Multilevel Structure Extraction-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
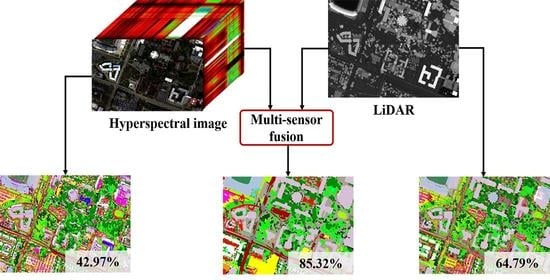
- A multilevel structure feature extractor is constructed and exploited to model the spatial and contextual information from input images, which can better characterize the discrimination between different land covers.
- A general multi-sensor fusion framework is proposed based on feature extraction and probability optimization, which can effectively fuse multi-sensor remote sensing data, such as HSI, LiDAR, and synthetic aperture radar (SAR).
- Classification quality of the proposed method is examined on three datasets, which indicates that our method obtains outstanding performance over other state-of-the-art multi-sensor fusion techniques with regard to both classification accuracies and maps. We will also make the codes freely available on author’s Github repository: https://github.com/PuhongDuan.
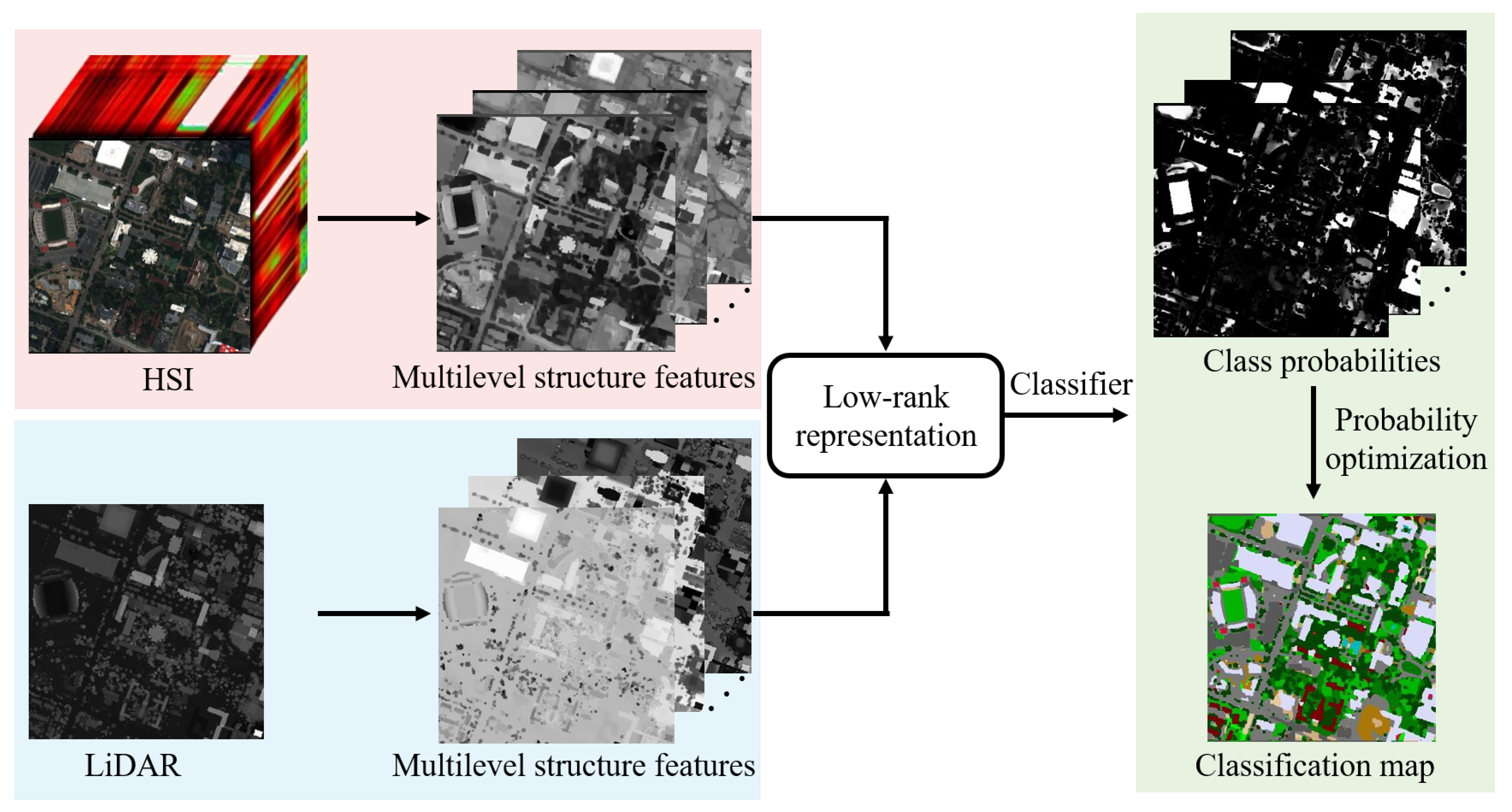
2. Methodology
2.1. Multilevel Structure Extraction
2.2. Feature Fusion
2.3. Probability Optimization
3. Experiments
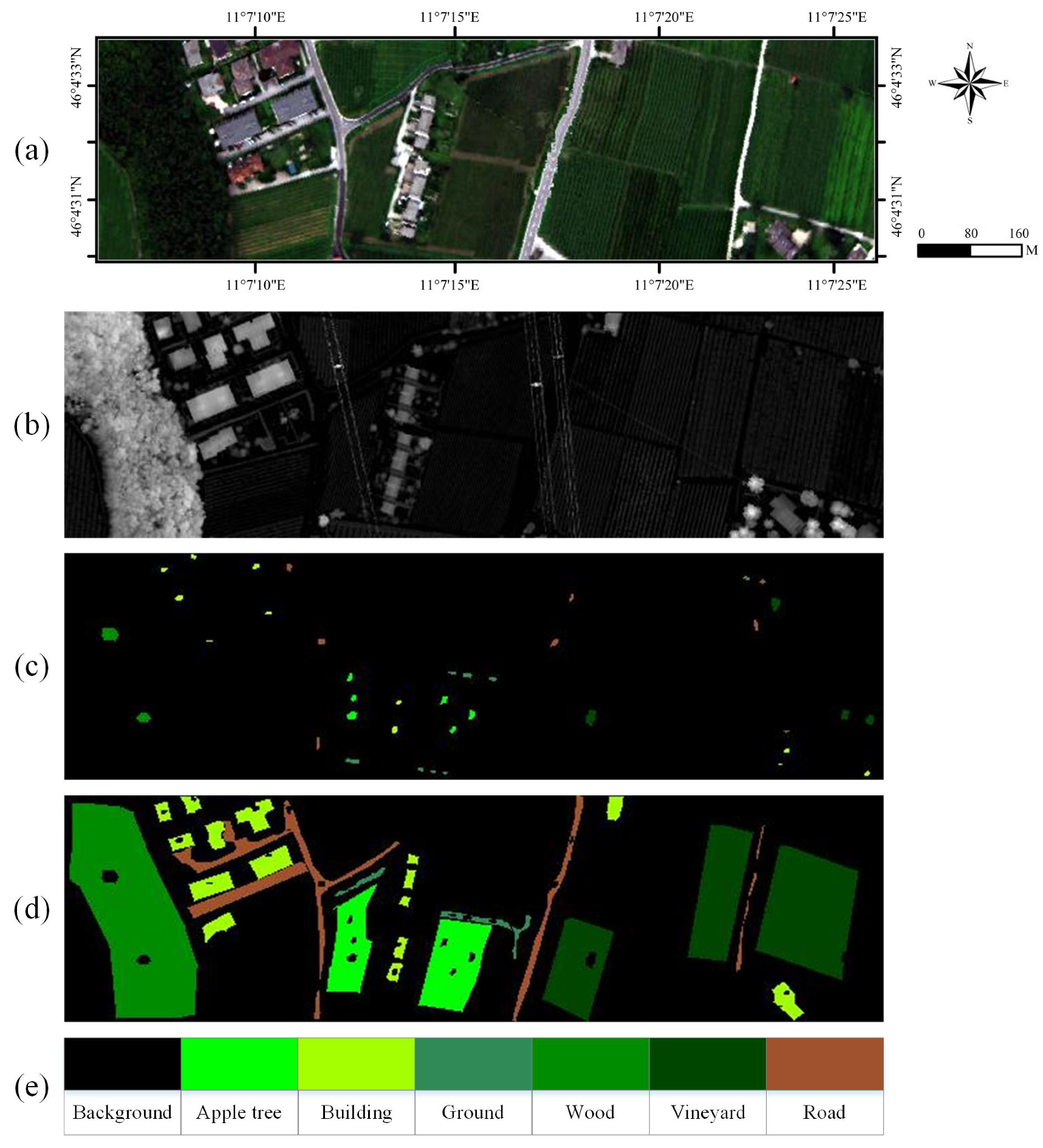
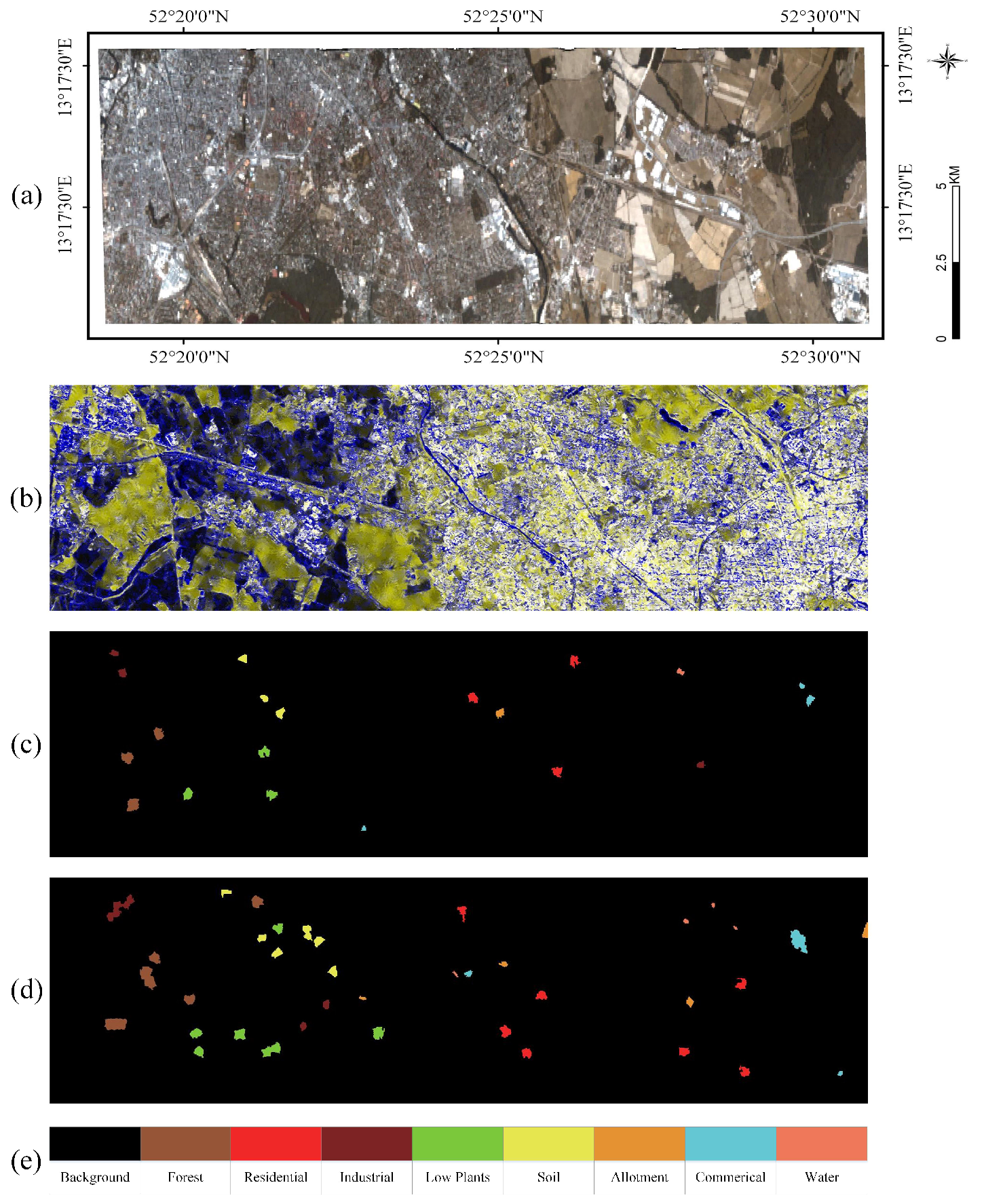
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Classification Results
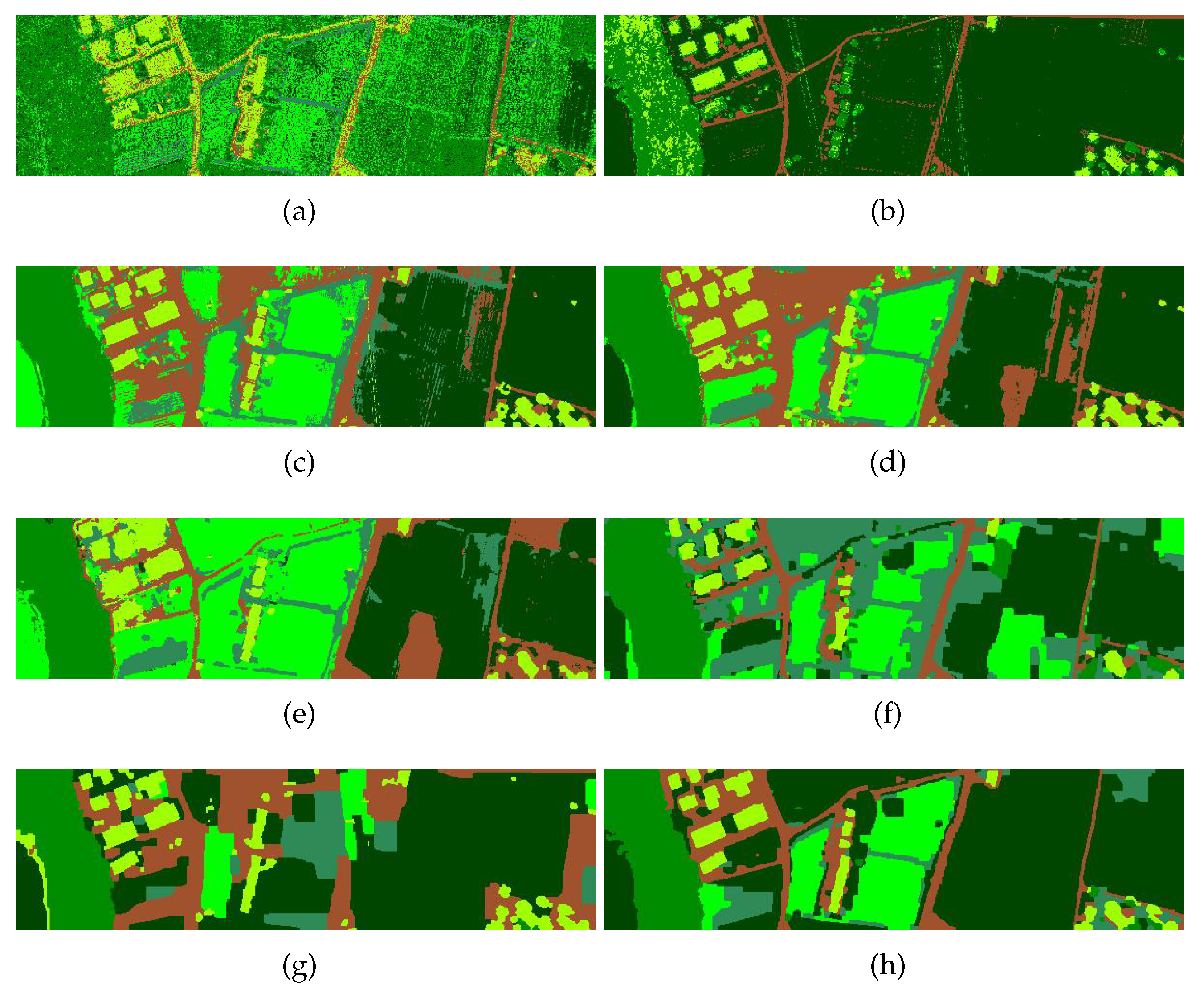
3.2.1. Trento Dataset
3.2.2. Berlin Dataset
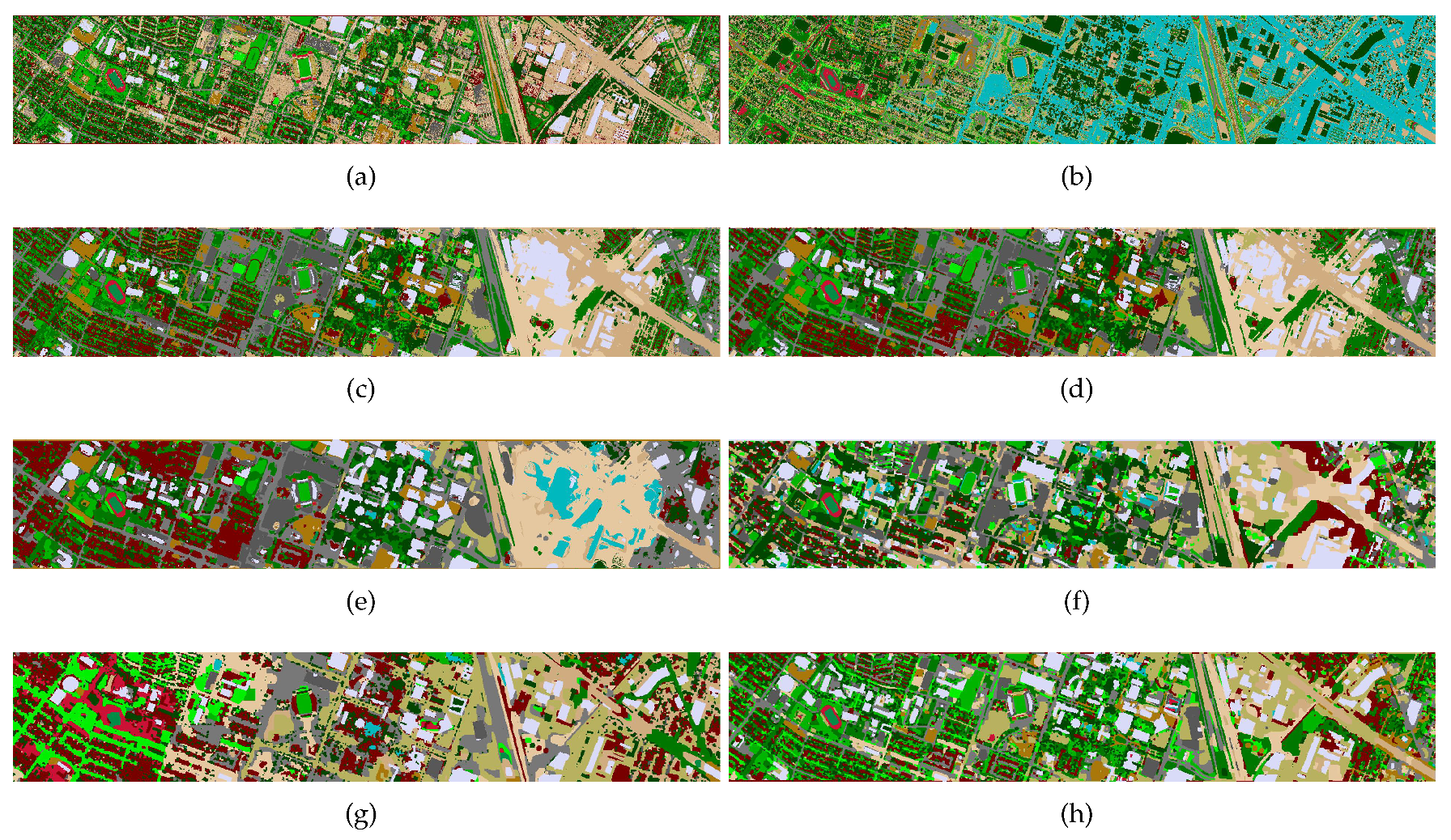
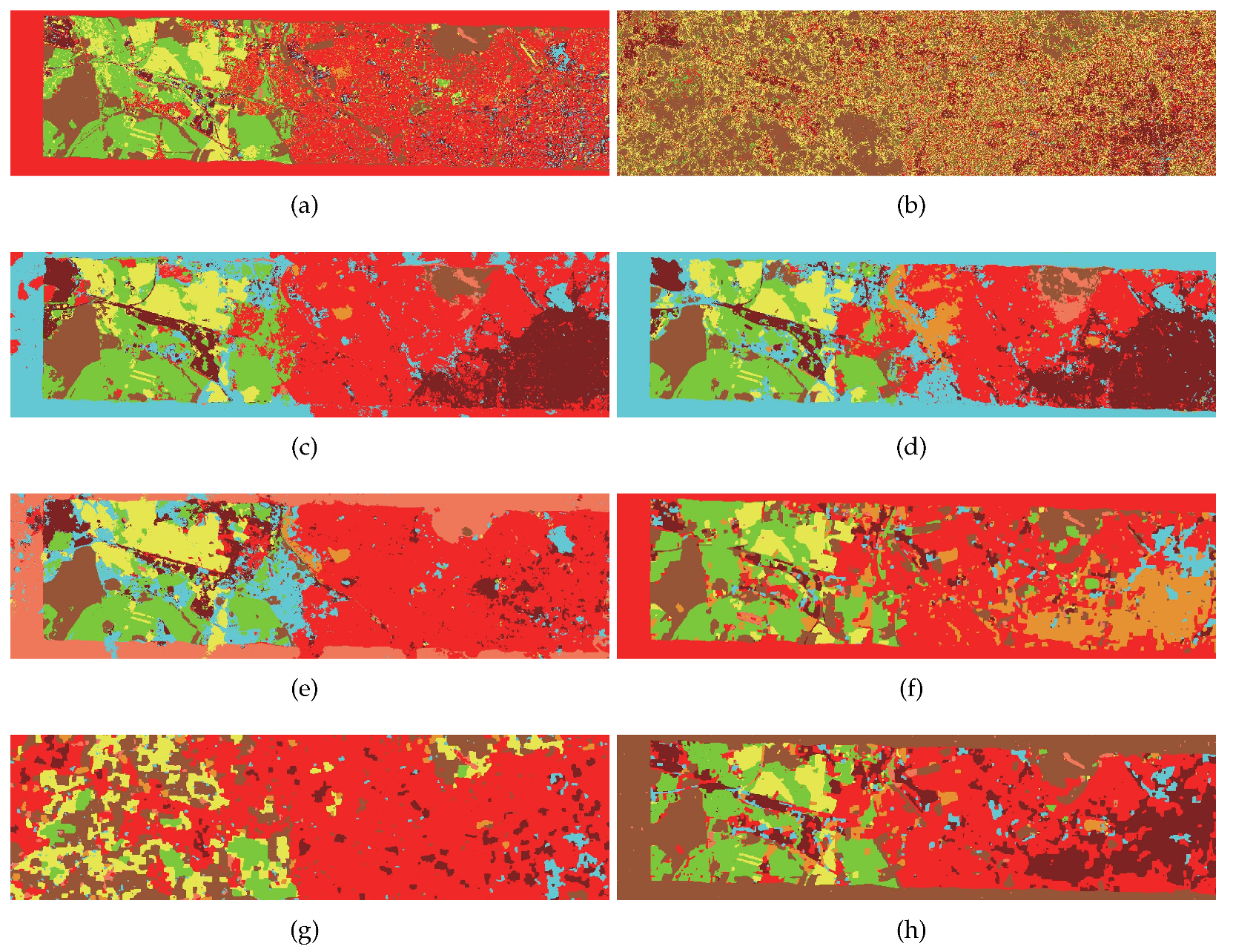
3.2.3. Houston 2013 Dataset
4. Discussion
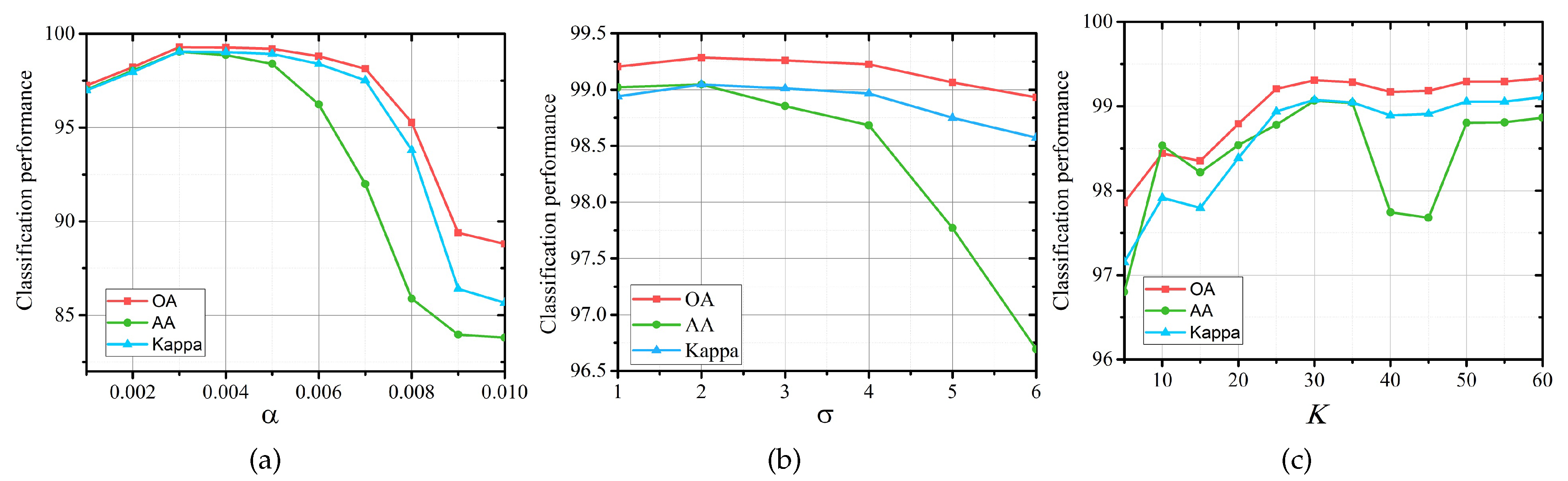
4.1. The Influence of Different Parameters
4.2. The Influence of Different Feature Extractors
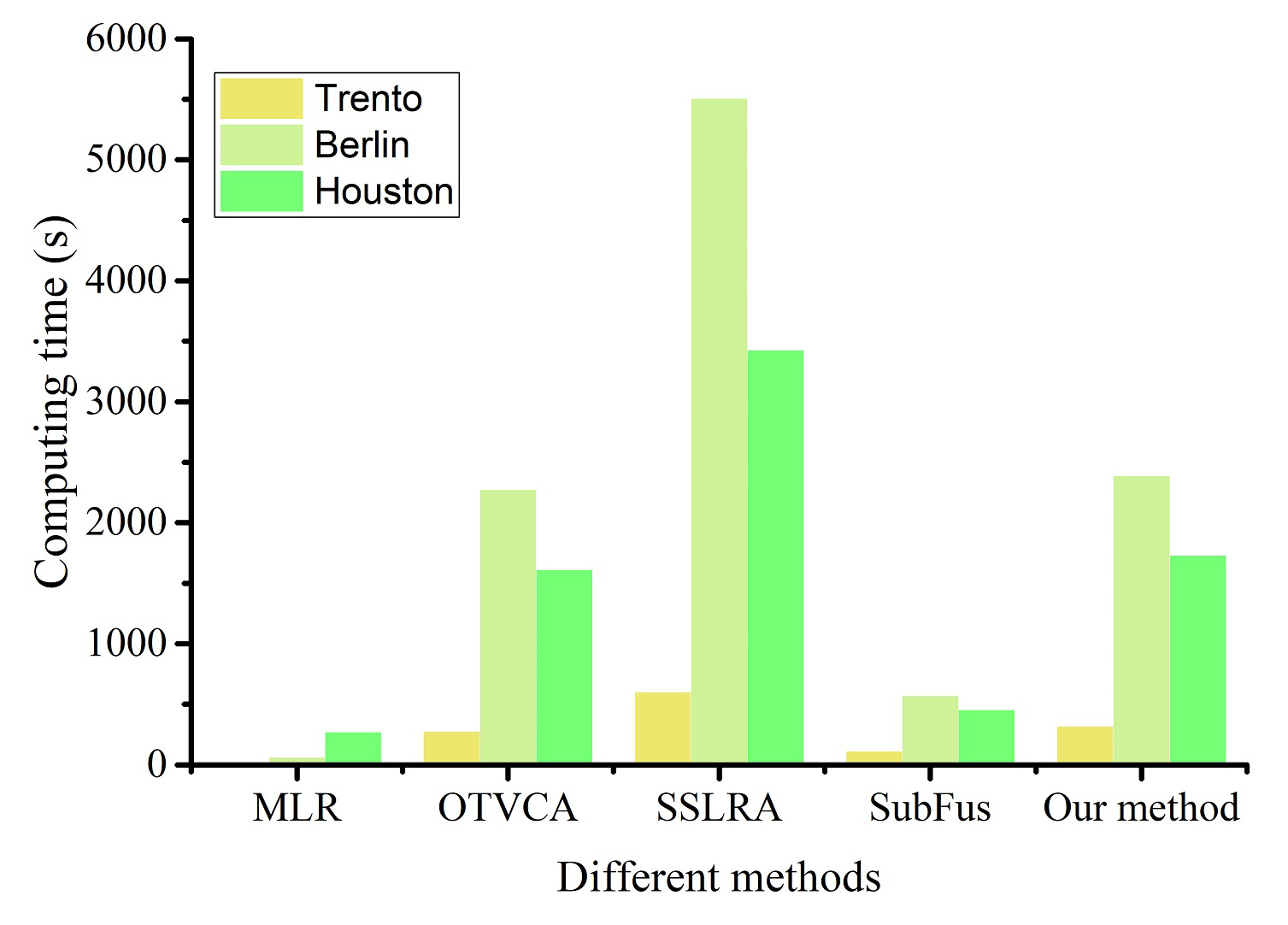
4.3. Computing Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Yokoya, N.; Wang, Q.; Hofle, B.; Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F.; Chi, M.; Anders, K.; Gloaguen, R.; et al. Multisource and Multitemporal Data Fusion in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 6–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Liao, W.; Du, P. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Classification With Semisupervised Graph Fusion. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, F.; Zhou, J.; Awrangjeb, M.; Gao, Y. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Discriminant Correlation Analysis for Land Cover Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3905–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Duan, P.; Li, S. Hyperspectral image visualization with edge-preserving filtering and principal component analysis. Inf. Fusion 2020, 57, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Lai, J.; Kang, J.; Kang, X.; Ghamisi, P.; Li, S. Texture-aware total variation-based removal of sun glint in hyperspectral images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Kang, X.; Li, S.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Fusion of Multiple Edge-Preserving Operations for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10336–10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Hofle, B.; Zhu, X.X. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Fusion Using Extinction Profiles and Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3011–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Cerra, D.; Pato, M.; Carmona, E.; Prasad, S.; Yokoya, N.; Hansch, R.; Le Saux, B. Advanced Multi-Sensor Optical Remote Sensing for Urban Land Use and Land Cover Classification: Outcome of the 2018 IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X.X. Learning to propagate labels on graphs: An iterative multitask regression framework for semi-supervised hyperspectral dimensionality reduction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Hang, R.; Zhang, B.; Chanussot, J. Deep Encoder-Decoder Networks for Classification of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungert, L.; Coomes, D.A.; Ehrhardt, M.J.; Rasch, J.; Reisenhofer, R.; Schonlieb, C.B. Blind image fusion for hyperspectral imaging with the directional total variation. Inverse Problems 2018, 34, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Lai, J.; Ghamisi, P.; Kang, X.; Jackisch, R.; Kang, J.; Gloaguen, R. Component Decomposition-Based Hyperspectral Resolution Enhancement for Mineral Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Lei, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, W.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, D. Structure Tensor-Based Algorithm for Hyperspectral and Panchromatic Images Fusion. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, M.; Yang, S. Multispectral and Hyperspectral Image Fusion Based on Group Spectral Embedding and Low-Rank Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dian, R.; Fang, L.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. Fusing Hyperspectral and Multispectral Images via Coupled Sparse Tensor Factorization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4118–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, R.; Li, S.; Kang, X. Regularizing Hyperspectral and Multispectral Image Fusion by CNN Denoiser. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. SSR-NET: Spatial-Spectral Reconstruction Network for Hyperspectral and Multispectral Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Pizurica, A.; Bellens, R.; Gautama, S.; Philips, W. Generalized Graph-Based Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Morphological Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Gloaguen, R. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Fusion Using Extinction Profiles and Total Variation Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3997–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Benediktsson, J.A. Multisensor Composite Kernels Based on Extreme Learning Machines. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Sparse and Low-Rank Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6354–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadzadeh, M.; Li, J.; Prasad, S.; Plaza, A. Fusion of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Remote Sensing Data Using Multiple Feature Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Du, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Feature Extraction for Classification of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Patch-to-Patch CNN. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Wu, Z.; Shapiro, A.; Schultz, M.; Zipf, A. A Multi-Sensor Fusion Framework Based on Coupled Residual Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tao, R.; Li, W.; Li, H.C.; Du, Q.; Liao, W.; Philips, W. Joint Classification of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Hierarchical Random Walk and Deep CNN Architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 7355–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, E.R.; Roerdink, J.B.T.M.; Wilkinson, M.H.F. Connected Shape-Size Pattern Spectra for Rotation and Scale-Invariant Classification of Gray-Scale Images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedergnana, M.; Marpu, P.R.; Dalla Mura, M.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Bruzzone, L. Classification of Remote Sensing Optical and LiDAR Data Using Extended Attribute Profiles. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Signal Process. 2012, 6, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yan, Q.; Xia, Y.; Jia, J. Structure Extraction from Texture via Relative Total Variation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 139:1–139:10. [Google Scholar]
- Rasti, B.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Sveinsson, J.R. Hyperspectral Feature Extraction Using Total Variation Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6976–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, G.; Solo, V. lq Sparsity Penalized Linear Regression With Cyclic Descent. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, T.; Osher, S. The Split Bregman Method for L1-Regularized Problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2009, 2, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, T.; Fang, L.; Jia, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Probabilistic Fusion of Pixel-Level and Superpixel-Level Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7416–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A. Semisupervised Hyperspectral Image Segmentation Using Multinomial Logistic Regression With Active Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4085–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P.; Ulfarsson, M.O. Hyperspectral Feature Extraction Using Sparse and Smooth Low-Rank Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, B.; Ghamisi, P. Remote sensing image classification using subspace sensor fusion. Inf. Fusion 2020, 64, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Ghamisi, P.; Kang, X.; Rasti, B.; Gloaguen, R. Fusion of Dual Spatial Information for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. to be published. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Li, M.; Benediktsson, J.A. Extended random walker-based classification of hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Kang, X.; Li, S.; Ghamisi, P. Multichannel Pulse-Coupled Neural Network-Based Hyperspectral Image Visualization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2444–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debes, C.; Merentitis, A.; Heremans, R.; Hahn, J.; Frangiadakis, N.; van Kasteren, T.; Liao, W.; Bellens, R.; Pizurica, A.; Gautama, S.; et al. Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Fusion: Outcome of the 2013 GRSS Data Fusion Contest. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2405–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.; Müller, K.R. Kernel principal component analysis. In Artificial Neural Networks—ICANN’97: 7th International Conference Lausanne, Switzerland, October 8–10, 1997 Proceeedings; Gerstner, W., Germond, A., Hasler, M., Nicoud, J.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 583–588. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.; Kang, X.; Li, S.; Ghamisi, P. Noise-Robust Hyperspectral Image Classification via Multi-Scale Total Variation. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Benediktsson, J.A. Intrinsic Image Decomposition for Feature Extraction of Hyperspectral Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.; Benediktsson, J.A. Feature Extraction of Hyperspectral Images With Image Fusion and Recursive Filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3742–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, P.M.; Mattia, P.; Mauro, D.M.; Jon, A.B.; Lorenzo, B. Automatic Generation of Standard Deviation Attribute Profiles for Spectral-Spatial Classification of Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Trento Dataset | Berlin Dataset | Houston 2013 Dataset | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Train | Test | Name | Train | Test | Name | Train | Test | |
| 1 | Apple tree | 129 | 3905 | Forest | 1423 | 3249 | Healthy Grass | 50 | 1201 |
| 2 | Building | 125 | 2778 | Residential | 961 | 2373 | Stressed Grass | 50 | 1204 |
| 3 | Ground | 105 | 374 | Industrial | 623 | 1510 | Synthetic Grass | 50 | 647 |
| 4 | Wood | 154 | 8969 | Low Plants | 1098 | 2681 | Tree | 50 | 1194 |
| 5 | Vineyard | 184 | 10,317 | Soil | 728 | 1817 | Soil | 50 | 1192 |
| 6 | Road | 122 | 3252 | Allotment | 260 | 747 | Water | 50 | 275 |
| 7 | Total | 819 | 29,595 | Commerical | 451 | 1313 | Residential | 50 | 1218 |
| 8 | Water | 144 | 256 | Commercial | 50 | 1194 | |||
| 9 | Total | 5688 | 13,946 | Road | 50 | 1202 | |||
| 10 | Highway | 50 | 1177 | ||||||
| 11 | Railway | 50 | 1185 | ||||||
| 12 | Parking Lot1 | 50 | 1183 | ||||||
| 13 | Parking Lot2 | 50 | 419 | ||||||
| 14 | Tennis Court | 50 | 378 | ||||||
| 15 | Running Track | 50 | 610 | ||||||
| Total | 750 | 14,279 | |||||||
| Class | MLR | OTVCA | SSLRA | SubFus | Our Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | |
| Apple tree | 48.53 | 13.97 | 99.60 | 99.88 | 100.0 | 99.36 | 90.29 | 99.60 |
| Building | 58.56 | 53.99 | 95.15 | 95.55 | 97.76 | 97.77 | 93.21 | 97.00 |
| Ground | 84.10 | 0.00 | 43.35 | 80.96 | 98.75 | 54.99 | 43.23 | 100.0 |
| Wood | 59.49 | 90.93 | 99.98 | 100.0 | 99.85 | 99.92 | 99.98 | 100.0 |
| Vineyard | 62.20 | 65.41 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 89.12 | 96.04 | 78.91 | 99.52 |
| Road | 74.03 | 97.15 | 80.68 | 71.94 | 79.55 | 96.69 | 77.68 | 98.27 |
| OA | 59.15 | 72.55 | 95.03 | 95.25 | 93.79 | 96.68 | 86.50 | 99.31 |
| AA | 64.49 | 53.57 | 86.46 | 91.38 | 94.17 | 90.80 | 80.55 | 99.07 |
| Kappa | 46.59 | 61.70 | 93.47 | 93.75 | 91.85 | 95.56 | 81.66 | 99.07 |
| Class | MLR | OTVCA | SSLRA | SubFus | Our Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | |
| Forest | 90.27 | 33.24 | 100.00 | 99.97 | 97.20 | 97.36 | 41.82 | 99.54 |
| Residential | 69.19 | 34.59 | 63.04 | 76.27 | 85.59 | 76.39 | 51.57 | 73.62 |
| Industrial | 71.81 | 52.33 | 70.76 | 63.45 | 65.17 | 75.11 | 61.33 | 66.25 |
| Low Plants | 91.71 | 11.7 | 91.61 | 98.24 | 94.41 | 86.34 | 47.71 | 94.06 |
| Soil | 91.81 | 22.69 | 94.07 | 100.00 | 89.21 | 100.00 | 44.36 | 100.00 |
| Allotment | 65.54 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 59.24 | 17.27 | 14.33 | 100.00 | 94.37 |
| Commerical | 76.53 | 68.52 | 95.28 | 75.92 | 78.90 | 57.28 | 75.18 | 88.40 |
| Water | 55.88 | 22.22 | 56.96 | 100.00 | 75.78 | 88.39 | 51.16 | 100.00 |
| OA | 82.79 | 32.89 | 84.45 | 86.25 | 83.78 | 79.74 | 50.25 | 87.50 |
| AA | 76.59 | 30.66 | 83.96 | 84.14 | 75.44 | 74.40 | 59.14 | 89.53 |
| Kappa | 79.29 | 17.77 | 81.43 | 83.66 | 80.54 | 75.86 | 40.09 | 85.01 |
| Class | MLR | OTVCA | SSLRA | SubFus | Our Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | HSI | LiDAR | HSI + LiDAR | |
| Healthy Grass | 89.94 | 11.55 | 89.01 | 91.00 | 81.39 | 91.66 | 82.46 | 82.13 |
| Stressed Grass | 98.46 | 8.69 | 89.20 | 86.11 | 80.17 | 80.05 | 2.14 | 94.33 |
| Synthetic Grass | 89.69 | 46.38 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.60 | 100.00 | 72.24 | 100.00 |
| Tree | 78.85 | 31.32 | 84.88 | 87.97 | 87.31 | 76.21 | 64.73 | 98.68 |
| Soil | 89.16 | 6.26 | 98.24 | 98.32 | 100.00 | 99.13 | 64.58 | 89.71 |
| Water | 100.00 | 8.61 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 85.60 | 68.84 | 100.00 |
| Residential | 82.78 | 0.00 | 84.44 | 84.23 | 73.32 | 90.45 | 56.43 | 93.69 |
| Commercial | 81.96 | 0.00 | 93.04 | 96.54 | 54.04 | 88.80 | 77.70 | 99.37 |
| Road | 78.09 | 11.40 | 67.08 | 69.70 | 85.74 | 84.73 | 15.70 | 91.78 |
| Highway | 43.66 | 18.16 | 75.30 | 80.29 | 68.53 | 74.64 | 40.00 | 95.71 |
| Railway | 70.50 | 7.43 | 85.05 | 87.30 | 99.72 | 68.84 | 67.60 | 80.25 |
| Parking Lot1 | 85.39 | 0.00 | 89.19 | 87.17 | 74.54 | 88.61 | 87.30 | 96.59 |
| Parking Lot2 | 41.00 | 6.25 | 66.72 | 59.94 | 69.82 | 50.69 | 21.58 | 38.85 |
| Tennis Court | 94.13 | 36.63 | 92.27 | 100.00 | 99.60 | 66.99 | 20.30 | 94.57 |
| Running Track | 93.31 | 40.04 | 99.24 | 97.01 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 58.92 | 97.01 |
| OA | 76.33 | 20.24 | 86.01 | 86.77 | 82.41 | 82.56 | 46.04 | 88.96 |
| AA | 81.13 | 15.52 | 87.58 | 88.37 | 84.92 | 83.09 | 53.37 | 90.18 |
| Kappa | 74.42 | 15.13 | 84.88 | 85.71 | 80.98 | 81.19 | 42.37 | 88.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, P.; Kang, X.; Ghamisi, P.; Liu, Y. Multilevel Structure Extraction-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244034
Duan P, Kang X, Ghamisi P, Liu Y. Multilevel Structure Extraction-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244034
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Puhong, Xudong Kang, Pedram Ghamisi, and Yu Liu. 2020. "Multilevel Structure Extraction-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244034
APA StyleDuan, P., Kang, X., Ghamisi, P., & Liu, Y. (2020). Multilevel Structure Extraction-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244034