Recovering Missing Trajectory Data for Mobile Laser Scanning Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
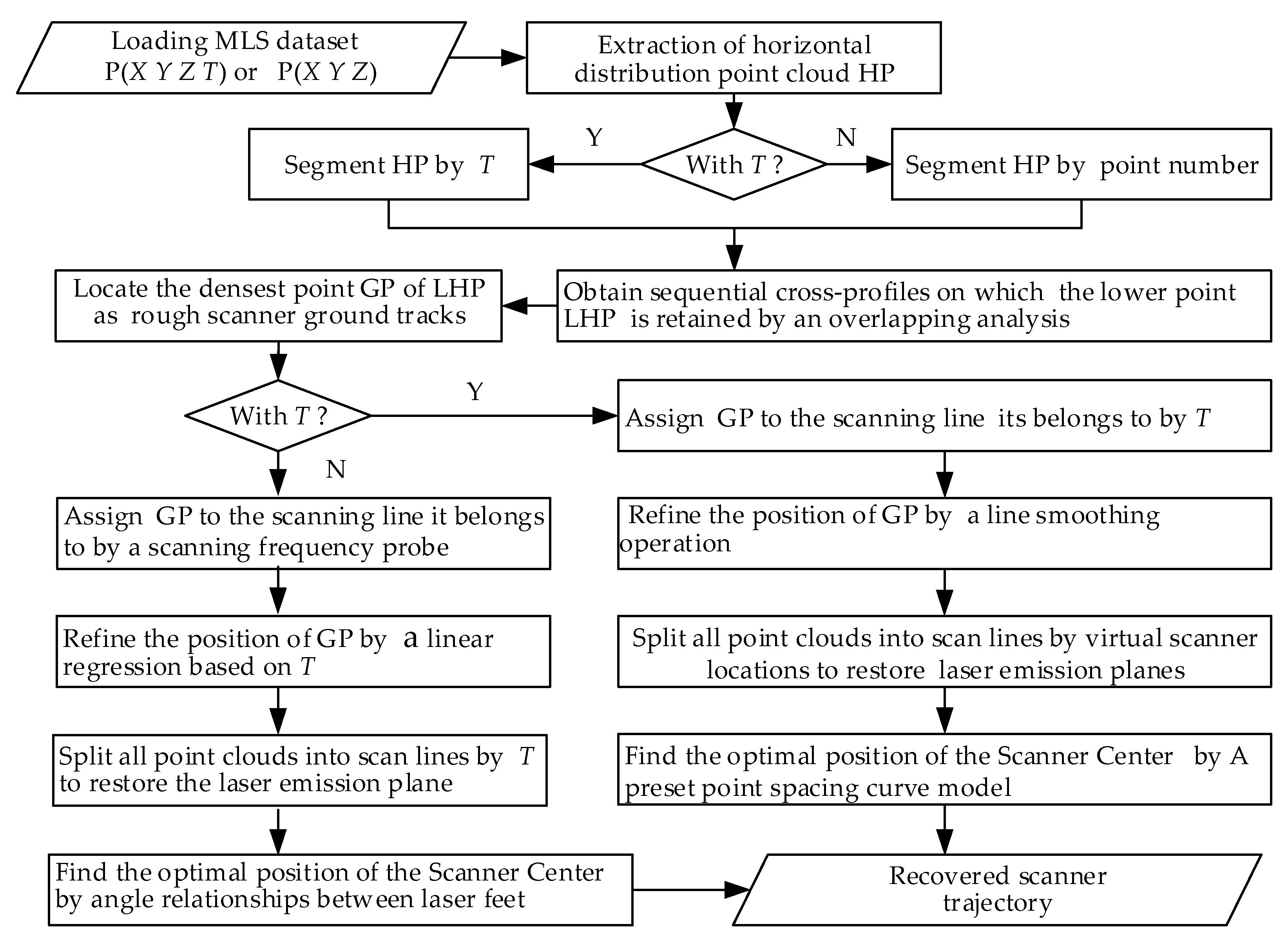
2. Methodology
2.1. Based on Three-Dimensional (3D) Coordinates and Acquisition Time of Point Cloud
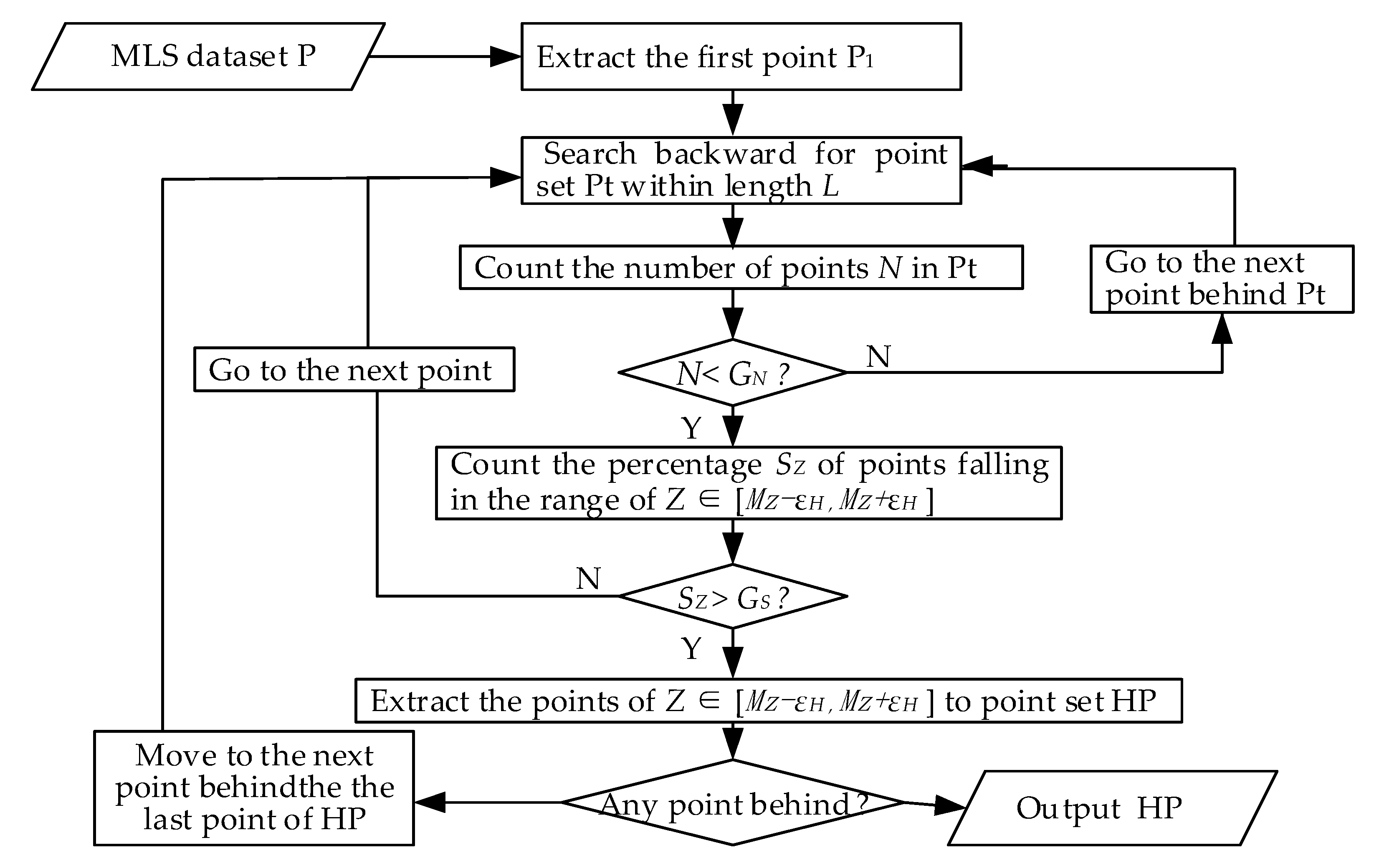
2.1.1. Rough Road Point Extraction
2.1.2. Road Point Filtering
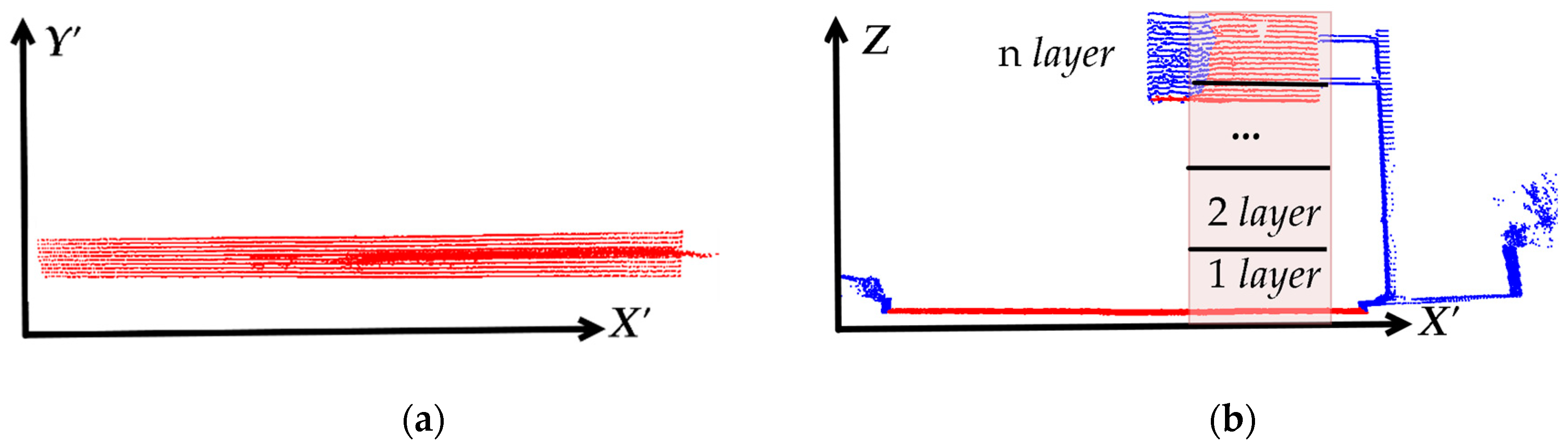
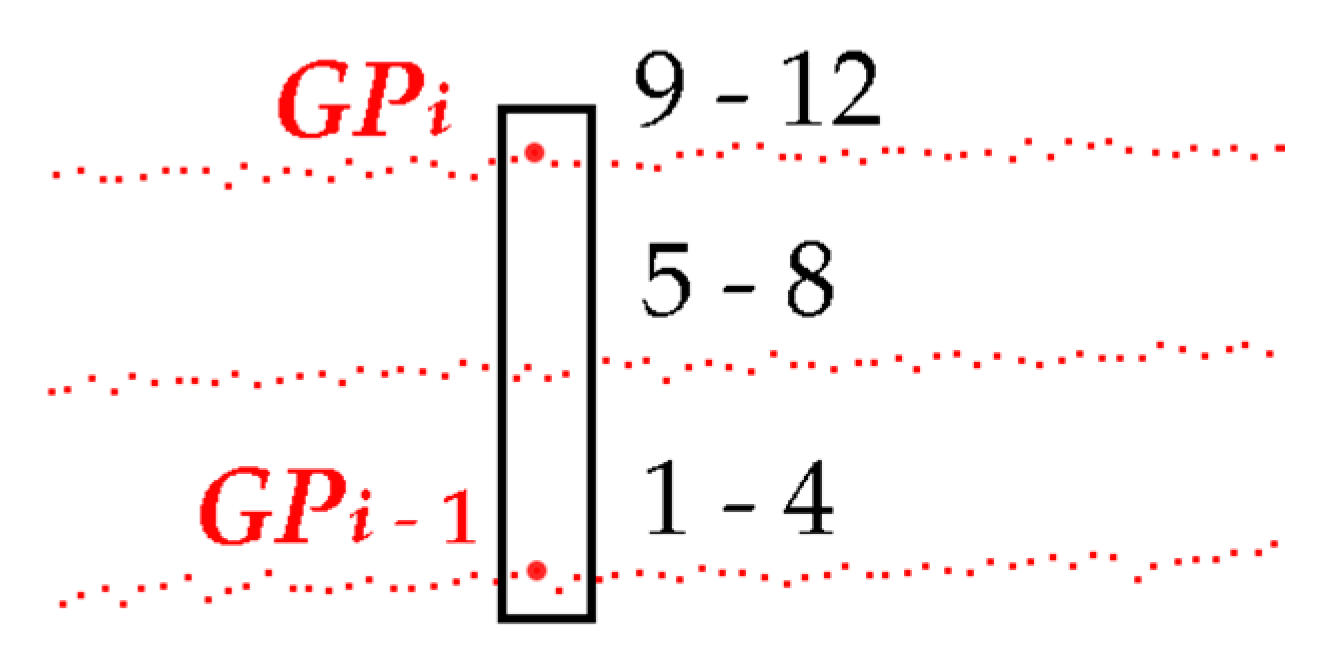
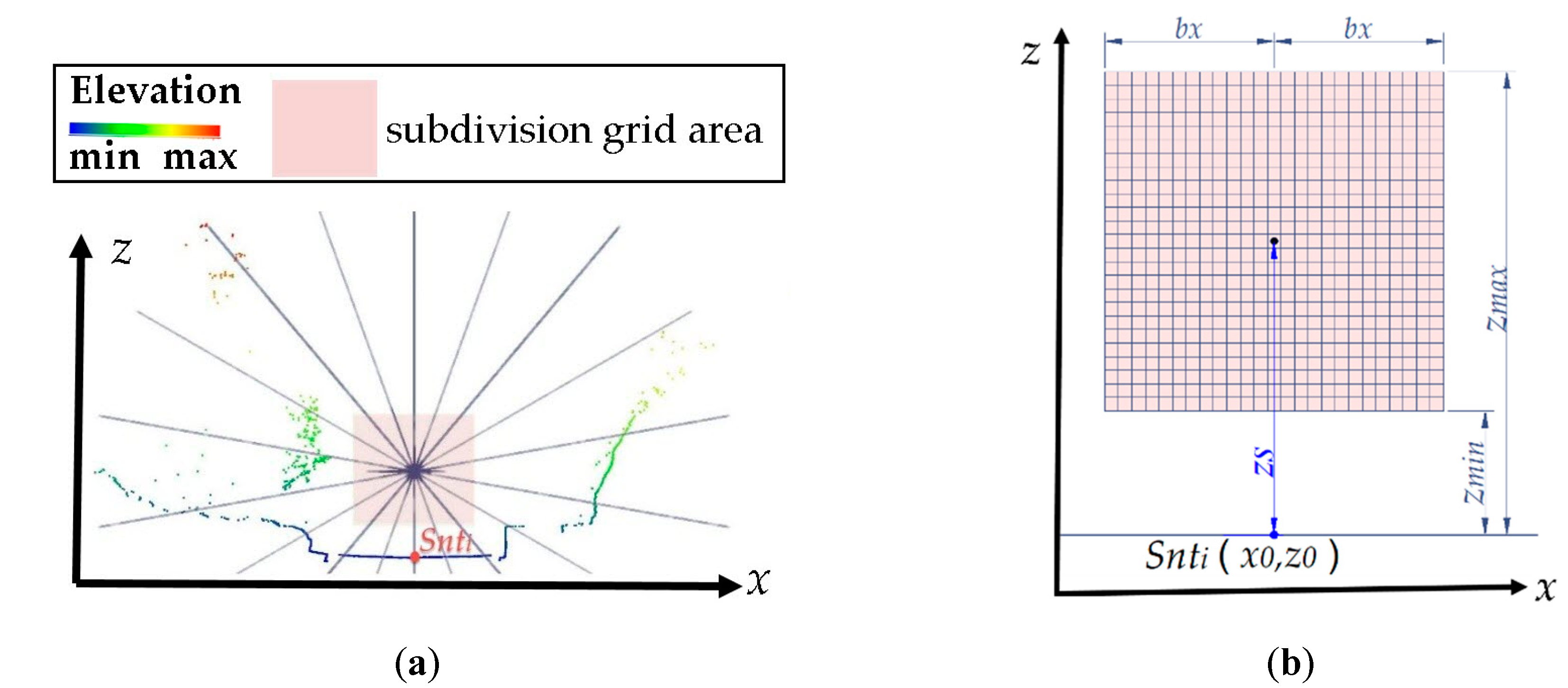
2.1.3. Point Density Analysis to Roughly Locate Scanner Ground Tracks
2.1.4. Refinement of Scanner’s Ground Trajectory
2.1.5. Reconstruction of Scanner Trajectory
- Calculate the time interval between adjacent points in the LHP to obtain sequence ∆T.
- Statistically analyze ∆T and take the first quartile Q1 as an approximation of the laser’s emission interval ∆t because the percentage of the laser beam without echo in road point cloud is generally less than 25%.
- Mark the number of emissions of the first point of P as 1, and calculate the number of emissions of the other point using Equation (8):where SNi represents the number of emissions of the ith point in P.
- Calculate the difference in SNi. The points satisfying SNi − SNi-1 = 0 are multiple echo points. Remove them to facilitate subsequent data processing.
2.2. Based on Ordered 3D Coordinates of Point Cloud
2.2.1. Refinement of Scanner’s Ground Trajectory
2.2.2. Separating Point Clouds into Scanning Lines
2.2.3. Reconstruction of Scanner Trajectory
3. Experiments
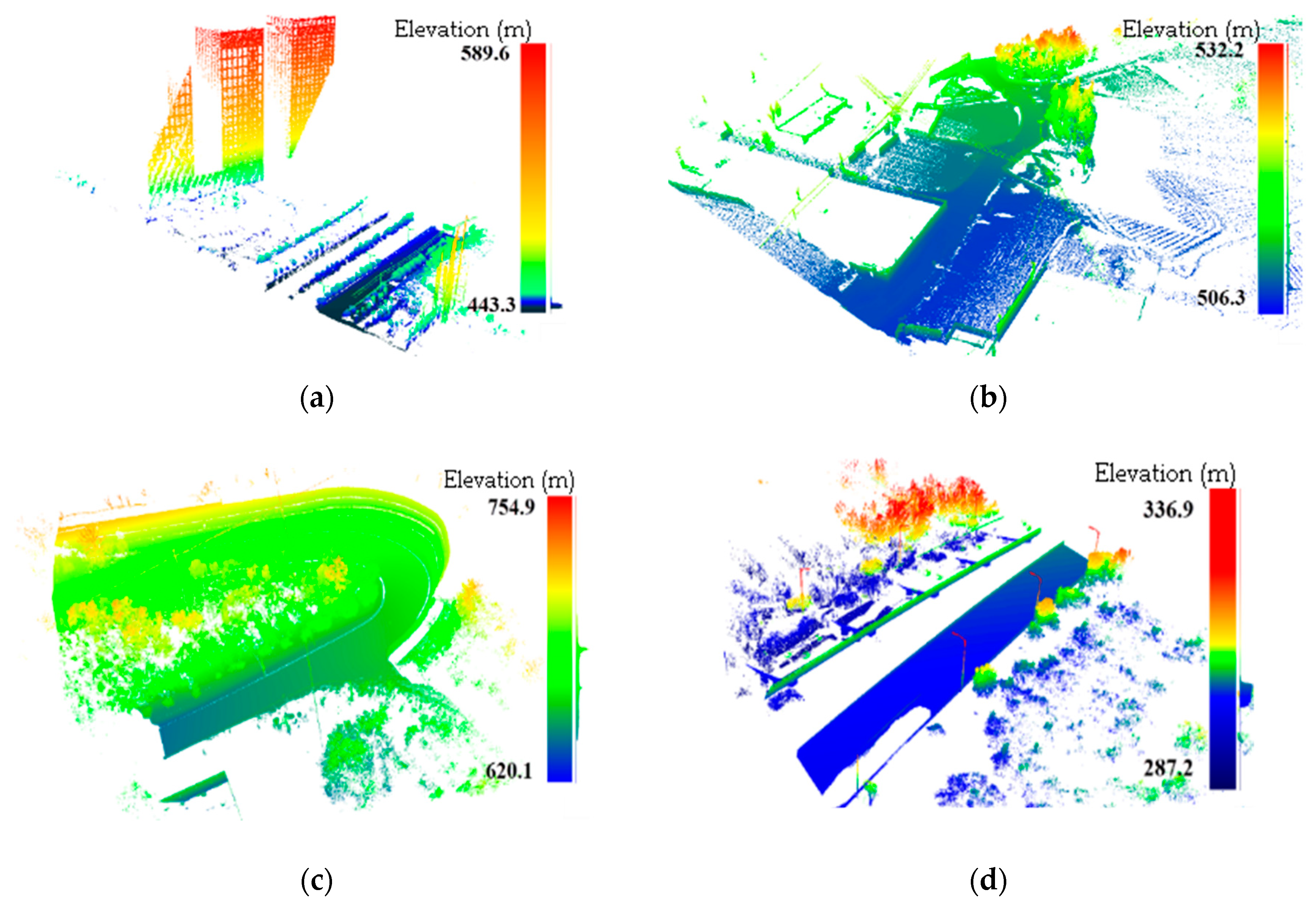
3.1. Test Data
3.2. Results
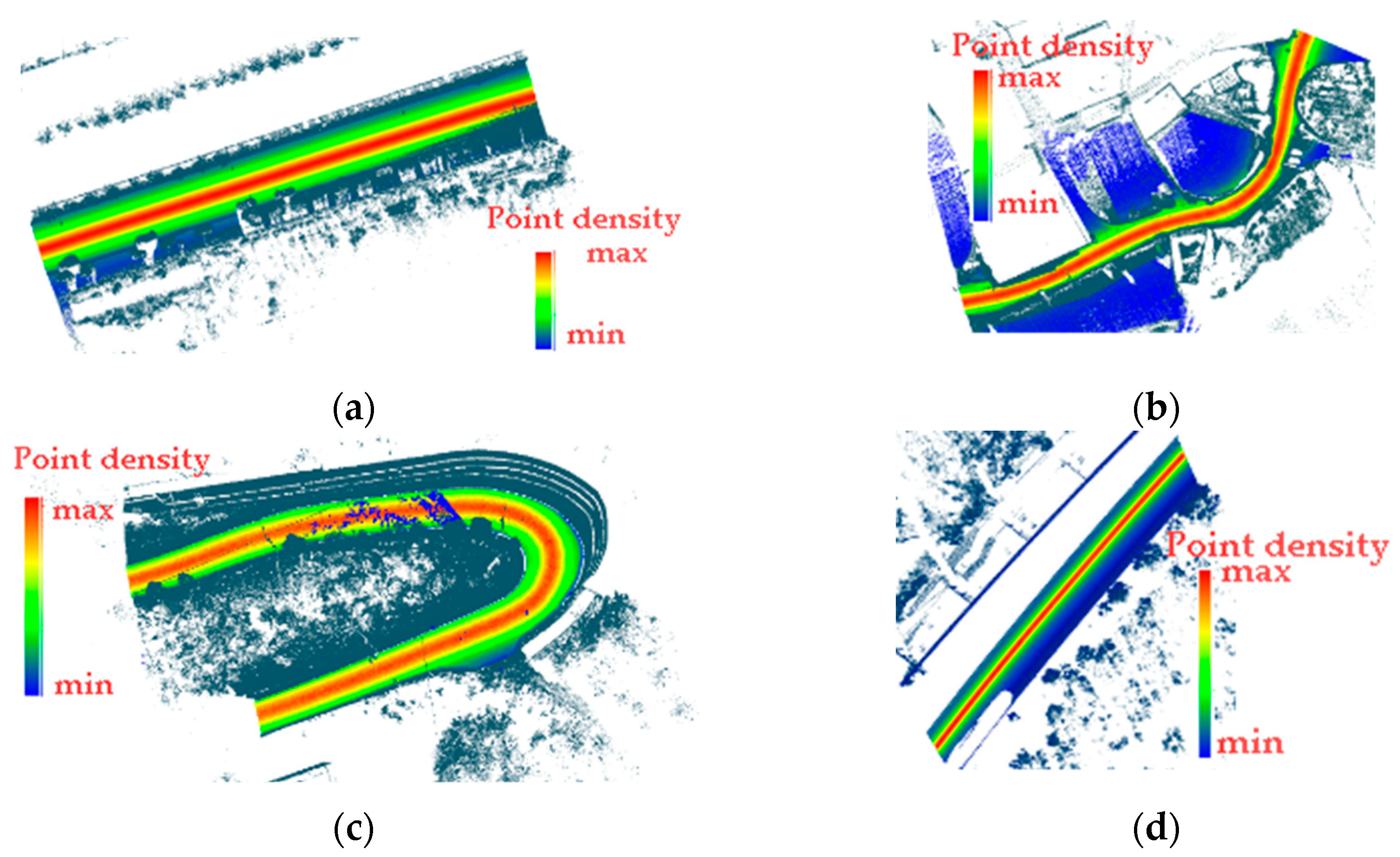
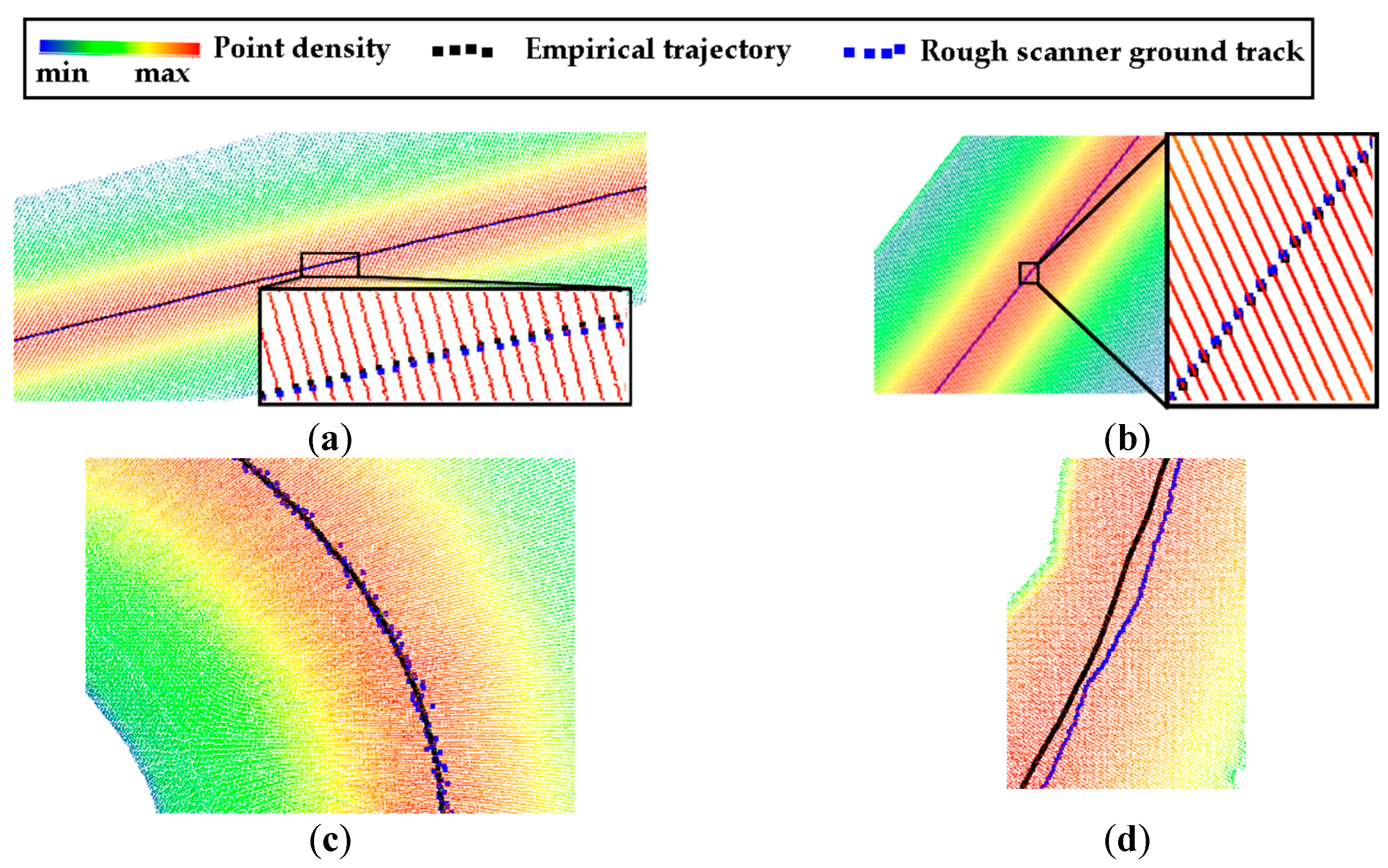
3.2.1. Road High Density Area and Scanner Ground Traces
3.2.2. Reconstructed Scanner Track
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Road Line Type
4.2. Road Conditions
4.3. Position of Scanner Installation
4.4. Environment Surrounding the Road
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, B.; Tu, J.; Yao, J.; Li, L. A Novel Octree-Based 3-D Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Classification in Road Environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7799–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halawany, S.I.; Lichti, D.D. Detecting road poles from mobile terrestrial laser scanning data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 704–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.L.; You, C.B.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Fan, X.L.; Li, J. Recovery of urban 3D road boundary via multi-source data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 156, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhong, R.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Wang, C.; Qin, C.; Sun, H.; Li, R. 3-D Deep Feature Construction for Mobile Laser Scanning Point Cloud Registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1904–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargoum, S.A.; El Basyouny, K. A literature synthesis of LiDAR applications in transportation: Feature extraction and geometric assessments of highways. GIScience Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 864–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liang, F.; Li, B.; Peng, X. 3D local feature BKD to extract road information from mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y. Computing multiple aggregation levels and contextual features for road facilities recognition using mobile laser scanning data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J. Automated extraction of ground surface along urban roads from mobile laser scanning point clouds. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, M.; Kankare, V.; Vastaranta, M.; Liang, X.; Lin, Y.; Vaaja, M.; Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H.; Kaartinen, H.; et al. Tree mapping using airborne, terrestrial and mobile laser scanning—A case study in a heterogeneous urban forest. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wei, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Automated extraction of street-scene objects from mobile lidar point clouds. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5839–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Chapman, M. Mobile Laser Scanned Point-Clouds for Road Object Detection and Extraction: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, A.K.; Lohani, B. Extraction of road surface from mobile LiDAR data of complex road environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4655–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyun, W.; Huan, L.; Chenglu, W.; Jun, C.; Peng, L.; Yiping, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, J. Road Boundaries Detection Based on Local Normal Saliency From Mobile Laser Scanning Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2085–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Rutzinger, M.; Vosselman, G.; Oude Elberink, S. Recognizing basic structures from mobile laser scanning data for road inventory studies. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, S28–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, H.; Cheng, W. 3D Road Surface Extraction From Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 1595–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Zai, D.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, M.; Lin, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, C. 3-D Road Boundary Extraction From Mobile Laser Scanning Data via Supervoxels and Graph Cuts. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.-A.; Chiu, C.-M. Pole-Like Road Object Detection from Mobile Lidar System Using a Coarse-to-Fine Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4805–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balado, J.; Martinez-Sanchez, J.; Arias, P.; Novo, A. Road Environment Semantic Segmentation with Deep Learning from MLS Point Cloud Data. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balado, J.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Arias, P.; Garrido, I. Point clouds to indoor/outdoor accessibility diagnosis. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, IV-2/W4, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fang, L.; Li, J. Semi-automated extraction and delineation of 3D roads of street scene from mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Che, E.; Olsen, M.J.; Parrish, C. Efficient and robust lane marking extraction from mobile lidar point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 147, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Cuenca, B.; García Cortés, S.; Ordóñez Galán, C.; Alonso, M.C.J. An approach to detect and delineate street curbs from MLS 3D point cloud data. Autom. Constr. 2015, 51, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Yue, W.; Shu, S.; Tan, W.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. A Voxel-Based Method for Automated Identification and Morphological Parameters Estimation of Individual Street Trees from Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 584–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinney, C.P.; Kumar, P.; Cahalane, C.; McCarthy, T. Initial results from European road safety inspection (eursi) mobile mapping project. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; Vol. XXXVIII, Part 5 Commission V Symposium; International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS): Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2010; Available online: http://mural.maynoothuniversity.ie/9271/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Holgado-Barco, A.; Gonzalez-Aguilera, D.; Arias-Sanchez, P.; Martinez-Sanchez, J. An automated approach to vertical road characterisation using mobile LiDAR systems: Longitudinal profiles and cross-sections. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Chapman, M.; Yang, B. Using mobile laser scanning data for automated extraction of road markings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Wang, C. Using Mobile LiDAR Data for Rapidly Updating Road Markings. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C. Automated extraction of manhole covers using mobile LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, H.; Jia, F.; Wang, C. Learning Hierarchical Features for Automated Extraction of Road Markings From 3-D Mobile LiDAR Point Clouds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, I.; Akinci, B.; González-Jorge, H.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Arias, P. A semi-automated method for extracting vertical clearance and cross sections in tunnels using mobile LiDAR data. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 59, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargoum, S.; El-Basyouny, K. Automated Extractaion of Road Features Using LiDAR Data: A Review of LiDAR Applications in Transportation. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Banff, AB, Canada, 8–10 August 2017; pp. 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Kohlmeyer, B.; Stroila, M.; Alwar, N.; Bach, J. Next generation map making: Geo-referenced ground-level LIDAR point clouds for automatic retro-reflective road feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Symposium on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, ACM-GIS 2009, Seattle, WA, USA, 4–6 November 2009; pp. 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Min, H. A 3D LiDAR Data-Based Dedicated Road Boundary Detection Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29623–29638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilán, M.; Riveiro, B.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Arias, P. Traffic sign detection in MLS acquired point clouds for geometric and image-based semantic inventory. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tsai, M.-J.; Han, J.-Y. Automatic reconstruction of road surface features by using terrestrial mobile lidar. Autom. Constr. 2015, 58, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cai, Z.; Luo, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, J. Automatic road extraction from mobile laser scanning data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing, Xiamen, China, 16–18 December 2012; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, H.; Tan, J.; Li, Z.; Xie, H.; Chen, C. Scan Line Based Road Marking Extraction from Mobile LiDAR Point Clouds. Sensors 2016, 16, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Mcelhinney, C.P.; Lewis, P.; Mccarthy, T. An automated algorithm for extracting road edges from terrestrial mobile LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 85, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervieu, A.; Soheilian, B. Road side detection and reconstruction using LIDAR sensor. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gold Coast, Australia, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, D. A new curb detection method for unmanned ground vehicles using 2D sequential laser data. Sensors 2013, 13, 1102–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; McElhinney, C.P.; Lewis, P.; McCarthy, T. Automated road markings extraction from mobile laser scanning data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 32, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppa, J.; Hyyppa, H.; Kukko, A. Retrieval Algorithms for Road Surface Modelling Using Laser-Based Mobile Mapping. Sensors 2008, 8, 5238–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargoum, S.A.; Karsten, L.; El-Basyouny, K.; Koch, J.C. Automated assessment of vertical clearance on highways scanned using mobile LiDAR technology. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gézero, L.; Antunes, C. Automated Road Curb Break Lines Extraction from Mobile LiDAR Point Clouds. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Lichti, D. Curb-based street floor extraction from mobile terrestrial lidar point cloud. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 39, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, H.; Wang, C. Automated Extraction of Urban Road Facilities Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Ming, C.; Cheng, W. Rapid inspection of pavement markings using mobile lidar point clouds. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B1, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J. A single-shot pose estimation approach for a 2D laser rangefinder. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 025105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, H.; DeRose, T.; Duchamp, T.; McDonald, J.; Stuetzle, W. Surface reconstruction from unorganized points. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, July 1992; Volume 26, pp. 71–78. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/133994.134011 (accessed on 10 March 2020).
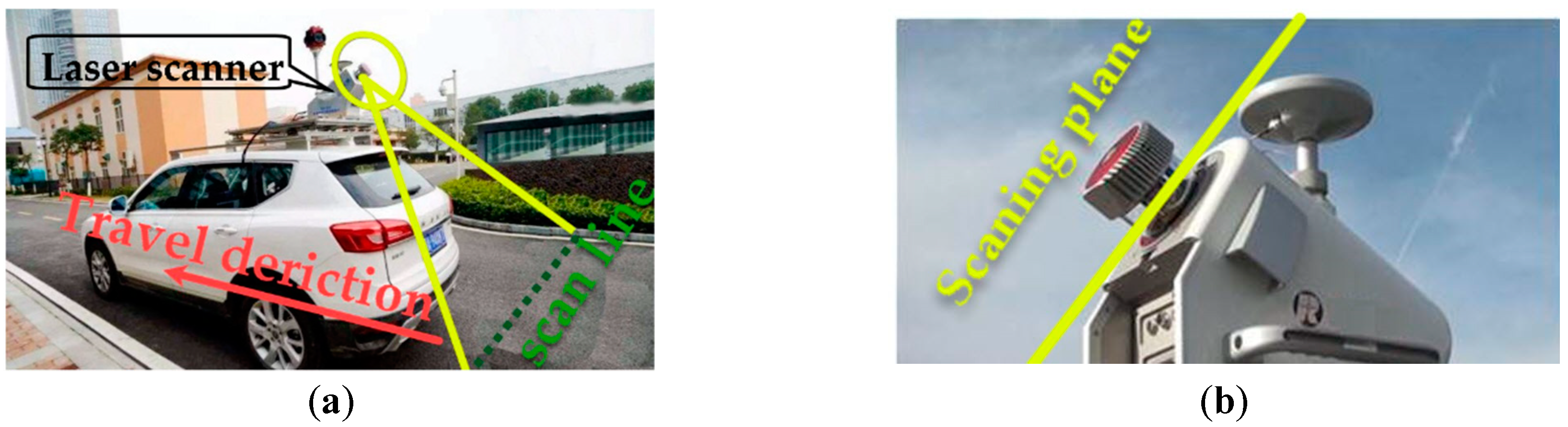





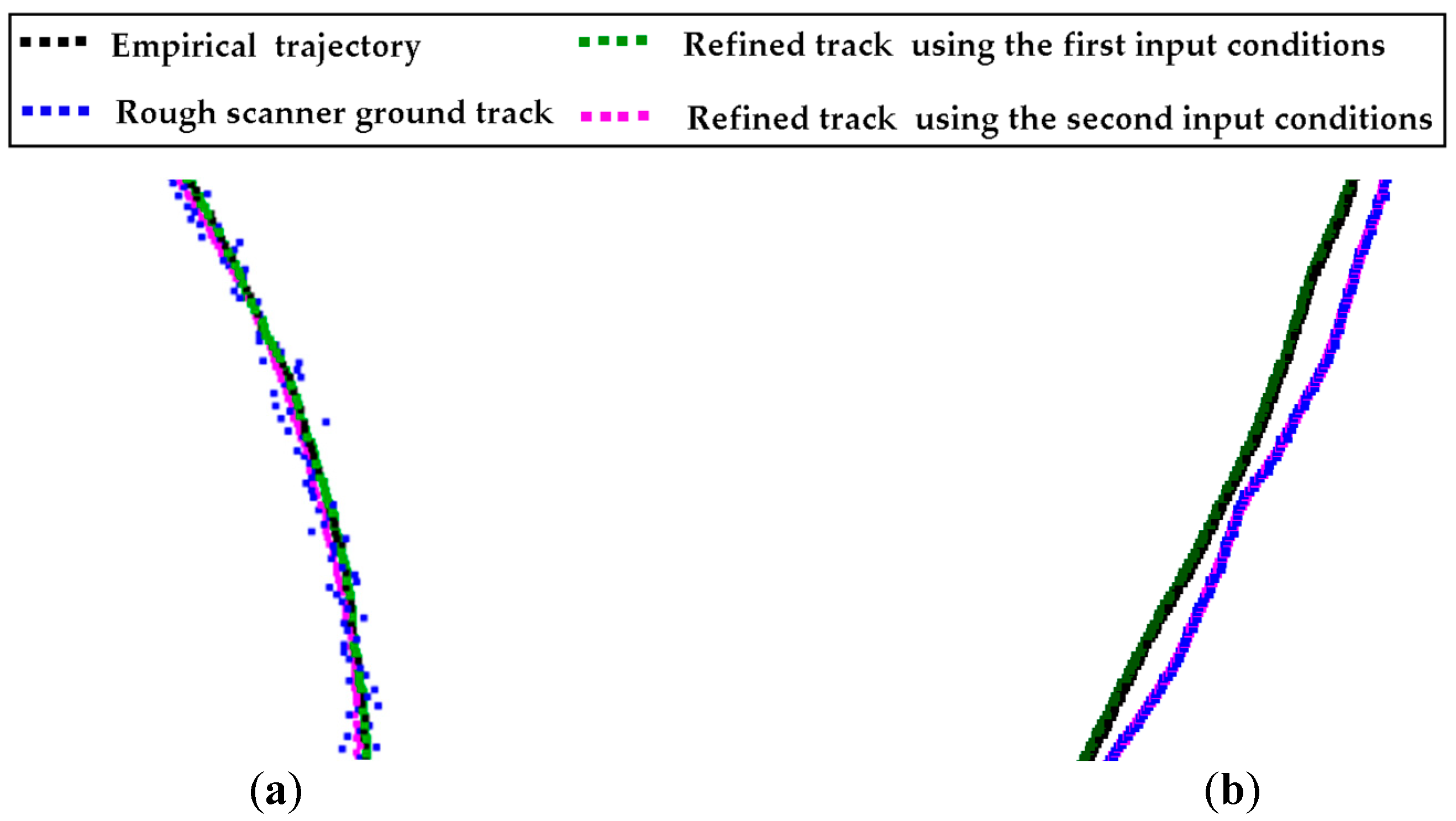
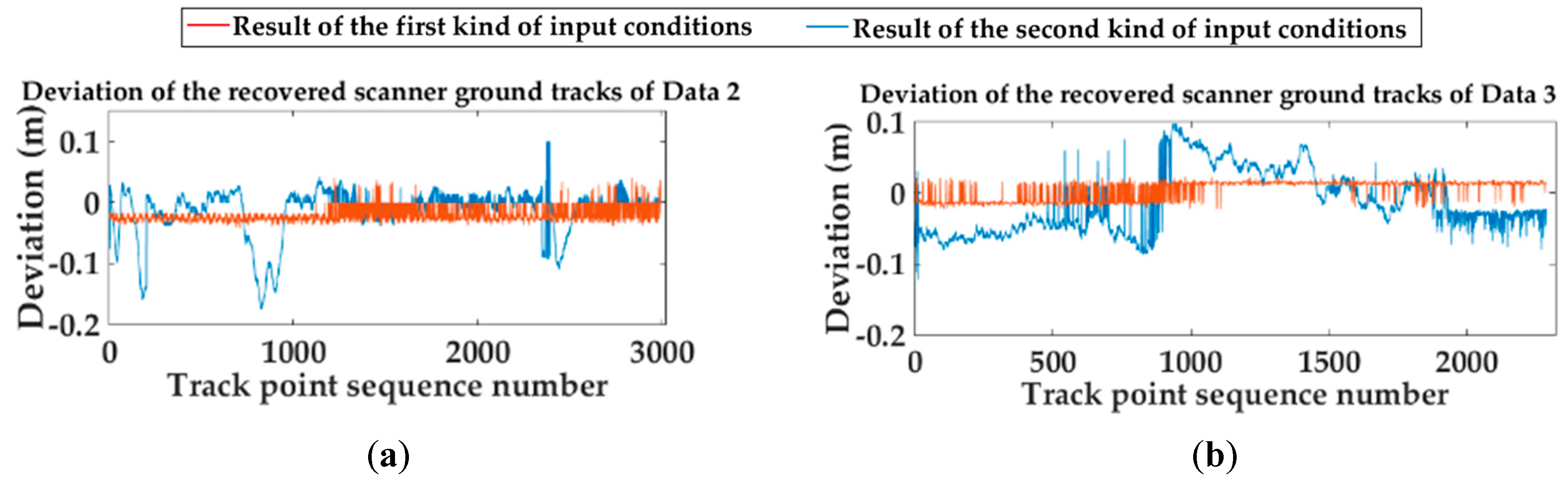
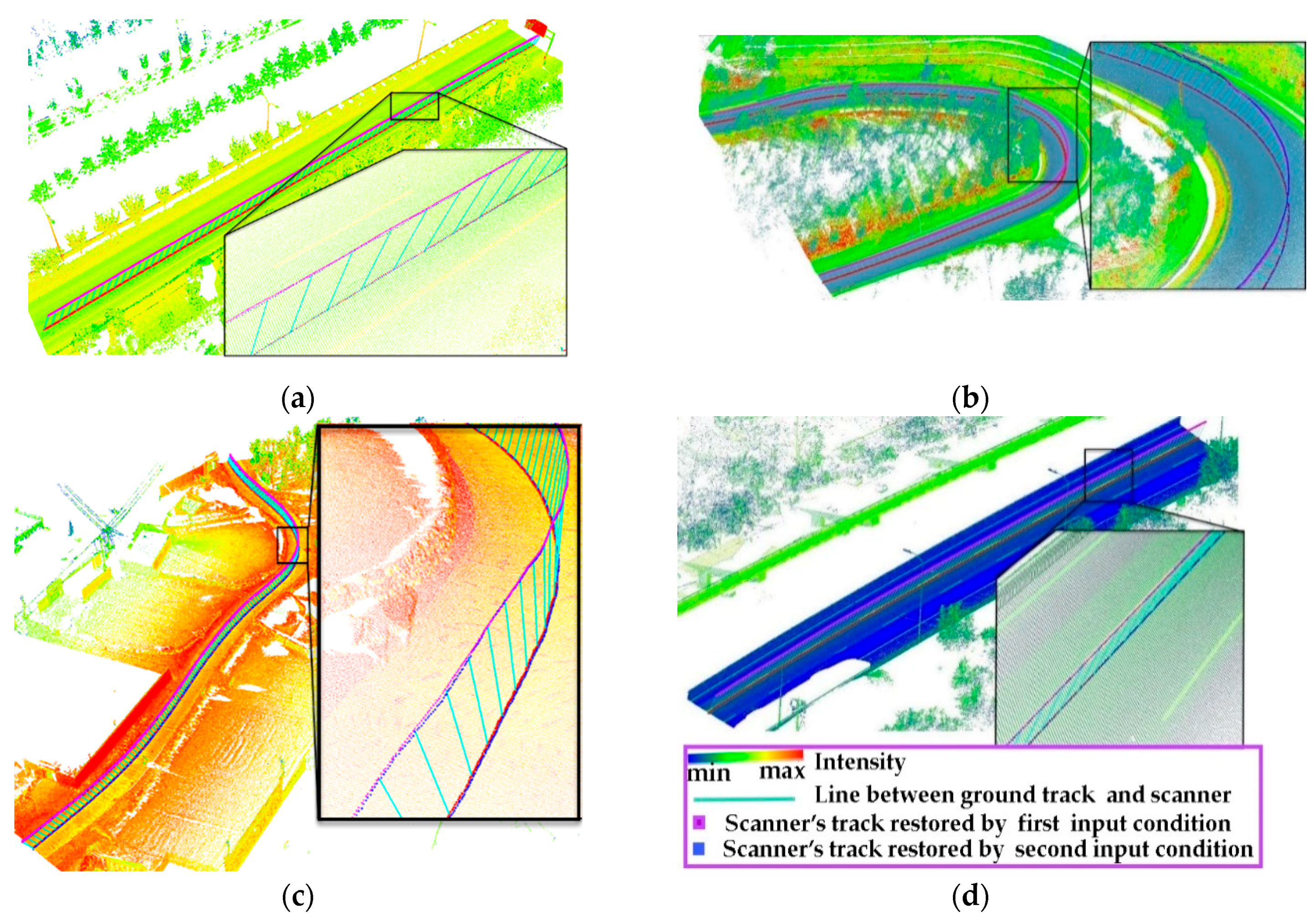
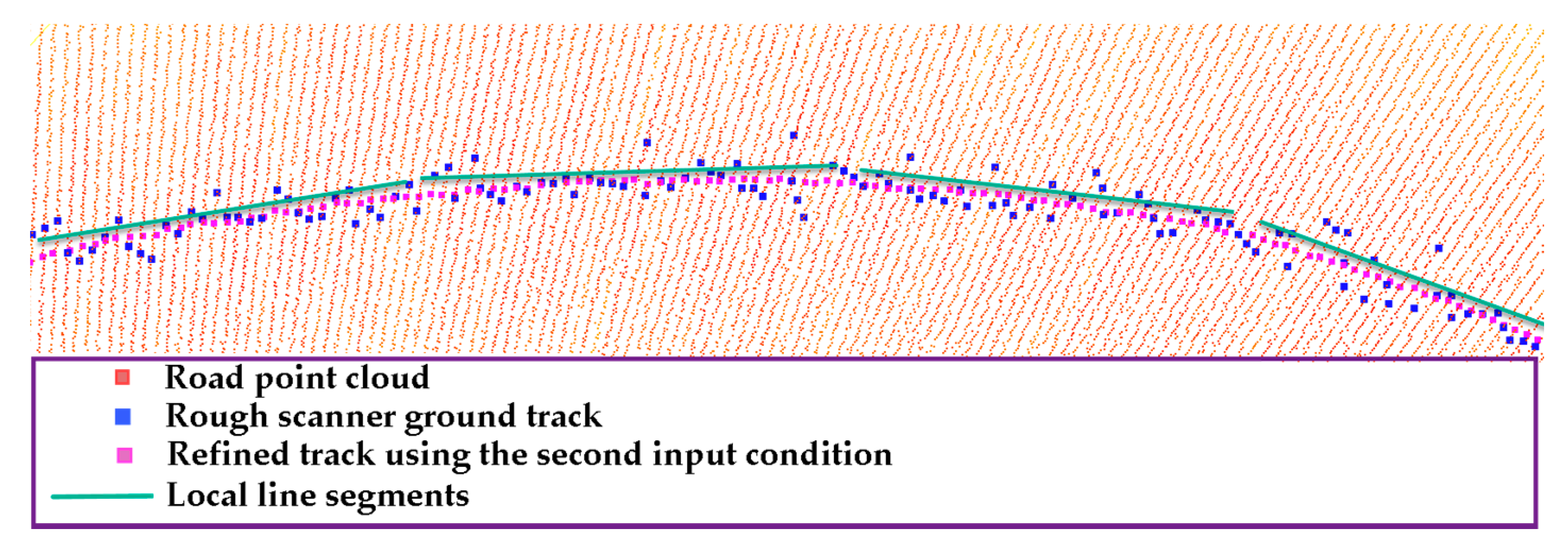

| Test Data | Site | Line Type | Road Surface Evenness | Road Slope (%) | Road Width (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1 | urban | straight | even 1 | H 3: 2, V 4: 3 | 8 |
| Data 2 | rural | curve | rough 2 | H: 3, V: 5 | 3.0–4.5 |
| Data 3 | winding | curve | rough | H: 8, V: 10 | 6.0 |
| Data 4 | viaduct | curve | even | H: 2, V: 2 | 10.0 |
| Test Data | Volume (Million Points) | Size (MB) | Road Length (m) | AS 1 (cm) | LS 2 (m) | PR 3 (%) | PM 4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1 | 2.8 | 172 | 115 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 73 | 0.01 |
| Data 2 | 3.6 | 235 | 120 | 0.9 | 0.11 | 60 | 0.05 |
| Data 3 | 3.2 | 324 | 140 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 70 | 0.10 |
| Data 4 | 2.1 | 217 | 130 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 87 | 5.14 |
| Test Data | Statistical Deviation | XY 1 (m) | Z 2 (m) | E 3 (m) | XY 4 (m) | Z 5 (m) | E 6 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1 | Maximum Average Variance | 0.034 | 0.093 | 0.094 | 0.103 | 0.141 | 0.151 |
| −0.003 | 0.031 | 0.031 | −0.008 | −0.089 | 0.089 | ||
| 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.016 | ||
| Data 2 | Maximum Average Variance | 0.103 | 0.112 | 0.117 | 0.171 | 0.214 | 0.230 |
| 0.026 | 0.039 | 0.041 | 0.033 | 0.040 | 0.046 | ||
| 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.045 | ||
| Data 3 | Maximum Average Variance | 0.055 | 0.107 | 0.102 | 0.157 | 0.149 | 0.171 |
| 0.006 | −0.012 | 0.013 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.032 | ||
| 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.015 | 0.018 | ||
| Data 4 | Maximum Average Variance | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.062 | 0.070 | 0.073 |
| −0.007 | 0.004 | 0.008 | −0.014 | 0.015 | 0.018 | ||
| 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, M.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, N. Recovering Missing Trajectory Data for Mobile Laser Scanning Systems. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060899
Zhong M, Sui L, Wang Z, Yang X, Zhang C, Chen N. Recovering Missing Trajectory Data for Mobile Laser Scanning Systems. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(6):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060899
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Mianqing, Lichun Sui, Zhihua Wang, Xiaomei Yang, Chuanshuai Zhang, and Nan Chen. 2020. "Recovering Missing Trajectory Data for Mobile Laser Scanning Systems" Remote Sensing 12, no. 6: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060899
APA StyleZhong, M., Sui, L., Wang, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, C., & Chen, N. (2020). Recovering Missing Trajectory Data for Mobile Laser Scanning Systems. Remote Sensing, 12(6), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060899








