Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary Using Electromagnetic Induction
Abstract
1. Introduction
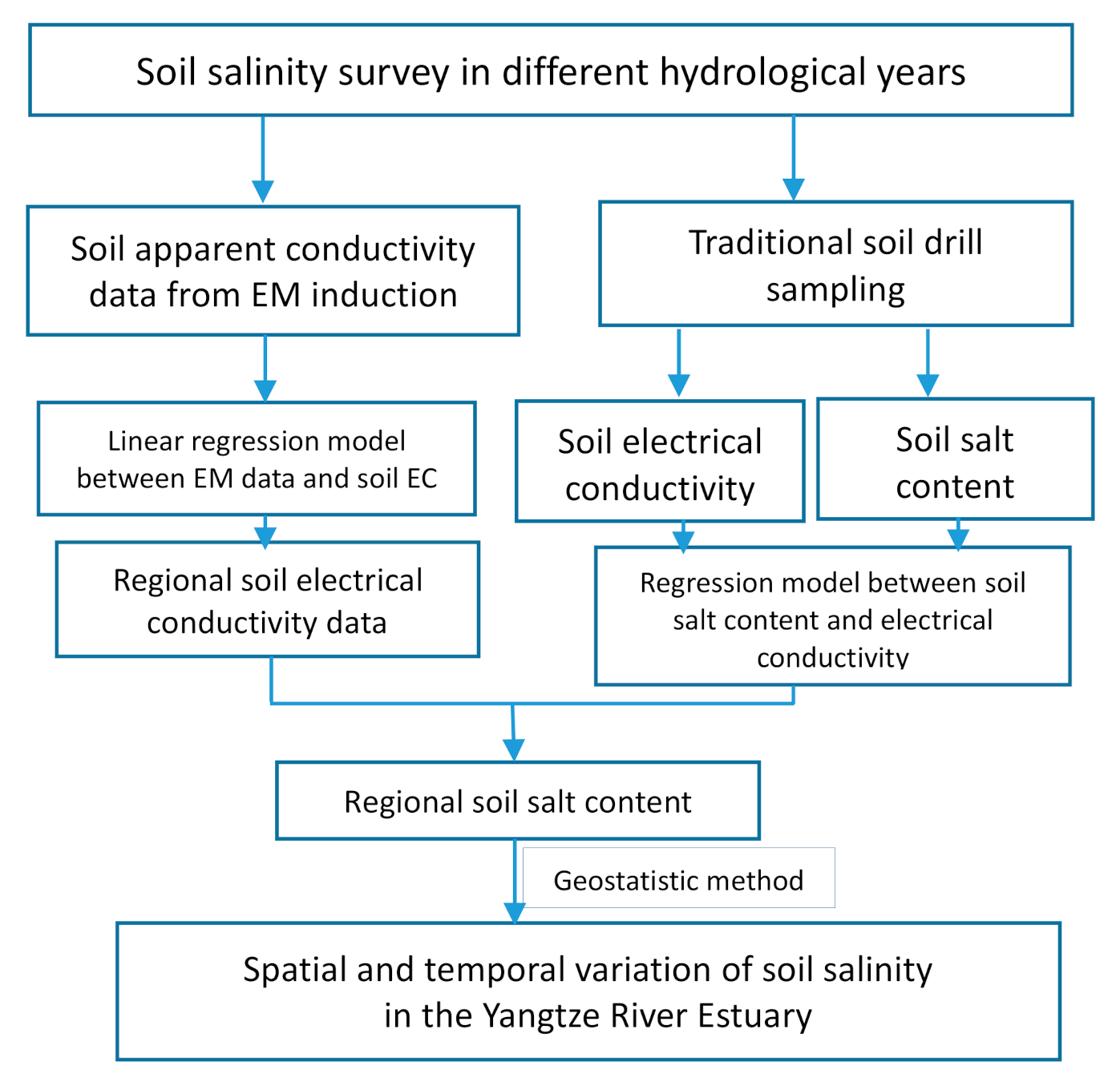
2. Materials and Methods
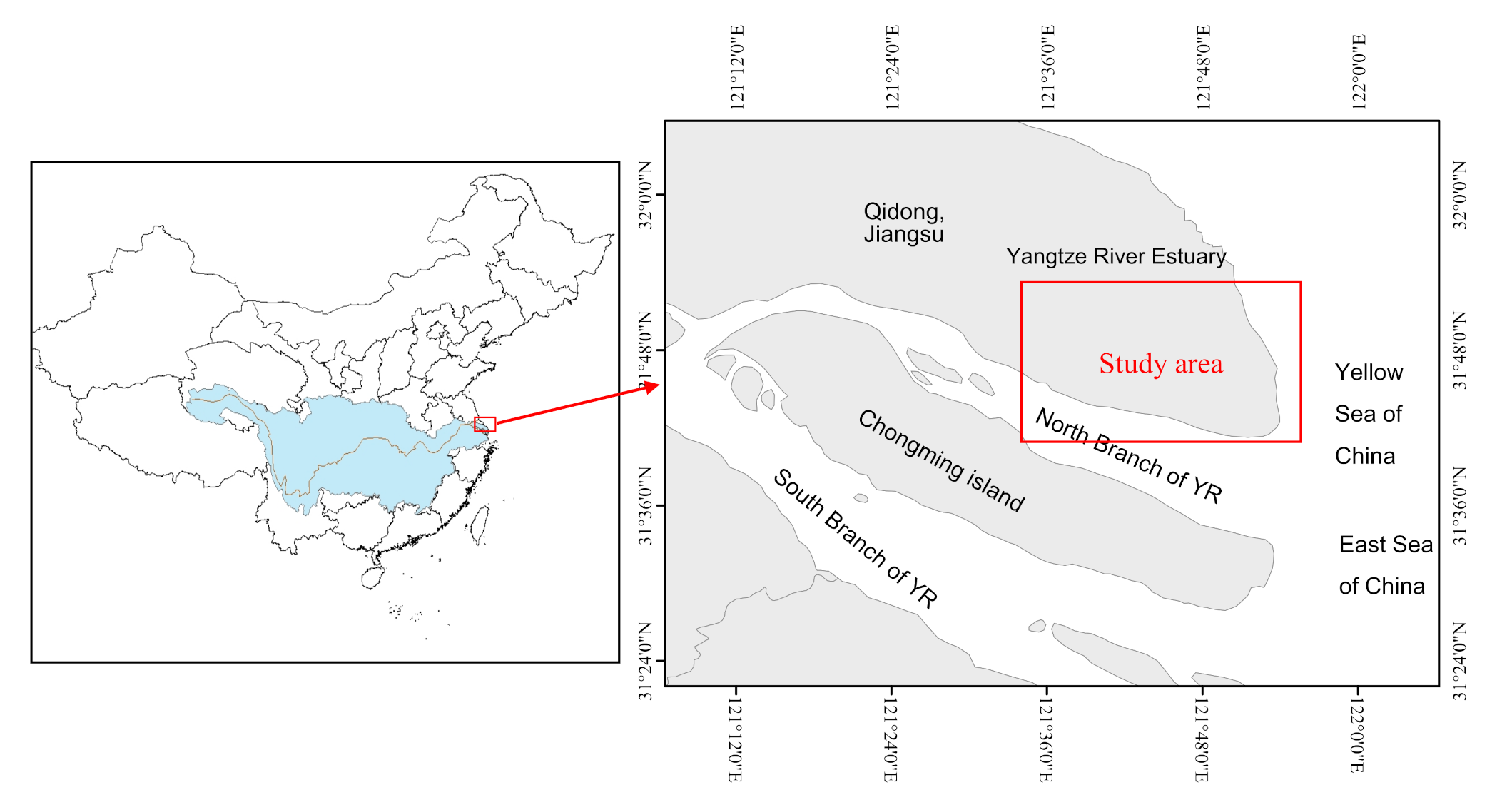
2.1. Study Area
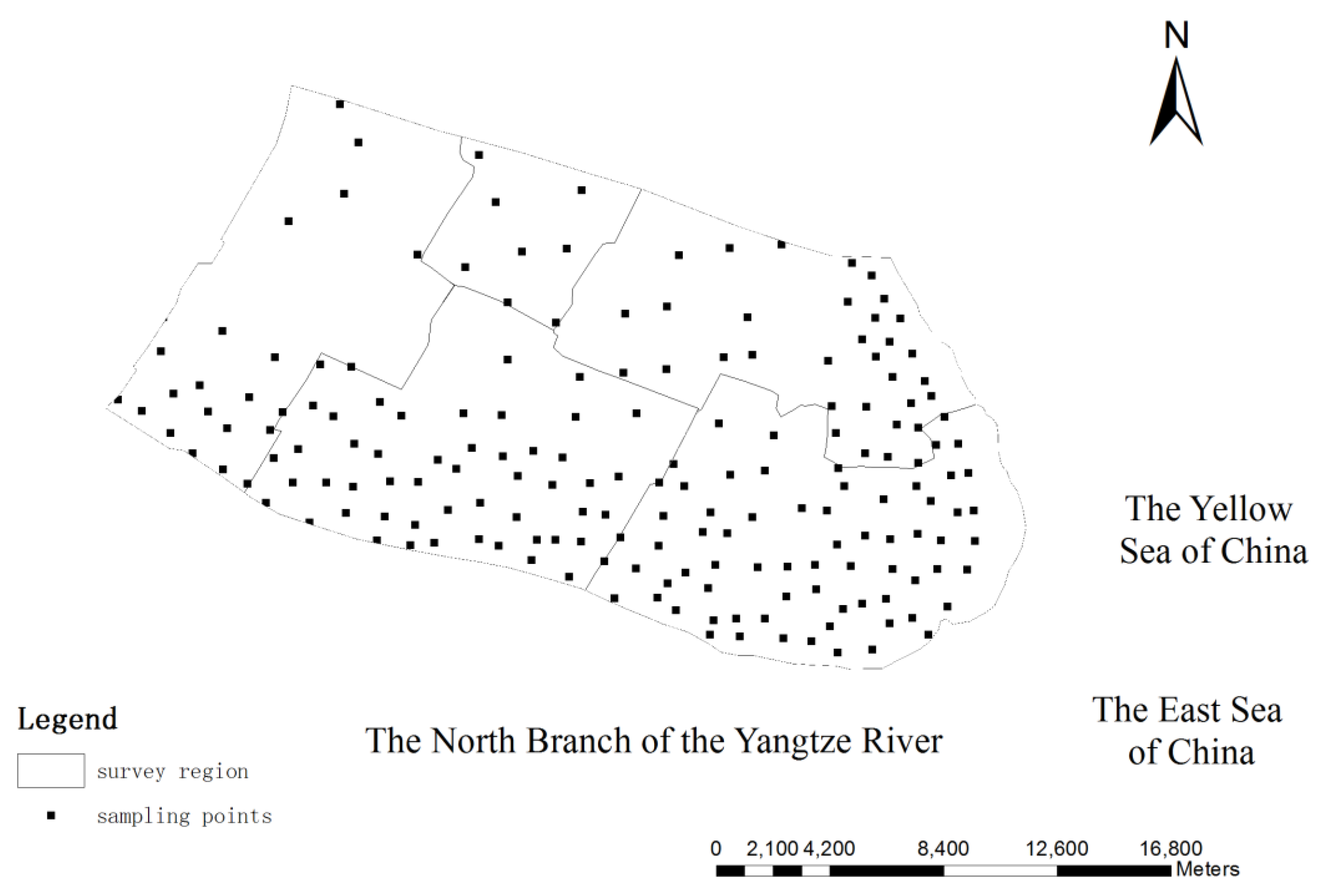
2.2. Soil Sampling Method and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. EM Measurement Method
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Classical Statistical Analysis
2.4.2. Geostatistical Analysis Method
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Modeling Soil Salt Content and Calibration with Measured Value in Field
3.1.1. Soil Electrical Conductivity Interpreted by ECa Measurements
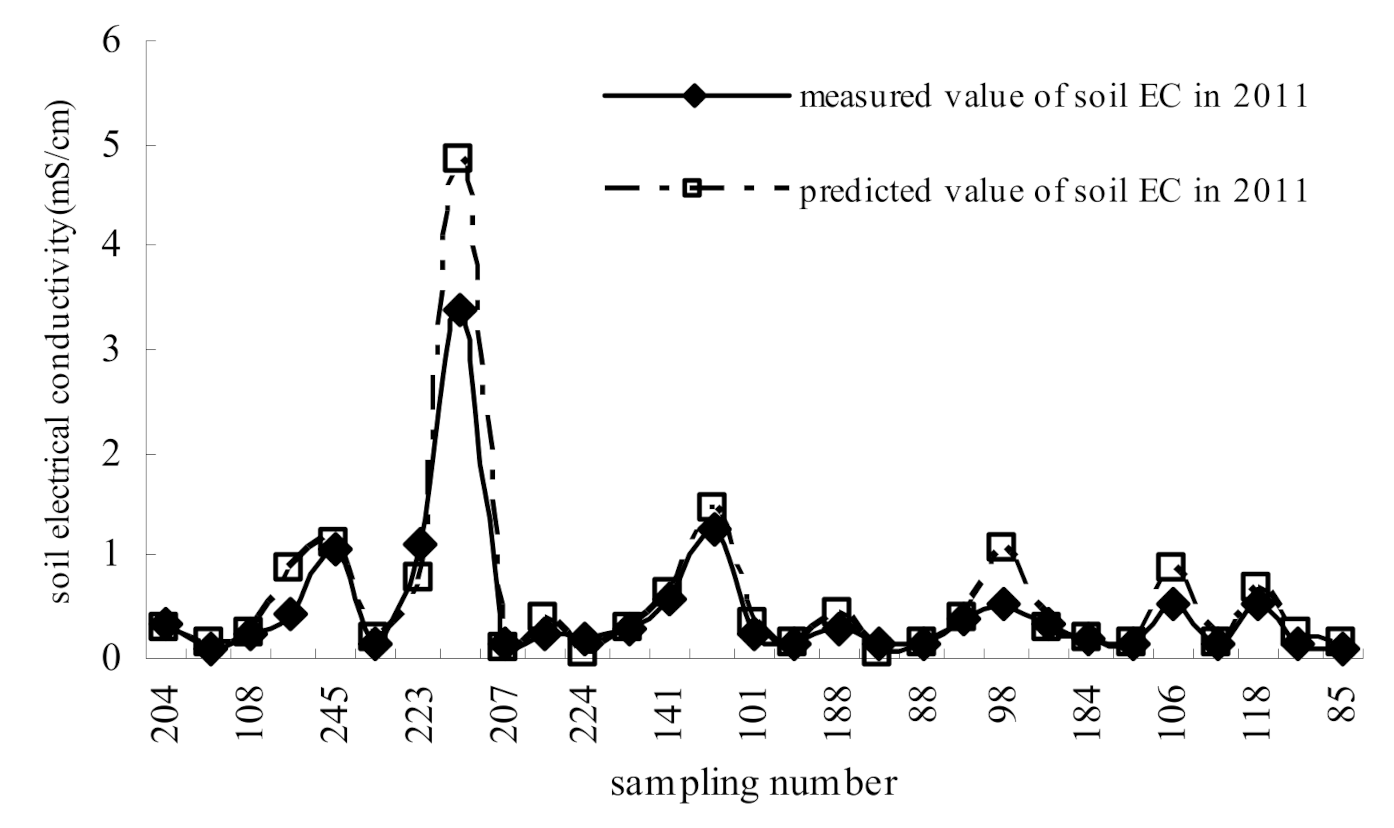
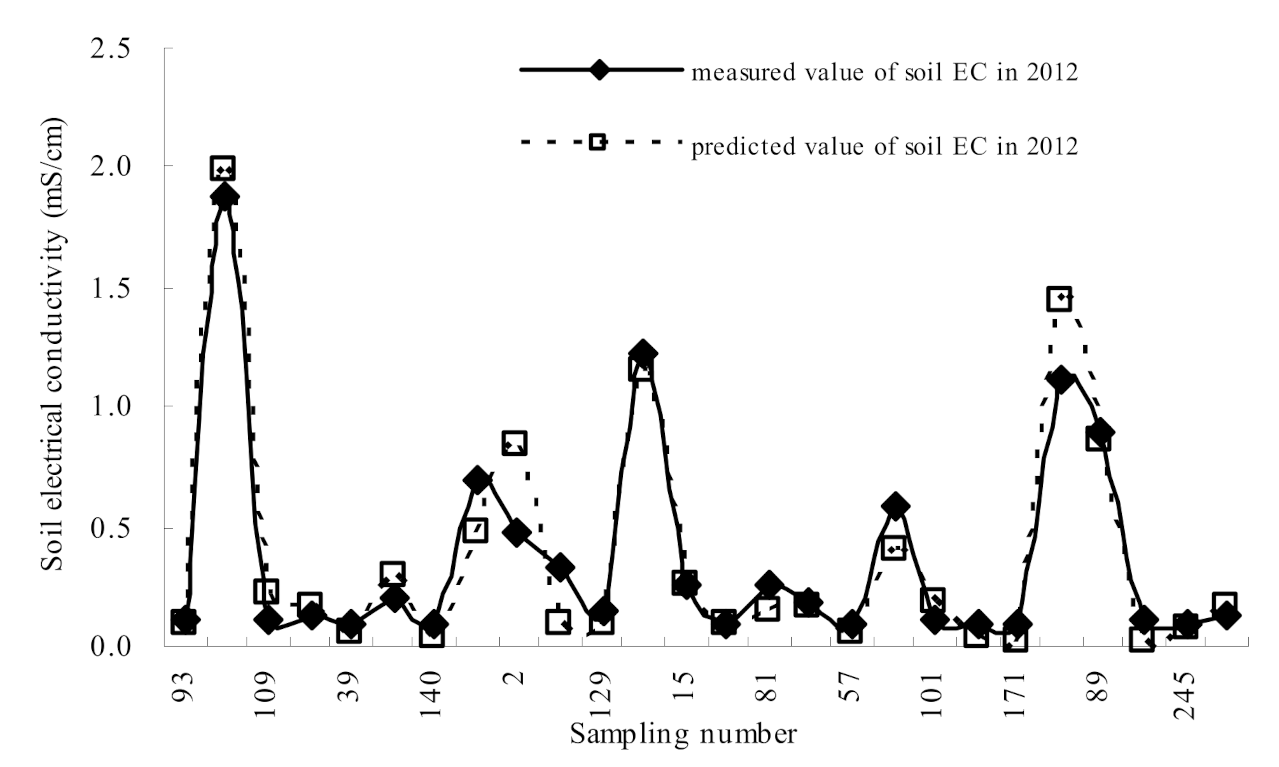
3.1.2. Validation of Soil Electrical Conductivity Interpreted from ECa Measurements
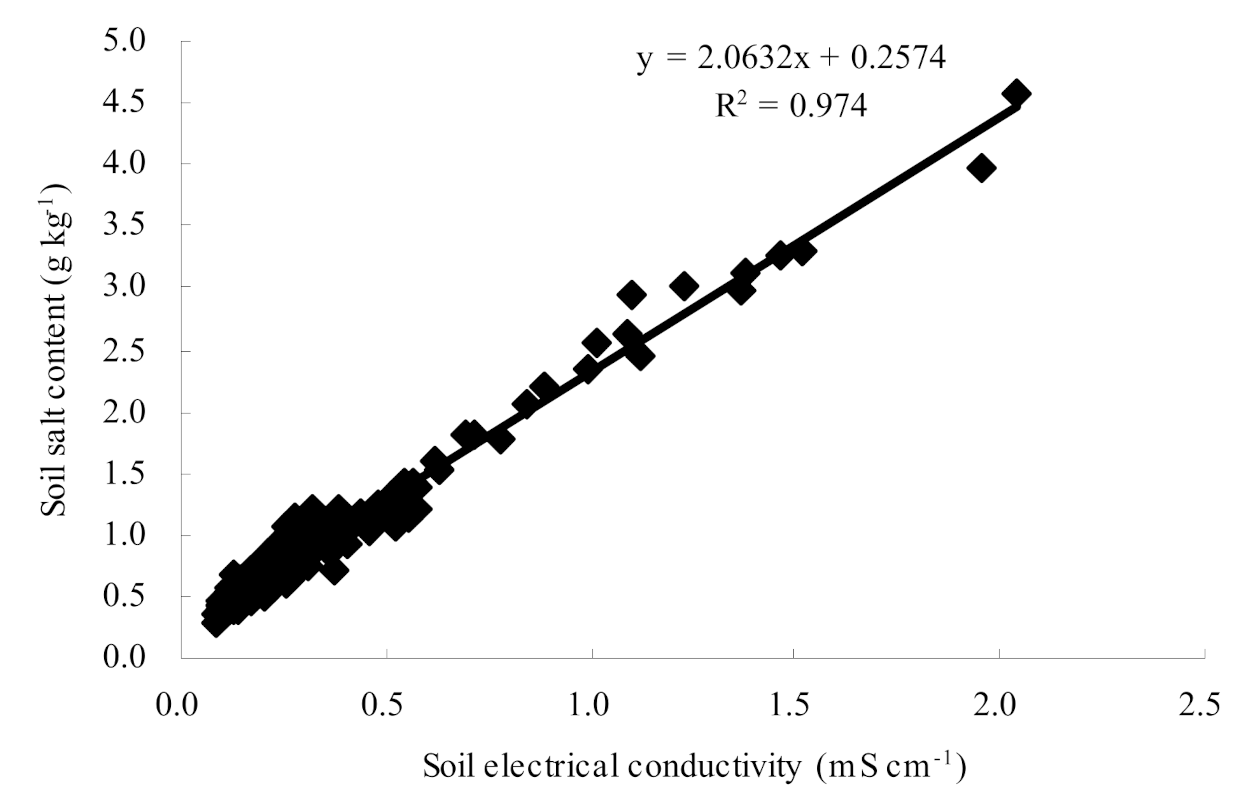
3.1.3. Soil Salt Content Interpreted by ECa Measurements
3.2. Classical Statistical Analysis of Regional Soil Salinity
3.3. Semivariogram Analysis
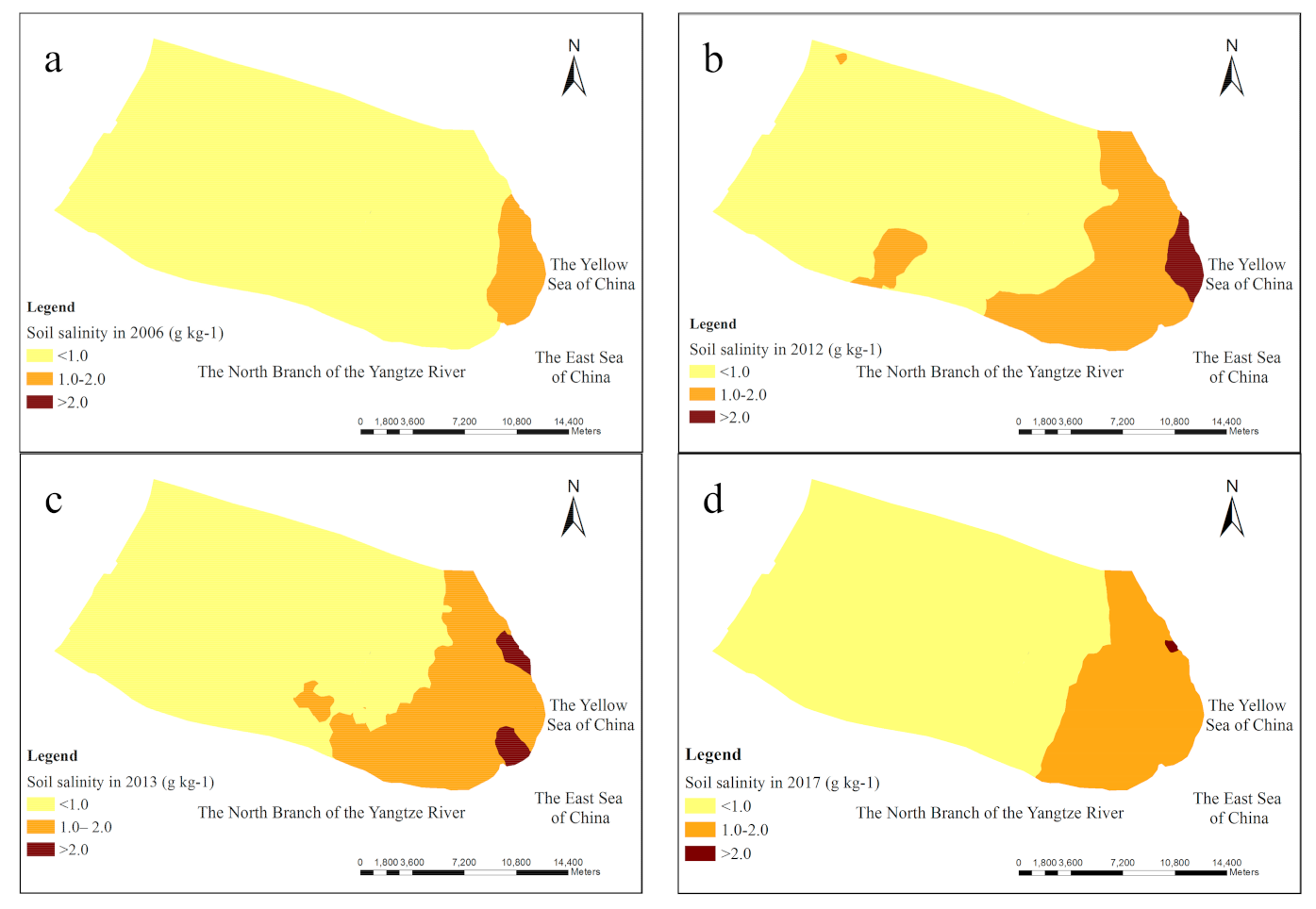
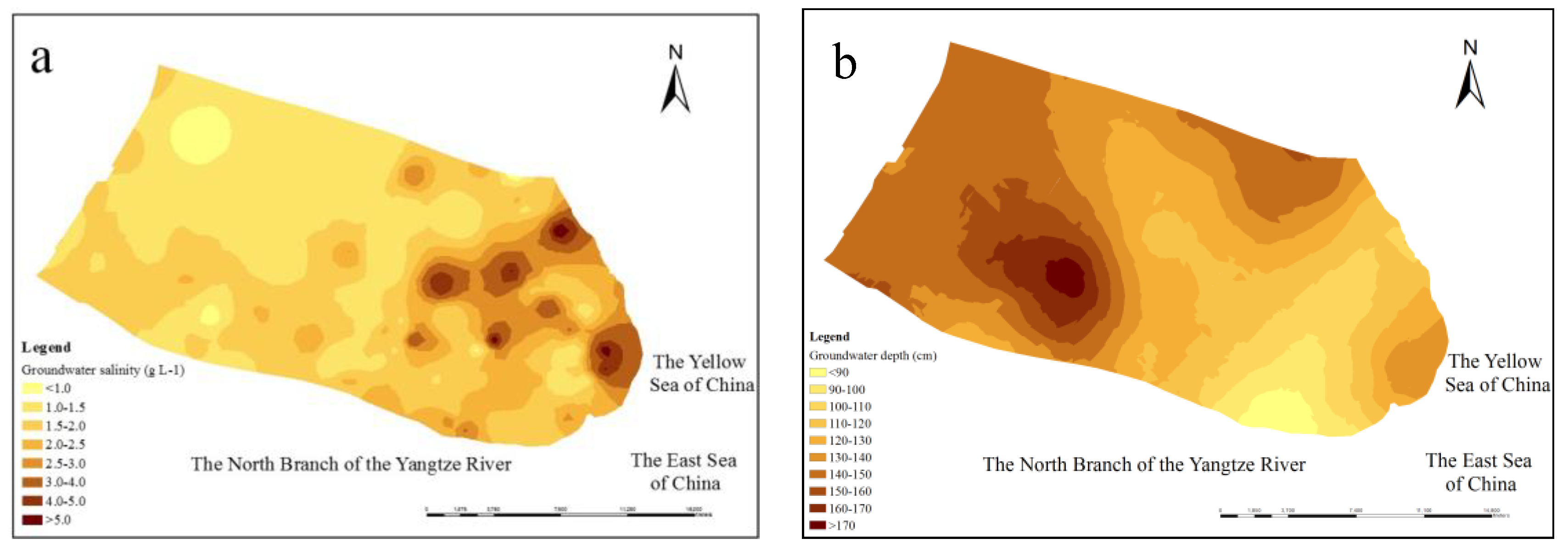
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Soil Salinity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rady, M.M. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, yield, antioxidant system and cadmium content of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants under salinity and cadmium stress. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.; Zinck, J. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Soil salinity evolution and its relationship with dynamics of groundwater in the oasis of inland river basins: Case study from the Fubei region of Xinjiang Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 140, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, G.; Garg, N. Alleviation of salt-induced ionic, osmotic and oxidative stresses in Cajanus cajan nodules by AM inoculation. Plant Biosyst. 2011, 145, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Dong, H.Z.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, D.M. Effects of Soil Salinity and Plant Density on Yield and Leaf Senescence of Field-Grown Cotton. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2011, 198, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Li, H.Z.; Qiao, S.J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.P.; Liu, X.L. Effect of salinity on seed germination, seedling growth, and phys-iological characteristics of Perilla frutescens. Plant Biosyst. 2012, 146, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.J.; Dite, D.; Suvada, R.; Pis, V.; Ikrenyi, I. Hordeum geniculatum in the Pannonian Basin: Ecological requirements and grassland vegetation on salt-affected soils. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; ITPS. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Kempen, B.; de Sousa, L. Global mapping of soil salinity change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhu, S.Q.; Yu, R.P. Saline Soil in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Karlen, D.L.; Tomer, M.D.; Neppel, J.; Cambardella, C.A. A preliminary watershed scale soil quality assessment in north central Iowa, USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 99, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.P.; Song, J.; Wang, B.S.; Feng, G. Relationships between ion and chlorophyll accumulation in seeds and adaptation to saline environments in Suaeda salsa populations. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. Asp. Plant Biol. 2012, 146, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.J.; Cai, M.; Chen, S.S.; Chen, L.; Lan, H.Y. Seed germination, plant growth and physiological responses of Salsola ikon-nikovii to short-term NaCl stress. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelef, O.; Lazarovitch, N.; Rewald, B.; Golan, G.A.; Rachmilevitch, S. Root halotropism: Salinity effects on Bassia indica root. Plant Biosyst. 2010, 144, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewald, B.; Leuschner, C.; Wiesman, Z.; Ephrath, J.E. Influence of salinity on root hydraulic properties of three olive varieties. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. Asp. Plant Biol. 2011, 145, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, J.M.M.; Abdelfattah, A.; Matula, S.; Doležal, F. Effect of Fertigation on Soil Salinization and Aggregate Stability. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141, 05014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Peng, J. Field-Scale Characterization of Spatio-Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in Three Dimensions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, S.; Shi, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F. Using Apparent Electrical Conductivity as Indicator for Investigating Potential Spatial Variation of Soil Salinity across Seven Oases along Tarim River in southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmemet, I.; Ghulam, A.; Tiyip, T.; Elkadiri, R.; Ding, J.-L.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Abliz, A.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Abliz, A.; et al. Monitoring Soil Salinization in Keriya River Basin, Northwestern China Using Passive Reflective and Active Microwave Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8803–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Mai, W.; Zhao, Z. Study on key technologies of ecological management of saline alkali land in arid area of Xinjiang. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 3636, 7064–7068. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, G.; Yu, M. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Soil Salinity in Arid Areas of South Xinjiang Using Electro-magnetic Induction. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.Z.; Liu, G.M.; Yang, J.S.; Zhang, M.M.; He, L.D.; Shao, H.B.; Yu, S.P. Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity in Bohai Sea Coastal Wetlands, China: Partition into Four Management Zones. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, F.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Fu, T.; Su, Q. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Soil Salinity During Dry and Wet Seasons in the Southern Coastal Area of Laizhou Bay, China. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2020, 49, 260–270. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Bangladesh: Climate Change and Sustainable Development; Report No. 21104-BD; World Bank, Rural Development Unit, South Asia Region: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2000; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlani, A.K.; Sovacool, B.K. Building responsiveness to climate change through community based adaptation in Bangladesh. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2011, 16, 845–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, M.C.; Farzamian, M.; Paz, A.M.; Castanheira, N.L.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Santos, F.M. Assessing soil salinity dynamics using time-lapse electromagnetic conductivity imaging. SOIL 2020, 6, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.P.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P. Impact Study of Impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir on Salt-Water Dynamics and Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary. J. Environ. Inform. 2020, 36, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.J.; Zhao, L.Y.; Wang, S.W. Analysis of the dynamic impact of Three-Gorge Project on regime of soil water and salt in Yangtze River Delta. Cluster Comput. 2016, 19, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Kotb, T.H.; Watanabe, T.; Ogino, Y.; Tanji, K.K. Soil salinization in the Nile Delta and related policy issues in Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.L.; Yan, Y.X. Impact of water conservancy project on ecosystem and environment of the Yangtze River estuary. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2003, 12, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.J.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhu, J.R. Determination of critical flow for saline water intrusion into water source area of Yangtze River estuary and guarantee measures. Yangtze River 2011, 42, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Xu, H.G. Impacts of the Yangtze River Three-Gorege Hydro-engineering works on the Yangtze estuar. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Valley 1995, 4, 242–246, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Wu, Y.Q.; Talor, S.; Zhao, B. Influence of the Three Gorges Project on saltwater intrusion in the Yangtze River Estuary. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.; Yang, J.S.; Liu, G.M. Impact on soil salinization in Yangtze River estuary by Three-Gorge project. J. Liaoning Tech. Univ. 2009, 28, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.J.; Yang, J.S.; Liu, G.M.; Yang, Q.Y. Application of Grey System Theory Evaluating the Influencing Factors of soil Salinity. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 41, 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J.; Ma, L.; Jiang, P.; Li, B.; Huang, F.; Wu, H. Digital soil mapping to enable classification of the salt-affected soils in desert agro-ecological zones. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Shi, Z.; Webster, R.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping the three-dimensional variation of soil salinity in a rice-paddy soil. Geoderma 2013, 195, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Electromagnetic Terrain Conductivity Measurement at Low Induction Numbers; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Application of soil electrical conductivity to precision agriculture: Theory, principles, and guidelines. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Laslett, G.M.; McBratney, A.B. Calibrating an electromagnetic induction instrument to measure salinity in soil under irrigated cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Odeh, I.O.A.; McBratney, A.B. Five geostatistical methods to predict soil salinity from electromagnetic induction data across irrigated cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 869–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forests: A case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 754, 142030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Minasny, B.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B.P. Digital mapping of soil salinity in Ardakan region, central Iran. Geoderma 2013, 213, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Kirda, C. Spatial and temporal changes of soil salinity in a cotton field irrigated with low-quality water. J. Hydrol. 2003, 272, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaik, A.; Van Meirvenne, M.; Tóth, T. Soil salinity mapping using spatiotemporal kriging Bayesian maximum entropy with interval soft data. Geoderma 2005, 128, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, S.M.; Rhoades, J.D.; Lund, L.J.; Corwin, D.L. Mapping soil salinity using calibrated electromagnetic measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Ahmed, M.F.; Odeh, I.O.A. Application of a mobile electromagnetic sensing system (MESS) to assess cause and management of soil salinization in an irrigated cotton-growing field. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J. Comparison of interpolation approaches based on spatial variability of apparent soil electrical conductivity with an electromagnetic induction. Trans. CSAE 2007, 23, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Kung, H.-T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Variation of Soil Salinization Risk Using GIS-Based Geostatistical Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis Method of Soil Agro-Chemistry; Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Corwind, L.; Leschs, M. Characterizing soil spatial variability with apparent soil electrical conductivity I. Survey protocols. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 103–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, K.R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Noninvasive soil water content measurement using electromagnetic induction. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.D.; Yang, S.X.; Xie, S.C. Soil Water Dynamics; Tsing Hua University Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A. Field-scale variability of soilproperties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Emmerson, R.H.C.; Lester, J.N. Geostatistical analysis of sampling uncertainty at the Tollesbury Managed Retreat site in Blackwater Estuary, Essex, UK: Kriging and cokriging approach to minimize sampling density. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 22, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Belkin, I.M. Temporal variation in the sediment load of the Yangtze River and the influences of human activities. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T. Material Flux in the Yangtze River Estuary; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Visconti, F.; de Paz, J.M. Sensitivity of soil electromagnetic induction measurements to salinity, water content, clay, organic matter and bulk density. Precis. Agric. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, D.; Arshad, M.; Zare, E.; Triantafilis, J. Reconnaissance scale mapping of salinity in three dimensions using EM38 and EM34 data and inversion modeling. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2936–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, M.K.; Slavich, P.G.; Irhas, Y.; Moore, N.; Rachman, A.; Ali, N.; Iskandar, T.; Hunta, C.; Caniago, C. Soil salinity in Aceh after the December 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.A.; Rasheed, M.A.; Youssef, R.A. Degradation hazard assessment of some soils North Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 156–161. [Google Scholar]

| Depth (cm) | Regression Model | EC1:5 = a × EM1v + b × EM1h + c × EM0.5v + d × EM0.5h + e | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | R2 | ||
| 0~20 | Stepwise regression model | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.006 | −0.108 | 0.787 |
| 0~20 | Enter regression model | −0.0084 | 0.0122 | 0.0016 | 0.0009 | −0.0184 | 0.841 |
| Statistics | 2006 | 2008 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.62 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 1.15 | 1.33 | 1.02 | 1.20 | 0.92 | 1.12 |
| Std. Error of Mean | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.11 | 0.74 | 1.74 | 0.82 | 1.12 | 0.62 | 1.07 | 0.52 | 0.70 |
| Coefficient of variation (CV, %) | 17.7 | 85.1 | 195.5 | 71.3 | 84.2 | 60.8 | 89.2 | 56.5 | 62.5 |
| Variance | 5.06 | 0.55 | 6.61 | 0.66 | 1.26 | 0.39 | 1.15 | 0.27 | 0.48 |
| Skewness | 0.12 | 5.36 | 0.19 | 2.42 | 3.55 | 2.87 | 5.22 | 3.62 | 2.52 |
| Std. Error of Skewness | 30.67 | 0.26 | 53.18 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| Kurtosis | 0.24 | 30.21 | 0.37 | 6.30 | 17.44 | 9.85 | 40.08 | 19.38 | 6.90 |
| Std. Error of Kurtosis | 0.62 | 0.52 | 12.93 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.37 |
| Range | 3.05 | 5.14 | 0.18 | 4.60 | 8.89 | 3.85 | 10.47 | 4.28 | 3.82 |
| Minimum | 0.32 | 0.58 | 0.89 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.54 |
| Maximum | 3.37 | 5.72 | 13.11 | 5.08 | 9.40 | 4.33 | 11.00 | 4.69 | 4.36 |
| Time | Model Type | C0 | Sill | Range | Nugget-Sill (%) | R2 | RSS | ME | ASE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Spherical | 0.035 | 0.069 | 25,480 | 50.7 | 0.982 | 2.68 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 0.240 | 0.343 |
| 2008 | Exponential | 0.002 | 0.086 | 10,350 | 198.4 | 0.846 | 1.10 × 10−3 | 0.038 | 0.355 | 0.423 |
| 2010 | Gussian | 0.193 | 0.549 | 31,211 | 35.2 | 0.954 | 5.98 × 10−3 | 0.031 | 0.391 | 0.546 |
| 2011 | Exponential | 0.150 | 0.251 | 21,880 | 59.8 | 0.861 | 3.56 × 10−3 | 0.068 | 0.897 | 1.023 |
| 2012 | Exponential | 0.079 | 0.140 | 20,120 | 56.4 | 0.845 | 1.75 × 10−3 | 0.034 | 0.314 | 0.576 |
| 2013 | Exponential | 0.169 | 0.248 | 21,455 | 68.2 | 0.835 | 2.26 × 10−3 | 0.031 | 0.410 | 0.845 |
| 2014 | Exponential | 0.053 | 0.106 | 12,600 | 49.5 | 0.909 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 0.022 | 0.247 | 0.446 |
| 2015 | Spherical | 0.104 | 0.150 | 23,692 | 69.1 | 0.527 | 5.09 × 10−3 | 0.035 | 0.393 | 0.776 |
| 2016 | Spherical | 0.050 | 0.118 | 6870 | 42.4 | 0.406 | 5.36 × 10−3 | 0.001 | 0.240 | 0.343 |
| 2017 | Exponential | 0.064 | 0.130 | 16,770 | 49.6 | 0.736 | 1.03 × 10−3 | 0.021 | 0.331 | 0.513 |
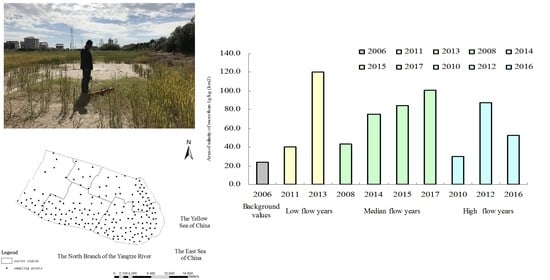
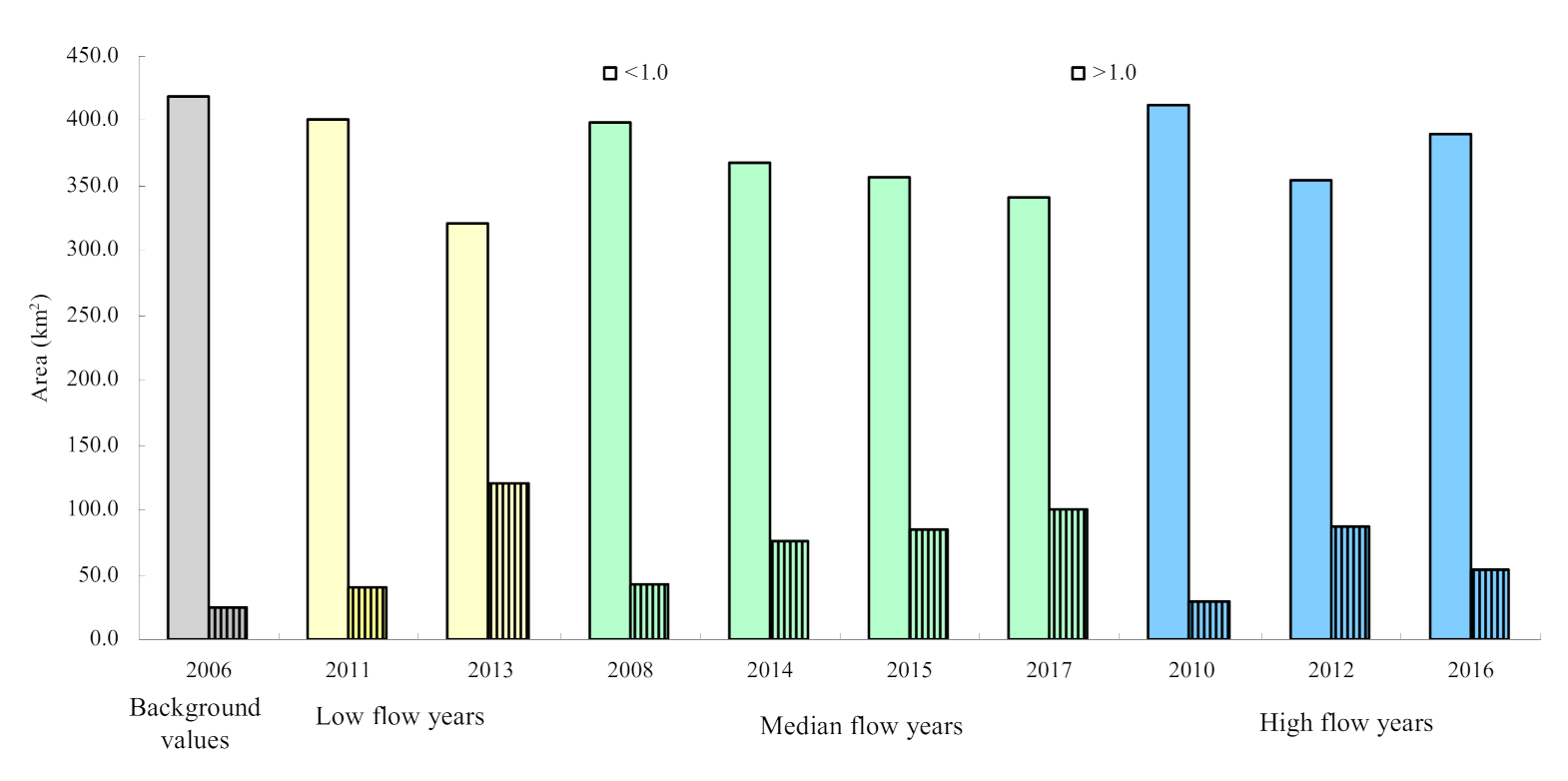
| Hydrological Types | Survey Year | Area of Different Salinity Grades (km2) | Annual Average Flow at Datong Station (m3 s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1.0 g kg−1 | >1.0 g kg−1 | |||
| Background value | 2006 | 418.0 | 23.7 | 21,937.7 |
| low flow year | 2011 | 401.7 | 40.0 | 21,091.2 |
| 2013 | 321.6 | 120.0 | 24,996.2 | |
| median flow year | 2008 | 398.2 | 43.4 | 26,159.9 |
| 2014 | 366.8 | 74.8 | 28,253.1 | |
| 2015 | 356.9 | 84.8 | 28,614.6 | |
| 2017 | 340.4 | 101.2 | 29,161.7 | |
| high flow year | 2010 | 412.0 | 29.6 | 32,218.3 |
| 2012 | 354.3 | 87.4 | 31,497.1 | |
| 2016 | 389.2 | 52.5 | 32,614.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary Using Electromagnetic Induction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101875
Xie W, Yang J, Yao R, Wang X. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary Using Electromagnetic Induction. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(10):1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101875
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wenping, Jingsong Yang, Rongjiang Yao, and Xiangping Wang. 2021. "Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary Using Electromagnetic Induction" Remote Sensing 13, no. 10: 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101875
APA StyleXie, W., Yang, J., Yao, R., & Wang, X. (2021). Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity in the Yangtze River Estuary Using Electromagnetic Induction. Remote Sensing, 13(10), 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101875