Sentinel-1 Data for Underground Processes Recognition in Bucharest City, Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
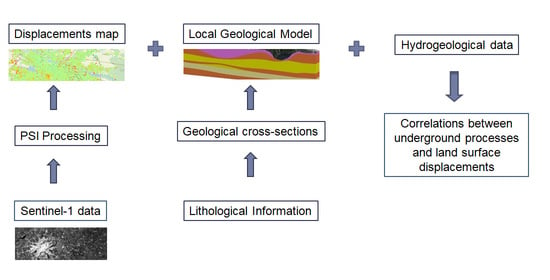
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SAR Data
Dv = (Dd sinθa + Da sinθd)/sin(θa + θd)
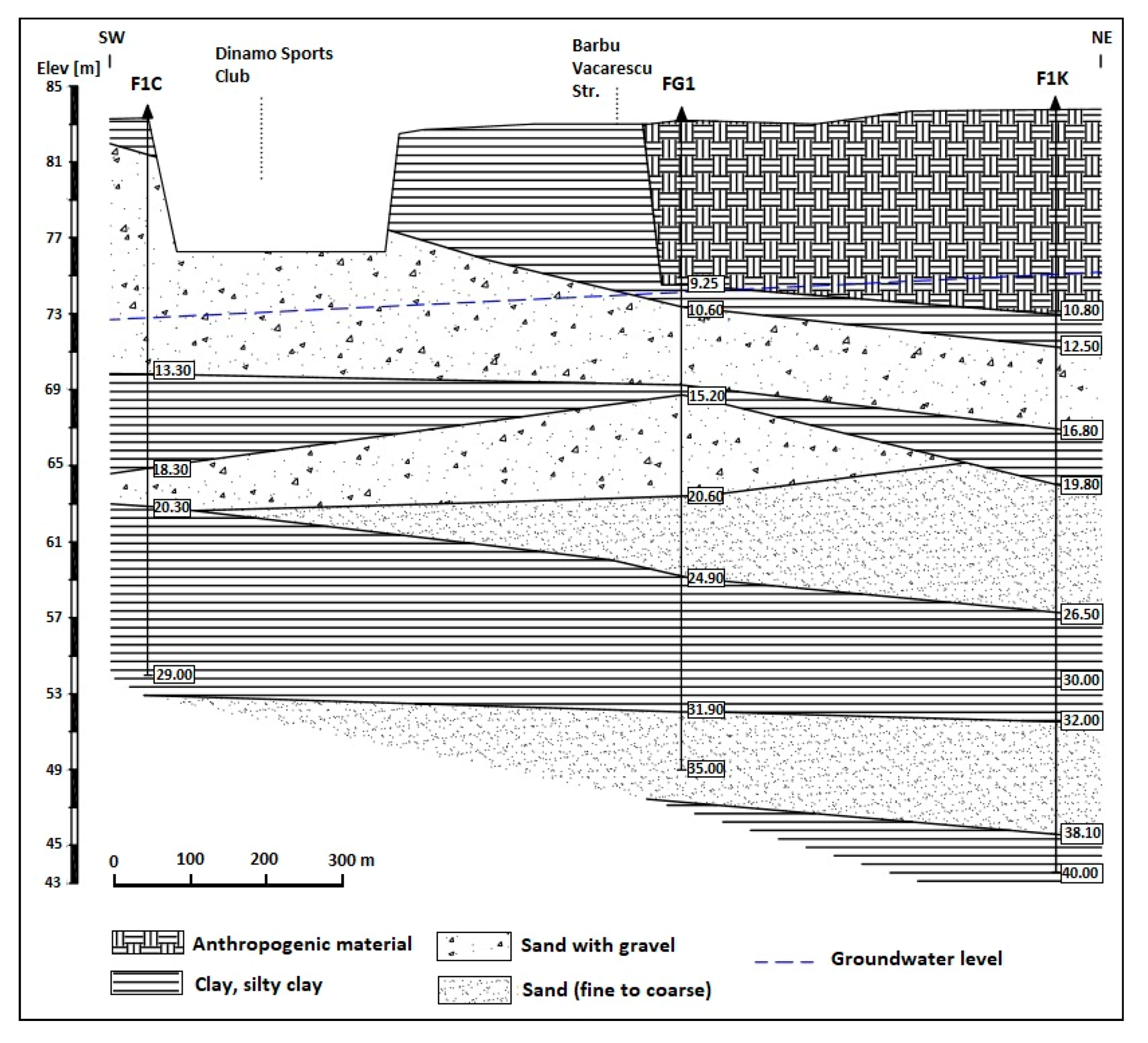
2.2. Development of the Urban Geological Model for the Study Area
- Collection of data consisting of lithological information from 16 boreholes with depths from 15 m up to 170 m; the 3D position of the boreholes was precisely measured;
- After analyzing the lithological and stratigraphical information of the boreholes, six geological cross-sections were generated, based on a digital elevation model (DEM) of the area;
- From the geological cross-sections, suplimentary interpolation points were used to generate the geological model;
- The structural units of the Quaternary deposits have been identified to generate the geological model.
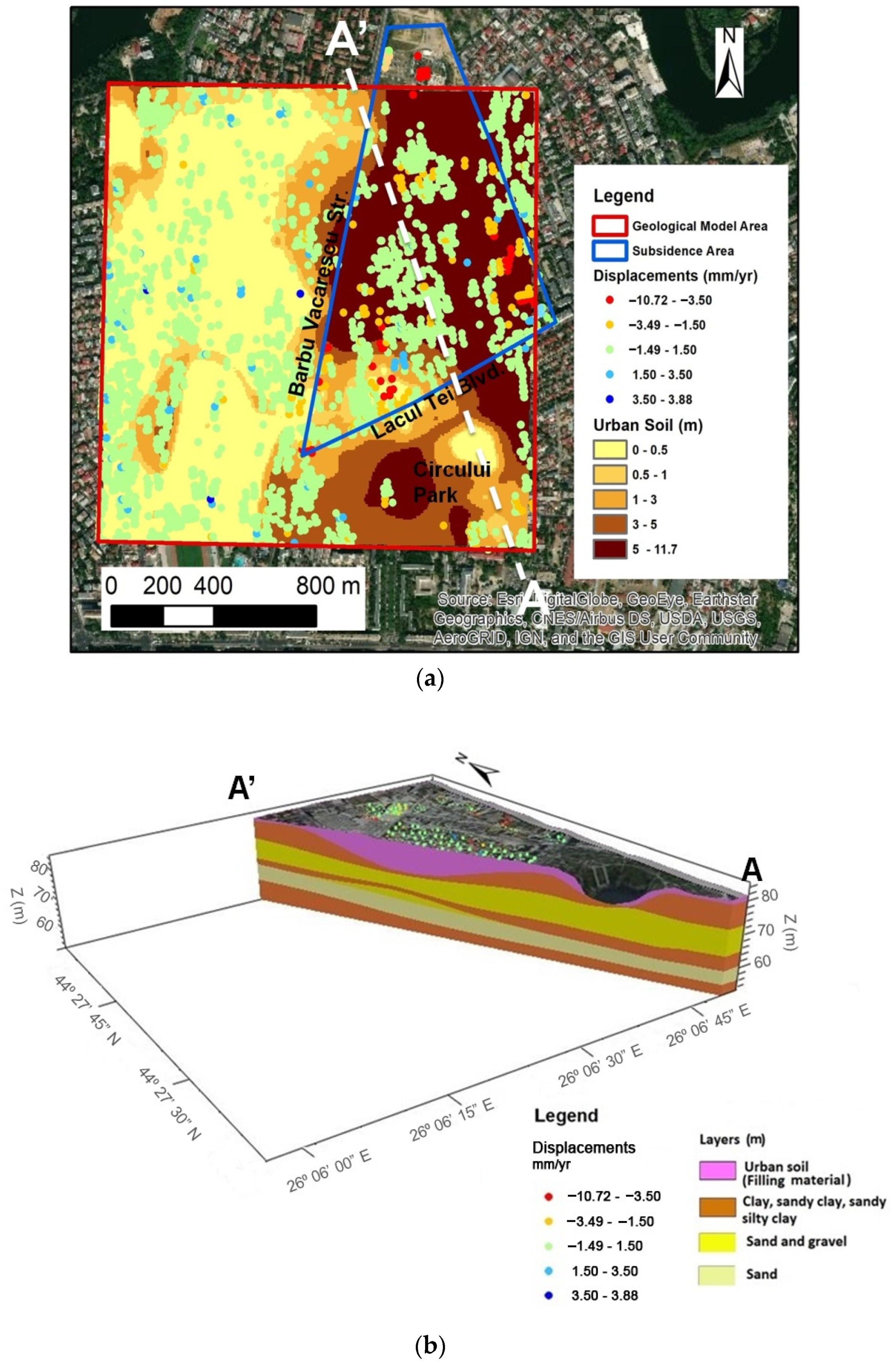
- Urban soil (anthropogenic material) layer, with depths up to approximately 12 m;
- Clay, sandy clay, and sandy silty clay layer with thicknesses up to 10 m;
- Sand and gravel layer with thicknesses up to 14 m;
- Discontinuous clay layer with thicknesses up to 5.3 m;
- Discontinuous sand and gravel layer with thicknesses up to 6 m;
- Sand layer with thicknesses up to 12 m;
- Clay layer with thicknesses up to 11.6 m.
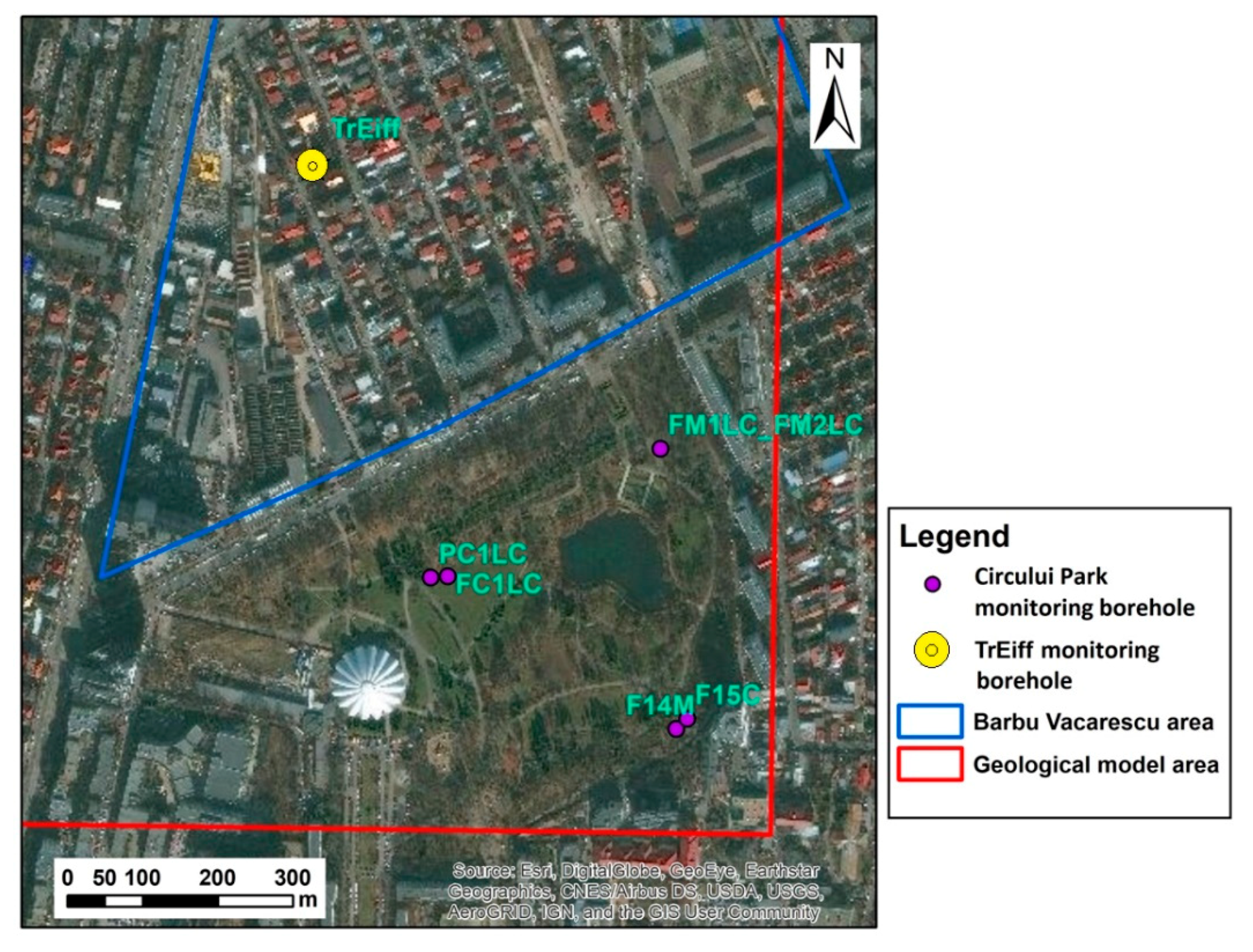
2.3. Hydrogeological Data Assemblage
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
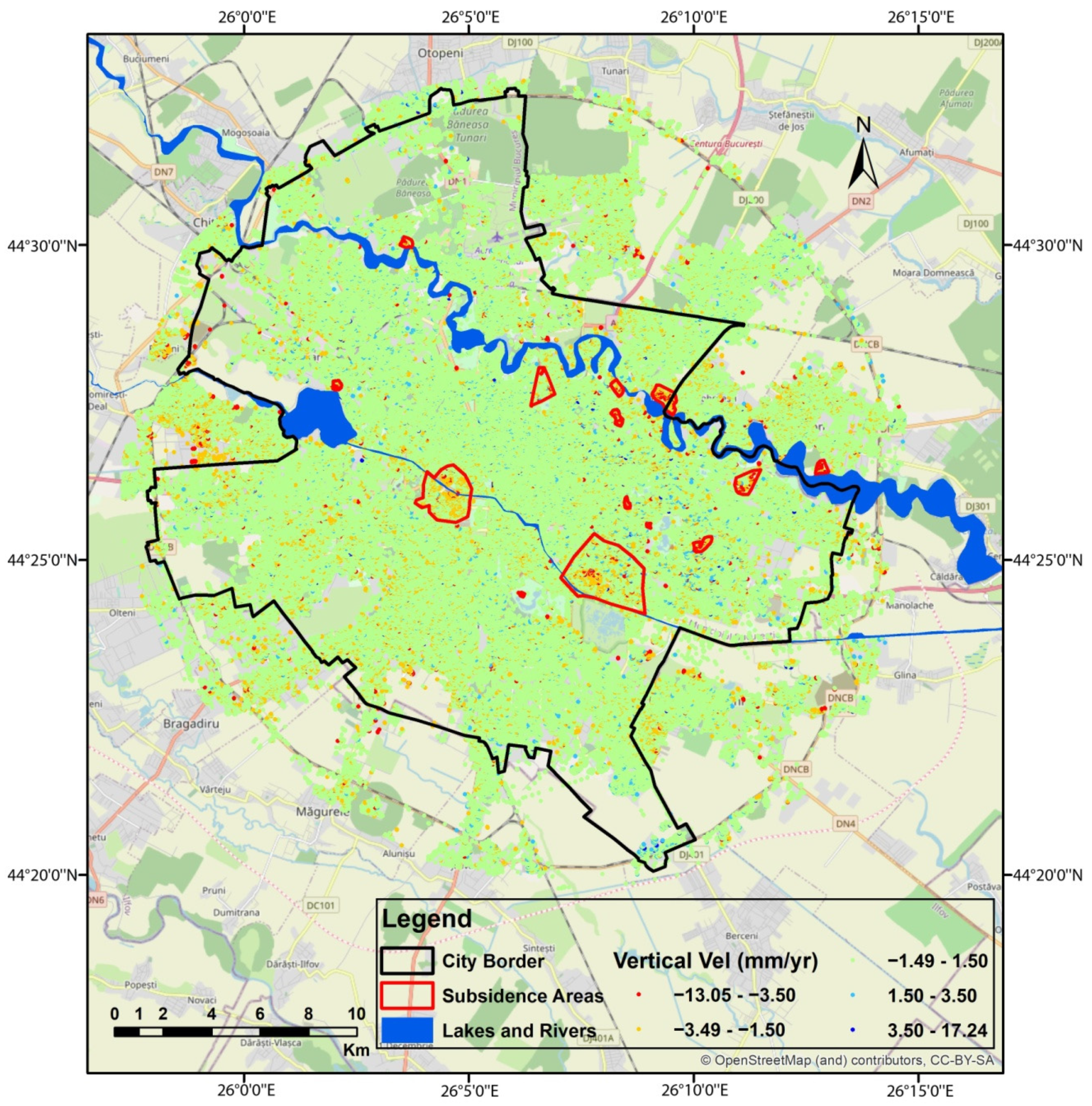
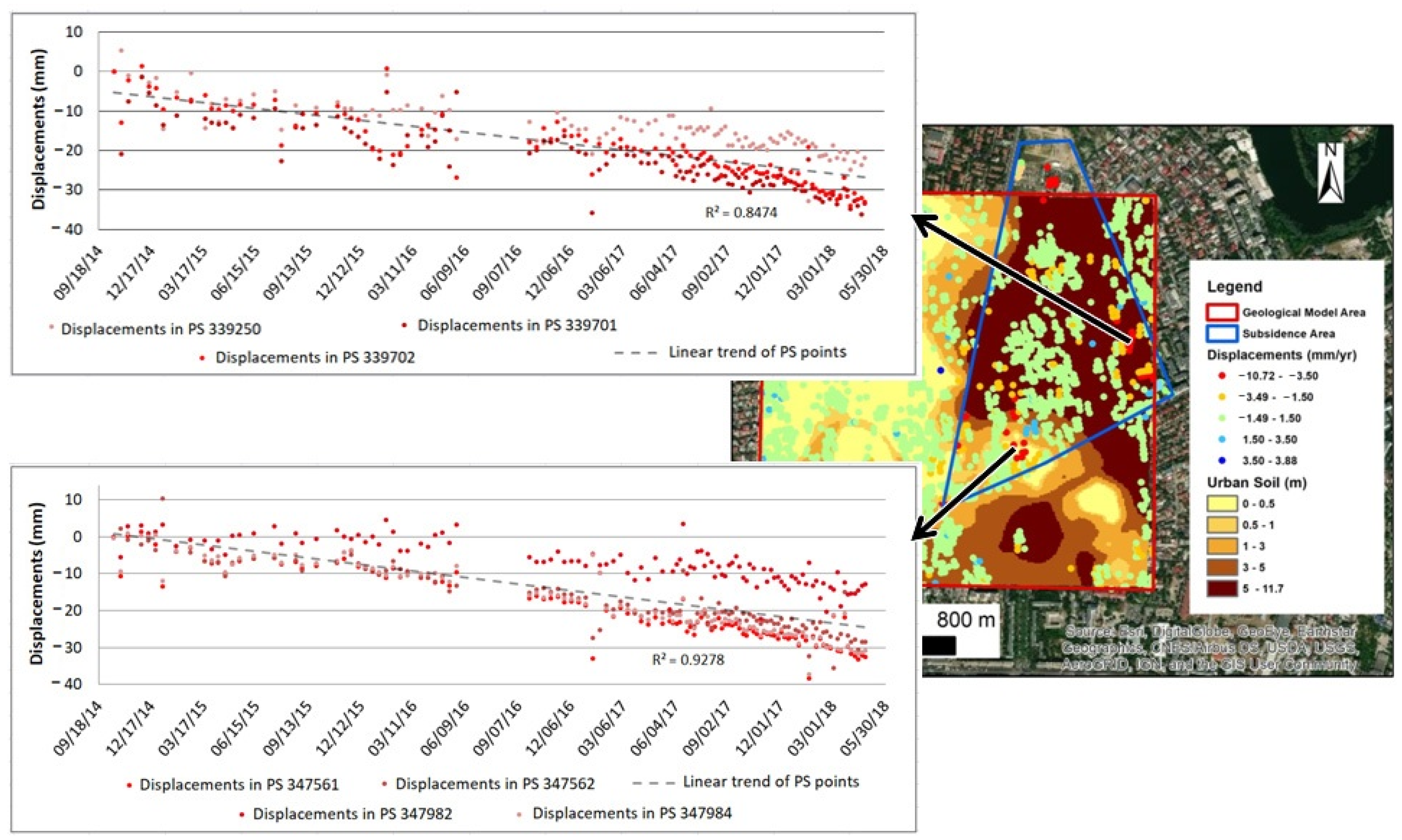
3.1. Bucharest City Vertical Displacements Map
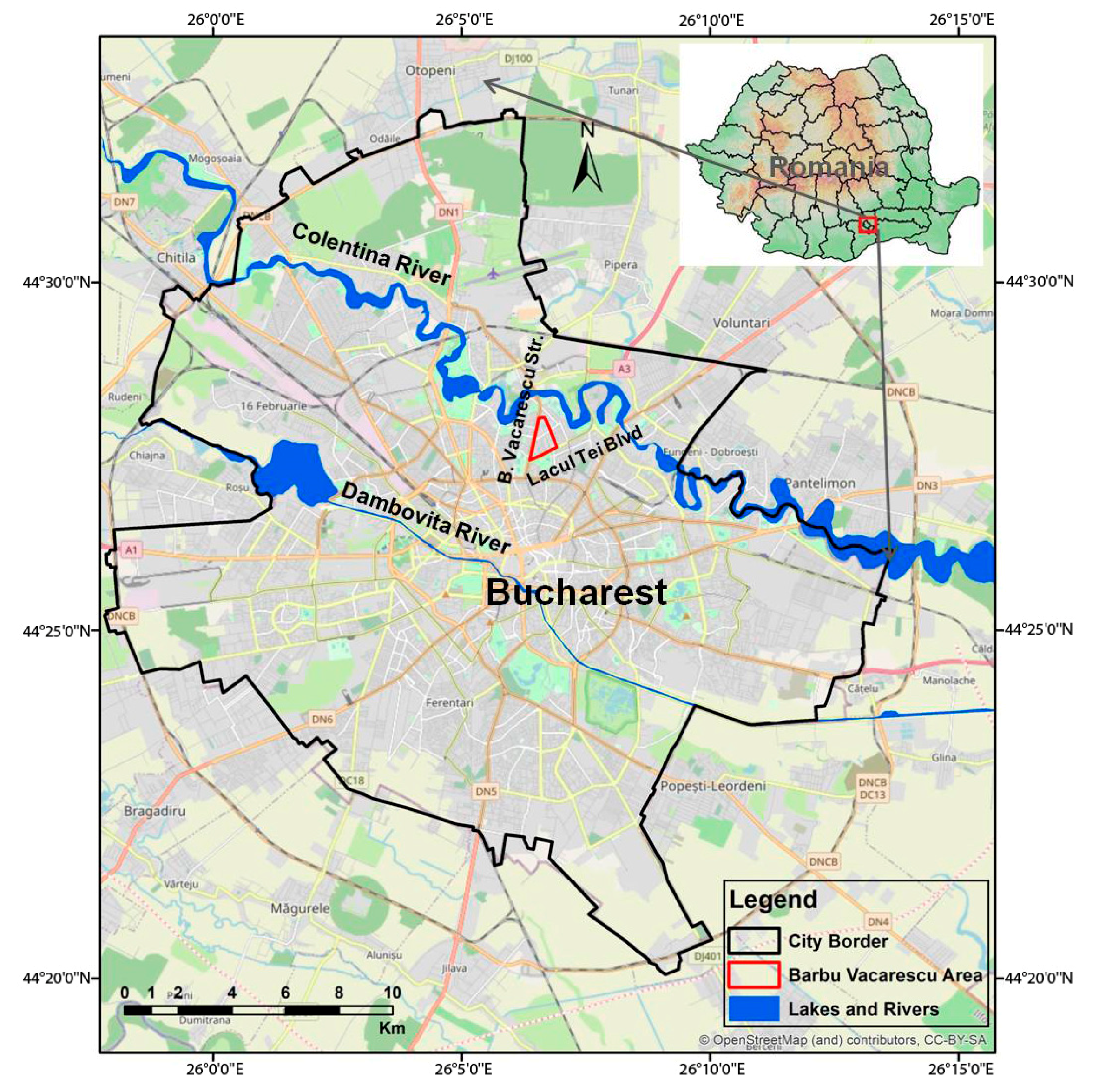
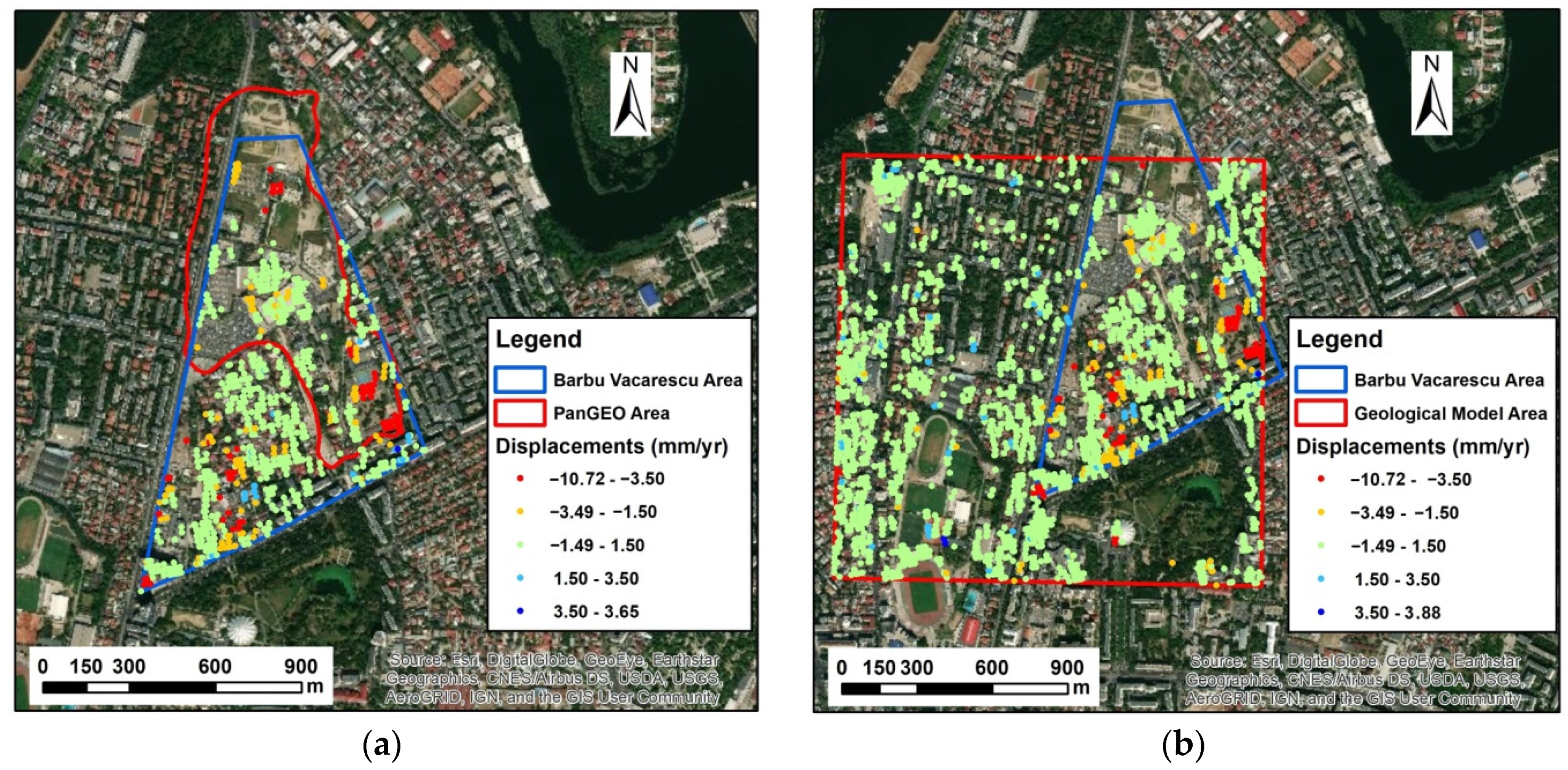
3.2. The Barbu Vacarescu Urban Area
3.2.1. Subsidence Analysis of the Anthropogenic and Geological Deposits in the Barbu Vacarescu Area
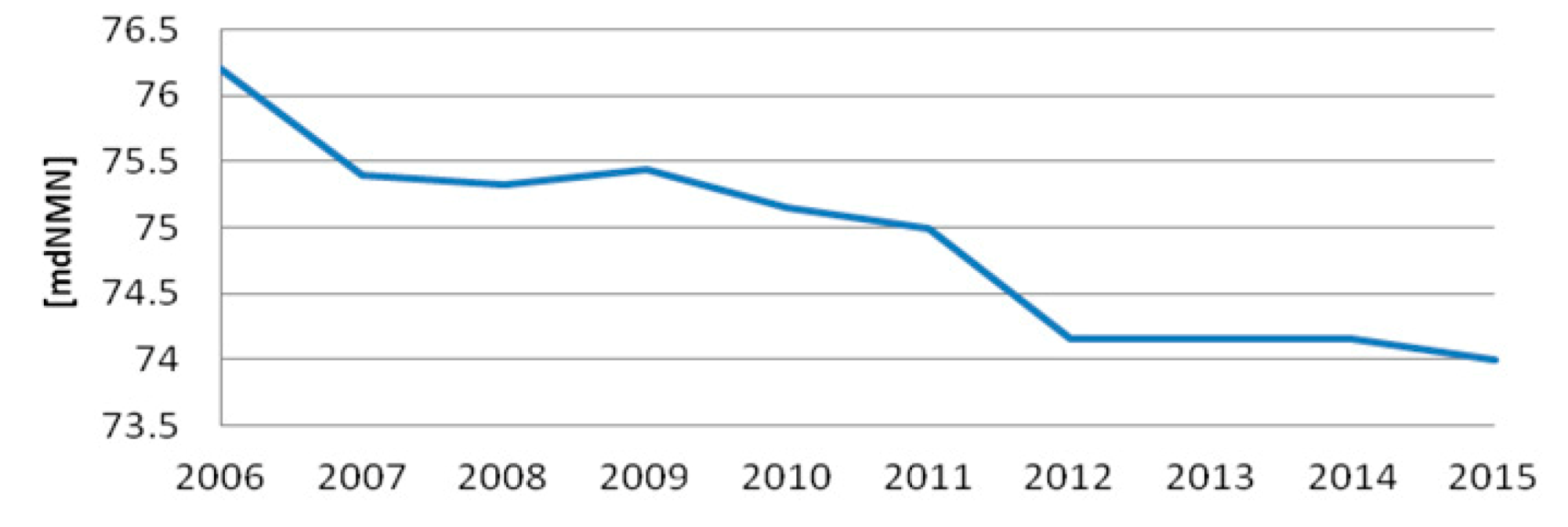
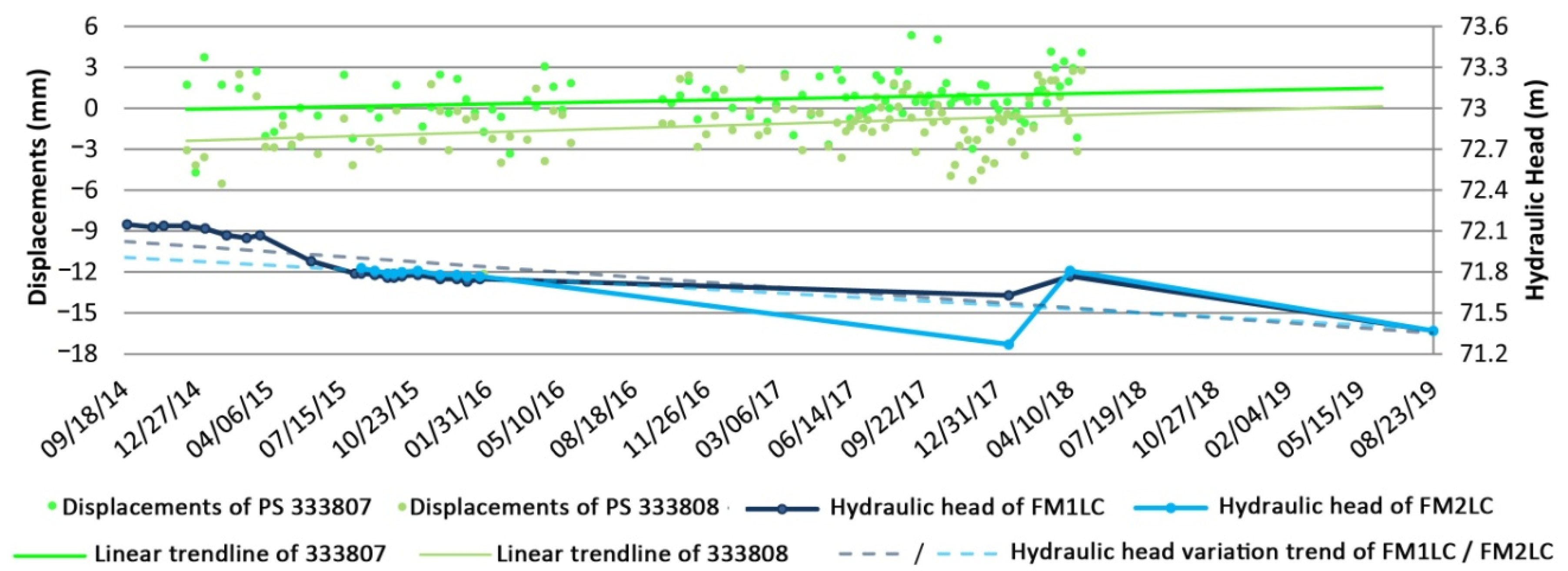
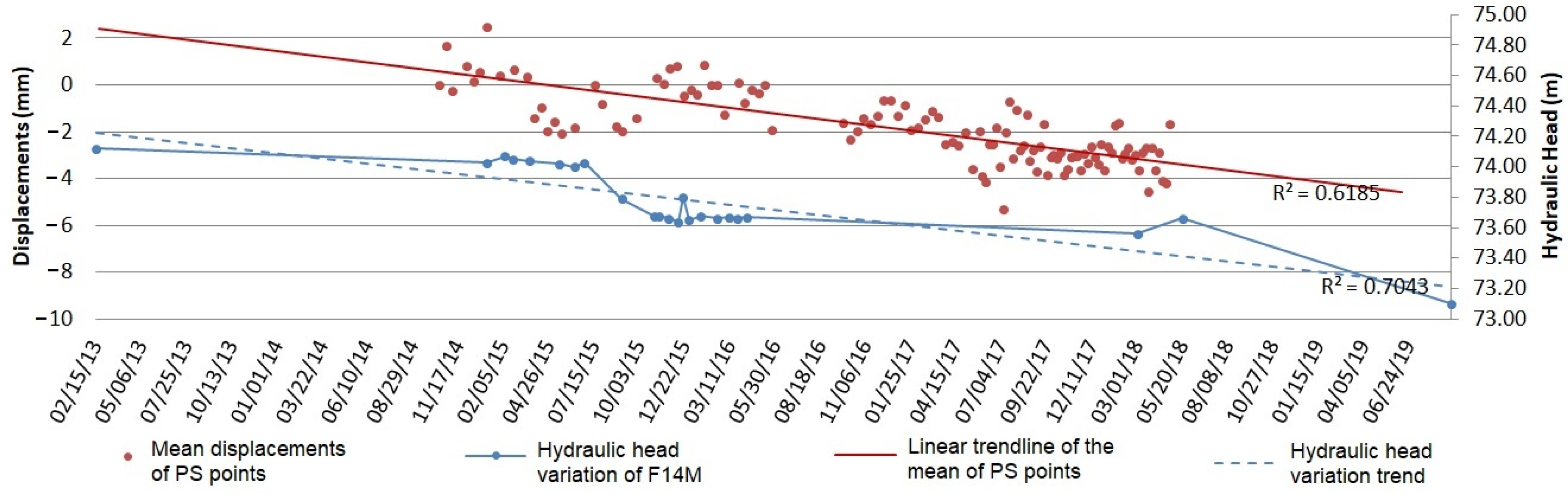
3.2.2. Relationship between Ground Surface Displacements and the Urban Aquifer System Dynamics in the Barbu Vacarescu Area
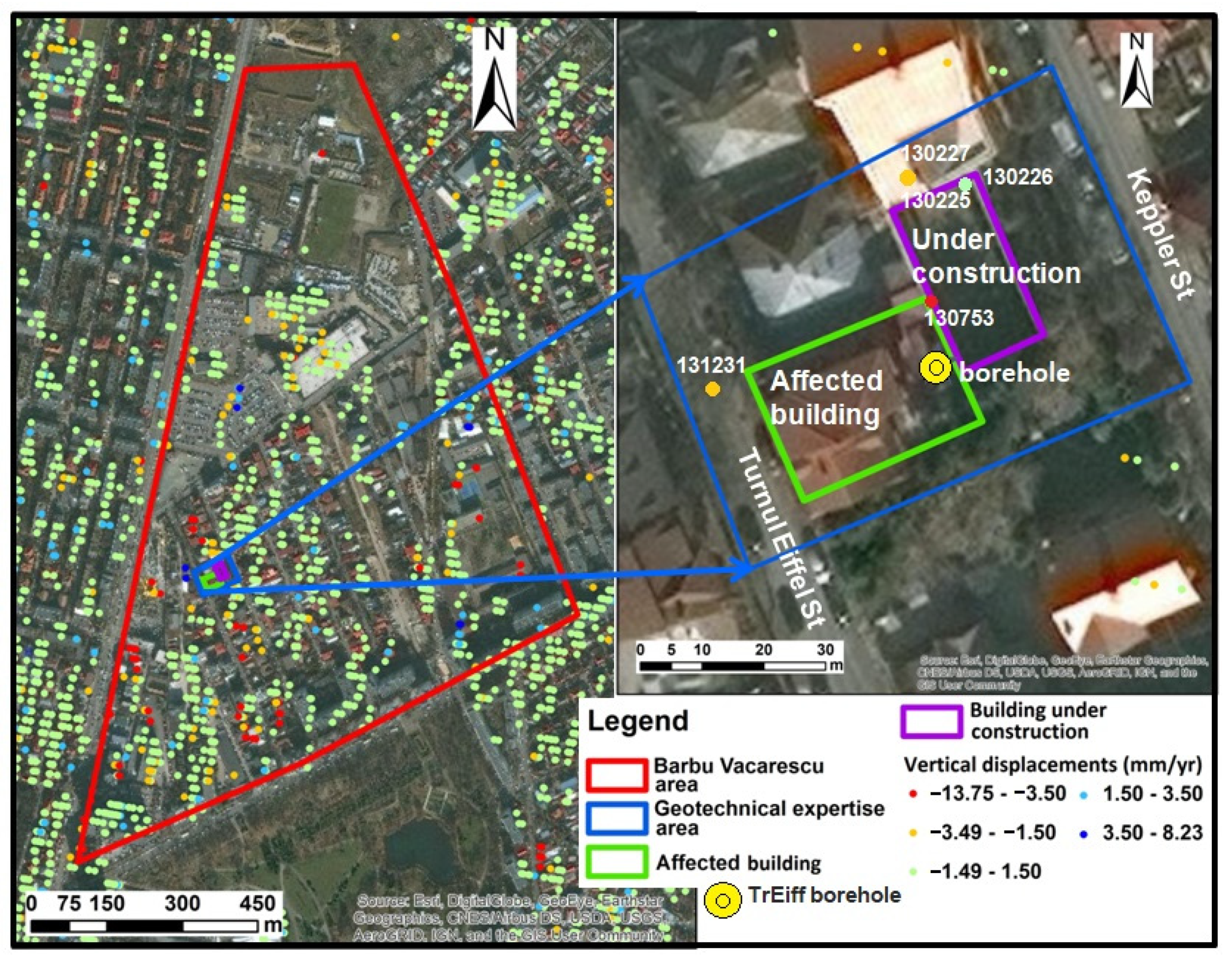
3.2.3. Study Case of a Building Situated in the Barbu Vacarescu Area
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Wibowo, I.R.R. On correlation between urban development, land subsidence and flooding phenomena in Jakarta. Proc. IAHS 2015, 370, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvinet, G.; Méndez, E.; Juárez, M. Recent information on Mexico City subsidence. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Seoul, Korea, 17–21 September 2017; pp. 3295–3298. [Google Scholar]
- Heleno, S.I.N.; Oliveira, L.G.S.; Henriques, M.J.; Falcao, A.P.; Lima, J.N.P.; Cooksley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P.; Fonseca, J.F.B.D. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry detects and measures ground subsidence in Lisbon. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Liu, G.X.; Li, Z.W.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Q. Ground Subsidence Monitoring in Hong Kong with Satellite SAR Interferometry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2004, 70, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakode, H.B.; Baier, K.; Jha, R.; Azzam, R. Impact of urbanization on groundwater recharge and urban water balance for the city of Hyderbad, India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, G.; Cakır, Z.; Ergintav, S.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Analysis of Secular Ground Motions in Istanbul from a Long-Term InSAR Time-Series (1992–2017). Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogu, C.R.; Gaitanaru, D.; Boukhemacha, M.A.; Serpescu, I.; Litescu, L.; Zaharia, V.; Moldovan, A.; Mihailovici, M.J. Urban Hydrogeology studies in Bucharest City, Romania. Procedia Eng. 2017, 209, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venvik, G.; Bang-Kittilsen, A.; Boogaard, F.C. Risk assessment for areas prone to flooding and subsidence: A case study from Bergen, West Norway. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radutu, A.; Nedelcu, I.; Gogu, C.R. An overview of ground surface displacements generated by groundwater dynamics, revealed by InSAR techniques. Procedia Eng. 2017, 209, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Arroyo-Domínguez, N.; Martel, R.; Calderhead, A.I.; Normand, J.C.L.; Gárfias, J.; Rivera, A. Land subsidence in major cities of Central Mexico: Interpreting InSAR-derived land subsidence mapping with hydrological data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 47, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Shamshiri, R.; Haghighi, M.H.; Wetzel, H.-U.; Akbari, B.; Nahavandchi, H.; Roessner, S.; Arabi, S. Quantifying groundwater exploration induced subsidence in the Rafsanjan plain, southeastern Iran, using InSAR timeseries and in situ measurements. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Doin, M.-P.; Lopez-Quiroz, P.; Tupin, F.; Fruneau, B.; Pinel, V.; Trouve, E. Mexico City Subsidence Measured by InSAR Time Series: Joint Analysis Using PS and SBAS Approaches. IEEE J. STARS 2012, 5, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Constan, A.; Ruiz-Armenteros, A.M.; Lamas-Fernandez, F.; Martos-Rosillo, S.; Delgado, J.M.; Bekaert, D.P.S.; Sousa, J.J.; Gil, A.J.; Cuenca, M.C.; Hanssen, R.F.; et al. Multi-temporal InSAR evidence of ground subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawal: The Montellano aquifer (SW Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.L. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.V.; d’Oreye, N.; González, P.J.; Tiampo, K.F.; Ertolahti, L.; Clague, J.J. Rapidly accelerating subsidence in the Greater Vancouver region from two decades of ERS-ENVISAT-RADARSAT-2 DInSAR measurements. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tomas, R.; Li, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Gong, X. Imaging Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Extraction in Beijing (China) Using Satellite Radar Interferometry. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Wdowinski, S.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Fumagalli, A. Recent subsidence of the Venice Lagoon from continuous GPS and interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Juan, A.; Pujades, E.; Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Crosetto, M.; Cuevas-González, M. Leveling vs. InSAR in urban underground construction monitoring: Pros and cons. Case of la sagrera railway station (Barcelona, Spain). Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, P.-Y.; Walstra, J.; Gerard, P.; Pirard, E.; Perissin, D.; Meyvis, B.; Devleeschouwer, X. A Study of Ground Movements in Brussels (Belgium) Monitored by Persistent Scatterer Interferometry over a 25-Year Period. Geosci. J. 2017, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Garfias, J.; Martel, R.; Brouard, C.; Rivera, A. InSAR to support sustainable urbanization over compacting aquifers: The case of Toluca Valley, Mexico. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 63, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence induced by urbanisation in the city of Rome detected by advanced InSAR technique and geotechnical investigations. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcari, M.; Albano, M.; Saroli, M.; Tolomei, C.; Lancia, M.; Moro, M.; Stramondo, S. Subsidence Detected by Multi-Pass Differential SAR Interferometry in the Cassino Plain (Central Italy): Joint Effect of Geological and Anthropogenic Factors? Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 9676–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Saroli, M.; Tolomei, C.; Moro, M.; Doumaz, F.; Pesci, A.; Loddo, F.; Baldi, P.; Boschi, E. Surface movements in Bologna (Po Plain- Italy) detected by multitemporal DInSAR. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, J.S. Guidebook to Studies of Land Subsidence due to Ground-Water Withdrawal; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bitelli, G.; Bonsignore, F.; Pellegrino, I.; Vittuari, L. Evolution of the techniques for monitoring at regional scale: The case of Emilia-Romagna region (Italy). Proc. IAHS 2015, 372, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radutu, A.; Gogu, R.C. Chronological reflection on monitoring urban areas subsidence due to groundwater extraction. In E3S Web of Conferences, Volume 85, Proceedings of the EENVIRO 2018 Conference: Sustainable Solutions for Energy and Environment, Cluj Napoca, Romania, 9–13 October 2018; Balan, M.C., Bode, F., Croitoru, C., Dogeanu, A., Georgescu, A., Georgescu, C., Nastase, I., Sandu, M., Eds.; EDP Sciences: Paris, France, 2019; p. 07015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direcția Regională de Statistică a Municipiului București. Available online: http://www.bucuresti.insse.ro/despre-bucuresti (accessed on 4 April 2020).
- Serpescu, I.; Radu, E.; Gogu, C.R.; Boukhemacha, M.A.; Gaitanaru, D.; Bica, I. 3D Geological model of Bucharest city quaternary deposits. In Proceedings of the 13th SGEM GeoConference on Sci and Technol in Geology, Exploration and Min, Albena, Bulgary, 16–22 June 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitanaru, D.; Gogu, C.R.; Boukhemacha, M.A.; Litescu, L.; Zaharia, V.; Moldovan, A.; Mihailovici, M.J. Bucharest city urban groundwater monitoring system. Procedia Eng. 2017, 209, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vîjdea, A.; Bindea, G. D7.1.33 GeoHazard Description for Bucharest. Report in the frame of FP7 PanGeo: Enabling Access to Geological Information in Support of GMES project; 2013. Available online: http://www.pangeoproject.eu (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Poncos, V.; Teleaga, D.; Boukhemacha, M.A.; Toma, S.A.; Serban, F. Study of urban instability phenomena in Bucharest city based on Ps-InSAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada; 2014; pp. 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Armaş, I.; Necşoiu, M.; Mendes, D.; Gheorghe, M.; Gheorghe, D. Ground displacement trends in an urban environment using Multi-Temporal InSAR analysis and two decades of multi-sensor satellite-based SAR Imagery. In Proceedings of the ESA SEOM Fringe 2015 Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Armas, I.; Mendes, D.; Popa, R.; Gheorghe, M.; Popovici, D. Long-term ground deformation patterns of Bucharest using multi-temporal InSAR and multivariate dynamic analyses: A possible transpressional system? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, M.; Armas, I.; Dumitru, P.; Calin, A.; Badescu, O.; Necsoiu, M. Monitoring subway construction using Sentinel-1 data: A case study in Bucharest, Romania. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2020, 41, 2644–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogu, C.R.; Serpescu, I.; Perju, S.; Gaitanaru, D.; Bica, I. Urban Groundwater Modeling Scenarios to simulate Bucharest city lake disturbance. In Proceedings of the 15th SGEM GeoConference on Sci and Technol in Geology, Exploration and Min, Albena, Bulgary, 18–24 June 2015; Volume 2, pp. 834–840. [Google Scholar]
- CCIAS. Scientific Report on Research Project: Assessment and Monitoring of the Urban Impact (Urban Infrastructures) on the Aquatic Environment Represented by the Lake in Circului Park), Beneficiary: Park, Lakes and Recreation Administration Bucharest [in Romanian]; Technical University of Civil Engineering Bucharest: Bucharest, Romania, 2015; (unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- Romanian National Institute of Statistics. Romanian Statistical Yearbook. Available online: https://insse.ro/cms/ro/tags/anuarul-statistic-al-romaniei (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar Interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer systemc compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Berardino, P.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E.; Fornaro, G. Urban subsidence inside the city of Napoli (Italy) observed by satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Thiele, A.; Hinz, S.; Meyer, F.J.; Hooper, A.; Agram, P.S. Comparison os Small Baseline Interferometric SAR Processors for Estimating Ground Deformation. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Calo, F. A Review of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture RADAR (InSAR) Multi-Track Approaches for the Retrieval of Earth’s Surface Displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Ruiz, A.M.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Perski, Z.; Bastos, L.C.; Gil, A.J.; Galindo-Zaldivar, J.; de Galdeano, C.S.; Alfaro, P.; et al. Multi-temporal InSAR for deformation monitoring of the Granada and Padul faults and the surrounding area (Betic Cordillera, southern Spain). Procedia Technol. 2014, 16, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, M.; Shirzaei, M. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift in Phoenix using InSAR time series and wavelet transforms. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 5822–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, I.; van Leijen, F.; Jonkman, S.; Hanssen, R. Applicability of satellite radar imaging to monitor the conditions of levees. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-Gonzales, M.; Devanthery, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatter Interferometry: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; Rosich, B.; Miranda, N.; Grimont, P. Sentinel-1 Mission Status. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Open Access Hub. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- European Space Agency, Sentinel Online, Interferometric Wide Swath. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar/acquisition-modes/interferometric-wide-swath (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, C. Nonlinear Subsidence Rate Estimation Using Permanent Scatterers in Differential SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Notti, D.; Colombo, A.; Cucchi, A.; Savio, G.; Giannico, C.; Bianchi, M. Geological Interpretation of PSInSAR Data at Regional Scale. Sensors 2008, 8, 7469–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Falabella, F.; Mastro, P.; Pepe, A. Generation of long-term InSAR ground displacement time-series through a novel multi-sensor data merging technique: The case study of the Shanghai coastal area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 154, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KSAT Ground Monitoring Services (KSAT-GMS). Available online: http://gms.ksat.no/ (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Dehls, J.F.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Lauknes, T.R.; Stodle, D.; Moldestad, D.A. INSAR.NO: A National InSAR Deformation Mapping/Monitoring Service in Norway- From Concept to Operations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019- IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5461–5464. [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Via, G.; Crosetto, M.; Crippa, B. Resolving vertical and east-west horizontal motion from differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar: The L’Aquila earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, B02310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foumelis, M. Vector-based approach for combining ascending and descending persistent scatterers interferometric point measurements. Geocarto Int. 2016, 33, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCIAS. Hydrogeological flow model for the Moesic aquifer system (Bucharest Area). Research project: Sedimentary Media Modeling Platform For Groundwater Management In Urban Areas (SIMPA). Scientific Report, No 10 [in Romanian]; Technical University of Civil Engineering Bucharest: Bucharest, Romania, 2013; (unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- Gogu, R.C.; Velasco, V.; Vazquez-Sune, E.; Gaitanaru, D.; Chitu, Z.; Bica, I. Sedimentary media analysis platform for groundwater modeling in urban areas. In Advances in the Research of Aquatic Environment. Environmental Earth Sciences; Lambrakis, N., Stournaras, G., Katsanou, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Manea, S. Technical Expertise for a Building Situated on Turnul Eiffel Str.; 2016; (unpublished). (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Research and Development for Land Reclamation “ISPIF” Bucharest. Study on the Geotechnical Zoning of Bucharest City; 1977; (unpublished). (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Stanciu, A.; Lungu, I. Tasarea Construcțiilor. In Fundații- Fizica și Mecanica Pământurilor, 1st ed.; Editura Tehnica: Bucharest, Romania, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 781–799. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Jia, P. Investigation of Land Subsidence Based on the Column Element Settlement Model in a Soft-Soil Area. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellenius, B.H. Pile Foundations. In Foundation Engineering Handbook; Fang, H.Y., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 511–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogu, C.R.; Gaitanaru, D.; Tormo, R.; Radutu, A. Report INXCES (Innovations for eXtreme Climatic EventS, https://inxces.eu/) submitted to Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research and Innovation, CCCDI-UEFISCDI grant number 48/2013 Cofound-202-INXCES, with PNCDI III; 2016; (unpublished). (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]




| Satellite | Acquisition Mode | Orbit Type | Track | Number of Acquisitions | Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel 1 | Interferometric Wide Swath (IW) | Ascending | 131 | 115 | 14 October 2014/26 April 2018 |
| Descending | 109 | 153 | 13 October 2014/25 April 2018 |
| No. | Borehole Code | Aquifer Stratum |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | F15C | Shallow |
| 2 | PC1LC | Shallow |
| 3 | FC1LC | Shallow |
| 4 | FM2LC | Shallow |
| 5 | FM1LC | Middle |
| 6 | F14M | Middle |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radutu, A.; Venvik, G.; Ghibus, T.; Gogu, C.R. Sentinel-1 Data for Underground Processes Recognition in Bucharest City, Romania. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244054
Radutu A, Venvik G, Ghibus T, Gogu CR. Sentinel-1 Data for Underground Processes Recognition in Bucharest City, Romania. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244054
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadutu, Alina, Guri Venvik, Traian Ghibus, and Constantin Radu Gogu. 2020. "Sentinel-1 Data for Underground Processes Recognition in Bucharest City, Romania" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244054
APA StyleRadutu, A., Venvik, G., Ghibus, T., & Gogu, C. R. (2020). Sentinel-1 Data for Underground Processes Recognition in Bucharest City, Romania. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4054. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244054