Abstract
People’s interactions with each other form the social relations in society. Understanding human social relations in the public space is of great importance for supporting the public administrations. Recognizing social relations through visual data captured by remote sensing cameras is one of the most efficient ways to observe human interactions in a public space. Generally speaking, persons in the same scene tend to know each other, and the relations between person pairs are strongly correlated. The scene information in which people interact is also one of the important cues for social relation recognition (SRR). The existing works have not explored the correlations between the scene information and people’s interactions. The scene information has only been extracted on a simple level and high level semantic features to support social relation understanding are lacking. To address this issue, we propose a social relation structure-aware local–global model for SRR to exploit the high-level semantic global information of the scene where the social relation structure is explored. In our proposed model, the graph neural networks (GNNs) are employed to reason through the interactions (local information) between social relations and the global contextual information contained in the constructed scene-relation graph. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed local–global information-reasoned social relation recognition model (SRR-LGR) can reason through the local–global information. Further, the results of the final model show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. In addition, we have further discussed whether the global information contributes equally to different social relations in the same scene, by exploiting an attention mechanism in our proposed model. Further applications of SRR for human-observation are also exploited.
1. Introduction
Social relations broadly exist in our daily lives, and influence societal development and behavior [1]. It is of great importance to observe the social relations among people to understand their social lives in public spaces, as this is critical for public administrations. Remote sensing cameras have been widely used for observing human activities in the areas of public health and administration, and the emerging computer vision techniques have empowered more sophisticated methods for human observation. Recently, researchers in the computer vision field have had increasing interest in social relation recognition (SRR) [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Inspired by the classical social psychology theories [9,10,11], various datasets [2,3,12,13,14] with annotated social relations have been collected to understand the associations of person pairs in images or videos. As a sub-task in computer vision, accurate recognition of social relations may contribute to a broad range of high-level tasks, such as scene understanding for graph generation [15,16] and group activity analysis [17,18].
In the past decade, significant progress has been made in SRR through many efforts from researchers. Generally speaking, SRR development has gone through three stages.
(1) In the early stage, researchers [12,19,20,21,22,23] contributed to finding out genetic similarity contained in facial images for kinship verification. They hand-crafted the features (e.g., facial features, relative position and head pose) and then classified specific kinships using machine learning methods. Kinship verification is still one of the research hotspots of SRR [24,25,26].
(2) With the rise of detailed relation datasets [2,3] and the advancement of deep neural networks (DNNs), researchers went beyond kinship verification, aiming for broader social relations such as friends, couples and even dance team members. In this stage, DNNs, especially convolution neural networks (CNNs) [27,28], were introduced to extract high-dimension semantic information from person pairs and even scenes for more accurate relation classification.
(3) In stages (1) and (2), a fixed paradigm, where social relations of person pairs in a still images were always considered independently, was followed for SRR. To address this limitation, Li et al. [8] summarized the strong correlations (local information) between pair-wise social relations using a probability function and designed a new graph neural network (GNN) to infer the relations for each image for better SRR performance. Li et al.’s work represented the new stage for SRR. However, their work has not explored the global contextual cues given by the whole scene, which has been proven to be important [2,5,6].
It is worth noting that the global context contains not only the scene features extracted by [2,5,6] but also all the social relations in the same scene, which have not been exploited so far. In addition, it is also vital to find a way to better fuse the local information of pair-wise personal relations with the global contextual information of the scene. Hence, in this paper, we propose a local–global information-reasoned model for SRR (SRR-LGR) to exploit the local information of pair-wise personal relations and the global contextual information from the scene-relation graph. In this model, all the social relations in an image and the scene feature are treated as nodes to construct a topological graph. Then gated graph neural network (GGNN) [29] and graph convolutional network (GCN) [30] are introduced to exploit the local and global information respectively. Finally, the reasoned local information and global information are concatenated to recognize specific social relations.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
(1) Global information from the scene-relation graph is proposed for SRR. The new proposed global information deepens the understanding of scene information, which refers to the scene features extracted by the scene recognition model and all the social relations in the same scene.
(2) A SRR-LGR model is proposed that considers the addition of the new global information to explore the local–global information using our constructed scene-relation graph. Specifically, the local information is reasoned using GGNN; meanwhile, GCN is introduced to exploit the global information. In addition, we select the different nodes to represent the local information and global information and concatenate them for better SRR.
(3) Extensive experiments were carried out on the People in Social Context (PISC) [2] dataset and the People in Photo Album (PIPA) [3] dataset. Experimental results show that our proposed model can exploit local–global information for more accurate recognition. In addition, we also conducted experiments using the model with the attention mechanism to verify that the global information made equal contributions to different social relations in the same scene. The results of our model also outperformed the state-of-the-art methods.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, related works on SRR and graph models are reviewed. Section 3 elaborates our proposed method from the overall framework to important sub-modules. Detailed experiments are described in Section 4, including related datasets, experimental settings, a comparison with the state-of-the-art methods, an ablation study, a contribution analysis of the global information and running time analysis. Section 5 discusses some potential values and possible applications of our model. Section 6 concludes this paper.
2. Related Work
In this section, we first offer a literature review about SRR to present its development trends. Then, we review the related works about GNNs, which are introduced to explore the local–global information in our framework.
2.1. Social Relation Recognition
SRR started with kinship verification, which mainly focused on the facial similarities to identify whether two individuals were related. Although the relational works are old, they are still classical and have had contributions to the subsequent study. Wang et al. [19] introduced a model to characterize the correlations among facial appearance, identity and social relation and optimized the model with a maximum likelihood algorithm. Xia et al. [20] extracted the features of appearance and the facial structure information to improve the accuracy of kinship verification. Dibeklioglu et al. [21] exploited features of facial dynamics and spatio-temporal appearance and employed them in kinship verification to improve the accuracy. Lu et al. [12] proposed a multiview, neighborhood, repulsed metric learning method to solve the misclassification of interclass samples lying in relatively close positions and collected two face-based kinship datasets (i.e., KFW-I and KFW-II) to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The two datasets pushed forward the kinship verification research significantly so that related studies have been the hot spots in the SRR community. For example, Li et al. [26] combined GNNs with kinship verification and proposed a graph-based reasoning network, which outperformed the state-of-the-art methods in KFW-I and KFW-II.
Meanwhile, growing attention on detailed relation recognition has been arising. Li et al. [2] proposed a dual-glance model to extract features related to person pairs and paid attention on the contextual regions of interest for jointly predicting social relations. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed model, the People in Social Context (PISC) dataset was collected to verify the performance of the model. Besides, Sun et al. [3] extended the People in Photo Album (PIPA) [31] dataset for detailed relation recognition based on social domain theory [9]. The collection of the two datasets provided data support for detailed relation recognition and attracted an increasing number of researchers to work in this subfield. Wang et al. [4] reasoned the interactions between features of a person pair and contextual objects of interest using GGNN and introduced a graph attention mechanism to select discriminative contextual objects for SRR. Goel et al. [5] extracted the scene information and the attribute context to construct a knowledge graph and utilized gated recurrent units (GRUs) to iteratively reason this graph, and further generated a social relation graph. Zhang et al. [6] constructed two graphs (i.e., a person-object graph and a person-pose graph) and fused scene information to jointly predict social relations. Rather than using GNNs, Wang et al. [7] proposed a deep supervised feature selection framework to reduce redundant information and select effective features directly contributing to SRR.
The aforementioned works based on the person-pair paradigm only concentrated on one social relation in a standalone still image. Li et al. [8] proposed a new image-based paradigm that considered the logical constraints of social relations and designed a new graph relational reasoning network to explicitly satisfy these constraints. However, the global contextual information, which concentrates on the scene features and all the social relations in this scene, was not considered, and the scene features could not be easily fused into the graph.
2.2. Graph Neural Networks
GNNs were outlined by Gori et al. [32] for the first time and extended by Scarselli et al. [33] and Gallicchio et al. [34]. They were designed to operate on topological graph data in nonEuclidean space. With the foundation of these works, an increasing number of GNNs were proposed to solve corresponding problems, such as [29,30,35,36]. Different GNNs infer the graph by different ways, which can be divided into four categories [37]: recurrent graph neural networks (RecGNNs) [29,38], convolutional graph neural networks (ConvGNNs) [30,39], graph autoencoders (GAEs) [40,41] and spatial-temporal graph neural networks (STGNNs) [42,43]. GAEs and STGNNs are mainly utilized to generate new graphs and extract spatial-temporal information, respectively. Hence, these two types of GNNs are not suitable for the task in this paper. RecGNNs concentrate on the information exchange between nodes so that they are good for exploiting interactions among nodes, as in [4]. On the contrary, the spectral ConvGNNs conduct a convolutional operation on the graph to exploit the information of topological structure. For example, Kearnes et al. [44] modeled molecular structures for drug design.
With the rapid development of GNNs, many research communities tended to take advantage of GNNs for the promotion of their tasks, such as semantic segmentation [45], action recognition [46,47] and sentiment analysis [48,49]. Given the power of exploiting topological information, GNNs were introduced to model some interactions for SRR, such as the GGNN in [4], the GCN in [6] and the newly designed graph relational reasoning network in [8]. Hence, the GGNN [29] for the local information and the GCN [30] for the global information were used in the design of the SRR-LGR model in this paper.
3. Method
In this section, we elaborate on our SRR-LGR model. First, the overall framework of this model is introduced briefly. Then the node generation module is illustrated in detail. Next, we show the local–global information reasoning modules. Finally, we present how to fuse the local–global information and how to classify the specific social relations.
3.1. Overall Architecture
Suppose there are n pairs of social relations, then our constructed scene-relation graph (i.e., a set of all nodes) can be described as follows.
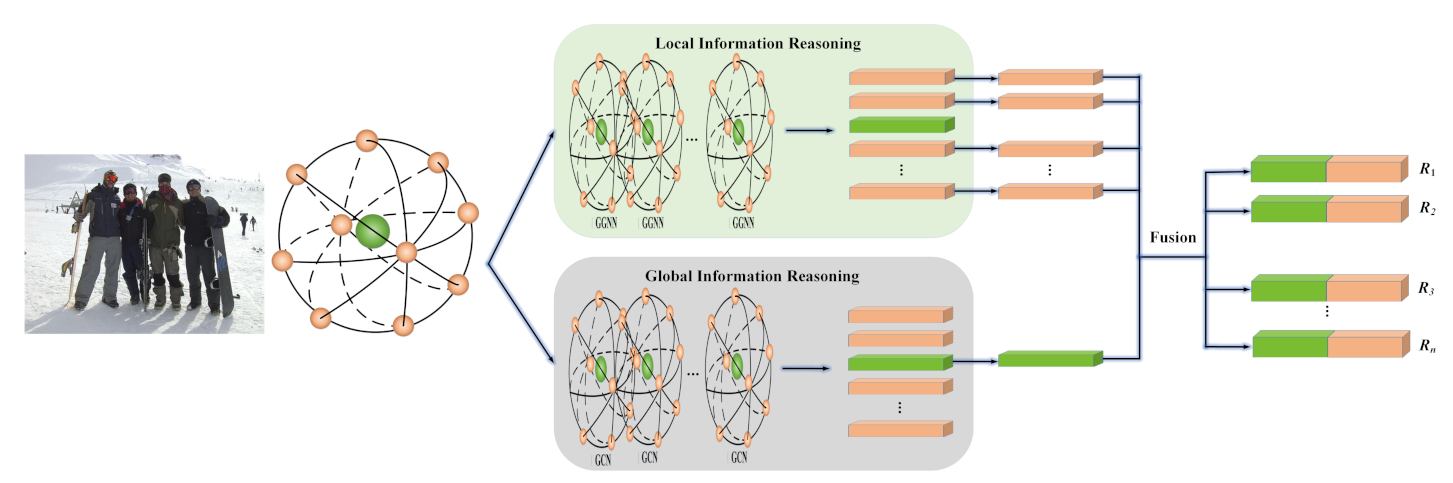
where (it also can be represented by ) denotes a scene node representing a scene feature, and the other nodes denote the social relation nodes representing pairs of social relations in this scene. For the edges, all the nodes, including the scene node, connect to each other so that one is adjacent to the other ones. Based on these definitions, the proposed SRR-LGR is given in Figure 1, where we have simplified the graph structure by only showing a subset of the edges. Each orange node stands for the social relation of one person pair, and the number of orange nodes can be as high as the number of social relations in the image. Similarly, the only green node represents the scene feature of the entire image.
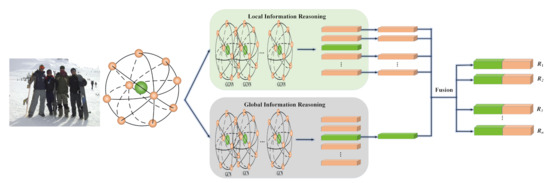
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of our proposed model. We first treat the social relations and the scene feature as nodes to construct a relation-scene graph, where one orange node represents a pair of people and the green node represents the scene feature. Then the constructed graph is reasoned by local–global information reasoning modules to obtain the local information and the global information. Finally, they are concatenated for social relation classification.
Next, we introduce GGNN and GCN to reason through the local–global information contained in the graph. GGNN has an emphasis on the information exchange between nodes, and GCN concentrates on the entire topological structure. The reasoning of GGNN exchanges the local information between orange nodes representing social relations, whereas the scene node obtains the global information with the awareness of social relation structure of the whole scene after the reasoning of GCN. Finally, each orange node and green node are concatenated for recognizing a specific social relation.
3.2. Node Generation Module
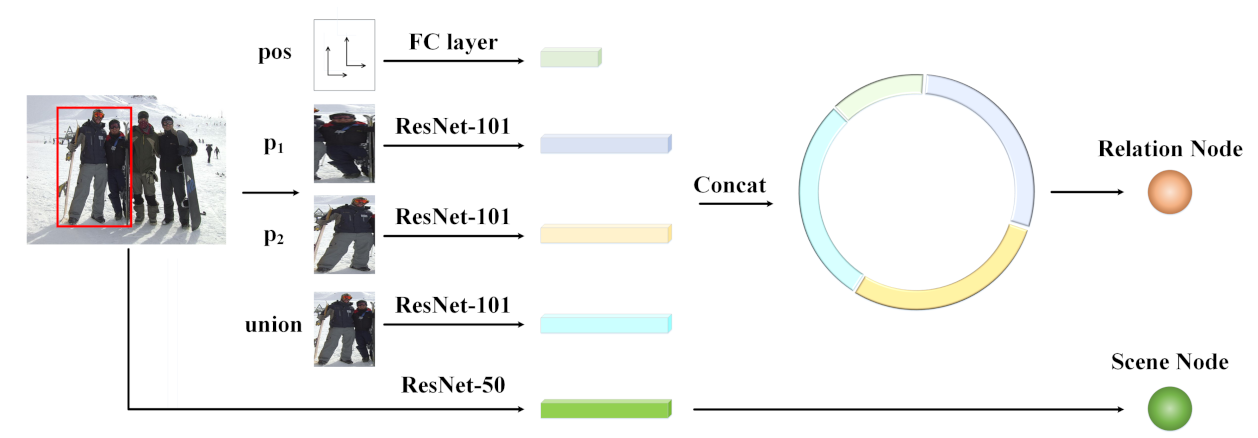
In this subsection, we introduce the generation of nodes in the scene-relation graph, which contains two types of nodes (i.e., the social relation nodes and the scene node). As shown in Figure 2, the node generation module consists of two parts, i.e., the social relation node generation (SRNG) part and the scene node generation (SNG) part. An orange node represents a pair, and thus a social relation. Take the social relation between and in the red bounding box as an example. We concatenate the features from three patches of , and their union extracted by pretrained models on ImageNet [50], and the relative position extracted by a fully-connected layer, to generate the social relation representations of the two individuals (i.e., and ). The application of ResNet-101 is followed by [2,4,6], which also outperforms ResNet-50 on the ImageNet dataset [50]. Furthermore, the scene information is extracted by the pretrained ResNet-50 model to generate the global scene representation, and ResNet-50 outperforms the other models on the Places365-Standard dataset [51]. Notably, the FC layer outputs 256-dimension features and the three ResNet-101s output 2048-dimensional features since their last classification layers are removed. For the scene extraction ResNet-50, its output dimensionality is 8192 as both the last classification layer and the first pooling layer are removed. The dimensions of node representations are 512 regardless of the node types.
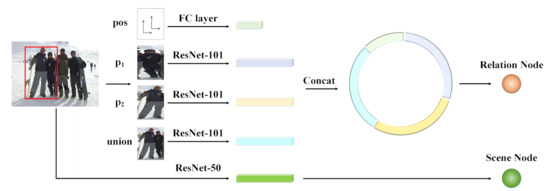
Figure 2.
Node generation module. Take two individuals in the red bounding box, for example. The features of their individual bodies, their union and the relative position are extracted to form social relation nodes. As for the scene node, it is generated by the features extracted from the entire image.
In order to adapt our tasks, we fine-tuned the SRNG part on PISC and PIPA datasets. In the process of fine-tuning, two fully connected layers were utilized to compress the -dimensional features. The first layer compressed the features to 4096 dimension and the second layer classified the 4096 dimensions to 3, 6 and 16 dimensions, corresponding to the PISC-Coarse task, PISC-Fine task and PIPA task, respectively. The final output was used to calculate the probability of each class by the SoftMax function and to determine the social relation. In the final model, we removed the second fully connected layer of the SRNG part and added a fully connected layer of 4096 dimensions to 512 dimensions to obtain the social relation node representation. For the SNG part, we added a fully connected layer from 8192 dimensions to 512 dimensions to generate the scene node representation.
3.3. Local–Global Information Reasoning
As GGNN has an emphasis on the information exchanges between nodes, and GCN concentrates on the entire topological structure, we elaborate the reasoning process of GGNN and GCN at the node and graph levels, respectively.
For GGNN [29], the node first aggregates the messages from its neighbors and then updates its representations using a GRU-like approach. As for the full connection among nodes, the computation can be expressed as follows:
where W is the trainable weight set and l represents the l-th iteration. After the above computation, becomes the new initial vector representation. According to [52], the GRU-like update process in our graph can be expressed as follows:
First, the update gate and the reset gate are calculated as follows:
Then, the updated node representation is computed by
where
In Equations (3)–(6), and denote the trainable weights, ⊙ denotes the Hadamard product, Tanh denotes the tanh function and the other symbols are the same as in Equation (2).
The number of iterations in Equation (2) can be set as a hyper-parameter L. Therefore, the final output (i.e., the set of nodes after GGNN reasoning) of GGNN after removing the scene node can be expressed as
GCN [30] defines the graph convolution based on the spectral graph theory [53]; hence, it can exploit the features of the entire graph like a filter. The convolution operation (i.e., the set of nodes after GCN reasoning) can be expressed as follows:
where H denotes the initial graph representation in Equation (1), and is the adjacency matrix with self-connections. The added is an identity matrix, which ensures that the information of each node itself is retained. The degree matrix , and W is the trainable weight matrix. After being activated by the function , the new graph representation can be obtained. We treat the reasoned scene node in as the global information.
3.4. Information Fusion and Classification
After obtaining the social relation representations and the global information, we concatenate them and calculate the per-class probability using a soft-max function error,
where denotes a fully-connected layer, denotes the probability of the j-th class of social relations and m denotes the number of social relation categories. The corresponding social relation class of the max probability is the final classification result.
4. Experiments and Results
In this section, we introduce our experimental implementation and analyze the experimental results. First, a brief introduction of the two datasets and the implementation details are presented. Then, we compare our proposed model with the state-of-the-art methods. Next, a group of ablation experiments are described, which verify the importance of the global information. We also analyze whether the global information contributes equally to different social relations in the scene. Finally, we analyze the computational complexity via running-time experiments.
4.1. Datasets
To validate the effectiveness of our proposed SRR-LGR model, extensive experiments were conducted on the PISC dataset and the PIPA dataset. Here, a brief introduction of the two datasets is presented.
The PISC dataset and PIPA dataset were collected from a broad range of data sources, including social media (i.e., Flickr, Instagram, Twitter, Google and Bing) and the other specific datasets (i.e., Visual Genome [54], MS-COCO [55] and YFCC100M [56]). In spite of the images from the other datasets, they are also related to human activities and similar to those images in social media. Li et al. [2] and Sun et al. [3] annotated various social relations in still images following different social psychological theories (i.e., the relational model theory [10] and social domain theory [9]), respectively.
For social relation division, each dataset contains two recognition tasks at the coarse and fine levels, which means that there are four types of relation definitions: (1) PISC-Coarse tasks, including intimate, nonintimate and no relation; (2) PISC-Fine tasks, including friends, families, couples, professional pairs, commercial pairs and no relation; (3) PIPA-Coarse tasks, including attachment, reciprocity, mating, hierarchical power and coalitional groups; (4) PIPA-Fine tasks, including 16 classes such as father–child, friends, lovers/spouses, presenter-audience and band members. We evaluated our method on the PISC-Coarse task, PISC-Fine task and PIPA-Fine task (“PIPA” task defaults to "PIPA-Fine" task in the following part). Accordingly, per-class recall and mean average precision (mAP) for the PISC task and top-1 accuracy for the PIPA task were used to evaluate the performance of our model.
For the split of training set, validation set and testing set, the details are shown in Table 1 according to the specific recognition tasks.

Table 1.
Numbers of images and social relation samples. For example, 16,142/49,017 means 16,142 images with 49,017 social relation samples.
4.2. Training Strategy and Parameter Setting
To decrease the difficulty of training and remove the limitation of computational source, we trained our model part by part based on transfer learning. Specifically, we first trained the node generation module and then optimized the local information reasoning module while freezing the parameters of node generation module. With the same transfer learning method, the global information reasoning module was trained and optimized.
In the process of training, we optimized our model on one Nvidia GeForce RTX 2080 Ti using Adam [57] optimizer under the deep learning framework named Pytorch. Batch size, learning rate, learning attenuation and number of epochs were set to 24, , and 200 respectively. Additionally, the learning decay reduced to 10% per 10 epochs. For the numbers of layers of GGNN and GCN, they were set to 3 and 1, respectively.
It is worth noting that two methods of data augmentation were adopted, which were suggested by the collector of the PISC [2] dataset. One reverses the people of the person pair, and the other horizontally flips the full image. Both methods can obtain more minority samples.
4.3. Comparison with State-Of-The-Art Methods
To demonstrate the performance of our proposed method, we compare it here with the state-of-the-art ones. First though, we provide a brief introduction for each method.
Dual-glance [2]. This model is the baseline method of PISC dataset, which extracts features using two channels named glances in the paper. The first glance extracts the features of a person pair similarly to our model, while the second glance extracts the features of regions of interest detected by Faster RCNN [58]. Then attention mechanism is used to weight each region, and finally the outputs of the two glances are concatenated for social relation prediction.
DSFS [7]. This paper proposed a deep supervised feature selection framework which aims to reduce the feature redundancy from multi-source data and select the discriminative features for SRR. Specifically, the framework fuses deep learning algorithm with - to learn effective features from two views (i.e., group feature selection and dimensional feature selection).
GRM [4]. This model constructs a graph which treats the features of persons and the contextual objects in the scene as nodes. Next, GGNN is introduced to reason through the constructed graph, and the weights for two types of nodes are calculated using an attention mechanism. Finally, the vector representations of person nodes concatenate the weighted ones of object nodes for SRR.
MGR [6]. Multi-granularity features are exploited using different methods, including features between persons and objects contained in the person-object graph, correlations of pose between two persons contained in the person-pose graph and the scene information from the full image. In this model, GCN reasons the constructed graphs and pretrained ResNet-101 on ImageNet [50] extracts the scene information. At last, these multi-granularity features jointly predict the social relations.
SRG-GN [5]. The framework first extracts the features of person pair attributions (i.e., age, gender and clothing) from the single-body image and the information of relation attributions (i.e., scene and activity). Then the two kinds of attribution information are inferred using GRUs and a message passing scheme, and the final output of reasoning is used to classify the social relations.
GRN [8]. To exploit the interactions among social relations in an image, a novel graph relational reasoning network was designed to model the logical constraints among different types of social relations contained in the constructed virtual relation graphs. In the graph, the node representation comes from the person patches in the feature map obtained by a convolutional neural network.
As shown in Table 2, our proposed model achieved superiority over the existing state-of-the-art methods in the PISC-Coarse task, PISC-Fine task and PIPA task. Specifically, the proposed SRR-LGR model achieved 84.8%, a 1.7% improvement compared with the GRN, in the PISC-Coarse task; and 73.0%, a 0.3% improvement compared with the GRN, in the PISC-Fine task, which constitute the best results on PISC tasks. In the PIPA task, the top-1 accuracy was up to 66.1%, a 1.7% improvement over the previous best MGR.

Table 2.
Here we compare our model with the state-of-the-art methods on PISC-Coarse, PISC-Fine and PIPA datasets. As in [4,8], we use the per-class recall rate and mean average precision (mAP) for PISC and the top-1 accuracy for PIPA.
Like the baseline method, i.e., dual-glance, our model also extracts the features of the relative position, the two bounding boxes of the person pair and their union. For the scene features, dual-glance detects the objects of interest in the scene as the scene features. However, our model made great improvements of 5.1% in the PISC-Coarse task, 9.8% in the PISC-Fine task and 6.5% in the PIPA task, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our constructed graph and the reasoned local–global information. On the other hand, GRN, it also considers the local information while the global information is ignored; hence, our model increased the accuracy by 1.7% in the PISC-Coarse task, 0.3% in the PISC-Fine task and 1.8% in the PIPA task. This comparison demonstrates that it is important to take the global information into account.
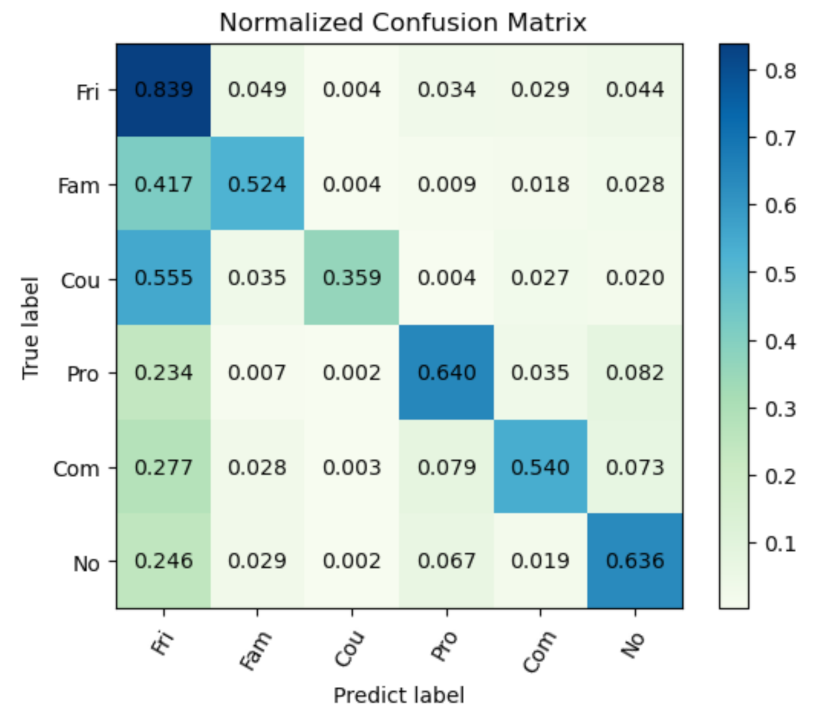
Next, we analyze the per-class recall in the PISC task to elaborate this characteristic of this model. In the PISC-Coarse task, our model outperformed the GRN in both the mAP and the per-class recall. It can be noticed from Table 2 that our proposed work cannot always outperform the existing work in terms of per-class recall. In order to better understand this point, the confusion matrix in the PISC-Fine task is given in Figure 3.
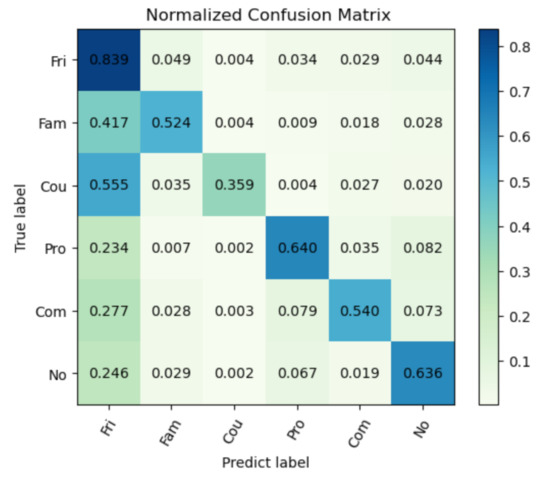
Figure 3.
Confusion matrix in the PISC-Fine task. The values from the upper left corner to the lower right corner on the diagonal represent the per-class recall.
As shown in Figure 3, the model performed well in recognizing friends, professionals and no relation; for friends in particular, the per-class recall was up to 83.9%. However, differently from the good performance in the PISC-Coarse task, there were some minor problems in detail in the PISC-Fine task. It can be observed that many samples were misclassified into the social relation friend, especially the families and couples.
All these three social groups (i.e., friends, families and couples) have intimate relations, which may be the cause of the difficulty when discriminating the features of them. In Figure 4, we present some true positive (TP) samples of the relation friend (row 1), couple samples misclassified to friends (row 2), and family samples misclassified to friends (row 3). These samples (i.e., friend, family, and couple) share similar features visually, but there still exist some distinguishing features. For the couples, the two individuals are always one male and one female. In addition, they are likely to be closer than the friends, especially in sample (d). For family, their ages may be different (e.g., take a father and a daughter). Besides the gender and age differences, activity is another factor with which to discriminate the different social relations. For example, the couples in sample (e) were dating and the family members in the sample (h) were having a family dinner.

Figure 4.
True positive (TP) samples of the relation friend (row 1, a–c), samples misclassified as couples (row 2, d–f) and samples misclassified as being family (row 3, g–i).
In addition, although data augmentation was adopted to alleviate the data imbalance, the samples of the class friend were still too many compared with family and couple samples—one of the reasons for the misclassifications. As listed in Table 3, the number of the friend pairs was greater than those of family and the couple. The number of couples was only about one tenth of the number of friends.

Table 3.
Sample distribution of the PISC dataset.
Nevertheless, our proposed SRR-LGR model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of the overall metric (i.e., mAP), which demonstrates the effectiveness of our model.
4.4. Ablation Study
To evaluate the performance of our designed SRR-LGR model, a group of ablation experiments were conducted.
(1) Concatenation. This is the baseline method, which simply concatenates all extracted features from person pair and scene and directly predicts the social relation.
(2) Local information. On top of the baseline method, the local information reasoning channel is added and then the output of this channel is used to recognize social relations.
(3) Local–global information. In addition to the local information reasoning channel, the global contextual information reasoning channel is also added to jointly classify social relations.
The results of this group of ablation experiments are listed in Table 4. To begin with, we implemented the paradigm shift by using GGNN to reason through the local information in our constructed graph. By this means, the performance of recognizing social relations obtained great improvements, 4.9%, in the PISC-Coarse task, 6.5% in the PISC-Fine task and 2.9% in the PIPA task, respectively. This proves that the local information is of vital importance for SRR. After the addition of the global information, we can see the overall improvements in the PISC-Coarse task and the PISC-Fine task but a worsening in the PIPA task. This indicates, in our opinion, that the contribution of global information varies for different social relations. Furthermore, since the classification tasks went from coarse to fine (i.e., numbers of categories were 3, 6 and 16), it became more difficult to distinguish the subtle differences. For the PISC-Coarse task with only three categories, the local information could reason through the logical constraints among social relations and achieve great performance. This is due to the simplicity of the triple classification; the global information has barely any impact on it. So after fusing the global information, the mAP improved by a slight 0.1% in the PISC-Coarse task. However, for the PISC-Fine task and the PIPA task with more label categories, local information alone was not adequate to discriminate the different social relations; hence, the global information has a greater impact on improving the discriminative ability, which facilitates the increase of the accuracy for an SRR. Therefore, the mAP went up by 1.8% in the PISC-Fine task. In the PIPA task, the top-1 accuracy slightly decreased by 0.6%, which was possibly because the global information in this task is more difficult and cannot correspond to the each class of the 16 social relations. Even so, the top-1 accuracy was still superior compared to the other state-of-the-art methods.

Table 4.
A group of ablation experiments to evaluate the vital importance of local–global information by adding corresponding modules.
4.5. The Contribution of the Global Information for Different Social Relations
As discussed in Section 4.4, the global information contributes to the social relations in the scene. In order to further find out if the global information contributes equally to different social relations, we introduced the attention mechanism to exploit this point, motivated by [2,4,7]. Li et al. [2] and Wang et al. [4] introduced the attention mechanism to weigh the contributions of different objects in a scene. Wang et al. [7] also proposed a deep supervised feature selection (DSFS) framework to reduce the redundancy of the multi-source features. Experiments have demonstrated that the attention mechanism does not make sense for global information, and the global information is little redundant. Here, we give the implementation process of the attention mechanism and present the possible reasoning.
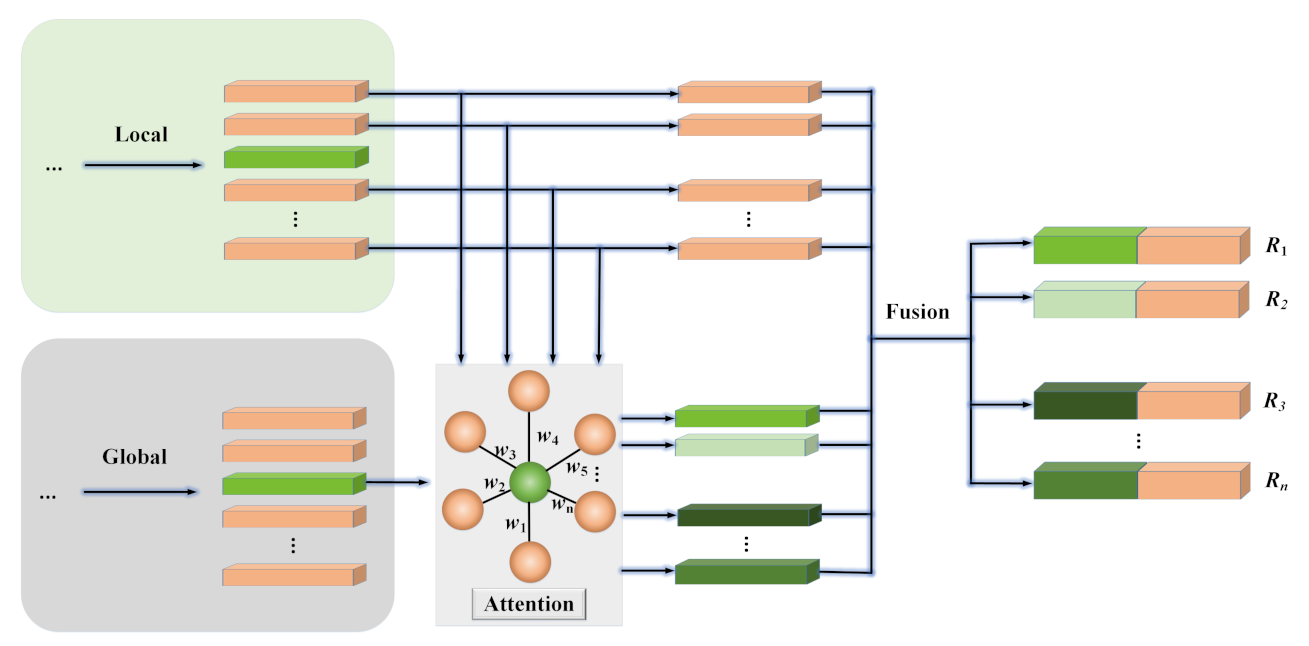
As shown in Figure 5, we introduced an extra attention mechanism to weigh the contributions of the global information to different social relations in the same scene.
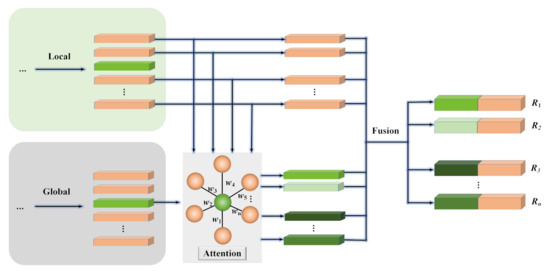
Figure 5.
The simplified overall architecture with the extra attention mechanism.
In order to weigh the contribution of the global information for each social relation node , an attention mechanism is introduced to capture the global information weighted by the local information. We first compute the hidden state inspired by low-rank linear pooling method [59] as follows:
where ⊙ denotes the Hadamard product, and are the trainable weights and Relu denotes the ReLU activation function.
Then we can compute the attention weight and use the sigmoid function to normalize the weight:
where and bias are also the trainable weight and bias and is a scaling factor, denoting the length of .
Thus, the corresponding weighed global information of each social relation can be expressed as follows:
Finally, we concatenate and to classify social relations.
The above is the implementation process of the attention mechanism, and the models achieved the same effectiveness no matter whether the attention mechanism was added or not. We visualized the weights of the attention mechanism in Figure 5 and found that they are the same. All of these facts demonstrate that the global information makes the same contribution to different social relations in the same scene.
Li et al. [2] and Wang et al. [4] have proved that the objects in a scene made different contributions to social relations. However, the global information contains not only the overall information of the scene but also the social relations in the same scene, and even the classified social relation also exists in the global information. In the same scene, people always interact each other, which means each social relation is related to the other ones. This may be the reason why the global information always makes equal contributions when we classify some of all the social relations in the scene. Nevertheless, the global information makes the model improvement over the state-of-the-art methods. We will also make the code and the two models (i.e., without the attention mechanism and with it) available for this discussion.
4.6. Running Time Analysis
Our method takes the local information (i.e., the logical constraints among social relations) into account, so we can recognize all the social relations in an image at the same time. This leads to the higher efficiency of our method compared to most pair-based methods, which classify the social relations pair by pair. We followed Li et al. [8] and implemented running-time experiments with different batch sizes on the PIPA dataset using a Nvidia GeForce RTX 1080 Ti GPU. We firstly introduce the three representative methods and ours as follows:
GRM [4]. One of the pair-based methods—that is, it recognizes the social relations in an image pair by pair. Dual-glance [2], DSFS [7], MGR [6] and SRG-GN [5] also belong to this type.
SRR-LGR (Ours). Our method, the image-based method, can classify all the social relations in an image.
Pair CNN [8]. It is the baseline method that recognizes the social relations using two bounding boxes for the person pair. Additionally, it is also a pair-based method. To be fair, we conducted the experiments using the Pair CNN provided by [8].
GRN [8]. It is also an image-based method.
The comparative results are listed in Table 5, and the “-” in the table represents the memory overflow.

Table 5.
Comparisons of running time (seconds/image) under different batch sizes for SRR on the PIPA dataset with the accuracy.
Compared with the pair-based method (i.e., GRM [4]), our method is much faster and achieves ∼ speed-ups, which shows the benefits of the image-based method (i.e., recognizing all the social relations in an image simultaneously). Considering the Pair CNN [8] method, its efficiency is slightly higher than that of our method because our model extracts more comprehensive features and utilizes a more effective method to achieve better performance. It can be observed that our model was 19.7% more accurate in the PISC-Coarse task, 24.8% in the PISC-Fine task and 8.1% in the PIPA task over the Pair CNN method. In addition, since there were on average bounding boxes per image on the testing set of the PIPA dataset, we could achieve higher speed when more individuals exist in an image. Compared with the image-based GRN method, it is faster about two times than our method because its input is one patch, whereas our inputs are four patches and one vector. However, our method considers the extra and effective global information and improved performance by 1.7% in the PISC-Coarse task, 0.3% in the PISC-Fine task and 1.8% in the PIPA task. Generally speaking, our method achieves a good balance between the efficiency and the accuracy.
In order to further demonstrate the efficiency and computational complexity, we calculated the numbers of float-point operations (Flops), the numbers of parameters and the memory requirements (i.e., size of parameters) of different modules of our model, and the results are given in Table 6. It can be observed that the key local–global information reasoned module expends little in the way of computational resources; that is, this module is effective and low-cost. As for the dynamics of the number of the social relations in an image, the number of the nodes in the constructed graph is also dynamic so that the three values are approximate. In addition, we set the number of social relation classes as six (i.e., the number of output classes in the PISC-Fine task) to calculate these values.

Table 6.
The computational complexity of different modules of our model, i.e., the node generation module, the local information reasoning module, the global information reasoning module and the final social relation classification layer.
5. Discussion
Social relations in public spaces demonstrate the high-level features of human beings socially. Observing them has great potential for deeply understanding how people interact with each other, and gaining a better understanding of human behaviors. In this section, we discuss the potential value and the possible application of our proposed model for sensing and observing human dynamics, and thus deepening the understanding of human activities in the urban public space and providing some useful information for the urban designer and the administrator.
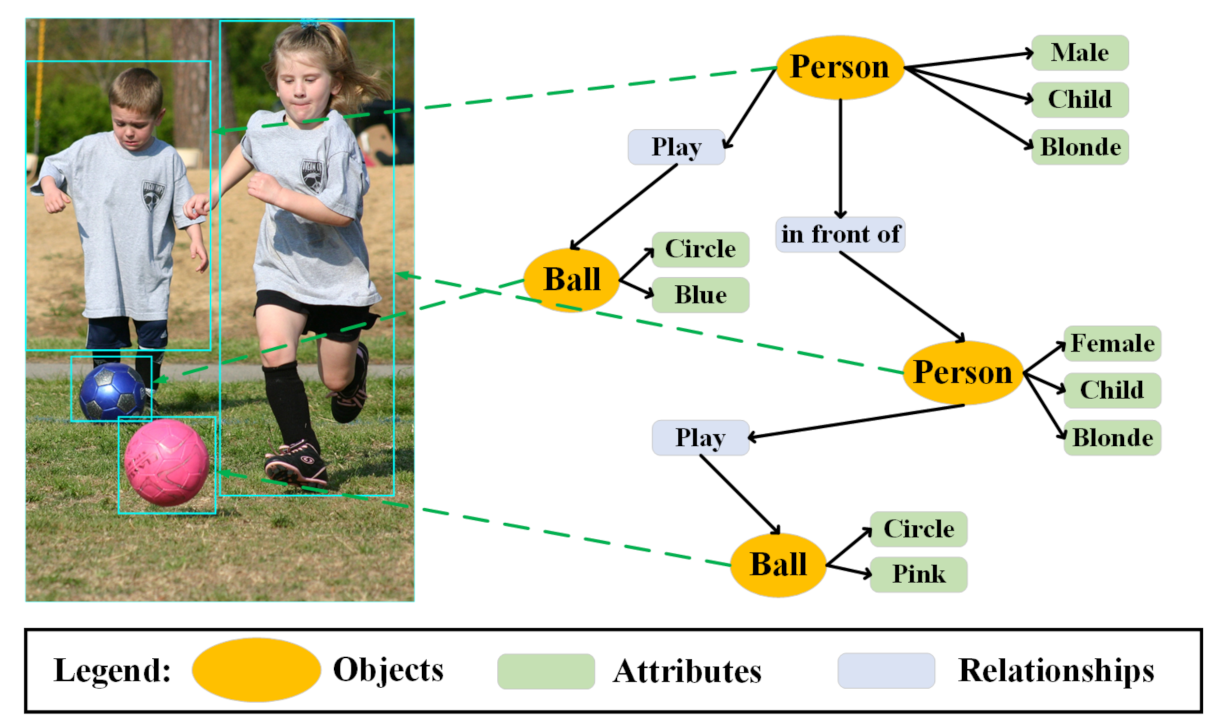
In order to understand human dynamics, we need to find out what kinds of people are in the scene, how humans are connected with their surroundings and how they are connected with each other. Thus, the scene graph can be firstly applied to provide low-level information. As shown in Figure 6, the scene graph contains objects, their low-level attributes and their relationships. In this realm, some studies have been completed: see the real-world scene graph dataset [60], the visual genome dataset [54], the scene graph generation methods (i.e., the Pixel2Graph model [61], the MotifNet model [62], the KERN model [63]) and the evaluation metrics for measuring a model’s capability of capturing the semantics of relations [64].
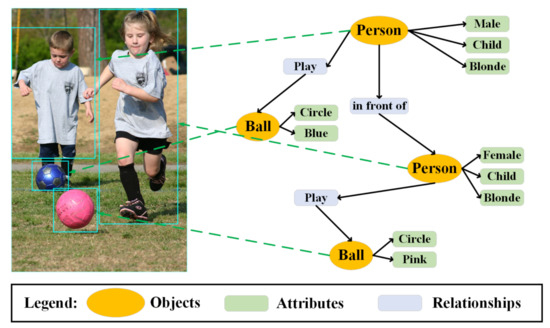
Figure 6.
The scene graph, depicting the objects, their low-level attributes and their relationships.
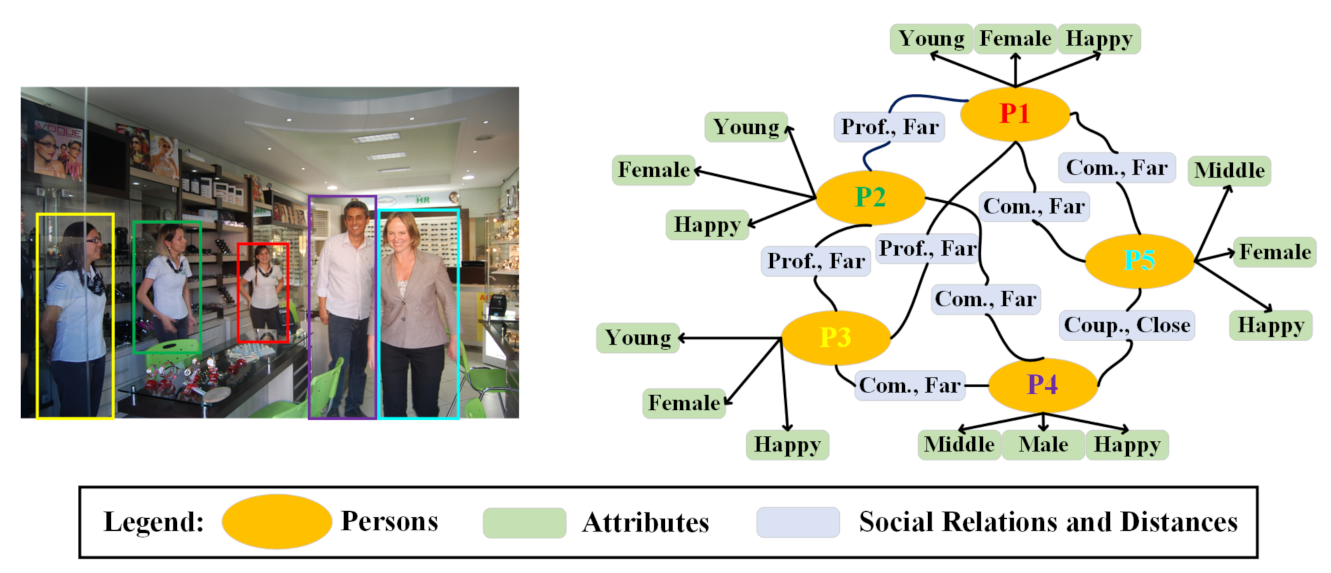
Although a scene graph contains the majority of objects and their relationships, there is still much information, e.g., social distances, social relations and each individual’s emotions, which have not been considered comprehensively. In particular, social distancing detection [65] and assistance [66] are important to slow down the spread of Covid-19. Thus, it is necessary to generate high-level semantic information to contain the low-level attributes and high-level semantic information. In order to fulfill this goal, social relation graph generation can be applied. Goel et al. [5] made some effort to propose a novel multi-task framework for social relation graph generation. However, the accuracy of SRR still needs to be improved further, the information in the graph needs to be enriched and datasets for scene graphs and social relation graphs need to be collected for more detailed graphs. Figure 7 presents a typical social relation graph, where the low-level (i.e., ages, genders and positions for social distance) and high-level attributes (emotions, activities, etc.) of individuals are depicted, and their social relations and distances are also included. Based on social relation graph, varieties of applications can be implemented for different human-observation tasks.
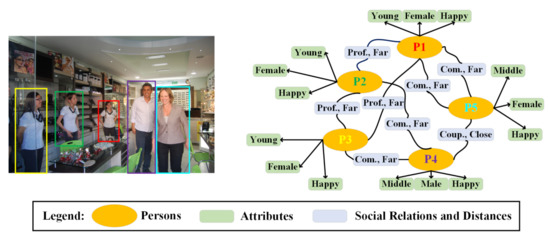
Figure 7.
The social relation graph, depicting individuals, their low-level/high-level attributes and their social relations.
Besides applying graph to deeply represent human organization, the predictions of social vitality may come true based on a social relation graph. Social vitality is a new concept and a more intuitive metric, which not only represents the types of the human interactions but also reflects the quality of the urban public spaces to a certain extent. In human-oriented urban planning, it is a key factor for the quality evaluation of urban public space with which to estimate the human-related metrics. Social relations are human interactions at a high level; hence they are suitable for estimating the human-related metrics. In our opinion, social vitality consists of various factors, which can be expressed as follows:
where denotes the social relations, and the more classes of social relations there are, the higher the social vitality is. E denotes another high-level attribution of people, i.e., emotion, which reflects the intensity and quality of social interactions. A and G denote the age and gender, respectively. Their richness can reflect whether the public space is suitable for various groups with different ages and genders. N denotes the number of people, which is a simple and vital factor. The urban public spaces of high quality are most likely used for leisure, exercise, sports and other activities. According to these factors, we can draw a social relation graph as shown in Figure 7 (partial social relations are neglected). Social relation graph generation still faces some challenges, such as the low accuracy of SRR and emotion recognition in a complex scene. In addition, how to quantify the indexes mentioned in Equation (13) is another issue. In future work, we will construct a uniform framework to promote the SRR task and to further generate more accurate social relation graphs. The specific computational process will be improved too. Only with a more accurate and detail social relation graph can we provide more meaningful information on human activities for supporting human-oriented observations.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we considered the global contextual information of a scene’s features and all the social relations in the same scene to gain deeper understanding of SRR. Specifically, GGNN and GCN were introduced to reason through the local information for interactions among person pairs, and the global information by considering all of the structural information of the constructed scene-relation graph. An ablation study demonstrated that our SRR-LGR model can exploit the local–global information for social relation prediction. Overall, the proposed SRR-LGR model outperformed the state-of-the-art methods on the PISC dataset and PIPA dataset. We have also found that the discriminative ability for the global information is still not sufficient for cases where the numbers of label categories are substantially large. In addition, how to mine the total structural information of a group for more accurate recognition is another key issue in the future, which is the vital factor as to whether this proposal can be applied to observing social relations in public spaces. Finally, how to apply SRR based on remote sensing cameras and how to further support the city-scale public administration (including social distancing detection and social relation graph generation) are still open for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Q.; data curation, L.L.; formal analysis, L.L. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, L.Q.; methodology, L.L. and L.Q.; Project administration, L.Q.; resources, L.Q.; supervision, L.Q. and L.L.; validation, Y.W.; writing—original draft, L.Q. and L.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.C. and Y.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, grant number 61871278.
Data Availability Statement
Not appliable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reis, H.T.; Collins, W.A.; Berscheid, E. The relationship context of human behavior and development. Psychol. Bull. 2000, 126, 844–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Kankanhalli, M. Dual-glance model for deciphering social relationships. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2669–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Schiele, B.; Fritz, M. A domain based approach to social relation recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Ren, J.; Yu, W.; Cheng, H.; Lin, L. Deep reasoning with knowledge graph for social relationship understanding. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 1021–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, A.; Ma, K.T.; Tan, C. An end-to-end network for generating social relationship graphs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11178–11187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhou, A.; Ma, H.; Mei, T. Multi-granularity reasoning for social relation recognition from images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 1618–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Du, X.; Shu, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, J. Deep supervised feature selection for social relationship recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Duan, Y.; Lu, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, J. Graph-based social relation reasoning. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bugental, D.B. Acquisition of the algorithms of social life: A domain-based approach. Psychol. Bull. 2000, 126, 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiske, A.P. The four elementary forms of sociality: Framework for a unified theory of social relations. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 99, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesler, D.J. The 1982 interpersonal circle: A taxonomy for complementarity in human transactions. Psychol. Rev. 1983, 90, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, X.; Tan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, J. Neighborhood repulsed metric learning for kinship verification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 331–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.; Tang, X. Learning social relation traits from face images. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3631–3639. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Yan, C.; Mei, T. Social relation recognition from videos via multi-scale spatial-temporal reasoning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3561–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Choy, C.B.; Li, F. Scene graph generation by iterative message passing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3097–3106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Kalantidis, Y.; Rohrbach, M.; Paluri, M.; Elgammal, A.; Elhoseiny, M. Large-scale visual relationship understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI Conference on Aritificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 9185–9194. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Vahdat, A.; Hu, H.; Mori, G. Structure inference machines: Recurrent neural networks for analyzing relations in group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4772–4781. [Google Scholar]
- Haanju, Y.; Emo, T.; Seo, J.; Choi, S. Detection of interacting groups based on geometric and social relations between individuals in an image. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 93, 498–506. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gallagher, A.; Luo, J.; Forsyth, D. Seeing people in social context: Recognizing people and social relationships. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 169–182. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Shao, M.; Luo, J.; Fu, Y. Understanding kin relationships in a photo. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2012, 14, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibeklioglu, H.; Salah, A.A.; Gevers, T. Like father, like son: Facial expression dynamics for kinship verification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1497–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lu, J.; Yuan, J.; Tan, Y. Large margin multi-metric learning for face and kinship verification in the wild. In Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Singapore, 1–5 November 2014; pp. 252–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Shang, Y.; Yan, H.; Guo, G. Ensemble similarity learning for kinship verification from facial images in the wild. Inf. Fusion 2016, 32, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Zheng, F.; Shao, L. Learning a multiple kernel similarity metric for kinship verification. Inf. Sci. 2018, 430–431, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, K.; Xu, M.; Guo, G. Learning deep compact similarity metric for kinship verification from face images. Inf. Fusion 2018, 48, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, K.; Lu, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, J. Graph-based kinship reasoning network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceeding of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zemel, R.; Brockschmidt, M.; Tarlow, D. Gated graph sequence neural networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Paluri, M.; Taigman, Y.; Fergus, R.; Bourdev, L. Beyond frontal faces: Improving person recognition using multiple cues. In Proveedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4804–4813. [Google Scholar]
- Gori, M.; Monfardini, G.; Scarselli, F. A new model for learning in graph domains. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005; pp. 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli, F.; Gori, M.; Tsoi, A.C.; Hagenbuchner, M.; Monfardini, G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallicchio, C.; Micheli, A. Graph echo state networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, C.; Ritzert, M.; Fey, M.; Hamilton, W.L.; Lenssen, J.E.; Rattan, G.; Grohe, M. Weisfeiler and Leman go neural: High-order graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 4602–4609. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, Z.R.; Shabbir, M. Interpretable multi-scale graph descriptors via structural compression. Inf. Sci. 2020, 533, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Kozareva, Z.; Dai, B.; Smola, A.; Song, L. Learning steady-states of iterative algorithms over graphs. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholmsmässan, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1106–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, C.; Ma, Q. Dual graph convolutional networks for graph-based semi-supervised classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference (WWW), Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Zheng, C.; Cheng, W.; Aggarwai, C.C.; Song, D. Learning deep network representations with adversarially regularized autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 2663–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Bojchevski, A.; Shchur, O.; Zügner, D.; Günnemann, S. NetGAN: Generating graphs via random walks. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stochholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 610–619. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Long, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C. Graph wavenet for deep spatial-temporal graph modeling. In Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 1907–1913. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Lin, Y.; Feng, N.; Song, C.; Wan, H. Attention based spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for traffic flow forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI Conference on Aritificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Kearnes, S.; McCloskey, K.; Berndl, M.; Pande, V.; Riley, P. Molecular graph convolutions: Moving beyond fingerprints. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, J. Graph-FCN for image semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Neural Networks (ISNN), Moscow, Russia, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wu, G. Learning actor relation graphs for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9956–9966. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Cui, B.; He, Y.; Yu, S. Progressive relation learning for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lan, X. Facial expression recognition using spatial-temporal semantic graph network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 1961–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, L.; Xie, H.X.; Shuai, H.H.; Cheng, W.H. MER-GCN: Micro-expression recognition based on relation modeling with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), Shenzhen, China, 6–8 August 2020; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Li, F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, D.K.; Vandergheynst, P.; Gribonval, R. Wavelets on graphs via spectral theory. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2011, 30, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisshna, R.; Zhu, Y.; Groth, O.; Johnson, J.; Hata, K.; Kravitz, J.; Chen, S.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, L.; Shamma, D.A.; et al. Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 123, 32–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Thomee, B.; Shamma, D.A.; Friedland, G.; Elizalde, B.; Ni, K.; Poland, D.; Borth, D.; Li, L.J. YFCC100M: The new data in multimedia research. Commun. ACM 2016, 59, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; On, K.W.; Lim, W.; Kim, J.; Ha, J.W.; Zhang, B.T. Hadamard product for low-rank bilinear pooling. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Krihna, R.; Stark, M.; Li, L.J.; Shamma, D.A.; Bernstein, M.S.; Li, F.F. Image retrieval using scene graphs. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3668–3678. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Deng, J. Pixels to graphs by associative embedding. In Proceedings of the 31th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zellers, R.; Yatskar, M.; Thomson, S.; Choi, Y. Neural motifs: Scene graph parsing with global context. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5831–5840. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Yu, W.; Chen, R.; Lin, L. Knowledge-embedded routing network for scene graph generation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6156–6164. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Zhao, J.; Wen, B.; Zhang, Y. Explaining the semantics capturing capability of scene graph generation models. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 110, 107427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Azarmi, M. DeepSOCIAL: Social distancing monitoring and infection risk assessment in COVID-19 pandemic. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Yang, K.; Constantinescu, A.; Stiefelhagen, R. Helping the blind to get through COVID-19: Social distancing assistant using real-time semantic segmentation on RGB-D video. Sensors 2020, 20, 5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).