Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in Monsoon Season over South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
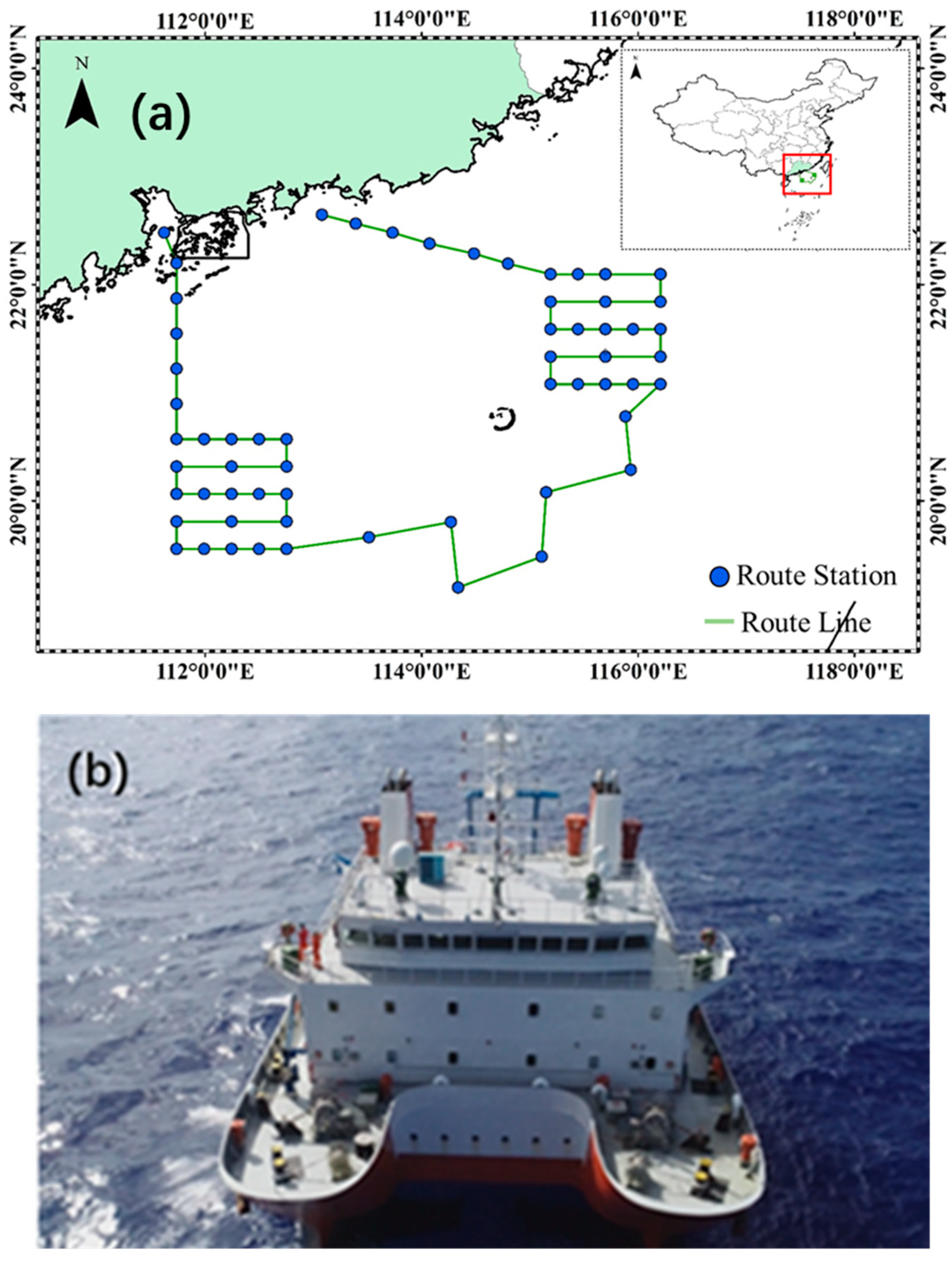
2.1. Parsivel2 Disdrometer and Dataset
2.2. Analysis Methods
3. Results
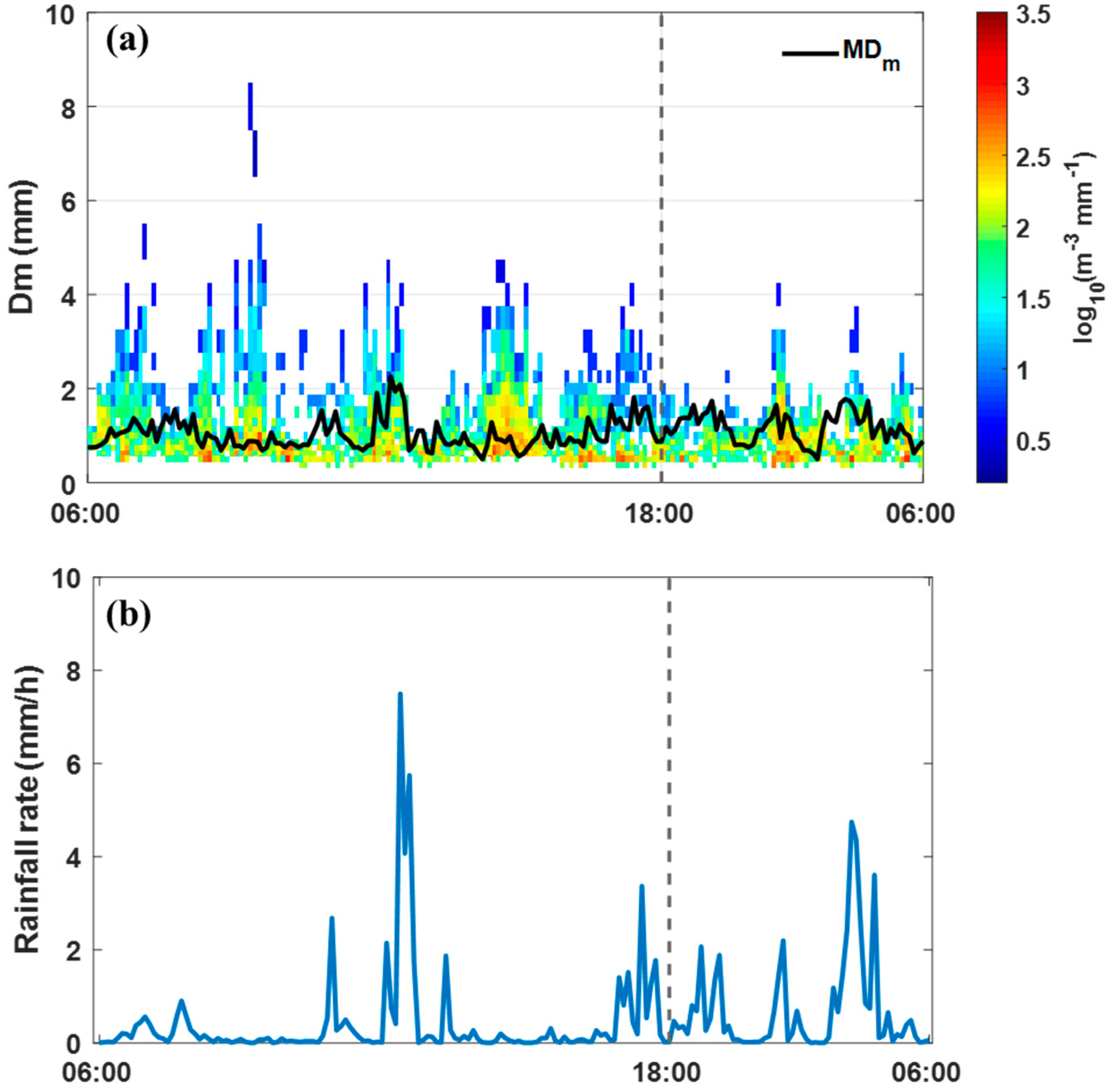
3.1. Diurnal Featuresof Rain DSD
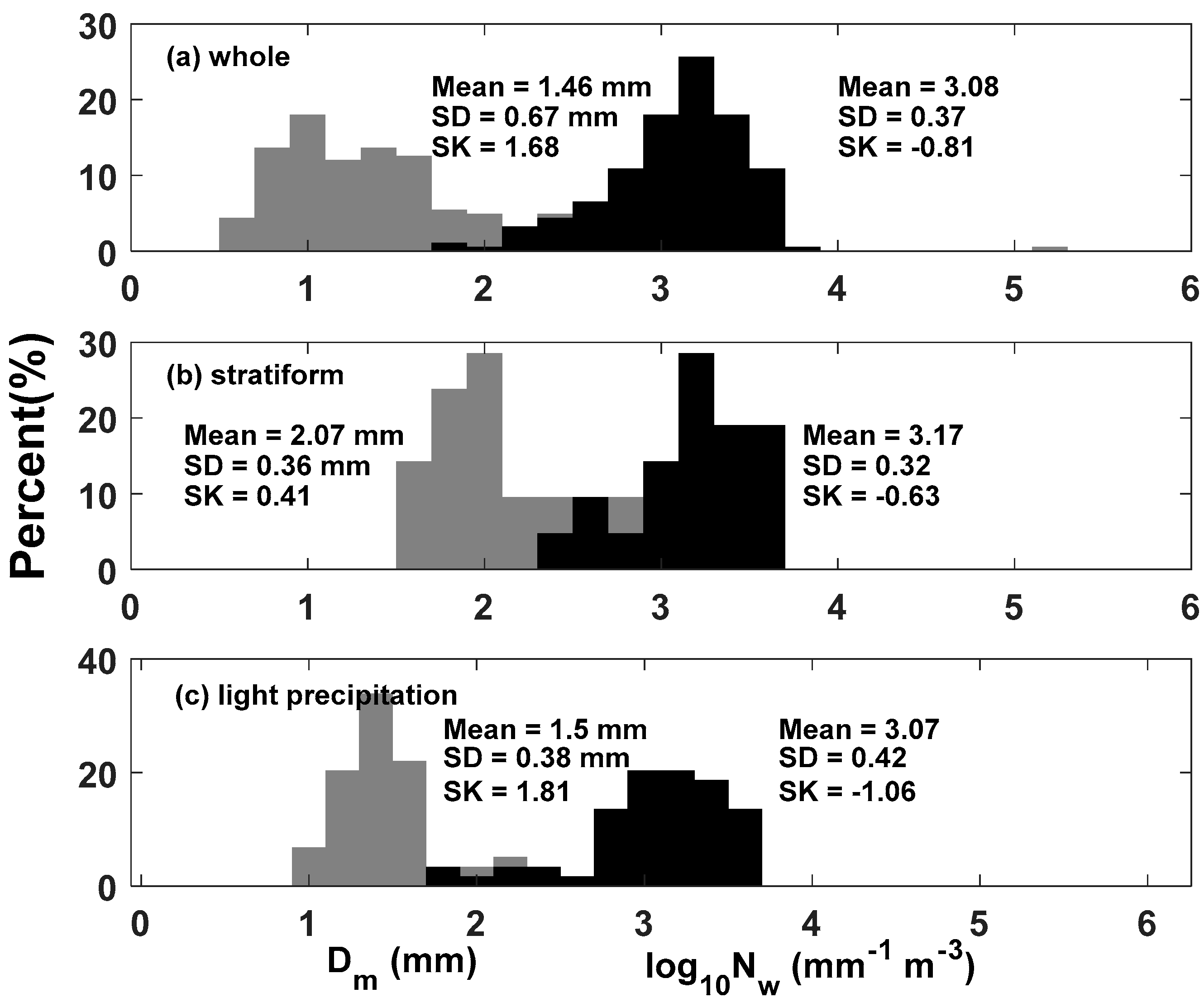
3.2. DSDs in Stratiform and Light Precipitation
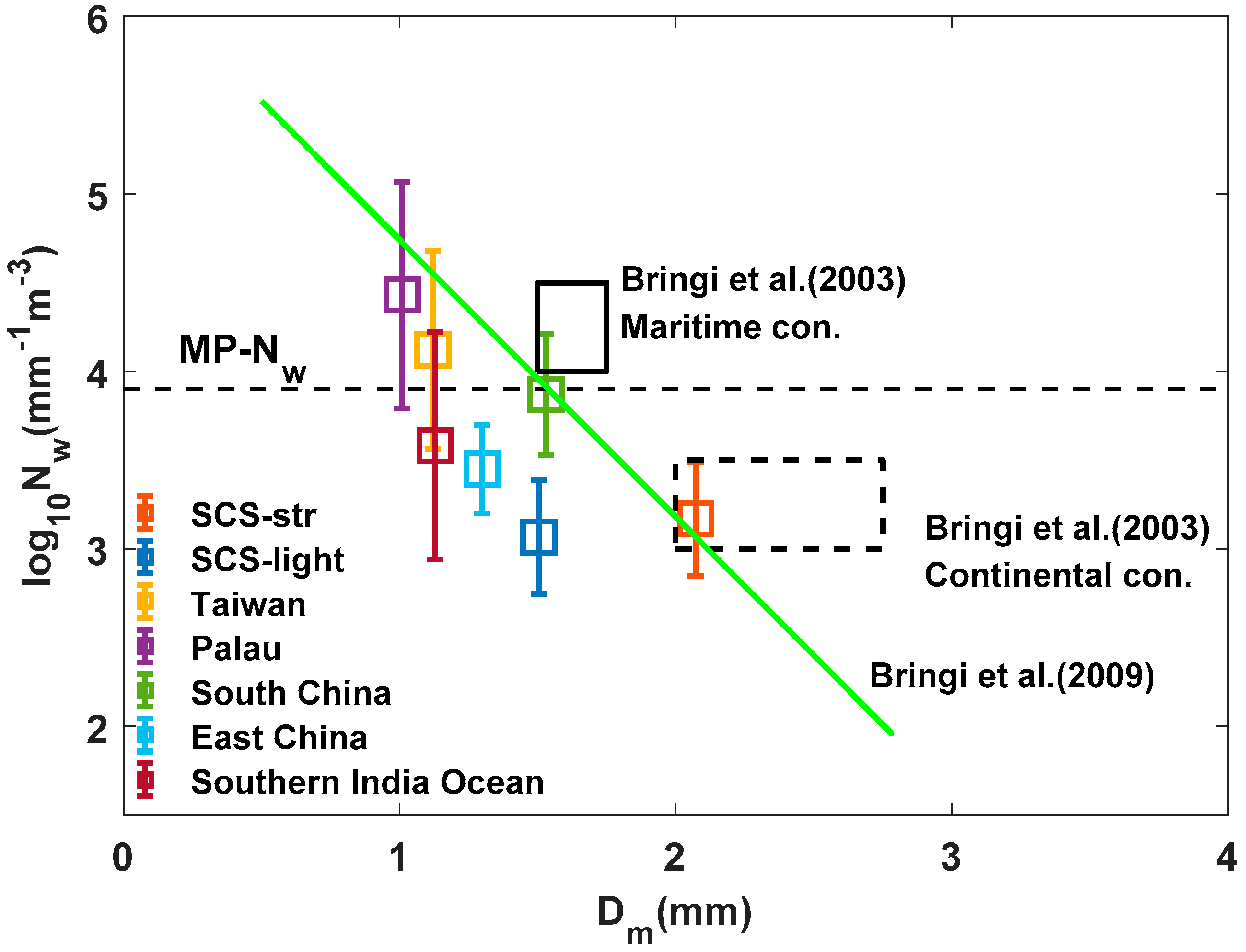
3.3. Composite Raindrop Spectra
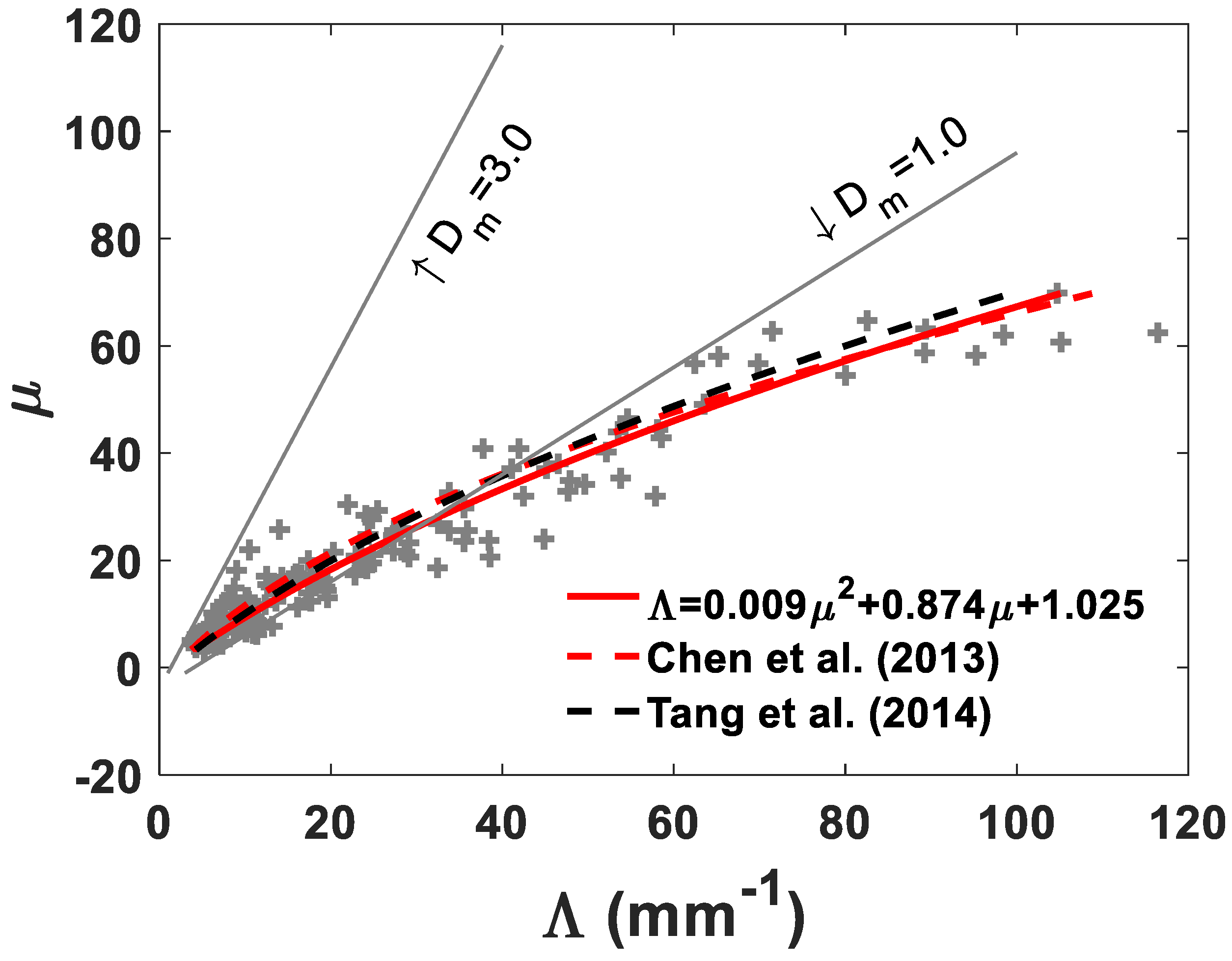
3.4. Shape–Slope (μ-Λ) Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
- (1)
- The SCS sees a high-frequency occurrence of rainy day, while light daily rainfall is more prevalent during the summer monsoon period.
- (2)
- The diurnal variation of DSD is less pronounced in the SCS, likely due to few convective activities over the open ocean.
- (3)
- The histograms of all datasets show a positive skewedness, whereas the histograms are negatively skewed. Meanwhile, there is a high variability in and for the raindrop observations.
- (4)
- Classification of SCS rainfall into stratiform and light precipitation found a lower drop concentration than other regions. The SCS’s stratiform precipitation is similar to the continental convective of Bringi et al. [16].
- (5)
- Medium and large-sized drops existed in the stratiform precipitation, which is potentially affected by the dominant cold rain process during the monsoon season over the SCS.
- (6)
- The - relationship derived from a truncated moment method over the SCS is similar to that in northern and eastern China, and raindrops over the SCS have smaller values than those in Florida. The rainfall over the SCS primarily composed of stratiform and light precipitation, with a relatively higher concentration of large raindrops in stratiform precipitation compared with other regions. This study attempts to investigate the microphysical characteristics of DSD in the SCS. Given the short observation time, the results of this study are still-limited to the precipitation samples and do not cover the entire SCS. The characteristics of DSD in the SCS could serve as a reference for measuring the small-sized drops and improving the algorithm of precipitation in NASA GPM in the open ocean. Further research will focus on the deep investigation of convective rain type over the SCS. More work is underway to prepare for a new field campaign in the coming scientific expedition over the SCS in the summer of 2021, and a further understanding of the DSD characteristics over China is expected in the near future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Brandes, E.A. Improving Parameterization of Rain Microphysics with Disdrometer and Radar Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raupach, T.H.; Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N.; Berne, A. Reconstructing the Drizzle Mode of the Raindrop Size Distribution Using Double-Moment Normalization. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijlenhoet, R.; Torres, D.S. Measurement and parameterization of rainfall microstructure. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Initialization and Numerical Forecasting of a Supercell Storm Observed during STEPS. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, F.S.; Cimini, D.; Montopoli, M. Investigating precipitation microphysics using ground-based microwave remote sensors and disdrometer data. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.-H.; Kang, M.-Y.; Lee, D.-I.; Uyeda, H. Rainfall estimation by S-band polarimetric radar in Korea. Part I: Preprocessing and preliminary results. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Bi, Y.; Xu, W. Characteristics of summer and winter precipitation over northern China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruintjes, R.T. A review of cloud seeding experiments to enhance precipitation and some new prospects. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulbrich, C.W.; Atlas, D. Microphysics of Raindrop Size Spectra: Tropical Continental and Maritime Storms. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2007, 46, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Guo, C.; Feng, L. Characteristics of the raindrop size distributions and their retrieved polarimetric radar parameters in northern and southern China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135–136, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, D.; Liang, Z.; Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Min, C.; Li, H. Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in the Monsoon Season Observed in Southern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in the Meiyu Season Observed in Eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop Size Distribution Measurements at 4500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiebel, J.; Van Baelen, J.; Anquetin, S.; Pointin, Y.; Boudevillain, B. Impacts of orography and rain intensity on rainfall structure. The case of the HyMeX IOP7a event. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 142, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, R.S.; Moraes, M.C.D.S.; Sauvageot, H. Raindrop Size Distribution and Radar Parameters in Coastal Tropical Rain Systems of Northeastern Brazil. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop Size Distribution in Different Climatic Regimes from Disdrometer and Dual-Polarized Radar Analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Konwar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Jain, A.R. Characteristics of Rain Integral Parameters during Tropical Convective, Transition, and Stratiform Rain at Gadanki and Its Application in Rain Retrieval. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 1245–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deo, A.; Walsh, K.J. Contrasting tropical cyclone and non-tropical cyclone related rainfall drop size distribution at Darwin, Australia. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Meneghini, R.; Zawadzki, I. Global and Local Precipitation Measurements by Radar. Meteorol. Monogr. 2003, 30, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Joss, J. An Optical Disdrometer for Measuring Size and Velocity of Hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, J.; Waldvogel, A. Ein spektrograph für niederschlagstropfen mit automatischer auswertung. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1967, 68, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldvogel, A. TheN0Jump of Raindrop Spectra. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schönhuber, M.; Lammer, G.; Randeu, W.L. One decade of imaging precipitation measurement by 2D-video-distrometer. Adv. Geosci. 2007, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokay, A.; Kruger, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Comparison of Drop Size Distribution Measurements by Impact and Optical Disdrometers. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriovsky, B.J.; Bradley, A.; Eichinger, W.E.; Krajewski, W.F.; Kruger, A.; Nelson, B.R.; Creutin, J.-D.; Lapetite, J.-M.; Lee, G.; Zawadzki, I.; et al. An Experimental Study of Small-Scale Variability of Radar Reflectivity Using Disdrometer Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Petersen, W.A.; Tokay, A.; Schultz, C.; Gatlin, P. Drop size distribution comparisons between Parsivel and 2-D video disdrometers. Adv. Geosci. 2011, 30, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.Y.; Chen, L.X. A Review of Recent Research on the East Asian Summer Monsoon in China. In Monsoon Meteorology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.T.; Johnson, R.; Keenan, T.; Cifelli, R.; Gerlach, J.; Thieleandamp, O.; Rickenbach, T.; Tsay, S.-C. A Report of the Field Operations and Early Results of the South China Sea Monsoon Experiment (SCSMEX). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, D.I.; Eriksson, P.; Pfreundschuh, S.; Klepp, C.; Jones, D.C. On the distinctiveness of observed oceanic raindrop distributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 6969–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokay, A.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. Development and Evaluation of the Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters for the NASA Global Precipitation Measurement Mission Ground Validation Program. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, H.; Xie, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y. Microphysical Characteristics of Precipitation during Pre-monsoon, Monsoon, and Post-monsoon Periods over the South China Sea. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The Shape–Slope Relation in Observed Gamma Raindrop Size Distributions: Statistical Error or Useful Information? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Wei, M.; Ge, R.; Li, F.; Ruan, Y. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in south China summer based on the vertical structure derived from VPR-CFMCW. Atmos. Res. 2019, 222, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, H.; Vonnisa, M.; Katsumata, M. Determination of Intraseasonal Variation of Precipitation Microphysics in the Southern Indian Ocean from Joss–Waldvogel Disdrometer Observation during the CINDY Field Campaign. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepp, C. measurement network for surface validation—OceanRAIN. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Meneghini, R.; Tokay, A. Uncertainties of GPM DPR Rain Estimates Caused by DSD Parameterizations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2014, 53, 2524–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Le, M. Evaluation of profile classification module of GPM-DPR algorithm after launch. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 5174–5177. [Google Scholar]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. Evaluation of the New Version of the Laser-Optical Disdrometer, OTT Parsivel. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Kingsmill, D.; Nance, L.B.; Löffler-Mang, M. Observations of Precipitation Size and Fall Speed Characteristics within Coexisting Rain and Wet Snow. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bumke, K.; Seltmann, J. Analysis of Measured Drop Size Spectra over Land and Sea. ISRN Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokay, A.; Bashor, P.G. An experimental study of small-scale variability of raindrop size distribution. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 2348–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bechini, R. An Improved Dual-Polarization Radar Rainfall Algorithm (DROPS2.0): Application in NASA IFloodS Field Campaign. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 917–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.C.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G. Errors in Estimating Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters Employing Disdrometer and Simulated Raindrop Spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Smith, E.A. Convective–Stratiform Precipitation Variability at Seasonal Scale from 8 Yr of TRMM Observations: Implications for Multiple Modes of Diurnal Variability. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4087–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Smith, E.A. Mechanisms for Diurnal Variability of Global Tropical Rainfall Observed from TRMM. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5190–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, W.M.; Jacobson, R.W. Diurnal Variation of Deep Cumulus Convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 1977, 105, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seela, B.K.; Janapati, J.; Lin, P.-L.; Reddy, K.K.; Shirooka, R.; Wang, P.K. A Comparison Study of Summer Season Raindrop Size Distribution between Palau and Taiwan, Two Islands in Western Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Sekine, S. Diurnal Variation of Convective Activity over the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 72, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Siems, S.; Belušić, D.; Manton, M.J.; Huang, Y. A Climatology of the Precipitation over the Southern Ocean as Observed at Macquarie Island. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2015, 54, 2321–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, J.L.J.; Schumacher, C.; Humes, K.; Funk, A. Drop-Size Distribution Variations Associated with Different Storm Types in Southeast Texas. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Cloud Microphysical Properties, Processes, and Rainfall Estimation Opportunities. In Radar and Atmospheric Science: A Collection of Essays in Honor of David Atlas; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, S.; Boutle, I. An improved representation of the raindrop size distribution for single-moment microphysics schemes. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X. The Concept of “Normalized” Distribution to Describe Raindrop Spectra: A Tool for Cloud Physics and Cloud Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
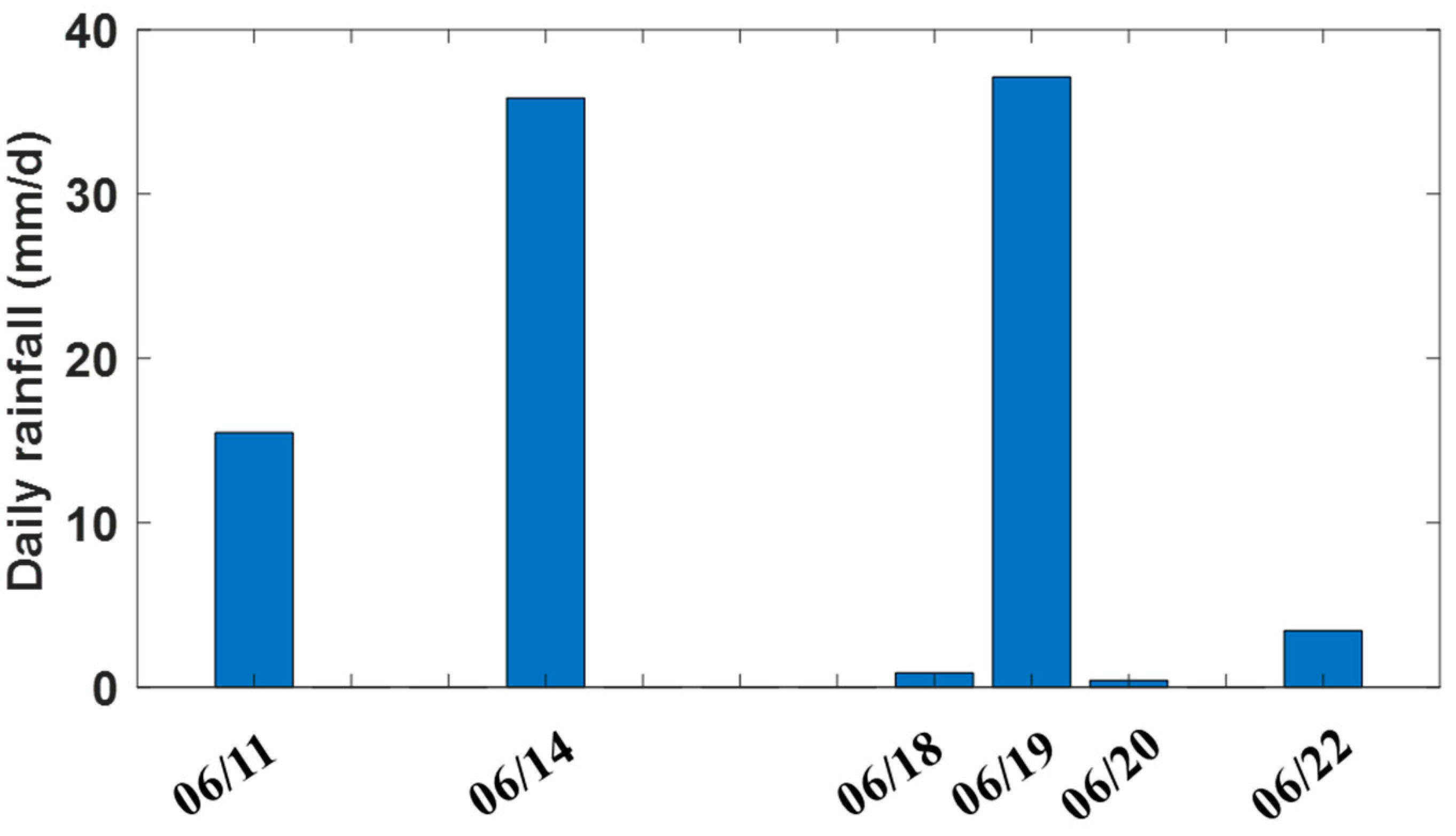
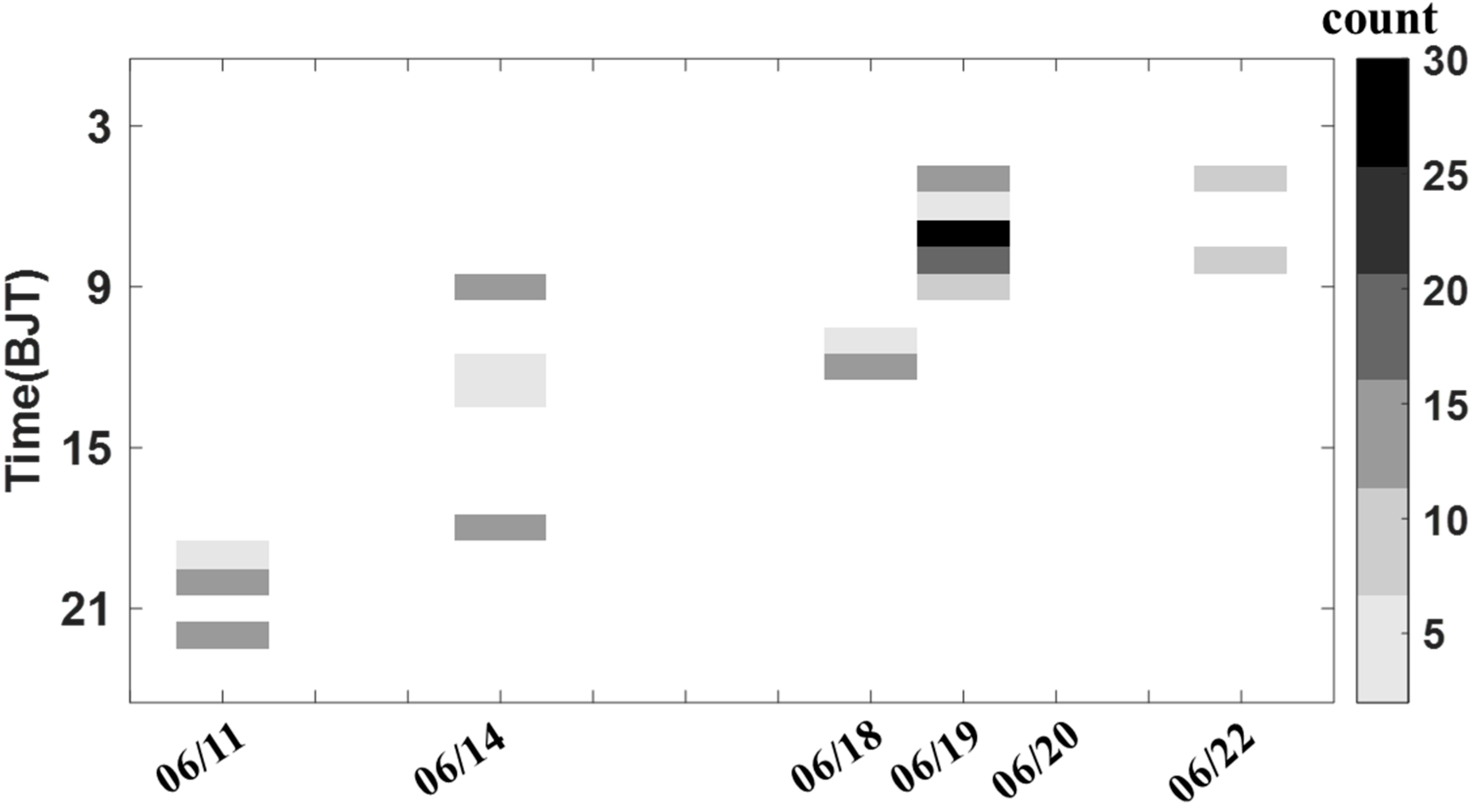

| Time (BJT) | No. of Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 20190611 | 30 | 2.20 | 3.31 |
| 20190614 | 45 | 7.49 | 5.14 |
| 20190618 | 30 | 3.37 | 1.57 |
| 20190619 | 74 | 4.75 | 2.73 |
| 20190620 | 15 | 0.50 | 1.30 |
| 20190622 | 9 | 4.49 | 2.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, A.; Pang, Y. Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in Monsoon Season over South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152878
Huang C, Chen S, Zhang A, Pang Y. Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in Monsoon Season over South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152878
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chaoying, Sheng Chen, Asi Zhang, and Ying Pang. 2021. "Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in Monsoon Season over South China Sea" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152878
APA StyleHuang, C., Chen, S., Zhang, A., & Pang, Y. (2021). Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in Monsoon Season over South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152878