Abstract
Off the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica an area of open water—the Terra Nova Bay Polynya (TNBP)—persists throughout the austral winter. The development of this coastal polynya is driven by extreme katabatic winds blowing down the slopes of Transantarctic Mountains. The surface-atmosphere coupling and ABL transformation during the katabatic wind events between 18 and 25 September 2012 in Terra Nova Bay are studied, using observations from Aerosonde unmanned aircraft system (UAS), numerical modeling results and Antarctic Weather Station (AWS) measurements. First, we analyze how the persistence and strength of the katabatic winds relate to sea level pressure (SLP) changes in the region throughout the studied period. Secondly, the polynya extent variations are analysed in relation to wind speed changes. We conclude that the intensity of the flow, surface conditions in the bay and regional SLP fluctuations are all interconnected and contribute to polynya development. We also analyse the Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System (AMPS) forecast for the studied period and find out that incorrect representation of vertical ABL properties over the TNBP might be caused by overestimated sea ice concentrations (SIC) used as model input. Altogether, this research provides a unique description of TNBP development and its interactions with the atmosphere and katabatic winds.
1. Introduction
Terra Nova Bay is located in the western Ross Sea, between Cape Washington in the North and the Drygalski Ice Tongue in the south, along the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica (Figure 1). An ice-free stretch of sea persists there throughout the winter—the Terra Nova Bay Polynya (TNBP), forced by sea ice removal from the coast by strong offshore winds and maintained due to the presence of Drygalski Ice Tongue, which blocks the transport of ice from the south [1]. The extent of the recurring polynya is defined by the distance between open water with frazil ice formation near the coast and the downwind area where the ice becomes compact. During winter the mean area occupied by the TNBP varies between 1000 and 1300 km [2], but some observations indicate that it can reach even 8500 km [3].
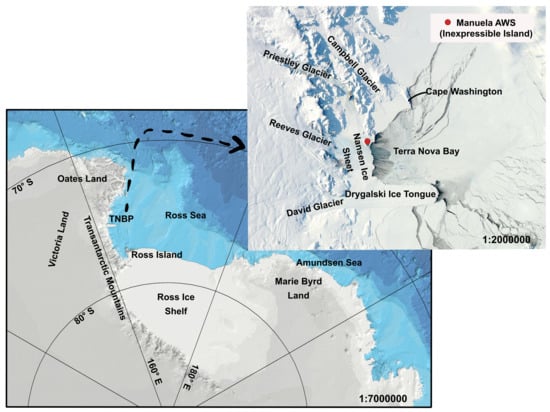
Figure 1.
Map of Terra Nova Bay area. Satellite image for 20 September 2012 from the NASA Worldview application (https://worldview.earthdata.nasa.gov), part of the NASA Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS).
Previous studies have shown that extreme winds on the coast of the Antarctic are a result of combined influence of the forcing from temperature inversion over sloping terrain and synoptic scale pressure gradients [4,5]. What is more, Turner et al. [5] concludes that the enhancement of the strong wind events is dependent on the location of the storm offshore and Ebner et al. [6] adds that when a cyclone moves from west to east along the Anatarctic coast it promotes the intensification of a downslope flow. Likewise, the passage of a low pressure system in the Ross Sea or presence of a cyclone to the east of Terra Nova Bay is often accompanied by stronger and longer extreme winds events [7,8]. Thus, in Terra Nova Bay, where several different flow regimes from various valleys meet, wind reaches high speed and drives the expansion of the polynya [9]. However, not every downslope flow can be regarded as a katabatic one because this term refers strictly to the flow of negatively buoyant, radiatively cooled air [10]. Whereas, as mentioned above, intensive winds blowing in Terra Nova Bay might be driven by a number of different factors associated with local and regional weather conditions. The determination of the exact nature of the flow requires detailed analysis of thermodynamic evolution of air coming through the valleys of the Transantarctic Mountains, which is beyond the scope of this paper. We conclude that extreme winds studied in the presented article are probably a result of several forces acting together, but for simplicity, strong (>20 m/s) downslope winds (from west-northwest) are referred to as “katabatic”. Although, we acknowledge that they are rather a mix of katabatic, downslope and offshore flow.
The development of katabatic winds begins in the interior of the Antarctic due to intensive radiative cooling of the surface and a consecutive buildup of near-surface inversion layer, which has lower temperature than the air downslope. This cold, negatively buoyant air is driven downslope through the valleys of the Transantarctic Mountains, due to gravitational pull and thermodynamic forcing. In the coastal area near Terra Nova Bay the primary and wider route of flow descent is Reeves Glacier and the secondary one is the Priestly Glacier [8,11] (Figure 1). Once the katabatic wind reaches the shore, it spreads laterally over the ocean and can propagate over a long distance, depending on the duration and intensity of the flow. Gradual removal of sea ice from the coast and the interaction of relatively warm open water with cold katabatic flow results in strong atmosphere-surface coupling. In consequence, heat and moisture are exchanged upward and momentum is transferred downward [12]. As the energy from the surface is absorbed by the atmosphere, the formation of new sea ice takes place, which is then transported further away from the coast by offshore winds. Simple numerical modelling studies [13] state that wind is a major contributor to sea ice divergence, but in the areas where polynya expansion is most significant, it might be accompanied by ocean currents. However, it is generally agreed that the key factors responsible for the development of coastal polynyas like TNBP are wind and topography [6,14]. Observations of oceanic boundary layer reveal that ocean heat loss to the atmosphere drives the production of unconsolidated frazil ice, producing bulges of warm salty water directly beneath the ocean surface [15]. A continuous formation of sea ice and resulting rejection of salt increases the density of near–surface water [16] and produces the densest water in the ocean—the Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW). Studies indicate that TNBP may contribute about 10% of all AABW formed in the Ross Sea [2] and therefore plays a crucial role in the global thermohaline circulation. Whereas, the total ice production in TNBP has been estimated at 53 ± 5 km/year [17].
First reports about strong, persistent winds blowing in Terra Nova Bay come from the journals of the Northern Party of Robert F. Scott’s Terra Nova Expedition, which was stranded at the area throughout the winter [18]. Further observations of extreme katabatic events in Terra Nova Bay were largely limited to the summer season, as harsh, austral winter conditions of the Antarctic coast present a challenging environment for field campaigns. In consequence, scientists turned their attention toward satellite based studies [3,12,19] and numerical modelling [2,7,20]. The first observations of the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) over the polynya were made with manned aircraft in late 1980s [12]. Since then a number of campaigns covering different branches of science have taken place in the bay, including studies of atmospheric chemistry [21], seawater chemistry [22], biology [23] and physical oceanography [24]. The first late winter measurements of the atmosphere and surface state in Terra Nova Bay have been done in September 2009 by Aerosonde unmanned aerial systems (UAS) [25] and were followed up by a second successful Aerosonde UAS field campaign in September 2012 [26], which provided a comprehensive three-dimensional description of the atmosphere over TNBP. Nevertheless, all of mentioned observations are limited to short periods of time and for now the only source of continuous meteorological data from the coastal area of the bay are Antarctic Automatic Weather Stations (AWS) installed in the region in the 1980s and maintained by the cooperative efforts of the University of Wisconsin and other partners [27]. Observations from mentioned campaigns, satellite data and AWS stations have been used in many numerical modelling studies of the katabatic wind events (e.g., [28,29,30,31,32]). In general, models perform well when it comes to large scale weather patterns but struggle to accurately represent low level properties of the atmosphere, especially over complex coastal topography [7,33]. Thus, the accuracy of the models is limited by their horizontal resolution [33]. Another reason behind model errors is representation of sea ice which, according to Bourassa et al. [34], has significant impact on models results on the wide range of spatiotemporal scales.
In this study the surface and atmospheric conditions in Terra Nova Bay between 18 and 25 September 2012 are analysed based on the numerical modelling simulations, satellite images and in-situ atmospheric measurements. The results of numerical weather prediction (NWP) simulations are obtained from the Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System (AMPS) [35], which is a real–time Polar Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) system run over Antarctica, and from Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA). Satellite images of sea ice concentration (SIC) come from the AMSR2 sensor [36] and ice surface temperature (IST) from Visible Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) [37]. Continuous measurements of meteorological parameters in the upwind part of the bay are obtained from the Manuela AWS station located on the Inexpressible Island (Figure 1). The key element of presented research is UAS observations from September 2012 [26]—the only source of data about atmospheric conditions above polynya. Wind speed and temperature measured during simultaneous flights in both downwind and cross wind directions are analysed in relation to surface sea ice concentration and temperature. Both UAS Aerosonde and and Manuela AWS observations are also used for the validation of AMPS model predictions for 18–25 September. Furthermore, large scale fluctuations of sea level pressure (SLP) are studied to determine the influence of synoptic conditions on the frequency of extreme katabatic events. Altogether, the purpose of our study is to provide a detailed description of the TNBP surface and atmospheric state during and between polynya events, along with a brief analysis of the AMPS model results from the studied period.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. UAS Flights
The Aerosonde UAS is a small (3.6 m wingspan, 19–21 kg take-off weight), robotic, pusher-prop aircraft capable of carrying a variety of instrument packages and performing well in polar winter conditions. During analysed flights it was equipped with the sensors of air temperature, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure and surface temperature. Data from surface temperature sensor was only available for a certain percentage of the flights and is not considered in the presented article. The wind speed and wind direction were calculated indirectly, based on the measurements of flight heading and speed from the UAS Piccolo Avionics system. Detailed technical description of data processing, the aircraft and its capabilities can be found in Cassano et al. [26]. During the campaign in 2012, 9 missions were flown from McMurdo Station, Antarctica to Terra Nova Bay on 13, 18, 19, 22 and 25 September. On those days, once the Aerosonde UAS flew past the Drygalski Ice Tongue the flight height was lowered to approximately 100–150 m and the measurement phase of the flight over TNBP began. The flight patterns above TNBP can be divided into two types (Figure 2). The goal of the first one was to sample the downstream evolution of the air mass coming off the continent as the aircraft passed over the bay. Those downwind transects included repeated profiles of the atmosphere, made by the aircraft ascending and descending in the spiral pattern, from approximately 100 m to the top of the ABL (Figure 2a). The aim of the second type of flight was to measure crosswind variability of the atmospheric state over TNBP (Figure 2b). Therefore, the Aerosonde UAS flew in horizontal lines, roughly perpendicular to the low level flow, moving away from the coast with every new line. Spiral profiles were flown at the beginning, approximately at mid-point and at the end of each of these cross-wind legs. On 18, 19, 22 and 25 September both the crosswind and downwind transects were flown above the surface of Terra Nova Bay, including repeated, second downwind transects conducted in order to sample the changes in the atmospheric state after a few hours. The analysis presented in this article focuses on UAS observations of wind speed, wind direction and temperature with an emphasis on the vertical profiles observed during 6 of the Aerosonde flights (Table 1). A MatLab smoothing method of moving average of the elements of a vector, using a fixed window length of 3 was applied to analysed profiles. Data smoothing did not change the outcome of our analysis of the measurements but only made the profiles easier to read in presented figures (Figures 6–10).
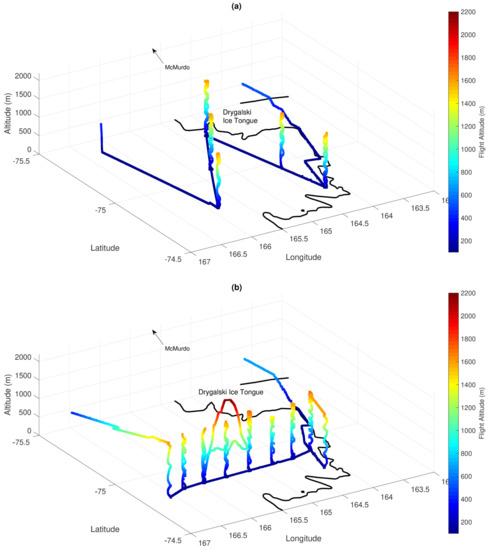
Figure 2.
UAS Aerosonde crosswind (a) and transect (b) flights on the 25 September 2012.

Table 1.
Aerosonde UAS flights analysed in the presented article.
In the analysis of UAS Aerosonde profiles we use the term “katabatic” when the flow is coming from west–northwest directions [11] and wind speeds exceeds ∼20 m/s, in agreement with previous studies of Knuth and Cassano [11], Maqueda et al. [38]. Based on those conditions a horizontal and vertical extent of the katabatic flow can be estimated. Meanwhile, Vignon et al. [39] defines katabatic layer as the layer of the atmosphere where downslope wind exceeds certain speed and is capped by temperature inversion. While we agree that in many cases temperature inversion is a reasonable measure of katabatic layer’s depth, we use it to define the depth of boundary layer, which is more relevant in the analysis of surface–atmosphere interactions.
The UAS Aerosonde data presented in this study are openly available in the United States Antarctic Program Data Center (http://gcmd.nasa.gov/getdif.htm?NSF-ANT10-43657, doi:10.15784/600125).
2.2. Manuela AWS
Manuela AWS is a part of the University of Wisconsin AWS network collecting meteorological data from a number of locations in the Antarctic [27]. This AWS station on Inexpressible Island (74.96S, 163.7E) has been in operation since 1984. Sensors of air temperature, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed and direction are mounted on the 3 m tower. The accuracy of the sensors is, approximately: ±0.5 C for temperature, ±0.1 hPa for pressure, ±2% for humidity, and ±2% for wind speed and direction. Measurements are transmitted hourly via the ARGOS network and subjected to a quality control by the University of Wisconsin. The results, for the studied period, are provided in 1 h intervals. Wind speed and direction, along with temperature observations from the station are analysed for the description of the upwind conditions during katabatic winds events.
2.3. Satellite Data
Satellite images of sea ice concentration and ice surface temperature provide us with a detailed description of surface conditions and enable an analysis of surface-atmosphere coupling in the Terra Nova Bay.
2.3.1. Sea Ice Concentration
Sea ice concentration images provided by the Institute of Environmental Physics, University of Bremen [36] (https://seaice.uni-bremen.de/sea-ice-concentration-amsr-eamsr2/) are calculated daily, in near real time, from the AMSR2 sensor data. AMSR2, a successor of AMSR-E(Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS) is carried by the “Shizuku” (GCOM-W1) satellite, launched on 18 May 2012 and delivering data since August 2012. The frequency used for the calculation of SIC from brightness temperature is 89 GHz and the images are retrieved with the ARTIST Sea Ice (ASI) algorithm [40]. All swatch SIC data of one calendar day are resampled into various polar stereographic grids using the nearest neighbour routine. The regional maps, including the one for the area of Ross Sea, have a grid spacing of 3.125 km.
The approximate area of the polynya is calculated based on the maps of SIC. First, the gray coloured maps of SIC below 70% in Terra Nova Bay are generated and then the program Pixie is called to determine the spatial extent of the polynya. Pixie is a program created for the image analysis and available for free on GitLab (https://gitlab.com/seadata-software/pixie). It is a python script that applies simple methods of image recognition for given color intensity threshold, from 0 (black) to 255 (white). For the presented study, to calculate spatial coverage of the pixels forming the polynya, a threshold of 254 (corresponding to SIC of 70%) has been determined as the most suitable and is applied for all images. Next, the program creates binary maps of pixels classified as polynya area and calculates, taking into account spatial dimensions of created map and the number of pixels present in the whole image, the total area of SIC below 70% in km2. The value of 70% have been chosen based on the comparative analysis of IST and SIC images and similar studies of spatial polynya coverage [32,41,42]. It has to be noted that it is a rough estimation of polynya spatial extent, created to illustrate SIC changes with different synoptic and regional atmospheric conditions.
2.3.2. Ice Surface Temperature
Ice surface temperature data come from the radiance data acquired by the Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) and processed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center [37]. The VIIRS instrument flies on board the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (NPP) satellite. The VIIRS sea IST is computed from bands M15 (10.763 m) and M16 (12.013 m) of brightness temperature, using the split window method of Yu and Rothrock [43]. A reported accuracy of the applied algorithm [44] is ±1 K. The presence of cloud cover or melt ponds and leads in the summer season may cause erroneous interpretation of the surface; however, in the case considered in this article they are both either scarce or absent (winter season). Datasets with a spatial resolution of 750 m are provided at least daily, but for the areas were swaths overlap (near poles), may appear more frequently. For the considered period at least one image, without or with minimal clouds obstruction, is available for further analysis.
2.4. Numerical Modelling Results
2.4.1. Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System
AMPS is a real time mesoscale modelling system providing numerical forecasts for the Antarctic since 2000 [45]. It is run at the Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology (MMM) Division of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). In the period considered in our research AMPS used a Polar WRF Model version 3.2.1., developed at the Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center at Ohio State University. The model was initialised twice a day, at 0000 and 1200 UTC. For the western Ross Sea the horizontal resolution was 5 km. Air column is divided into 44 terrain following eta levels. The boundary conditions were assimilated by the WRF Data Assimilation System (WRFDA) with a three dimensional variational data assimilation (3DVAR) approach from the output of NCEP Global Forecast System (GFS; [46]). Sea ice concentration was specified from daily SSM/I data. More detailed description of this version of the AMPS and the Polar WRF set-up for the Antarctic are available in Bromwich et al. [47]. The goal of the presented study is to evaluate part of the AMPS output, in particular wind speed, direction and air temperature, in relation to the UASs measurements and satellite images during the extreme katabatic events over the TNBP.
2.4.2. MERRA Reanalysis
The Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) data spans the period between 1979 and February 2016, thus covering the modern satellite era. The MERRA dataset was created with version 5.2.0 of the Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) atmospheric model and data assimilation system (DAS). The horizontal resolution of the output is 0.5× 0.66 with 72 vertical layers. MERRA provides scientists with a state-of-art global analysis, with a focus on improved estimates of the global hydrological cycle. Furthermore, MERRA puts the observations from NASA’s Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites into a climate context [48]. In our analysis, MERRA output is used for the investigation of synoptic scale sea level pressure changes in the Ross Sea between 18 and 25 September.
3. Synoptic Overview of the Ross Sea and Terra Nova Bay Region
Regional scale circulation near Terra Nova Bay is dominated by the Amundsen Sea Low (ASL), a permanent region of low pressure located in the South Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean, including the Ross Sea, Amundsen Sea and the Bellingshausen Sea. This region, with Ross Sea [49] and Adélie Land [50] in particular, is known for significant cyclone activity due to the interaction of cold, dry continental air with relatively warm, moist air from the Southern Ocean. The large scale winter atmospheric circulation in this region is characterised by alternating low and high pressure systems forming in the lower latitudes (60–70S) and moving from west to east along the Antarctic coast. Studies indicate that presence of a synoptic cyclone in the eastern part of Ross Sea with isobars parallel to the Transantarctic Mountains results in the generation of katabatic events in Ross Ice Shelf and Terra Nova Bay [51].
Figure 3 shows the evolution of SLP in the Ross Sea region throughout the period of 18–25 September 2012. On 18 September the sea level pressure (SLP) in the Ross Sea is dominated by a strong cyclone located near Marie Byrd Land (Figure 3a,b) with 940 hPa at its centre. A gradual increase of the SLP toward Victoria Land, with 970 hPa measured by Manuela AWS on Inexpressible Island, is accompanied by wind speeds of up to ∼30 m/s (Figure 4a and Figure 5a). Strong wind speeds and SLP difference between TNBP and eastern Ross Sea of ∼20 hPa persists till 20 September (Figure 5a). In the following days, between 20 and 22 September, the cyclone moves further toward the east, with decreasing influence on the Ross Sea SLP (Figure 3c–e). On 20 September, a small low pressure system approaches from the north and moves to the east, maintaining a ∼10 hPa pressure difference between the slopes of the Transantarctic Mountains and the central Ross Sea. Exceptionally strong winds, above 35 m/s are measured by Manuela AWS on 21 and 22 September and the polynya remains open with an area of SIC lower than 70% covering 2838 km2 on 22 September. On 23 September the cyclone moves further to the east and an anticyclone approaches from north-west increasing the SLP in the region up to 998–1000 hPa over the Ross Sea and almost 1000 hPa at the Manuela AWS (Figure 3e,f). In consequence, the pressure gradient between Terra Nova Bay coast and eastern Ross Sea decreases to a few hPa on 23 September and wind speed at Manuela AWS slows down to only few m/s (Figure 5a). Under those circumstances the polynya starts to freeze over and only a small patch of 53 km2 of low SIC remains in Terra Nova Bay. On the following day, the high pressure system retreats to the north and on 25 September a small cyclone appears offshore Oates Land, increasing the pressure gradient between the Oates Land and the coast of Terra Nova Bay to ∼15 hPa (Figure 3h). Simultaneously, wind speed on Inexpressible Island increases to ∼35 m/s and the SIC in Terra Nova Bay decreases again. In consequence, on 25 September polynya reaches the size of ∼2407 km2 (Figure 3h).
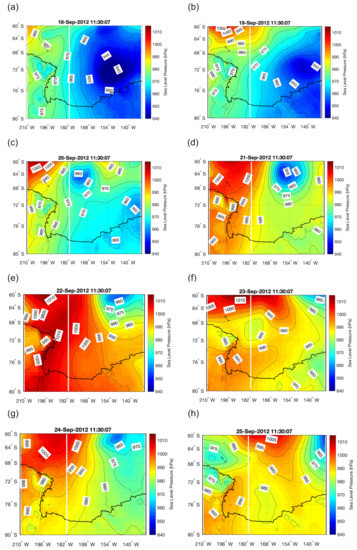
Figure 3.
Sea level pressure maps for the Ross Sea area from MERRA dataset. Every image represents situation from a single hour of 11:30 a.m. on a consecutive days between 18 and 25 September 2020 (a–h).
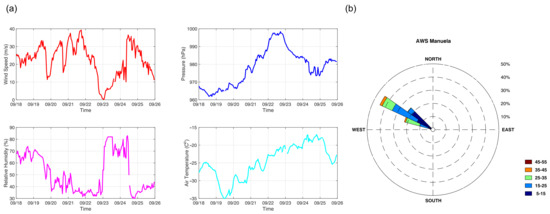
Figure 4.
Measurements from Manuela AWS for the period of 18–25 September 2012 (http://amrc.ssec.wisc.edu).
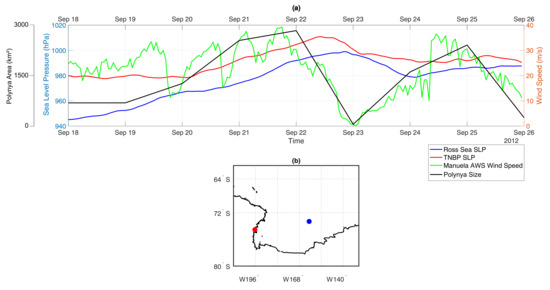
Figure 5.
(a) Plotted together: MERRA sea level pressure from the point in the Ross Sea area and the point in Terra Nova Bay (marked in (b)), Manuela AWS wind speed and polynya surface area. (b) Location of the plots from (a).
Presented relationship between the synoptic scale SLP changes and the wind speed variations in Manuela AWS indicates, in agreement with other studies from the region (e.g., [4,5,6]), that pressure gradient between the slopes of the Transantarctic Mountains and the Ross Sea is partially responsible for the occurence of extreme wind events in TNBP. As explained by e.g., Ebner et al. [6], Renfrew and Anderson [52] the clear sky conditions and development of stable boundary layer on the slopes, after the passage of synoptic cyclone, leads to the development of downslope winds. However, when considering the relationship between katabatic winds and polynya extent we also have to take into account, among others, the balance between the ice production in the open water zone and the movement of the offshore pack ice out of Terra Nova Bay. The complete understanding of processes associated with polynya expansion requires additional studies of dynamic and thermodynamic processes in sea ice and the oceanic mixed layer, which determine spatiotemporal changes in sea ice concentration, thickness and drift velocities. They are beyond the scope of this study.
Upwind Conditions on Inexpressible Island
Manuela AWS is located in the transition zone between Terra Nova Bay and Nansen Ice Sheet, hence provides a valuable source of information about katabatic flow properties before it enters the Ross Sea. Between 18 and 25 September 2012, the prevailing wind direction is west–northwest, which is typical for katabatic wind regimes in this region [11,53] (Figure 4b). The wind speed varies from ∼1 m/s to ∼40 m/s, preceding the periods of polynya closing and opening. Manuela AWS measurements indicate that the katabatic flow coming off the slopes of Transantarctic Mountains has the properties of the air in the interior of the continent, it is dry and cold (Figure 4a). For the first few days, 18–22 September, the air temperature remains lower than −20 C and relative humidity below 70% together with generally high wind speeds (∼20–25 m/s), interrupted by short periods of winds below 20 m/s. Strongest wind speeds, above 30 m/s, coincide with an air humidity decrease below 60% or even 40%, and a few degrees temperature drop. The closing of the polynya on the 23rd corresponds to significant changes in the air properties on the Inexpressible Island. For a short time wind speed is below 5 m/s, air humidity above 80% and air temperatures increases to −20 C, revealing a reduced flow of continental air. Another polynya opening, on 25 September is preceded by significant increase of wind speed to ∼35 m/s and decrease of relative humidity to ∼40% in the Manuela AWS station, with only a small change of temperature (Figure 4a).
4. The Atmosphere–Surface Coupling during Different Stages of Polynya Development
The Aerosonde UAS flight days coincide with different phases of polynya development. The first stage, found on 18 and 19 September, corresponds to the early phase of polynya expansion–an opening mode, accompanied by increasing intensity of the katabatic wind. On the days of 22 and 25 September the TNBP grows in size, but the horizontal and vertical extent of intensive offshore flow is smaller. Overall, the two periods differ in terms of local and regional atmospheric conditions and polynya influence on the ABL. Note that most of the analysed UAS Aerosonde flights align with the direction of near-surface winds, with the exception of Profiles 9, 10, 11 from 25 September, which are located along the flight path perpendicular to the low level flow. Furthermore, when we refer to “upwind”, we mean an upstream area near the Inexpressible Island and Nansen Ice Sheet, while “downwind” applies to downstream area of TNBP further offshore. In the following paragraphs the atmosphere–surface coupling during the measurements is studied in detail, with additional description of atmospheric and surface conditions from the days between UAS Aerosonde flights.
4.1. 18 and 19 September 2012
On 18 September Terra Nova Bay is mostly covered by sea ice, with small area of SIC below 20% near Nansen Ice Sheet (Figure 6c). The wind speed on 18 September exceeds 23 m/s near the coast (Profiles 1, 2) and slows down by few m/s further offshore (Profiles 3,4; Figure 6b). Thus, katabatic layer extends up to ∼500 m in profiles 1, 2 and up to ∼200 m in profiles 3, 4 on 18 September (Figure 6b). Small changes of temperature (∼1 C–2 C) with the distance offshore, observed on 18 September (Figure 6 and Figure 7a), indicate little transfer of heat between the ice covered ocean and the atmosphere due to low IST and high SIC. Meanwhile, downwind decrease of wind speed suggests momentum loss from the atmosphere to the ice and ocean surface, which drives the ice away from the coast and generates waves. In general, temperature decreases with height in profiles 1–4, although there is a weak inversion at the height of ∼100 m in profile 4 (Figure 6a). This is in agreement with Bromwich [54], who found warm signature in thermal infrared wavelengths related to katabatic flow, resulting from vertical mixing due to turbulence generated by very strong winds.
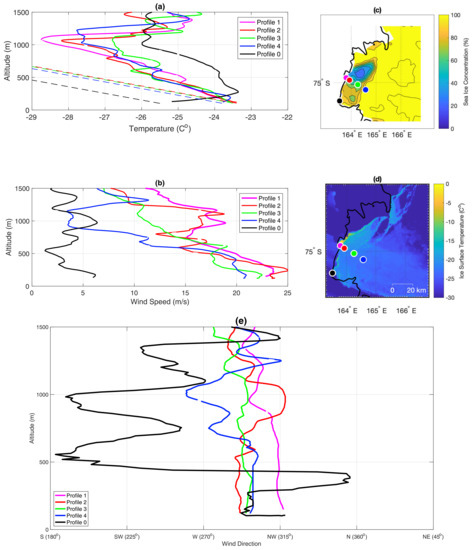
Figure 6.
Vertical measurements of temperature (a), wind speed (b) and wind direction (e), with the locations of UAS Aerosonde flights plotted on the map of SIC (c) and IST (d) on 18 September 2012. Dashed lines on the temperature plot represent dry adiabatic lapse rate. Profiles started at: 10:17 UTC (1); 11:00 UTC(2); 11:34 UTC (3); 12:19 UTC (4); 10:22 UTC (0).
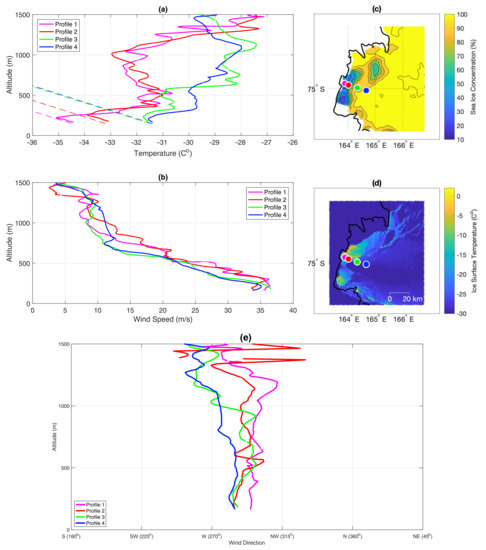
Figure 7.
UAS Aerosonde measurements from 19 September 2012. Subfigures labeled as in Figure 6. Profiles started at: 10:06 UTC (1); 10:40 UTC (2); 11:08 UTC (3); 11:35 UTC (4).
Profile 0, located on the southwestern edge of Terra Nova Bay, is outside of the strong katabatic flow and thus offers a view of the lower atmosphere not influenced by strong winds, discussed previously (Figure 6a,b). Due to an imbalance between the outgoing longwave radiation and the downwelling solar and longwave radiation the surface based inversion is present there, as is common in the polar regions. Stable inversion layer extends up to ∼300 m, where the temperature starts to decrease with height. At the altitude of ∼1000 m the atmosphere becomes warmer and more uniform and at ∼1200 m the difference between profile 0 and other measurements is reduced. Wind speed in this area is much lower than in other profiles and fluctuates around 5 m/s in the whole profile. Interestingly, wind direction in this point varies considerably with height from west-northwest-north up to ∼400 m and south-southwest-west up to ∼1400 m. In general, atmospheric properties in the location of profile 0 are distinctly different and resemble conditions from the interior of the Antarctic. Such contrast over a relatively small distance between profiles 0 and 1 (∼17 km) demonstrates the impact of katabatic winds on local and regional atmospheric properties.
On 19 September the polynya is larger and the ABL properties change (Figure 7a–c). The temperature lapse rate is dry adiabatic in profiles 1 and 2 up to 300 m of altitude and in the first few meters of the flight in profiles 3 and 4 (Figure 7a). In comparison to 18 September (Figure 6), the low level air is several degrees colder and capped by an inversion below 500 m (Figure 7a). The cold low level air, together with consistently intensive (∼35 m/s), west-northwest flow marks the strengthening of the katabatic flow (Figure 7b,e). The katabatic layer expands in the vertical and horizontal directions reaching ∼500 m in all profiles.
In general, temperature lapse rate higher or equal to dry adiabatic lapse rate, means that convection can occur in the ABL. The top of convective layer is marked by temperature inversion. The formation of the convective boundary layer on 19 September is a result of large temperature difference between the surface of open, or covered by thin layer of ice, water and cold air associated with katabatic flow. Therefore, as the surface is much warmer than the incoming air, the atmosphere is heated from below. However, when the strength of the flow increases on 19 September, the effects of surface–atmosphere interactions are limited to a narrow layer of the atmosphere due to continuous, intensive advection of air near the surface (Figure 7b). This ongoing flow transports the released heat further offshore and the remnant of the convective layer is also present over the areas of high SIC and compact sea ice (profile 4, Figure 7a), as in the numerical modelling of Dare and Atkinson [31]. Hence, a 3 C temperature difference between profile 1 and 4 (Figure 7a) is a result of polynya warming of the atmosphere upstream and spreading of this warm air downstream.
4.2. 22 and 25 September 2012
Manuela AWS station measurements (Figure 4 and Figure 5a) and satellite images reveal that through 19 and 22 September 2012 the wind speed on Inexpressible Island exceeds 20 m/s for most of the time and polynya expands further into the bay, in comparison to 18 and 19 September (Figure 6 and Figure 7c). However, the disappearance of SLP difference between Terra Nova Bay and the Ross Sea on 23 of September (Figure 5a) is accompanied by significant decrease of wind speed on Inexpressible Island (Figure 4a) and SIC increase in the bay (Figure 5a). On the following day, 24 of September, as the wind gains speed and SLP decreases in the eastern part of Ross Sea (Figure 3g), the polynya opens again in Terra Nova Bay (Figure 5a). However, Manuela AWS measurements indicate that throughout 25 September wind speed gradually decreased, together with pressure gradient between the Ross Sea and studied area (Figure 5a).
On 22 September the SIC in Terra Nova Bay is low and the polynya is significantly bigger than on 19 September, covering the area of ∼2838 km2 (Figure 5a). Consequently, a continuous transfer of heat from the surface leads to the development of unstable conditions and warming of the atmosphere. The first four profiles from 22 September show that the closer to the coast the profile is located, the colder is the air and faster the flow (Figure 8a,b). Temperature increases with the distance offshore from −20 C to −17 C and wind speed decreases from ∼24 m/s to 10 m/s in the lowest layer of the flights (Figure 8b). In the first two profiles the temperature lapse rate is dry adiabatic up to a height of ∼200 m and up to ∼400 m in profiles 3 and 4. However, a stable ABL is present at the bottom of profiles 3 and 4 probably due to increasing SIC at these locations and limited transfer of heat. The dry adiabatic lapse rate above this shallow, stable layer reflects the remnants of convection from further upwind. The dominating wind direction in all profiles is west-northwest up to ∼500 m, changing to south-southwest and finally southeast with altitude (Figure 8e). In general, profiles 1–4 differ from each other up to height of ∼500 m indicating the extent of the ABL influenced by the TNBP. Furthermore, the warming and deepening of convective boundary layer in the lowest 200 to 400 m in the profiles from 22 September is a classic picture of air mass modification above polynya [30,55].
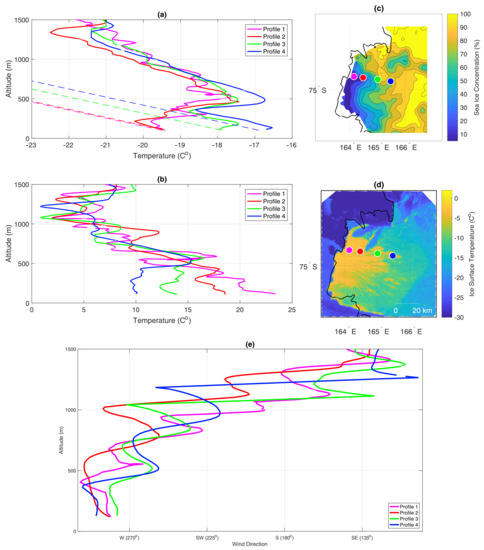
Figure 8.
UAS Aerosonde measurements from 22nd of September 2012. Subfigures labelled as in Figure 6. Profiles started at: 07:56 UTC (1); 08:34 UTC (2); 09:21 UTC (3); 10:05 UTC (4).
On the 25 of September the SIC in Terra Nova Bay is below 50% over a wide stretch of water near the coast (Figure 9c). The first 4 profiles are lined up perpendicularly to the coast. In all of them we can see extensive mixing and convection, as the temperature lapse rate is adiabatic till ∼600 m of altitude in first three profiles and even higher in profile 8 (Figure 9a). Elevated inversion and intensive mixing indicate that warm air from the surface penetrated deeply into the ABL. Furthermore, unstable conditions in profiles located far from the shore demonstrate us how the heat gained from the surface upstream is spread horizontally over a large distance (Figure 9a). Wind speed in profile 1 varies significantly with height and exceeds 20 m/s in almost the whole profile (Figure 9b). In the next two profiles the strength of the flow does not fall below 15 m/s, but as we move further from the coast the wind speed starts to decrease and in profile 4 reaches ∼12 m/s in the lowest layer of the ABL. Wind direction along the perpendicular line created by profiles 1–4 varies between southwest-west and above ∼1000 m changes to west.
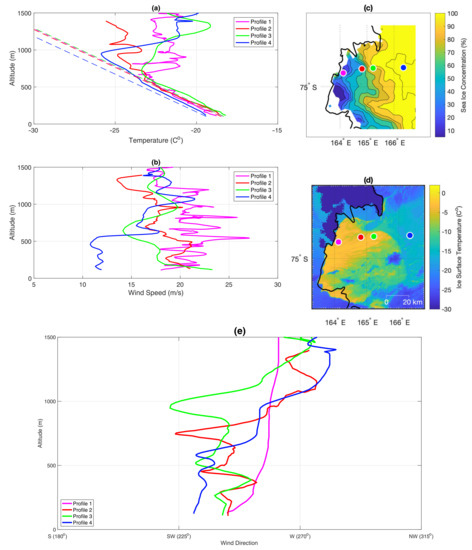
Figure 9.
UAS Aerosonde measurements from 25th of September 2012. Subfigures labeled as in Figure 6. Profiles started at: 07:25 UTC (1); 08:33 UTC (2); 09:13 UTC (4); 11:47 UTC (5).
Profiles 5–7 form a line across Terra Nova Bay. They are located over areas of SIC below 20–30% and show significant warming of the ABL from the surface (Figure 10a). Main temperature inversion in all profiles is located above ∼700 m of altitude; however, the temperature lapse rate is dry adiabatic in the first 200–300 m, marking the depth of the boundary layer. Moving from north to the south, the temperature in the lowest layer of the ABL decreases from −17 C (profile 5) to −22 C (profile 7) (Figure 10a). On the other hand, the wind speed in lowest layer of the atmosphere varies from 5 m/s in Profile 5 to 23 m/s in profile 6 and 12 m/s in Profile 7 (Figure 10b). Wind direction in profile 7 and 6 alternates between west-southwest in the whole profile, although the changes are bigger and expanding to south or west in profile 6. In the most northern profile, nr 5, the wind blows from west-southwest in the lowest layer of the ABL and then varies with altitude between northwest-southwest. The lack of katabatic signature in profiles 5 and 7 is due to their location on the verge of TNBP and away from main glacier flow, whereas profile 6 show a low level, downslope flow, consistent with the measurements from Figure 9.
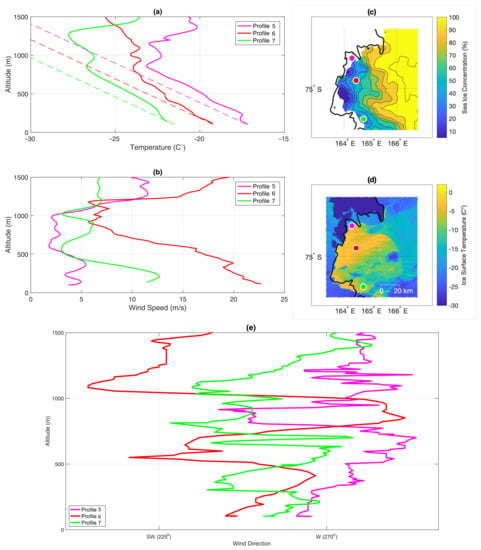
Figure 10.
UAS Aerosonde measurements from 25th of September 2012. Subfigures labeled as in Figure 6. Profiles started at: 09:28 UTC (5); 10:13 UTC (6); 11:14 UTC (7).
In contrast to previous days, when the dowslope flow was dominated by the katabatic component, on 25 September it is rather synoptically forced. Such conclusion can be made based on the variations of wind direction in all profiles, which include southwestern component in the lowest layer of the ABL. The low SLP north of Terra Nova Bay, near Oates Land, resulted in high pressure gradient between those areas of ∼15 hPa, which explains the southwestern direction of the flow throughout 25 September.
5. Validation of AMPS Results
The following analysis focuses on the UAS Aerosonde profiles (Figure 11), examined in Section 4 and Manuela AWS observations from the period of 18–25 September 2012. (Figure 4). The AMPS profiles, from the nearest model grid point to the location of UAS Aerosonde measurements, are compared with observations. The hourly AMPS output from 12 to 24 h forecasts is used in the analysis. The model output time closest to the beginning of UAS Aerosonde profile is used, thus, for profile starting at 07:25 UTC we analyse AMPS forecast from 07:00 UTC.
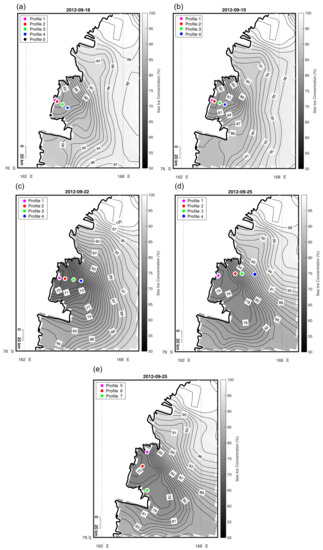
Figure 11.
Location of the UAS Aerosonde profiles with maps of AMPS sea ice concentration for profiles 1–4 from 18, 19, 22, 25 September 2012 (a–d) and profile 5-7 from 25 September 2012 (e).
A statistical analysis of AMPS model capability to simulate vertical and temporal changes of temperature and wind speed was carried out. We study the AMPS potential to reproduce vertical properties of the atmosphere (temperature and wind) during different stages of polynya development, along with temporal changes of wind speed on the Inexpressible Island. The atmosphere, from the lowest (∼100 m) up to the highest UAS Aerosonde flight altitude, has been divided into three vertical bins: lower (100–500 m), middle (500–1000 m) and upper (1000–1500 m). The following statistics are calculated for each of the bins and for the AWS observations, for both temperature and wind speed: RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error), Pearson’s correlation coefficient (Corr. coef.) and MBE (Mean Bias Error) (Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). The hypothesis of no correlation between UAS Aerosonde and AMPS profiles is tested with the p-value test. The correlation is regarded as significant when the p-value is smaller than the level of significance = 0.05. Furthermore, we consider the fit between model output and UAS Aerosonde measurements as good, when the Pearson’s correlation coefficient exceeds 0.70 and the RMSE, as well as MBE does not exceed a few C and m/s.

Table 2.
Statistics for the comparison of AMPS results and AWS Manuela observations between 18 and 25 September 2012. T—temperature, WS—wind speed.

Table 3.
Statistics for the comparison of AMPS results and UAS Aerosonde profiles in the lowest layer of the atmosphere (∼100–500 m). T—temperature, WS—wind speed.

Table 4.
Statistics for the comparison of AMPS results and UAS Aerosonde profiles in the middle layer of the atmosphere (500–1000 m). T—temperature, WS—wind speed.

Table 5.
Statistics for the comparison of AMPS results and UAS Aerosonde profiles in the upper layer of the atmosphere (1000–1500 m). T—temperature, WS—wind speed.
5.1. Manuela AWS and AMPS Model Time Series for Temperature and Wind Speed
A time series of wind speed and temperature for the nearest model grid point to Manuela AWS are compared with the measurements from the station for the period between 18 and 25 September. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient, RMSE and MBE are calculated to assess the correlation between modelled and observed values (Table 2). Obtained correlation coefficients indicate that temperature variations with time are slightly better simulated than wind speed (0.89 and 0.84, respectively). On average, as represented by the values of MBE, the differences between AMPS model results and Manuela AWS observations are small. However, short spikes in the AMPS time series of temperature and wind speed (Figure 12), together with RMSE of ∼2 C and ∼5 m/s (Table 2), indicate that sometimes the model tends to overestimate temporal variations of the katabatic flow. To the advantage of AMPS, the general pattern of temperature and wind speed changes throughout the studied period is well simulated, in particular intensive katabatic flow on the 18–22 and 25 September and its absence on 23 of September.
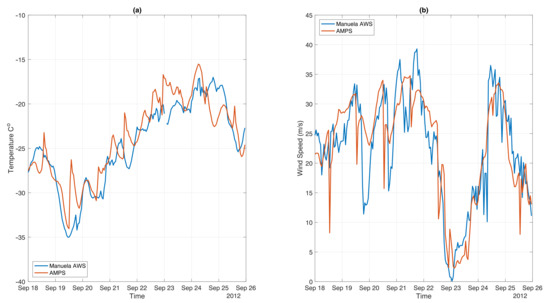
Figure 12.
Observations from Manuela AWS station and model results from the nearest point to Manuela AWS location for (a) temperature and (b) wind speed between 18 and 25 September 2012.
5.2. AMPS Results for 18 September 2012
In contrast to UAS Aerosonde measurements, a strong, low level inversion is present in the model results for profile 2 (Figure 13a). In consequence, correlation coefficient for this profile is negative in the lowest bin (Table 3). Overall, despite being interrupted by few, weak inversions, observed temperature decreases gradually with height from ∼100 m to ∼1100 m of altitude (Figure 13a). Whereas, in the AMPS results, the low level inversion layer is overlaid by colder air, which cools down steadily up to the top of the profile (Figure 13a). Therefore, due to similar lapse rates the model reproduces temperature profile well in the middle bin of the atmosphere (Table 4), although it is overestimated by ∼3.4 C. In the upper layer of the atmosphere due to absence of strong temperature inversion at ∼1100 m, the agreement between modelled and observed temperatures is poor (Table 5, Figure 13a). Meanwhile, the shape of wind speed profile is well simulated by the model up to 700 m of altitude (Figure 13b). At this height, modelled wind speed continues to decrease slowly, reaching few m/s in the uppermost layer, whereas the observed one fluctuates around 15 m/s till ∼1100 m and then slows down to ∼10 m/s. In consequence, the fit between AMPS and UAS Aerosonde wind speed in profile 2, is moderately good in the lowest and uppermost bins, even though the strength on the flow is overestimated in low altitudes (∼4 m/s) and underestimated in the highest one (∼−6.5 m/s) (Figure 13b).
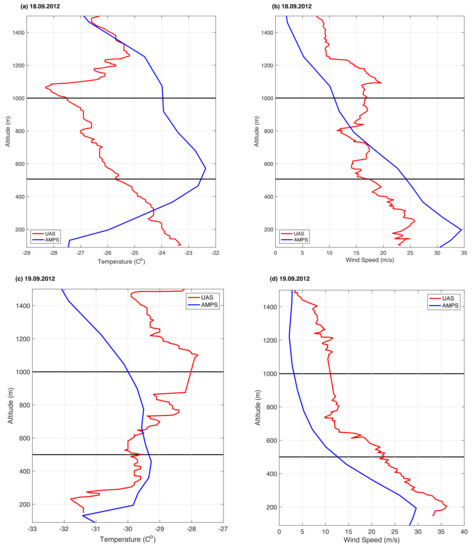
Figure 13.
Exemplary profiles from UAS Aerosonde observations and AMPS model results. (a,b) Profile nr. 2, 18.09.2012. (c,d) Profile nr. 4, 19.09.2012.
The aforementioned, low level inversion is present in profiles 0 and 4, which are well simulated by the model in the lowest layer of the atmosphere (∼100 m–500 m) (Table 3). The good fit at this locations might also be related to similar SICs, in AMSR2 sensor data and sea ice map applied to the model (∼85–100%) (Figure 11). In the same manner as in profile 2, temperature in the middle bin is quite well reproduced in all profiles, although a bit overestimated (Table 4). Whereas, in the uppermost layer the AMPS model fails to reproduce UAS Aerosonde measurements of temperature and correlation coefficients are negative (Table 5). Moving on to wind speed in the lowest bin it is, in contradiction to temperature, well simulated in profiles 1, 2, 3 but with quite large RMSE of ∼5–9 m/s (Table 3). The strength of the katabatic flow is, as in profile 2, overestimated. Whereas, in the overlapping layer (500–1000 m) wind speed changes with altitude are properly simulated only in profiles 3, 4 and 0, thus the ones located downstream and away from the downslope flow (Table 4). Model results for profile 3 also agree with observations in the uppermost layer, although the strength of the flow is underestimated (Table 5). Therefore, wind speed in profile 3 was well simulated throughout all bins, despite the fact that high correlation for temperature was only found in the middle one. Good fit between modelled and observed wind speeds at 1000–1500 m is also found in profiles 1 and 2 (Table 5).
5.3. AMPS Results for 19 September 2012
Temperature and wind speed in the lowest layer of the atmosphere are well reproduced by the AMPS model in all profiles from 19 September (Table 3). In the most downstream profile, nr 4, temperature is a bit overestimated up to the height of ∼600 m, where modelled and observed temperatures start to differ (Figure 13c). In the AMPS results temperature decreases with height from the beginning of middle bin up to the top height of the profiles (Figure 13c). Whereas, in the observations it generally increases up to ∼1100 m and then cools down with height. In consequence, the fit between modelled and measured temperatures in profile 4 is poor in the middle layer (Table 4) and quite good in the uppermost one (Table 5). Due to lack of mentioned atmosphere warming between the ∼600–1100 m the AMPS model underestimates temperatures in the 1000–1500 m layer by ∼−2 C (Figure 13c, Table 5). The shape of wind speed profile is well simulated in the first two bins, although flow intensity is underestimated by ∼7.5 m/s (Table 3 and Table 4). In the uppermost layer of the atmosphere, measured wind speed decreases with height, while in the model it remains almost constant (∼5 m/s) (Figure 13d), thus the agreement between both profiles is poor (Table 5). Furthermore, modeled profile 4 does not include small fluctuations of wind speed, which are present in UAS Aerosonde measurements (Figure 13d).
Overall, temperatures in the lowest bin, in all profiles from 19 September are well simulated and only a bit overestimated (∼1–2 C) (Table 3). In contrast, statistics for middle bin indicate poor agreement between modelled and observed temperatures (Table 4). Whereas, in the uppermost one the correlation for temperature is relevant only in profiles 3 and 4 (Table 5). In terms of wind speed, the AMPS results are highly correlated with measurements in both lowest and middle bins, although in the downstream profiles the RMSE is quite high (∼5–8 m/s). In general, on 19 September the model reproduces very well the properties of strong, katabatic flow in the lowest layer of the atmosphere. However, AMPS fails to simulate atmosphere warming in the upper bins and, while reproducing the shape of wind speed profile very well, underestimates the strength of the flow in all layers, which leads to poor agreement at higher altitudes (Table 5).
5.4. AMPS Results for 22 September 2012
AMPS model results and UAS Aerosonde measurements from 22 September contradict each other in the lowest layer of the atmosphere (Figure 14a, Table 3). The low level inversion is too strong and wind speed is too high in the model results for profile 3 (Figure 14a,b). However, higher in the atmosphere (∼500 m) both modelled and observed temperature, as well as wind speed, start to decrease with height (Figure 14a,b). In fact, AMPS and UAS Aerosonde profiles between the altitudes of 500–1000 m are very similar. In consequence, in the middle layer the correlation is high and the RMSE small (Table 4). Good fit between compared profiles of temperature continues into the uppermost layer (Figure 14a). The same cannot be said about wind speed, as modelled and observed profiles differ from each other in the highest altitudes in terms of lapse rate and strength (Figure 14b).
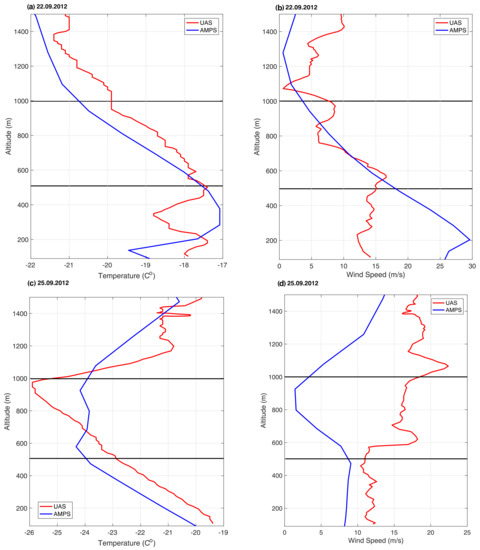
Figure 14.
Exemplary profiles from UAS Aerosonde observations and AMPS model results. (a,b) Profile nr 3, 22.09.2012. (c,d) Profile nr. 4, 25.09.2012.
Moving on to other profiles from 22 September, both temperature and wind speed in the lowest layer are poorly simulated by the AMPS model (Table 3). Good fit between model results and observations is found only for wind speed in profile 1 with high correlation coefficient (0.98) and low bias (−0.97 m/s) (Table 3). In opposition to the poorly simulated lowest layer of the atmosphere, the middle bin is much better reproduced (Table 4). The correlation for both wind speed and temperature is positive and high with RMSE smaller than ∼1 C for temperature and 4 m/s for wind speed. In the uppermost bin, temperature is well reproduced in profiles 1 and 3, with small bias and RMSE (∼0.5–1 C) (Table 5). Whereas, the AMPS results for wind speed at the highest altitudes does not match those found in the observations (Table 5).
5.5. AMPS Results for 25 September 2012
Unstable conditions in profile 4, in the lowest layer of the atmosphere from 25 September, are well reproduced by the AMPS model (Figure 14c). Temperature is underestimated by ∼1 C and wind speed by ∼3 m/s (Table 3). However, higher up in the atmosphere the fit between modelled and observed properties of profile 4 is poor. While in UAS Aerosonde measurements temperature decreases with height up to ∼1000 m of altitude, in the model air maintains almost constant temperature of −24–−23 C in the middle bin (Figure 14c). Furthermore, in both model results and observations the stretch of the atmosphere between 500 and 1000 m is overlaid by inversion layer, but in the measurements the inversion is stronger and overlapped by a layer of warmer air (Figure 14c). In consequence, the fit for profile 4 in terms of temperature is good only in the lowest bin. Moving on to wind speed, the AMPS and UAS Aerosonde profiles have contrasting shapes throughout the middle and uppermost bins (Figure 14d). In the lowest layer of the atmosphere the modelled flow is a bit weaker than the observed one but similar to observations maintains constant speed up to 500 m of altitude (Figure 14d).
Other temperature profiles from 25 September are also well reproduced by the model in the lowest bin, as indicated by high values of correlation coefficient (±0.95 in most profiles) (Table 3). The RMSE is relatively low, with an exception of profiles 1 and 3 where temperature is underestimated by ∼5 C (Table 3). On the other hand, wind speed is not well reproduced in AMPS models results, and only in profiles 6 and 7 the fit between compared profiles can be considered as moderately good. Insignificant correlations indicate that as in profile 4 (Figure 14d), wind speed does not change much with height up to 500 m of altitude. Moving on to the middle bin, a good fit between compared profiles is only present in profiles 2, 6, 7 for temperature and profile 6 for wind speed, although temperatures are underestimated by 3–4 C and wind speed is overestimated by ∼4 m/s (Table 4). In other profiles the correlation is either insignificant or minor. In the uppermost layer, good fit for temperature is found in profiles 1 and 4, thus the upwind and downwind ones (Table 5). Wind speed between 1000 and 1500 m is well reproduced in profile 2 and 7, although it is a bit underestimated (Table 5).
6. Discussion
This study focuses on the short period of time between 18 and 25 September 2012. Throughout those few days two cyclones moved from west to east along the Antarctic coast, the extent of TNBP changed from several tens of km2 to more than 2000 km2 and wind speed on Inexpressible Island varied between few m/s to more than 35 m/s (Figure 5a). Thus, even though the UAS Aerosonde measurements covered only few days, they provide valuable information about the atmospheric properties during different stages of polynya development.
Ebner et al. [6], Jolly et al. [56], Parish and Cassano [57] determined that synoptic scale pressure gradient plays an important role in determining the surface wind field in the coastal regions of the Antarctic and is crucial in the occurrence of extremely strong downslope flow. Turner et al. [5] in turn demonstrated that the location of the storm track plays an important role in the enhancement of the katabatic flow down the valleys. Short analysis of pressure gradient between Inexpressible Island and eastern Ross Sea and the movement of the cyclones in the region (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5) agrees with aforementioned findings. In the same way as described in Ebner et al. [6] the cyclone moving from west to east through 18–19 and 20–21 September (Figure 3a,b) along the Antarctic coast promotes the intensification of a downslope flow (Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8b). However, as explained by Jolly et al. [56], when the synoptic pressure gradient is reduced, mesoscale dynamics play a larger role in regulating the surface winds. Such situation is found on 25 September when the pressure gradient of ∼15 hPa between Oates Land and Terra Nova Bay increases due to the development of a mesoscale cyclone (Figure 3). In consequence, the direction of the flow shifts from northwest, which is typical for katabatic winds, to southwest. Furthermore, the analysis of Manuela AWS and UAS Aerosonde measurements indicates that while the flow on 18 and 19 September has mostly katabatic origin, due to low temperature and humidity, on the following days it has a more diverse background.
Similar to Ebner et al. [6] the katabatic winds are strongest at the beginning of polynya development, on 18 and 19 September (Figure 5a). As the intensive wind persists for a certain time the polynya starts to expand further into the bay (Figure 5a), in agreement with the conclusions of (i.a., Ciappa et al. [3], Yoon et al. [58]). The more opened is the polynya, the more intensive is the heat exchange between the surface and the atmosphere, which leads to deeper mixing in the ABL. The weakening of the flow and change in the weather conditions on Inexpressible Island (Figure 4), as well as in TNBP (Figure 5a) occurs within few hours leading to SIC increase in the polynya. Rapid reduction of polynya size and decrease in downslope flow strength are common in coastal regions of the Antarctic [59].
In general, UAS Aerosonde show us how complex the relationship and connections between surface, ABL and the flow from the interior of the continent is. The most intensive flows bring very cold and dry air (19 September, Figure 4) into the bay causing a drop in the temperatures (Figure 7a). As the winds drive the ice away from the shore the sea surface starts to release heat into the ABL to overcome a huge difference between air–water temperatures (up to 40 C). Intensive flow of air and decreasing sea ice cover drive the development of unstable boundary layer [60]. At the beginning of polynya development (18 and 19 September), the atmospheric conditions are more homogenous (Figure 6 and Figure 7), in response to relatively uniform surface properties and downslope flow. Whereas, when the SIC decreases, TNBP expands (Figure 5a) and the surface conditions vary between compact ice, frazil ice, sea ice floes and open water. In response, the profiles from 22 September differ from each other (Figure 8). Temperature inversion is present in the profiles further from the coast, while in those closer to the coast, where SIC is lower, temperatures decrease with height (Figure 8a). Additionally, comparison of profiles from 19 and 22 September show that very intensive winds are accompanied by low level inversion, which is absent or located at higher altitude in the profiles with lower wind speed. The development of deeper ABL in calmer wind conditions is well supported by past polynya studies [30,55,61,62].The last day of UAS Aerosonde flights is particularly interesting. In all profiles from 25 September the temperature lapse rate is approximately adiabatic, thus the convection takes place in the first 500 m (at least) of the ABL (Figure 9a). In comparison to 22 September the air above the boundary layer, near 500 m, has cooled by 5 C from conditions on the 22 September, with the pronounced inversion near 500 m on the 22nd no longer evident on the 25 September. Considering that the winds exceed 20 m/s only near the coast and in the northern part of the bay and flow from the southwest (Figure 9e), we can assume that the origins of the flow were different from the previous days. The direction of the wind (southwest) confirms our previous statement that the flow in Terra Nova Bay on this day is driven by pressure difference between Oates Land and the region of TNBP. Furthermore, we assume that weaker flow of cold air from the interior of the Antarctic on 25 September made the development of unstable conditions in a large portion of the ABL possible.
Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System predictions were evaluated, based on UAS Aerosonde observations and Manuela AWS measurements. The upwind conditions on an Inexpressible Island are well resolved by the model. The fluctuations of the katabatic flow throughout studied period, with its strengthening between 18 and 22 September, as well as abrupt weakening on 23 September are present in the model results (Figure 12). In terms of vertical structure of the atmosphere the AMPS model ability to reproduce temperature and wind speed in the air column depends on time and location of the UAS Aerosonde profile. On 19 September, despite underestimation of wind speed throughout the whole profile (Figure 13d), the AMPS model very well simulates the properties of cold and strong, low level katabatic flow (Figure 13c,d). Whereas on 18 and 22 September AMPS profiles include low level inversions, which are absent in the measurements (Figure 13a) or much weaker (Figure 14, accompanied by overestimated wind speed in the lowest layer of the atmosphere (Figure 13b and Figure 14b). Therefore, on those days the model tends to overrate the strength of the katabatic flow and underestimate atmosphere warming.
On 22 September, the upper layer of the atmosphere is better resolved than the lower one (Figure 14a,b) due to overestimated katabatic flow and different surface conditions. In fact, SIC data from AMSR2 sensor often does not match the one found in the AMPS model. Satellite based SIC maps show low concentrations (10–20%) over the polynya and high values (80–95%) on its edge due to the accumulation of newly formed ice. Whereas, in the AMPS model the SIC does not fall below 70% in the areas of polynya formation and gradually increases with the distance offshore (Figure 11). Inadequate surface conditions may also be responsible for aforementioned, too strong inversions (Figure 13a) or smaller height of unstable boundary layer (Figure 14c) due to limited heat exchange.
On 25 September the model reproduced unstable conditions from the lowest layer of the atmosphere, together with weak wind speed and south-westerly direction of the flow (Figure 14c,d and Figure 15d) very well. Furthermore, temperature and wind speed in the AMPS model results change steadily with height and in most cases do not include any jumps or second inversions found in UAS Aerosonde observations (Figure 13 and Figure 14), especially in the upper bin. Their origins are hard to define based on the available amount of data. Additionally, wind speed tends to decrease faster with height than in the measurements (Figure 13b and Figure 14b), which leads to higher values of RMSE and MBE (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). AMPS also erroneously simulates the temperature lapse rate and underestimates the upper atmosphere cooling (Figure 13c) and warming (Figure 14c) with height.
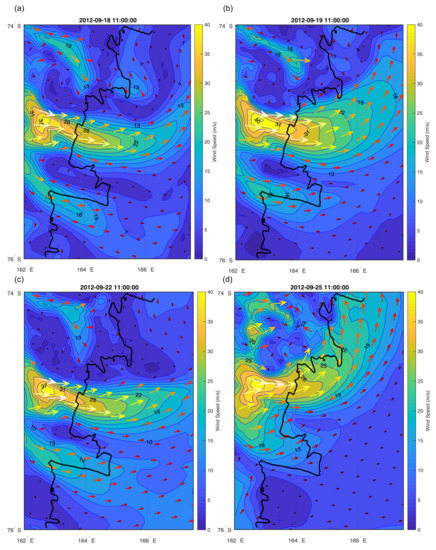
Figure 15.
AMPS model wind speed results for Terra Nova Bay region for the days of UAS Aerosonde flights, (a) 18, (b) 19, (c) 22, (d) 25 September 2012.
To summarise, in comparison to large scale climate models, which are unable to resolve katabatic wind events, the AMPS model represents the spatial distribution and intensity of strong winds near Terra Nova Bay quite well (Figure 15). However, the path of the flow might in some cases be too narrow or too wide, leading to high overestimation and underestimation of wind speed (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). Additionally, inadequate surface conditions, particularly the lack of SIC variations throughout the day in Terra Nova Bay, causes errors in both temperature and wind speed simulations. This is in agreement with conclusions of Bourassa et al. [34], who highlighted the importance of an accurate SIC data in numerical modelling of polar regions. Considering, that the variations of sea ice coverage in the bay, together with the intensity of the downslope flow (Figure 4a), may change quite rapidly, the AMPS model is probably unable to represent them accurately (e.g., 22 September). Furthermore, good/poor correlation for modelled wind speed profiles is not, in many cases, related to good/poor correlation for temperature profiles (e.g., profile 1, 2, 3 from 18 September; Table 3). Therefore, the errors in model results are related to both misrepresentation of katabatic flow intensity and surface conditions.
Due to lack of direct observations and increasing availability of satellite images, the majority of TNBP studies focused on polynya size and the relationship between its size and the strength of katabatic winds. UAS Aerosonde measurement give us a rare opportunity to study the ABL over Terra Nova Bay during different stages of polynya development and varying intensity of downslope/offshore flow. The surface conditions and properties of the downslope flow are interconnected and together affect temperature and wind speed throughout the ABL and the bay. Considering that our study focuses only on a few days, it only gives us a glimpse into the processes taking place in Terra Nova Bay in response to katabatic wind events and changing synoptic conditions. More observations are needed to fully understand the extreme winds and atmosphere–surface interactions in TNBP and improve predictions made by numerical weather prediction models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, J.J.C. and M.W.; methodology, J.J.C. and M.W.; formal analysis, M.W. and J.J.C.; investigation, M.W.; data curation, M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W.; writing—review and editing, J.J.C.; visualisation, M.W.; supervision, J.J.C.; project administration, M.W.; funding acquisition, M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Polish National Science Centre grant No.2019/32/T/ST10/00171 Submesoscale atmospheric boundary layer processes over inhomogenous sea ice.
Acknowledgments
The UAS field campaign was supported by United States National Science Foundation grant ANT 0739464.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Kurtz, D.; Bromwich, D. A Recurring, Atmospherically Forced Polynya in Terra Nova Bay. In Oceanology of the Antarctic Continental Shelf; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWoert, M. Wintertime dynamics of the Terra Nova Bay polynya. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 7753–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciappa, A.; Pietranera, L.; Budillon, G. Observations of the Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica) polynya by MODIS ice surface temperature imagery from 2005 to 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, T.; Bromwich, D. Reexamination of the Near-Surface Airflow over the Antarctic Continent and Implications on Atmospheric Circulations at High Southern Latitudes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Chenoli, S.; abu Samah, A.; Marshall, G.; Phillips, T.; Orr, A. Strong wind events in the Antarctic. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, L.; Heinemann, G.; Haid, V.; Timmermann, R. Katabatic winds and polynya dynamics at Coats Land, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2014, 26, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, P.; Bindoff, N.; Bergamasco, A. The sea ice dynamics of Terra Nova Bay and Ross Ice Shelf Polynyas during a spring and winter simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D. An Extraordinary Katabatic Wind Regime at Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, E.; McDonald, A.; Coggins, J.; Rack, W. Atmospheric forcing of sea ice anomalies in the Ross Sea polynya region. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, T.; Cassano, J. The Role of Katabatic Winds on the Antarctic Surface Wind Regime. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, S.; Cassano, J. An Analysis of Near-Surface Winds, Air Temperature, and Cyclone Activity in Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica, from 1993 to 2009. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, T.R.; Bromwich, D.H. Instrumented Aircraft Observations of the Katabatic Wind Regime Near Terra Nova Bay. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1570–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Ohshima, K.; Nihashi, S.; Kimura, N.; Tamura, T. Variability and ice production budget in the Ross Ice Shelf Polynya based on a simplified polynya model and satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 6234–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Yao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, S. Trends in the Stability of Antarctic Coastal Polynyas and the Role of Topographic Forcing Factors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.; Smith, M.; Thomson, J.; Stammerjohn, S.; Ackley, S.; Loose, B. Frazil ice growth and production during katabatic wind events in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3329–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnett, P.; Key, E. Chapter 4 Meteorology and Atmosphere–Surface Coupling in and around Polynyas. In Polynyas: Windows to the World; Smith, W., Barber, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 74, pp. 127–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Nihashi, S.; Iwamoto, K. Global view of sea-ice production in polynyas and its linkage to dense/bottom water formation. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.; Kurtz, D. Experiences of Scott’s Northern Party: Evidence for a relationship between winter katabatic winds and the Terra Nova Bay polynya. Polar Rec. 1982, 21, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.; Bromwich, D. Satellite observed behavior of the Terra Nova Bay Polynya. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1983, 88, 9717–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, S.; Parmiggiani, F. Wind over Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica) during a polynya event: Eta model simulations and satellite microwave observations. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2013, 128, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Hedgecock, I.; Landis, M.; Stevens, R. Intensive atmospheric mercury measurements at Terra Nova Bay in Antarctica during November and December 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, M.; Gregoris, E.; Barbaro, E.; Barbante, C.; Piazza, R.; Gambaro, A. Fragrances in the seawater of Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, L.; Feletti, M.; Francomacaro, B.; Mariottini, G. Summer coastal zooplankton biomass and copepod community structure near the Italian Terra Nova Base (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, G.; Meloni, R.; Picco, P. Current, Temperature and Salinity Observations in the Terra Nova Bay Polynya Area. In Oceanography of the Ross Sea Antarctica; Springer: Milano, Italy, 1999; pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, S.; Cassano, J.; Maslanik, J.; Herrmann, P.; Kernebone, P.; Crocker, R.; Logan, N. Unmanned aircraft system measurements of the atmospheric boundary layer over Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, J.; Seefeldt, M.; Palo, S.; Knuth, S.; Bradley, A.; Herrman, P.; Kernebone, P.; Logan, N. Observations of the atmosphere and surface state over Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica, using unmanned aerial systems. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, A.; Weidner, G.; Keller, L.; Thom, J.; Cassano, J. Antarctic Automatic Weather Station Program: 30 Years of Polar Observation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, T. A Numerical Study of Strong Katabatic Winds over Antarctica. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.; Du, Y.; Parish, T. Numerical Simulation of Winter Katabatic Winds from West Antarctica Crossing Siple Coast and the Ross Ice Shelf. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallée, H. Air-sea interactions over Terra Nova Bay during winter: Simulation with a coupled atmosphere-polynya model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 13835–13849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, R.; Atkinson, B. Numerical modeling of atmospheric response to polynyas in the Southern Ocean sea ice zone. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 16691–16708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Willmes, S.; Heinemann, G.; Rozman, P.; Timmermann, R.; Schröder, D. Evaluation of simulated sea-ice concentrations from sea-ice/ocean models using satellite data and polynya classification methods. Polar Res. 2011, 30, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.; Monaghan, A.; Manning, K.; Powers, J. Real-Time Forecasting for the Antarctic: An Evaluation of the Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System (AMPS). Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.; Gille, S.; Bitz, C.; Carlson, D.; Cerovecki, I.; Clayson, C.; Cronin, M.; Drennan, W.; Fairall, C.; Hoffman, R.; et al. High-Latitude Ocean and Sea Ice Surface Fluxes: Challenges for Climate Research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.; Monaghan, A.; Cayette, A.; Bromwich, D.; Kuo, Y.; Manning, K. Real-Time Mesoscale Modeling Over Antarctica: The Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsheimer, C.; Spreen, G. AMSR2 ASI sea ice concentration data, Arctic, version 5.4 (NetCDF) (July 2012–December 2018). PANGAEA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschudi, M.; Riggs, G.; Hall, D.; Romón, O. VIIRS/NPP Ice Surface Temperature 6-Min L2 Swath 750m; Version 1; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, M.M.; Willmott, A.; Biggs, N. Polynya Dynamics: A Review of Observations and Modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2004, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, É.; Traull, É.O.; Berne, A. On the fine vertical structure of the low troposphere over the coastal margins of East Antarctica. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4659–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmigianni, F. Multi-year measurement of Terra Nova Bay winter polynya extents. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2011, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massom, R.; Harris, P.; Michael, K.; Potter, M. The distribution and formative processes of latent-heat polynyas in East Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1998, 27, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Rothrock, D. Thin ice thickness from satellite thermal imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 25753–25766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, J.; Mahoney, R.; Liu, Y.; Romanov, P.; Tschudi, M.; Appel, I.; Maslanik, J.; Baldwin, D.; Wang, X.; Meade, P. Snow and ice products from Suomi NPP VIIRS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12816–12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.; Kuo, Y.; Bresch, J.; Cassano, J.; Bromwich, D.; Cayette, A. The Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Polar Meteorology and Oceanography, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 May 2001; pp. 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Center, E.M. The GFS atmospheric model. Natl. Centers Environ. Predict. Off. Note 2003, 442, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Bromwich, D.; Otieno, F.; Hines, K.; Manning, K.; Shilo, E. Comprehensive evaluation of polar weather research and forecasting model performance in the Antarctic. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.; Suarez, M.; Gelaro, R.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Liu, E.; Bosilovich, M.; Schubert, S.; Takacs, L.; Kim, G.; et al. MERRA: NASA’s Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3624–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.; Bromwich, D. Mesoscale cyclogenesis dynamics over the southwestern Ross Sea, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 12973–12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.; Steinhoff, D.; Simmonds, I.; Keay, K.; Fogt, R. Climatological aspects of cyclogenesis near Adélie Land Antarctica. Tellus Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2011, 63, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefeldt, M.; Cassano, J.; Parish, T. Dominant Regimes of the Ross Ice Shelf Surface Wind Field during Austral Autumn 2005. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 1933–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfrew, I.; Anderson, P. The surface climatology of an ordinary katabatic wind regime in Coats Land, Antarctica. Tellus Ser. Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2002, 54, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolio, S.; Buzzi, A. Mechanisms of Antarctic katabatic currents near Terra Nova Bay. Tellus A 2002, 54, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D. Satellite Analyses of Antarctic Katabatic Wind Behavior. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1989, 70, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, E.; Lachlan-Cope, T.; Renfrew, I.; King, J. Convective heat transfer over thin ice covered coastal polynyas. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, B.; McDonald, A.; Coggins, J.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Cassano, J.; Lazzara, M.; Graham, G.; Plank, G.; Petterson, O.; Dale, E. A Validation of the Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System Using Self-Organizing Maps and High-Density Observations from SNOWWEB. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2016, 144, 3181–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, T.; Cassano, J. Forcing of the Wintertime Antarctic Boundary Layer Winds from the NCEP–NCAR Global Reanalysis. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoon, S.; Lee, W.; Stevens, C.; Jendersie, S.; Nam, S.; Yun, S.; Hwang, C.; Jang, G.; Lee, J. Variability in high-salinity shelf water production in the Terra Nova Bay polynya, Antarctica. Ocean Sci. 2020, 16, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.; Kurtz, D. Katabatic wind forcing of the Terra Nova Bay polynya. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1984, 89, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, G. The polar regions: A natural laboratory for boundary layer meteorology—A review. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, L.; Schröder, D.; Heinemann, G. Impact of Laptev Sea flaw polynyas on the atmospheric boundary layer and ice production using idealized mesoscale simulations. Polar Res. 2011, 30, 7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K. On the boundary-layer flow over a Canadian Archipelago polynya. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1986, 35, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).