Abstract
The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Double-Moment 7-Class (WDM7) cloud microphysics scheme was developed to parameterize cloud and precipitation processes explicitly for mesoscale phenomena in the Korean Integrated Model system. However, the WDM7 scheme has not been evaluated for any precipitating convection system over the Korean peninsula. This study modified WDM7 and evaluated simulated convection during summer and winter. The suggested modifications included the integration of the new fall velocity–diameter relationship of raindrops and mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase precipitable hydrometeors (the latter is for representing mixed-phase particles). The mass-weighted terminal velocity for snow and graupel has been suggested by Dudhia et al. (2008) to allow for a more realistic representation of partially rimed particles. The WDM7 scheme having an additional hail category does not apply this terminal velocity only for hail. Additionally, the impact of enhanced collision-coalescence (C-C) efficiency was investigated. An experiment with enhanced C-C efficiency overall improved the precipitation skill scores, such as probability of detection, equitable threat score, and spatial pattern correlation, compared with those of the control experiment for the summer and winter cases. With application of the new mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase hydrometeors, the hail mixing ratio at the surface was considerably reduced, and rain shafts slowed down low-level winds for the winter convective system. Consequently, the simulated hydrometeors were consistent with observations retrieved via remote sensing. The fall velocity–diameter relationship of raindrops further reduced the cloud ice amount. The proposed modifications in our study improved the simulated precipitation and hydrometeor profiles, especially for the selected winter convection case.
1. Introduction
The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Single-Moment 6-Class (WSM6) [1] and WRF Double-Moment 6-Class (WDM6) [2] cloud microphysics schemes use the same ice microphysical processes, which are based on Hong et al. [3], and contain three ice categories: snow, graupel, and ice crystals. The WDM6 cloud microphysics scheme predicts the number concentrations of liquid-phase hydrometeors together with the mixing ratios of five hydrometeors: rain, snow, graupel, cloud water, ice crystals, and water vapor. Meanwhile, WSM6 only predicts the mixing ratio of six hydrometers. Previous studies have shown the superiority of double-moment microphysics schemes over single-moment ones in simulating moist convection over the Korean peninsula [4,5,6]. However, a deficiency in double-moment schemes in simulating solid-phase hydrometeors was also reported when they were used to simulate warm-type heavy rainfall [4] and winter precipitating convection over Korea during the International Collaborative Experiments for Pyeongchang 2018 Olympic and Paralympic winter games (ICE-POP 2018) [7].
To overcome the limitation of cloud microphysics schemes in simulating precipitation and reflectivity in deep convective systems, i.e., having only three ice categories [8,9], Bae et al. [10] developed the WRF Single-Moment 7-Class (WSM7) and WRF Double-Moment 7-Class (WDM7) microphysics schemes by introducing a new hydrometeor category (hail) into the WSM6 and WDM6 schemes. WSM7 and WDM7, which have four ice categories, predict the mixing ratio of four solid-phase hydrometeors, namely, snow, graupel, hail, and ice crystals, together with water vapor, cloud water, and rain mixing ratios. The difference between WSM7 and WDM7 is the prediction of the number concentrations of liquid-phase hydrometeors (e.g., cloud droplets and rain), including the number concentration of cloud condensation nuclei. The hail mixing ratios in WSM7 or WDM7 can be predicted following a development strategy that is based on Tao et al. [9] and Lang et al. [11]. Lang et al. [11] and Bae et al. [10] presented the benefits of using a microphysics scheme with cloud ice as the fourth category in simulating the radar reflectivity of convective systems over the North American continent. However, the WSM7 (or WDM7) scheme has not been evaluated for any convective system over the Korean peninsula.
The ultimate goal of cloud microphysics schemes is to accurately predict precipitation through the parameterization of detailed microphysics processes. The mixing ratio of precipitable hydrometeors, such as rain, snow, graupel, and hail at the surface, which is predicted on the basis of tens of microphysics processes, is converted to precipitation amount. Among the several microphysics processes in cloud microphysics schemes, collision-coalescence (C-C) processes are the major sinks or sources needed to generate mixing ratios of hydrometeors, especially solid-phase precipitable ones [7,12]. Grasso et al. [12] reported a lack of simulated cloud ice from the WSM6 scheme over the upper atmosphere, unlike the observed feature from the GOES-13 satellite. The reduction in the C-C process efficiency of cloud ice by snow led to increased cloud ice in anvil clouds. Their findings provide guidance as to which C-C process should be reformulated, in a more physical manner, to solve problems in simulating anvil clouds.
Hydrometeor characteristics, namely, density, size distribution, fall velocity–diameter (V–D) relationship, and mass–diameter relationship, are also important for predicting hydrometeors’ mixing ratios. Previous studies have shown the importance of the V–D relationship for simulated hydrometeors’ distribution and convection [13,14]. Kim et al. [13] noted that the V–D relationship of raindrops in WS(D)M6, including WS(D)M7, considerably deviates from the observed relationship. However, when they introduced the measured V–D relationship for raindrops by Gunn and Kinzer [15], the simulated precipitation amount was further deteriorated for the mesoscale rainfall case over south Korea with WSM5 and WSM6 [13]. This study introduced the identical V–D relationship of raindrops [15] with Kim et al. [13] and investigated its impacts on the simulated surface precipitation both during winter and summer seasons. Meanwhile, Dudhia et al. [16] suggested a new method of allowing graupel and snow to exist as mixed-phase particles by assigning a single terminal velocity weighted by the graupel and snow mixing ratios. They noted that reduced graupel production influenced the simulated cloud structure and surface precipitation. WS(D)M6 adopts the mass-weighted terminal velocity suggested by Dudhia et al. [16]. However, WS(D)M7 does not apply this weighted velocity in the hail category; thus, hail is not allowed to exist as a mixture with snow and/or graupel. This causes an inconsistency in hydrometeor characteristics.
The purpose of our study was to modify the WDM7 scheme and investigate the effects of the introduced modifications on the simulated precipitating convection. These modifications are related to the C-C efficiency, V–D relationship of raindrops, and mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase precipitating hydrometeors (snow, graupel, and hail). The WDM7 scheme is being considered as a cloud microphysics option for the next-generation mesoscale model in the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). Section 2 describes the simulated convection cases. In Section 3, the experimental setup, including the WRF model configuration and sensitivity experiment design, is presented. The results and summary are presented in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Case Description
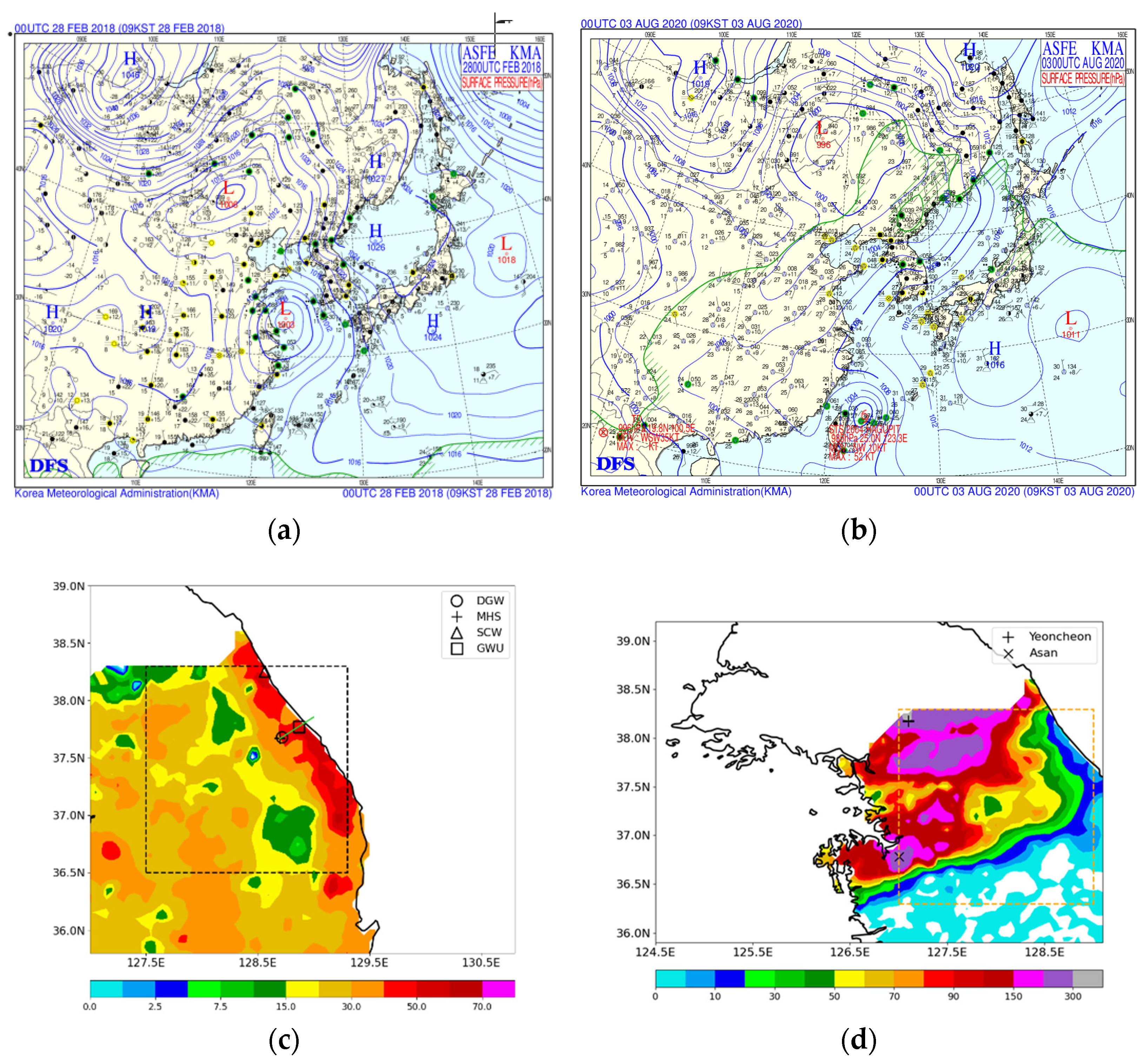
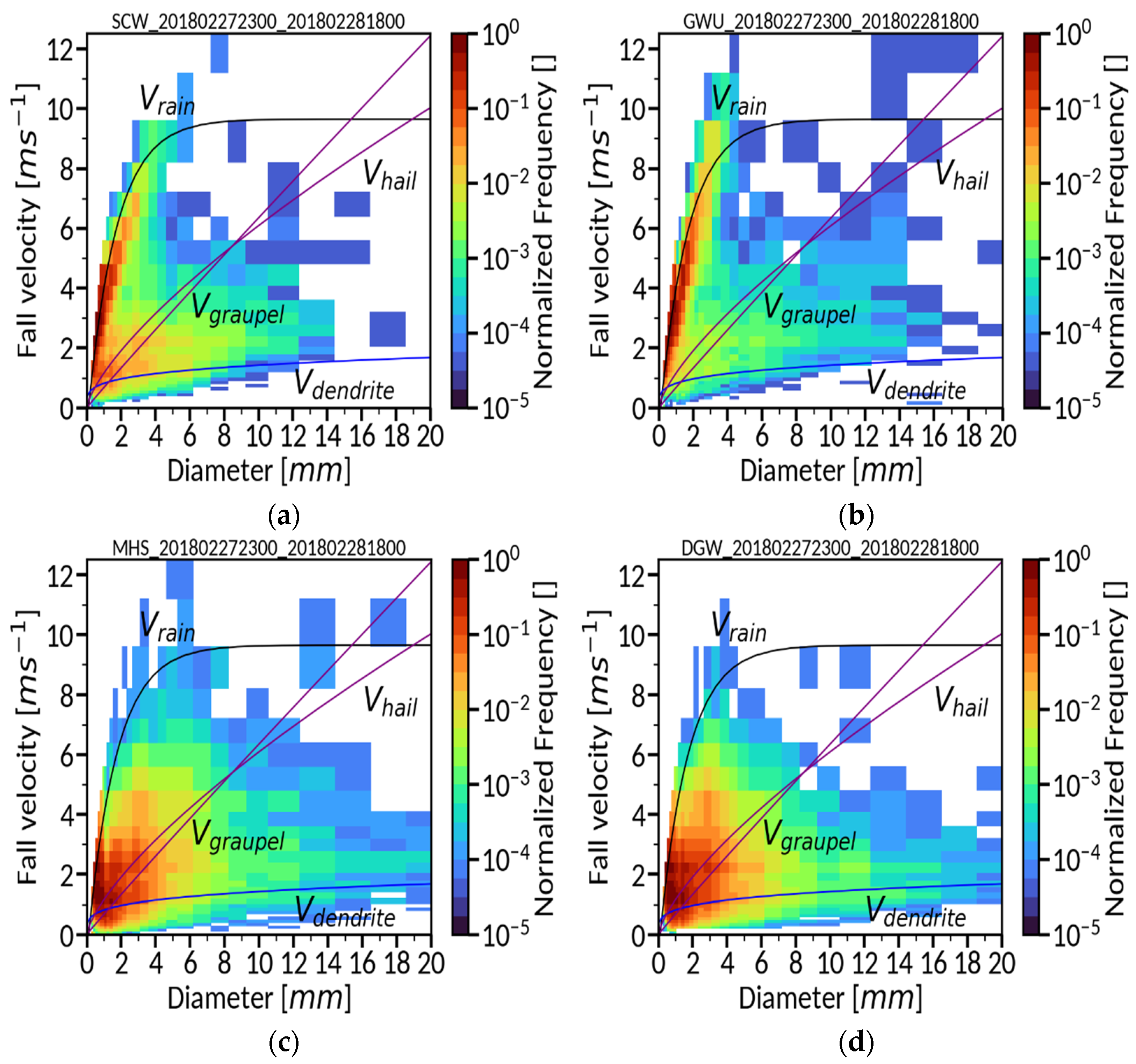
We used two convection cases to evaluate the performance of the modified WDM7. CASE1 takes place in winter and illustrates a heavy snowfall event during the ICE-POP 2018 field campaign period over Korea. A low-pressure system develops near Shanghai and passes through the southern part of the Korean peninsula. Meanwhile, a high-pressure system is identified over the eastern coast of the peninsula (Figure 1a). This synoptic environment leads to a strong pressure gradient over the northeastern part of the Korean peninsula, which strengthens the easterly winds and brings snowfall over the corresponding region. On 27–28 February 2018, 40 cm-depth snow was measured at the site marked with a circle in Figure 1c (DGW). Figure 1c depicts the observed precipitation amount (mm) from an automatic weather station (AWS). There exist 604 AWS sites over South Korea. The spatial resolution of AWS sites is 13 km on average. AWS measures precipitation amount using the weight precipitation gauge with an auto-empting capability. The Cressman method [17] is utilized to interpolate AWS-measured precipitation data, which has taken the quality control procedures proposed by the World Meteorological Organization into a 5 km horizontal grid spacing. The frequency distributions of the measured particle fall velocity at the surface indicate that the particle type at the coastal sites (SCW and GWU) is rain (Figure 2a,b), and that observed at the mountain sites (MHS and DGW) is fast-falling, graupel-like snow particles (Figure 2c,d). In addition, naked-eye observation revealed that there were no hail-like particles on 27–28 February 2018.
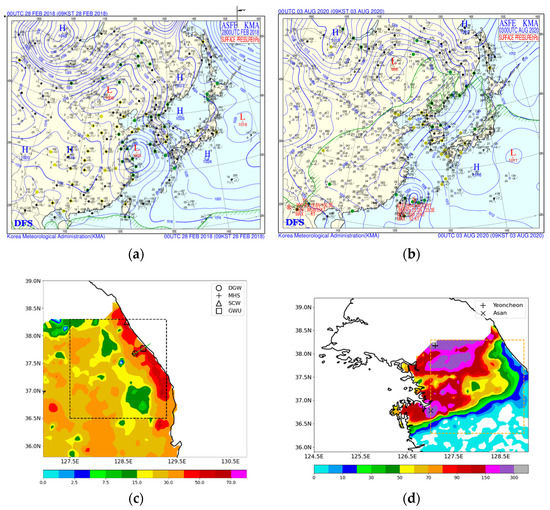
Figure 1.
Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) surface weather chart: (a) 28 February 2018, 0000 UTC (CASE1); (b) 3 August 2020, 0000 UTC (CASE2). Accumulated precipitation values (mm) obtained from the AWS observation: (c) CASE1, throughout 19 h from 27 February 2018, 2300 UTC, to 28 February 2018, 1800 UTC; (d) CASE2, throughout 30 h from 2 August 2020, 0000 UTC, to 3 August 2020, 0600 UTC. The green solid line and marks in (c) represent the locations of the vertical cross-sections in Figure 11 and observation sites in Figure 2. The “x” mark in (d) indicates Asan and “+” mark represents Yeoncheon, where the maximum precipitation during the analysis period is observed.
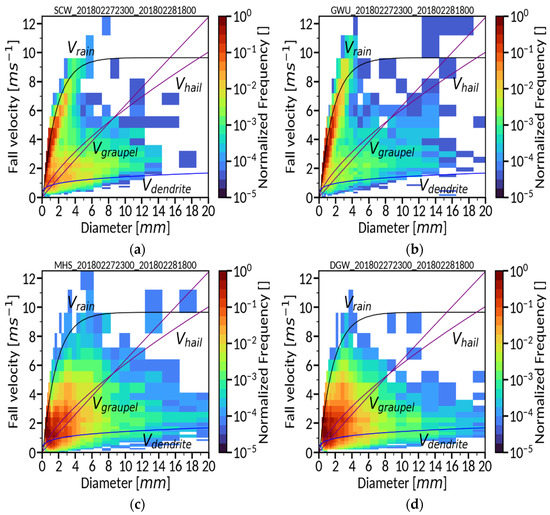
Figure 2.
Frequency distribution of measured particle fall velocity as a function of diameter using Parsivel disdrometers [18,19] from 27 February 2018, 2300 UTC, to 1 March 2018, 0300 UTC: (a,b) at two mountain sites (MHS and DGW); (c,d) at two coastal sites (SCW and GWU). The solid lines indicate the relationships between particle fall velocity and diameter for four hydrometeor types (rain, graupel, hail, and dendrite) at sea level. The fall velocity curve of rain is the power law fit to the Gunn–Kinzer data [20], and the dendrite and graupel/hail curves are derived from the previous observed data [21,22].
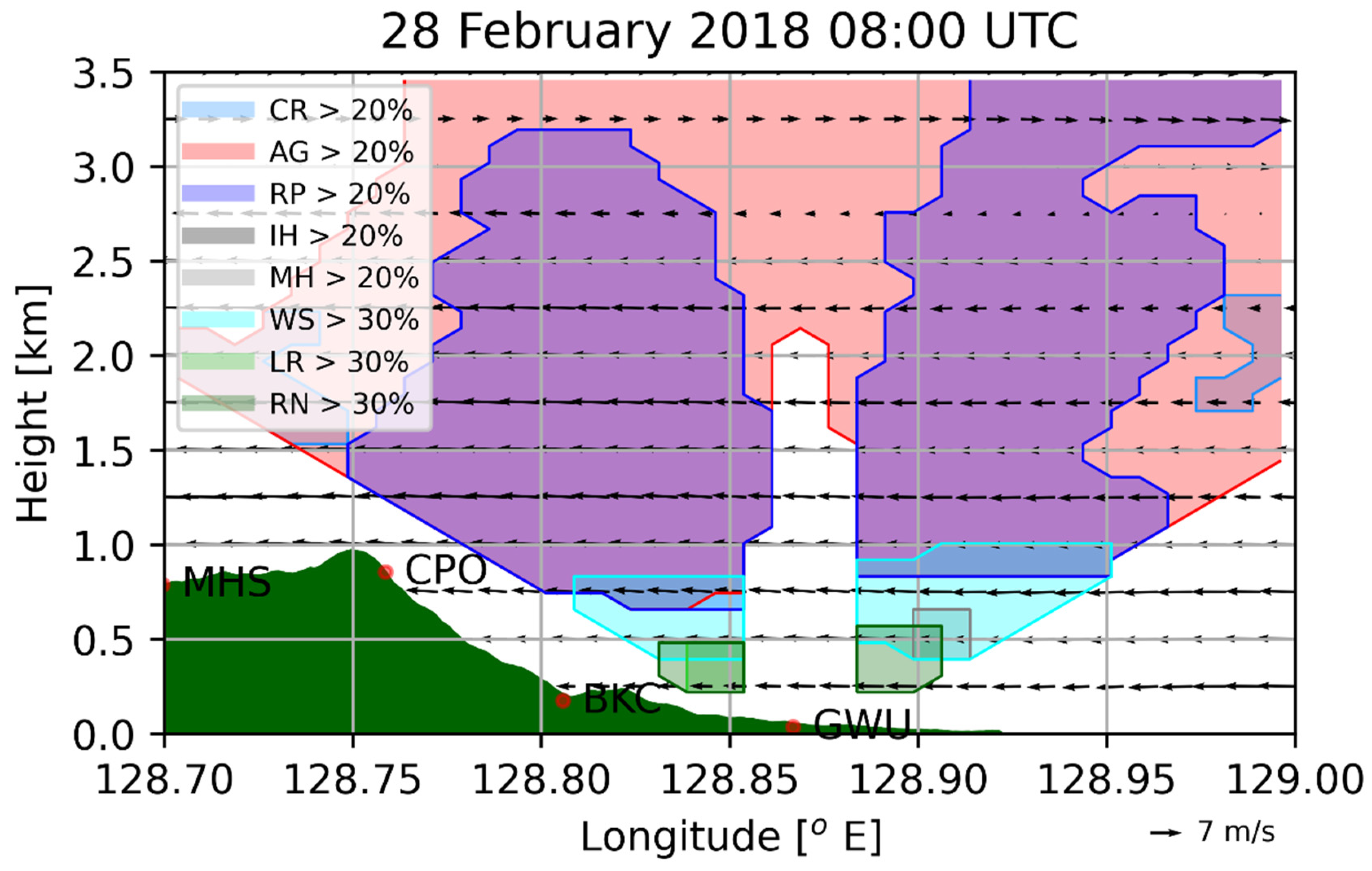
Figure 3 shows the classified hydrometeors; the data were obtained from a polarimetric MXpol radar at the GWU site on 28 February 2018, 0800 UTC, which was 1 h earlier than the observed maximum precipitation time. The proportion of each hydrometeor is estimated on the basis of the algorithm proposed by Besic et al. [23,24]. The hydrometeors are classified as crystal (CR), aggregate (AG), rimed snow particles (RP), vertically aligned ice (VI), ice hail/graupel (IH), melting hail (MH), wet snow (WS), light rain (LR), or rain (RN). VI was not considered in this study, because its occurrence is rare. One advantage of this algorithm is the representation of hydrometeors’ mixture for a given sampling volume. For comparison, CR, AG, RP, IH, and RN are assigned to the simulated cloud ice, snow, graupel, hail, and rain, respectively. The observed LR can be interpreted as either cloud water or rain. The overlaid wind vectors (cross-barrier wind and vertical wind) were from radar-based three-dimensional wind fields and were retrieved from multiple surveillance Doppler radars at the same time [25,26]. Snow and graupel are the main hydrometeor types between the 1 and 3.5 km levels. Wet snow, which is not predicted in models, is primarily seen around the melting layers between the 0.5 and 1 km levels. Rain and light rain are produced below the 0.6 km level. Below the 3 km level, easterly winds are observed, and their strength is maximum at around the 1.2 km level.
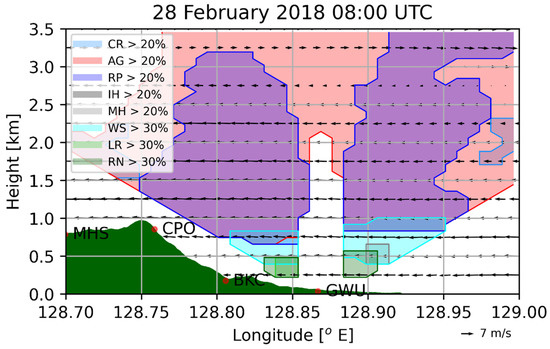
Figure 3.
Classified hydrometeors retrieved from MXPol radar on 28 February 2018, 0800 UTC: crystal (CR), aggregate (AG), rimed particles (RP), iced hail/graupel (IH), melting hail (MH), wet snow (WS), light rain (LR), and rain (RN). CR, AG, RP, IH, and RN are compared with the model-simulated cloud ice, snow, graupel, hail, and rain, respectively. The observed LR can be either cloud water or rain. Hydrometeors observed more than a certain percentage (20–30%) at the given volume are drawn. Overlaid wind (cross-barrier wind and vertical wind) is retrieved from multiple Doppler radars at the same time.
CASE2 is a heavy precipitation case occurring on 1–3 August 2020 (summer), over the central part of the Korean peninsula. Typhoon Hagupit, located near Taiwan, continuously provides a warm, moist air mass to the peninsula (Figure 1b). Brought through an unusually strong low-level jet stream, this warm, moist air meets cold, dry air at the upper level. This synoptic environment increases the convection instability over the central part of the Korean peninsula, subsequently causing heavy precipitation (Figure 1d). The maximum precipitation amount is about 300 mm over 24 h near Yeoncheon, Gyeonggi-do. The location of Yeoncheon is marked with a cross in Figure 1d.
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Model Configuration
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) version 4.1.3 [27], which was released in November 2019, was utilized in this research. The applied physics package includes the Yonsei University planetary boundary layer scheme [28], Rapid Radiative Transfer Model for General Circulation Models (RRTMG) longwave and shortwave radiation scheme [29], unified Noah land surface scheme [30], and Kain–Fritsch (KF) cumulus parameterization [31]. The KF scheme is used only in the outer domain (9 km). The WDM7 cloud microphysics scheme [10] with the bug fix from Lei et al. [32] is applied. The cloud microphysics processes in WDM7 are recoded to allow WDM7 to adopt the observed microphysical parameters during the ICE-POP 2018 field campaign. European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Reanalysis 5 (ERA5) data [33] are enforced every 6 h for the initial and boundary conditions of the model.
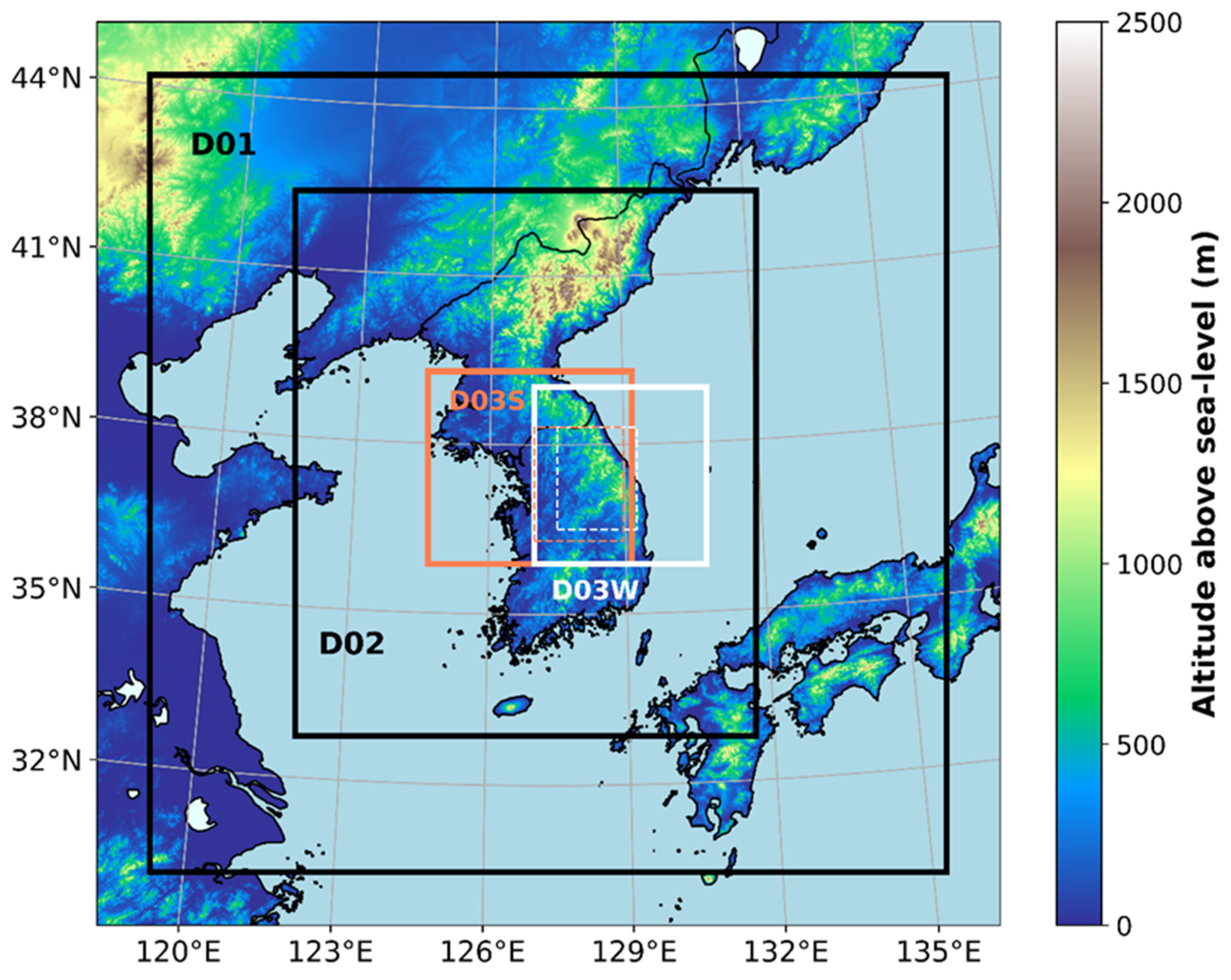
The three nested domains with horizontal grid spacings of 9, 3, and 1 km are configured (Figure 4). The outermost (D01), intermediate (D02), and innermost domains (D03) contain 169 × 169, 294 × 348, and 330 × 349 grid points, respectively, for CASE1. For CASE2, the number of grid points for D01 and D02 are the same as those in CASE1, but 390 × 369 grid points are applied for D03. The domain areas for D03 are drawn with the white square for CASE 1 and the orange square for CASE2 (Figure 4). In both cases, the number of vertical levels is 65, with a domain top height of 50 hPa. The integration time steps are 36, 12, and 4 s for D01, D02, and D03, respectively. For CASE1, model integration is conducted for 30 h from 27 February 2018, 1800 UTC; analysis is conducted from February 27, 2018, 2300 UTC, to 28 February 2018, 1800 UTC, by considering the model spin-up time. For CASE2, model integration is performed for 42 h from 1 August 2020, 1800 UTC; analysis is conducted from 2 August 2020, 0000 UTC, to 3 August 2020, 0600 UTC.
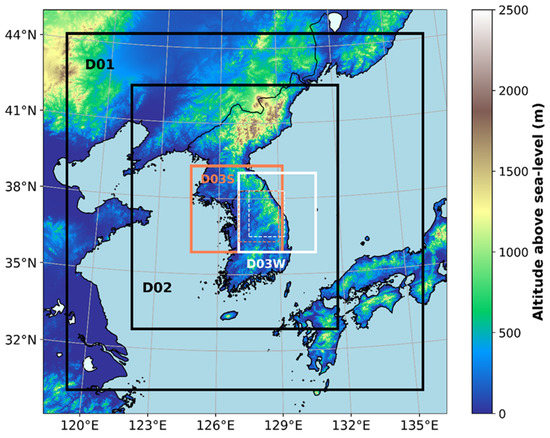
Figure 4.
Domain configuration for simulations with topography. Three nested domains with 9, 3, and 1 km resolutions are configured. The innermost domain, D03, is designed differently for each case. The white box is for CASE1, and the orange box is for CASE2. The analysis domain for each case is marked with a dotted line. Shading indicates the terrain height above sea level.
3.2. Sensitivity Experiments
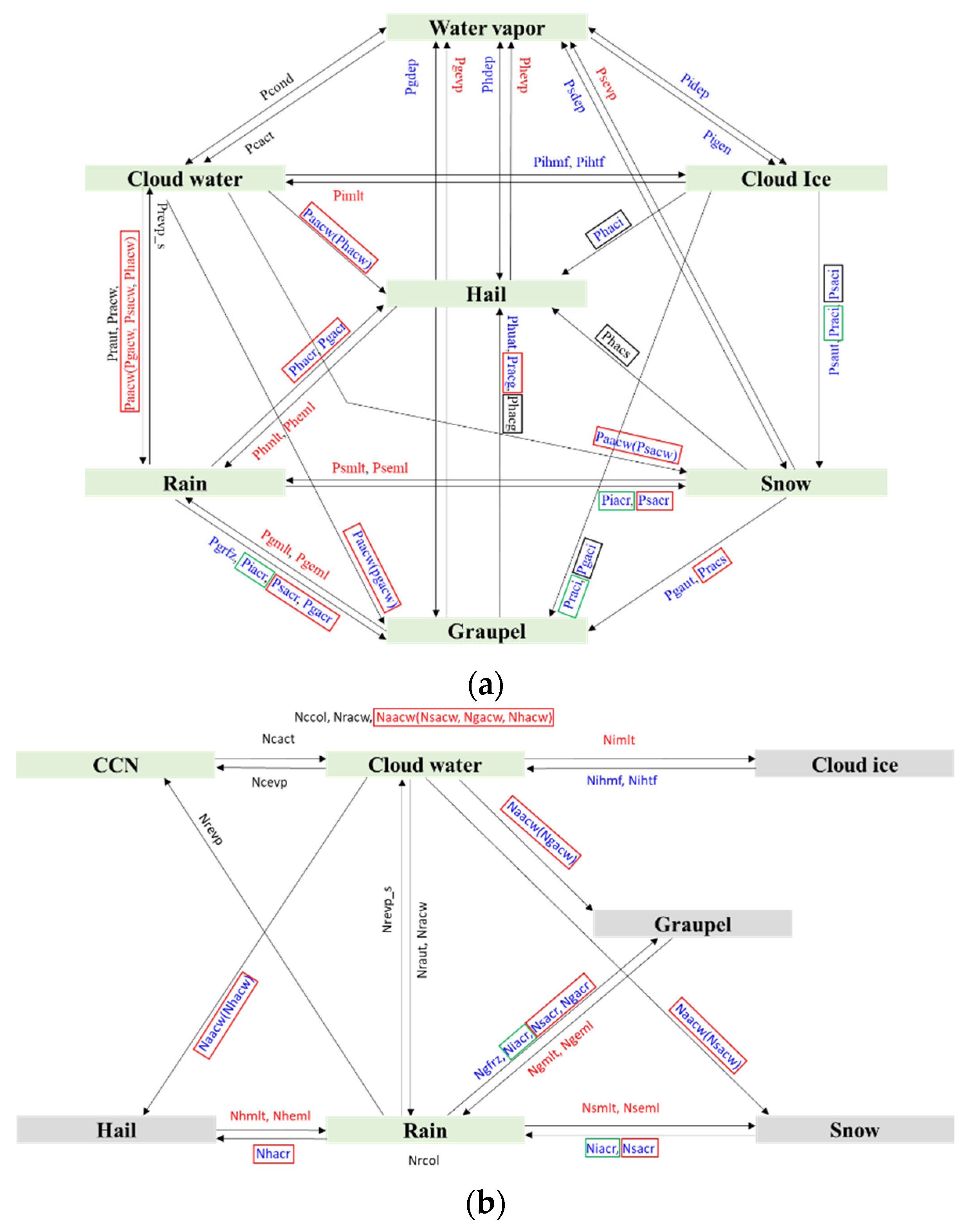
Three sensitivity experiments, namely, EFF, VAH, and VDR, are designed as shown in Table 1. The EFF experiment is conducted to evaluate the increased C-C efficiency. The C-C efficiency is reduced in WDM7 (personal discussion with Jimy Dudhia), CTL, to overcome the problem of freezing rain at the surface over the US and Canada. By contrast, the effect of C-C efficiency has not been evaluated for the precipitating convection over the Korean peninsula. The square of two hydrometeors’ mixing ratio is multiplied by the C-C processes in CTL, as noted in Table 2. In EFF, we remove the factor reducing the C-C efficiency, thus increasing the C-C processes. The processes in the green and red squares in Figure 5 are the ones affected by the increased C-C efficiency in EFF. More solid-phase precipitating particles, such as graupel, snow, and hail, can be generated with increased C-C efficiency. The microphysical processes in Figure 5 are defined in Table 3.

Table 1.
Summary of sensitivity experiments.

Table 2.
C-C efficiencies. The symbol and expression of the C-C efficiencies are noted with the cloud microphysical processes affected by the EFF experiment. The processes are defined in Table 3.
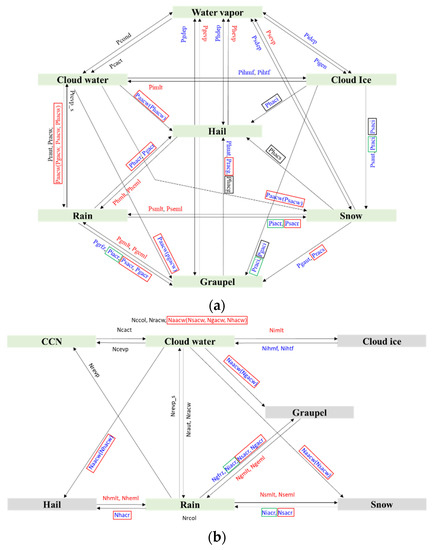
Figure 5.
Flowcharts of source/sink terms for prediction of (a) mass and (b) number concentration of hydrometeors in WDM7. The red (blue) terms are activated when the temperature is above (below) 0 °C, whereas the black terms are in the entire temperature regime. The hydrometeor number concentrations or mixing ratios in green boxes are predicted in the WDM7 scheme. The microphysics terms in green (black) squares are the ones affected by the modification of C-C efficiency (mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase precipitating hydrometeors). The terms in red squares are the ones affected by both modifications.

Table 3.
List of symbols for cloud microphysical processes.
The VAH experiment adopts the mass-weighted terminal velocity of all solid-phase precipitable hydrometeors (graupel, snow, and hail). In CTL, WDM7 applies the mass-weighted terminal velocity only for snow and graupel to represent the mixed-phase particles [16]. For consistent representation of the solid-phase hydrometeor characteristics, we also apply the mass-weighted terminal velocity to hail. In accordance with the method suggested by Dudhia et al. [16], the mass-weighted terminal velocity for snow, graupel, and hail () can be expressed as
where , , and are the mass-weighted terminal velocities of snow, graupel, and hail, respectively, and q is the mixing ratio of each hydrometeor. Subscripts S, G, and H stand for snow, graupel, and hail, respectively.
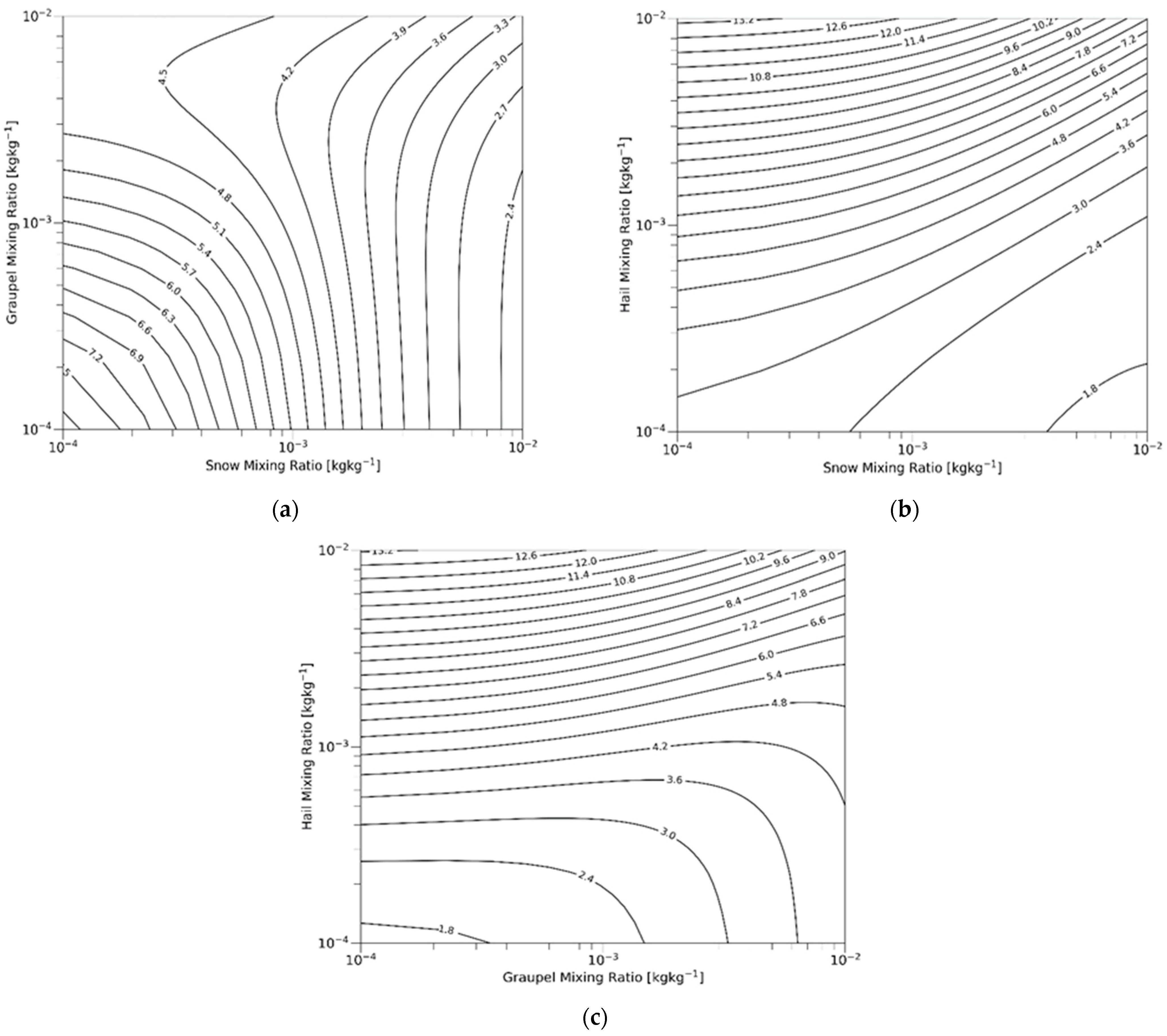
Figure 6 shows the calculated with respect to the pairs of mixing ratios. The other hydrometeor, not shown on the axis, is fixed at an amount of 0.1 g kg−1. Figure 6a shows as a function of the snow–graupel mixing ratio, and the mixing ratio of hail is fixed. decreases with snow–graupel mixing ratios because hail is more dense than graupel and snow. As the mixing ratio of hail increases, increases at the given amount of snow (or graupel) (Figure 6b,c). Meanwhile, decreases with increasing snow (graupel) except some ranges where the hail amount is relatively small in pairs with graupel (Figure 6c). Hence, the newly introduced terminal velocity is more sensitive to the mixing ratio of hail than those of graupel and snow. The C-C process of snow (graupel) by hail, phacs (phacg), is eliminated by introducing the new mass-weighted terminal velocity (Figure 5). The elimination of phacs and phacg always reduces hail amount and increases snow and graupel amount. Besides phacs and phacg, the processes in the black and red squares in Figure 5 are changed in VAH.
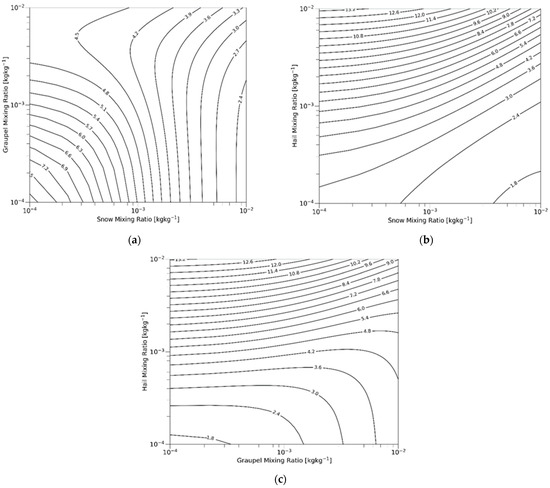
Figure 6.
Mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase precipitating hydrometeors () as a function of mixing ratio pairs for (a) snow and graupel, (b) snow and hail, and (c) graupel and hail. The other hydrometeor, not shown on the axis, is fixed at an amount of 0.1 g kg−1. All figures are drawn under the assumption of −10 °C air temperature.
To investigate the effects of the revised V–D relationship of raindrops on simulated convection using WDM7, we performed the VDR experiment. In VDR, the coefficients in the V–D relationship of raindrops are modified on the basis of observation [15], which is seen in Equation (2). With this revised relationship, the raindrop velocity increases in the diameter range of 0.27 mm to 3 mm relative to that in the original V–D relationship. Figure 3 in Kim et al. [13] compares the original and revised V–D relationships.
where ,, and are set as 5881, 1.03, and 202.4, respectively, in VDR in accordance with Kim et al. [13]. ⍴ and represent the air density and density of air at the reference state, respectively. By multiplying the factor, , in the V–D relationship in Equation (2), the relationship can be corrected depending on the height. Previous studies have also shown that the V–D relationship has a clear dependence on the height; thus, it should be corrected [34,35].
4. Results
4.1. Precipitating Convection during Winter
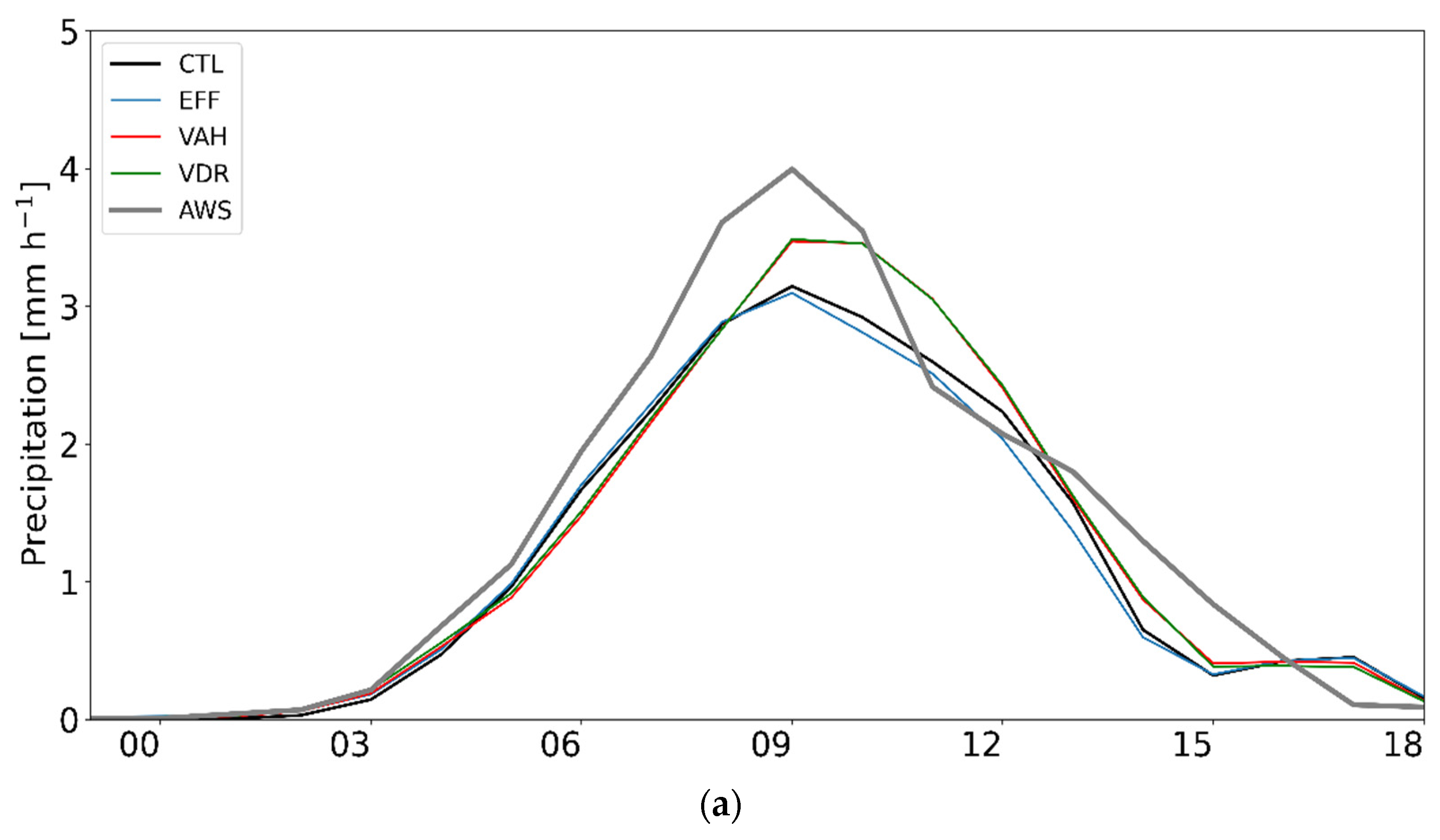
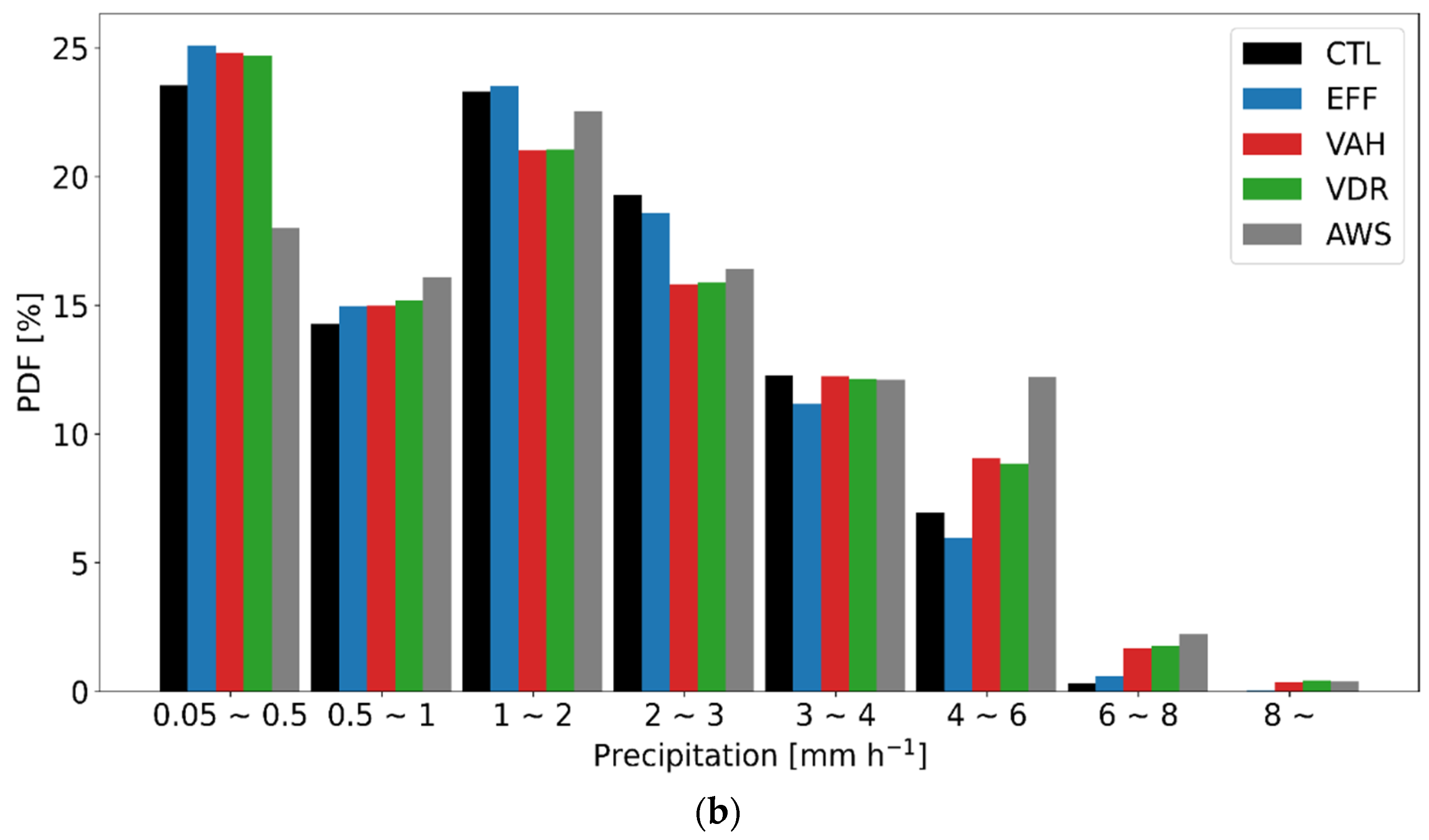
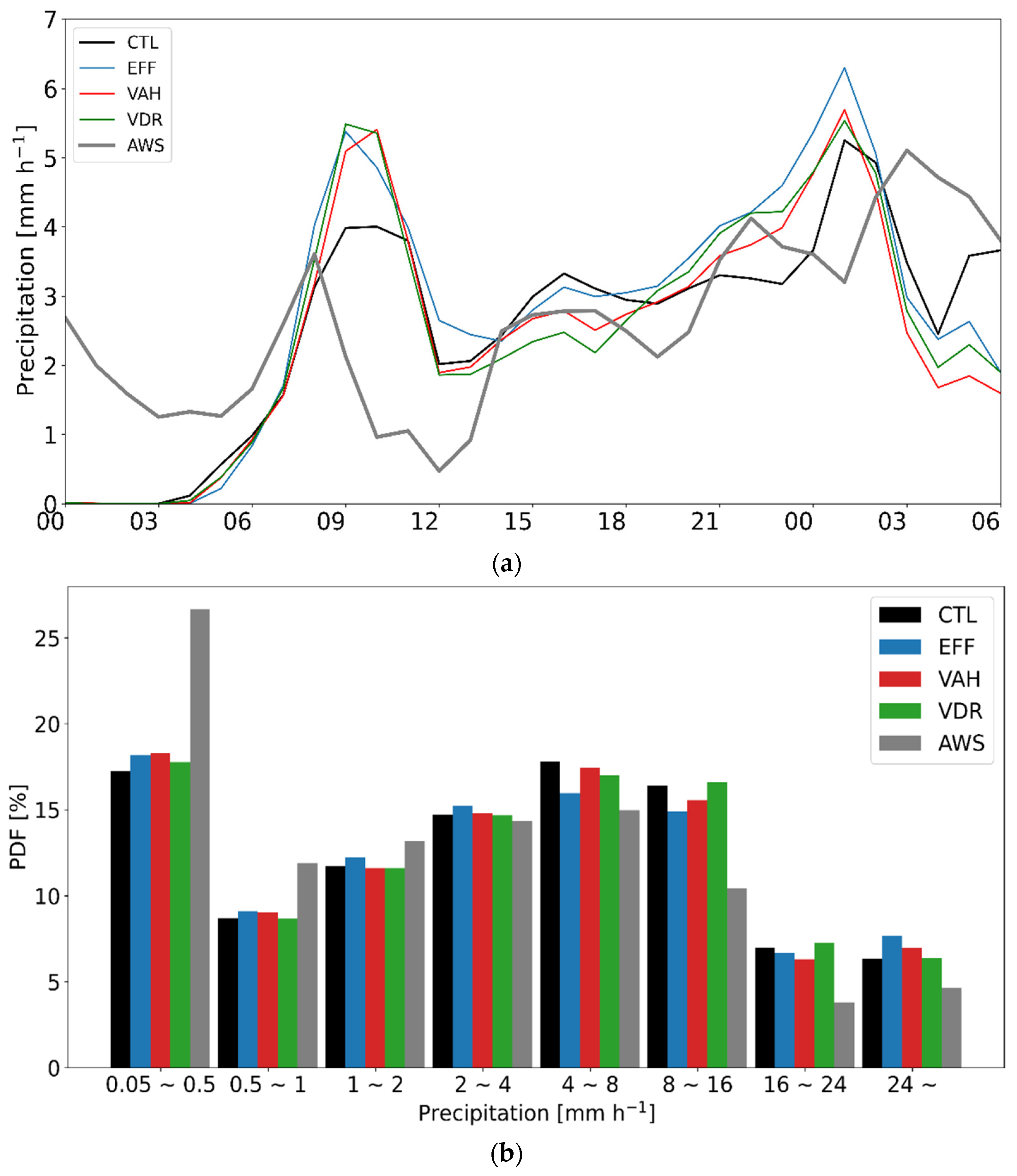
Figure 7 presents the time series of domain-averaged precipitation and its probability density functions (PDFs), as simulated from all experiments with the AWS observation for CASE1. All experiments well simulate the observed trend (peak of hourly precipitation on 28 February 2018, 0900 UTC), although the simulated precipitation is less than the observation, especially before the peak time (Figure 7a). All experiments produce more precipitation relative to the observation for the light precipitation category (less than 0.5 mm h−1), and they yield less precipitation relative to the observation for the heavy precipitation category (greater than 4 mm h−1) (Figure 7b). Both VAH and VDR enhance the precipitation in the heavy precipitation category and suppress that in the moderate precipitation category, which leads to more consistent results with the observation.
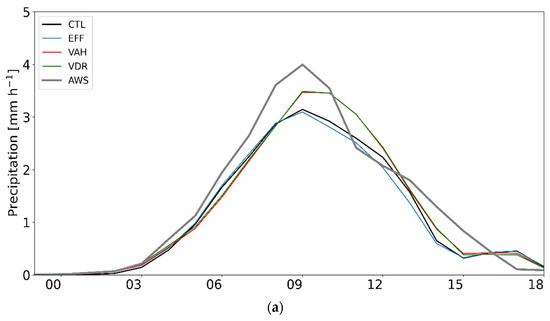
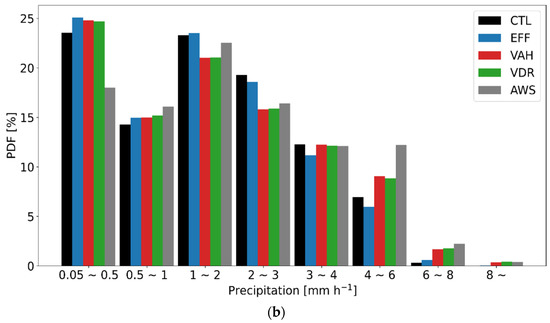
Figure 7.
(a) Time series of domain-averaged precipitation and (b) probability density functions (PDFs) of rain rate (mm h−1) throughout 19 h from 27 February 2018, 2300 UTC, to 28 February 2018, 1800 UTC (CASE1). The black, blue, orange, green, red, and gray lines represent the results from CTL, EFF, ICE, VDR, VAH, and AWS, respectively.
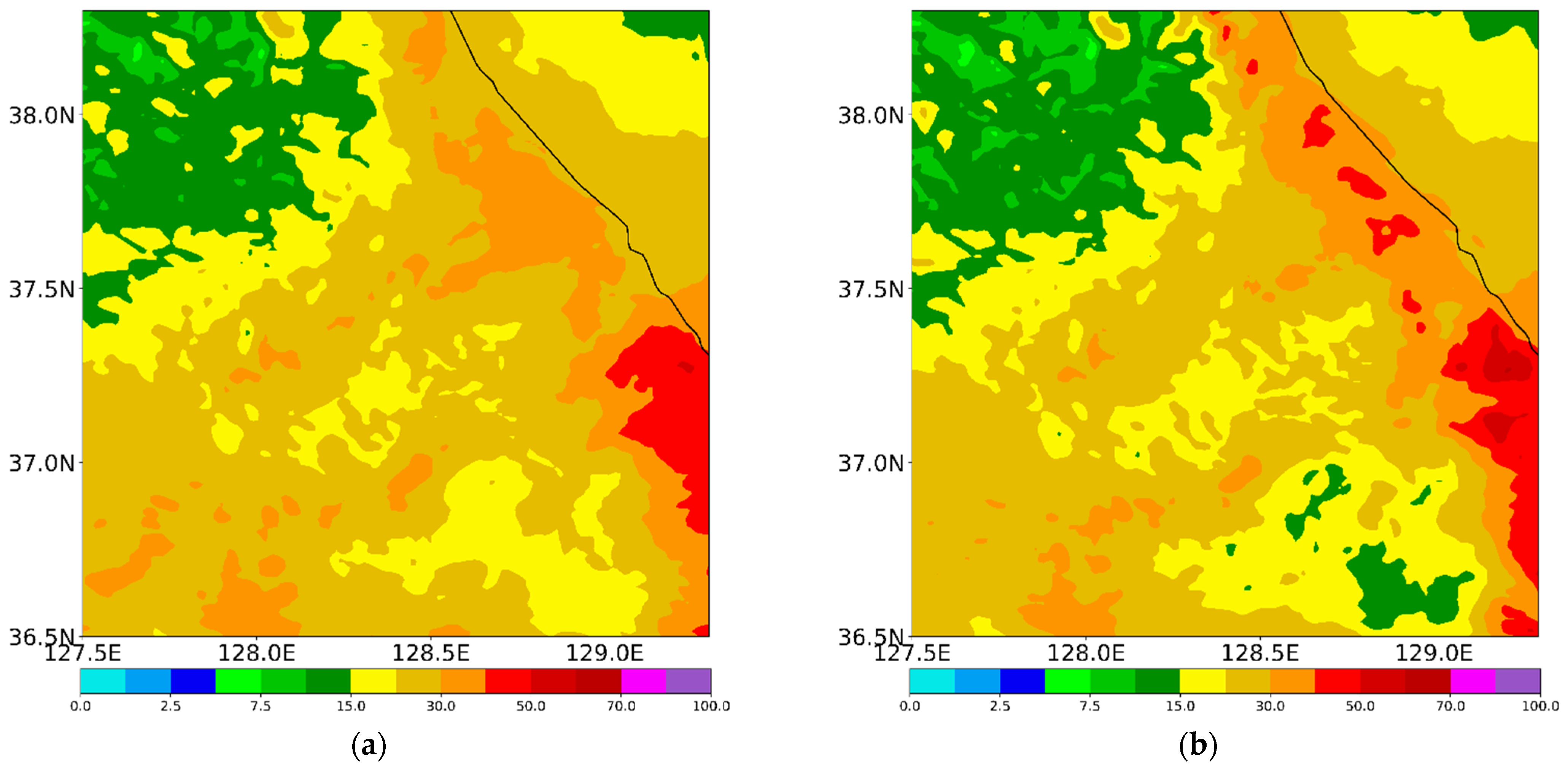
The spatial distribution of the accumulated precipitation from the experiments during the analysis period is shown in Figure 8. All experiments simulate more precipitation over the coastal region rather than the inland region, which agrees with the observation (Figure 1c and Figure 8). From Figure 9, which depicts the precipitation types at the surface, we can infer that CTL simulates mainly hail and liquid-type precipitation over the whole region (Figure 9a). This does not accord with the observation (Figure 2). Meanwhile, EFF simulates less precipitation relative to CTL, especially over the inland areas (Figure 8a,b). Even though EFF produces the least precipitation, it shows the best equitable threat score (ETS) and pattern correlation (PC) scores among all experiments (Table 4). The simulated surface precipitation type in EFF is similar to that in CTL (Figure 9a,b).
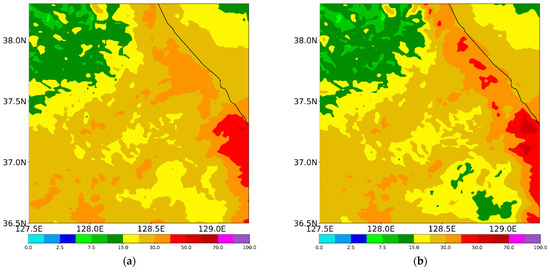
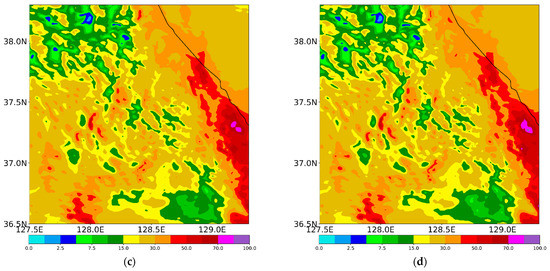
Figure 8.
Simulated precipitation (mm) from (a) CTL, (b) EFF, (c) VAH, and (d) VDR experiments for CASE1 during its analysis period (27 February 2018, 2300 UTC, to 28 February 2018, 1800 UTC).
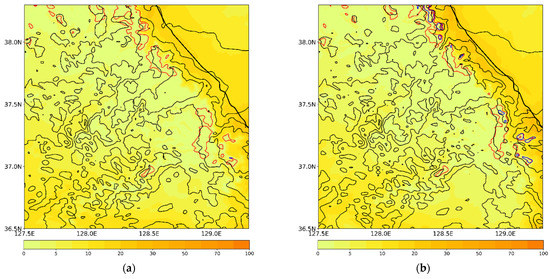
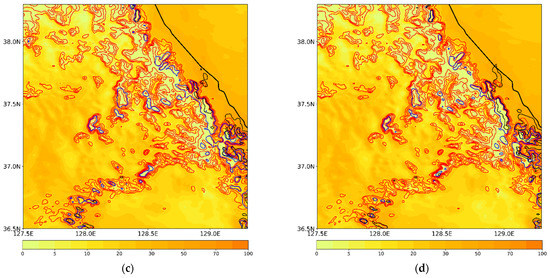
Figure 9.
Simulated precipitation (mm) contributed by rain (color shaded), snow (red line), graupel (blue line), and hail (black line) at the surface for (a) CTL, (b) EFF, (c) VAH, and (d) VDR. The contour interval for snow, graupel, and hail is 5 mm.

Table 4.
Statistical skill scores of probability of detection (POD), false alarm ratio (FAR), equitable threat score (ETS), bias, and pattern correlation (PC) of simulated precipitation of experiments for CASE1 and CASE2. The maximum accumulated precipitation amount during the analysis period is also noted. The observed maximum accumulated precipitation values from an automatic weather station (AWS) are 61 and 353 mm for CASE1 and CASE2, respectively. PC is calculated based on the Pearson correlation, and other skill indicators are based on the study of Nurmi [36].
The maximum precipitation is enhanced in all sensitivity experiments, especially VAH and VDR (Table 4 and Figure 8c,d). Bias and false alarm ratio (FAR) scores in VAH and VDR are better than those in EFF, but the POD, PC, and RMSE are lower (Table 4). ETS scores among three experiments, EFF, VAH, and VDR, show the same value. Over the mountainous region, a mixture of snow, graupel, and rain is simulated in VAH. Liquid-type precipitation is much more enhanced over the coastal region, which is highly comparable with the observed features (Figure 2b,d and Figure 9c). An accurate forecast of the surface precipitation type during winter is crucial for water resource management, winter sports, road condition, and similar applications. Therefore, the mixed-phase terminal velocity of solid-phase hydrometeors, including hail, should be included in the WDM7 scheme. As shown by the results of VAH and VDR, the impact of the revised V–D relationship of raindrops on the simulated precipitation and its type at the surface is not significant (Figure 8c,d and Figure 9c,d).
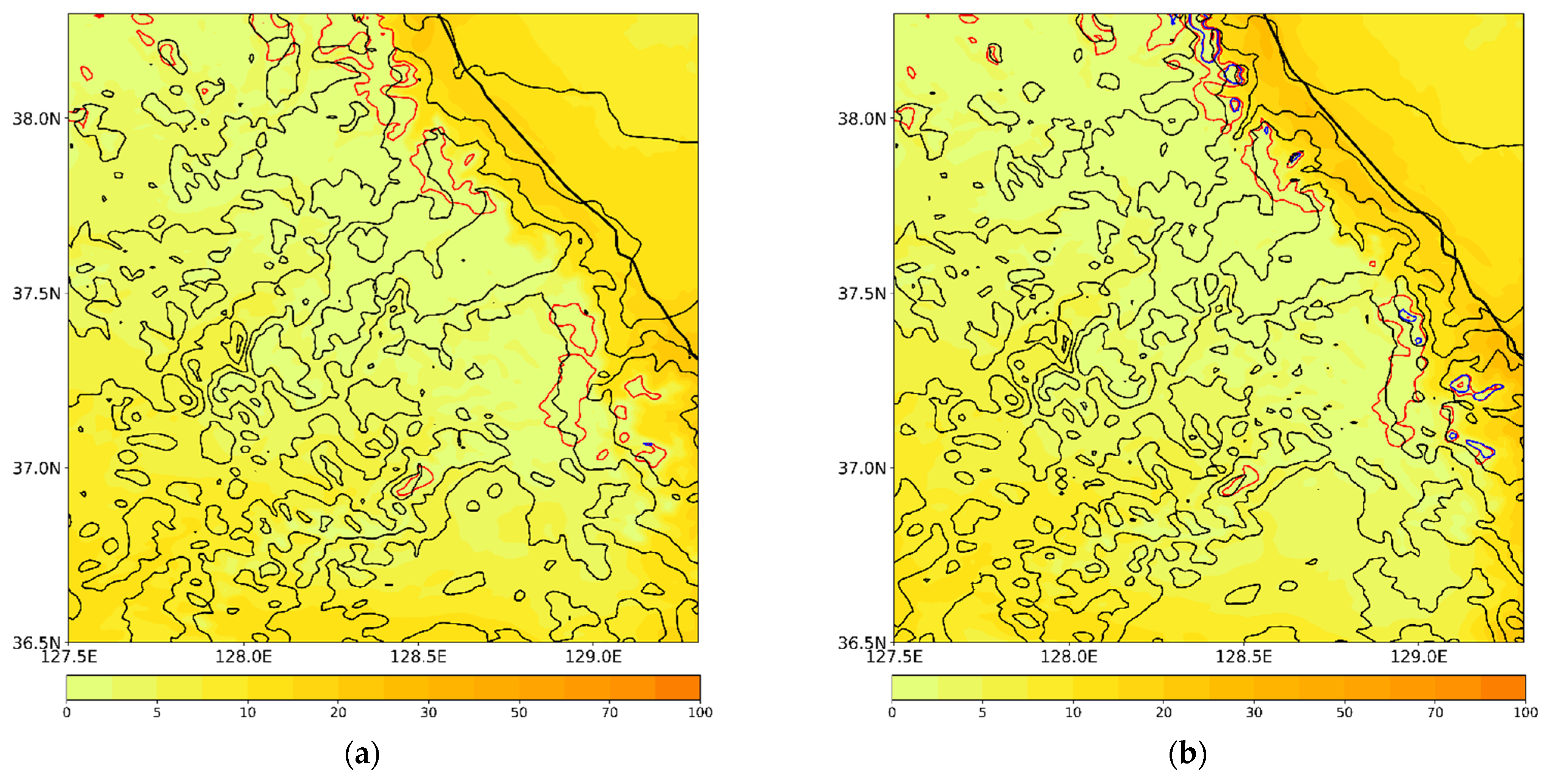
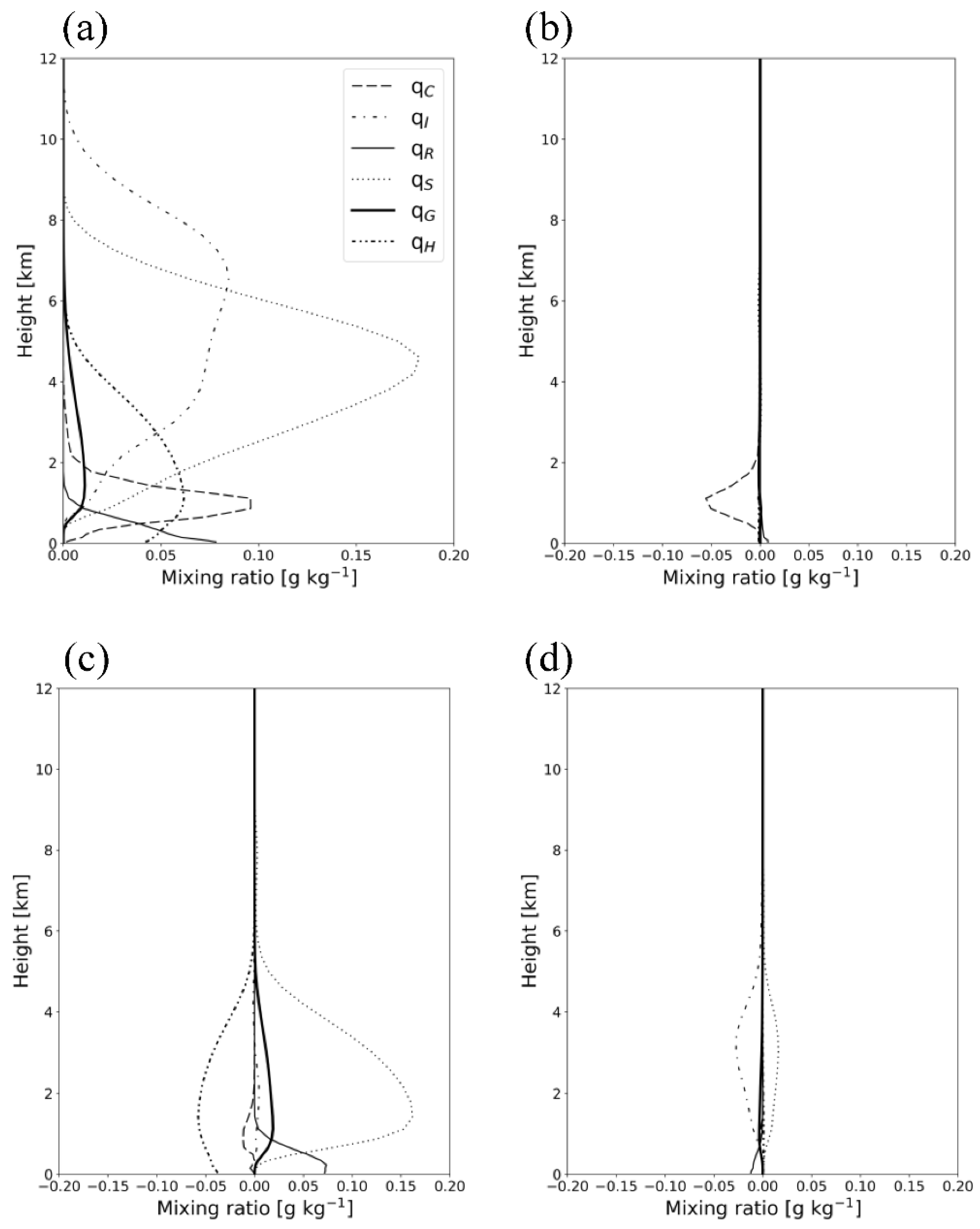
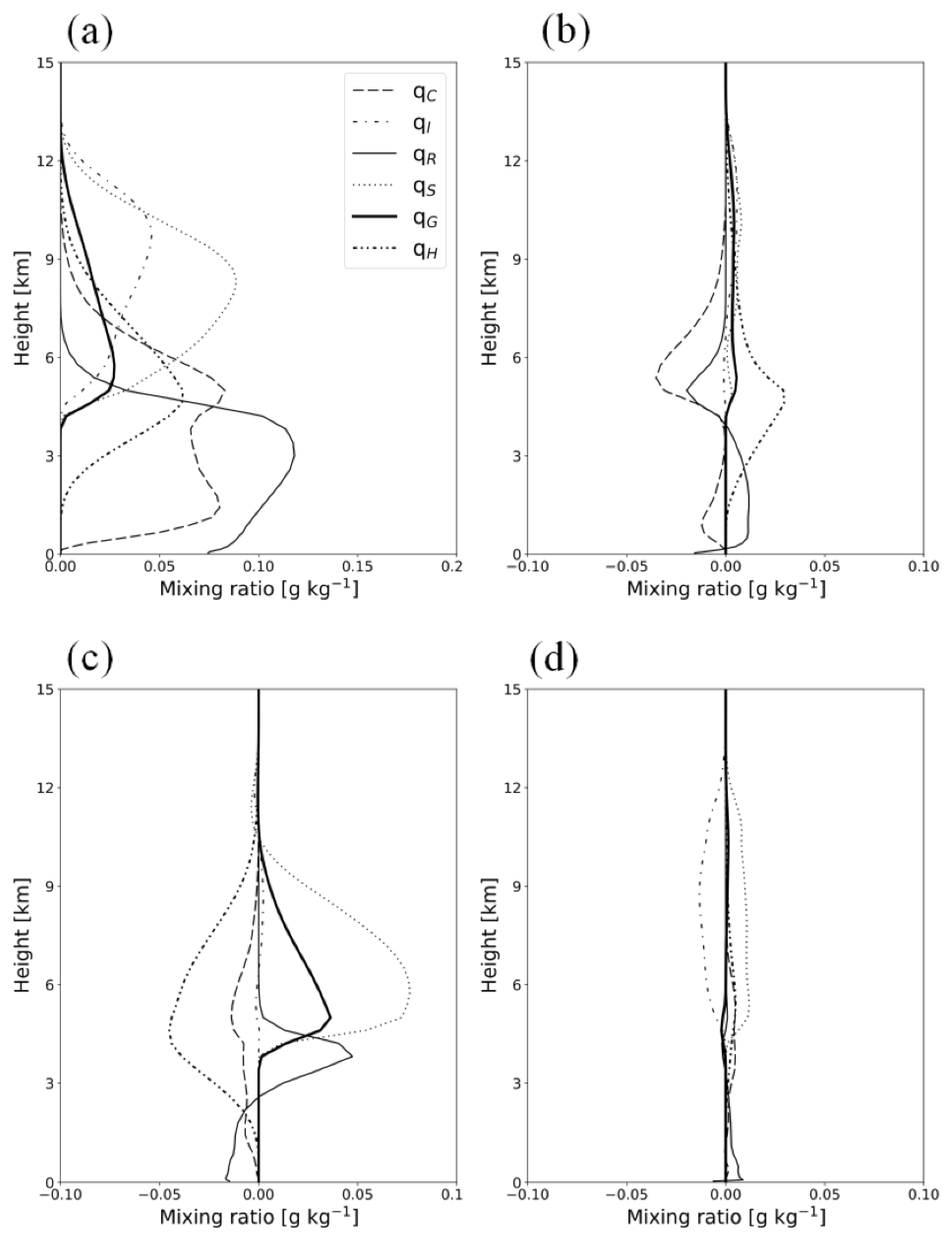
The time-domain-averaged mixing ratios of hydrometeors from the experiments are shown in Figure 10. The vertical cross-sections of the simulated hydrometeors’ mixing ratio on 28 February 2018, 0800 UTC, along the green line in Figure 10 are shown in Figure 11. A significant amount of cloud ice showing a maximum amount of 0.08 g kg-1 at the 7 km level exists below the 11 km level in CTL (Figure 10a). Snow and graupel are present between the 0.5 and 9 km levels, whereas hail is found between the surface and the 6 km level. The cloud water mixing ratio is simulated below the 4 km level, showing its maximum amount of 0.096 g kg−1 at the 1 km level. Figure 11a shows a considerable cloud water quantity below the 2 km level in CTL along the windward side over the mountain. Compared with the radar-retrieved observations, CTL overestimates cloud water and cloud ice above the 0.5 km level (Figure 3 and Figure 11a). In addition, the low-level wind speed between the 1 km and 2.5 km level is decreased, and an ascending air current over the mountain region is exaggerated in CTL.
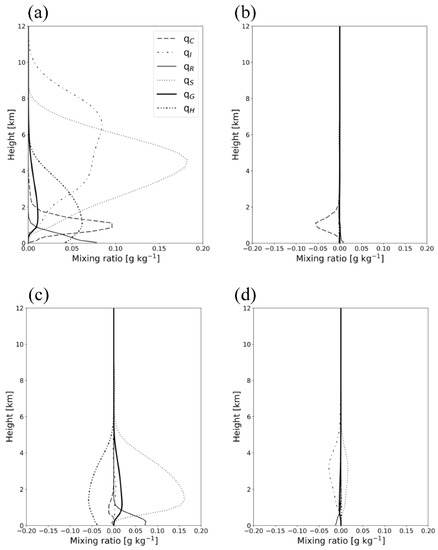
Figure 10.
(a) Vertical profiles of time-domain-averaged mixing ratios of hydrometeors from CTL (CASE1). The differences in the averaged hydrometeor mixing ratios between the experiments are also presented: (b) EFF minus CTL; (c) VAR minus EFF; (d) VDR minus VAH.
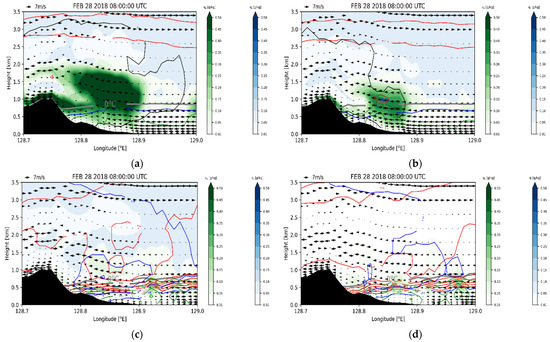
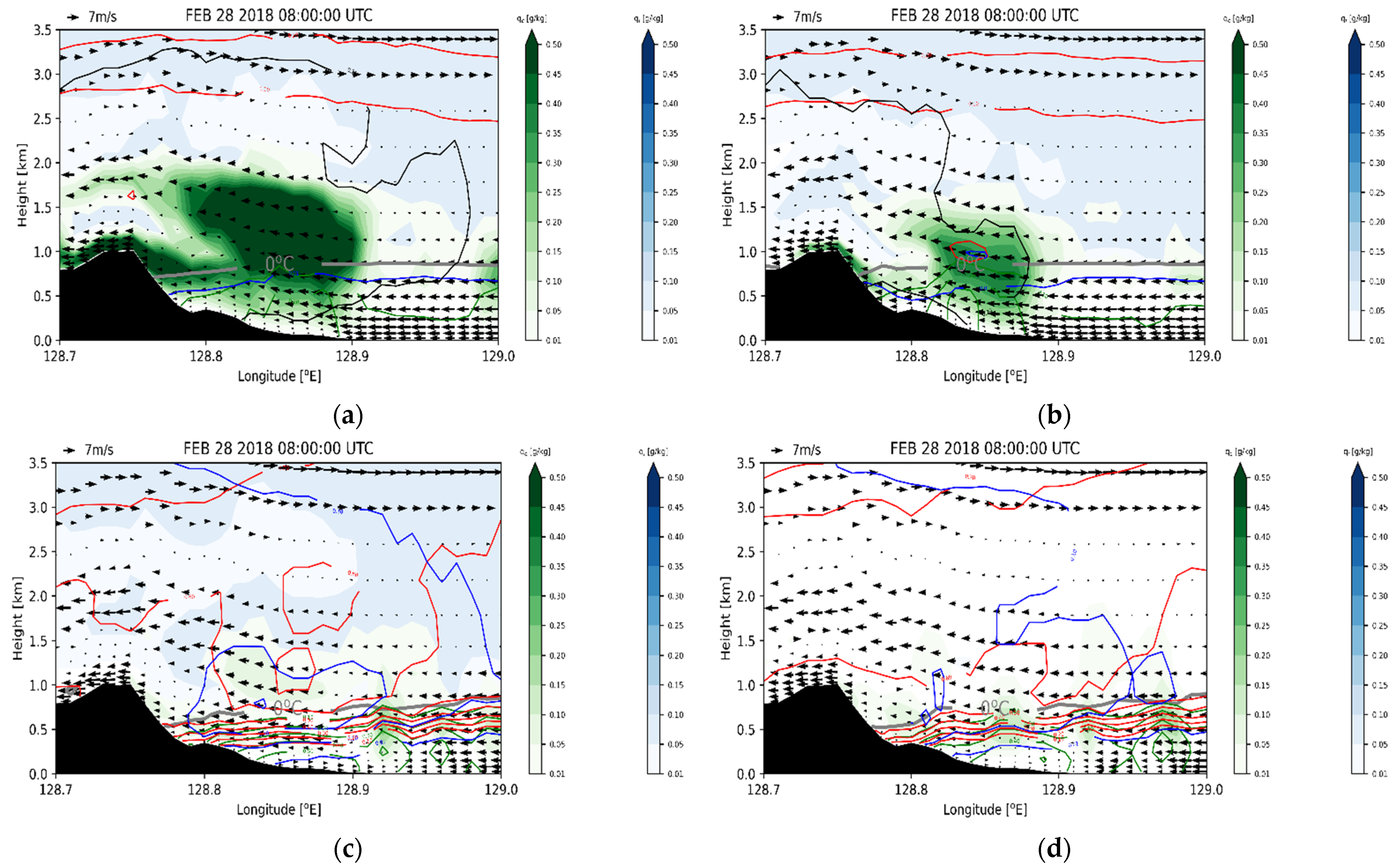
Figure 11.
Vertical cross-sections of simulated snow (red line), graupel (blue line), hail (black line), and rain (green line) mixing ratios with wind fields along green solid line in Figure 1d on 28 February 2018, 0800 UTC for (a) CTL, (b) EFF, (c) VAH, and (d) VDR experiments. The mixing ratios of cloud water and cloud ice are shaded green and blue, respectively. Contour lines of graupel are at 0.01, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 g kg−1 and those of snow, hail, and rain are drawn using a 0.1 interval.
In EFF, the cloud water mixing ratio decreases compared with that in CTL (Figure 10b). The vertical cross-section in Figure 11b clearly shows that the solid-phase precipitable hydrometeors’ (graupel, snow, and hail) amount increases around the 1 km level, near 128.8°E (Figure 11b). The enhanced C-C processes in EFF induce an increased amount of solid-phase precipitable hydrometeors and a decreased amount of cloud water. The difference in the wind fields between CTL and EFF is not significant. The eliminated C-C processes (phacs and phacg) in VAH lead to large increases in snow and graupel and a decrease in hail by an amount of 0.06 g kg−1 (Figure 10c and Figure 11c). The increase in graupel and snow near the 0 °C level is obvious, producing abundant rain due to the melting of snow and graupel (Figure 11c). The cloud water mixing ratio also reduces below the 2 km level due to the enhanced C-C processes, such as Psacw and Pgacw. In VAH, the simulated wind speed below the 0.5 km level is considerably reduced, and this can be explained by the interrupted air flow due to rain shafts. VDR shows similar hydrometeor profiles to those of VAH except the cloud ice/snow amount. VDR reduces the cloud ice and increases the snow relative to the results of VAH (Figure 10c,d and Figure 11c,d). The enhanced raindrop velocity in VDR can enhance the C-C process between cloud ice and rain (Praci), the sink (source) of cloud ice (snow) (Figure 5a), thus altering the cloud ice and snow quantities. The simulated hydrometeors’ profiles in VDR are the most consistent with the radar retrievals (Figure 3 and Figure 11d).
4.2. Precipitating Convection during Summer
The time series of the domain-averaged precipitation and its PDFs for CASE2 (throughout 30 h from 2 August 2020, 0000 UTC, to 3 August 2020, 0600 UTC) are shown in Figure 12. The observed trend is well captured by the experiments, producing two peaks on 2 August 2020, 0900 UTC, and 3 August 2020, 0100 UTC (Figure 12a). However, the time of the first (second) peak in the simulations is later (earlier) than that in the observation. All experiments do not predict the precipitation during the first 3 h of the analysis period. CTL produces the least precipitation amount before 2 August 2020, 1400 UTC, and yields the most after 3 August 2020, 0200 UTC, compared with the other sensitivity experiments. Among these experiments, EFF produces the largest precipitation amount, especially after 2 August 2020, 1800 UTC. All experiments suppress the precipitation activities in the light precipitation categories (less than 2 mm h−1) relative to the observation (Figure 12b). For the moderate and heavy precipitation categories, in which the precipitation intensity is greater than 4 mm h−1, all experiments simulate more precipitation, which contradicts the result of CASE1. As in CASE1, EFF enhances the precipitation in the light and heavy precipitation categories. VAH increases the precipitation amount in the category between 4 and 16 mm h−1 but decreases that in the intense precipitation category (greater than 16 mm h−1) relative to EFF. Meanwhile, compared with VAH, VDR produces more precipitation for the categories between 8 and 24 mm h−1 but produces less when the rain rate is greater than 24 mm h−1.
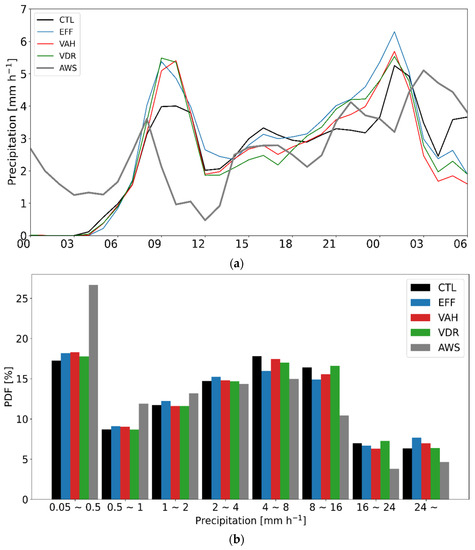
Figure 12.
(a) Time series of domain-averaged precipitation and (b) probability density functions (PDFs) of rain rate (mm h−1) throughout 30 h from 2 August 2020, 0000 UTC, to 3 August 2020, 0600 UTC (CASE2). The black, blue, orange, green, red, and gray lines represent the results from CTL, EFF, ICE, VDR, VAH, and AWS, respectively.
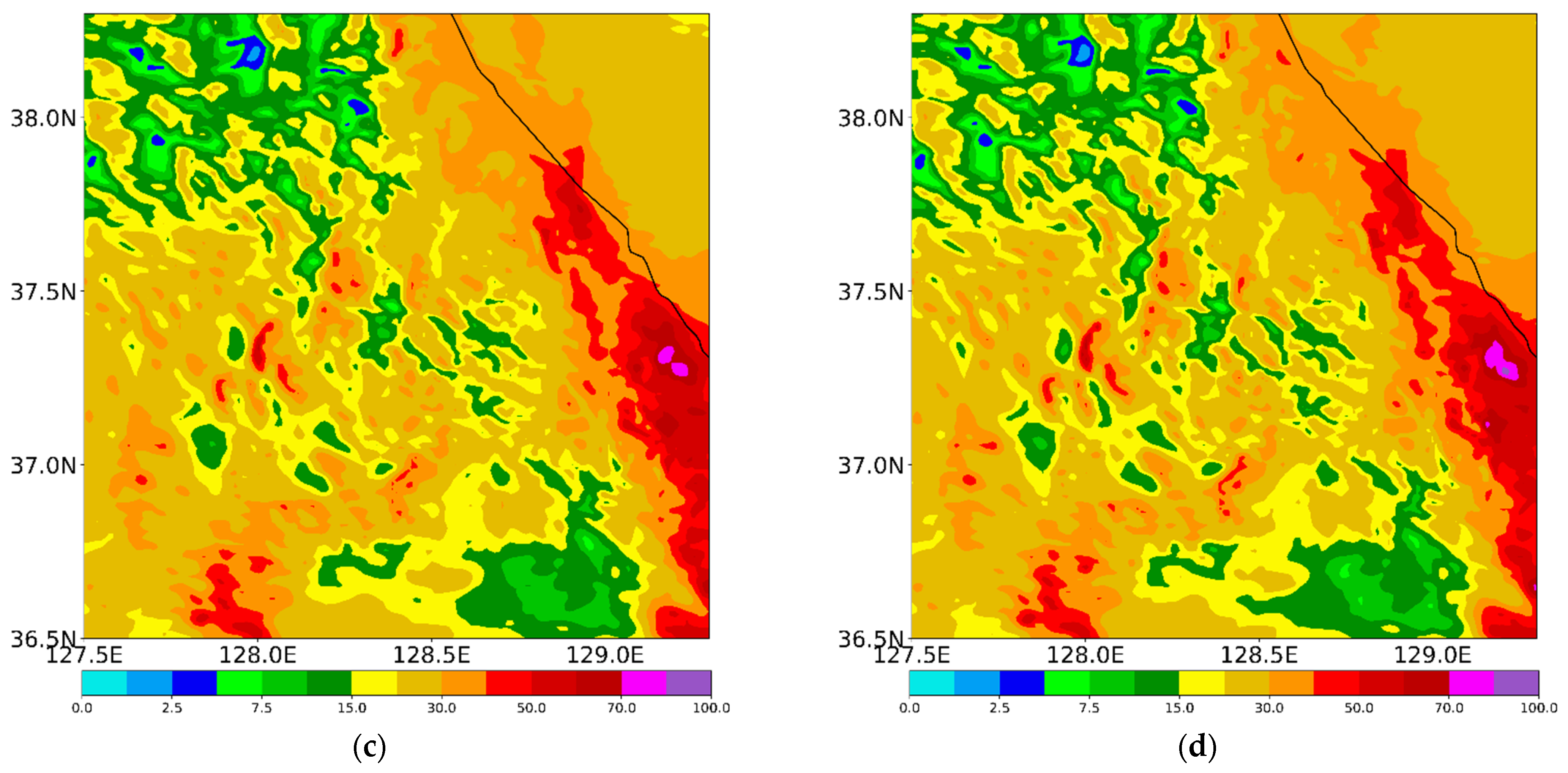
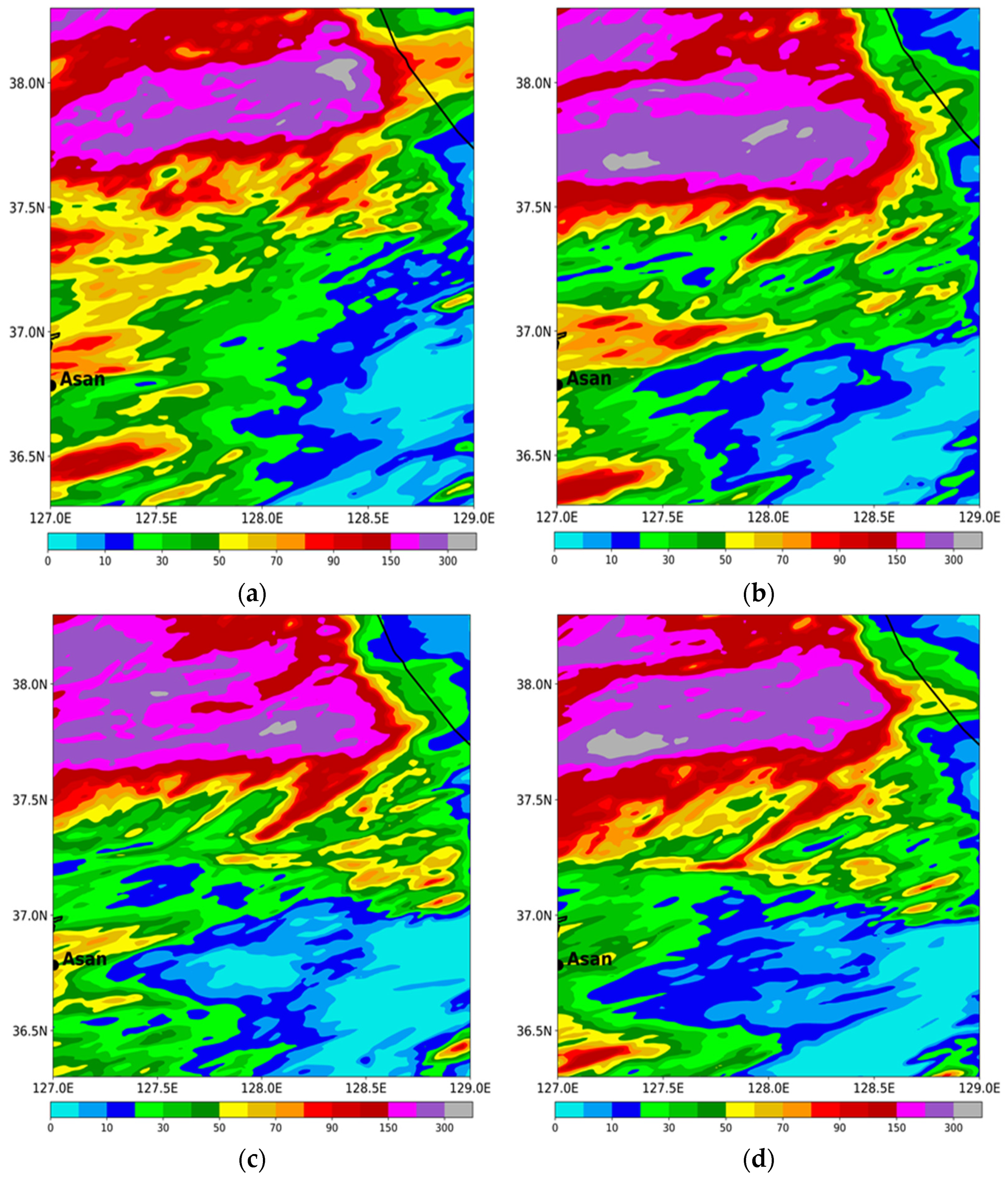
Figure 13 presents the simulated precipitation during the analysis period for CASE2. All experiments produce the localized precipitation over the central part of the Korean peninsula. The region of maximum precipitation in the sensitivity experiments (EFF, VAH, and VDR) is moved westward compared with that in CTL, thus presenting better skill scores (Table 4). Another maximum precipitation near Asan, which lies in the southwestern part of the analysis domain, is underestimated in all experiments relative to the observation (Figure 1d and Figure 13). The increased precipitation amount in EFF shows the best ETS and bias scores (Table 4). With the incorporation of the mass-weighted velocity in WDM7, the precipitation amount is reduced, especially over the regions of maximum precipitation, as seen in VAH. As shown in Kim et al. [13], the precipitation amount increases with the new V–D relationship of raindrops in VDR. Due to the increased fall velocity in the diameter range of 0.27 mm to 3 mm, the enhanced C-C process between cloud water and rain can generate more precipitation at the surface. The maximum precipitation is also excessively enhanced in VDR (Table 4).
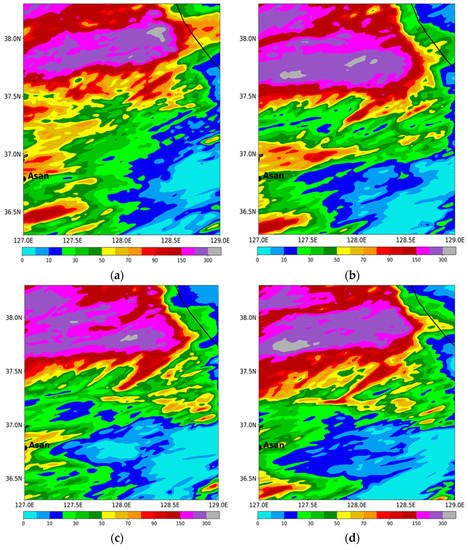
Figure 13.
Simulated precipitation (mm) from (a) CTL, (b) EFF, (c) VAH, and (d) VDR experiments for CASE2 during its analysis period (2 August 2020, 0000 UTC, to 3 August 2020, 0600 UTC).
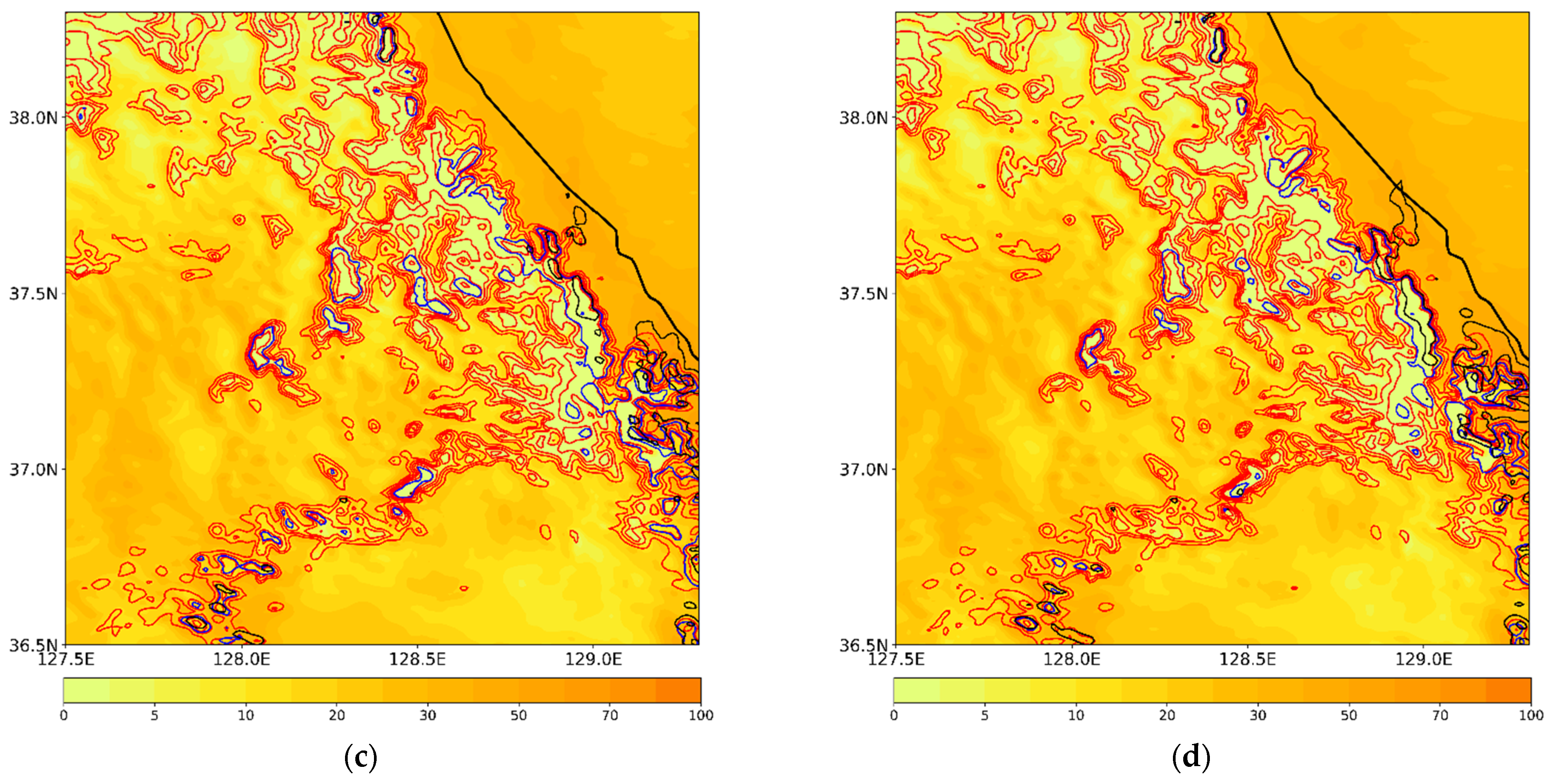
The vertical profiles of the time-domain-averaged mixing ratio of hydrometeors from CTL and differences between the experiments are shown in Figure 14. As shown in EFF, the mass of the solid-phase-precipitating hydrometeors, such as snow, graupel, and hail, is enhanced due to more conversion from the liquid-phase hydrometeors (Figure 14b). Consistently, the cloud water–rain mixing ratio is reduced by an amount of 0.03 g kg−1 over the corresponding level. The enhanced melting from snow, graupel, and hail increases the rain mixing ratio below the 4 km level, leading to the enhanced surface precipitation in EFF. As seen in CASE1, the amount of hail significantly decreases by an amount of 0.05 g kg−1 with the use of the new mass-weighted terminal velocity, resulting in increases in snow and graupel (Figure 14c). The increase in rain at the melting layer is caused by the efficient melting of graupel and snow. In VDR, an increase in the rain mixing ratio is distinct at the surface. Moreover, the cloud ice mixing ratio decreases, and that of snow increases; this finding is identical to the results shown in CASE1.
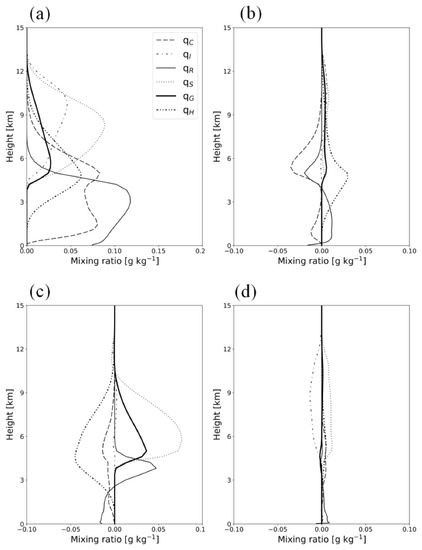
Figure 14.
(a) Vertical profiles of time-domain-averaged mixing ratios of hydrometeors from CTL (CASE2). The differences in the averaged hydrometeor mixing ratios between the experiments are also presented: (b) EFF minus CTL; (c) VAR minus EFF; (d) VDR minus VAH.
5. Summary
This study evaluated the performance of the modified WDM7 microphysics scheme, focusing on the simulated surface precipitation and hydrometeor profiles. Even though the WDM7 scheme was developed in 2019 and is considered a microphysics scheme option in the WRF mesoscale model, it has not been extensively evaluated for any convective system over the Korean peninsula [10]. The proposed modifications involve the C-C efficiency, mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase hydrometeors, and observation-based fall velocity–diameter relationship of raindrops. Two precipitating convection cases covering the summer and winter seasons over the Korean peninsula are selected for evaluating the modified WDM7.
For the winter case, the control experiment (original WDM7 scheme) underestimates the precipitation, especially in the coastal region. The enhanced C-C efficiency reduces the total precipitation relative to that in the control experiment. However, in the coastal region, the maximum precipitation intensifies; the POD, FAR, ETS, and PC are better than those in the control experiment. Updrafts over the windward side aid in the formation of more solid-phase particles, such as hail, snow, and graupel, with the increased C-C efficiency. More raindrops from the efficient melting of solid-phase particles are predicted at the surface in the corresponding region. The simulated precipitation type from the experiment applying the mass-weighted terminal velocity of solid-phase hydrometeors is more comparable with the observation, in which the hail amount at the surface is greatly reduced. Certainly, the modification of the mass-weighted terminal velocity, including that of hail, should be included in the WDM7 scheme for consistent representation of the terminal velocities of all solid-phase precipitating particles. With the production of more precipitation for the intense precipitation category (greater than 4 mm h−1) and less precipitation for the precipitation categories between 1 and 3 mm h−1, the bias and FAR scores improve with this modification. The simulation with the observation-based fall velocity–diameter relationship of raindrops reduces the cloud ice above the 1 km level due to the enhanced C-C process between cloud ice and rain.
For the summer case, the maximum precipitation region in the sensitivity experiments is moved westward compared with the control simulation, thereby presenting better skill scores. The simulated mixing ratios of solid-phase precipitating particles in the upper atmosphere increase with the enhanced C-C efficiency. Increased solid-phase hydrometeors’ mass results in more surface precipitation (relative to the control results) by efficient melting processes. This alleviates the negative bias of the simulated precipitation in the control experiment. The effects of the mass-weighted terminal velocity and observation-based fall velocity of raindrops on the simulated precipitation are opposite. The simulated precipitation decreases with the mass-weighted terminal velocity but increases with the observation-based fall velocity of raindrops. The effects of these two revisions on the simulated hydrometeors’ profiles during summer are similar to those revealed by the experiments during winter. The introduced modification of C-C efficiency can increase the mixing ratios of solid-phase hydrometeors, and that of the mass-weighted terminal velocity including hail alleviates the problems producing excessive hail generation in WDM7 regardless of the simulated convections. However, the effects of the introduced modifications on the simulated precipitation can vary depending on the selected convection cases. The two selected convection cases in our study may not generalize the impacts on the simulated precipitation.
An adequate representation of hydrometeors’ fall speed and the efficiency of C-C processes are important in simulating hydrometeors and thus precipitation amount and type. The parameters utilized in fall speed and efficiency representation can vary under different convection environments. Even though the reduced C-C efficiency in WDM7 can overcome the problem of freezing rain at the surface over the US and Canada, our results from the two convection cases over the Korean peninsula show that the C-C efficiency should not be reduced for the realistic simulation of precipitation amount and distribution, especially during summer. For the consistent representation of terminal velocities among solid-phase hydrometeors and realistic simulation of hydrometeors’ profiles, the mass-weighted fall velocity, including that of hail, should be adopted in WDM7. The evaluation results in our study can help understand the behavior of the WDM7 microphysics scheme and give guidance on scheme modification in simulating precipitating convection over the Korean peninsula. In addition, the realistic representation of partially rimed particles can be possible by adopting the mass-weighted fall velocity in any cloud microphysics parameterization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-S.S.L.; Data curation, S.J., J.K. and K.K.; Formal analysis, S.J., K.-S.S.L. and J.K.; Funding acquisition, K.-S.S.L.; Investigation, S.J., K.-S.S.L. and J.K.; Methodology, S.J., K.-S.S.L., J.K. and K.K.; Project administration, K.-D.A. and Y.-H.L.; Supervision, K.-S.S.L. and G.L.; Validation, S.J. and J.K.; Visualization, S.J., J.K., K.K. and S.-J.C.; Writing—original draft, S.J. and K.-S.S.L.; Writing—review & editing, G.L. and S.-J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A4A1032646) and by the project of Numerical Modeling Center, “Development of Numerical Weather Prediction and Data Application Techniques” (KMA2018-00721).
Acknowledgments
The authors are greatly appreciative to the participants of the World Weather Research Program Research Development Project and Forecast Demonstration Project, International Collaborative Experiments for Pyeongchang 2018 Olympic and Paralympic winter games (ICE-POP 2018), hosted by the Korea Meteorological Administration. The authors would also like to thank Alexis Berne, Josué Gehring, Nikola Besic and Alfonso Ferrone for their contribution to the operation and maintenance of the MXPol radar and providing the hydrometeor classification product (https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.918315, Gehring et al. [37]).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-O.J. The WRF Single-Moment 6-class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.-S.S.; Hong, S.-Y. Development of an Effective Double-Moment Cloud Microphysics Scheme with Prognostic Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) for Weather and Climate Models. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 1587–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.-H. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of CLouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-J.; Sohn, B.-J. An Evaluation of WRF Microphysics Schemes for Simulating the Warm-type Heavy Rain over the Korean peninsula. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.-H.; Choo, S.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, G.-W. Evaluation of WRF Cloud microphysics Schemes Using Radar Observations. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 1571–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, K.-S.S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Ha, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; Ham, S.-J.; Dudhia, J. Evaluation of the WRF Double-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme for Precipitating Convection. Adv. Meteorol. 2010, 2010, 707253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, K.-S.S.; Chang, E.-C.; Sun, R.; Kim, K.-I.; Tapiador, F.J.; Lee, G.-W. Evaluation of Simulated Winter Precipitation Using WRF-ARW during the ICE-POP 2018 Field Campaign. Weather Forecast. 2020, 35, 2199–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Feng, Z.; Kennedy, A.; Mullendore, G.; Gilmore, M.; Tao, W.-L. Impacts of Microphysical Scheme on Convective and Stratiform Characteristics in Two High Precipitation Squall Line Events. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 11119–11135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, W.-K.; Wu, D.; Lang, S.; Chern, J.-D.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Fridlind, A.; Matsui, T. High-resolution NU-WRF Simulations of a Deep Convective Precipitation System during MC3E: Further Improvements and Comparisons between Goddard Microphysics Schemes and Observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 1278–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.Y.; Hong, S.-Y.; Tao, W.-K. Development of a Single-Moment Cloud Microphysics Scheme With Prognostic Hail for the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 55, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Tao, W.-K.; Chern, J.-D.; Wu, D.; Li, X. Benefits of a Fourth Ice Class in the Simulated Radar Reflectivities of Convective Systems Using a Bulk Microphysics Scheme. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3583–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, L.; Lindsey, D.T.; Lim, K.-S.S.; Clark, A.; Bikos, D.; Dembek, S.R. Evaluation of and Suggested Improvements to the WSM6 Microphysics in WRF-ARW Using Synthetic and Observed GOES-13 Imagery. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 3635–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Lim, K.-S.S.; Kim, K.-I.; Lee, G.-W. Effects of the Realistic Description for the Terminal Fall Velocity-Diameter Relationship of Raindrops on the Simulated Summer Precipitation over South Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 30, 421–437. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, K.-S.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, J.-O.J.; Dudhia, J. Sensitivity Study of Cloud-Resolving Convective Simulations with WRF Using Two Bulk microphysical Parameterizations: Ice-Phase Microphysics versus Sedimentation Effects. J. Appl. Meteor. 2009, 48, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The Terminal Velocity of Fall for Water Droplets in Stagnant Air. J. Meteor. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudhia, J.; Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, K.-S. A New Method for Representing Mixed-Phase Particle Fall Speeds in Bulk Microphysics Parameterization. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 86, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cressman, G. An operational objective analysis system. Mon. Weather Rev. 1959, 87, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Joss, J. An Optical Disdrometer for Measuring Size and Velocity of Hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. Evaluation of the New Version of the Laser-Optical Disdrometer, OTT Parsivel2. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastave, R.C.; Sckhon, R.S. Doppler Radar Characteristics of Precipitation at Vertical Incidence. Rev. Geophys. Sp. Phys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Jung, S.H.; Park, H.M.; Kwon, S.; Lin, P.L.; Lee, G.-Y. Classification of Precipitation Types Using Fall Velocity-Diameter Relationships from 2D-Video Disdrometer Measurements. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Szakáll, M.; Jost, A.; Giammanco, I.; Wright, R. A Comprehensive Observational Study of Graupel and Hail Terminal Velocity, Mass Flux, and Kinetic Energy. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besic, N.; Figuerasi Ventura, J.; Grazioli, J.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Hydrometeor classification through statistical clustering of polarimetric radar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4425–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besic, N.; Gehring, J.; Praz, C.; Figuerasi Ventura, J.; Grazioli, J.; Gabella, M.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Unraveling hydrometeor mixtures in polarimetric radar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4847–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liou, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-J. A Variational Multiple-Doppler Radar Three-Dimensional Wind Synthesis Method and its Impacts on Thermodynamic Retrieval. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 3992–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-L.; Kim, K.-I.; Liou, Y.-C.; Lee, G.-Y.; Yu, C.-K. Impact of Topography on Airflow and Precipitation in the Pyeongchang Area Seen from Multiple-Doppler Radar Observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 3401–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 4; NCAR Technical Notes NCAR/TN-556+STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019; p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative Forcing by Long-Lived Greenhouse Gases: Calculations with the AER Radiative Transfer Models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling and Advanced Land Surface-Hydrology Model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain-Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, D. Systematic Bias in the Prediction of Warm-Rain Hydrometeors in the WDM6 Microphysics Scheme and Modifications. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2019JD030756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, K.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, G.B.; Du Toit, P.S. Terminal Velocity of Raindrops Aloft. J. Appl. Meteor. 1969, 8, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beard, K.V. Terminal Velocity Adjustment for Cloud and Precipitation Drops Aloft. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, P. Recommendations on the Verification of Local Weather Forecasts; ECMWF Technical Memorandum. No. 430; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, J.; Ferrone, A.; Billault-Roux, A.-C.; Besic, N.; Berne, A. Radar and Ground-Level Measurements of Precipitation during the ICE-POP 2018 Campaign in South-Korea, PANGAEA; Earth System Science Data Discussions: Bremen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).