Vegetation Dynamic Changes and Their Response to Ecological Engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Sources and Preprocessing
3.1.1. NDVI Data and Preprocessing
3.1.2. Meteorological Data Sources and Preprocessing
3.1.3. Socioeconomic Data
3.2. Specific Research Methods
3.2.1. Linear Regression Method
3.2.2. The Cumulative Departure from the Mean
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Results
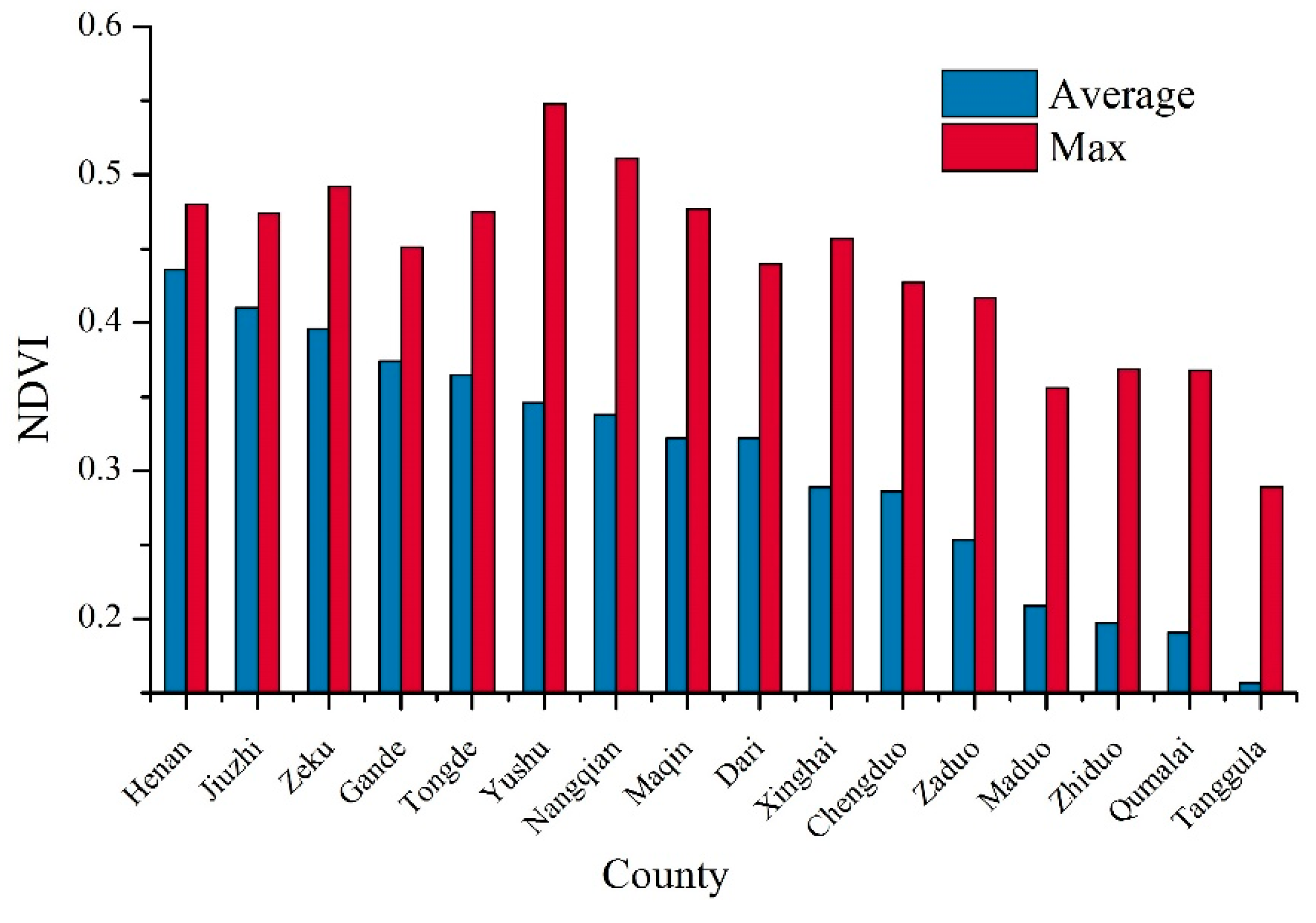
4.1. NDVI Distribution Characteristics
4.2. NDVI Interannual Variation Characteristics
4.3. The Spatial Variation Tendency of Vegetation from 1982 to 2015
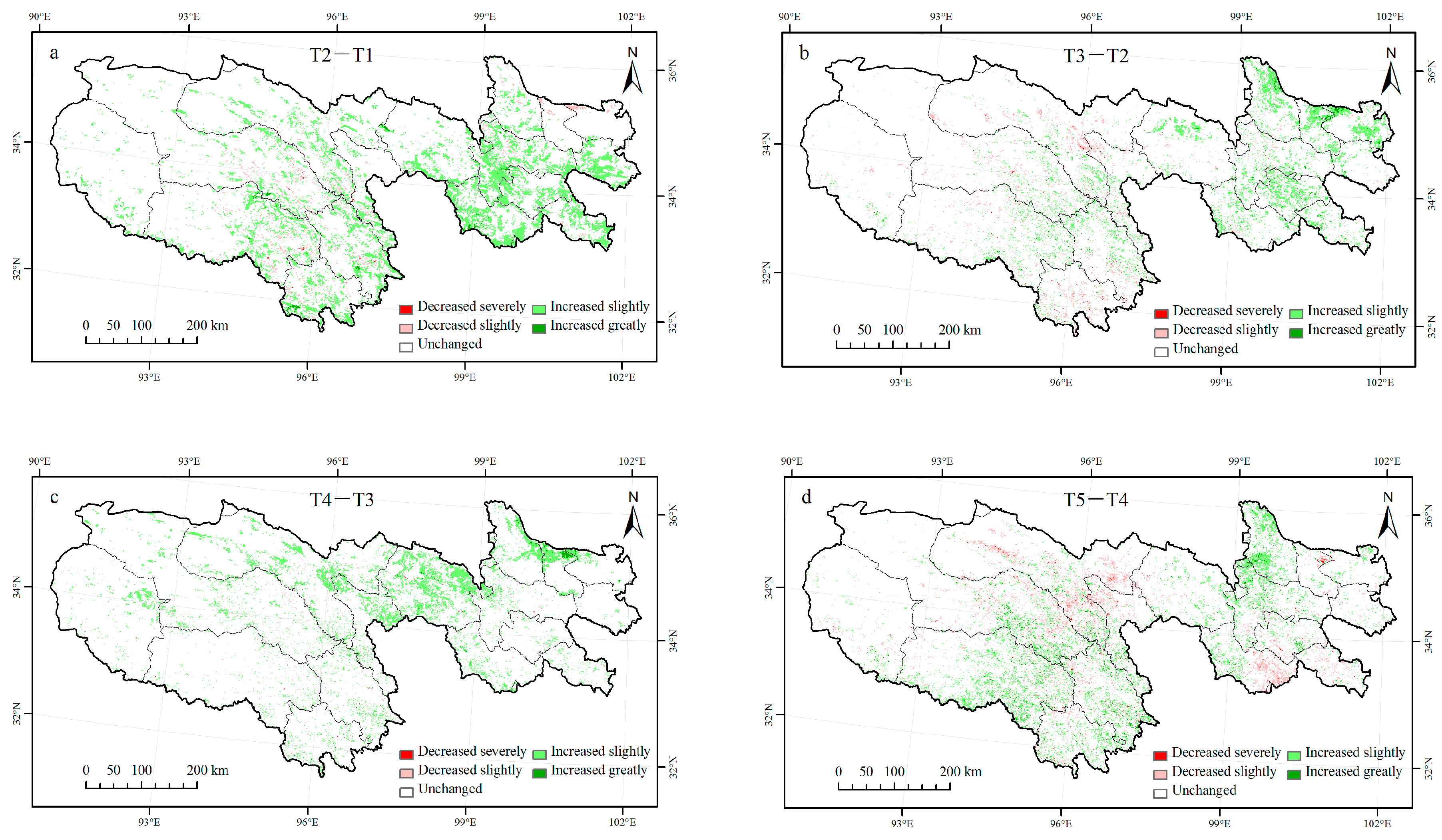
4.4. Spatial Variation of Vegetation in Different Periods
5. Analysis of the Factors Influencing the Vegetation NDVI Changes
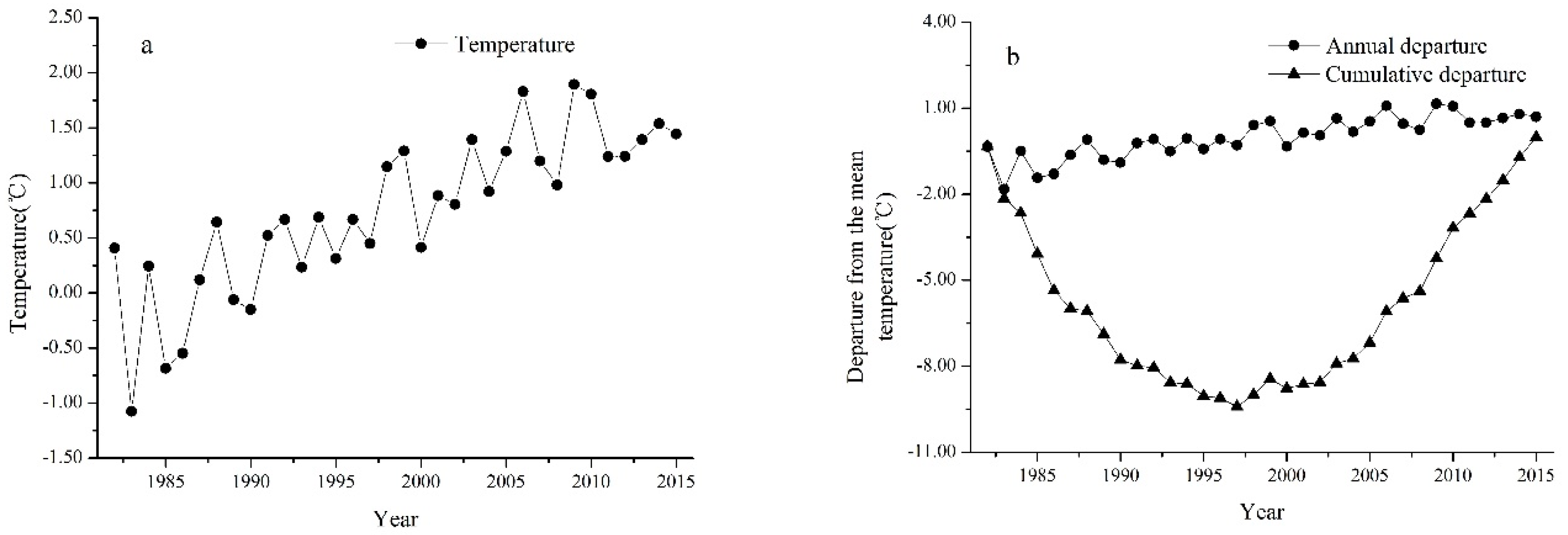
5.1. Temporal Change Characteristics of Climate Factors
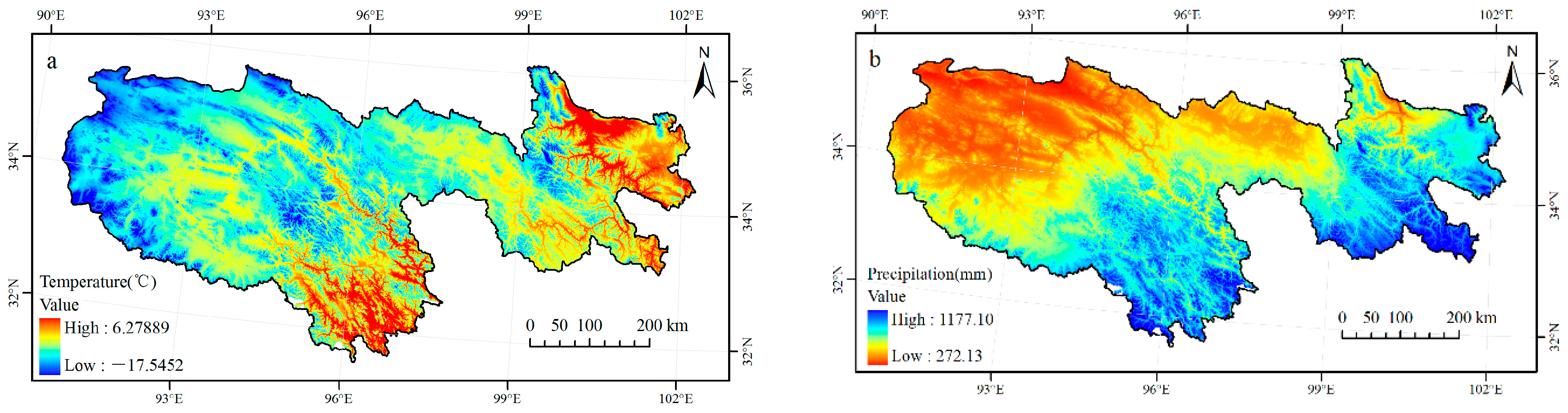
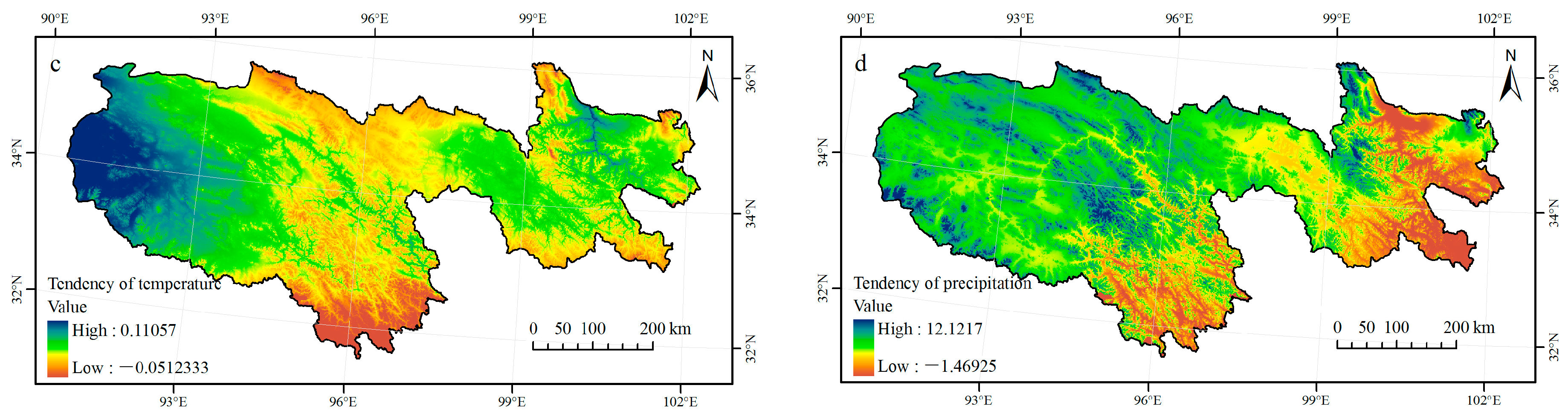
5.2. Spatial Distribution and Variation Tendency Characteristics of Climatic Factors
5.3. Correlation Analysis between the NDVI and Climatic Factors
5.4. Human Activities
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. Changes in satellite-derived vegetation growth trend in temperate and boreal Eurasia from 1982 to 2006. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3228–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Trend analysis of vegetation dynamics in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. Integr. Monit. Assess. Manag. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Myneni, R.B.; Keeling, C.D.; Tucker, C.J.; Asrar, G.; Nemani, R. Increased plant growth in the northern high latitudes from 1981 to 1991. Nature 1997, 386, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, L.; Cao, C.; Fang, J.; Myneni, R.B.; Pinzon, E.J.; Tucker, C.J.; Piao, S. Recent change of vegetation growth trend in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Yan, C.; Li, X.; Qian, D.; Feng, K. Changes in wetlands and surrounding land cover in a desert area under the influences of human and climatic factors: A case study of the Hongjian Nur region. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Goetz, S.; Sellers, P.J.; Nickeson, J.E. Satellite remote sensing of surface energy balance: Success, failures, and unresolved issues in FIFE. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 19061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Interannual variability of vegetation in the United States and its relation to el-nino southern oscillation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 71, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hong, F.; Zong, J. Resource Resources and Their Sustainable Utility in the “Three-River Headwaters” Region. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2005, 13, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Fan, J. Ecological construction achievements assessment and its revelation of ecological project in Three Rivers Headwaters Region. Chin. J. Nat. 2013, 35, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, G.; Fu, B. Response of vegetation to climate change and human activity based on NDVI in the Three-River Headwaters region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 5495–5504. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, Q. Vegetation coverage change and its response to climate change in Three-River Headwaters Region. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 21, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L. Spatial characteristic of vegetation change in the source regions of the Yangtze River, Yellow River and Lancang River in China. Geogr. Res. 2007, 26, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Chang-Ting, W.; Run-Jun, L.; Guang-Min, C.; Qi-Lan, W.; Lu-Ming, D.; Jian-Jun, S. Soil carbon and nitrogen contents along elevation gradients in the source region of Yangtze, Yellow and Lantsang Rivers. J. Plant Ecol. 2006, 30, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, R. A study on water protection forest system in the middle-upper Yangze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2009, 18, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Wei, C.; Dan, W.; Guo, G.; Jiang, F. Cost-benefit analysis of the ecological protects in the Three-River Headwaters Region based on ecosystem services values. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2018, 26, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Baolin, L.; Lili, X.; Tao, Z.; Jinsong, G.E.; Fei, L. Analysis of NDVI Change Trend and Its Impact Factors in the Three-River Headwater Region from 2000 to 2013. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.-Q.; Jiaerheng, A.; Zhao, C.; Fang, G.-L.; Yin, J.; Xiang, B.; Yuan, X.-J.; Fang, S.-F. Dynamic changes in vegetation NDVI from 1982 to 2012 and its responses to climate change and human activities in Xinjiang, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 3567–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.Y.; Xiao, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J. Vegetation change and its response to climate change in Three-River Source Region. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2006, 2, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Qiong, C.; Qiang, Z.; Haifeng, Z.; Fenggui, L. Spatial disparity of NDVI response in vegetation growing season to climate change in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Lin, G.; Zhao, Z. The response of temporal and spatial change of vegetation index to hydrothermal condition in the Three-Rivers Headwaters Region. Pratacultural Sci. 2011, 28, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D. The spatial-temporal changes of vegetation coverage in the Three-River Headwater Region in recent 12 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 897–908. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Luo, C.; Zhao, X. Land use change in the Three-River Headwaters in recent 40 years. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yan, J.; Wan, J. The spatial-temporal changes of vegetation restoration on loess plateau inShaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 960–970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, H. Responses of vegetation changes to climatic variations in Hulun Buir grassland in past 30 Years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, S.J.; Fiske, G.J.; Bunn, A.G. Using satellite time-series data sets to analyze fire disturbance and forest recovery across Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, K.C.; Beck, P.S.A.; Berner, L.T.; Goetz, S.J.; Baccini, A.; Buermann, W. Vegetation productivity patterns at high northern latitudes: A multid forest recovery across Canada. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 20, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Yan, C.; Li, X.; Qian, D.; Feng, K. Monitoring the response of vegetation dynamics to ecological engineering in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China from 1982 to 2014. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Ren, C. Integrating AVHRR and MODIS data to monitor NDVI changes and their relationships with climatic parameters in Northeast China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. NDVI-based vegetation responses to climate change in an arid area of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Lu, L. Comparison study of spatial interpolation methods of air temperature over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2003, 22, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, F.M. Interpolating mean rainfall using thin plate smoothing splines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, L.T.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Yang, Q.K.; Li, R. Introduction of the professional interpolation software for meteorology data-Anusplinn. Meteorol. Mon. 2008, 34, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T. Golmud City Residential Segregation Study 2014; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. The Research of Tanggula Town Master Planning under the Perspective of Landscapeecology; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang-wen, F.; Quan-qin, S.; Jun-bang, W.; Zhou-qi, C.; Hua-ping, Z. An analysis of temporal-spatial dynamics of grazing pressure on grassland in Three Rivers Headwater Region. Chin. J. Grassl. 2011, 33, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.-B.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.-L. Spatiotemporal dynamics of grassland coverage in response to climate change from 1982 to 2012 in the Three Rivers Source Region, China. Pratacultural Sci. 2017, 34, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Shi, P.; Peng, S. Vegetation phenology change in Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2013 and its related meteorological factors. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Peng, J. Spatiotemporal variation of the vegetation coverage in Qinghai Plateau based on MODIS NDVI data. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2016, 30, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Zhao, X.; Li, G.W.; Peng, L. Spatial-temporal variations in NDVI in vegetation-growing season in Qinghai based on GIMMS NDVI3g.v1 in past 34 years. Pratacultural Sci. 2018, 35, 713–725. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, G.; Peng, J. Temperature variation in recent 50 years in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Qinghai Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; Quan, S.; Feng, T.; Hai, Z. Changes in grassland yield and grazing pressure in the Three Rivers Headwater Region before and after the implementation of the eco-restoration project. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 23, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Xu, X.; Ge, J.; Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Gong, G.; et al. Assessment on the effects of the first-stage ecological conservation and restoration project in Sanjiangyuan region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Song, G.U.; Wen-jiang, S.U.; Sha, J.; Rui-xiang, X.; Jianshe, X.; Juan, Z. Spatial pattern and its variations of aridity/humidity during 1971-2020 in Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Arid Land Geogr. 2012, 35, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.W.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, J.B.; Harris, W.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhong, H.P.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, R.G. Assessment of effects of climate change and grazing activity on grassland yield in the Three Rivers Headwaters Region of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Influence of human activities on variation of vegetation cover in the Three-River Source Region. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Zong, L.; Han, B.S.; Huang, C.H. Development and cause of aeolian desertification in alpine region—In case of Maduo County in Yellow River source area. J. Desert Res. 2007, 27, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.Y.; Dong, Z.B.; Lu, J.F.; Yan, C.Z. Spatial and temporal changes of desertification land and its influence factors in source region of the Yellow River from 1975 to 2005. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L. Rural Household Energy Consumption and Energy Poverty in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau-Case of Qinghai Province 2019; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Shengkui, C. Yak dung use as fuel and nutrient loss in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhai, Y.; Chao, S.; Du, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. The impact of Cordyceps sinensis excavation on grassland vegetation in the Sanjiangyuan region. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Rudi, H.; Xingmin, M.; Jerry, M.; Guangju, Z.; Violette, G.; Coen, R. Distinguishing the impacts of human activities and climate variability on runoff and sediment load change based on paired periods with similar weather conditions: A case in the Yan River, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in hilly southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Month | n | a | b | R2 | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 275,927 | 0.866 | 0.005 | 0.628 | 0.039 |
| 2 | 275,808 | 0.893 | 0.008 | 0.661 | 0.034 |
| 3 | 275,810 | 0.891 | 0.005 | 0.658 | 0.036 |
| 4 | 275,691 | 0.977 | −0.001 | 0.707 | 0.035 |
| 5 | 275,578 | 0.862 | −0.029 | 0.755 | 0.084 |
| 6 | 276,054 | 0.971 | −0.007 | 0.811 | 0.077 |
| 7 | 276,686 | 0.988 | 0.010 | 0.800 | 0.092 |
| 8 | 276,775 | 0.954 | 0.020 | 0.784 | 0.094 |
| 9 | 276,262 | 0.902 | 0.003 | 0.789 | 0.089 |
| 10 | 275,819 | 0.925 | −0.012 | 0.714 | 0.070 |
| 11 | 275,635 | 0.900 | 0.000 | 0.658 | 0.044 |
| 12 | 274,984 | 0.873 | 0.005 | 0.619 | 0.041 |
| Change Type | The Significance Level of F Test | Number of Pixels | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Significant increase | p < 0.05 | 138,120 | 53.0 |
| weakly significant increase | p < 0.1 | 6008 | 2.3 |
| insignificant increase | p > 0.1 | 26,919 | 10.3 |
| Significant decrease | p < 0.05 | 62,467 | 24.0 |
| weakly significant decrease | p < 0.1 | 4165 | 1.6 |
| insignificant decrease | p > 0.1 | 22,803 | 8.8 |
| Periods | Time Stage | Engineering Projects | Project Implementation Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1987–1989 | Time period before the projects | |
| T2 | 1998–2000 | PFSYR | 1989–2000 |
| T3 | 2003–2005 | Establishing a national nature reserve | |
| T4 | 2010–2012 | EPCQS I | 2000–2012 |
| T5 | 2013–2015 | EPCQS II | From 2013 to present |
| Level | T2–T1 | T3–T2 | T4–T3 | T5–T4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change in NDVI | Level | Number of Pixels | % | Number of Pixels | % | Number of Pixels | % | Number of Pixels | % |
| ≤−0.10 | Decreased severely | 64 | 0.02 | 208 | 0.08 | 36 | 0.01 | 520 | 0.19 |
| −0.10 −0.05 | Decreased slightly | 3709 | 1.35 | 5615 | 2.09 | 927 | 0.34 | 11,341 | 4.21 |
| −0.05 0.05 | Unchanged | 234,808 | 85.24 | 245,416 | 91.30 | 246,885 | 91.34 | 236,769 | 87.93 |
| 0.05 0.10 | Increased slightly | 36,348 | 13.19 | 16,736 | 6.23 | 22,030 | 8.15 | 18,736 | 6.96 |
| ≥0.10 | Increased greatly | 543 | 0.20 | 816 | 0.30 | 412 | 0.15 | 1902 | 0.70 |
| Weather Stations | Wudaoliang | Tuotuohe | Maduo | Dari | Tongde | Jiuzhi | Nangqian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | −5.49 | −3.51 | −3.24 | −0.59 | 2.48 | 1.04 | 4.51 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 297.67 | 307.96 | 362.58 | 567.25 | 421.19 | 685.57 | 517.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, X.; Liang, X.; Yan, C.; Xing, X.; Jia, H.; Wei, X.; Feng, K. Vegetation Dynamic Changes and Their Response to Ecological Engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244035
Zhai X, Liang X, Yan C, Xing X, Jia H, Wei X, Feng K. Vegetation Dynamic Changes and Their Response to Ecological Engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244035
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Xiaohui, Xiaolei Liang, Changzhen Yan, Xuegang Xing, Haowei Jia, Xiaoxu Wei, and Kun Feng. 2020. "Vegetation Dynamic Changes and Their Response to Ecological Engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244035
APA StyleZhai, X., Liang, X., Yan, C., Xing, X., Jia, H., Wei, X., & Feng, K. (2020). Vegetation Dynamic Changes and Their Response to Ecological Engineering in the Sanjiangyuan Region of China. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244035







