Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Recovery of Precise Orbits and Clock Offsets with PPP-B2b Corrections
2.2. Assessment of the Recovered PPP-B2b Orbits and Clock Offsets
2.3. PPP Positioning with the Recovered PPP-B2b Orbits and Clocks
3. Experiments, Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment Results of PPP-B2b Orbit/Clock Corrections
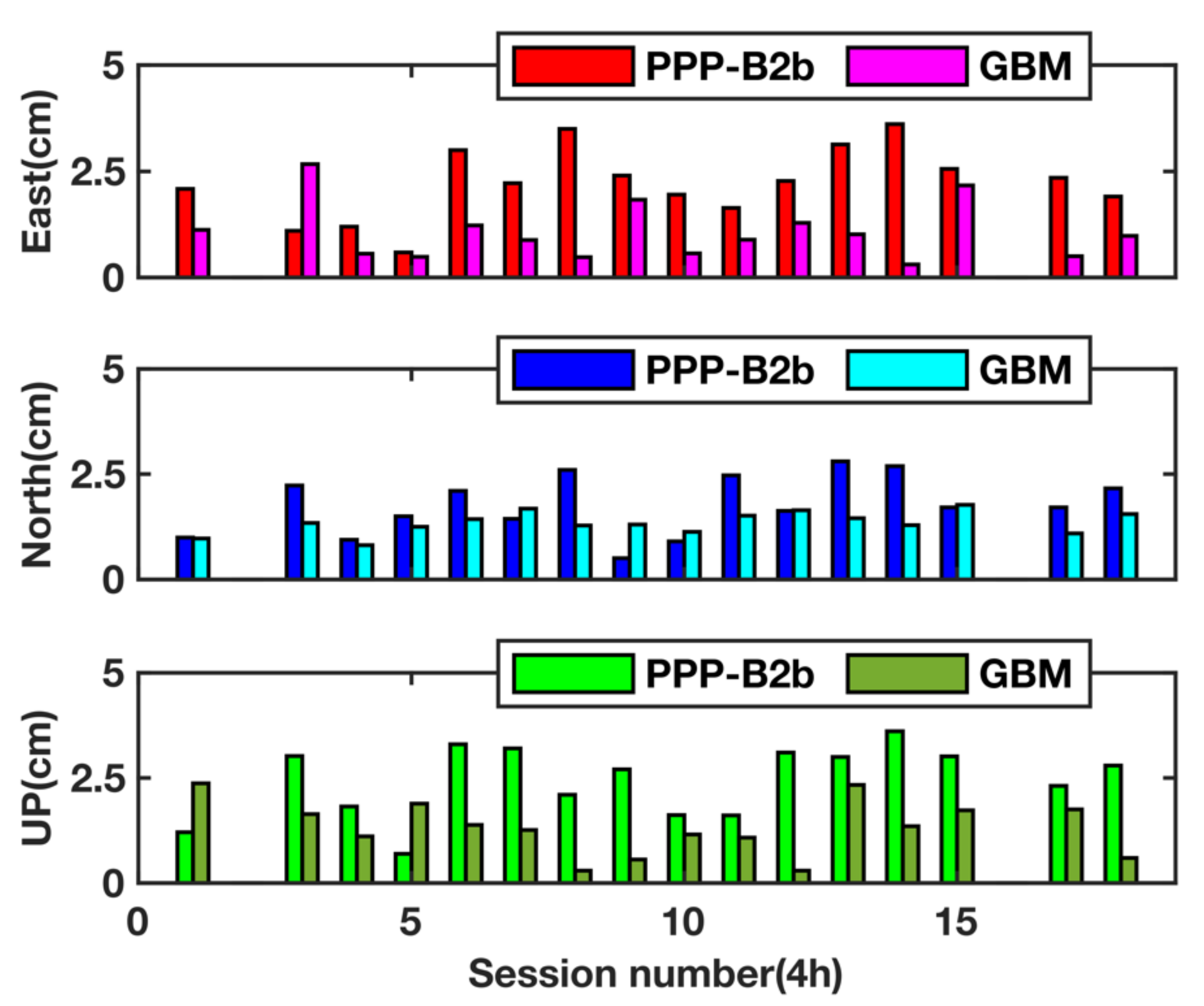
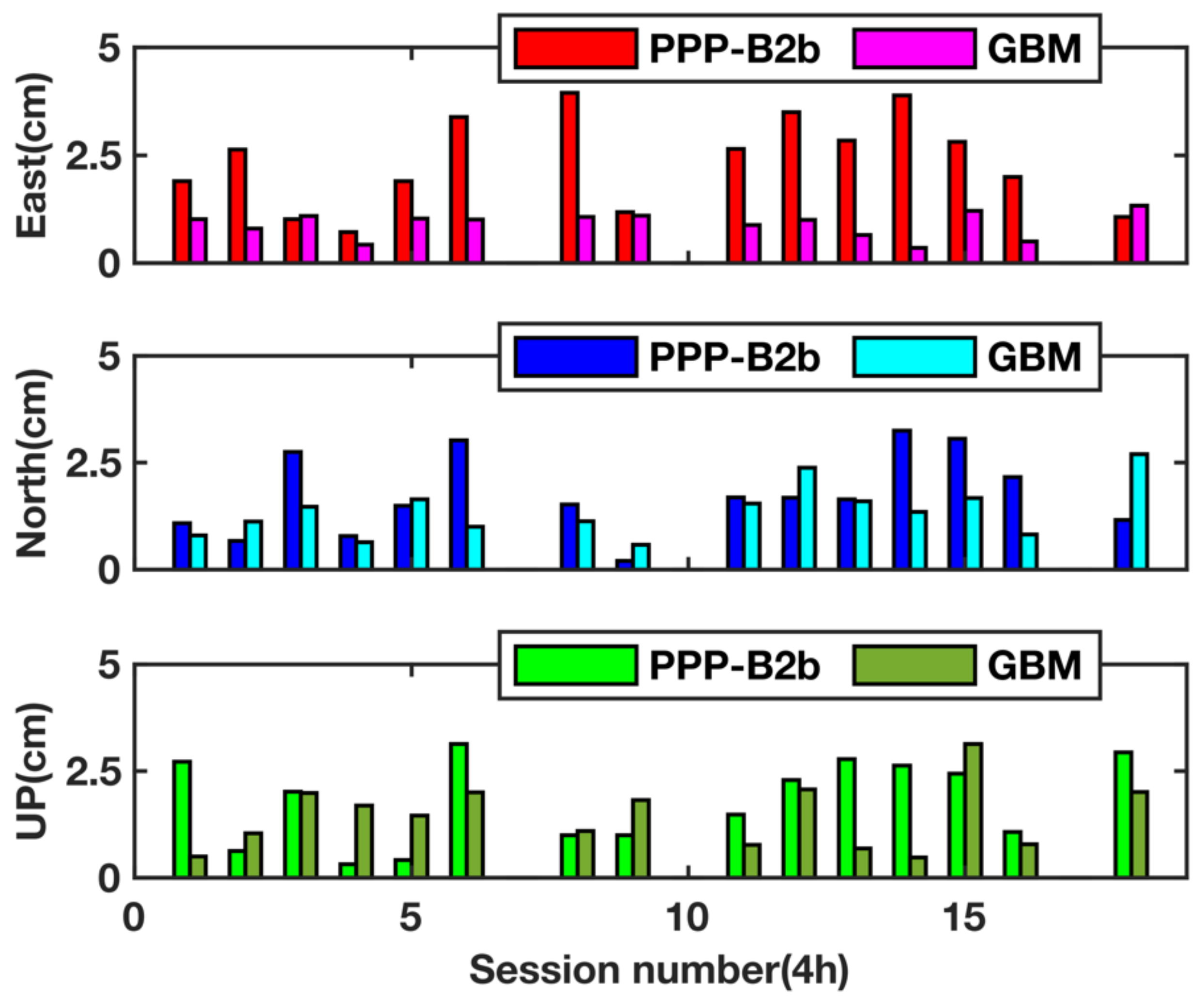
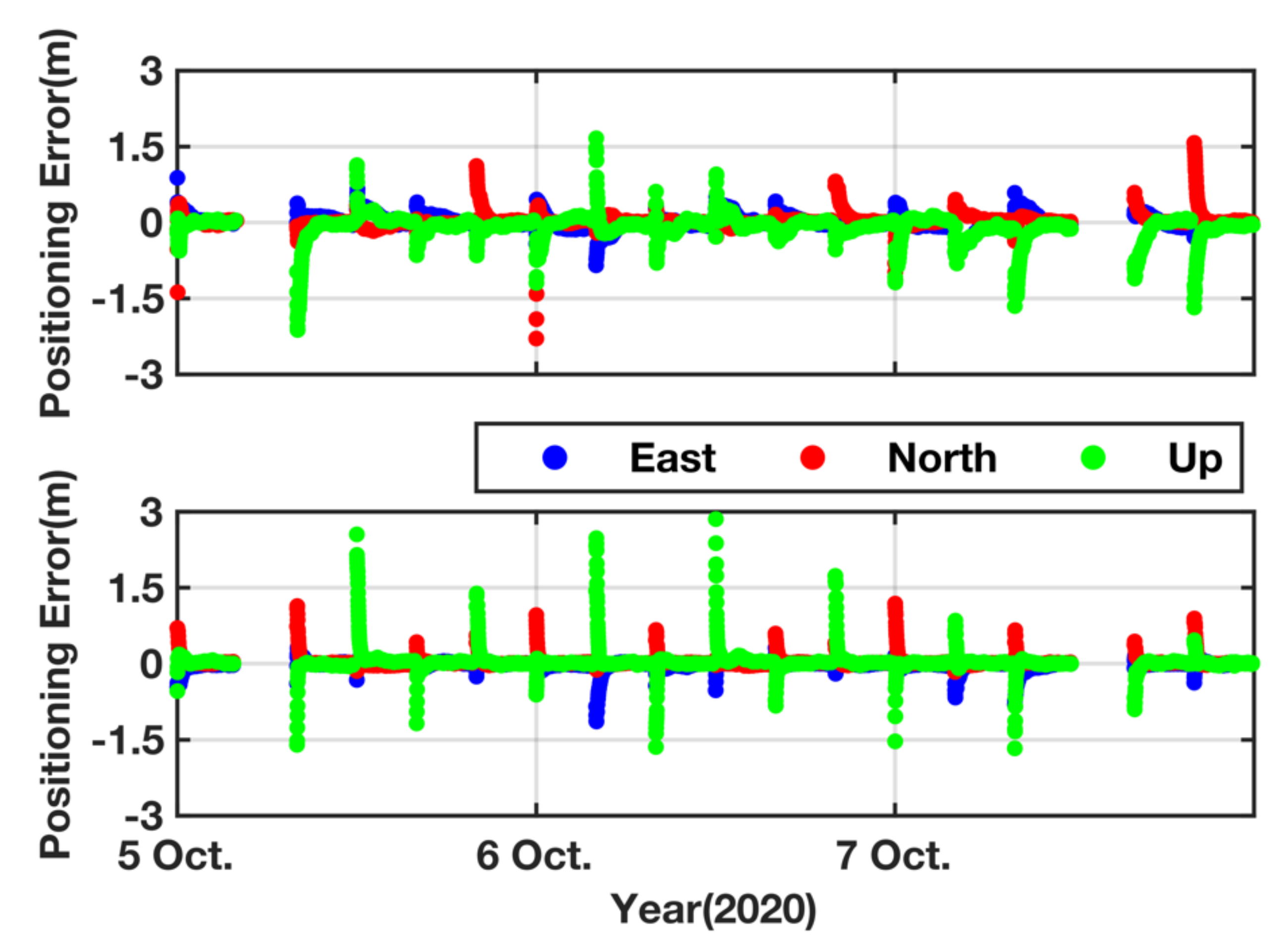
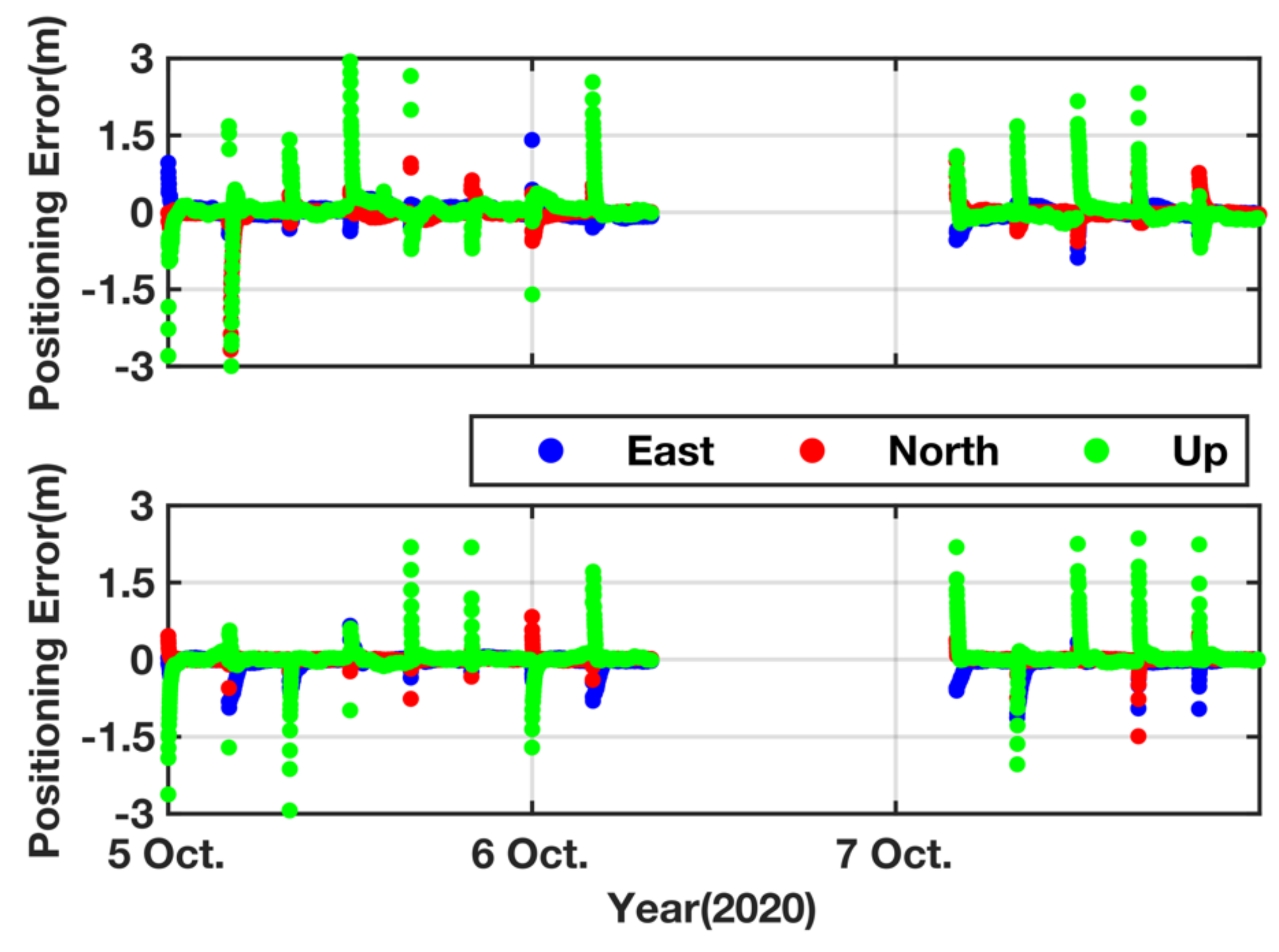
3.2. PPP Tests
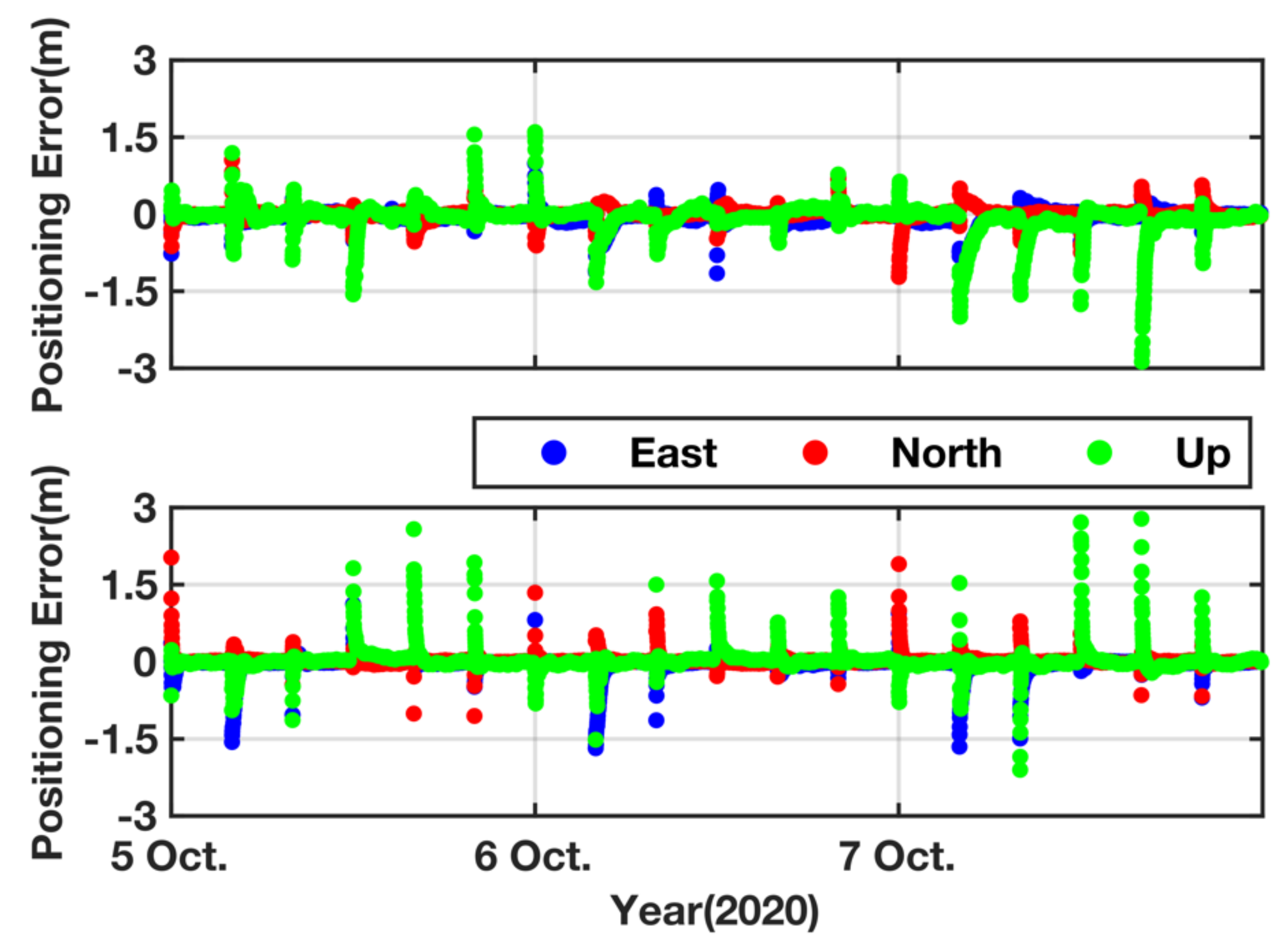
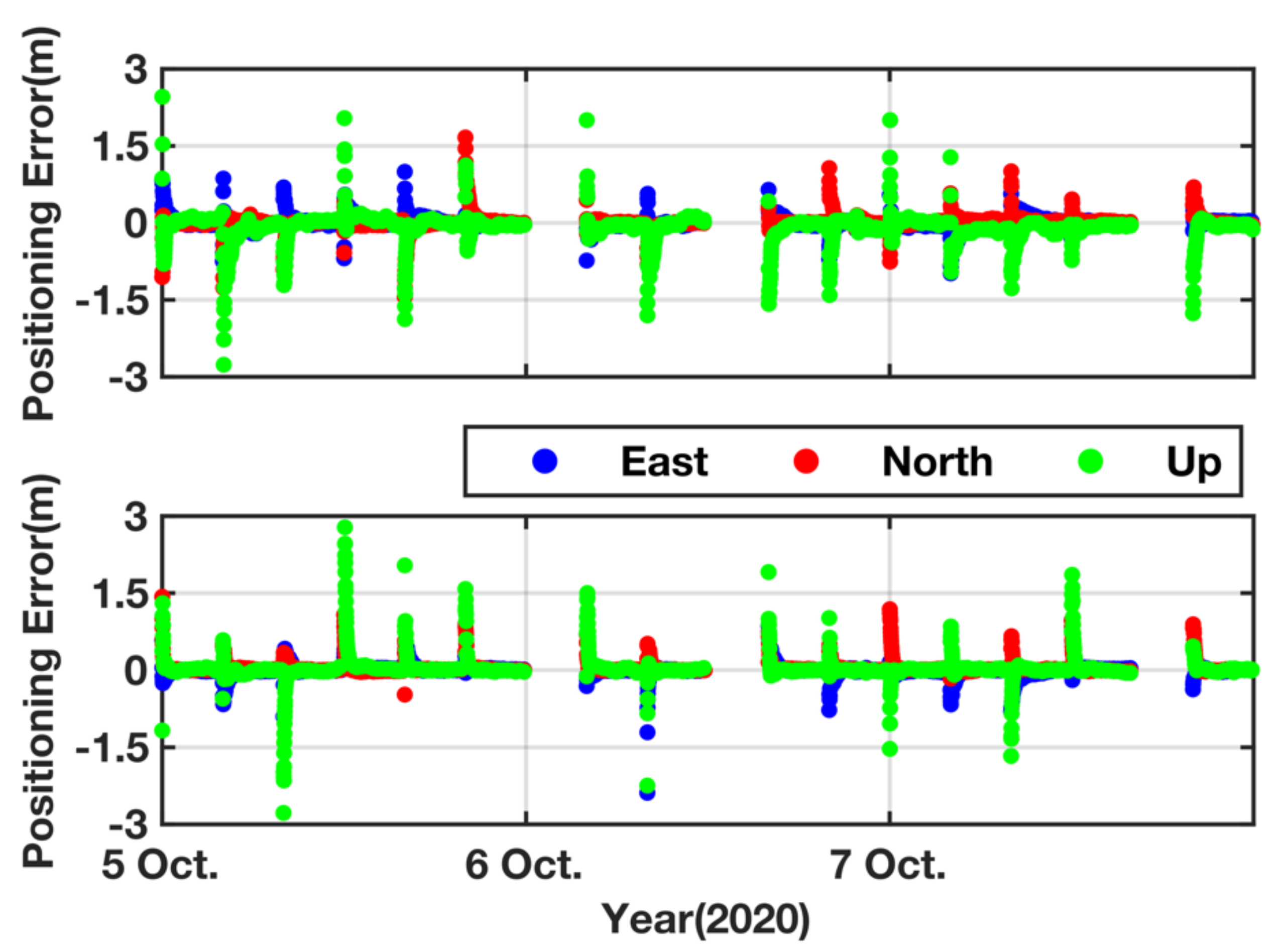
3.2.1. Static Mode
3.2.2. Kinematic Mode
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, J.; Guo, H.; He, H. Contribution of the Compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. Development of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 4.0). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201912/P020191227430565455478.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- China Satellite Navigation Office. China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201712/P020171221333863515306.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Shen, J.; Dai, X. Preliminary assessment of the navigation and positioning performance of BeiDou regional navigation satellite system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Freeshah, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F. BDS multi-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with new B2a/B2b/B2a + b signals and legacy B1I/B3I signals. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. The Application Service Architecture of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 1.0). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201912/P020191227333024390305.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning Using IGS Orbit and Clock Products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. PPP-RTK based on undifferenced and uncombined observations: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Teferle, F.N.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H. Kinematic precise point positioning at remote marine platforms. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, R.M.; Saka, M.H.; Ozulu, M.; İlçi, V. Kinematic precise point positioning using GPS and GLONASS measurements in marine environments. Measurement 2017, 109, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; He, K. An offshore real-time precise point positioning technique based on a single set of BeiDou short-message communication devices. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocken, C.; Johnson, J.; Van Hove, T.; Iwabuchi, T. Atmospheric water vapor and geoid measurements in the open ocean with GPS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shi, C.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yanagidani, T. High-rate precise point positioning (PPP) to measure seismic wave motions: An experimental comparison of GPS PPP with inertial measurement units. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, C.O.; Gurlek, E. Experimental testing of high-rate GNSS precise point positioning (PPP) method for detecting dynamic vertical displacement response of engineering structures. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zus, F.; Lu, C.; Ning, T.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Retrieving high-resolution tropospheric gradients from multiconstellation GNSS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Bender, M. Real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor: Precise point positioning with orbit, clock, and phase delay corrections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhao, C.; Fairbairn, D.; Watson, D.; Ge, M. Multi-GNSS precise point positioning for precision agriculture. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Mervart, L.; Lukes, Z.; Rocken, C.; Dousa, J. Real-time clock and orbit corrections for improved point positioning via NTRIP. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2007, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–35 September 2007; pp. 1992–1998. [Google Scholar]
- El-diasty, M. Development of Real-Time PPP-Based GPS/INS Integration System Using IGS Real-Time Service for Hydrographic Surveys. J. Survey. Eng. 2016, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegedor, J.; Lapucha, D.; Ørpen, O.; Vigen, E.; Melgard, T.; Strandli, R. The new G4 service: Multi-constellation precise point positioning including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2015, Tampa, FL, USA, 14–18 September 2015; pp. 1089–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Chen, Y.; Lie, A.; Zeitzew, M.; Zhang, Y. StarFire SF3: Worldwide centimeter-accurate real time GNSS positioning. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2016, Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 3295–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, R.; Landau, H.; Nitschke, M.; Glocker, M.; Seeger, S.; Chen, X.; Deking, A.; BenTahar, M.; Zhang, F.; Ferguson, K.; et al. RTX positioning: The next generation of cm-accurate real-time GNSS positioning. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2011, Portlan, OR, USA, 20–23 September 2011; pp. 1460–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, S.; Sato, Y.; Miya, M.; Ota, K.; Hirokawa, R.; Takiguchi, J. Design of Integrity Function on Centimeter Level Augmentation Service (CLAS) in Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2016, Portland, OR, USA, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 3258–3263. [Google Scholar]
- Namie, H.; Okamoto, O.; Kubo, N.; Yasuda, A. Initial performance evaluation of centimeter-class augmentation system using Quasi-Zenith Satellite System. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2018, 101, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Hernandez, I.; Rodríguez, I.; Tobías, G.; Calle, J.D.; Carbonell, E.; Seco-Granados, G.; Simón, J.; Blasi, R. Testing GNSS high accuracy and authentication-galileo’s commercial service. Insid. GNSS 2015, 10, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Susi, M.; Borio, D. Kalman filtering with noncoherent integrations for Galileo E6-B tracking. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2020, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Nie, X.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Design and implementation of a BDS precise point positioning service. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2020, 67, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Beta Version). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201912/P020191227331847498839.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Zhou, W. Accuracy Analysis of GNSS Hourly Ultra-Rapid Orbit and Clock Products from SHAO AC of iGMAS. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: A multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Montenbruck, O. Consistency of MGEX Orbit and Clock Products. Engineering 2020, 6, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Chu, F.Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, J. Apparent clock and TGD biases between BDS-2 and BDS-3. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, R. Initial assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system signal-in-space range error. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F.; Prange, L.; Dach, R.; Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Montenbruck, O. Galileo orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, P.; Liu, T.; Yuan, Y. A single-receiver geometry-free approach to stochastic modeling of multi-frequency GNSS observables. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, N. Relativity in the Global Positioning System Imprint/Terms of Use. Living Rev. Relativ. 2003, 6, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-T.; Wu, S.C.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Lichten, S.M. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Conference, Durango, CO, USA, 19–22 August 1991; pp. 1647–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions (2010); Bureau International Des Poids et Mesures Sevres: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sakic, P.; Mansur, G.; Mannel, B. A prototype for a multi-GNSS orbit combination. In Proceedings of the European Navigation Conference, Bonn, Germany, 23–24 November 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)–Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Zhou, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of orbit, clock and ionospheric corrections from five currently available SBAS L1 services: Methodology and analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Chen, G.; Jiao, W.; Chen, K.; Xu, T.; Wang, H. An Initial Analysis and Assessment on Final Products of iGMAS. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2016 Proceeding, Changsha, China, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 515–527. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Short note: A global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
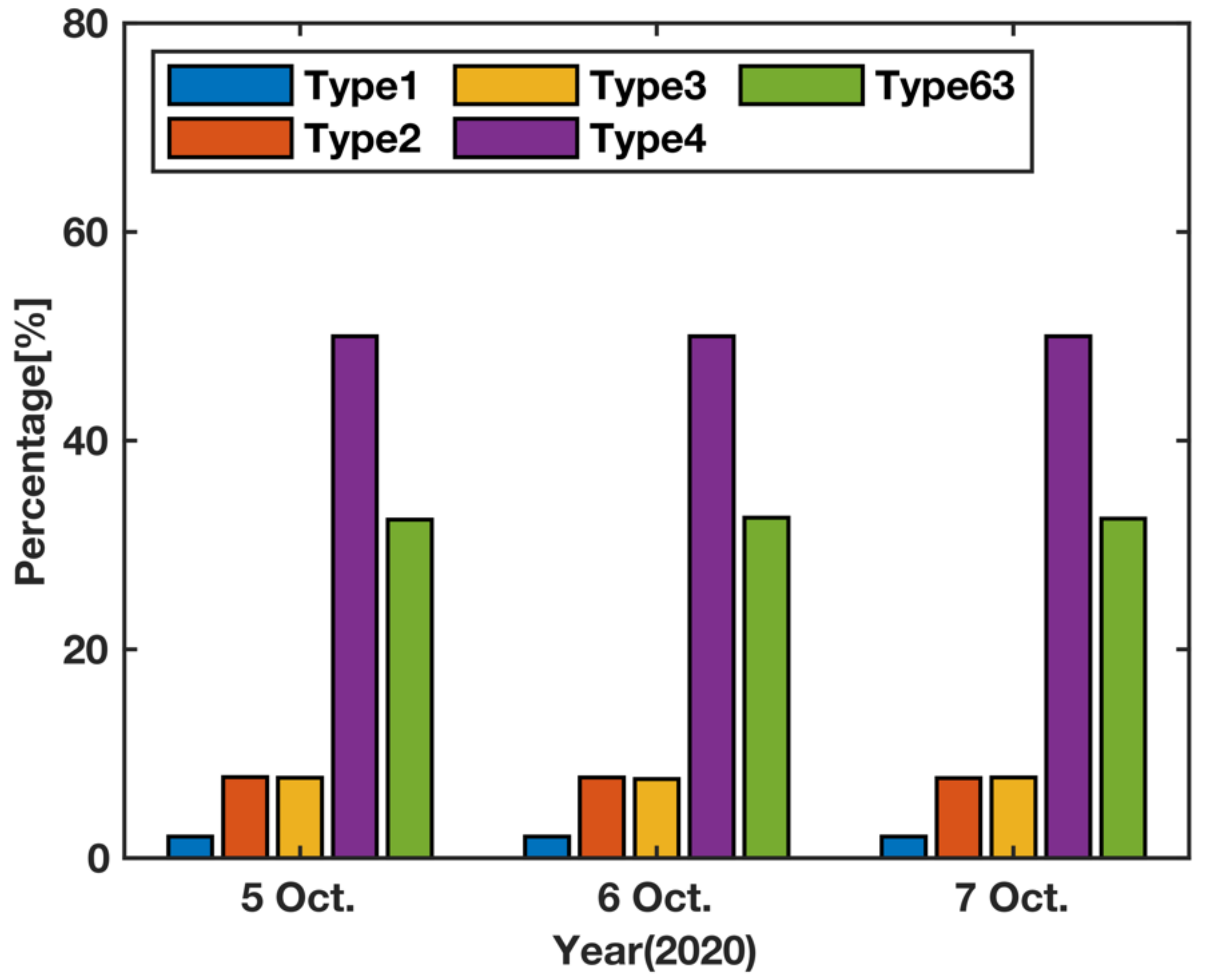
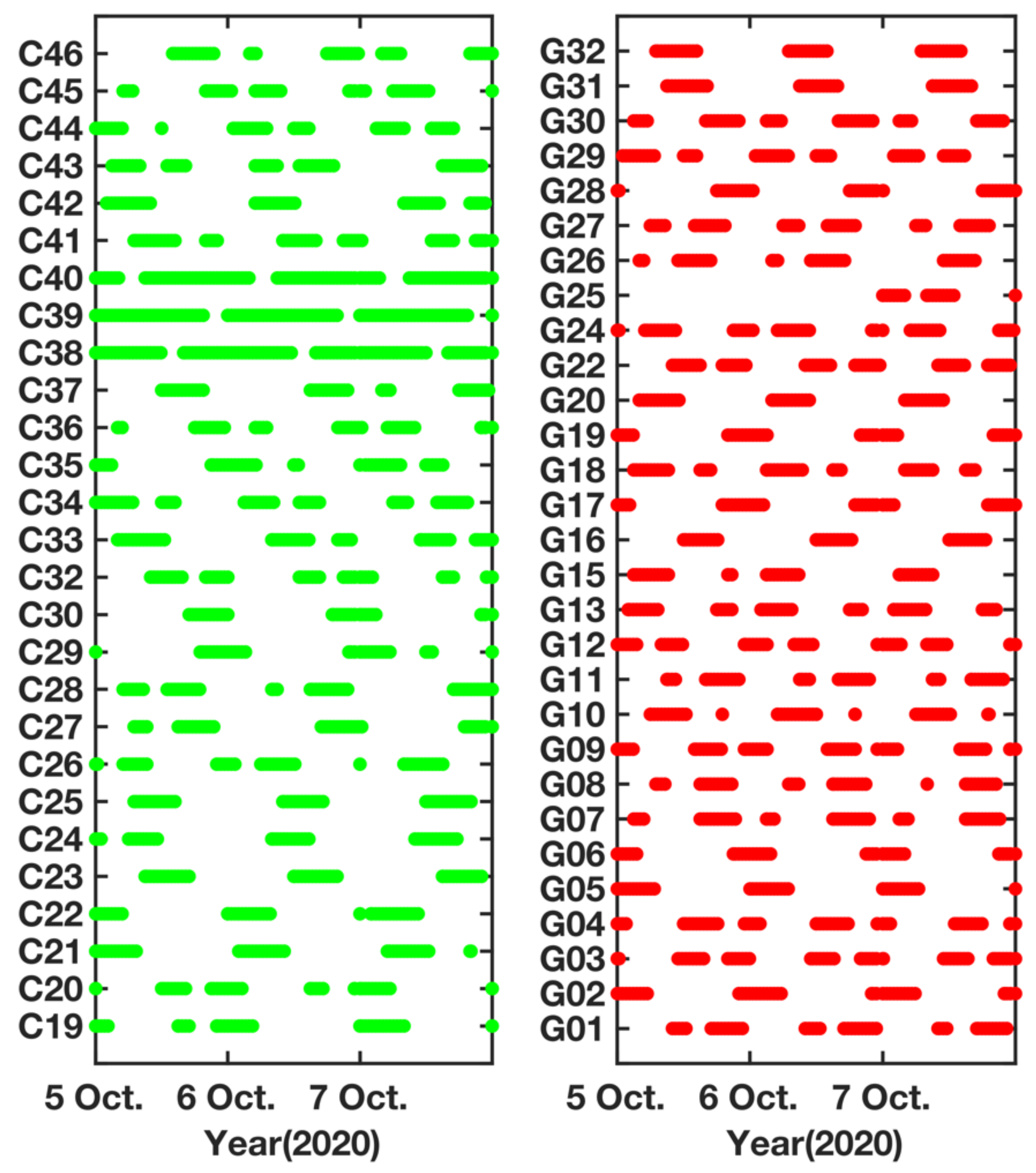

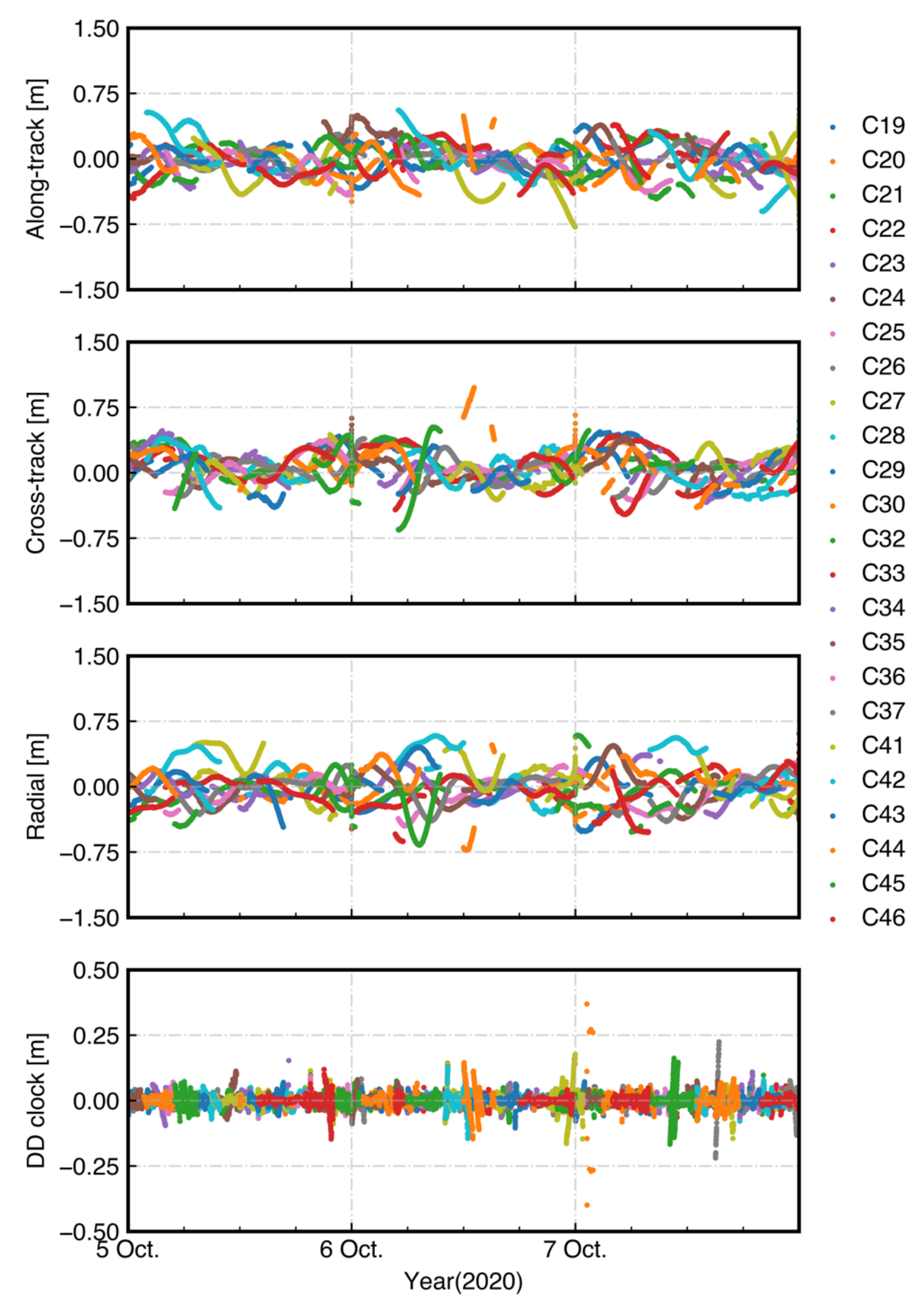
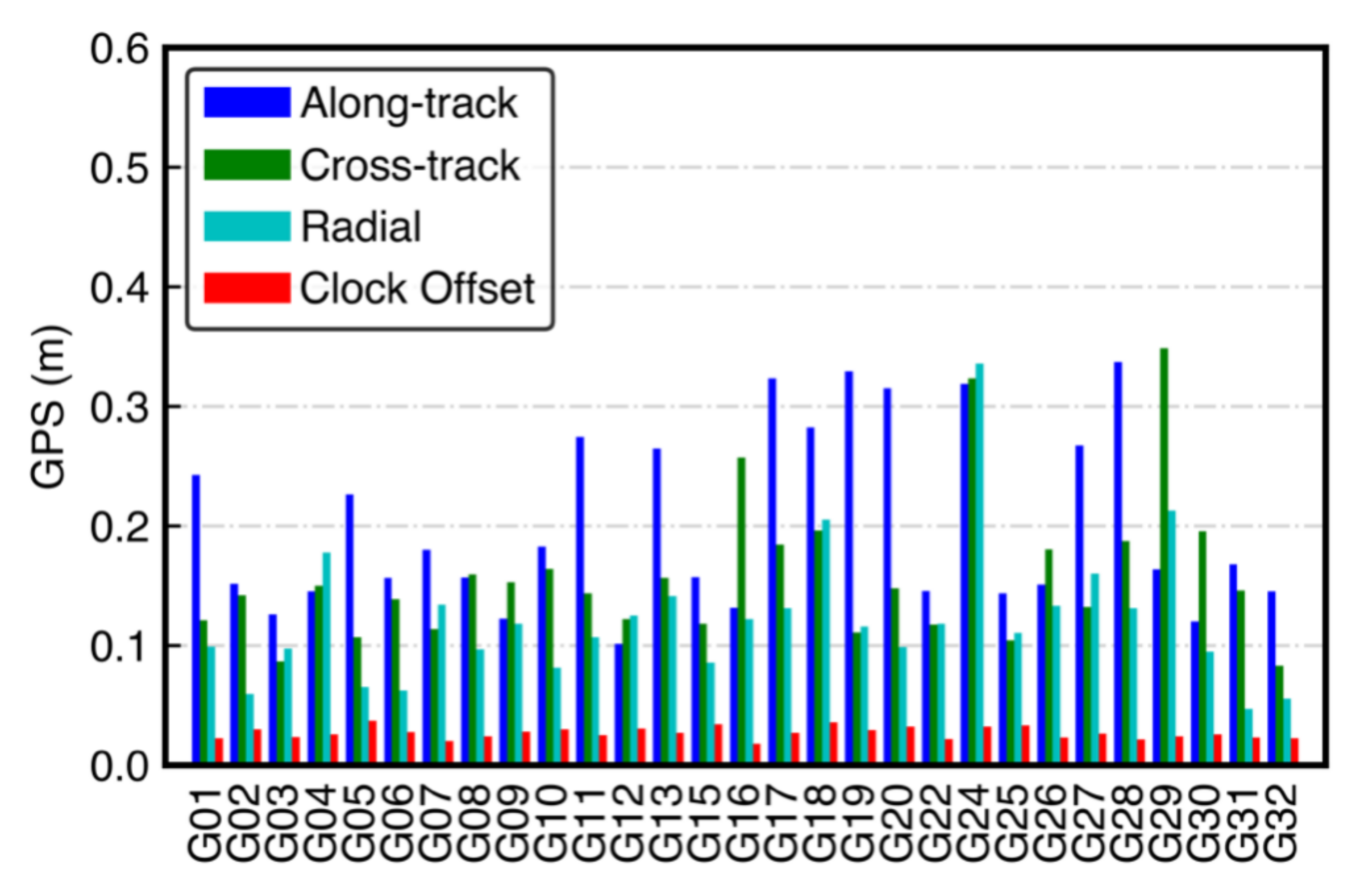





| Message Type | Correction Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | Satellite mask |
| 2 | Satellite orbit correction and user range accuracy |
| 3 | Differential code bias |
| 4 | Satellite clock correction |
| 5 | User range accuracy index |
| 6 | Clock correction and orbit correction–combination 1 |
| 7 | Clock correction and orbit correction–combination 2 |
| 8–62 | Reserved |
| 63 | Null |
| Message Type | Sample Rate (s) | Nominal Validity (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48 | -- |
| 2 | 48 | 96 |
| 3 | 48 | 86,400 |
| 4 | 6 | 12 |
| 63 | -- | -- |
| RMS-A 1 | RMS-C 2 | RMS-R 3 | STD-CLK 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | 16.0 | 13.4 | 10.4 | 2.7 |
| BDS | 13.1 | 14.5 | 13.8 | 2.2 |
| Item | Models/Strategies |
|---|---|
| GNSS System | GPS and BDS-3 |
| Signal selection | GPS: L1/L2 and BDS-3: B1C/B2a |
| Observables | Dual-frequency code/phase ionosphere-free combinations |
| Sampling rate | 30 s |
| Cutoff elevation | 10° |
| Observable noise | Raw code: 0.5 m in zenith direction Raw phase: 0.005 m in zenith direction |
| Weight method | Elevation dependent weight [38] |
| Phase windup | Corrected [41] |
| Relativistic effect | Corrected [40] |
| Sagnac effect | Corrected [40] |
| Shapiro time delay | Corrected [40] |
| Tidal effect | Solid tide, ocean loading and pole tide were corrected according to IERS Conventions 2010 [42] |
| Troposphere | Zenith dry delay: corrected with Saastamoinen model, while meteorological parameters were calculated by applying global pressure and temperature (GPT) model [47] Zenith wet delay: estimated for each epoch as a random walk noise with a process noise of 2 cm/sqrt(h) Mapping function: global mapping function (GMF) [48] |
| Phase Ambiguity | Estimated as a float constant for each ambiguity arc |
| Estimator | Kalman filter |
| PPP-B2b Service | GBM Products | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E 1 | N 2 | U 3 | H 4 | 3D 5 | E 1 | N 2 | U 3 | H 4 | 3D 5 | |
| BJF1 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.2 |
| KUN1 | 2.1 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
| SHA1 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| WUH1 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 3.0 | 3.6 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| PPP-B2b Service | GBM Products | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | H | 3D | E | N | U | H | 3D | |
| BJF1 | 8.0 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 12.3 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 5.4 |
| KUN1 | 9.2 | 3.1 | 8.3 | 9.6 | 12.7 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 6.0 |
| SHA1 | 7.1 | 3.6 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 10.9 | 3.5 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 6.2 |
| WUH1 | 8.1 | 4.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 11.3 | 3.4 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112050
Nie Z, Xu X, Wang Z, Du J. Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(11):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112050
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Zhixi, Xiaofei Xu, Zhenjie Wang, and Jun Du. 2021. "Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance" Remote Sensing 13, no. 11: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112050
APA StyleNie, Z., Xu, X., Wang, Z., & Du, J. (2021). Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sensing, 13(11), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112050






