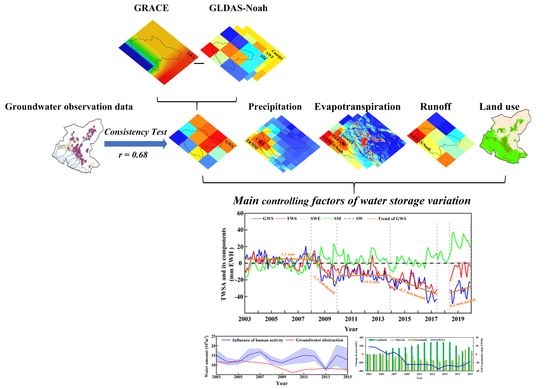
Improved Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance in Northwestern China Using GRACE Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
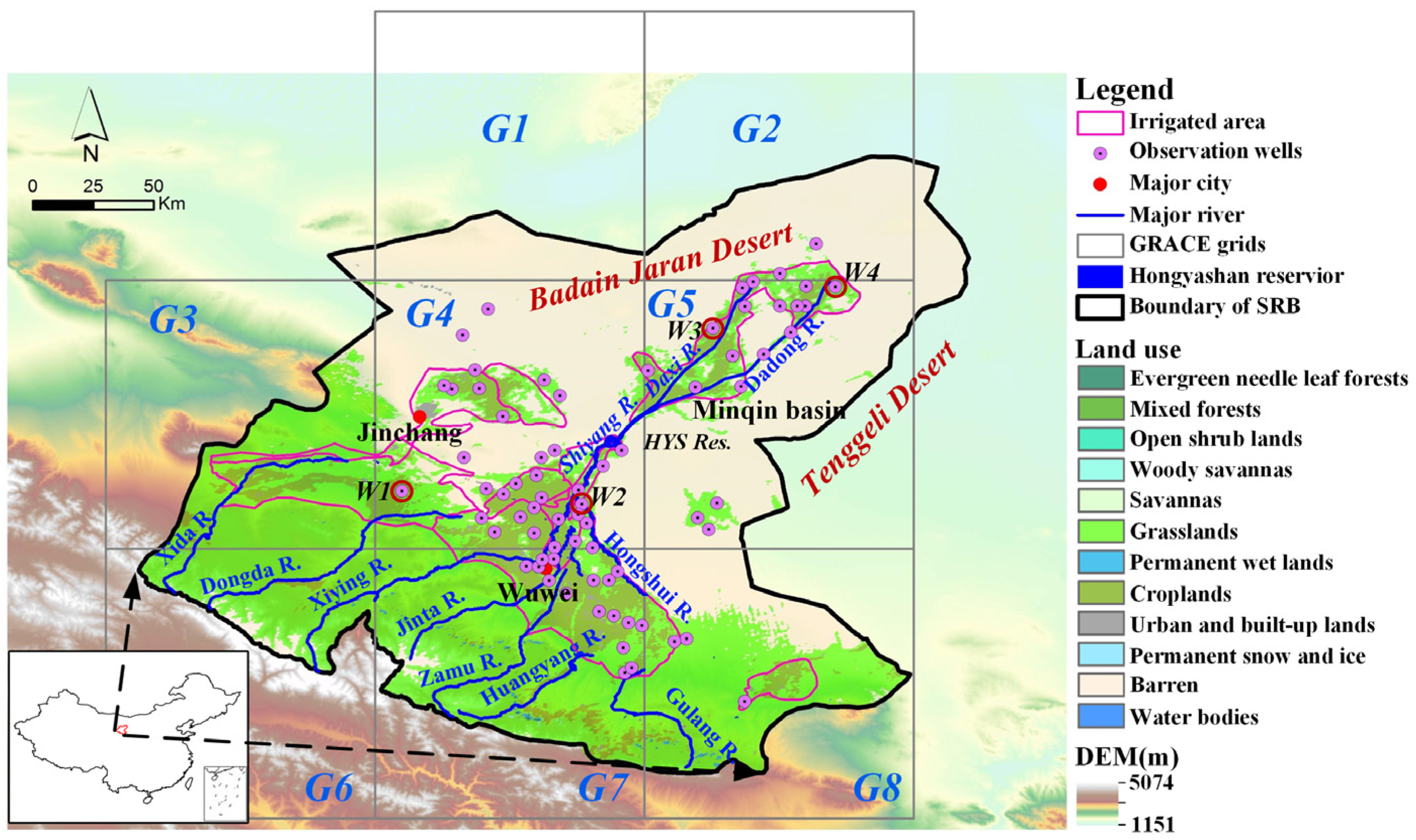
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Principle of Terrestrial Water Balance
2.2.2. Terrestrial Water Storage Variations
2.2.3. Groundwater Storage Variations
2.2.4. GLDAS Model Data
2.2.5. Precipitation Data
2.2.6. ET Data
2.2.7. Land-Cover Data from MODIS
2.2.8. Mutation Test Methods
Mann-Kendall Nonparametric Mutation Test
Moving T-Test Method
2.2.9. Correlation Analysis and Data
3. Results and Discussion
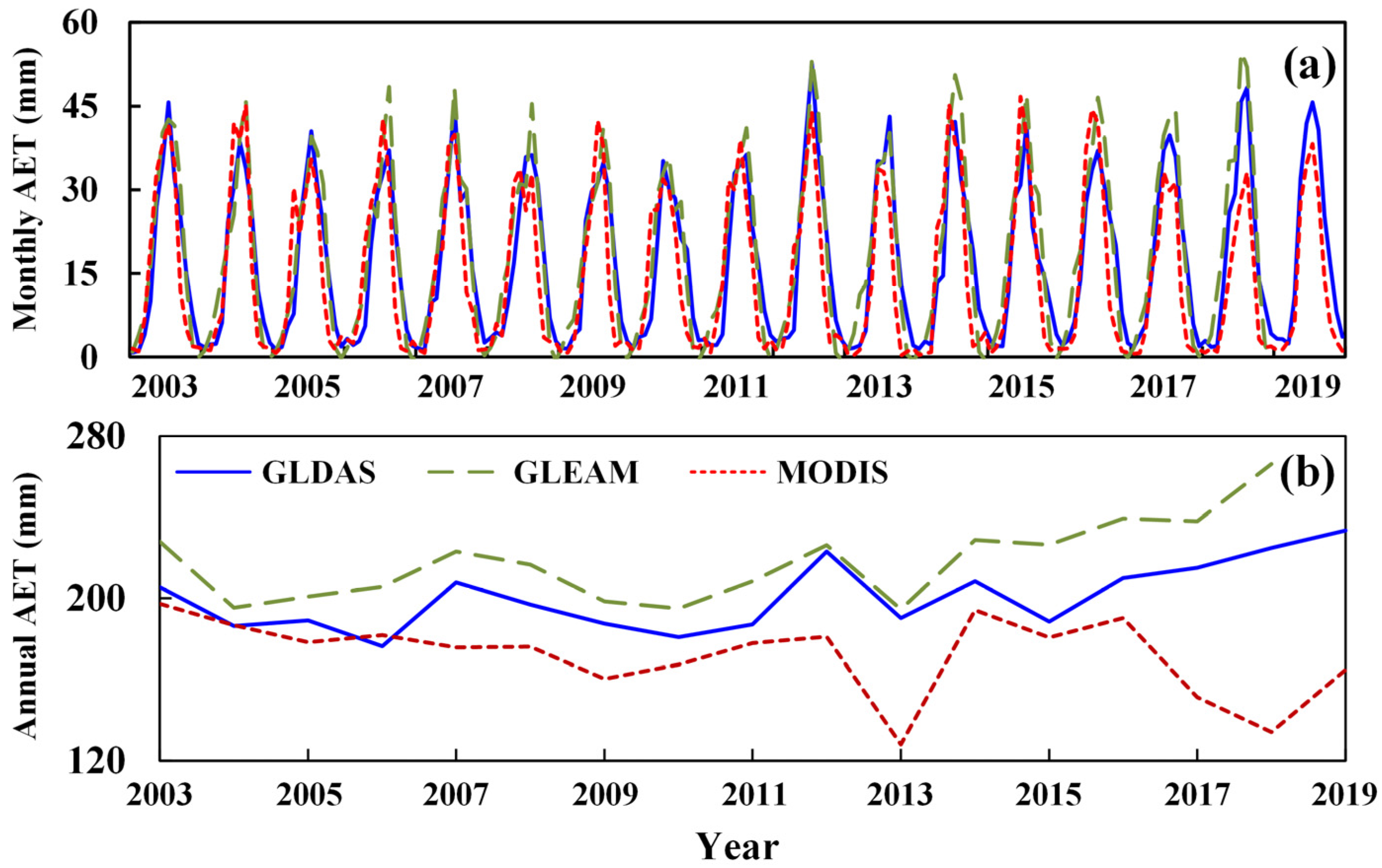
3.1. Changes in Precipitation and Actual Evapotranspiration in the SRB
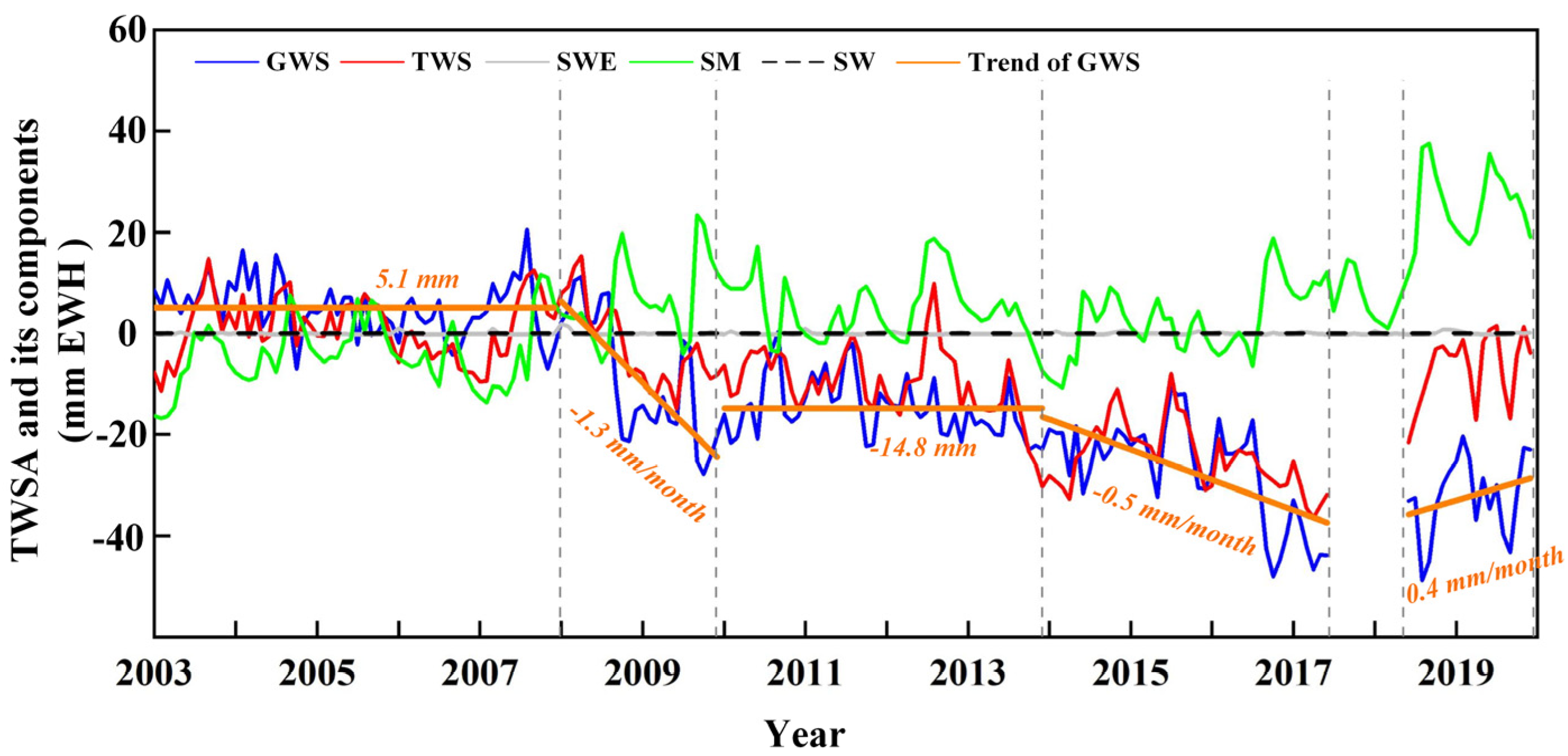
3.2. Variations of TWSA Data and Their Components
3.3. Abrupt Change in GWS Variations
3.4. Evaluation of the Water Balance before and after the Key Management Plan
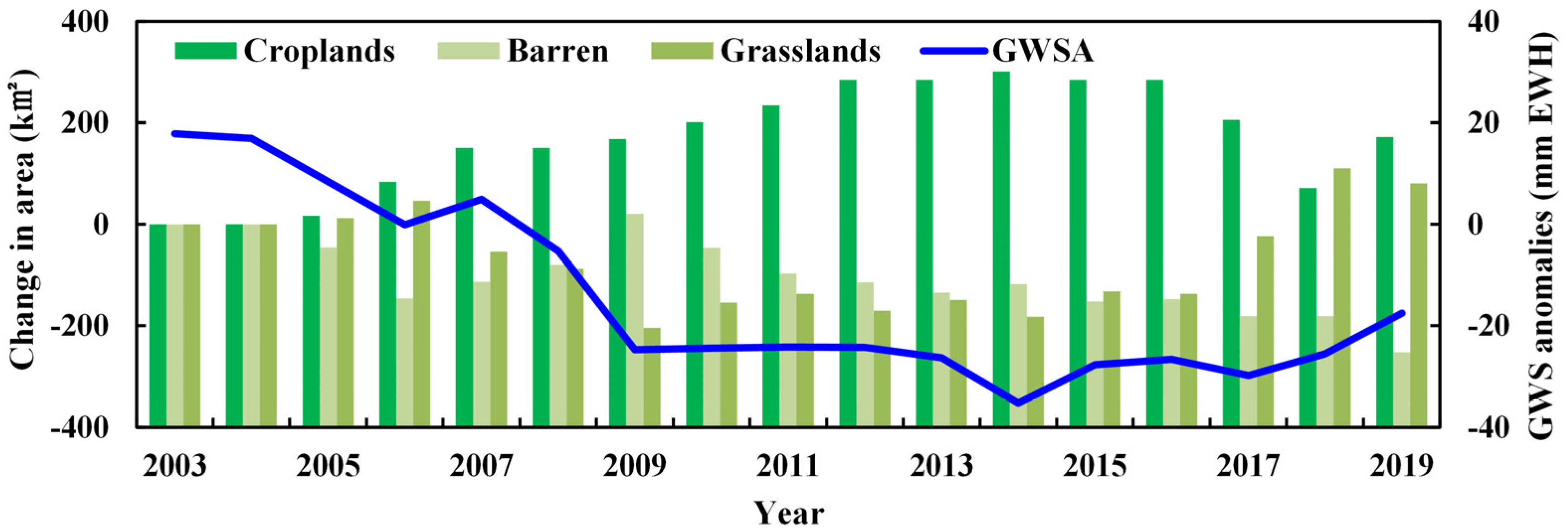
3.5. Land-Use Changes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the SRB
4. Conclusions
- The variation in GWS obtained by GRACE and GLDAS was compared to the data from groundwater observation wells, and the results from the two sources show consistency of the wells (r = 0.68), indicating that the GRACE was reliable for GWS monitoring in the SRB. GWS in the SRB had a slow downward trend from 2003 to 2016. After 2018, GWS increased by approximately 0.4 mm/mon, which was approximately 3.84 × 108 m³ per year. Additionally, the GRACE-observed TWSA was fairly well-correlated with the GWSA (r = 0.81).
- Different datasets of precipitation and actual ET data in the SRB were used to analyze their relationship with the GWSA. There was a correlation between the variation in GWS in the current year and the difference between precipitation and actual ET change in the previous year (r = 0.61). From 2003 to 2006, due to the increase in precipitation, GWS remained stable, and from 2007 to 2009, due to the decrease in precipitation and the increase in cropland area, GWS decreased significantly. The downward trend of GWS was curbed near 2009, and the rate of decline after 2009 was 96% lower than that before 2009. From 2011 to 2016, GWS in the middle and lower reaches of the SRB decreased by approximately 0.44 × 108 m³, which is 91% less than that of 4.86 × 108 m³ from 2007 to 2010.
- By using the water balance method, the change in GWS affected by human activities was obtained, and the influencing factors were discussed. The change in GWS affected by human activities rose before 2007 and then decreased, which was consistent with the change in groundwater depletion in the SRB. Land-use change in the middle and lower reaches of the SRB also showed that the increasing rate of the crop area gradually slowed down after 2011 and significantly decreased after 2016. Natural vegetation areas gradually increased, and GWS also gradually rose, which indicated that, through a series of governance activities in the SRB, the reduction in water storage caused by human activities was effectively reduced, and the ecological environment of the SRB gradually recovered.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global Hydrological Cycle and World Water Resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Doell, P. Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrogeol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L.; Long, D. Ground referencing GRACE satellite estimates of groundwater storage changes in the California Central Valley, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikow, L.F.; Kendy, E. Groundwater depletion: A global problem. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.Z.; Su, P.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Ram, R. Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis–desert ecotone in an arid region: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yang, W.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Burek, P.; Pan, Y.; You, L.; Wada, Y. South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jin, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shrestha, S. Integrating satellite observations and human water use data to estimate changes in key components of terrestrial water storage in a semi-arid region of North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; James, L.A. Watershed science: Linking hydrological science with sustainable management of river basins. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, D. Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramillien, G.; Frappart, F.; Cazenave, A.; Güntner, A. Time variations of land water storage from an inversion of 2 years of GRACE geoids. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 235, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Feng, G. Large-scale variations of global groundwater from satellite gravimetry and hydrological models, 2002–2012. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 106, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Famigliett, J.S.; Scanlon, B.R.; Rodell, M. Groundwater Storage Changes: Present Status from GRACE Observations. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Chen, J.; Kato, H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Nigro, J.; Wilson, C.R. Estimating groundwater storage changes in the Mississippi River basin (USA) using GRACE. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, V.G.; Yong, B.; Tourian, M.J.; Ndehedehe, C.E.; Shen, Z.; Seitz, K.; Dannouf, R. Characterization of the hydro-geological regime of Yangtze River basin using remotely-sensed and modeled products. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H.; Wang, F.; Pan, S. Influences of climatic variability and human activities on terrestrial water storage variations across the Yellow River basin in the recent decade. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Zheng, W.; Jiao, J.J.; Han, S.; Zhang, M. Assessing Underground Water Exchange between Regions Using GRACE Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Resources Department of Gansu Province; Gansu Provincial Development and Reform Commission. In Key Governance Planning Project Report of Shiyang River Basin; Open Report in Chinese; 2007; pp. 1–94. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/200806/P020191104623858217901.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Gu, J.J.; Guo, P.; Huang, G.H. Achieving the objective of ecological planning for arid inland river basin under uncertainty based on ecological risk assessment. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1485–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, J.T. Spatiotemporal differentiation of ecosystem services in the Shiyang River Basin from 2005 to 2015. Arid. Zone Res. 2019, 36, 474–485. [Google Scholar]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Steele-Dunne, S.C.; Gunter, B.C.; Ditmar, P.G.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Sun, Y.; Xia, T.; Wang, Z. Improving estimates of water resources in a semi-arid region by assimilating GRACE data into the PCR-GLOBWB hydrological model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2053–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Tian, W.; Zhao, J.S. Coupled surface water-groundwater model and its application in the arid Shiyang River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Sun, A.Y.; Schmied, H.M.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Wiese, D.N.; Wada, Y.; Long, D.; Reedy, R.C.; et al. Global models underestimate large decadal declining and rising water storage trends relative to GRACE satellite data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1080–E1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, D.; Shen, Y.; Sun, A.; Hong, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Drought and flood monitoring for a large karst plateau in Southwest China using extended GRACE data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Ries, J.C.; Tapley, B.D. Variations of the Earth’s figure axis from satellite laser ranging and GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swenson, S.; Chambers, D.; Wahr, J. Estimating geocenter variations from a combination of GRACE and ocean model out-put. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltier, W.R.; Argus, D.F.; Drummond, R. Comment on “An Assessment of the ICE-6G_C (VM5a) Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Model” by Purcell et al. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yang, Y.; Wada, Y.; Hong, Y.; Liang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yong, B.; Hou, A.; Wei, J.; Chen, L. Deriving scaling factors using a global hydrological model to restore GRACE total water storage changes for China’s Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Ma, J.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, J. Comparison of soil moisture in GLDAS model simulations and in situ observations over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2658–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, W.; Wang, G.; Gao, Z.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Lou, D. Comparisons of remote sensing and reanalysis soil moisture products over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 146, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Cui, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Evaluation of GLDAS-1 and GLDAS-2 Forcing Data and Noah Model Simulations over China at the Monthly Scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2815–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Hong, Y.; Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L. Global analysis of spatiotemporal variability in merged total water storage changes using multiple GRACE products and global hydrological models. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. Spatiotemporal changes in China’s terrestrial water storage from GRACE satellites and its possible drivers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11976–11993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, B.; Miralles, D.G.; Lievens, H.; Van Der Schalie, R.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Fernández-Prieto, D.; Beck, H.E.; Dorigo, W.A.; Verhoest, N.E.C. GLEAM v3: Satellite-based land evaporation and root-zone soil moisture. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1903–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.R.H.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.G.C.A.; Dolman, A.J. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Chen, D.; Sun, L. Evaluation of evapotranspiration estimates for two river basins on the Tibetan Plateau by a water balance method. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shao, Q. Spatial-temporal variation of terrestrial evapotranspiration in China from 2001 to 2010 Using MOD16 Products. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A. User Guide to Collection 6 MODIS Land Cover (MCD12Q1 and MCD12C1) Product; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS Collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A.; Krankina, O.N.; Baccini, A.; Woodcock, C.E.; Sibley, A.; Sun, G.; Kharuk, V.; Elsakov, V. Hierarchical mapping of Northern Eurasian land cover using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric test against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, R.; Slack, J.R. A Nonparametric Trend Test for Seasonal Data with Serial Dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.L.; Li, J.F.; Lv, X.; Long, H.L. Analysis of the Characteristics of Runoff in Manasi River Basin in the Past 50 Years. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J. Evaluation of groundwater sustainability in the arid Hexi Corridor of Northwestern China, using GRACE, GLDAS and measured groundwater data products. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Qian, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z. Assessing impact of irrigation water on groundwater recharge and qual-ity in arid environment using CFCs, tritium and stable isotopes, in the Zhangye Basin, Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.J.-F.; Swenson, S.C.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Rodell, M. Remote sensing of groundwater storage changes in Illinois using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE). Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Chambers, D. Evaluation of groundwater storage monitoring with the GRACE satellite: Case study of the High Plains aquifer, central United States. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Jiao, J.J. Evaluation of Groundwater Storage Variations in Northern China Using GRACE Data. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Han, D.; Zheng, C. Impacts of thickening unsaturated zone on groundwater recharge in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H. Assessment on total water consumption control and governance effects in the inland river basin of northwest regions: Case study of Heihe and Shiyang River Basin. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2021, 40, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Gao, Z.H. Variation of vegetation coverage in Minqin county since 2001. Arid. Zone Res. 2017, 34, 337–343. [Google Scholar]







| Items | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|
| TWSA from GRACE | 0.5° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| CMA | 0.5° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| TRMM 3B43 | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| ET, SWE, SM, Plant canopy surface water and Runoff from NOAH_2.1 | 1° | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| MODIS ET | 1 km | Monthly | 2003–2019 |
| GLEAM ET | 0.25° | Monthly | 2003–2018 |
| Land cover from MODIS | 0.05° | Yearly | 2003–2019 |
| Groundwater observation wells | — | Monthly | 2007–2018 |
| Period | Change of GWS During the Period | Change Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equivalent Water Height | Water Volume | ||
| 2003–2006 | −17.9 mm | −3.58 × 108 m3 | −4.5 mm/year |
| 2007–2010 | −24.3 mm | −4.86 × 108 m3 | −6.1 mm/year |
| 2010–2016 | −2.2 mm | −0.44 × 108 m3 | −0.3 mm/year |
| 2016–2019 | 9.1 mm | 1.82 × 108 m3 | 2.3 mm/year |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yin, W. Improved Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance in Northwestern China Using GRACE Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142672
Liu X, Hu L, Sun K, Yang Z, Sun J, Yin W. Improved Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance in Northwestern China Using GRACE Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Litang Hu, Kangning Sun, Zhengqiu Yang, Jianchong Sun, and Wenjie Yin. 2021. "Improved Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance in Northwestern China Using GRACE Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142672
APA StyleLiu, X., Hu, L., Sun, K., Yang, Z., Sun, J., & Yin, W. (2021). Improved Understanding of Groundwater Storage Changes under the Influence of River Basin Governance in Northwestern China Using GRACE Data. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142672