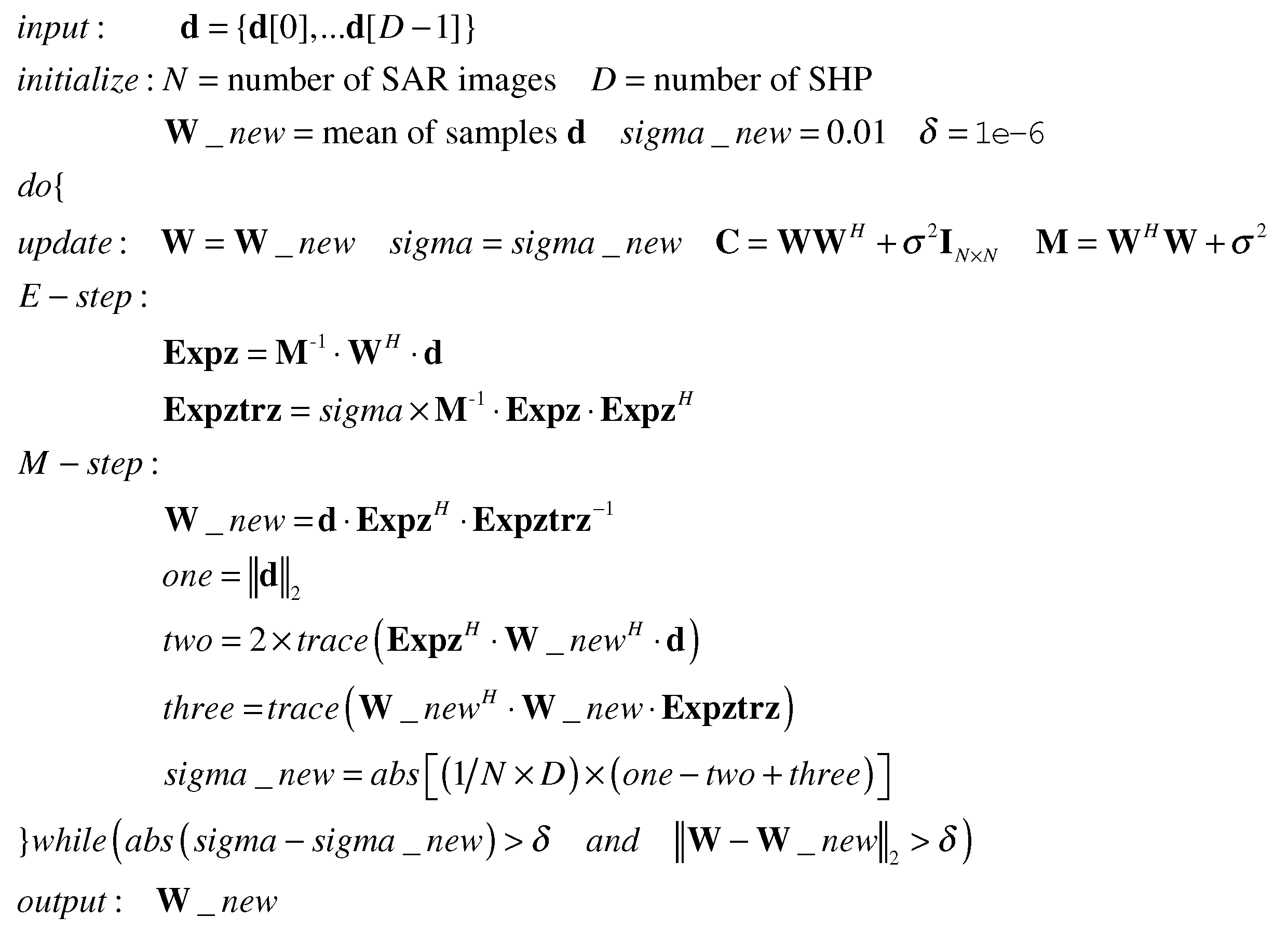Abstract
In order to minimize the influence of decorrelation noise on multi-temporal interferometric synthetic aperture radar (MT-InSAR) applications, a series of phase reconstruction methods have been proposed in recent years. Unfortunately, current phase reconstruction methods generally exhibit a low computational efficiency due to their high non-linearity, in particular in the case that the dimension of a SAR stack is high. In this paper, a new approach is proposed to efficiently resolve phase reconstruction problems. This approach is inspired by the theory of probabilistic principle component analysis. A complex valued probability generative model is constructed to portray a phase reconstruction process. Moreover, in order to resolve such a model, a targeted algorithm based on the idea of expectation maximization is designed and implemented. For validation purposes, the proposed approach is compared to the traditional eigenvalue decomposition-based method by using simulated data and 101 real Sentinel-1A SAR images. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can accelerate the phase reconstruction process drastically, in particular when a high-dimensional SAR stack is required to be processed.
1. Introduction
Multi-temporal interferometric synthetic aperture radar (MT-InSAR) techniques have been widely recognized as potential remote sensing tools for monitoring ground surface movements. Such techniques overcome the drawbacks of the traditional differential radar interferometry and are capable of mapping the time-series of ground displacement within millimeter accuracy [1]. In recent years, they have been increasingly applied in tectonic movements [2,3], land subsidence [4,5], volcanic activities [6,7], landslides [8,9] and underground minings [10,11], railways [12,13], bridges [14,15,16].
One of the most classic MT-InSAR techniques is the so-called persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI), which was proposed in the early 2000s [17,18]. This technique uses a stack of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, thereby isolating ground deformation signals on points with low phase dispersion by taking account into different spatial-temporal characteristics of different interferometric phase components. Such points are commonly referred to as permanent scatterers (PS). It has been repeatedly pointed out that the density of PS can be only well-preserved in urban areas. In the areas with rare human activities, it can be less than 10 PS/km2 [19]. Evidently, low PS density will prevent the phenomenon of ground deformation from being comprehensively exhibited, which limits the broad practicability of the MT-InSAR techniques.
Let N be the dimension of a SAR image stack, in the PSI theory, interferograms are generated with respect to a pre-selected master acquisition. That is, the phase observations of each target will be extracted from interferograms. It is unavoidable that some interferograms are with long spatial and/or temporal spans. Consequently, the corresponding interferometric signals might be severely decorrelated, leading to a decrease in stable points. To mitigate the influence of decorrelation, a series of small baseline style MT-InSAR techniques were successively proposed [20,21,22]. Such methods assess the decorrelation level of all possible interferometric pairs based on a pre-defined criterion (commonly using spatial/temporal baseline) and choose highly-correlated pairs for subsequent interferometric analyses. As interferometric decorrelation is induced by various of factors, it is nearly impossible to use a fixed pair selection method for all situations.
In 2008, Guarnieri et al. [23] proposed a so-called phase liking method to minimize the influence of decorrelation noise. For a given point, the method firstly constructs a complex coherence matrix based on the averaged interferometric phase of every pair. Based on the coherence matrix, a maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) is defined, thereby reconstructing interferometric signals. Following the idea of phase linking, Ferretti et al. [19] systematically proposed the SqueeSAR technique. The technique mainly has two distinct features. Firstly, instead of the traditional boxcar processing, a coherence matrix is constructed by averaging statistically homogeneous pixels (SHPs). The signal-to-noise ratio of a coherence matrix is hence improved. Secondly, the phase triangulation algorithm (PTA) is introduced to assure an optimum phase reconstruction result. In 2007, Francesco et al. [24] applied eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) to coherence matrices. The corresponding eigenvector with the largest eigenvalue can be considered to be the reconstructed interferometric signals [25]. In recent years, phase reconstruction techniques have been widely applied to various MT-InSAR applications [26,27,28,29].
One of the most attractive advantage of the MT-InSAR techniques is that it is capable of providing accurate deformation time-series measurements. In order to reflect the temporal evolutions of ground displacements more comprehensive, time-series products are expected as dense as possible. Therefore, the newly launched SAR satellites usually have relatively short orbit repeat cycles. Let us take the European Space Agency (ESA)’s Sentinel-1 mission as an example. Its repeat cycle is 12 days, while the repeat cycle of the ESA’s previous EnviSAT mission is 35 days. Moreover, the Sentinel-1 mission is designed as a two-satellite constellation [30], which implies that the corresponding repeat cycle can be as low as 6 days. That is to say, when MT-InSAR techniques are applied to such kind of data, the dimension of the corresponding SAR stacks could be very high, in particular in long-term deformation monitoring applications. Ansari et al. [31] pointed out that the MLE based phase reconstruction methods have a super-nonlinear computational complexity and proposed a sequential estimator to accelerate the reconstruction process on high-dimensional SAR stacks. However, as this method achieves high computational efficiency at the expense of losing coherence information, the reliability of reconstruction might not be assured. Ansari et al. [32] further pointed out that the EVD method is superior to the MLE based methods in the aspect of computational efficiency. In addition, they suggested us to use the EVD method to process a high-dimensional SAR stack. Indeed, the computational complexity of the EVD method can be approximately denoted as [33,34]. It indicates that the required execution time will be considerably increased when the dimension of a SAR stack is getting higher. In other words, the EVD method is still not an ideal method to efficiently reconstruct interferometric signals from a high-dimensional SAR stack. In this paper, a new approach is developed in order to efficiently reconstruct interferometric signals. This method is inspired by the theory of probabilistic principle component analysis (PPCA), which defines a complex valued probability generative model depicting the phase reconstruction process. Further, a targeted expectation maximization process is designed and implemented to resolve the model. On the premise that the accuracy of the proposed method is at the same level as that of the traditional EVD method, the computational complexity can be reduced to , where M is the number of SHPs. The phase reconstruction process can be therefore significantly accelerated, especially in the case of dealing with a high-dimensional SAR stack.
This paper is arranged as follows. Traditional phase reconstruction methods, in particular the EVD method, are reviewed in Section 2. Next, the complex valued probability generative model and the corresponding resolution strategy are discussed in Section 3. In Section 4, the proposed method is applied to test data, and its performance is carefully investigated. This paper is concluded in Section 5. Most of the problems in this paper are discussed from the perspective of probability theory. The readers are referred to [35] for more details.
2. Background
Let N denote the dimension of a SAR stack. Given a pixel p, its observation sample vector can be expressed as:
where stays for matrix transposition. represents the complex reflectivity value associated with the n-th SAR image. Let M be the number of samples associated with p. Based on the central limit theorem, the observation samples, , follow a zero-mean N-variate complex circular Gaussian distribution. Therefore, the probability density function (PDF) of the data conditioned on interferometric phase can be expressed as [36]:
where denotes the Hermitian conjugation, is the coherence matrix, and , , where is p’s “true” phase value with respect to the n-th SAR image [19]. In real applications, by assuming that the sample vectors are statistically independent, the coherence matrix can be estimated as follows:
Allowing the decomposition of to its modulus and argument, can be further expressed as:
where indicates an estimate of the coherence value on the interferometric pair with respect to the m-th and the n-th SAR observations, and stands for the interferometric phase.
MLE based approaches factorize the coherence matrix as:
where . The maximum likelihood estimation of is obtained by minimizing the absolute value of its logarithm:
where ∘ represents the Hadamard product. Ferretti et al. [19] proposed a Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (BFGS) based optimizer to resolve the above problem, which is the most widely used method in the MLE based phase reconstruction.
The EVD approach proposes a factorization of to two full-rank complex matrices and one diagonal real matrix :
where is constructed with the orthogonal signal subspace and noise subspaces for a set of SAR sample vectors. According to the principle of beamforming method [37] in the SAR tomography, the eigen-decomposition based phase estimator can be expressed by an objective function [25]:
which is constrained by . Comparing Equation (8) to Equation (6), the first eigenvalue-eigenvector pair provides the best approximation of under a single elementary scattering mechanism. The dominant interferometric signals on a given pixel are hence derived, which can be noted as:
3. Methodology
3.1. Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis (PPCA)
The PPCA theory essentially augments the linear projection from the principal space to the observed data space by assuming that the observed data are corrupted by isotropic Gaussian noise. When the observation noise variance is zero, PPCA is equivalent to the standard principal component analysis (PCA) [38]. Indeed, PPCA explains the standard PCA from the viewpoint of probability, which can be deduced from the Gaussian latent variable generative model. The Gaussian latent variable model of given observed signals can be written as:
where represents an observation vector, the matrix is a dimensional loading matrix, denotes the vector of latent variables, is the mean vector of the signals, and denotes the noise component which is independent of . Generally, is set in this model so that latent variables can provide a briefer explanation of the dependences between observations. The Gaussian latent variable model assumes that both and have Gaussian distributions with zero mean, i.e., and , where is a identity matrix and is a diagonal matrix. According to the Gaussian linearity property, should also follow the Gaussian distribution: , where .
Further supposing that is isotropic (i.e., ), the probability density function of can be deduced as follows:
where . It follows a Gaussian distribution as well. According to this, the logarithmic likelihood function for a set of observation vectors can be expressed as:
where represents the unknown parameters, is the covariance matrix of , and stands for the trace operator. In [39], it is deduced that the likelihood is maximized when
where the q column vectors in the matrix are the principal eigenvectors of , with corresponding eigen values in the diagonal matrix , and is an arbitrary orthogonal rotation matrix. Consequently, the global maximum of the likelihood can be represented by principal eigenvectors. That is to say, the Gaussian latent variable generative model with is actually a probabilistic model of PCA. In addition, due to the introduction of latent variables, the computationally efficient expectation maximization (EM) algorithm can be utilized to estimate the model parameters.
3.2. Probability Generative Model of SAR Observations
Inspired by the principle of PPCA, the generative model of SAR observations is carefully constructed in this section. It must be noted that the form of this model is much more complicated than that of the traditional PPCA, as the SAR observations are complex random variables. In this paper, this model is referred to as the complex probabilistic principal component analysis (CPPCA) model:
where denotes the loading matrix, is the vector of latent variables and is the noise component. and obey complex circular Gaussian distribution (i.e., and ), respectively. According to the linear property of the complex circular Gaussian distribution, the probabilistic density function of can be deduced and written as:
where , and the unknown parameter set is . With the use of Equation (15), the log-likelihood of a given complex-valued observation dataset can be expressed as:
As previously mentioned, can be solved through the EM algorithm, which regards the vector of latent variables and as the “missing” data and the “complete” data, respectively. The log-likelihood of the “complete” data can be expressed as:
Hence, the joint probabilistic density function can be deduced:
where denotes -norm operator. Based on the Bayes’ rule, the conditional distribution of can be obtained:
where . In general, the EM algorithm contains two processing steps: E-step and M-step. In E-step, the expectation of with respect to the distribution of is calculated based on the following formulation:
where represents expectation operator. Based on the Bayes’ rule, the conditional distribution of the latent variable vector can be obtained and expressed as:
where . The expectations involved in Equation (20) hence can be deduced:
In the M-Step, the parameter of the -th iteration can be updated according to the following formulation:
where is the estimated parameter obtained during the -th iteration. The EM algorithm will be terminated when the convergence condition ( is the iterative accuracy) reaches. Otherwise, the E-step and the M-step will be operated repeatedly. To sum up, the pseudo-codes is given in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
The pseudo-codes of the proposed method.
3.3. Obtain the Reconstructed Phase Vector from a CPPCA Solution
The gradient of the log-likelihood (Equation (16)) with respect to can be deduced as [35]:
where the superscript * stands for conjugate operator. There are three possible solutions for Equation (24) when exists. The first one is . It does not make any sense, as it indicates a zero observation vector. The second is , . On the ground that there is no chance to obtain an infinite number of samples, it would not take place in practice. The third case is , , and all potential solutions for may be written as:
where and are composed of the principal eigenvectors and corresponding eigenvalues of , respectively, and is an arbitrary orthogonal rotation matrix.
As it only requires the eigenvector with the largest eigenvalue to reconstruct interferometric signals, Equation (25) can be rewritten as:
where represents the rotation parameter. Equation (26) and Equation (9) have a similar mathematical form. As a result, can be considered to be reconstructed signals. Note that only the phase component is concerned in the phase reconstruction. The reconstructed phase based on the CPPCA method consists of three parts: the phases of , and . The phase of is the expected interferometric phase, and the subsequent two can be eliminated in the differential process.
In the traditional EVD approach, the eigenvalue can be directly used to evaluate the reliability of a phase reconstruction result. In the CPPCA case, the eigenvalue can be obtained by separating from the estimate of . Unfortunately, such a separation operation is time-consuming. In [19], a so-called goodness of fitness (GoF) factor is proposed for the reliability assessment purpose. However, it is defined based on the upper triangular matrix of . In this paper, in order to further reduce the computational cost, a pseudo-GoF (PGoF) factor is designed:
where stands for the observed phase on the n-th SAR image.
4. Results
For validation purposes, the proposed CPPCA method was compared to the EVD method by utilizing both simulated data and real data. To investigate the performance of the proposed method more comprehensively, two programming languages—Python and C++—were used to implement all the algorithms. Moreover, the well known linalg.eig and Eigen libraries were directly adopted to implement the Python and the C++ versions of the EVD method, respectively. The simulated data were processed based on the Python implementations. On the other hand, as the volume of the real data is relatively large, the parallel C++ versions of the both methods were applied for time saving concerns. All calculations were executed on a work station with an Intel i9-9920X processor and 64 GB of memory. It must be noted that the computational capability of the work station is relatively weak. If the proposed method can be applied to a supercomputer, its performance might be exhibited more prominently.
4.1. Simulated Data
When generating simulated data, the dimension of the SAR stack is set to . The number of samples was set to . The following steps were adopted to simulate a group of M sample vectors with respect to a certain point. Firstly, uniform distributed random numbers between zero and one were generated. They were used to form an N-dimensional vector. This vector is denoted as , which is considered to be the “real” interferometric signals. Next, the latent vector , which contains M complex numbers, was generated based on Gaussian distribution. Based on a pre-configured standard deviation , a zero-mean vector was simulated. Finally, a set of M observation samples was obtained based on , and by using Equation (14).
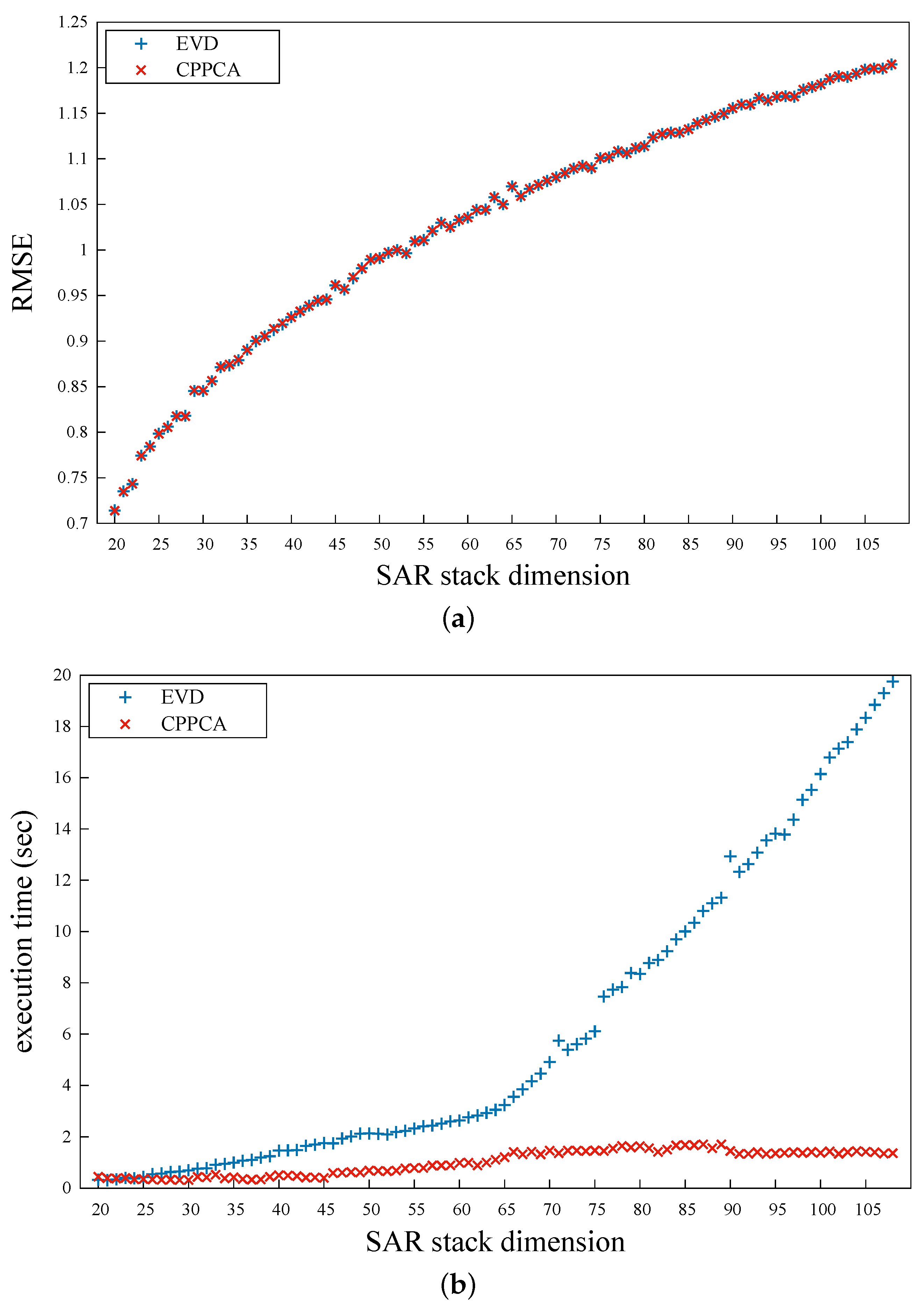
For a given stack dimension N, 1000 groups of simulated samples were generated, which were processed by the EVD and the CPPCA method, respectively. In order to evaluate the accuracy of the two methods, the root mean square errors (RMSE) of the results were calculated, as demonstrated in Figure 2a. No apparent differences between the two methods can be observed from this figure, which implies that the proposed method has an equivalent accuracy to the conventional EVD method. The execution times of the two methods are presented in Figure 2b. It can be clearly observed that the EVD method exhibited a super non-linear computational complexity. On the other hand, the execution time required by the CPPCA method was virtually never influenced by the stack dimension. When , the EVD method spent around 19.75 s on the reconstruction process. In contrast, the CPPCA method only required about 1.37 s. Apparently, the proposed CPPCA method was far superior to the EVD method in the aspect of computational efficiency.
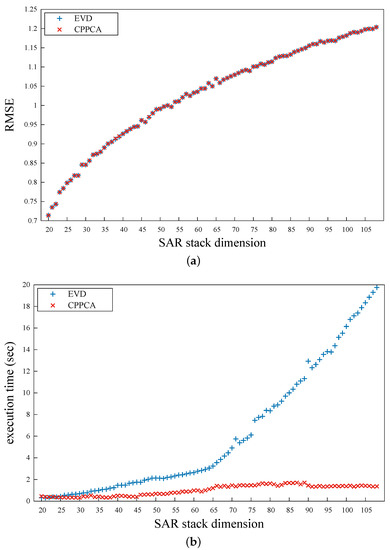
Figure 2.
The RMSEs (a) and the execution times (b) under different SAR stack dimensions.
4.2. Real Data
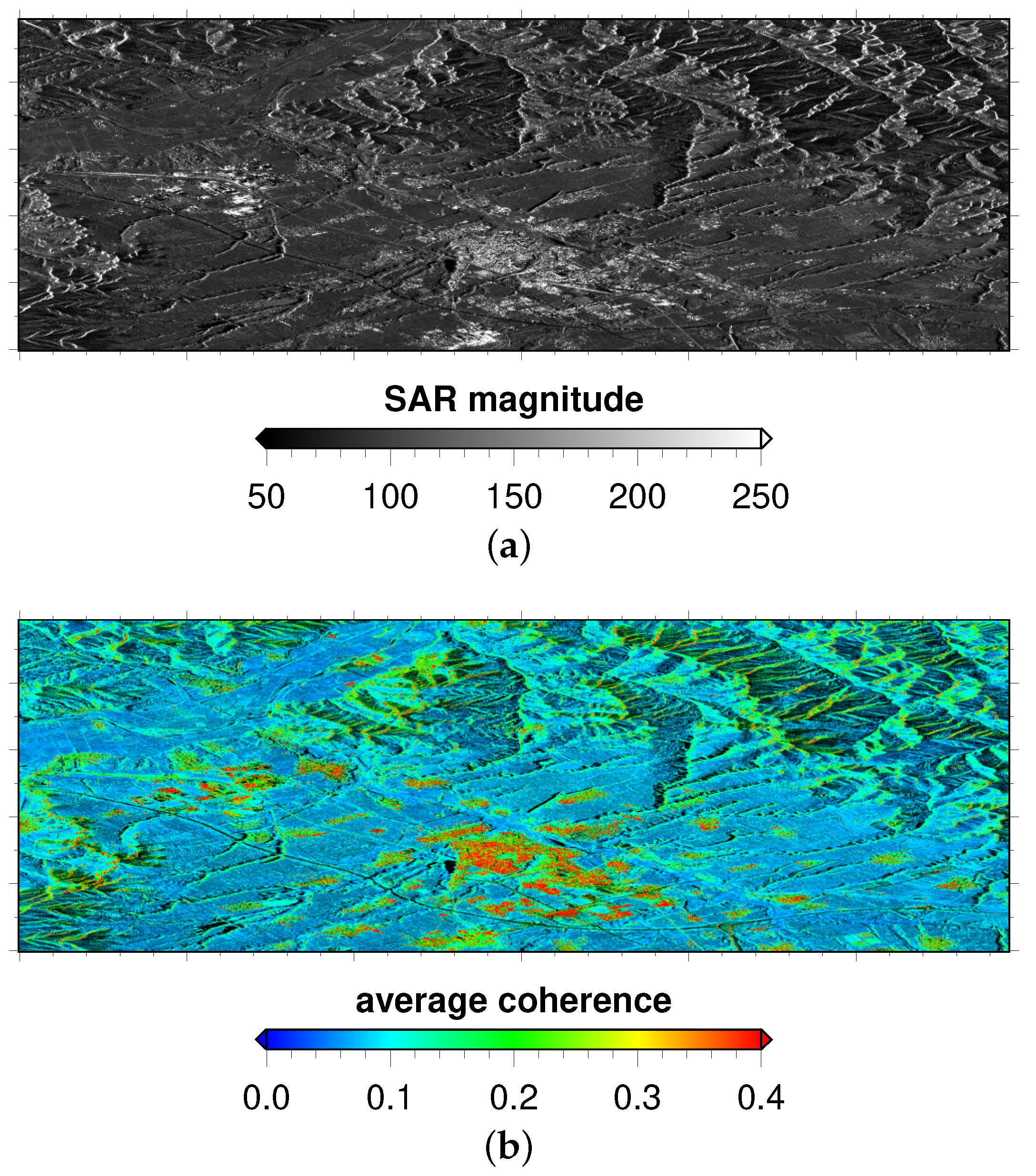
101 Sentinel-1A interferometric wide-swath (IW) SAR images were used to further evaluate the proposed CPPCA method. These images were acquired from January 2017 to February 2020 over the Handan City, Hebei Province, China. The image acquired on 27 September 2019 was firstly selected as the master image. As the images were acquired in terrain observation by progressive scans (TOPS) mode, the most widely used enhanced spectral diversity (ESD) [40] method was carefully carried out to register other images to the master. To facilitate the discussion, the registered images were cropped to a relatively small size (approximately 1000 pixels in azimuth direction and 3000 pixels in range direction). The 1-arc seconds digital elevation model (DEM) provided by the shuttle radar topography mission (SRTM) was used to estimate the topographic phase contributions. It must be noted that the topography induced phase signals were removed from the registered images before phase reconstruction. The average amplitude map with respect to the registered images is presented in Figure 3a. It can be observed that the upper part of the study area is dominated by rugged mountains which cause strong layover/foreshortening effect. On the other hand, the lower part is relatively flat, where a small county is situated. To examine the interferometric coherence of the input data, an overall coherence map is calculated by averaging each off-diagonal element’s magnitude of each pixel’s coherence matrix, which is represented in Figure 3b. Clearly, the interferometric coherence is well preserved over the county region covered by artificial architectures. However, the rest areas, in different degrees, are severely influenced by the decorrelation phenomenon. In these areas, the density of output products could be extremely low if traditional MT-InSAR techniques are applied to the original SAR data.
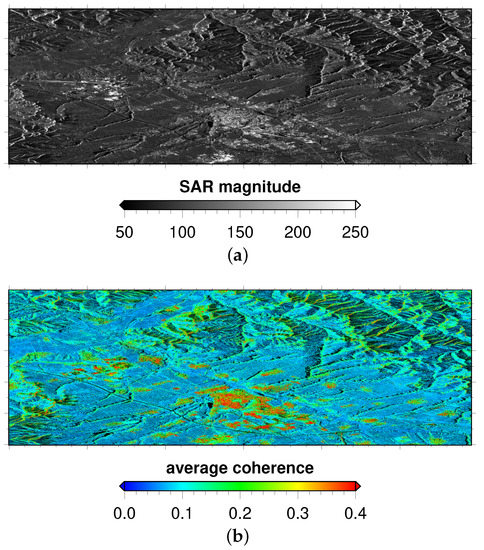
Figure 3.
(a) The average SAR amplitude; (b) the average coherence map overlaid on (a).
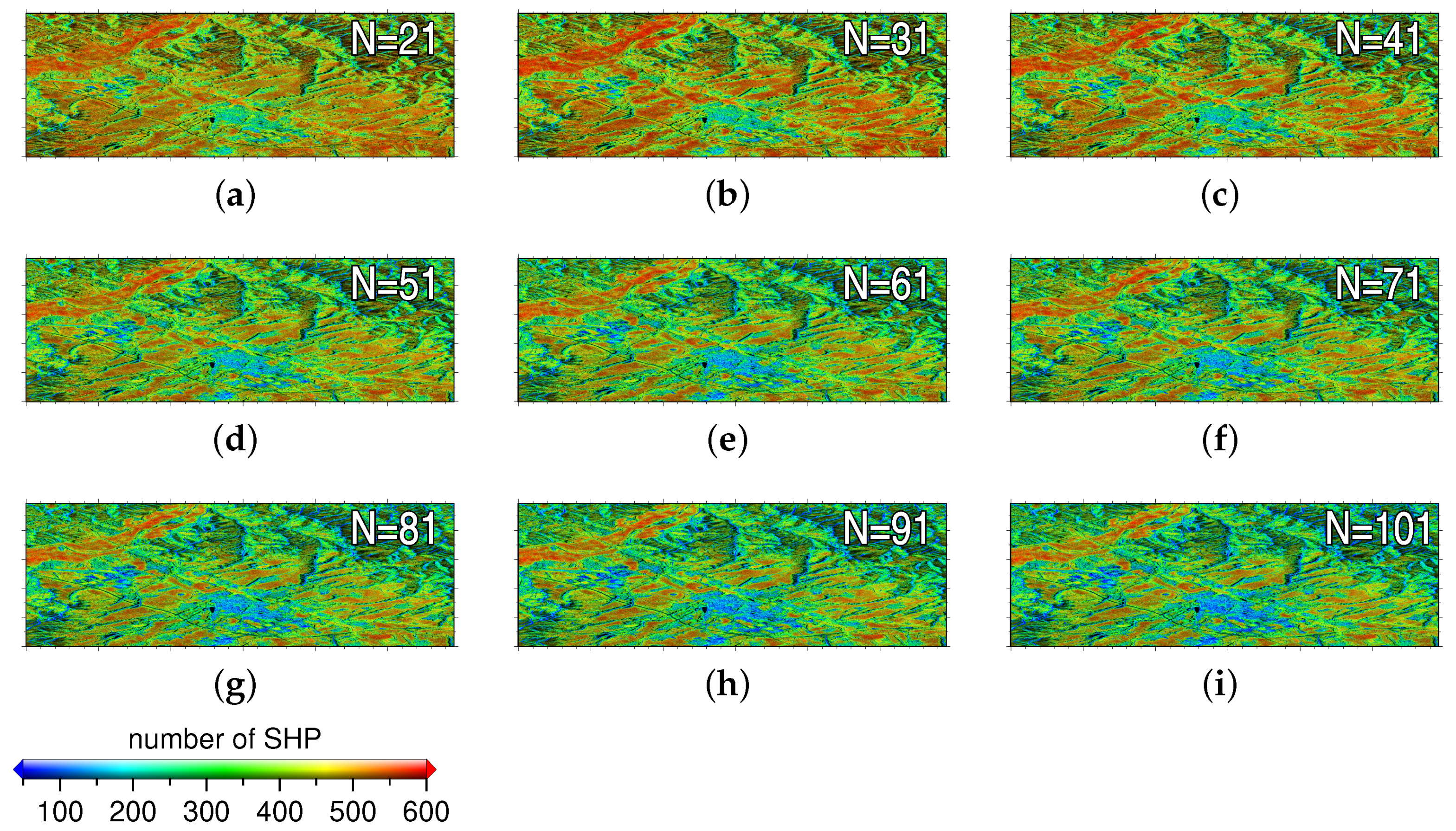
For the purpose of deep investigation, the two methods were applied to the SAR stack constructed by the first N images (). Following the idea of [19], a SHP identification process based on Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test was introduced into the phase reconstruction process to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the observation sample vectors. The corresponding window size was set to . The SHP number with respect to each pixel was recorded and the corresponding results are illustrated in Figure 4. As can be seen from the figure, the number of SHPs associated with each pixel decreased gradually as the stack dimension arises. It indicated the improvement of the SHP identification accuracy, as more samples were available for the KS test. In the areas covered by artificial architectures, where the PS points were densely distributed, small SHP numbers (less than 50) were observed.

Figure 4.
The number of SHP maps overlaid on the average SAR amplitude under a stack dimension of 21 (a), 31 (b), …, 101 (i).
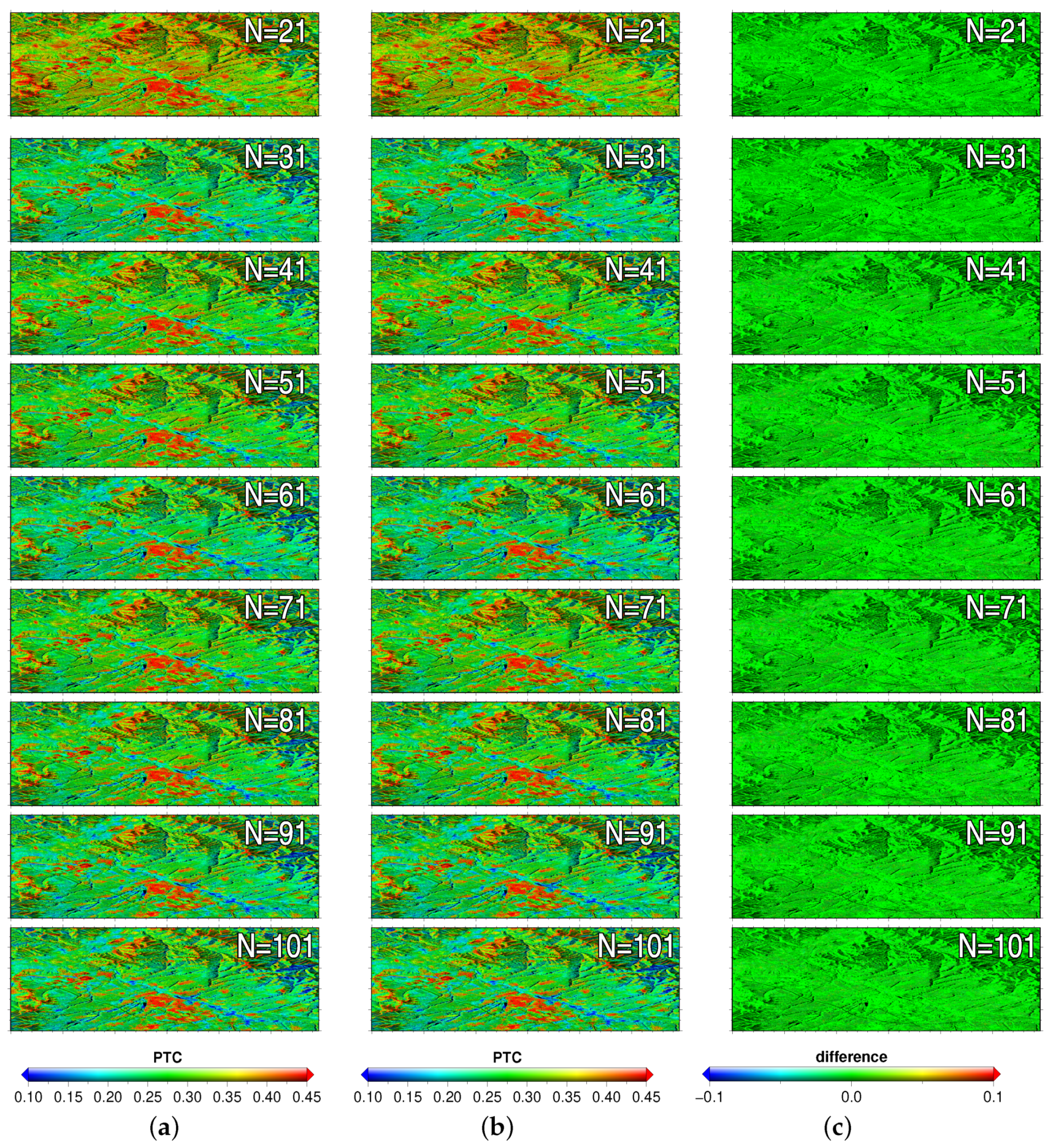
In order to evaluate the reliability of the both methods, the PGoF values with respect to each phase reconstruction result were calculated. The PGoF maps from the EVD and the CPPCA methods are demonstrated in the first column and the second column of Figure 5, respectively. It can be observed that each PGoF map was highly correlated to the average coherence map. In addition, the overall magnitude of each PGoF map was greater than that of the coherence map (Figure 3b). Consequently, it can be considered that the interferometric coherence of the input data was improved by the phase reconstruction process. The last column of Figure 5 presents the PGoF differences between the EVD and the CPPCA results. Obviously, the PGoF difference on each pixel was approximately equal to zero. Therefore, it can be concluded that the proposed method was as reliable as the traditional EVD method.
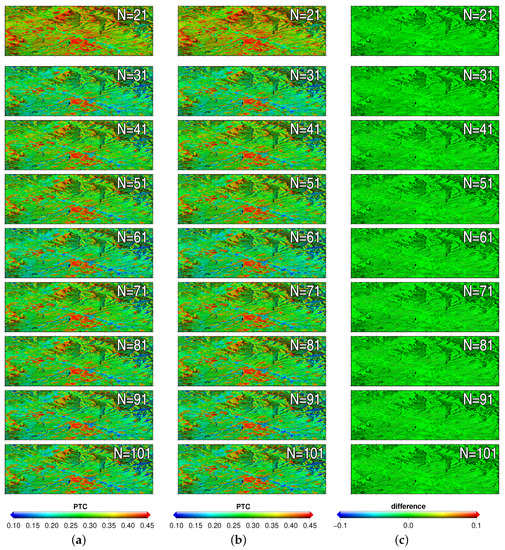
Figure 5.
The PGoF maps from the EVD method (a) and the CPPCA method (b) under different SAR stack dimensions. The corresponding difference maps are listed in (c).
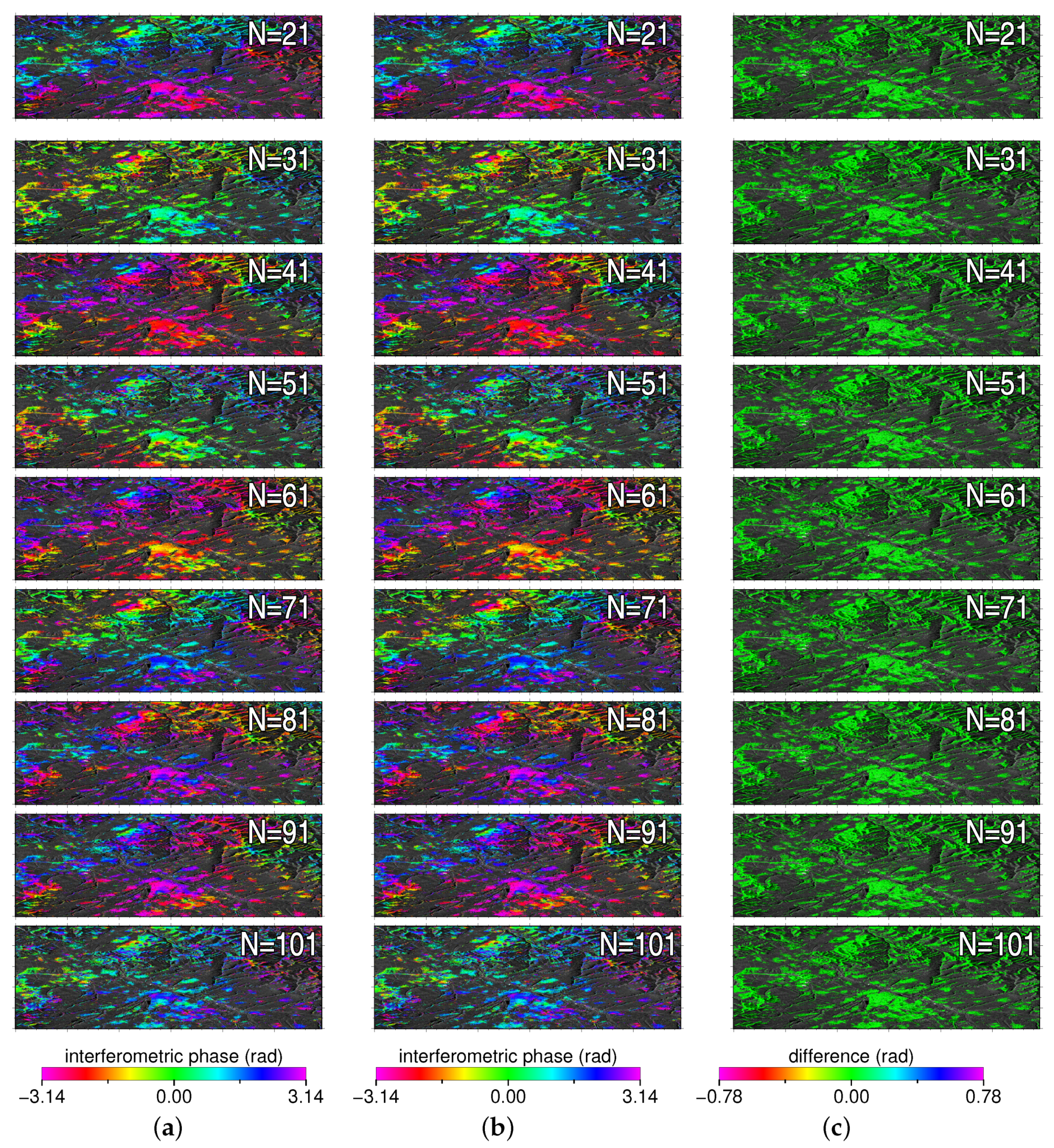
For every case of N, the interferograms with the largest temporal baseline were generated based on the EVD and the CPPCA results, respectively (see Figure 6a,b). Under a certain value of N, an interferogram was affected by the temporal decorrelation to the utmost extent, which was especially suitable for demonstrating the capability of phase reconstruction techniques. It must be noted that the interferometric signals generated based on unreliable phase reconstruction results could be severely deviated from the true values. Therefore, the pixels whose PGoF values less than 0.3 were deleted for the purpose of intuitive representation. As can be seen from Figure 6, the signals contained in each interferogram appear a good consistency and no obvious high frequency noises are presented. The phase difference maps between the EVD and the CPPCA interferograms were generated via conjugated multiplications, as shown in Figure 6c. Since no abrupt signals could be observed, the interferometric signals from the CPPCA method agreed well with those from the EVD method.
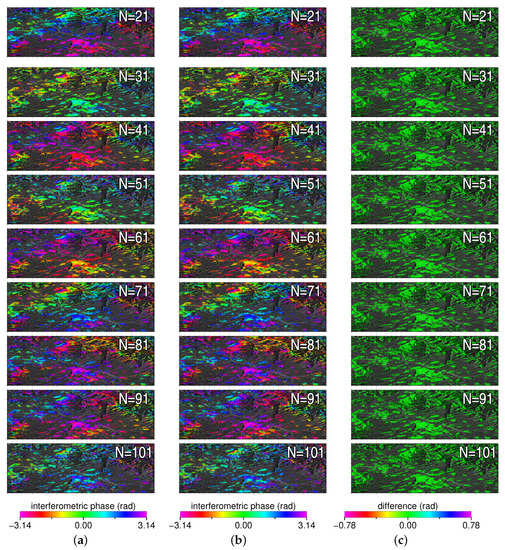
Figure 6.
The reconstructed interferograms from the EVD method (a) and the CPPCA method (b) under different SAR stack dimensions. The corresponding difference maps are listed in (c).
The approximate execution times of the two methods are listed in Table 1. When , the time required by the proposed CPPCA method was around 53% of that required by the EVD method. As N rose, such a CPPCA/EVD time cost ratio (TCR) was basically getting lower and lower. When N reached 101, the corresponding TCR was 10%. Evidently, the excellent computational efficiency of the proposed CPPCA method was further confirmed, in particular in the case of dealing with high dimensional SAR stacks.

Table 1.
The execution times required by the EVD and the CPPCA methods under different SAR stack dimensions.
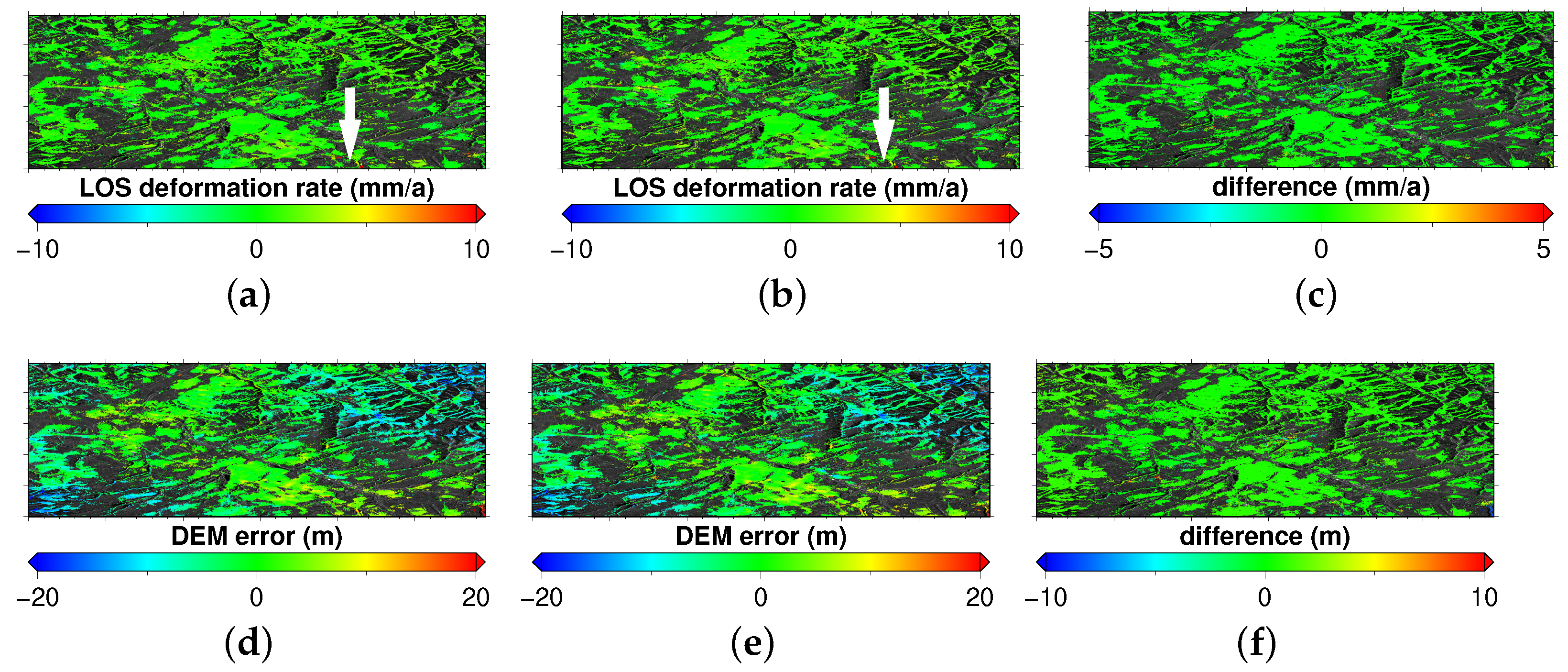
A PSI style MT-InSAR processing plan was further applied to the full SAR stack (N = 101) reconstructed by the proposed CPPCA method. The PGoF was used as the criterion for selecting pixels with low phase dispersion and the corresponding threshold was set to 0.3. Overall, 763,843 pixels were picked out. Next, a reference network with respect to such pixels was constructed based on Delaunay triangulation. In total, the network contained 2,289,832 arcs. The local derivative based searching method [41] was used to inverse the double-differenced annual deformation rates and DEM errors. The ensemble phase coherence (EPC) [17] was used to screen unreliable estimates on each arcs. The threshold of EPC was set to 0.6, leading to a deletion of 38,998 arcs. The iterative reweighted least squares based integration method [42] was used to recover the absolute estimates on each pixel. The resulting annual deformation rate and DEM error maps are represented in Figure 7b,e. As can be seen from the deformation rate map, except for a very small portion of regions (e.g., the place indicated by the white arrow), no obvious ground surface displacements took place during the period of image acquisition. To some extent, a nonlinear trend seemed to be presented in the DEM error map. This is believed to be induced by the relevance of ephemeris data. The reconstructed stack from the conventional EVD method was processed as well. The corresponding results are presented in Figure 7a,d. The corresponding difference maps were generated, which are shown in Figure 7c,f. It can be clearly observed that the results from the both methods were almost identical to each other in the vast majority of regions. Hence the reliability of the proposed CPPCA method was further validated.
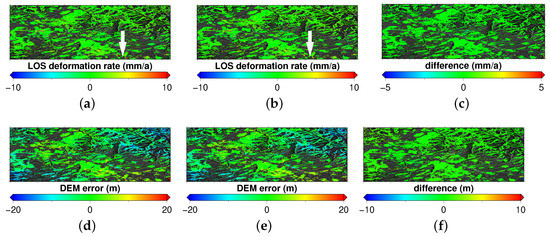
Figure 7.
The annual deformation rate/DEM error maps obtained based on the EVD results (a,d) and the CPPCA results (b,e). The corresponding difference maps are presented in (c,f).
5. Discussion
This paper presents a new method, namely CPPCA, for the phase reconstruction problem in MT-InSAR applications. This method models SAR observation sample vectors from the perspective of probability. By resolving the optimization problem defined with respect to this model, the reconstructed interferometric signals can be derived. Theoretically, this method has an equivalent accuracy compared to the EVD method. The most distinct feature of the proposed method is that no coherence matrix is required to be generated during the entire phase reconstruction process. Moreover, this method has an excellent computational efficiency, which makes it especially suitable for high-dimensional SAR stacks.
As can be observed from the previous section, the proposed CPPCA method seems to perform “worse” on the real data than on the simulated data. Let us take as an example. The proposed CPPCA method requires 1.44 s to deal with the simulated data, which is approximately 1/12 of the traditional EVD method’s time expenditure. On the other hand, the execution time required by the CPPCA method for the real data is 1/10 of that of the EVD method. As mentioned previously, a constant is used to generate simulated data. In the case of real data, M is larger than 300 on average (although the number of SHPs on each pixel decreases as the dimension of the SAR stack rises), as a relatively large window size is used for SHP identification. As mentioned previously, the computational complexity of probabilistic principle component analysis can be denoted as . That is to say, the computational complexity of the proposed CPPCA method highly depends on the number of samples. This is the main reason causing the inconsistent performances of the CPPCA method on the simulated and the real data. Therefore, in real applications, the computational performance of the CPPCA phase reconstruction can be effectively improved by decreasing the window size for sample selection. However, if the window size is unreasonably small, a solid statistical analysis cannot be assured, and hence inaccurate phase reconstruction results will be obtained.
It has been repeatedly suggested that phase reconstruction can be considered to be a filter process with respect to SAR observation vectors [31,41]. From the perspective of signal processing, the quality of filter results is highly dependent to the signal-to-noise ratio of the original data. In other words, in the area with low coherence, no phase reconstruction methods are capable of providing reliable interferometric phase estimates. Therefore, to ensure the accuracy of MT-InSAR measurements, such unreliable results have to be deleted before subsequent interferometric analyses. In the last experiment, in order to retrieve the corresponding annal deformation rate and DEM error maps, a commonly used MT-InSAR processing strategy is applied to the phase reconstruction results from the both EVD method and CPPCA method. The proposed PGoF factor is used to mask unreliable phase reconstruction estimates. For the purpose of comprehensive validation, a relatively low PGoF is used. Therefore, a small portion of phase reconstruction results, either from the proposed CPPCA method or the conventional EVD method, might be severely biased from the “true” interferometric phase values. Where this is the case, biased double-differenced deformation rate and DEM error estimates will be contained in the reference networks. Hence the final maps integrated from such networks will be contaminated in local areas. This is the main reason why the deformation rate/DEM error maps from the two methods are different from each other within a tiny portion of areas. Therefore, a relatively higher PGoF factor (e.g., no less than 0.4) is suggested to be used in real applications to assure the accuracy of MT-InSAR measurements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and K.Z.; methodology, S.L. and K.Z.; software, K.Z. and F.G.; validation, F.G.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, F.G. and J.M.; resources, K.Z.; data curation, Y.W., K.Z. and S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, F.G.; writing—review and editing, K.Z.; visualization, J.M.; supervision, K.Z.; project administration, K.Z.; funding acquisition, K.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42074034) and Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau (Grant No. cstc2019jxj100007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The Sentinel-1 data were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://asf.alaska.edu/ (accessed on 3 March 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the European Space Agency for providing Sentinel-1 data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Millillo, P.; Giardina, G.; DeJong, M.J.; Daniele, P.; Giovanni, M. Multi-temporal InSAR structural damage assessment: The London crossrail case study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.J.; Sun, Q.; Gao, G.J. Vertical and horizontal displacements of Los Angeles from InSAR and GPS time series analysis: Resolving tectonic and anthropogenic motions. J. Geodyn. 2016, 99, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, G.; Yan, S. Crustal deformation in linfen area studied by MT-InSAR. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3022–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Application of multi-temporal Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (MT-InSAR) technique to land deformation monitoring in Warri Metropolis, Delta State, Nigeria. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1220–1227. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Li, X.; Guo, R. Mechanism of Land Subsidence of Plateau Lakeside Kunming City Cluster (China) by MT-InSAR and Leveling Survey. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 115, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebmeier, S. Application of independent component analysis to multi-temporal InSAR data with volcanic case studies. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 8970–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling-Yun, J.I.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Q.L.; Liu, R.C.; Qin, S.L. Deformation Characteristic and Magma Chamber Parameters of Agung Volcano by SBAS-InSAR. J. Seismol. Res. 2013, 36, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Cianflone, G.; Tolomei, C.; Brunori, C.A.; Monna, S.; Dominici, R. Landslides and Subsidence Assessment in the Crati Valley (Southern Italy) Using InSAR Data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. Quantitative hazard and risk assessment for slow-moving landslides from Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Landslides 2014, 11, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzovic, M.; Ghulam, A. Evaluation of land subsidence from underground coal mining using TimeSAR (SBAS and PSI) in Springfield, Illinois, USA. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zou, Y. Investigation on Mining Subsidence Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR and Time-Series Analysis of the Small Baseline Subset—Case Study of Working Faces 22201-1/2 in Bu’ertai Mine, Shendong Coalfield, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.P.; Hanssen, R.F. Nationwide railway monitoring using satellite SAR interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Gagliardi, V.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Tosti, F. Integration of InSAR and GPR Techniques for Monitoring Transition Areas in Railway Bridges. NDT E Int. 2020, 115, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazecky, M.; Hlavacova, I.; Bakon, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Perissin, D.; Patricio, G. Bridge displacements monitoring using space-borne X-band SAR interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, V.; Benedetto, A.; Ciampoli, L.B.; D’Amico, F.; Tosti, F. Health monitoring approach for transport infrastructure and bridges by satellite remote sensing persistent scatterers interferometry (PSI). In Proceedings of the Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications XI, Online, 21–25 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Wang, C.; Qin, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q. Time-Series Analysis on Persistent Scatter-Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR) Derived Displacements of the Hong Kong–Zhuhai–Macao Bridge (HZMB) from Sentinel-1A Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Buckley, S.M.; Ding, X.; Qiang, C.; Luo, X. Estimating Spatiotemporal Ground Deformation With Improved Permanent-Scatterer Radar Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Tebaldini, S. On the exploitation of target statistics for SAR interferometry applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3436–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. PS processing with decorrelating targets. In Proceedings of the Envisat Symposium 2007, ESA Communication Production Office, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fornaro, G.; Verde, S.; Reale, D.; Pauciullo, A. CAESAR: An approach based on covariance matrix decomposition to improve multibaseline–multitemporal interferometric SAR processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2050–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagios, E.; Sakkas, V.; Novali, F.; Bellotti, F.; Ferretti, A.; Vlachou, K.; Dietrich, V. SqueeSAR™ and GPS ground deformation monitoring of Santorini Volcano (1992–2012): Tectonic implications. Tectonophysics 2013, 594, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Adam, N. A distributed scatterer interferometry approach for precision monitoring of known surface deformation phenomena. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5454–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradella, W.R.; Ferretti, A.; Mura, J.C.; Colombo, D.; Gama, F.F.; Tamburini, A.; Santos, A.R.; Novali, F.; Galo, M.; Camargo, P.O.; et al. Mapping surface deformation in open pit iron mines of Carajás Province (Amazon Region) using an integrated SAR analysis. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; Rosich, B.; Grimont, P.; Miranda, N.; Shurmer, I.; O’Connell, A.; Torres, R.; Krassenburg, M. Sentinel-1 Mission Status. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; De Zan, F.; Bamler, R. Sequential estimator: Toward efficient InSAR time series analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5637–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; De Zan, F.; Bamler, R. Efficient phase estimation for interferogram stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4109–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Geometric Structure of High-Dimensional Data and Dimensionality Reduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.N.; Netto, S.L.; de Campos, M.L.R.; Diniz, P.S.R. Low-complexity DoA estimation based on Hermitian EVDs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 10–13 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, N. Multivariate Statistical Inference; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, N.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.C. Mathematical framework for phase-triangulation algorithms in distributed-scatterer interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F.; Pardini, M.; Fornaro, G.; Serafino, F.; Verrazzani, L.; Costantini, M. Linear and adaptive spaceborne three-dimensional SAR tomography: A comparison on real data. Radar Sonar Navig. IET 2009, 3, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ge, Z.; Song, Z. Robust modeling of mixture probabilistic principal component analysis and process monitoring application. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E.; Bishop, C.M. Probabilistic principal component analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2010, 61, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe-Martínez, N.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Rodríguez González, F.; Brcic, R.; Shau, R.; Geudtner, D.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Interferometric processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2220–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Meng, G.; Dai, Y. A very fast phase inversion approach for small baseline style interferogram stacks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Ng, H.M. Monitoring ground surface deformation over the North China Plain using coherent ALOS PALSAR differential interferograms. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).