Abstract
A cloud property retrieved from multispectral imagers having spectral channels in the shortwave infrared (SWIR) and/or midwave infrared (MWIR) is the cloud effective particle radius (CER), a radiatively relevant weighting of the cloud particle size distribution. The physical basis of the CER retrieval is the dependence of SWIR/MWIR cloud reflectance on the cloud particle single scattering albedo, which in turn depends on the complex index of refraction of bulk liquid water (or ice) in addition to the cloud particle size. There is a general consistency in the choice of the liquid water index of refraction by the cloud remote sensing community, largely due to the few available independent datasets and compilations. Here we examine the sensitivity of CER retrievals to the available laboratory index of refraction datasets in the SWIR and MWIR using the retrieval software package that produces NASA’s standard Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)/Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer suite (VIIRS) continuity cloud products. The sensitivity study incorporates two laboratory index of refraction datasets that include measurements at supercooled water temperatures, one in the SWIR and one in the MWIR. Neither has been broadly utilized in the cloud remote sensing community. It is shown that these two new datasets can significantly change CER retrievals (e.g., 1–2 µm) relative to common datasets used by the community. Further, index of refraction data for a 265 K water temperature gives more consistent retrievals between the two spectrally distinct 2.2 µm atmospheric window channels on MODIS and VIIRS. As a result, 265 K values from the SWIR and MWIR index of refraction datasets were adopted for use in the production version of the continuity cloud product. The results indicate the need to better understand temperature-dependent bulk water absorption and uncertainties in these spectral regions.
1. Introduction
Clouds are the strongest modulator of the Earth’s shortwave and longwave radiative budget with direct importance to the hydrological cycle. Their feedbacks in response to global warming are not well understood, either regionally or globally, constituting the largest source of inter-model uncertainty in climate sensitivity (e.g., [1,2,3]), in particular for low liquid water marine clouds [4,5]. Further, indirect forcing assessments that couple clouds with aerosol emissions remain highly uncertain, constituting the largest climatic radiative forcing component uncertainty [6]. Global cloud properties (extent, height, phase, optical properties and microphysics) and their spatial/temporal variation are essential for understanding processes, establishing and monitoring climatologies and model evaluation. In particular, the remote sensing of liquid water cloud effective particle radius (CER) from spaceborne and airborne multispectral imagers has been a vital tool for studying cloud-aerosol interactions and associated cloud radiative (e.g., [7]), water content (e.g., [8]), droplet concentration (e.g., [9]; review by [10]) and precipitation (e.g., [11,12]) sensitivities.
CER, the ratio of the third to second moment of the cloud particle size distribution, is fundamentally a radiative quantity as retrieved from imager spectral reflectance measurements in the shortwave infrared (SWIR) 1.6 and 2.2 µm and/or the midwave infrared (MWIR) 3.7 µm atmospheric windows. Development of liquid cloud CER retrieval algorithms goes back several decades (e.g., [13,14,15,16,17]). The physical basis is that relative to cloud reflectance in effectively non-absorbing visible (VIS) and near-infrared (NIR) spectral channels, the SWIR and MWIR cloud reflectance depends strongly on the non-unity cloud particle single scattering albedo (SSA). In turn, the SSA of a spherical liquid water droplet depends on both the droplet size and the imaginary index of refraction of bulk liquid water.
While a number of instrument and cloud radiative transfer modeling error sources can impact SWIR/MWIR CER retrieval uncertainties (summarized for the NASA Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) standard cloud product in [18] and references therein), the more fundamental source of error investigated here is the accuracy to which the complex index of refraction is known for liquid water over a useful range of atmospheric temperatures, including supercooled liquid cloud temperatures that are globally common (e.g., satellite studies of [19,20]). Such a study has not been reported in the literature.
As discussed in Section 2.2, uncertainties in laboratory index of refraction measurements and published compilations are difficult to quantify and vary greatly depending on the spectral range and the laboratory methodology. However, comparisons between independent laboratory measurements provide a useful constraint.
Within the operational satellite cloud remote sensing community, there is a general consistency in the choice of index of refraction datasets, largely due to the few available independent laboratory measurements and compilations to choose from, as well as for consistency with other retrieval teams. The commonly used datasets go back more than four decades [21,22,23,24]. Our study incorporates two more recent laboratory index of refraction datasets that apparently have not been used to date for global satellite retrievals (or at least not widely used and documented) and that include measurements at supercooled water temperatures. These datasets, one in the SWIR [25] and one that includes the MWIR [26], result in CER retrieval sensitivities of as much as 1–2 µm (Section 3.2), which is significant in the context of other retrieval error sources as discussed in that section as well as community requirements (e.g., [27,28,29]). Only fixed index of refraction datasets have been considered in this retrieval study, i.e., the use of cloud-top temperature retrievals to interpolate index of refraction datasets has not yet been investigated.
The study was largely motivated, as further discussed in Section 3.2, by the development of the NASA Aqua MODIS and Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) cloud continuity products (CLDPROP) continuity cloud product and the challenges encountered in achieving CER retrieval consistency in the spectrally mismatched 2.2 µm windows (central wavelengths at 2.13 µm for MODIS and 2.25 µm for VIIRS) when using the otherwise common algorithm and accounting for potential radiometric differences [30,31]. As a result of the study described here, the CLDPROP algorithms use the index of refraction datasets of [25] at 265 K for the SWIR channel cloud radiative models and, for consistency in the MWIR, the dataset of [26] interpolated to 265 K (from available tabulated data at 258 K and 269 K).
2. Datasets and Methodology
2.1. Overview of Satellite Imager Cloud Retrievals
Here we provide a brief overview of imager spectral cloud property information and CER retrieval physics, providing background for the complex index of refraction sensitivity study presented in Section 3.
For any single particle, SSA is the ratio of the scattering cross section to the total extinction cross section, ranging from unity for conservative scattering to <1 when absorption is present. For the atmospheric window spectral channels principally used for liquid water cloud optical and microphysical retrievals (see Table 1), only the SWIR and MWIR channels have significant droplet absorption for multiple scattering cloud problems (see Section 3.1), with the VIS and NIR multiple scattering being essentially conservative over typical liquid water cloud optical thickness (COT) ranges. As mentioned, CER retrievals are predominantly derived from droplet absorption, which is dependent on droplet size and the imaginary index of refraction of bulk liquid water, though the scattering phase function and directional scattering parameters (e.g., the asymmetry parameter (g)) also vary with droplet size. In comparison, conservative scattering in the VIS/NIR, with a dependence only on the real part of the index of refraction, has a relatively weak dependence on particles size through g and thereby has strong information content on total cloud layer extinction or COT. Therefore, measurements in two or more spectral channels taken from a combination of VIS/NIR and/or SWIR/MWIR provide information content for simultaneously retrieving CER and COT. Detailed descriptions of the physical basis of such retrievals are given in the Section 1 summary references. While CER and COT are coupled retrievals (though are mostly orthogonal for optically thick clouds), our interest in this study is in understanding CER retrieval sensitivity to the imaginary index of refraction. The MODIS standard and MODIS/VIIRS continuity cloud products provide separate two-channel CER retrievals for various combinations of VIS/NIR (VNIR) and/or SWIR/MWIR channels. Section 3.2 will discuss the three CER retrievals that come from the use of a VIS/NIR channel in combination with a 1.6, 2.2 and 3.7 µm atmospheric window channel.

Table 1.
Nominal central wavelength of common spectral channels used in satellite imager optical and microphysical remote sensing algorithms for liquid water clouds, and their instrument number designation (in parentheses), for Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer suite (VIIRS) and Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI). The shortwave infrared (SWIR) and midwave infrared (MWIR) channels have substantial droplet absorption with single scattering albedo (SSA) appreciably less than unity.
While Mie calculations are used for cloud liquid droplet (spherical particles) radiative transfer problems, analytic approximations are insightful. A simple but reasonably accurate analytic form for imager cloud remote sensing problems gives, at some wavelength λ, the co-single scattering albedo 1-SSA(λ) α(λ)*CER, where α(λ) is the bulk path absorption coefficient for liquid water in units of inverse distance [32]. Using the notation n + ik for the complex index of refraction, the spectral absorption coefficient can be written in terms of the imaginary index of refraction as α(λ) = 4πk(λ)/λ. Therefore, to the extent that a retrieved CER at some wavelength is largely determined from the measured (inferred) cloud droplet co-albedo divided by k, relative uncertainties in k map directly to relative uncertainties in the CER retrieval, i.e., .
The CER sensitivity to various index of refraction datasets is examined using optical property retrievals from the SWIR/MWIR spectral channels available on the Aqua MODIS [33,34] and SNPP VIIRS [35,36] imaging spectroradiometers. For completeness, Table 1 also includes spectral channels for the GOES-R series Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI), which encompasses related imagers used by the international operational community, that was developed to have spectral overlap with VIIRS for providing cloud properties [37].
This study uses version 1.1 of NASA’s MODIS/VIIRS continuity cloud optical property algorithm (product filename designation CLDPROP). This algorithm, publicly released in 2019, closely follows that of the NASA MODIS Collection 6.1 (C6.1) product (filenames MOD06 and MYD06 for MODIS Terra and Aqua, respectively [18]) but modifies the cloud mask and cloud-top property algorithms to use only the spectral channels that are common to the two imagers [31,38]. Cloud mask and optical property retrievals are, at nadir, 750 m for VIIRS (M-bands) and 1 km for MODIS (higher spatial resolution channels aggregated into a merged 1 km L1B file). CLDPROP Aqua MODIS [39] SNPP VIIRS files [40] are generated at the NASA Atmosphere Science Investigator-led Processing System (A-SIPS) at the University of Wisconsin and distributed from the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Level-1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (LAADS) [41]. Standard MOD/MYD06 cloud product files [42,43] are produced at MODAPS, a processing system associated with LAADS.
2.2. Index of Refraction Datasets
We begin with a summary of common index of refraction datasets used for CER retrievals in operational cloud products, followed by a short description of those and other datasets. The spectral and laboratory temperature(s) for the key datasets being discussed are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of liquid water complex index of refraction datasets examined in the study.
2.2.1. Index of Refraction Datasets Commonly Used in Cloud Microphysical Retrievals
The SWIR/MWIR wavelength-dependent liquid water complex refractive indices used in the MODIS standard cloud product algorithm [18] were taken from [23] (Palmer and Williams) for 1.0 < λ < 2.6 μm and [24] (Downing and Williams) for λ > 3.5 μm. The Community Cloud retrieval for Climate (CC4CL) product [45] uses the same datasets but partitions them differently (Palmer and Williams in the SWIR up to 2.0 μm and Downing and Williams for λ > 2.0 μm). A separate MODIS cloud product developed for use by the NASA Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) science team also uses Downing and Williams for CER retrievals in the 3.7 μm window channel [46]. The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) imager Pathfinder Atmosphere (PATMOS/PATMOS-x) product [47,48] uses Palmer and Williams from the NIR to 2.0 µm and then Downing and Williams for λ > 2.0 μm (personal communication). Other well-known CER satellite data records include the following, though we were unable to find published documentation for the SWIR/MWIR index of refraction datasets used in their production: AVHHR products from [49,50], along-track scanning radiometers (ATSR-2/AATSR) products [51], AVHRR and Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI) products from CM-SAF [52].
2.2.2. Discussion of Available Index of Refraction Datasets
While not cited above with respect to the SWIR/MWIR, the compilation of [22] (Hale and Querry) is well known and does include all spectral regions of interest in cloud remote sensing. It is used, for example, in the MODIS standard product [18] for VNIR spectral channels up to 1 µm that provide COT information for synergistic COT and CER retrievals. It is of relevance here because of the reliance of later SWIR/MWIR index of refraction datasets that made use of, or were compared with, the Hale and Querry compilation. In addition, it provides an excellent introductory review of the history and state of laboratory measurements up to that point, including the still cited paper by [21] (Irvine and Pollack, said to have been itself a compilation of 30 publications in the literature in addition to analysis of published laboratory near-normal reflectance measurements). The compilation’s optical constant data in the SWIR spectral region were taken primarily from [53] (Collins), [54] (Curcio and Petty, laboratory measurements at 20 C) and [55,56] (at 25 C according to Hale and Querry). In the MWIR and through the thermal IR, Hale and Querry note that the better datasets seemed to be those from [56,57] (Robertson and Williams).
Palmer and Williams reported on their 27 C laboratory measurements, using spectral reflectance measurements from a liquid water-air interface to infer the real part of the index of refraction (n) and transmittance measurements through a range of quartz cell path lengths to determine the absorption coefficient (α) and the imaginary part of the index of refraction (k). Their measurements covered the spectral range 0.36–2.67 µm. The representative absorption standard deviation was graphically included for a couple of spectral regions as a metric for uncertainty. These standard deviations are difficult to read from the plots but are said to be “fairly small” in the 2 µm spectral region. By comparison, a plot of their measurements for the water absorption minimum at about 2.2 µm appear to be up to 20% larger than points taken from Hale and Querry and Irvine and Pollack, though absorption at spectrally adjacent, and more absorbing, wavelengths look to be in close agreement. Agreement between the three datasets appears to be within 10% or better for the 1.6 µm absorption minimum, with Palmer and Williams once again finding larger absorption relative to the earlier two datasets (see their Figure 3).
Downing and Williams revisited several of the previous water optical constant publications with the intent of providing recommendations for atmospheric studies. The main datasets examined were earlier works mostly associated with the same experimenters: Robertson and Williams, [58] and Hale and Querry. For the imaginary index of refraction in the SWIR and MWIR, Downing and Williams appear to have relied on the absorption measurements of Robertson and Williams, which is consistent with a statement given in [59] (Bertie and Lan) in referring to the Downing and Williams dataset. The Robertson and Williams measurements were, once again, said to be made at approximately 27 °C. The uncertainty in k between various analysis approaches used by Downing and Williams generally appear to be quite small in the MWIR atmospheric window but are not able to be quantified (see their Figure 1). However, for comparison, the broad spectral water absorption measurements at 25 °C of Bertie and Lan included the 3.57–4.3 µm spectral region; they state that their measurements in that region are within 4% of those reported by Downing and Williams.
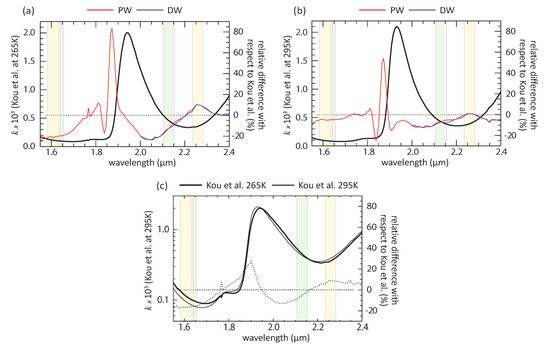
Figure 1.
Liquid water spectral imaginary index of refraction (k) from three data sources from the 1.6 through 2.2 µm SWIR atmospheric windows. The imaginary index of refraction is shown on the left ordinate by the thick black line for Kou et al. at laboratory temperatures of (a) 265 K and (b) 295 K. The percent difference relative to Kou et al. for the Palmer and Williams (PW) and Downing and Williams (DW) datasets, both for a nominal 300 K temperature, are shown on the right ordinate. The nominal half-power bandpasses for the relevant MODIS (green shading) and VIIRS (yellow) channels are also shown. The two Kou et al. datasets and their relative difference (dashed line) are shown in (c).
Both the accuracy of the laboratory spectral SWIR/MWIR absorption measurements (typically at a fixed temperature) and the temperature-dependence of that absorption are relevant to cloud retrieval problems where a significant fraction of liquid water cloud observations occur at a range of temperatures including supercooled temperatures potentially as low as the homogenous water freezing temperature of about 235 K (e.g., satellite studies of [19,20]). The datasets discussed above make use of laboratory measurements that were nominally performed at room temperature.
A number of studies examined the temperature sensitivity of water optical constants at warm temperatures (>0 °C). Curcio and Petty cited the measurements of Collins, noting that, when the temperature was raised to 95 °C, the absorption intensity in the major NIR/SWIR absorbing bands increased while the band spectral locations shifted to slightly shorter wavelengths. Reference [60] measured temperature dependencies from 2 µm through the thermal infrared at temperatures of 5 °C, 27 °C and 70 °C; their discussion, focusing on the absorbing bands (as opposed to window bands used in cloud retrievals), noted various shifts in the absorption band spectral locations as well as intensity in the infrared. In a similar spectral range, Reference [61] looked at optical constants for several temperatures from 1–50 °C, focusing on the major absorption regions and offering molecular interpretations for their results (e.g., explanation for decreasing absorption with temperature in the 2.9 µm band). Reference [62] made measurements in similar spectral ranges and temperatures to parameterize temperature sensitivities to isotopic concentration. More recently, the measurements of [44] (Zasetsky et al.) confirmed that supercooled (down to 243 K) water droplet extinction and absorption in the 6000 to 450 cm−1 (about 1.6–22 µm) spectral region was significantly different than at room temperature, and were able to attribute the cause to the increasing fraction of small low density molecular clusters at colder temperatures.
Using their own laboratory transmittance measurements in the 0.67–2.5 µm spectral range, Reference [25] (Kou et al.) reported values of the imaginary part of the refractive index at a single supercooled liquid water temperature of −8 °C (an average) as well as at 22 °C. They also reported k for ice at T = −25 °C in the 1.45–2.5 µm spectral range. It is worth noting that the main goal of the study was to reduce the relatively large uncertainty in ice spectral absorption and that, assuming k for the liquid phase was relatively accurately known from earlier studies, liquid water measurements were performed as a reference to test their laboratory equipment. Regardless, their supercooled −8 °C liquid water measurements were unique in the literature. Different transmittance path lengths were used to obtain spectral absorptance in the 15%–80% range as well as check for consistency. Along with spectral tables of k, the measurement error in obtaining k, using both the absorptance standard deviation and the path length uncertainty, was also provided and typically in the 1%–3% range in the SWIR. Tabular spectral resolution in the SWIR atmospheric windows is about 5–10 nm.
The Kou et al. supercooled liquid water k spectrum is similar to the 22 °C spectrum, but with absorbing features shifted to longer wavelengths by roughly 1–20 nm. Figure 1b shows the Kou et al. 22 °C (295 K) k spectrum to be fairly similar to the 27 °C (300 K) values given in Palmer and Williams and Downing and Williams (shown as differences relative to Kou et al.). As mentioned earlier, the MODIS standard cloud retrieval algorithm [18] uses the Palmer and Williams dataset for these channels. Differences in the window regions used for cloud remote sensing problems (shaded regions) range from about −5% in the 1.64 µm MODIS and VIIRS channels to −10% in the MODIS 2.13 µm channel, and with very little difference in the 2.25 µm VIIRS channel. Figure 1a shows the same plot but using the Kou et al. −8 °C (265 K) k spectrum; here the differences are more significant, ranging from about −20% in the 1.64 µm and 2.13 µm channels, to +10% in the 2.25 µm channel. As noted in Section 2.1, relative differences in k roughly map into relative differences in CER. Note that Bertie and Lan recommend the Kou et al. dataset for this spectral region, stating that the error in the k values was unlikely to exceed 4%. Figure 1c shows that a negative spectral shift in the band absorption features at the warmer temperature is a crucial consequence of the temperature dependence.
With relevance to MWIR cloud retrievals, Zasetsky et al. and [26] (Wagner et al.) both reported temperature-dependent spectral index of refraction using extinction measurements for a distribution of water droplets. The Wagner et al. spectral extinction measurements (2.2–9.0 µm) were made in the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Aerosol Interaction and Dynamics in the Atmosphere (AIDA) expansion chamber. At supercooled chamber temperatures of 238, 252, 258 and 269 K, the droplet spectral index of refraction was adjusted to fit measurements to Mie calculations starting with values from Bertie and Lan. The iterative Mie methodology includes simultaneously solving for parameters of an analytic size distribution, as well as iterations on n using the Kramer–Kronig integral transform. Since chamber extinction measurements are made for a droplet distribution using an inversion that matches measurements to Mie calculations, the methodology is inherently similar to satellite cloud retrieval algorithms (Section 3). The Zasetsky et al. droplet extinction measurements (2.5–22 µm) were made at 240, 253, 263 and 273 K using a cryogenic flow tube, also with an iterative inversion method based on Mie scattering (also using Bertie and Lan as a first guess, though with a different iterative approach than that used by Wagner et al.). The technique used to produce these two datasets can be considered as providing an in situ inference of the index of refraction that is directly applicable to cloud droplet remote sensing problems; on the other hand, the technique is not independent of theoretical assumptions and radiative transfer tools used in cloud retrieval algorithms. A comparison of the results from the two datasets is given in Wagner et al. and, for the scales shown in their comparison plots, indicated generally good agreement across the spectrum for similar temperatures.
However, Figure 2 shows the Wagner et al. 269 K k spectrum compared with Downing and Williams used by the MODIS standard cloud retrieval algorithm [18] as well as the Zasetsky et al. 263 K dataset (both shown as differences relative to Wagner et al.). In the MODIS and VIIRS channels (green and yellow shading, respectively), Downing and Williams is about 10% larger than Wagner et al. while Zasetsky et al. is well outside either of the other two in the window region (e.g., over 200% larger than Wagner et al. at 3.8 µm). While the Wagner et al. data do not sufficiently cover the 2.2 µm atmospheric window to be useful for cloud retrievals, it should be noted that their reported k values match well with Kou et al. at 2.2 µm yet are twice as large as Kou et al. at 2.3 µm.
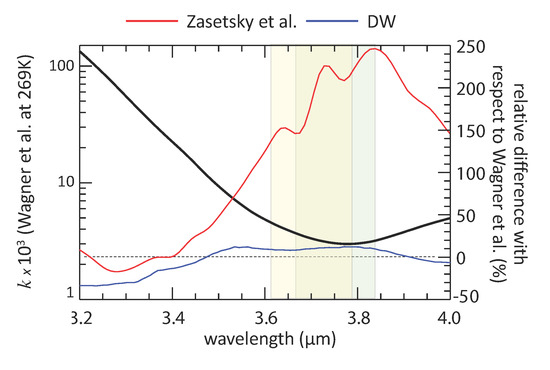
Figure 2.
Similar to Figure 1 but for the 3.7 µm MWIR atmospheric window and the Wagner et al. 269 K dataset. Differences in k relative to Wagner et al. are shown for the datasets of DW at 300 K and Zasetsky et al. at 263 K. The nominal half-power bandpasses for the most relevant MODIS (green shading) and VIIRS (yellow, [35]) channels are also shown.
While, to our knowledge, operational CER imager retrievals have not made use of these relatively recent datasets, there has been some radiative and retrieval work done with them. Using the measurements of Zasetsky et al. and Wagner et al. [63] examined the impact on longwave radiative flux calculations of the complex index of refraction of liquid water at supercooled temperatures relative to the Downing and Williams dataset, as well as the impact on downwelling longwave ice cloud retrieval errors from supercooled water. Moreover, with an emphasis on radiative flux calculations, [64] compiled a temperature-dependent complex index of refraction dataset using sources discussed in this section for wavelengths up to about 22 µm. Reference [65] used the Kou et al. dataset for cloud thermodynamic phase detection from Hyperion, a hyperspectral imaging spectrometer that flew on NASA’s EO-1 satellite.
3. Results
As previously discussed, CER retrievals for cloud multiple scattering problems are predominantly derived from particle size distribution absorption information and, to a lesser extent, the asymmetry parameter. Both quantities spectrally vary with droplet size and the imaginary index of refraction of bulk water. Here we show the sensitivity of liquid water scattering properties in the relevant MODIS and VIIRS effective radius retrieval channels to the candidate index of refraction datasets discussed in Section 2, along with the resulting temporally/spatially gridded cloud droplet retrieval sensitivities for both sensors.
3.1. Cloud Droplet Single Scattering Properties
Mie calculations of droplet single scattering co-albedo (1-SSA) as a function of CER are shown in Figure 3. Calculations at each CER are made using a modified gamma droplet size distribution with an effective variance of 0.10, consistent with the forward modeling assumption in the NASA MODIS and VIIRS cloud algorithms [18,31]. The dashed lines in each panel represent the index of refraction dataset used in the MODIS standard cloud product algorithm, while the two solid lines indicate candidate datasets examined in detail in this study. The thick solid lines are the supercooled (265 K) temperature datasets adopted for the MODIS/VIIRS cloud continuity optical property algorithm as shown in Section 3.2 [31], with the exception that the MWIR scattering properties are shown for the 269 K laboratory measurements (for comparison with Figure 2) instead of a 265 K interpolated value. While the plots provide a CER lower limit of 2 µm, the retrieval algorithms of Section 3 (and all CLDPROP and MYD06 production code) reject droplet retrievals less than 4 µm.
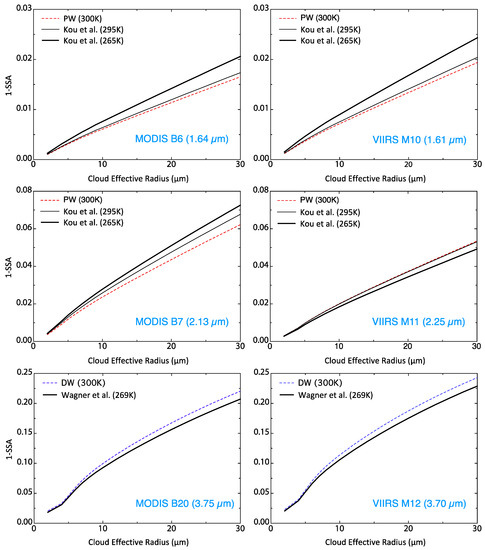
Figure 3.
MODIS (left column) and VIIRS (right column) SWIR and MWIR channels droplet co-albedo (1-SSA) versus effective radius for the index of refraction datasets used in the retrieval sensitivity studies of Section 3.2. PW and DW represent the datasets of Palmer and Williams and Downing and Williams, respectively, used in the MODIS standard cloud optical product. The thick solid line represents the dataset adopted for the MODIS/VIIRS cloud continuity product.
As an example, the figure shows that the MODIS 2.13 µm channel co-albedo for a 10 µm droplet CER varies from 0.024 (Palmer and Williams) to 0.028 (Kou et al. at 265 K) which is significant, especially for multiple scattering cloud problems. To appreciate this significance graphically, if the optical thickness is known from a VIS/NIR spectral channel, the CER retrieval from a SWIR/MWIR reflectance measurement is primarily a retrieval of droplet absorption in the channel. Therefore, if a 10 µm CER is retrieved from the MODIS 2.13 µm channel using the Palmer and Williams dataset—as is done in the MODIS standard cloud product—Figure 3 indicates that the Kou et al. 265 K dataset would give a CER almost 2 µm smaller (i.e., the CER corresponding to the location where a co-albedo of 0.24 intersects the thick Kou et al. line). This graphical result is consistent with (see Section 2.1) which gives a CER reduction of 1.7 µm. However, the opposite sensitivity occurs for the VIIRS 2.25 µm channel, where the Kou et al. 265 K dataset would result in a CER about 1 µm larger then when using the Palmer and Williams dataset. As will be shown in Section 3.2, the large MODIS liquid water CER bias relative to VIIRS in these 2.2 µm window channels when using the Palmer and Williams dataset is greatly reduced with Kou et al. at 265 K. With the exception of the MODIS 2.13 µm channel, the Palmer and Williams 300 K SWIR dataset gives co-albedos reasonably consistent with the Kou et al. 295 K dataset which is closest in temperature.
Because of the closer spectral correspondence between MODIS and VIIRS in the 1.6 and 3.7 µm channels, in addition to the relatively small gradient in k in these spectral regions (Figure 1 and Figure 2), changes in the MODIS and VIIRS CER for Kou et al. or Wagner et al. compared with the MODIS standard algorithm datasets are all of the same sign and act to decrease (increase) CER retrievals in the 1.6 µm (3.7 µm) channels. As a result, CER retrieval differences between the sensors in each of these two window channels will be similar regardless of which of the two datasets is used. However, resulting intra-sensor channel-to-channel CER changes can be substantial between the datasets. Note that other radiative modeling error sources that can contribute to spectral CER differences are discussed in [31] (see Section 4), including sensor radiometric calibration biases and cloud microphysical vertical heterogeneity.
Since the upper temperature reported by Wagner et al. was limited to 269 K, it is not clear whether the methodology at room temperature would have yielded results consistent with Downing and Williams. Note that the Zasetsky et al. dataset gives co-albedos in the 3.7 µm spectral region that are much larger than both Wagner et al. or Downing and Williams (about a factor of two larger over much of the CER space). Being such a significant outlier, the dataset was not further investigated for use in this study.
Changes in asymmetry parameter with index of refraction dataset will also affect the cloud reflectance and therefore, if significant, would need to be considered in the above interpretation. However, g differences were found to be insignificant in the MODIS 1.64 and 2.13 µm channels (changes of about 0.04% and 0.1%, respectively, for a 10 µm CER). Even in the 3.7 µm spectral region (Figure 4), the g sensitivity to index of refraction is quite small (0.5% for a 10 µm CER, though as large as about 1.6% at 4 µm). Regardless, the slight decrease in g for the Wagner et al. dataset shown in Figure 4 acts to increase reflectance in the MWIR channels, as does the decrease in absorption (bottom row of Figure 3), with both sensitivities acting together to increase CER retrievals relative to the standard product’s Downing and Williams dataset.
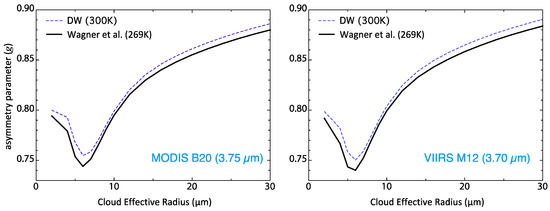
Figure 4.
Same as Figure 3 but for the MWIR channel droplet asymmetry parameter.
3.2. Cloud Effective Radius Retrievals
All VIIRS retrievals discussed below include the SWIR relative radiometric adjustments discussed in [30]. However, the impact of the adjustments in those channels (2%–3%) were found to be relatively small compared with the index of refraction dataset choices discussed in this section. The VIIRS and MODIS continuity algorithm sensitivity runs for the results of this section, both pixel-level (Level-2) and 1° gridded monthly aggregations (Level-3) [66], were generated at the A-SIPS to ensure consistency with production code. That consistency includes Level-3 VIIRS aggregations being limited to the narrower MODIS view geometry swath and the restoral of VIIRS onboard bow-tie pixel deletion to provide similar pixel sampling. Since the MODIS and VIIRS 2.2 µm atmospheric window spectral locations are distinctly different, collectively they are referred to below as the 2.x µm channels when useful for simplifying the narrative.
The cloud optical retrieval algorithm makes use of pre-computed lookup tables (LUTs) of cloud bidirectional reflectance and, for the MWIR, emissivity for various surfaces and solar/view geometries across the CER and COT solution space. To simplify the cloud retrieval sensitivity discussion, the following terminology is used to differentiate the SWIR and MWIR index of refraction datasets examined: 265 K LUTs (calculations using the datasets of Kou et al. at 265 K and Wagner et al. interpolated to 265 K, respectively) and 300 K LUTs (calculations using the datasets of Palmer and Williams and Downing and Williams, respectively). As a reminder, while the 300 K LUTs are used in the MODIS standard product (MYD06), the 265 K LUTs were chosen for the publicly available VIIRS and MODIS CLDPROP. This choice will be discussed in Section 4.
While the Wagner et al. MWIR dataset does include the full complex index of refraction, the real part of the index of refraction is not reported in the SWIR measurements of Kou et al. Therefore, we defaulted to using n(λ) from Palmer and Williams in the results that follow. Published values of n given in Palmer and Williams, Downing and Williams and Wagner et al. for the imager SWIR channels indicate that absolute differences are no greater than about 0.005 (maximum in the VIIRS 2.25 µm channel for Wagner et al. interpolated to 265 K versus Palmer and Williams at 300 K). Sensitivity tests using a difference in n of 0.005 for that 2.25 µm channel show that the impact on co-albedo is minimal (<1% for CER>5 µm and <0.5% for CER > 10 µm) compared to changes in k between the evaluated datasets in Figure 3 (middle, right hand panel). Though larger impacts from defaulting to n from Palmer and Williams cannot be ruled out, it is highly likely that this assumption has no effect on the overall results or conclusions from this study.
Without consideration of which index of refraction dataset is most correct for a given spectral channel and cloud temperature, it is useful first to examine LUT retrieval sensitivities and how they compare to other CER retrieval error sources. Figure 5 shows gridded CER retrieval sensitivities for February 2014. Retrievals for northern polar latitudes are not available since these microphysical cloud algorithms are daytime only. The left column is the retrieved CER for the VIIRS v1.1 continuity cloud product production version (265 K LUTs) minus the CER from the same VIIRS algorithm but using LUTs consistent with the MODIS standard product (300 K LUTs). The right column is the same sensitivity test but for MODIS, i.e., MODIS v1.1 CER (265 K LUTs) minus MODIS v1.1 CER (300 K LUTs). The corresponding ±60° latitude area-weighted means and their differences are shown in Figure 6 for land and ocean scenes separately since liquid water cloud properties vary between the two regimes (e.g., [67]). As expected from Figure 3, changes in the 2.x µm channel CER retrievals for VIIRS and MODIS continuity algorithms are in opposite directions since the two sensors have their channel located on different sides of the k sensitivity curves (Figure 1a). The 265 K LUTS reduce the overall difference in the VIIRS and MODIS CER means to 0.25 µm (land) and 0.02 µm (ocean), respectively. Some regional dependences are seen, especially for tropical 3.7 µm differences. This demonstrates, along with the right column images of Figure 7 and Figure 8 (discussed later), the critical need for having common radiative transfer model assumptions when endeavoring to achieve inter-sensor product continuity.
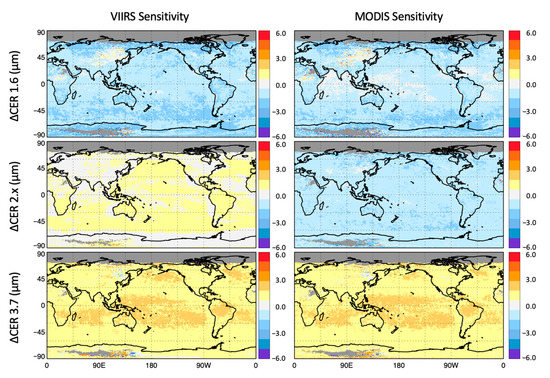
Figure 5.
Differences in gridded cloud effective particle radius (CER) for February 2014. Left column is VIIRS v1.1 cloud continuity algorithm CERs, with lookup tables (LUTs) computed from the 265 K index of refraction datasets, minus CER from the VIIRS v1.1 algorithm using the 300 K LUTs. Right column is MODIS v1.1 CERs using the 265 K LUTS minus MODIS v1.1 using 300 K LUTS.
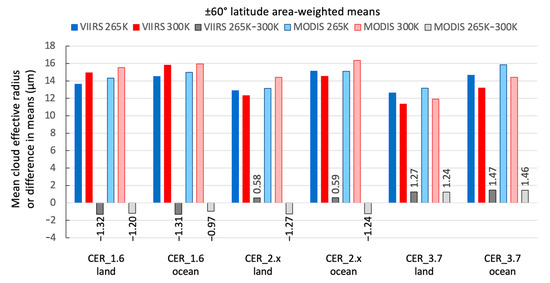
Figure 6.
Calculated ±60° latitude mean CER from Figure 5 for the 265 K (blue) and 300 K (red) LUTs, and differences (gray shading with value labels). Means for VIIRS (dark red/blue shading) and MODIS (light shading) are given for each SWIR/MWIR retrieval categorized by land and ocean scenes.
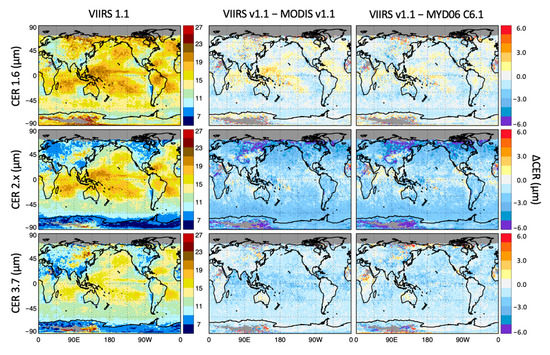
Figure 7.
Comparison of February 2014 gridded (1°) mean spectral CER retrievals from Aqua MODIS and Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP) VIIRS using the same SWIR and MWIR index of refractions datasets as in the MODIS standard cloud optical property algorithm for all images (i.e., 300 K LUTs, see text for details). Mean CER for the VIIRS continuity algorithm (equivalent to version 1.1 other than index of refraction dataset choices) are shown in the left column. CER differences are shown between VIIRS and the corresponding MODIS continuity means (middle), and between VIIRS and the standard MODIS C6.1 Level-3 product MYD08 (right).
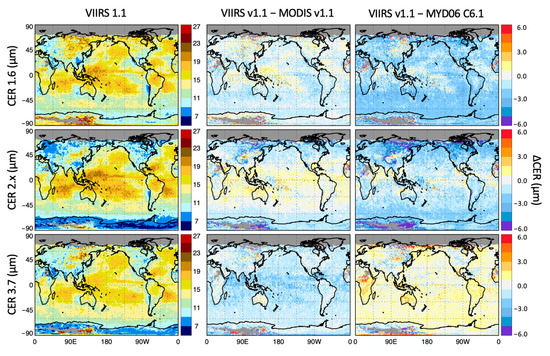
Figure 8.
Same as Figure 7 but for the Kou et al. and Wagner et al. index of refraction datasets used in the publicly released version 1.1. VIIRS and MODIS continuity property algorithm. Note the smaller middle panel differences for the SWIR retrievals.
Cloud optical property retrieval uncertainties for several error sources (measurement and model) are calculated as part of the retrieval code as discussed in [18]. MYD06 liquid water cloud CER daily aggregated uncertainties (assuming unity correlation for error sources within a 1° grid) are typically in the 5%–15% (or about 1–2 µm) range for low clouds during February [68], though there are strong dependencies on other cloud properties, solar and view angle geometry, surface type, etc. Generally speaking, index of refraction differences map into retrieval uncertainties that are of the same magnitude as other collective error sources currently considered in the MODIS and VIIRS products.
Figure 7 shows global gridded mean spectral CER retrievals and differences for February 2014 using 300 K LUTs for the VIIRS and MODIS continuity algorithm (version 1.1) as well as for the archived C6.1 MYD06 product. This quantifies the ability to provide continuity between the sensors if the standard MODIS cloud product index of refraction datasets had continued to be used. The most substantial VIIRS minus MODIS CER differences (middle and right column images) occur for the 2.x µm channels (i.e., 2.13 and 2.25 µm for MODIS and VIIRS, respectively) with differences typically about −2 to −3 µm. It was this discrepancy that provided the impetus for investigating alternate index of refraction datasets, i.e., it was readily apparent (e.g., Figure 3) that use of the 265 K Kou et al. data for forward radiative cloud calculations in this spectral region would increase VIIRS CER retrievals (due to larger droplet absorption) while reducing the MODIS retrievals (smaller absorption), thereby reducing the strong VIIRS minus MODIS bias. The lesson learned is that forward model deficiencies are brought into stark relief when pressed into the service of providing retrieval closure/consistency over wavelengths where scattering/absorption properties change significantly. The 1.6 and 3.7 µm channel retrieval differences are also significant but to a lesser extent. Since the same index of refraction datasets are used for all retrievals, similar differences seen between VIIRS and both MODIS algorithms indicate that the differences are not dominated by algorithm implementation discrepancies between the sensor codes.
To filter for higher quality retrievals, the pixel aggregations of Figure 7 and subsequent results do not include successful retrievals for pixels that are identified as partly cloudy (PCL) by the algorithm’s clear sky restoral module [18]. Note that the MYD06 algorithm uses a 250 m cloud mask test as part of the PCL determination over maritime scenes in addition to cloud edge detection that is the only test used in the continuity algorithms [31]. As a result, the pixel population in MYD06 is slightly smaller than for either the MODIS or VIIRS continuity population. In addition, cloud masking and related cloud edge detection is dependent on sensor pixel field-of-view which can be substantially different between VIIRS M-band and MODIS as sensor view angle increases [35,69]. Despite the somewhat different pixel populations, in practice the results of Figure 7 and subsequent figures were not noticeably sensitive to PCL filtering, e.g., VIIRS minus MODIS continuity CER differences are only slightly larger over some ocean regions when including the PCL population.
Figure 8 shows the same set of images as Figure 7 but using 265 K LUTs for the v1.1 continuity algorithms only (identical to files publicly available in the LAADS archive). As expected, the Kou et al. dataset results in a significant decrease in the MODIS 2.13 µm CER retrieval along with a smaller increase in the VIIRS 2.25 µm channel, thereby reducing the differences seen in Figure 7 for both the MODIS continuity and standard algorithm. Changes in the CER differences in the 1.6 µm and 3.7 µm channels for the associated middle images are small relative to Figure 7 because the changes in k between the index of refraction datasets in the two figures are similar (both sign and magnitude), though differences between VIIRS and MYD06 (right column) are now more substantial. Overall, these alternate index of refraction datasets provide better CER agreement (middle column) across the two sensors compared with the datasets used in the MODIS standard algorithm (middle column, Figure 7). The area-weighted means over ±60° latitude calculated from the gridded results of Figure 8 are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Area-weighted ±60° latitude mean CER and differences in means for the panels of Figure 8, separated by land and ocean scenes.
4. Discussion
As seen in Figure 3, the Palmer and Williams 300 K dataset used for the MODIS standard algorithm SWIR channels gives co-albedos very close to that of Kou et al. 295 K (closest in temperature) for the 1.6 µm channels and the VIIRS 2.25 µm channel. However, the MODIS 2.13 µm channel co-albedo is significantly larger at 295 K compared with Palmer and Williams, but not enough to reduce the overall global CER difference achieved from the Kou et al. 265 K dataset that results in even larger co-albedos [31]. Recognizing the CER retrieval sensitivity to temperature, and based on the improvements shown (Figure 8 and Table 3) and the results in Figure 9 below, the 265 K datasets were chosen for use in the continuity algorithm SWIR retrievals. While not all liquid water radiative cloud tops are at 265 K, it is a reasonable global choice (e.g., Figure 9 and [20]) and much more defensible than using index of refraction datasets from room temperature measurements.
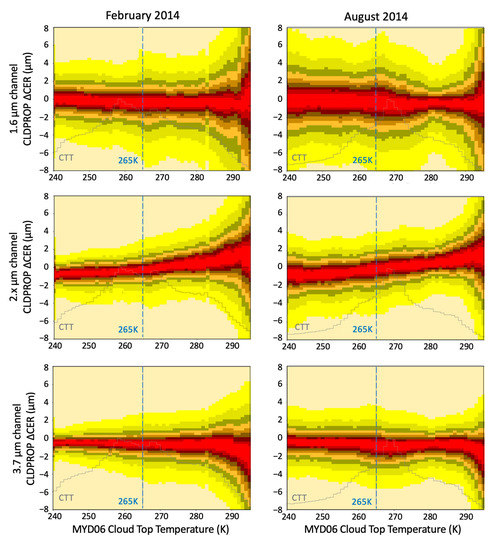
Figure 9.
Monthly distribution of cloud continuity products (CLDPROP) v1.1 liquid water spectral CER VIIRS minus MODIS differences for February 2014 (left column) and August 2014 (right). Each cloud-top temperature (CTT) bin is normalized to its maximum count. The 265 K temperature corresponding the index of refraction datasets used in the CLDPROP algorithms are shown as a reference. The CTT distribution (solid gray line) is taken from the MODIS standard product (MYD06) which was available in the merged files used for the analysis (see text for details).
For temperature consistency with the SWIR, the Wagner et al. dataset interpolated to 265 K was also chosen for the MWIR 3.7 µm retrievals instead of the room temperature Downing and Williams dataset. However, as already mentioned, there is no means for assessing differences between Wagner et al. and Downing and Williams at a common measurement temperature. Though this is therefore a riskier dataset choice, no reasonable alternatives are available for consideration.
Separating the dependence of CER on index of refraction from measurement (radiometric calibration) and other model error sources is difficult. If the Kou et al. index of refraction dataset at 265 K chosen for use in the 2.x µm CER algorithm is physically correct, then it is reasonable to expect that the VIIRS minus MODIS CER difference would be dependent on cloud-top temperature (CTT). This was investigated by binning monthly global liquid water CER retrievals as a function of CTT. Since the analysis requires comparison of pixel-to-pixel retrievals from two platforms (Aqua, Suomi NPP), match files were created using the spatial co-location methodology of [70] (further details in Section 2.2.4 of [30]). Liquid water cloud VIIRS minus MODIS CER differences (ΔCER) are shown in Figure 9 for February and August 2014. The distributions are calculated from all latitudes and surface types during those months, with VIIRS and MODIS co-locations required to be within 10 min of each other and both sensor’s view zenith and solar scattering angles matching to within 5°. The ΔCER distribution in each CTT bin in Figure 9 is self-normalized by the maximum value in each CTT bin for better clarity of the distribution. As with previous gridded aggregations, the retrieval population does not include pixels flagged as partly cloudy.
Figure 9 shows the ΔCER versus CTT distribution for 2.x µm to have a positive correlation, with an increase in ΔCER of approximately 1.2 µm between 265 K and 290 K for both months. This positive correlation is consistent with the results of Figure 3. However, the CTT distribution (gray line) shows that the frequency of 290 K radiative cloud tops is much less than for 265 K for both months. In contrast, ΔCER for the 1.6 and 3.7 µm retrievals are flat to within a couple of tenths of a micrometer over the same temperature range, which is physically consistent with those channels showing co-albedo changes with temperature of the same sign for the chosen index of refraction datasets (Figure 3).
The 2.x µm CER temperature dependence also suggests that the results seen in Figure 7 and Figure 8 are unrelated to solar reflectance calibration adjustments which would not be expected to have a scene temperature dependence in these channels. While systematic biases in spectral atmospheric corrections associated with differences in cloud-top pressure cannot be completely ruled out [71], these might be expected to bias both 2.x µm channels in the same direction. We conclude that the LUT temperature dependence is the most likely error source candidate.
The results shown in the middle row Figure 9 suggest that temperature-interpolated LUTs consistent with cloud-top temperature retrievals may be warranted for a 2.x µm CER algorithm when CTTs are greater than 265 K (the available range of Kou et al. laboratory temperatures). However, these laboratory data are limited to just two discrete temperature measurements (265 K and 295 K) and, thus, too sparse to resolve likely k non-linearities between those temperatures. Further, supercooled liquid water cloud temperatures are frequently less than 265 K [19,20]. Nevertheless, it would be valuable to study the impact of LUT temperature interpolation for this restricted subset of liquid water cloud temperatures.
5. Conclusions
Passive liquid water cloud effective particle radius retrievals from satellite or airborne multispectral imager SWIR and MWIR observations fundamentally depend on the complex index of refraction used in the forward radiative transfer modeling (i.e., bidirectional reflectance calculations in all SWIR/MWIR spectral channels along with emissivity calculations in the MWIR). More specifically, the relative uncertainty in the CER retrieval for a spherical liquid droplet is approximately inversely proportional to the relative uncertainty in the imaginary index of refraction used in the calculations (see Section 2.1 and Section 3.1). Despite this proportional dependence, the impact of k uncertainties on liquid water CER retrievals has not been adequately explored in SWIR/MWIR retrieval studies. This largely has been due to the lack of independent laboratory complex index of refraction datasets and compilations in the relevant spectral bands. For this reason, there has been general consistency in the choice of the liquid water index of refraction by the cloud remote sensing community, with those datasets being based on publications in the 1960s and 1970s (though measurements reported in one popular compilation traces back to the 1930s).
This study investigated several more modern (1990s and 2000s) laboratory liquid water index of refraction datasets that have not been broadly utilized in the imager retrieval community (bottom three rows of Table 2). In particular, global CER retrieval sensitivity studies were performed using the relatively recent index of refraction datasets of [25] (Kou et al.) in the SWIR and [26] (Wagner et al.) in the MWIR, compared with earlier datasets used in the production of the MODIS standard cloud product (MOD06/MYD06) ([23] (Palmer and Williams) and [24] (Downing and Williams)). Being more recent does not bestow inherently more accuracy, however the newer datasets examined did have the advantage of reporting measurements at supercooled water temperatures that are often more relevant to atmospheric conditions; the earlier datasets were reported at room temperature conditions. Thus, the retrieval sensitivity studies could examine a range of k temperature dependencies. While Kou et al. used bulk water transmittance measurements similar to previous work, Wagner et al. used a cloud chamber to measure droplet extinction that is, in principle, more consistent with the remote sensing problem though also utilizing similar assumptions and scattering theory.
The two new datasets were found to affect CER retrievals significantly (e.g., 1–2 µm) relative to the earlier datasets commonly used by the community. The sensitivity is also significant with respect to community requirements, e.g., Global Observing System for Climate (GCOS) essential climate variable (ECV) requirements (desired CER uncertainty specified as 1 µm with a stability of 1 µm/decade, Table 23 in [27]), the NASA Plankton Aerosol Cloud and ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission [28] that is currently in development and specifies the liquid CER retrieval uncertainty requirement as 25% (e.g., 2.5 µm for a common liquid CER of 10 µm), and the NOAA Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) program’s liquid water CER uncertainty objective of 10% (1 µm for a common liquid CER of 10 µm) [29]. Further, the differences varied in magnitude and sign depending on the spectral channel used for the CER retrieval. The sensitivity of the 1.6 and 3.7 µm window CER retrievals were similar in magnitude and sign for both MODIS and VIIRS due to the similar bandpass locations (see Figure 5). For the 2.2 µm atmospheric window, it was found that k for a 265 K water temperature (Kou et al.) resulted in more consistent CER retrievals between the two spectrally distinct channels on MODIS and VIIRS by decreasing MODIS retrievals and increasing VIIRS retrievals (Figure 5 and Figure 6). As a result, the 265 K measurements from the SWIR and MWIR index of refraction datasets were adopted for use in the production version of the NASA MODIS/VIIRS continuity cloud product. While it is hard to uniquely separate out other error sources that may underlie the 2 µm retrieval sensitivity results (e.g., radiometric calibration), the temperature-dependent CER results shown in Figure 9 lend credence to an index of refraction mechanism. Regardless, there remains a clear need to better understand temperature-dependent bulk water absorption and uncertainties in the SWIR and MWIR spectral regions.
Finally, note that a non-negligible temperature-dependent imaginary index of refraction also has been found for ice cloud particle scattering [72]. Though the impacts are greatest in the infrared, a study on the impact on cloud microphysical retrieval sensitivity to ice index of refraction in the SWIR/MWIR is also warranted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.; methodology, S.P. and K.M.; software, K.M. (analysis code), N.A. (analysis code), G.W. (Level-2), P.A.H. (Level-3), and R.E.H. (analysis code); formal analysis, S.P., K.M., and N.A.; data production assistance, R.E.H.; writing–review and editing, S.P. and K.M.; visualizations, N.A., K.M., and S.P.; project administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the NASA Earth Science Division Terra Aqua Suomi NPP 2017 ROSES solicitation (NNH17ZDA001N-TASNPP).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Steven Dutcher and Denis Botambekov from the NASA Atmosphere Science Investigator-led Processing System (A-SIPS), University of Wisconsin-Madison Space Science and Engineering Center, for their assistance in processing the VIIRS and MODIS Level-2 and Level-3 cloud continuity product files used in this study. We thank the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Level-1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (LAADS) (ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov) where production versions of the VIIRS and MODIS CLDPROP cloud continuity products and the MODIS standard cloud products are available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dufresne, J.-L.; Bony, S. An assessment of the primary sources of spread of global warming estimates from coupled atmosphere-ocean models. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 5135–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Klein, S.A.; Hartmann, D.L. Computing and partitioning cloud feedbacks using cloud property histograms. Part II: Attribution to changes in cloud amount, altitude, and optical depth. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3736–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.J.; Lambert, F.H.; Gregory, J.M. Origins of differences in climate sensitivity, forcing and feedback in climate models. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 40, 677–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Klein, S.A.; Taylor, K.E.; Andrews, T.; Webb, M.J.; Gregory, J.M.; Forster, P.M. Contributions of different cloud types to feedbacks and rapid adjustments in CMIP5. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 5007–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.D.; Klein, S.A. Low-cloud optical depth feedback in climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6052–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos, L.; Platnick, S. Radiative susceptibility of cloudy atmospheres to droplet number perturbations: 2. Global analysis from MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, E.M.; Platnick, S. Estimate of the impact of absorbing aerosol over cloud on the MODIS retrievals of cloud optical thickness and effective radius using two independent retrievals of liquid water path. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D05210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Rausch, J. Global and regional estimates of warm cloud droplet number concentration based on 13 years of AQUA-MODIS observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9815–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, D.P.; Sourdeval, O.; Zuidema, P.; Ackerman, A.; Alexandrov, M.D.; Bennartz, R.; Boers, R.; Cairns, B.; Chiu, J.C.; Christensen, M.; et al. Remote sensing of droplet number concentration in warm clouds: A review of the current state of knowledge and perspectives. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 409–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Leon, D.; Lebsock, M.; Snider, J.; Clarke, A.D. Precipitation driving of droplet concentration variability in marine low clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Stephens, G.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Wang, M.; Golaz, J.-C.; Yokohata, T.; Koshiro, T. Evaluation of the warm rain formation process in global models with satellite observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 3996–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S.; Cocks, T. Spectral reflectance of clouds in the near-infrared-comparison of measurements and calculations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 60, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, F.; Foot, J.S. Remotely sensed measurements of stratocumulus properties during fire using the C130 aircraft multichannel radiometer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; King, M.D. Determination of the optical-thickness and effective particle radius of clouds from reflected solar-radiation measurements. Part 1. Theory. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 1878–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.Y.; Rossow, W.B.; Lacis, A.A. Near-global survey of effective droplet radii in liquid water clouds using ISCCP data. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 465–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Twomey, S. Determining the susceptibility of cloud albedo to changes in droplet concentration with the Advanced Very High-Resolution Radiometer. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.G.; King, M.D.; Wind, G.; Amarasinghe, N.; Marchant, B.; Arnold, G.T.; Zhang, Z.; Hubanks, P.A.; Holz, R.E.; et al. The MODIS cloud optical and microphysical products: Collection 6 updates and examples from Terra and Aqua. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 502–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Rodier, S.; Xu, K.-M.; Sun, W.; Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Zhai, P.; Josset, D. Occurrence, liquid water content, and fraction of supercooled water clouds from combined CALIOP/IIR/MODIS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, B.; Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.; Arnold, G.T.; Riedi, J. MODIS Collection 6 shortwave-derived cloud phase classification algorithm and comparisons with CALIOP. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, W.M.; Pollack, J.B. Infrared optical properties of water and ice spheres. Icarus 1968, 8, 324–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, G.M.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the 200-nm to 200-μm wavelength region. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, K.F.; Williams, D. Optical-properties of water in near-infrared. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, H.D.; Williams, D. Optical constants of water in the infrared. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984–2012 1975, 80, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Labrie, D.; Chylek, P. Refractive-indexes of water and ice in the 0.65- to 2.5-µm spectral range. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Benz, S.; Möhler, O.; Saathoff, H.; Schnaiter, M.; Schurath, U. Mid-infrared extinction spectra and optical constants of supercooled water droplets. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 7099–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belward, A.; Bourassa, M.; Dowell, M.; Briggs, S.; Doman, H.; Holmlund, K.; Husband, R.; Quega, S.; Sounders, R.; Simmons, A.; et al. The Global Observing System for Climate: Implementation Needs; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Werdell, P.J.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Bontempi, P.S.; Boss, E.; Cairns, B.; Davis, G.T.; Franz, B.A.; Gliese, U.B.; Gorman, E.T.; Hasekamp, O.; et al. The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem Mission: Status, Science, Advances. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 1775–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) Level 1 Requirements Document Supplement (L1RDS); NOAA/NASA, 2019. Available online: https://www.jpss.noaa.gov/assets/pdfs/technical_documents/L1RDS.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Meyer, K.; Platnick, S.; Holz, R.; Dutcher, S. Derivation of shortwave radiometric adjustments for SNPP and NOAA-20 VIIRS for the NASA MODIS-VIIRS continuity cloud products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.; Wind, G.; Holz, R.E.; Amarasinghe, N.; Hubanks, P.A.; Marchant, B.; Dutcher, S.; Veglio, P. The NASA MODIS-VIIRS continuity cloud optical properties products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S.; Bohren, C.F. Simple approximations for calculations of absorption in clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.L.; Maymon, P.W.; Montgomery, H.E.; Ostrow, H. MODIS—Advanced facility instrument for studies of the earth as a system. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Angal, A.; Barnes, W.L.; Chen, H.; Chiang, V.; Geng, X.; Li, Y.; Twedt, K.; Wang, Z.; Wilson, T.; et al. Updates of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer on-orbit calibration uncertainty assessments. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; DeLuccia, F.; Liu, Q.; Blonski, S.; Lin, G.; Nishihama, M.; Pogorzala, D.; Oudrari, H.; et al. Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Sensor Data Record (SDR) User’s Guide; NOAA Technical Report NESDIS 142A; 2017. Available online: ncc.nesdis.noaa.gov/documents/documentation/viirs-users-guide-tech-report-142a-v1.3.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Xiong, X.; Butler, J.; Chiang, K.; Efremova, B.; Fulbright, J.; Lei, N.; McIntire, J.; Oudrari, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A. Assessment of S-NPP VIIRS on-orbit radiometric calibration and performance. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmit, T.J.; Griffith, P.; Gunshor, M.M.; Daniels, J.M.; Goodman, S.J.; Lebair, W.J. A closer look at the ABI on the GOES-R series. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, R.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Holz, R.E.; Dutcher, S.; Griffith, Z. The continuity MODIS-VIIRS cloud mask. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.; Wind, G.; Meyer, K.; Heidinger, A.; Frey, R.; Holz, R.; Li, Y.; Arnold, G.T.; Amarasinghe, N.; et al. Continuity atmosphere L2 MODIS cloud product (CLDPROP_L2_MODIS_Aqua). Atmos. SIPS Process. Syst. Univ. Wis. Available online: ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/CLDPROP_L2_MODIS_Aqua/ (accessed on 5 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.; Wind, G.; Meyer, K.; Heidinger, A.; Frey, R.; Holz, R.; Li, Y.; Arnold, G.T.; Amarasinghe, N.; et al. Continuity atmosphere L2 MODIS cloud product (CLDPROP_L2_VIIRS_SNPP). Atmosphere SIPS Process. Syst. Univ. Wis. Available online: ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/CLDPROP_L2_VIIRS_SNPP/ (accessed on 5 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- LAADS DAAC. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 8 August 2020).
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.; King, M.D.; Wind, G.; Meyer, K.; Menzel, W.P.; Frey, R.; Holz, R.; Baum, B.; Yang, P. MODIS atmosphere L2 cloud product (MOD06_L2). NASA MODIS Adapt. Process. Syst. Goddard Space Flight Cent. Available online: ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/MOD06_L2/ (accessed on 5 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.; King, M.D.; Wind, G.; Meyer, K.; Menzel, W.P.; Frey, R.; Holz, R.; Baum, B.; Yang, P. MODIS atmosphere L2 cloud product (MYD06_L2). NASA MODIS Adapt. Process. Syst. Goddard Space Flight Cent. Available online: ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/MYD06_L2/ (accessed on 5 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Zasetsky, A.Y.; Khalizov, A.F.; Earle, M.E.; Sloan, J.J. Frequency dependent complex refractive indices of supercooled liquid water and ice determined from aerosol extinction spectra. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 2760–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarragh, G.R.; Poulsen, C.A.; Thomas, G.E.; Povey, A.C.; Sus, O.; Stapelberg, S.; Schlundt, C.; Proud, S.; Christensen, M.W.; Stengel, M.; et al. The Community Cloud retrieval for CLimate (CC4CL)—Part 2: The optimal estimation approach. Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3397–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnis, P.; Sun-Mack, S.; Young, D.F.; Heck, P.W.; Garber, D.P.; Chen, Y.; Spangenberg, D.A.; Arduini, R.F.; Trepte, Q.Z.; Smith, W.L.; et al. CERES Edition-2 cloud property retrievals using TRMM VIRS and Terra and Aqua MODIS data—Part I: Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4374–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobowitz, H.; Stowe, L.L.; Ohring, G.; Heidinger, A.; Knapp, K.; Nalli, N.R. The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer Pathfinder Atmosphere (PATMOS) climate dataset: A resource for climate research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A.; Zhao, X.T. The Pathfinder Atmospheres–Extended AVHRR climate dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.; Albert, P.; Behr, H.D.; Caprion, D.; Deneke, H.; Dewitte, S.; Durr, B.; Fuchs, P.; Gratzki, A.; Hechler, P.; et al. Operational climate monitoring from space: The EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring (CM-SAF). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1687–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.-G.; Riihelä, A.; Mueller, R.; Meirink, J.F.; Sedlar, J.; Stengel, M.; Lockhoff, M.; Trentmann, J.; Kaspar, F.; Hollmann, R.; et al. CLARA-A1: A cloud, albedo, and radiation dataset from 28 yr of global AVHRR data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5351–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, C.A.; Siddans, R.; Thomas, G.E.; Sayer, A.M.; Grainger, R.G.; Campmany, E.; Dean, S.M.; Arnold, C.; Watts, P.D. Cloud retrievals from satellite data using optimal estimation: Evaluation and application to ATSR. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1889–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebeling, R.A.; Feijt, A.J.; Stammes, P. Cloud property retrievals for climate monitoring: Implications of differences between Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI) on METEOSAT-8 and Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) on NOAA-17. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.R. A new infra-red absorption band of liquid water at 2.52 μ. Phys. Rev. 1939, 55, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, J.A.; Petty, C.C. The near infrared absorption spectrum of liquid water. JOSA 1951, 41, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyev, K.Y. Radiation in the Atmosphere; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; ISBN 0-12-419050-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotarev, V.M.; Mikhailov, B.A.; Aperovich, L.I.; Popov, S.I. Dispersion and absorption of liquid water in the infrared and radio regions of the spectrum. Opt. Spectrosc. 1969, 27, 430. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, C.W.; Williams, D. Lambert absorption coefficients of water in the infrared*. JOSA 1971, 61, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusk, A.N.; Williams, D.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the infrared*. JOSA 1971, 61, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertie, J.E.; Lan, Z.D. Infrared intensities of liquids XX: The intensity of the OH stretching band of liquid water revisited, and the best current values of the optical constants of H2O(1) at 25 degrees C between 15,000 and 1 cm(-1). Appl. Spectrosc. 1996, 50, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, G.M.; Williams, D.; Rusk, A.N.; Querry, M.R. Influence of temperature on spectrum of water. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1972, 62, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkley, L.W.; Sethna, P.P.; Williams, D. Optical constants of water in the infrared: Influence of temperature. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1977, 67, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, Y. Infrared spectra of water. I. Effect of temperature and of H/D isotopic dilution. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 95, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.M.; Neshyba, S.; Walden, V.P. Radiative consequences of low-temperature infrared refractive indices for supercooled water clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11925–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.M.; Fergoda, M.; Neshyba, S. Temperature-dependent optical properties of liquid water from 240 to 298 K. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.R.; Kahn, B.H.; Green, R.O.; Chien, S.A.; Middleton, E.M.; Tran, D.Q. Global spectroscopic survey of cloud thermodynamic phase at high spatial resolution, 2005–2015. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubanks, P.; Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.; King, M.D.; Ackerman, S.; Holz, R.; Heidinger, A.; Li, Y.; Frey, R.; Walther, A.; et al. Level-3 Continuity Cloud Properties (CLDPROP_L3) Global Gridded Product User Guide; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2020.
- Oreopoulos, L.; Cho, N.; Lee, D. Using MODIS cloud regimes to sort diagnostic signals of aerosol-cloud-precipitation interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5416–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L3 MODIS Daily Imagery. Available online: https://atmosphere-imager.gsfc.nasa.gov/images/l3/daily (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Justice, C.; Vermote, E.; Privette, J.; Sei, A. The Evolution of U.S. Moderate Resolution Optical Land Remote Sensing from AVHRR to VIIRS. In Land Remote Sensing and Global Environmental Change; Ramachandran, B., Justice, C., Abrams, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 11, pp. 781–806. [Google Scholar]
- Holz, R.E.; Ackerman, S.A.; Nagle, F.W.; Frey, R.; Dutcher, S.; Kuehn, R.E.; Vaughan, M.A.; Baum, B. Global Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud detection and height evaluation using CALIOP. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Meyer, K.; Bennartz, R.; Platnick, S. Differences in liquid cloud droplet effective radius and number concentration estimates between MODIS collections 5.1 and 6 over global oceans. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, H.; Yang, P. Temperature dependence of ice optical constants Implications for simulating the single-scattering properties of cold ice clouds. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).