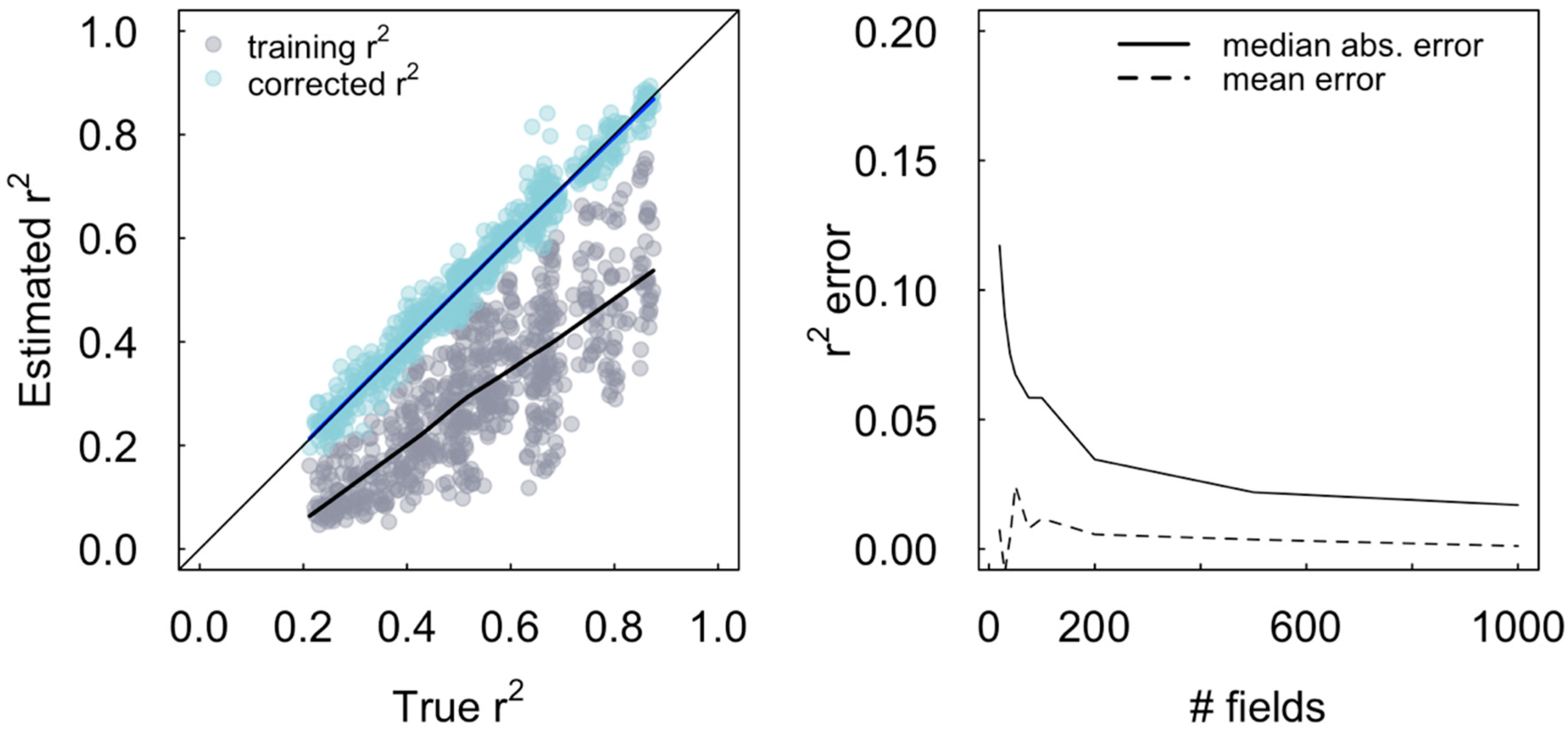
3.2. Simulations Illustrate the Value of Two Ground Measures
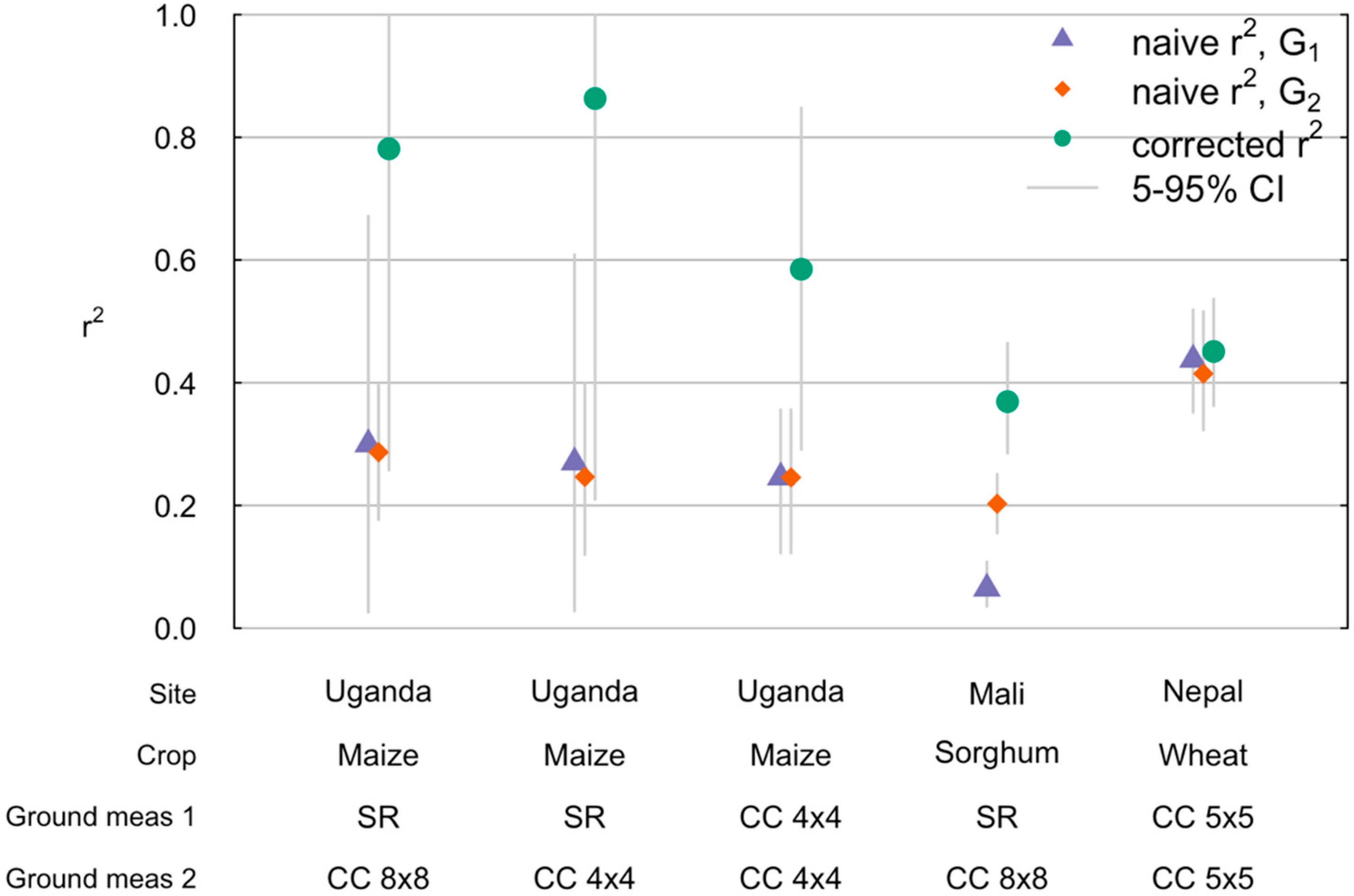
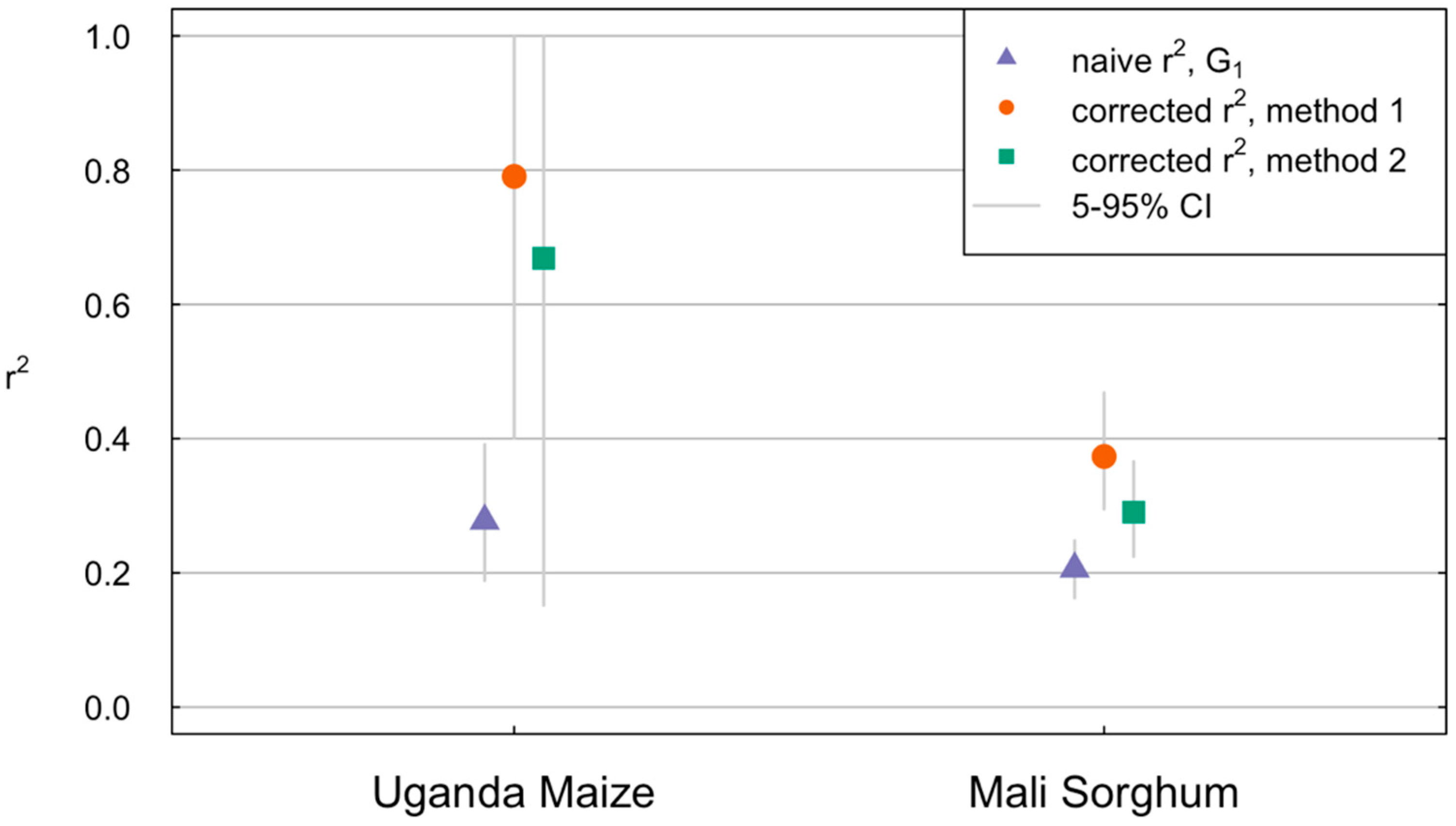
3.3. Correcting for Ground Noise Significantly Improves Performance Measures for Crop Yields
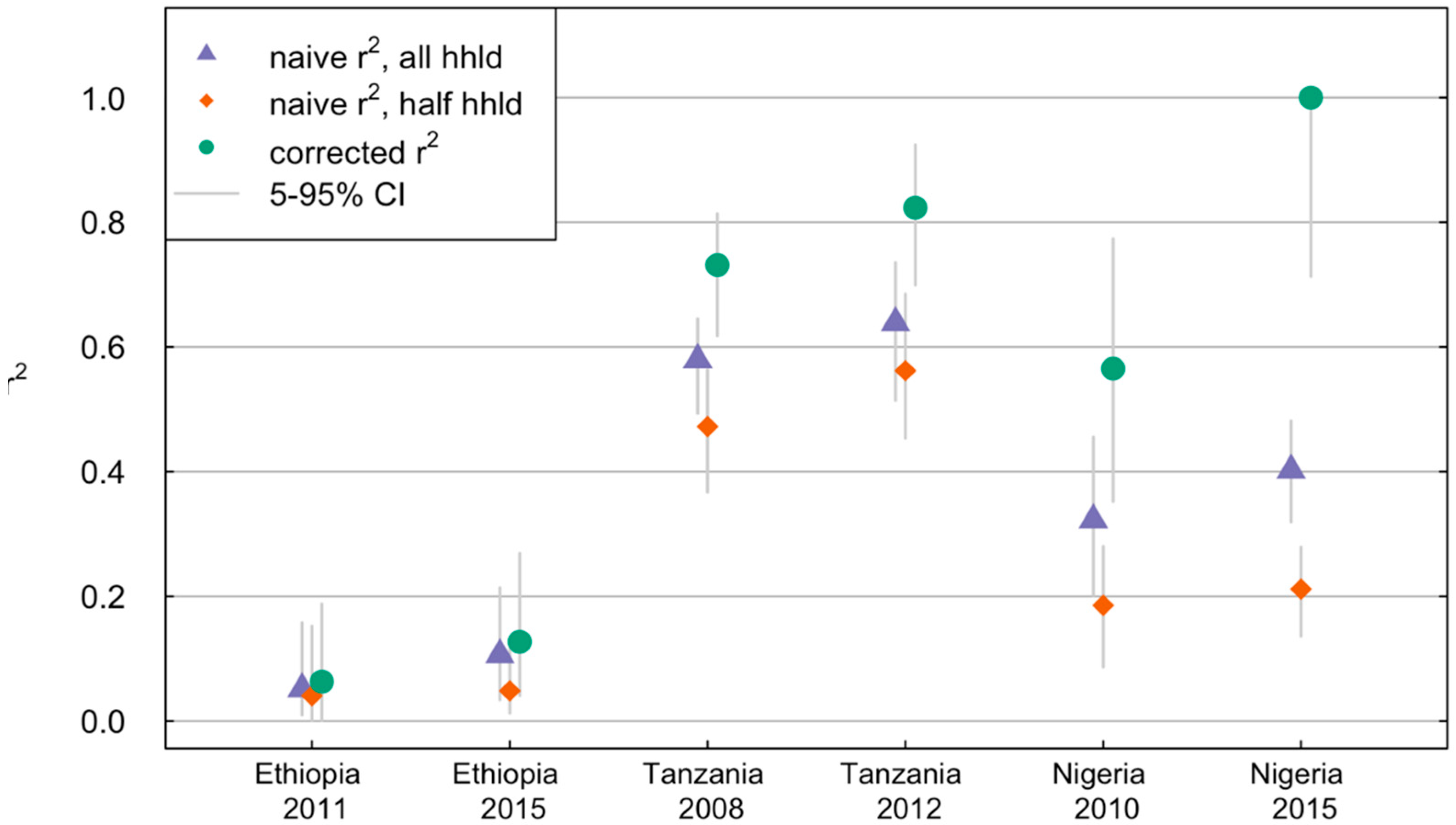
3.4. Correcting for Ground Noise Significantly Improves Performance Measures for Household Consumptions
3.5. Correcting Satellite Performance Measures in the Absence of Two Ground-Based Estimates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumenstock, J.; Cadamuro, G.; On, R. Supplementary Materials for Predicting poverty and wealth from mobile phone metadata. Science 2015, 350, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, E.; Meng, C.; Jean, N.; Tan, M.; Burke, M.; Ermon, S.; Uzkent, B.; Lobell, D. Predicting economic development using geolocated wikipedia articles. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, M.; Driscoll, A.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Using satellite imagery to understand and promote sustainable development. Science 2021, 371, eabe8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watmough, G.R.; Marcinko, C.L.J.; Sullivan, C.; Tschirhart, K.; Mutuo, P.K.; Palm, C.A.; Svenning, J.C. Socioecologically informed use of remote sensing data to predict rural household poverty. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirza, M.U.; Xu, C.; van Bavel, B.; van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M. Global inequality remotely sensed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e1919913118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W. A simplified approach for yield prediction of sugar beet based on optical remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Asner, G.P.; Ortiz-Monasterio, J.I.; Benning, T.L. Remote sensing of regional crop production in the Yaqui Valley, Mexico: Estimates and uncertainties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 94, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.J.; Traoré, P.C.S.; Blaes, X.; Baret, P.; Defourny, P. Estimating smallholder crops production at village level from Sentinel-2 time series in Mali’s cotton belt. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Lobell, D.B. Satellite-based assessment of yield variation and its determinants in smallholder African systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobell, D.B.; Azzari, G.; Burke, M.; Gourlay, S.; Jin, Z.; Kilic, T.; Murray, S. Eyes in the Sky, Boots on the Ground: Assessing Satellite- and Ground-Based Approaches to Crop Yield Measurement and Analysis. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Singh, B.; Srivastava, A.; McDonald, A.; Lobell, D.B. Mapping Smallholder Wheat Yields and Sowing Dates Using Micro-Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.M. An assessment of pre- and within-season remotely sensed variables for forecasting corn and soybean yields in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Capacity Needs Assessment for Improving Agricultural Statistics in Kenya; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank Group. Capacity Needs Assessment for Improving Agricultural Statistics in Uganda; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carletto, C.; Jolliffe, D.; Banerjee, R. From Tragedy to Renaissance: Improving Agricultural Data for Better Policies. J. Dev. Stud. 2015, 51, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, S.; Kilic, T.; Lobell, D.B. A new spin on an old debate: Errors in farmer-reported production and their implications for inverse scale—Productivity relationship in Uganda. J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 141, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Handbook on Crop Statistics: Improving Methods for Measuring Crop Area, Production and Yield; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fermont, A.; Benson, T. Estimating Yield of Food Crops Grown by Smallholder Farmers: A Review in the Uganda Context; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.; Perez, A.; Driscoll, A.; Azzari, G.; Tang, Z.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S.; Burke, M. Using publicly available satellite imagery and deep learning to understand economic well-being in Africa. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Di Tommaso, S.; You, C.; Djima, I.Y.; Burke, M.; Kilic, T. Sight for sorghums: Comparisons of satellite-and ground-based sorghum yield estimates in Mali. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campolo, J.; Güereña, D.; Maharjan, S.; Lobell, D.B. Evaluation of soil-dependent crop yield outcomes in Nepal using ground and satellite-based approaches. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayush, K.; Uzkent, B.; Tanmay, K.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S. Efficient Poverty Mapping from High Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Scipal, K.; Holmes, T.; De Jeu, R.; Naeimi, V.; Wagner, W. A possible solution for the problem of estimating the error structure of global soil moisture data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoffelen, A. Toward the true near-surface wind speed: Error modeling and calibration using triple collocation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 7755–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, K.A.; Bevis, L.E.M.; Barrett, C.B. Measurement Error Mechanisms Matter: Agricultural Intensification with Farmer Misperceptions and Misreporting. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2020, 103, 498–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobell, D.B.; Di Tommaso, S.; Burke, M.; Kilic, T. Twice Is Nice: The Benefits of Two Ground Measures for Evaluating the Accuracy of Satellite-Based Sustainability Estimates. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163160
Lobell DB, Di Tommaso S, Burke M, Kilic T. Twice Is Nice: The Benefits of Two Ground Measures for Evaluating the Accuracy of Satellite-Based Sustainability Estimates. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobell, David B., Stefania Di Tommaso, Marshall Burke, and Talip Kilic. 2021. "Twice Is Nice: The Benefits of Two Ground Measures for Evaluating the Accuracy of Satellite-Based Sustainability Estimates" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163160
APA StyleLobell, D. B., Di Tommaso, S., Burke, M., & Kilic, T. (2021). Twice Is Nice: The Benefits of Two Ground Measures for Evaluating the Accuracy of Satellite-Based Sustainability Estimates. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163160





