Ozone Continues to Increase in East Asia Despite Decreasing NO2: Causes and Abatements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. OMI Satellite Measurements
2.1.1. OMI Tropospheric O3 Partial Columns
2.1.2. Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO Columns
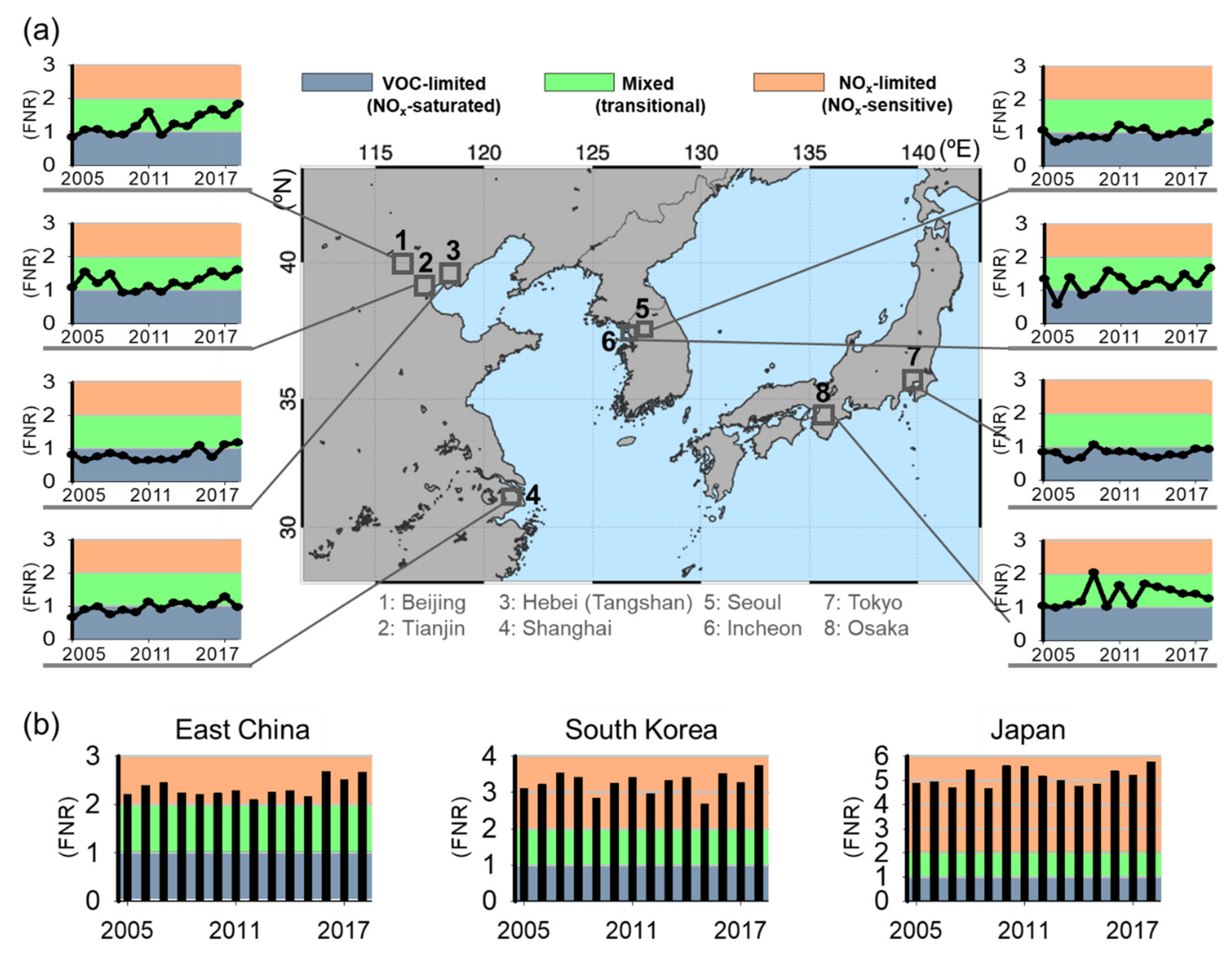
2.1.3. HCHO-to-NO2 Ratio (FNR) Analysis
2.2. In Situ Ground Observation Data
2.3. Climate and Air Quality Modeling Based on RCP Scenarios
3. Results
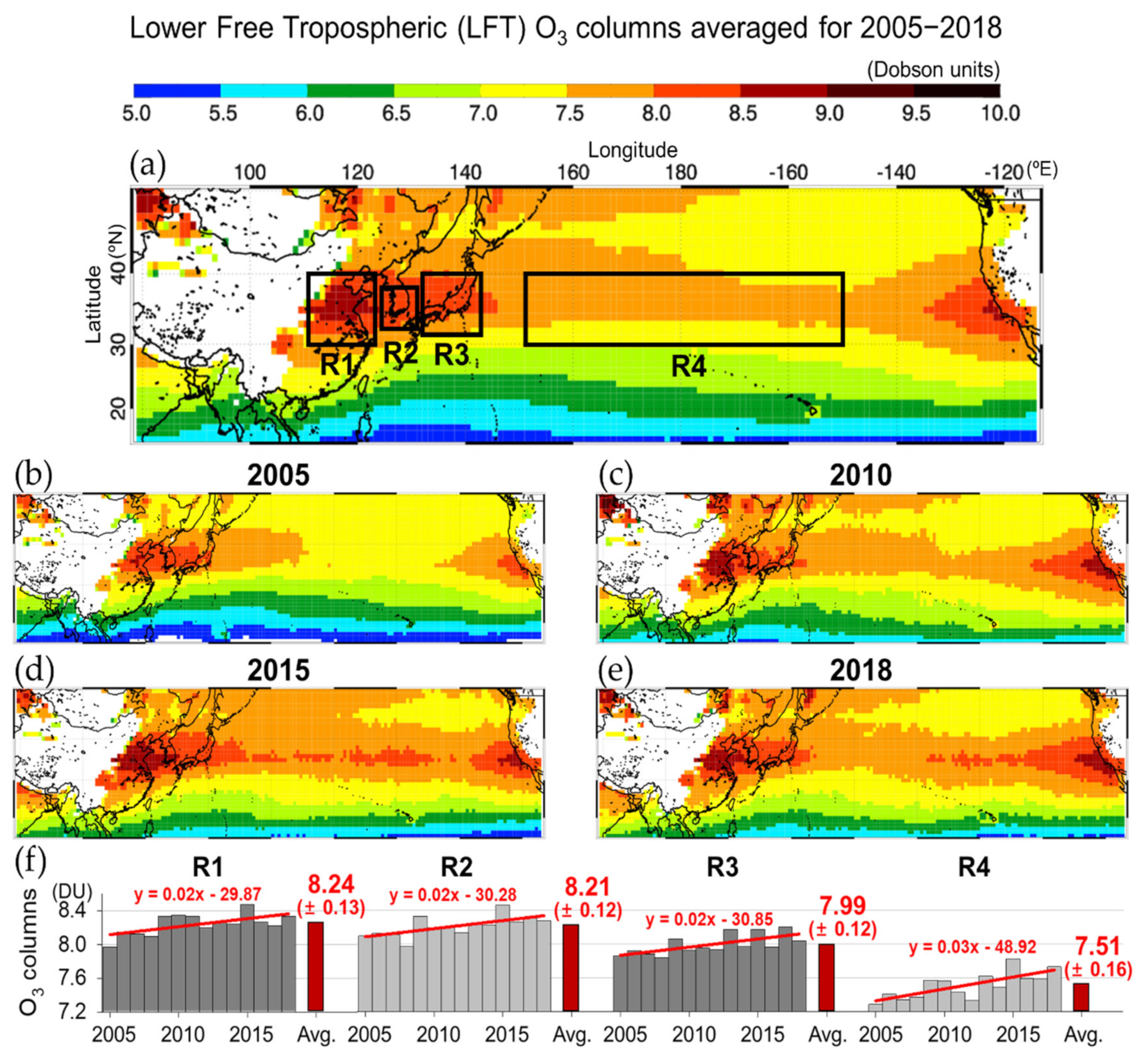
3.1. Lower Free Tropospheric O3 in the Asia–Pacific Region
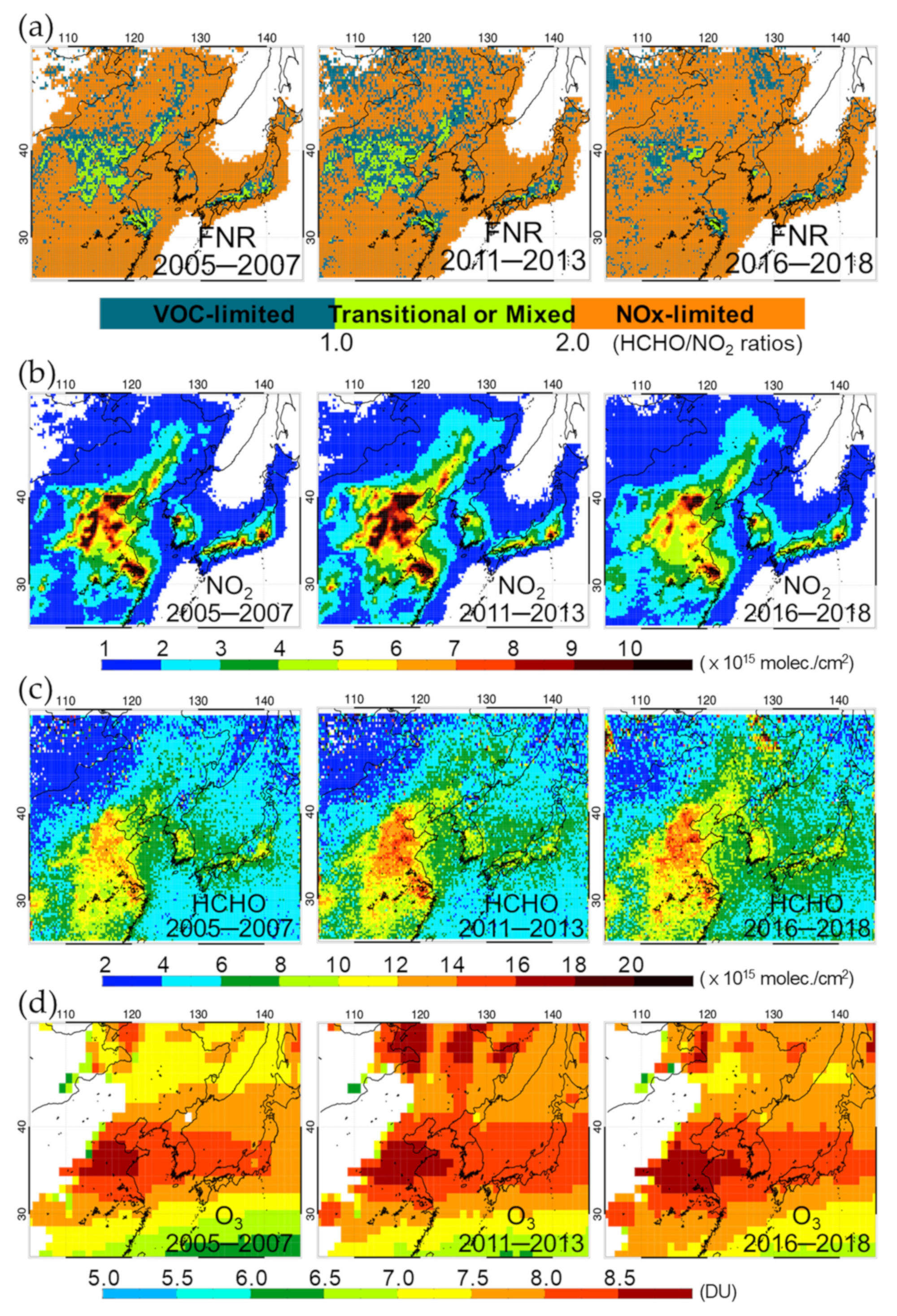
3.2. Changes in O3 Precursors: NO2 and HCHO
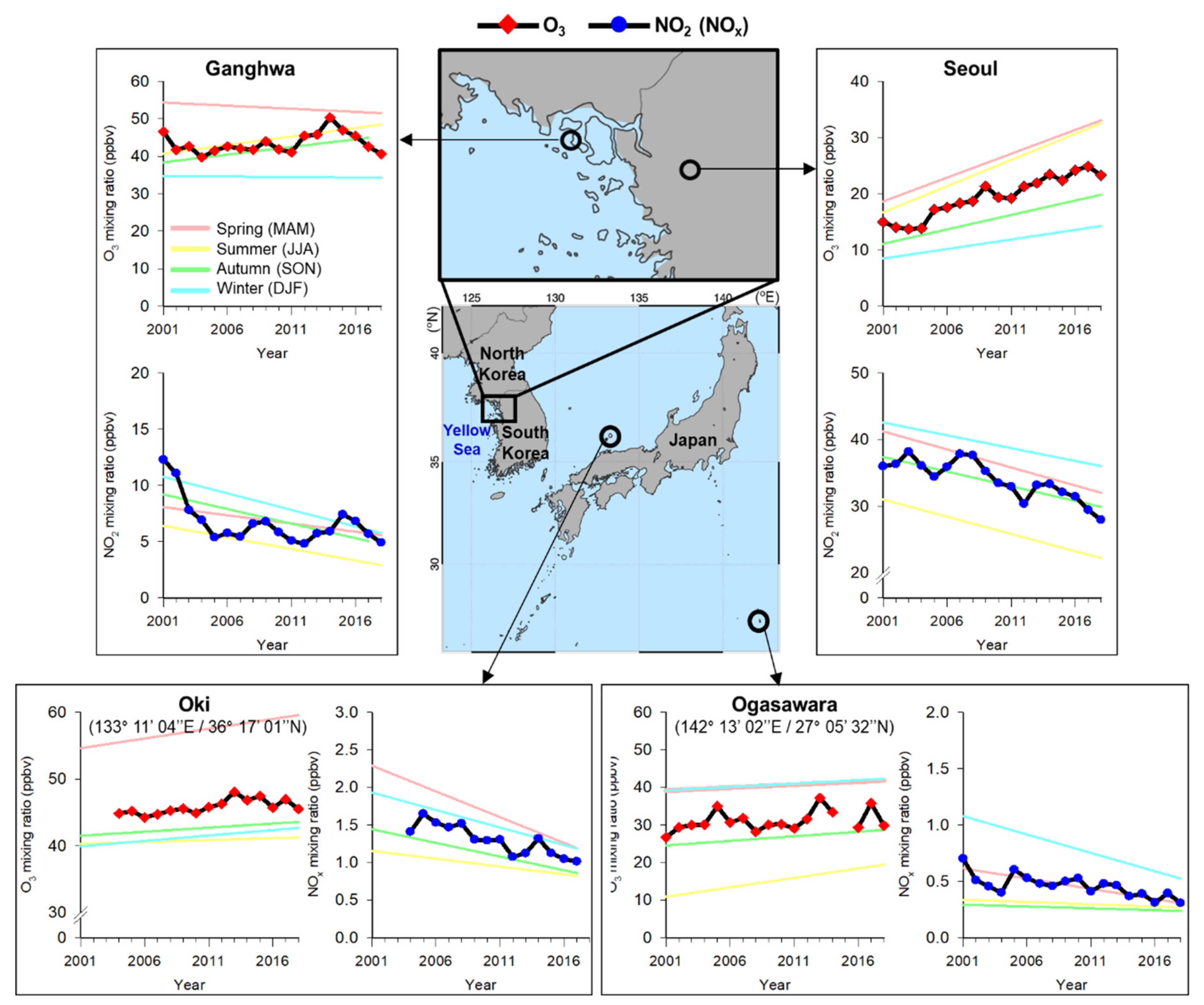
3.3. O3 Continues to Increase Despite Declining NO2 Levels
3.4. Diagnoses of Future O3 Abatements
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. IPCC, Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Arneth, A.; Harrison, S.P.; Zaehle, S.; Tsigaridis, K.; Menon, S.; Bartlein, P.J.; Feichter, J.; Korhola, A.; Kulmala, M.; O’donnell, D.; et al. Terrestrial biogeochemical feedbacks in the climate system. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, K.; Henze, D.K. Attribution of direct ozone radiative forcing to spatially resolved emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L22704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.A.; Parrish, D.; Goldstein, A.; Price, H.; Harris, J. Increasing background ozone during spring on the west coast of North America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, W.W.; Neu, J.L.; Williams, J.E.; Bowman, K.W.; Worden, J.R.; Boersma, K.F. Rapid increases in tropospheric ozone production and export from China. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, O.R.; Forster, C.; Parrish, D.; Trainer, M.; Dunlea, E.; Ryerson, T.; Hubler, G.; Fehsenfeld, F.; Nicks, D.; Holloway, J.; et al. A case study of transpacific warm conveyor belt transport: Influence of merging airstreams on trace gas import to North America. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D23S08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Horowitz, L.W.; Payton, R.; Fiore, A.M.; Tonnesen, G. US surface ozone trends and extremes from 1980 to 2014: Quantifying the roles of rising Asian emissions, domestic controls, wildfires, and climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2943–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jaffe, D.A. Trends and sources of ozone and sub-micron aerosols at the Mt. Bachelor observatory (mbo) during 2004–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Logan, J.A.; Murti, P.P. Effect of rising emissions on surface ozone in the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Jaffe, D.A.; Olson, J.R.; Bowman, K.W.; Worden, J.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Avery, M.A.; Cohen, R.C.; et al. Transpacific transport of ozone pollution and the effect of recent Asian emission increases on air quality in North America: An integrated analysis using satellite, aircraft, ozonesonde, and surface observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6117–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, O.R.; Parrish, D.D.; Stohl, A.; Trainer, M.; Nédélec, P.; Thouret, V.; Cammas, J.P.; Oltmans, S.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Tarasick, D.; et al. Increasing springtime ozone mixing ratios in the free troposphere over western North America. Nature 2010, 463, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, D.D.; Dunlea, E.J.; Atlas, E.L.; Schauffler, S.; Donnelly, S.; Stroud, V.; Goldstein, A.H.; Millet, D.B.; McKay, M.; Jaffe, D.A.; et al. Changes in the photochemical environment of the temperate North Pacific troposphere in response to increased Asian emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D23S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, O.R.; Oltmans, S.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Brioude, J.; Angevine, W.; Trainer, M.; Parrish, D.D.; Ryerson, T.R.; Pollack, I.; Cullis, P.D.; et al. Measurement of western U.S. baseline ozone from the surface to the tropopause and assessment of downwind impact regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D00V03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.A.; Cooper, O.R.; Fiore, A.M.; Henderson, B.H.; Tonnesen, G.S.; Russell, A.G.; Henze, D.K.; Langford, A.O.; Lin, M.; Moore, T. Scientific assessment of background ozone over the U.S.: Implications for air quality management. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, L.E.; Jaffe, D.A.; Hee, J.R. Causes of increasing ozone and decreasing carbon monoxide in springtime at the Mt. Bachelor Observatory from 2004 to 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasunuma, H.; Ishimaru, Y.; Yoda, Y.; Shima, M. Decline of ambient air pollution levels due to measures to control automobile emissions and effects on the prevalence of respiratory and allergic disorders among children in Japan. Environ. Res. 2014, 131, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, J. Estimating the effectiveness of vehicle emission regulations for reducing NOx from light-duty vehicles in Korea using on-road measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.P.; Lee, G. Trend of Air Quality in Seoul: Policy and Science. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, J.B.; Russell, A.G.; McRae, G.J. A new approach to photochemical pollution control: Implications of spatial patterns in pollutant responses to reductions in nitrogen-oxides and reactive organic gas emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, L.I. Low and high NOx tropospheric photochemistry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 16831–16838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Holloway, T. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 7229–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Fiore, A.M.; Murray, L.T.; Valin, L.C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Duncan, B.; Boersma, K.F.; Smedt, I.D.; González Abad, G.; Chance, K.; et al. Evaluating a space-based indicator of surface ozone-NOx-VOC sensitivity over midlatitude source regions and application to decadal trends. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 10439–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, S.U.; Song, C.K. A simple semi-empirical photochemical model for the simulation of ozone concentration in the Seoul metropolitan area in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5597–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nagashima, T.; Kong, L.; Ge, B.; Yamaji, K.; Fu, J.S.; Wang, X.; Fan, Q.; Itahashi, S.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Model evaluation and intercomparison of surface-level ozone and relevant species in East Asia in the context of MICS-Asia Phase III—Part 1: Overview. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12993–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, Y.J.; Park, R.J.; Schroeder, J.R.; Crawford, J.H.; Blake, D.R.; Weinheimer, A.J.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Yeo, H.; Fried, A.; et al. Evaluation of simulated O3 production efficiency during the KORUS-AQ campaign: Implications for anthropogenic NOx emissions in Korea. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Son, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, C.H. Interpretation of decadal-scale ozone production efficiency in the Seoul Metropolitan Area: Implication for ozone abatement. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 243, 117846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Chang, K.L.; Bourgeois, I.; Ziemke, J.R.; Strode, S.A.; Omen, L.; Sellitto, P.; Nedelec, P.; Blot, R.; et al. Aircraft observations since the 1990s reveal increases of tropospheric ozone at multiple locations across the Northern Hemisphere. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, H.W.; Seo, K.-H. A simple method for simulating horizontal ozone concentration fields over coastal areas: A case study of the Seoul metropolitan area, Korea. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Konopka, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Müller, R.; Plöger, F.; Riese, M.; Cai, Z.; Lu, D. Tropospheric ozone trend over Beijing from 2002–2010: Ozonesonde measurements and modeling analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8389–8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wei, X.L.; Ding, A.J.; Poon, C.N.; Lam, K.S.; Li, Y.S.; Chan, L.Y.; Anson, M. Increasing surface ozone concentrations in the background atmosphere of southern China, 1994–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6217–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Miao, J. Spatiotemporal variations in satellite-based formaldehyde (HCHO) in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China from 2005 to 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Lamsal, L.N.; Thompson, A.M.; Yoshida, Y.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Pickering, K.E. A space-based, high-resolution view of notable changes in urban NOx pollution around the world (2005–2014). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Beirle, S.; Zhang, Q.; van der A, R.J.; Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; He, K. NOx emission trends over Chinese cities estimated from OMI observations during 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9261–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souri, A.H.; Nowlan, C.R.; Abad, G.G.; Zhu, L.; Blake, D.R.; Fried, A.; Weinheimer, A.J.; Wisthaler, A.; Woo, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. An inversion of NOx and non-methane volatile organic compound (NMVOC) emissions using satellite observations during the KORUS-AQ campaign and implications for surface ozone over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9837–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, A.H.; Nowlan, C.R.; Wolfe, G.M.; Lamsal, L.N.; Chan Miller, C.E.; Abad, G.G.; Janz, S.J.; Fried, A.; Blake, D.R.; Weinheimer, A.J.; et al. Revisiting the Effectiveness of HCHO/NO2 Ratios for Inferring Ozone Sensitivity to Its Precursors using High Resolution Airborne Remote Sensing Observations in a High Ozone Episode during the KORUS-AQ Campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, S.; Liu, X.; Ono, A.; Yang, K.; Chance, K. Observation of ozone enhancement in the lower troposphere over East Asia from a space-borne ultraviolet spectrometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9865–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, T. An evaluation of the ability of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) to observe boundary layer ozone pollution across China: Application to 2005–2017 ozone trends. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6551–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, M.; Hayashida, S.; Sekiyama, T.T.; Deushi, M.; Ito, K.; Liu, X. Detectability assessment of a satellite sensor for lower tropospheric ozone responses to its precursors emission changes in East Asian summer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, S.; Kajino, M.; Deushi, M.; Sekiyama, T.T.; Liu, X. Seasonality of the lower tropospheric ozone over central China observed by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 184, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, S.; Kayaba, S.; Deushi, M.; Yamaji, K.; Ono, A.; Kajino, M.; Sekiyama, T.T.; Maki, T.; Liu, X. Study of Lower Tropospheric Ozone over Central and Eastern China: Comparison of Satellite Observation with Model. Simulation; Land-Atmospheric Research Applications in South and Southeast Asia; Vadrevu, K.P., Ohara, T., Justice, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 255–275. [Google Scholar]
- Levelt, P.F.; Joiner, J.; Tamminen, J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Bhartia, P.K.; Stein Zweers, D.C.; Duncan, B.N.; Streets, D.G.; Eskes, H.J.; van der A, R.J.; et al. The Ozone Monitoring Instrument: Overview of 14 years in space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5699–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkeveld, V.M.E.; Jaross, G.; Marchenko, S.; Haffner, D.; Kleipool, Q.L.; Rozemeijer, N.C.; Veefkind, J.P.; Levelt, P.F. In-flight performance of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1957–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Spurr, R.J.D. Vlidort: A linearized pseudo-spherical vector discrete ordinate radiative transfer code for forward model and retrieval studies in multilayer multiple scattering media. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 2006, 102, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bhartia, P.K.; Chance, K.; Spurr, R.J.D.; Kurosu, T.P. Ozone profile retrievals from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2521–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Jacob, D.J.; Liu, X.; Warner, J.X.; Yang, K.; Chance, K.; Thouret, V.; Nedelec, P. Global ozone–CO correlations from OMI and AIRS: Constraints on tropospheric ozone sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9321–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, X.; Chance, K.; Yang, K.; Bhartia, P.K.; Cai, Z.; Allaart, M.; Ancellet, G.; Calpini, B.; Coetzee, G.J.R.; et al. Validation of 10-year SAO OMI Ozone Profile (PROFOZ) product using ozonesonde observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2455–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Marchenko, S.V.; Celarier, E.A.; Bucsela, E.J.; Swartz, W.H.; Joiner, J. OMI Core Team, OMI/Aura nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Total and Tropospheric Column 1-Orbit L2 Swath 13×24 km V003; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://aura.gesdisc.eosdis.nasa.gov/data/Aura_OMI_Level2/OMNO2.003/ (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Bucsela, E.J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Celarier, E.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Swartz, W.H.; Bhartia, P.K.; Boersma, K.F.; Veefkind, J.P.; Gleason, J.F.; Pickering, K.E. A new stratospheric and tropospheric NO2 retrieval algorithm for nadir-viewing satellite instruments: Applications to OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2607–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Celarier, E.A.; Swartz, W.H.; Pickering, K.E.; Bucsela, E.J.; Gleason, J.F.; Martin, R.V.; Philip, S.; Irie, H.; et al. Evaluation of OMI operational standard NO2 column retrievals using in situ and surface-based NO2 observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11587–11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Abad, G.G.; Liu, X.; Chance, K.; Wang, H.; Kurosu, T.P.; Suleiman, R. Updated Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Ozone Monitoring Instrument (SAO OMI) formaldehyde retrieval. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillman, S. The Use of NOy, H2O2 and HNO3 as Indicators for the ozone-NOx- hydrocarbon Sensitivity in Urban Locations. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 14175–14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.M.; Fiore, A.; Boersma, K.F.; De Smedt, I.; Valin, L. Inferring changes in summertime surface ozone-NOx-VOC chemistry over US urban areas from two decades of satellite and ground-based observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6518–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.; Yoshida, Y.; Olson, J.; Sillman, S.; Martin, R.; Lamsal, L.; Hu, Y.; Pickering, K.; Retscher, C.; Allen, D.; et al. Application of OMI observations to a space-based indicator of NOx and VOC controls on surface O3 formation. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Jacob, D.J.; Chance, K.; Kurosu, T.P.; Palmer, P.I.; Evans, M.J. Global inventory of nitrogen oxide emissions constrained by space-based observations of NO2 columns. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Celarier, E.A.; Bucsela, E.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Dirksen, R.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y. Indirect validation of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide retrieved from the OMI satellite instrument: Insight into the seasonal variation of nitrogen oxides at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D05302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Brioude, J.; Cooper, O.R.; Frost, G.J.; Kim, C.H.; Park, R.J.; Trainer, M.; Woo, J.H. Transport of NOx in East Asia identified by satellite and in situ measurements and Lagrangian particle dispersion model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2574–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-B.; Cha, J.-S.; Hong, S.-C.; Choi, J.-Y.; Myoung, J.-S.; Park, R.J.; Woo, J.-H.; Ho, C.; Han, J.-S.; Song, C.-K. Projections of summertime ozone concentration over East Asia under multiple IPCC SRES emission scenarios. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Hong, S.-C.; Lee, J.-B.; Song, C.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J. Evaluation of temperature and precipitation on integrated climate and air quality modeling system (ICAMS) for air quality prediction. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 28, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- National Institute of Environmental Research. Development and Operation of the Integrated System on Climate and Air Quality (III); National Institute of Environmental Research: Inchon, Korea, 2010; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Hilboll, A.; Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P. Long-term changes of tropospheric NO2 over megacities derived from multiple satellite instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4145–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, A.H.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, W.; Woo, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J. Remote sensing evidence of decadal changes in major tropospheric ozone precursors over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2474–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, H.; Mori, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Ohizumi, T.; Itano, Y. Analysis of monitoring data of ground-level ozone in Japan for long-term trend during 1990–2010: Causes of temporal and spatial variation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Jia, S.; Ma, R.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. Lower tropospheric distributions of O3 and aerosol over Raoyang, a rural site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Swartz, W.H.; Marchenko, S.V.; Bucsela, E.J.; Chan, K.L.; Wenig, M.; Zara, M. The version 3 OMI NO2 standard product. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3133–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Satellite NO2 retrievals suggest China has exceeded its NOx reduction goals from the twelfth Five-Year Plan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellingiri, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Brown, R.J.C.; Jung, M.C. Changes in NOx and O3 concentrations over a decade at a central urban area of Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, S.; Morikawa, T.; Ito, A. Air pollution trends in japan between 1970 and 2012 and impact of urban air pollution countermeasures. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 7, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Cen, K. Quantitative assessment of industrial VOC emissions in China: Historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and projection. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Chameides, W.L.; Cardelino, C.; Kwok, J.; Blake, D.R.; Ding, A.; So, K.L. Ozone production and hydrocarbon reactivity in Hong Kong, Southern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 7, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Chang, J.S. On the indicator-based approach to assess ozone sensitivities and emissions features. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 3453–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, M.C. Effect of Selected Parameters on Predictions of a Photochemical Model; EPA-600/3-77-048; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1977.
- Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, D.; Hsu, S.; Gao, L. Spatial-temporal variations in surface ozone in Northern China as observed during 2009–2010 and possible implications for future air quality control strategies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2757–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Herrmann, E.; Nie, W.; Petaja, T.; Kerminen, V.-M.; et al. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Su, R.; Dong, H.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Exploring ozone pollution in Chengdu, southwestern China: A case study from radical chemistry to O3 -VOC-NOx sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Chang, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z. Volatile organic compounds measured in summer in Beijing and their role in ground-level ozone formation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00G06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, S.; Zheng, L.; Wu, R.; Li, J. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds and their role in ground-level ozone formation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; De Smedt, I.; Liao, H. Increases in surface ozone pollution in China from 2013 to 2019: Anthropogenic and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11423–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, X.; Chen, S. Increase in Surface Ozone over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the Surrounding Areas of China Inferred from Satellite Retrievals, 2005–2018. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-J.; Chang, L.-S.; Jaffe, D.A.; Bak, J.; Liu, X.; Abad, G.G.; Jo, H.-Y.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-B.; Kim, C.-H. Ozone Continues to Increase in East Asia Despite Decreasing NO2: Causes and Abatements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112177
Lee H-J, Chang L-S, Jaffe DA, Bak J, Liu X, Abad GG, Jo H-Y, Jo Y-J, Lee J-B, Kim C-H. Ozone Continues to Increase in East Asia Despite Decreasing NO2: Causes and Abatements. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(11):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyo-Jung, Lim-Seok Chang, Daniel A. Jaffe, Juseon Bak, Xiong Liu, Gonzalo González Abad, Hyun-Young Jo, Yu-Jin Jo, Jae-Bum Lee, and Cheol-Hee Kim. 2021. "Ozone Continues to Increase in East Asia Despite Decreasing NO2: Causes and Abatements" Remote Sensing 13, no. 11: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112177
APA StyleLee, H.-J., Chang, L.-S., Jaffe, D. A., Bak, J., Liu, X., Abad, G. G., Jo, H.-Y., Jo, Y.-J., Lee, J.-B., & Kim, C.-H. (2021). Ozone Continues to Increase in East Asia Despite Decreasing NO2: Causes and Abatements. Remote Sensing, 13(11), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112177






