Enhanced Simulation of an Asian Dust Storm by Assimilating GCOM-C Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observational Data
2.1. Assimilated GCOM-C Observations
2.2. Independent Observations Used for Evaluation
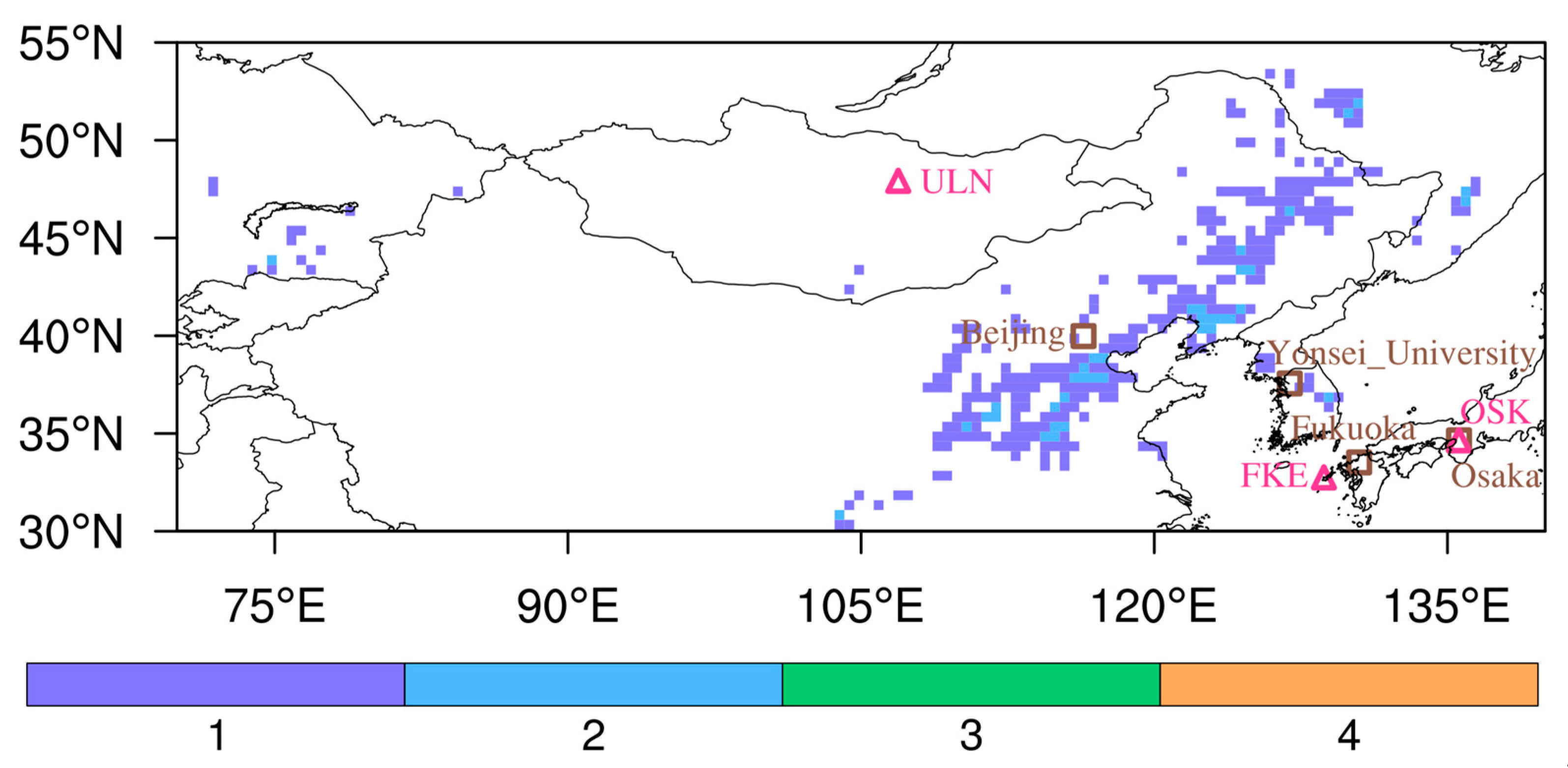
2.2.1. AERONET
2.2.2. AD-Net
3. Data Assimilation System
3.1. Forward Model
3.2. Data assimilation Methodology
4. Results
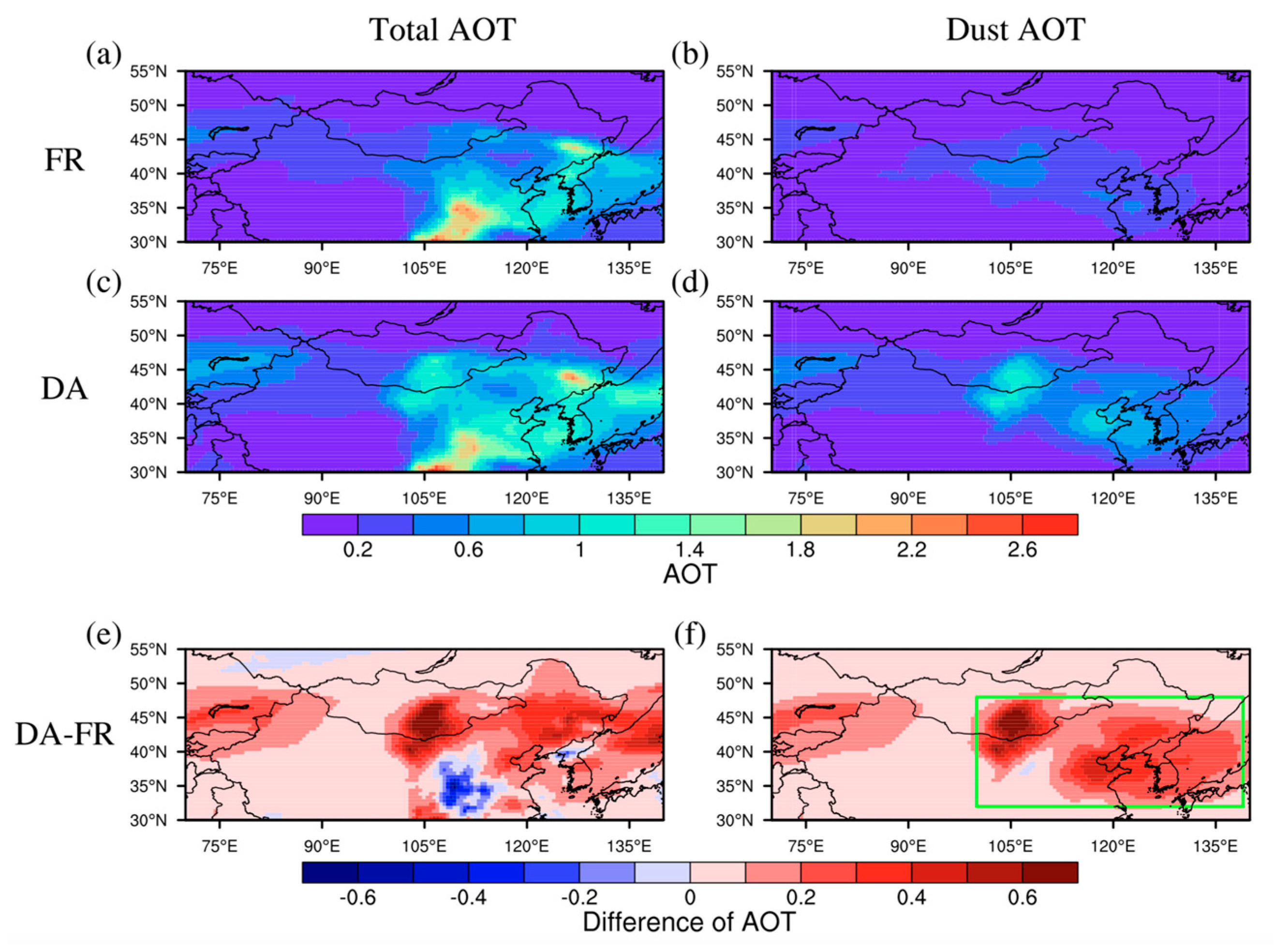
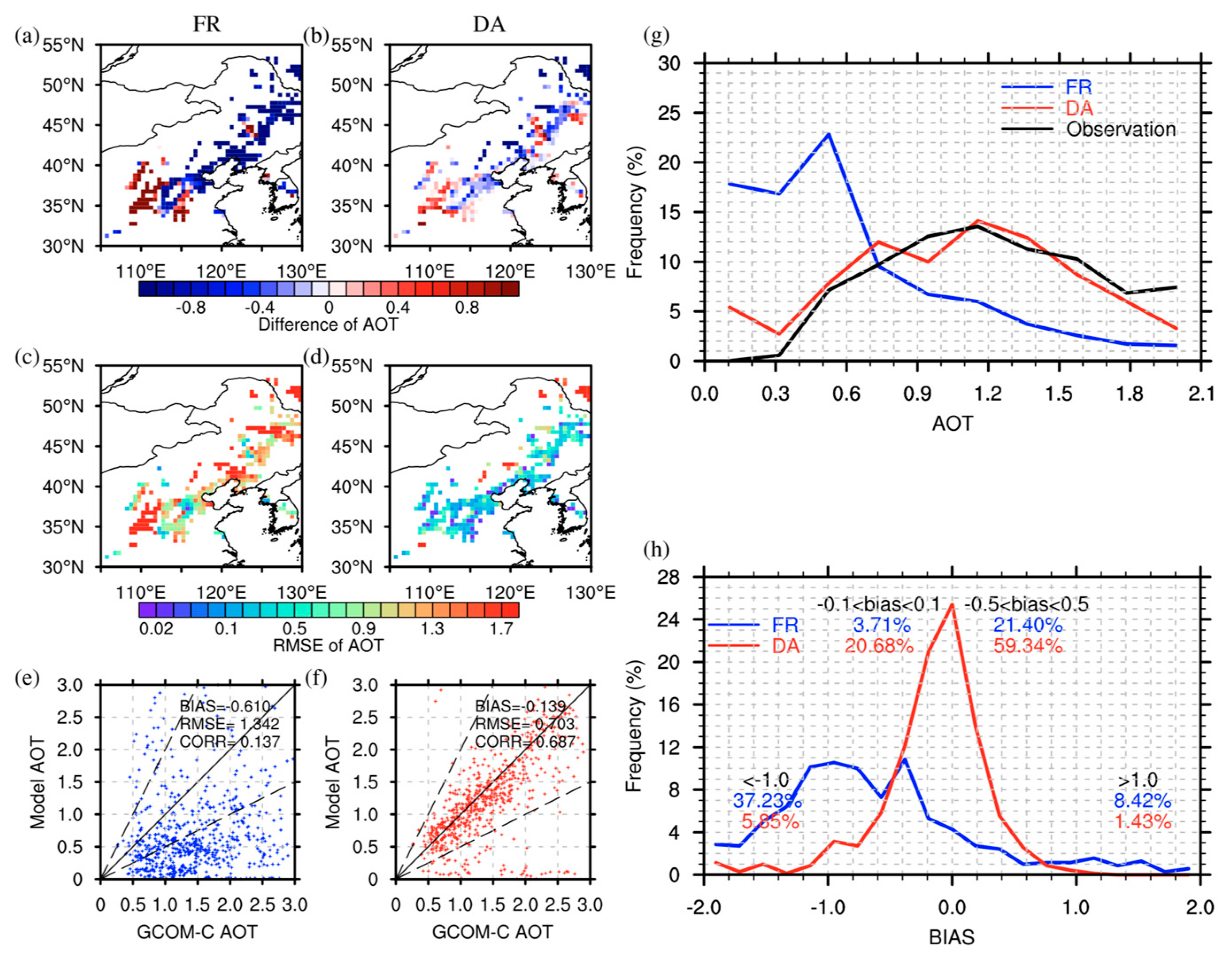
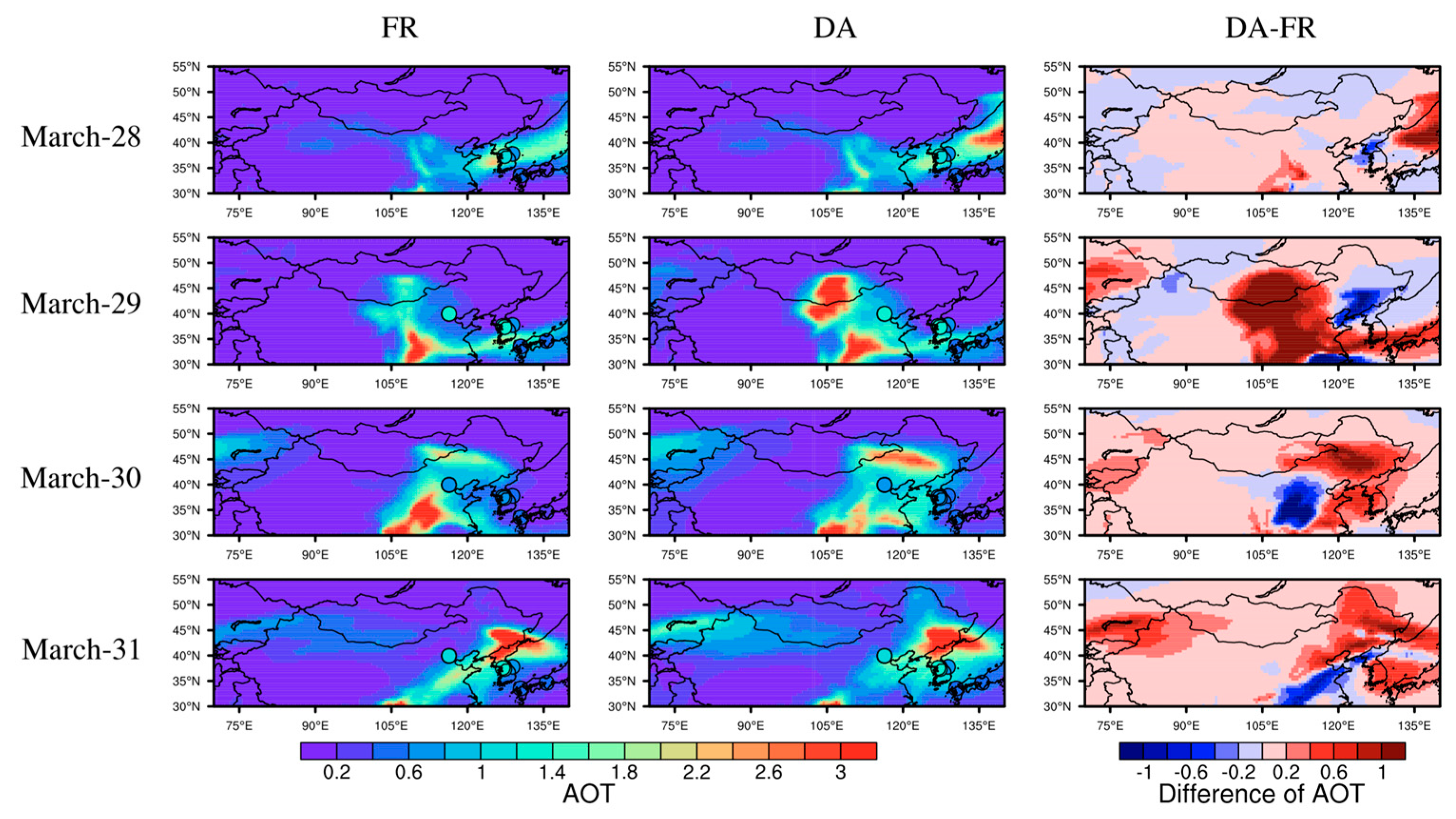
4.1. Sanity Check with GCOM-C AOTs
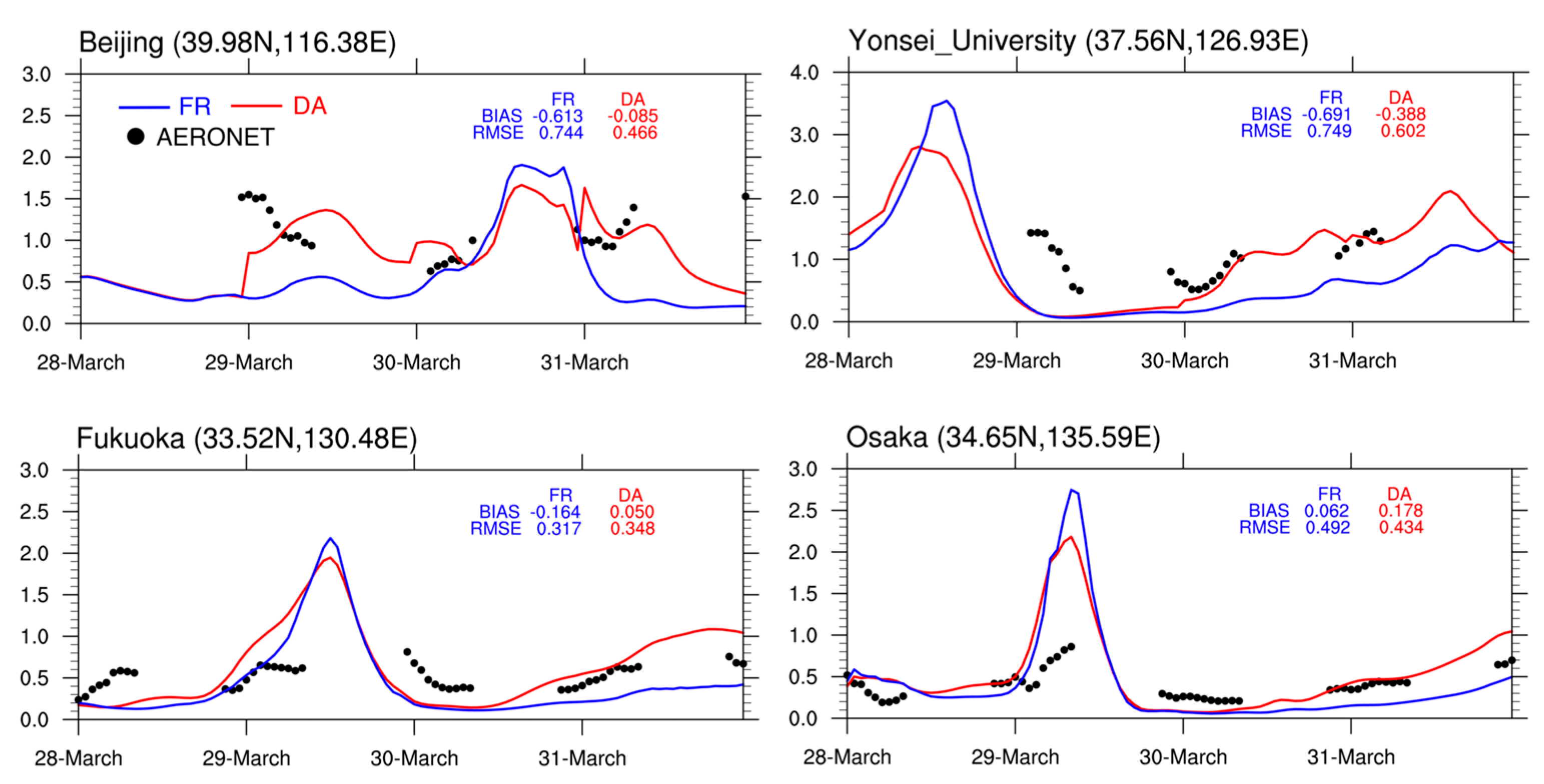
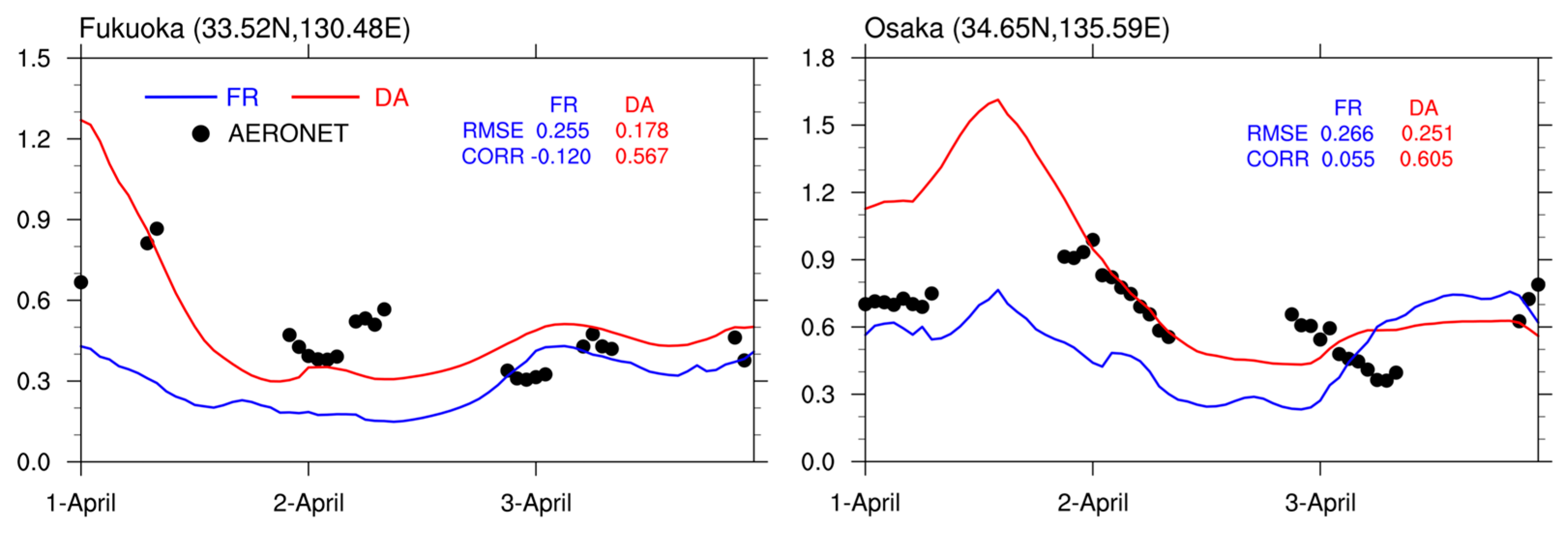
4.2. Verification with Independent AERONET Observations
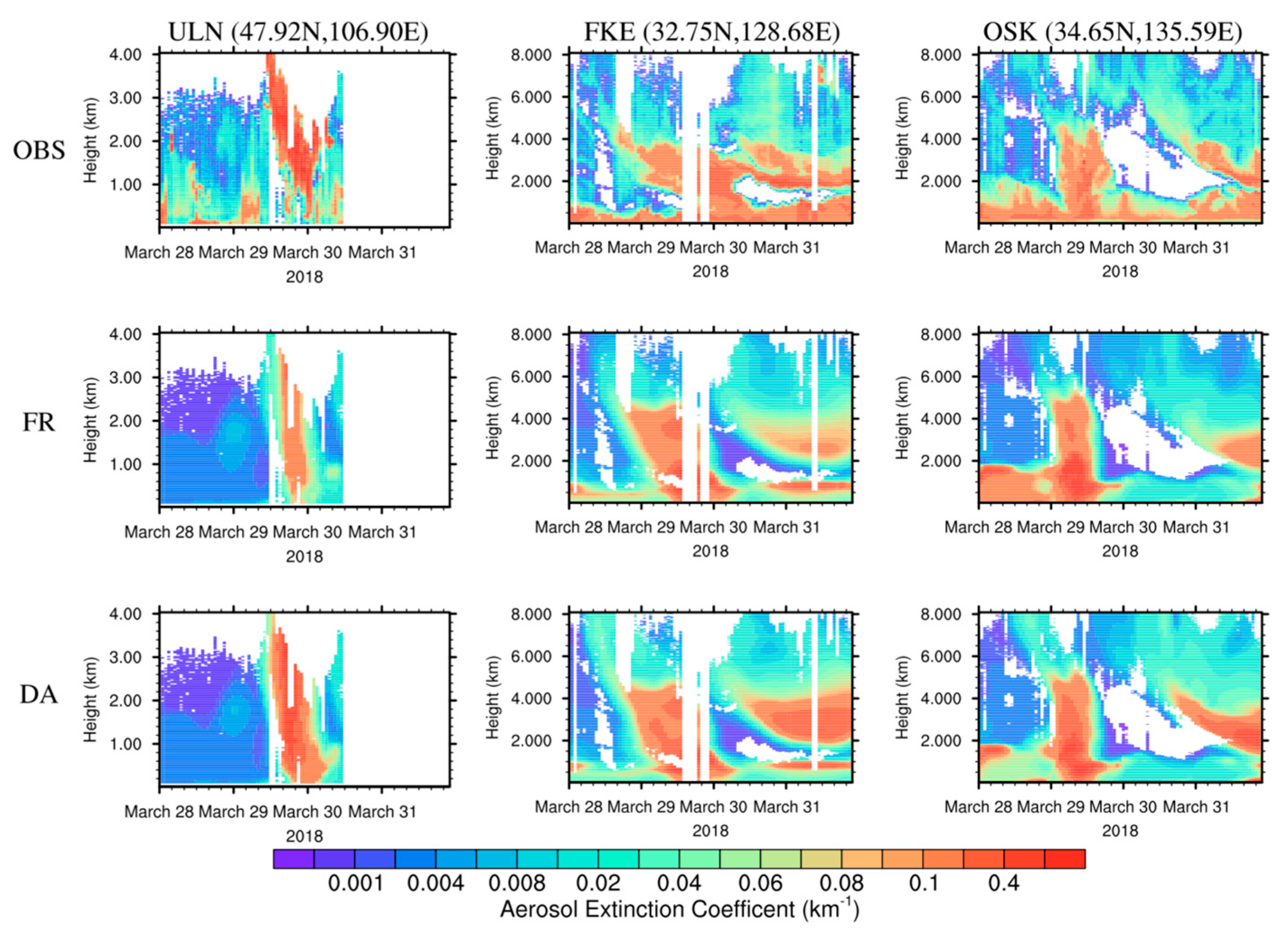
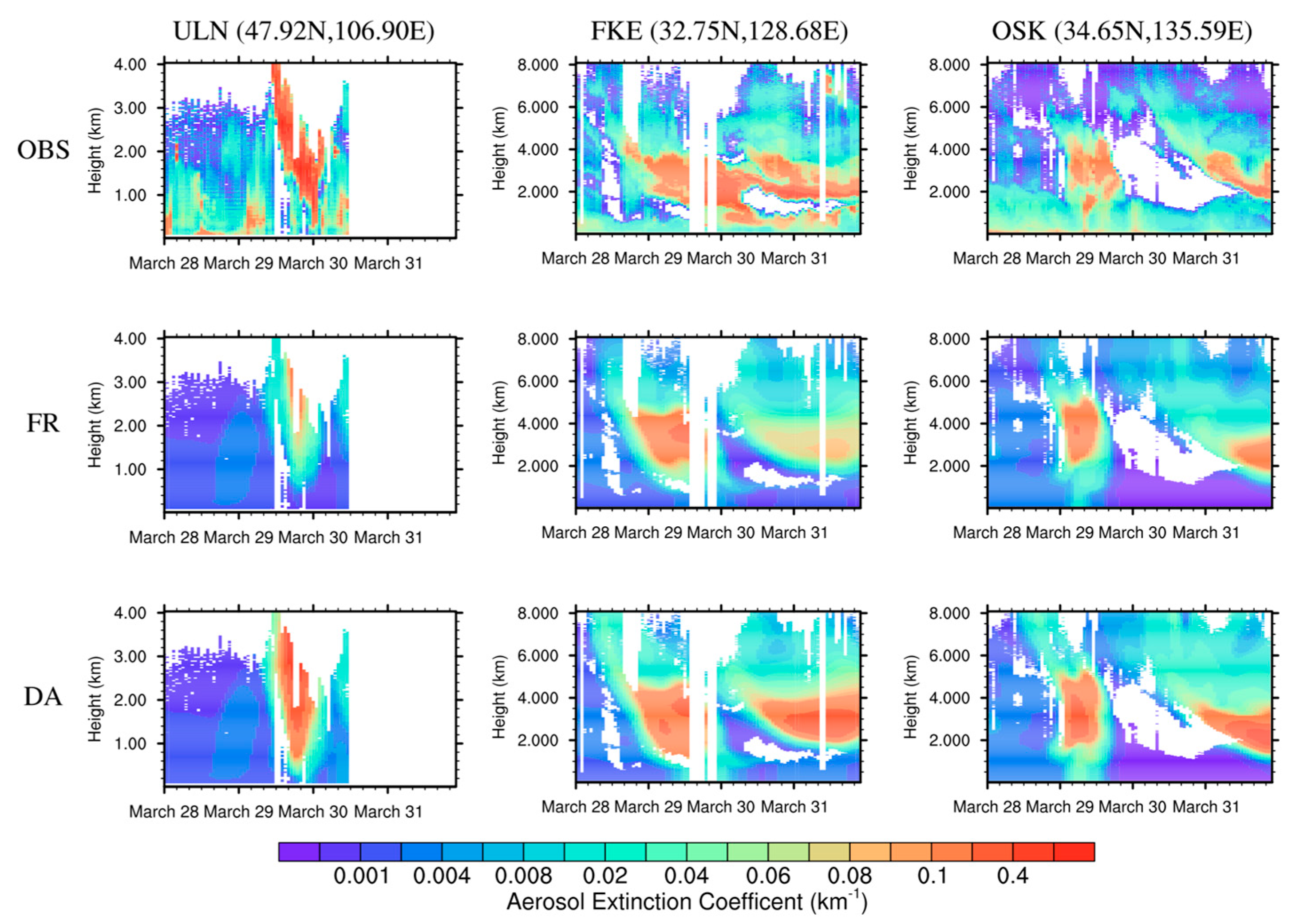
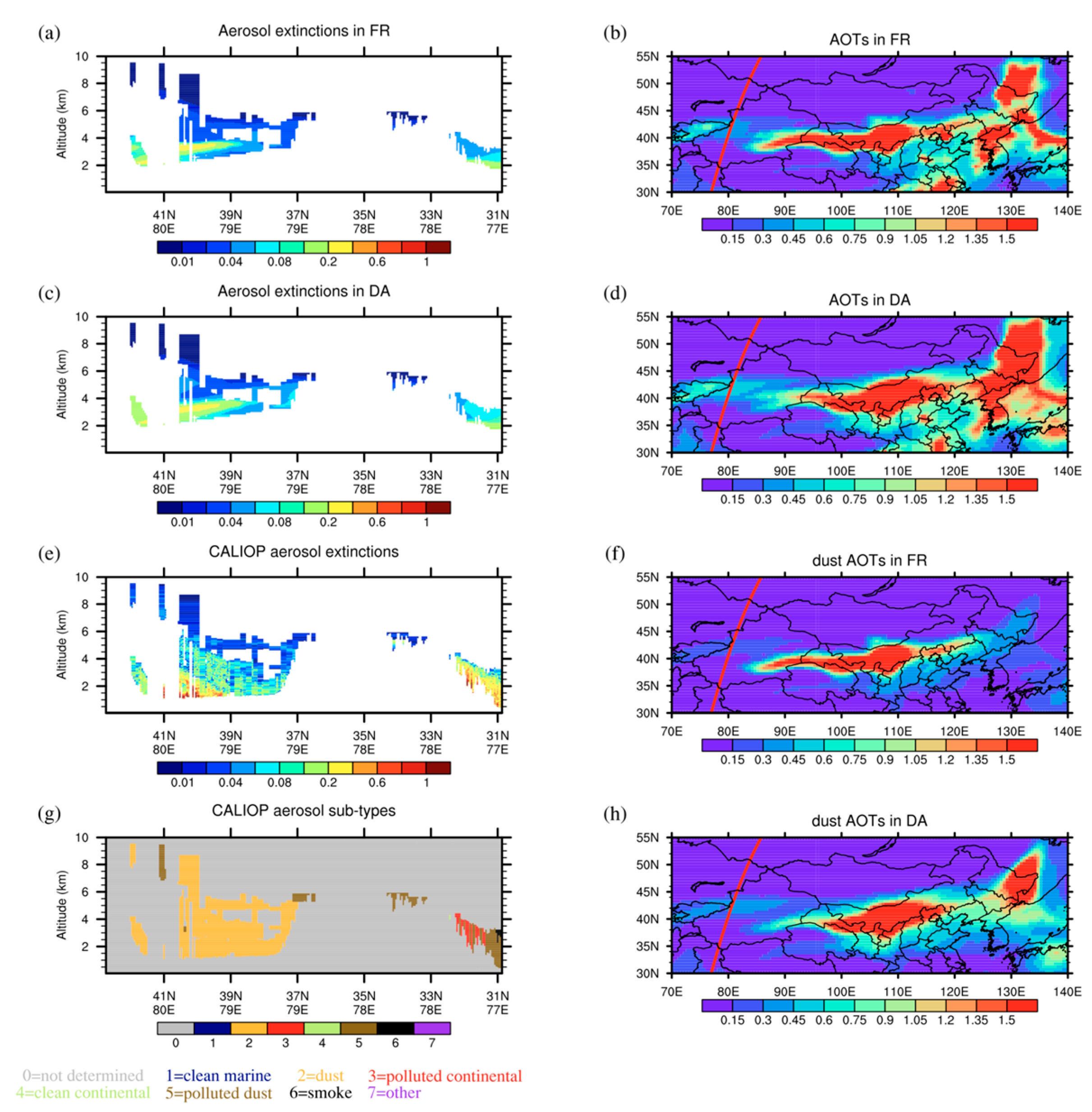
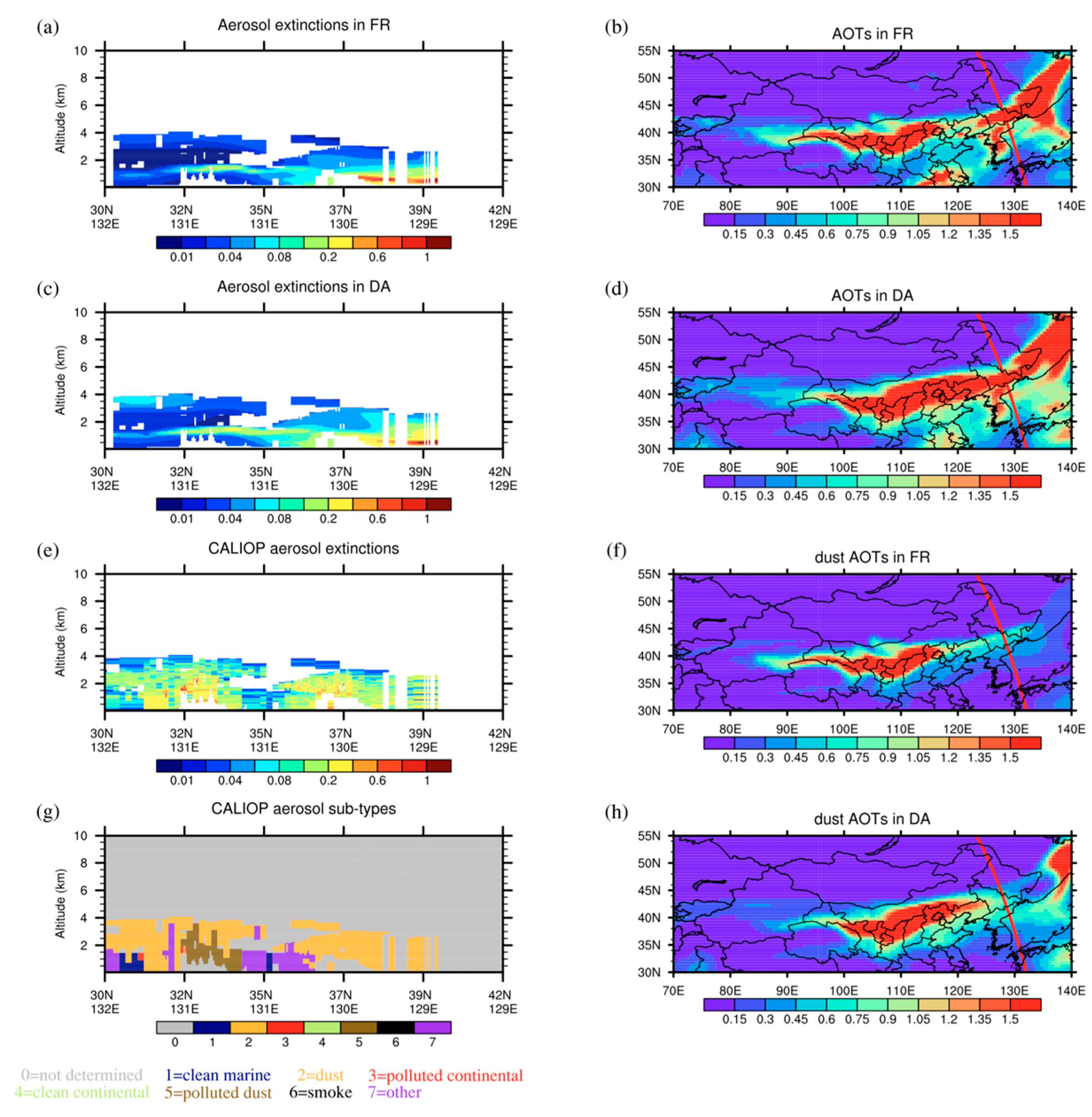
4.3. Vertical Structure of Aerosol Extinction Coefficients
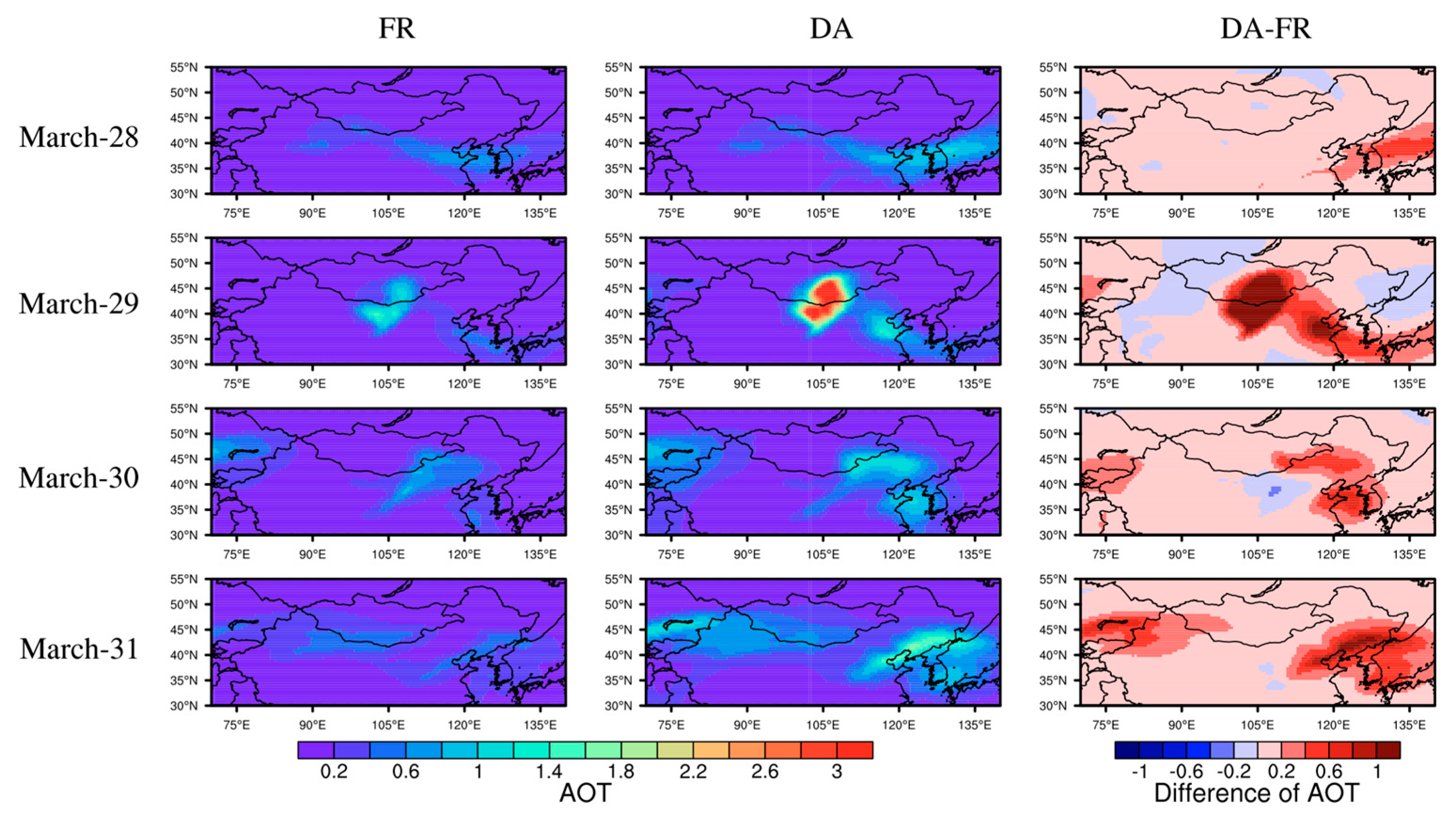
5. Discussion
6. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Su, J.; Tang, Q.; Minnis, P.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Q. Taklimakan Dust Aerosol Radiative Heating Derived from CALIPSO Observations Using the Fu-Liou Radiation Model with CERES Constraints. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Yan, H.; Yi, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Ayers, J.K. Dust Aerosol Effect on Semi-Arid Climate over Northwest China Detected from A-Train Satellite Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6863–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hua, S.; Alam, K.; Dai, T.; Cheng, Y. Tibetan Plateau Driven Impact of Taklimakan Dust on Northern Rainfall. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Yan, H. Climatology of Dust-Forced Radiative Heating Over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Surroundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, T.; Zhao, M.; Goto, D.; Bao, Q.; Takemura, T.; Nakajima, T.; Shi, G. Aerosol Effective Radiative Forcing in the Online Aerosol Coupled CAS-FGOALS-F3-L Climate Model. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Minnis, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Satellite-Based Assessment of Possible Dust Aerosols Semi-Direct Effect on Cloud Water Path over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, J.; Hua, S.; Jia, R. Impact of Dust-Polluted Convective Clouds over the Tibetan Plateau on Downstream Precipitation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hua, S.; Jia, R.; Huang, J. Effect of Aerosols on the Ice Cloud Properties Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9594–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A. Continuous Observations of Asian Dust and Other Aerosols by Polarization Lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D19S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Uno, I.; Nishikawa, M.; Shimizu, A.; Matsui, I.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Quan, H. Record Heavy Asian Dust in Beijing in 2002: Observations and Model Analysis of Recent Events: Record Heavy Dust in Beijing in 2002. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.; Lin, J.; Hu, K.; Wang, L.; Gong, H. Chinese Blue Days: A Novel Index and Spatio-Temporal Variations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgwell, A.J. Dust in the Earth System: The Biogeochemical Linking of Land, Air and Sea. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 2905–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-E.; Lim, J.-H.; Shim, J.-M.; Kwon, J.-I.; Kim, I.-N. Spring 2018 Asian Dust Events: Sources, Transportation, and Potential Biogeochemical Implications. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Murakami, H.; Miyazaki, R.; Honda, Y.; Nasahara, K.; Kajiwara, K.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Irie, H.; Toratani, M.; Hirawake, T.; et al. GCOM-C Data Validation Plan for Land, Atmosphere, Ocean, and Cryosphere. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2018, 16, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Fujii, H.; Murakami, H.; Hori, M.; Ono, A.; Igarashi, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T.; Honda, Y.; et al. Global Change Observation Mission (GCOM) for Monitoring Carbon, Water Cycles, and Climate Change. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, H.M.S.; Irie, H.; Damiani, A.; Momoi, M. Primary Evaluation of the GCOM-C Aerosol Products at 380 Nm Using Ground-Based Sky Radiometer Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust Cycle: An Emerging Core Theme in Earth System Science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.M. 3D Structure of Asian Dust Transport Revealed by CALIPSO Lidar and a 4DVAR Dust Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Dai, T.; Wang, H.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. Aerosol Characteristics over the Tibetan Plateau Simulated with a Coupled Aerosol–Climate Model (FGOALS-F3-L). Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2021, 14, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Long-Range Transport and Vertical Structure of Asian Dust from CALIPSO and Surface Measurements during PACDEX. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D23212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Jin, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Yumimoto, K. Transport of Mineral Dust from Africa and Middle East to East Asia Observed with the Lidar Network (AD-Net). SOLA 2019, 15, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wenig, M.; Yang, L. Impact of Long-Range Desert Dust Transport on Hydrometeor Formation over Coastal East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Dumka, U.C.; Rashki, A.; Psiloglou, B.E.; Gavriil, A.; Mofidi, A.; Petrinoli, K.; Karagiannis, D.; Kambezidis, H.D. Analysis of Intense Dust Storms over the Eastern Mediterranean in March 2018: Impact on Radiative Forcing and Athens Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong Park, C.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Shimizu, A.; Tatarov, B.; Kamei, A.; Hie Lee, C.; Uno, I.; Takemura, T.; Westphal, D.L. Long-Range Transport of Saharan Dust to East Asia Observed with Lidars. SOLA 2005, 1, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dai, T.; Cheng, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Goto, D.; Kikuchi, M.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Yoshida, M.; Zhang, P.; Husi, L.; Shi, G.; et al. Hourly Aerosol Assimilation of Himawari-8 AOT Using the Four-Dimensional Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 680–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Yumimoto, K.; Nagao, T.M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Murakami, H. Satellite Retrieval of Aerosol Combined with Assimilated Forecast. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 1797–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. MODIS Aerosol Product Analysis for Data Assimilation: Assessment of over-Ocean Level 2 Aerosol Optical Thickness Retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, A.; Morcrette, J.-J.; Boucher, O.; Dethof, A.; Engelen, R.J.; Fisher, M.; Flentje, H.; Huneeus, N.; Jones, L.; Kaiser, J.W.; et al. Aerosol Analysis and Forecast in the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Integrated Forecast System: 2. Data Assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Dai, T.; Goto, D.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Shi, G.; Nakajima, T. Investigating the Assimilation of CALIPSO Global Aerosol Vertical Observations Using a Four-Dimensional Ensemble Kalman Filter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13445–13467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.-C.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, T. Three-Dimensional Variational Assimilation of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth: Implementation and Application to a Dust Storm over East Asia: Aod Data Assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 Database—Automated near-Real-Time Quality Control Algorithm with Improved Cloud Screening for Sun Photometer Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Jin, Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.; Batdorj, D.; Sugimoto, N. Evolution of a lidar network for tropospheric aerosol detection in East Asia. Opt. Eng. 2016, 56, 031219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesenberg, J.; Hoff, R.M. GAW Plan for the implementation of the GAW Aerosol Lidar Observation Network GALION. In GAW Report; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 178. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, T.; Okamoto, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Numaguti, A.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Global Three-Dimensional Simulation of Aerosol Optical Thickness Distribution of Various Origins. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 17853–17873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T.; Uno, I.; Nakajima, T.; Higurashi, A.; Sano, I. Modeling Study of Long-Range Transport of Asian Dust and Anthropogenic Aerosols from East Asia: Study of Long-range Transport of Dust and Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 11-1–11-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T. Aerosol Distributions and Radiative Forcing over the Asian Pacific Region Simulated by Spectral Radiation-Transport Model for Aerosol Species (SPRINTARS). J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T.; Egashira, M.; Matsuzawa, K.; Ichijo, H.; O’ishi, R.; Abe-Ouchi, A. A Simulation of the Global Distribution and Radiative Forcing of Soil Dust Aerosols at the Last Glacial Maximum. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Tomita, H.; Miura, H.; Iga, S.; Nasuno, T. Development of a Global Cloud Resolving Model—A Multi-Scale Structure of Tropical Convections. J. Earth Simulator 2005, 3, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, M.; Matsuno, T.; Tomita, H.; Miura, H.; Nasuno, T.; Iga, S. Nonhydrostatic Icosahedral Atmospheric Model (NICAM) for Global Cloud Resolving Simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3486–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Tomita, H.; Yashiro, H.; Miura, H.; Kodama, C.; Seiki, T.; Noda, A.T.; Yamada, Y.; Goto, D.; Sawada, M.; et al. The Non-Hydrostatic Icosahedral Atmospheric Model: Description and Development. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Satoh, M. A New Dynamical Framework of Nonhydrostatic Global Model Using the Icosahedral Grid. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2004, 34, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kajikawa, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaura, T.; Yashiro, H.; Tomita, H. Deep Moist Atmospheric Convection in a Subkilometer Global Simulation: Convection in a Sub-Km Global Simulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4922–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, D.; Dai, T.; Satoh, M.; Tomita, H.; Uchida, J.; Misawa, S.; Inoue, T.; Tsuruta, H.; Ueda, K.; Ng, C.F.S.; et al. Application of a Global Nonhydrostatic Model with a Stretched-Grid System to Regional Aerosol Simulations around Japan. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Goto, D.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Dong, X.; Shi, G.; Nakajima, T. Simulated Aerosol Key Optical Properties over Global Scale Using an Aerosol Transport Model Coupled with a New Type of Dynamic Core. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, D.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Nakajima, T.; Takemura, T. Sensitivity of Aerosol to Assumed Optical Properties over Asia Using a Global Aerosol Model and AERONET: Sensitivity of Aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Jin, Y.; van Leeuwen, T.T. Global Fire Emissions and the Contribution of Deforestation, Savanna, Forest, Agricultural, and Peat Fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11707–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmüller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A Mosaic of Regional and Global Emission Grid Maps for 2008 and 2010 to Study Hemispheric Transport of Air Pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D. A Wind Tunnel Simulation of the Erosion of Soil: Effect of Soil Texture, Sandblasting, Wind Speed, and Soil Consolidation on Dust Production. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, G.; Sekiguchi, M.; Suzuki, K.; Goto, D.; Nakajima, T. Impacts of Meteorological Nudging on the Global Dust Cycle Simulated by NICAM Coupled with an Aerosol Model. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, B.R.; Kostelich, E.J.; Szunyogh, I. Efficient Data Assimilation for Spatiotemporal Chaos: A Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2007, 230, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Yamane, S.; Enomoto, T. Localizing the Error Covariance by Physical Distances within a Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF). SOLA 2007, 3, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.A.J.; Miyoshi, T.; Takemura, T.; Nakajima, T. Applying an Ensemble Kalman FIlter to the Assimilation of AERONET Observations in a Global Aerosol Transport Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2561–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.A.J.; Miyoshi, T.; Takemura, T.; Nakajima, T. Sensitivity Tests for an Ensemble Kalman FIlter for Aerosol Assimilation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6583–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Dai, T.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Goto, D.; Nakajima, T.; Shi, G. Effects of Data Assimilation on the Global Aerosol Key Optical Properties Simulations. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178–179, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T. Direct Radiative Effect of Aerosols Estimated Using Ensemble-Based Data Assimilation in a Global Aerosol Climate Model: Assimilation with Aerosol Climate Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, G.; Cohn, S.E. Construction of Correlation Functions in Two and Three Dimensions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 723–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, D.; Kikuchi, M.; Suzuki, K.; Hayasaki, M.; Yoshida, M.; Nagao, T.M.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; et al. Aerosol model evaluation using two geostationary satellites over East Asia in May 2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial Performance Assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Getzewich, B.J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rogers, R.R. The Global 3-D Distribution of Tropospheric Aerosols as Characterized by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3345–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Flag Name | Optional Bit Value | Description | Selected Bit Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Availability | 0 1 | Available Not Available | 0 |
| Land/Water Flag | 0 1 | Water Land | 1/0 |
| Coastal Flag | 0 1 | No Yes | 0 |
| Cloud Flag | 0 1 | Clear Cloudy | 0 |
| Aerosol Optical Thickness Confidence Flag | 00 01 10 11 | Very Good Good Marginal No Confidence or Fill | 00 |
| Sun Glint Flag | 0 1 | No Yes | 0 |
| Stray Light Flag | 0 1 | No Yes | 0 |
| Cloud Shadow Possibility Flag | 0 1 | No Yes | 0 |
| Uncertain Surface Reflectance Flag | 0 1 | No Yes | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Dai, T.; Goto, D.; Murakami, H.; Yoshida, M.; Shi, G.; Nakajima, T. Enhanced Simulation of an Asian Dust Storm by Assimilating GCOM-C Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13153020
Cheng Y, Dai T, Goto D, Murakami H, Yoshida M, Shi G, Nakajima T. Enhanced Simulation of an Asian Dust Storm by Assimilating GCOM-C Observations. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13153020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yueming, Tie Dai, Daisuke Goto, Hiroshi Murakami, Mayumi Yoshida, Guangyu Shi, and Teruyuki Nakajima. 2021. "Enhanced Simulation of an Asian Dust Storm by Assimilating GCOM-C Observations" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13153020
APA StyleCheng, Y., Dai, T., Goto, D., Murakami, H., Yoshida, M., Shi, G., & Nakajima, T. (2021). Enhanced Simulation of an Asian Dust Storm by Assimilating GCOM-C Observations. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13153020






