Adaptive Iterated Shrinkage Thresholding-Based Lp-Norm Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Imagery Target Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
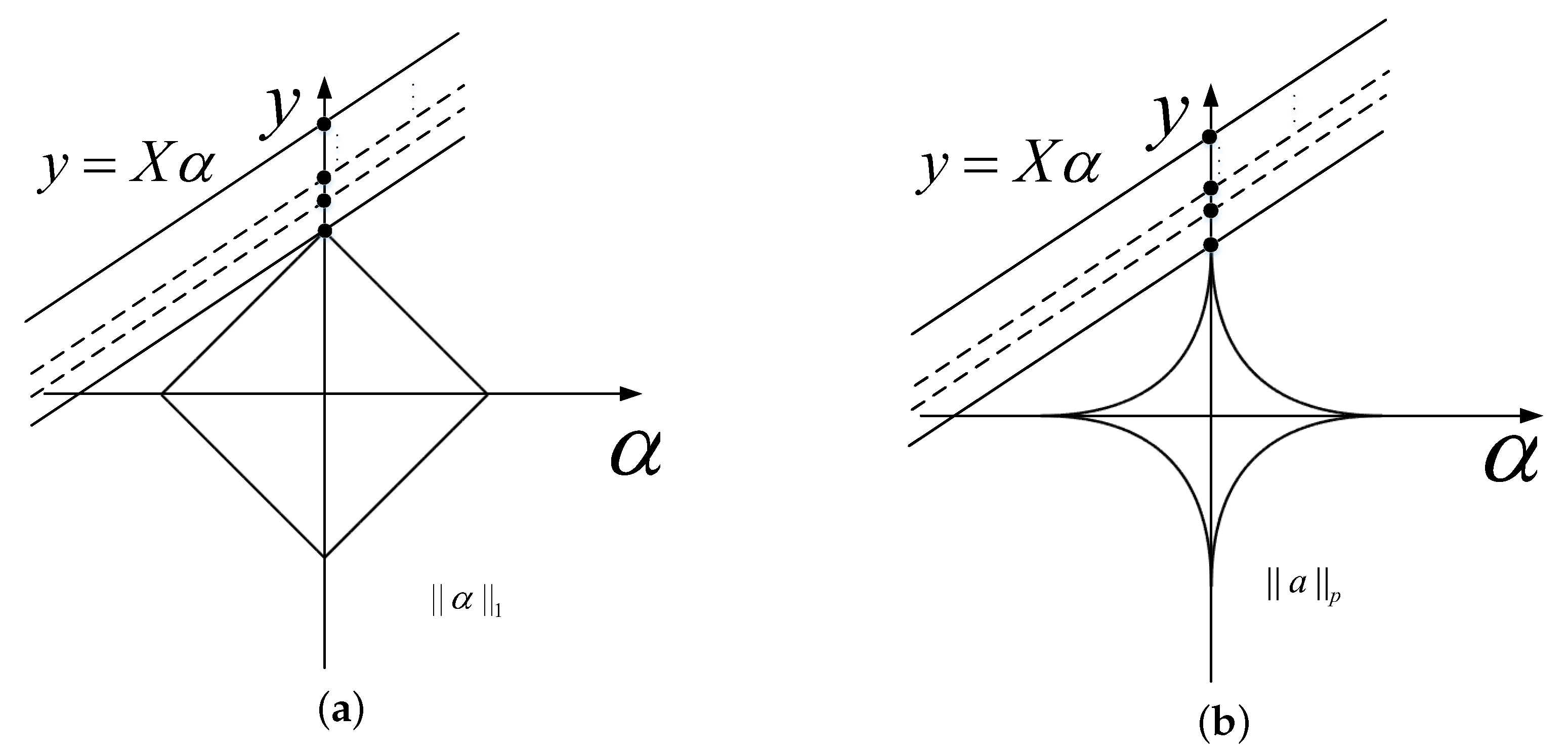
2. Sparse Representation Detector with -norm
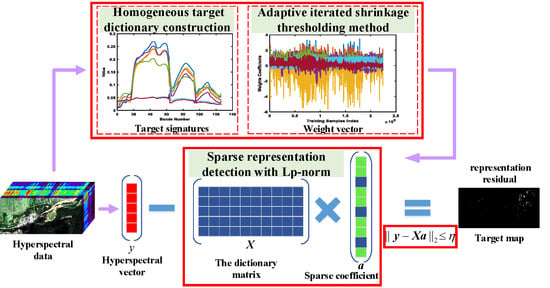
3. Proposed Target Detection Framework
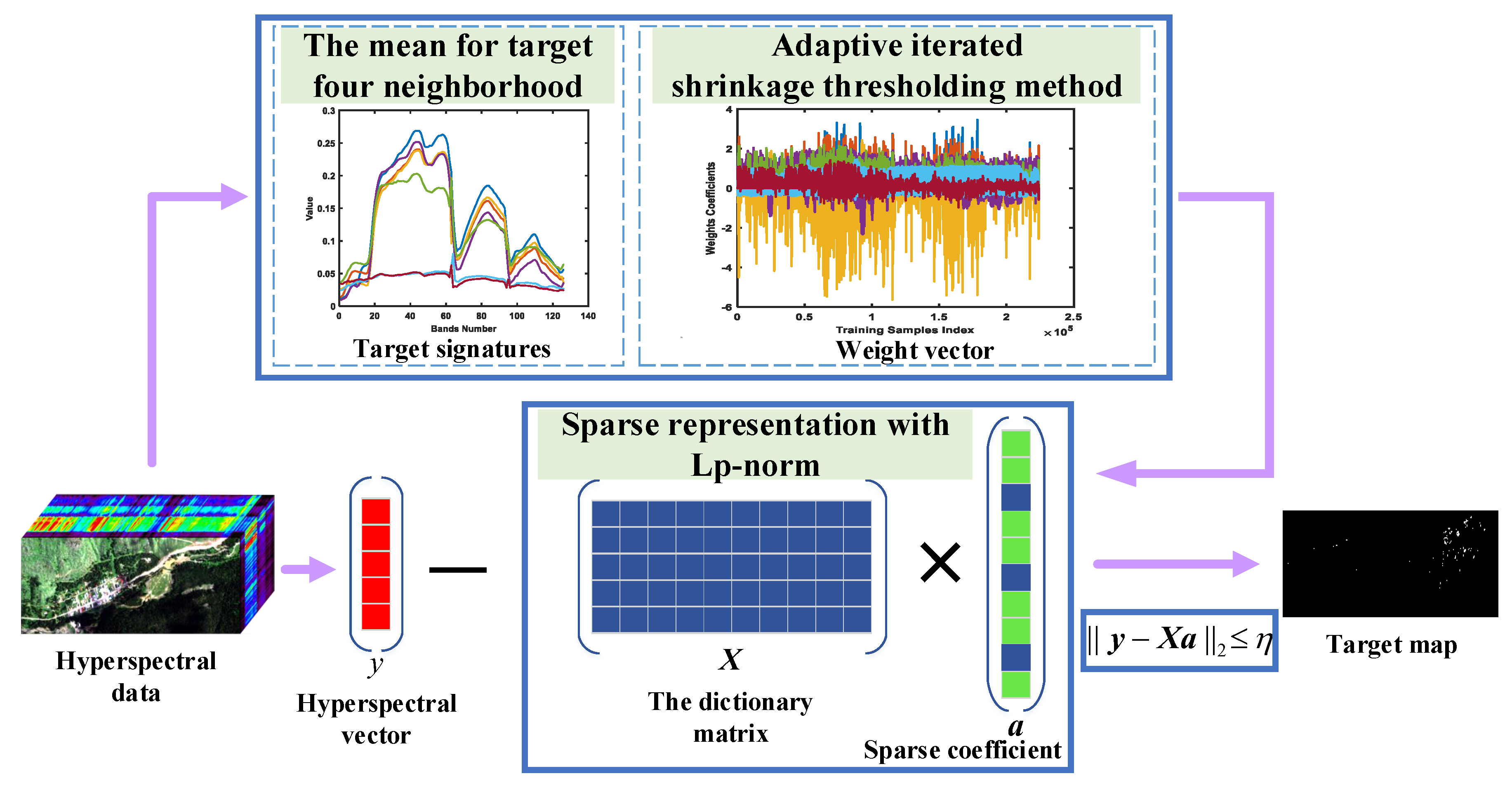
3.1. Homogeneous Target Dictionary Construction
3.2. Sparse Representation Detector with -norm
| Algorithm 1 (AISTM): |
| Input: |
| 1. Calculating the thresholding value by Equation (14); |
| 2. If ; |
| 3. ; |
| 4. Else |
| 5. ; |
| 6. ; |
| 7. Iterate on ; |
| 8. Calculating the corresponding by Equation (15); |
| 9. ; |
| 10. End |
| Output: . |
- (i)
- if ;
- (ii)
- ;
- (iii)
- ; and
- (iv)
- for
4. Experiments and Discussion
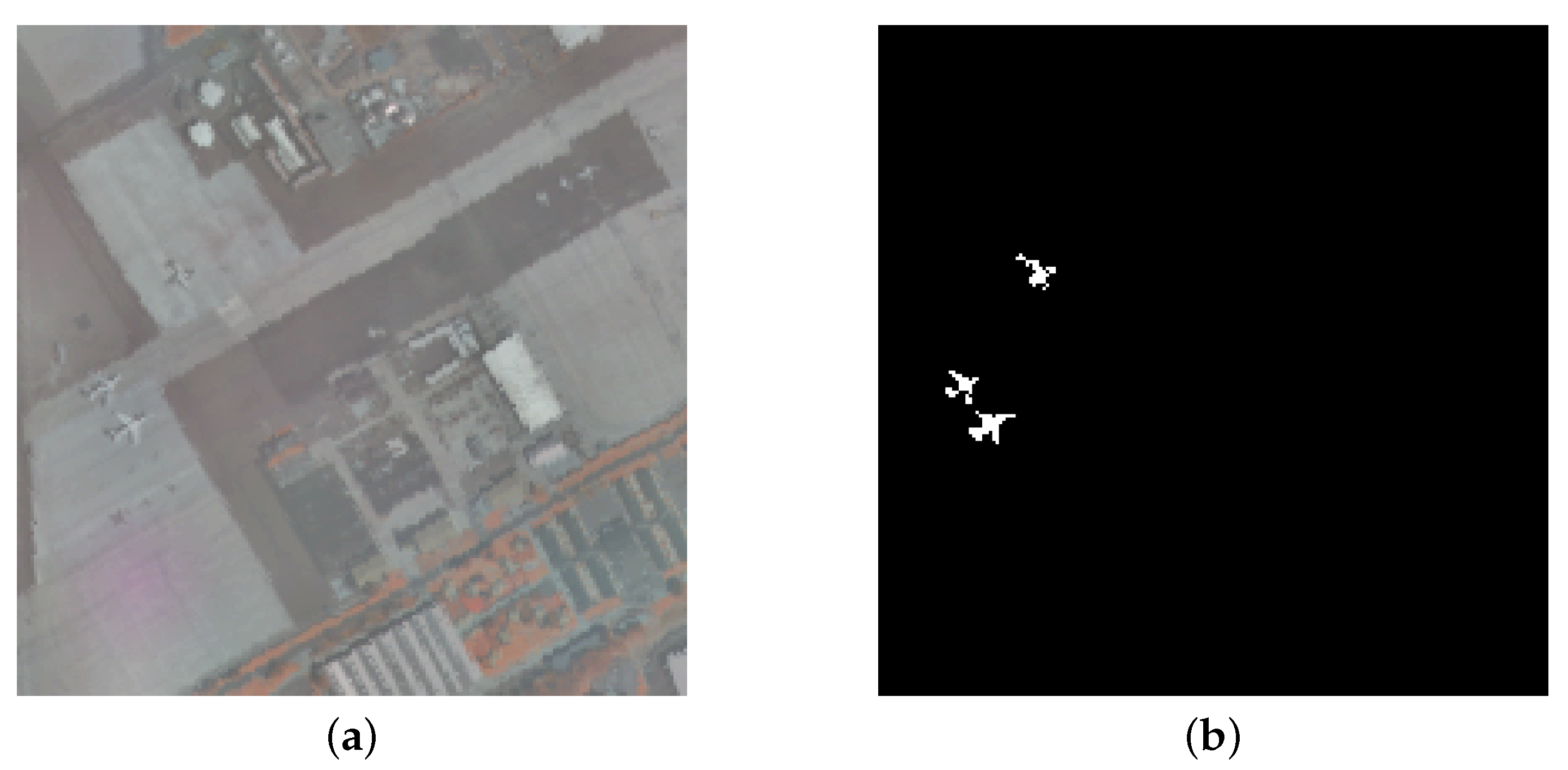
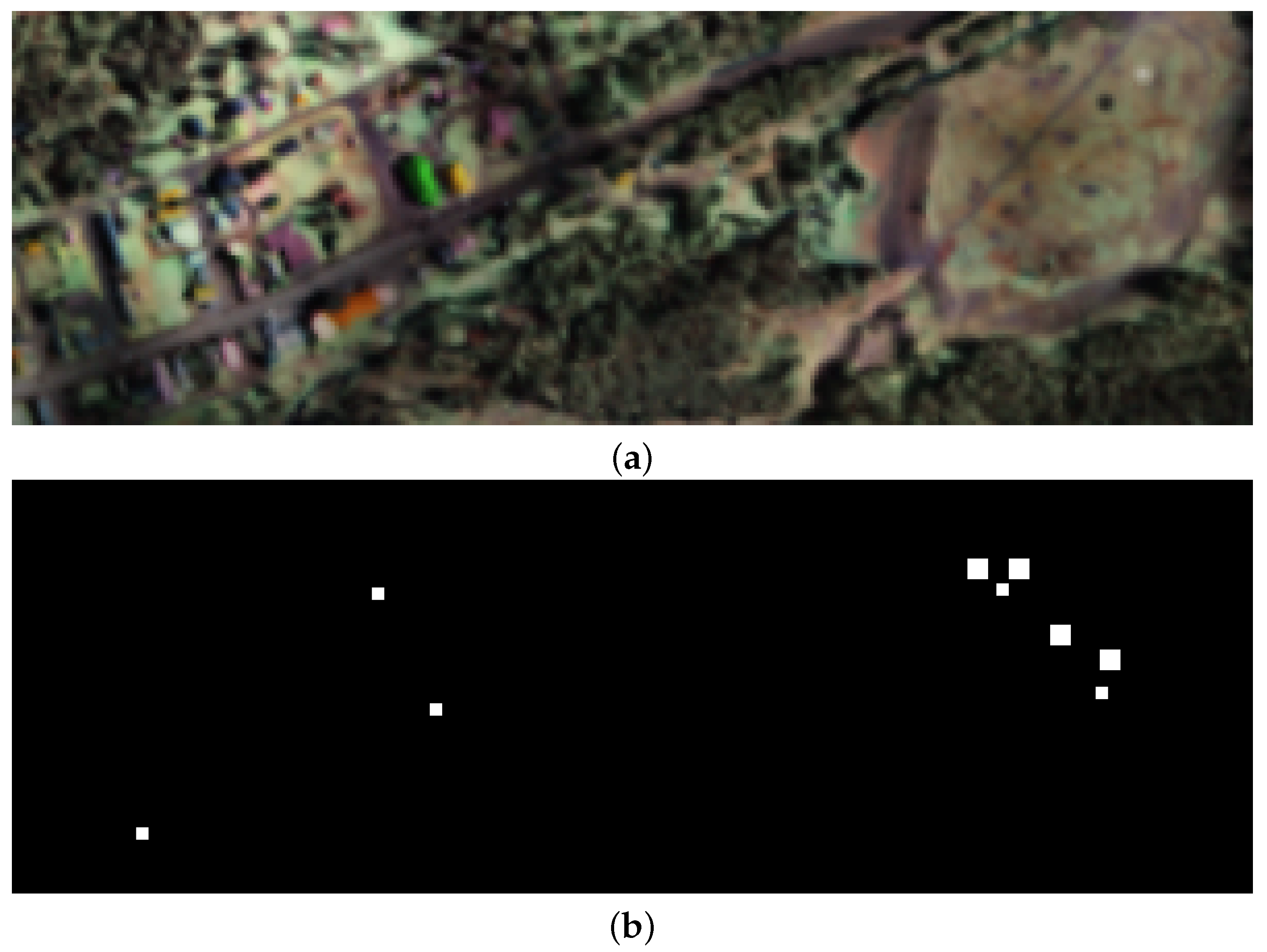
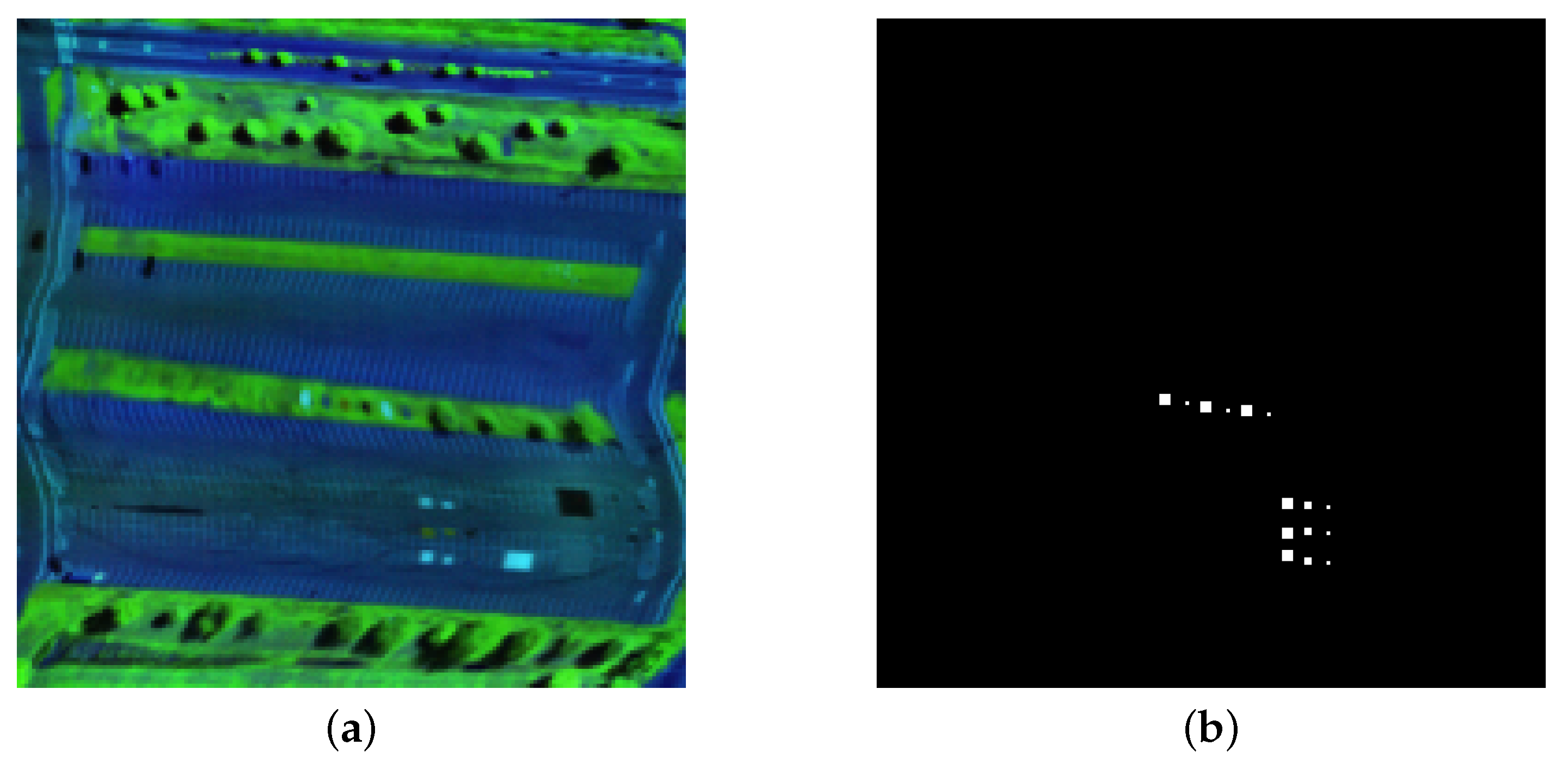
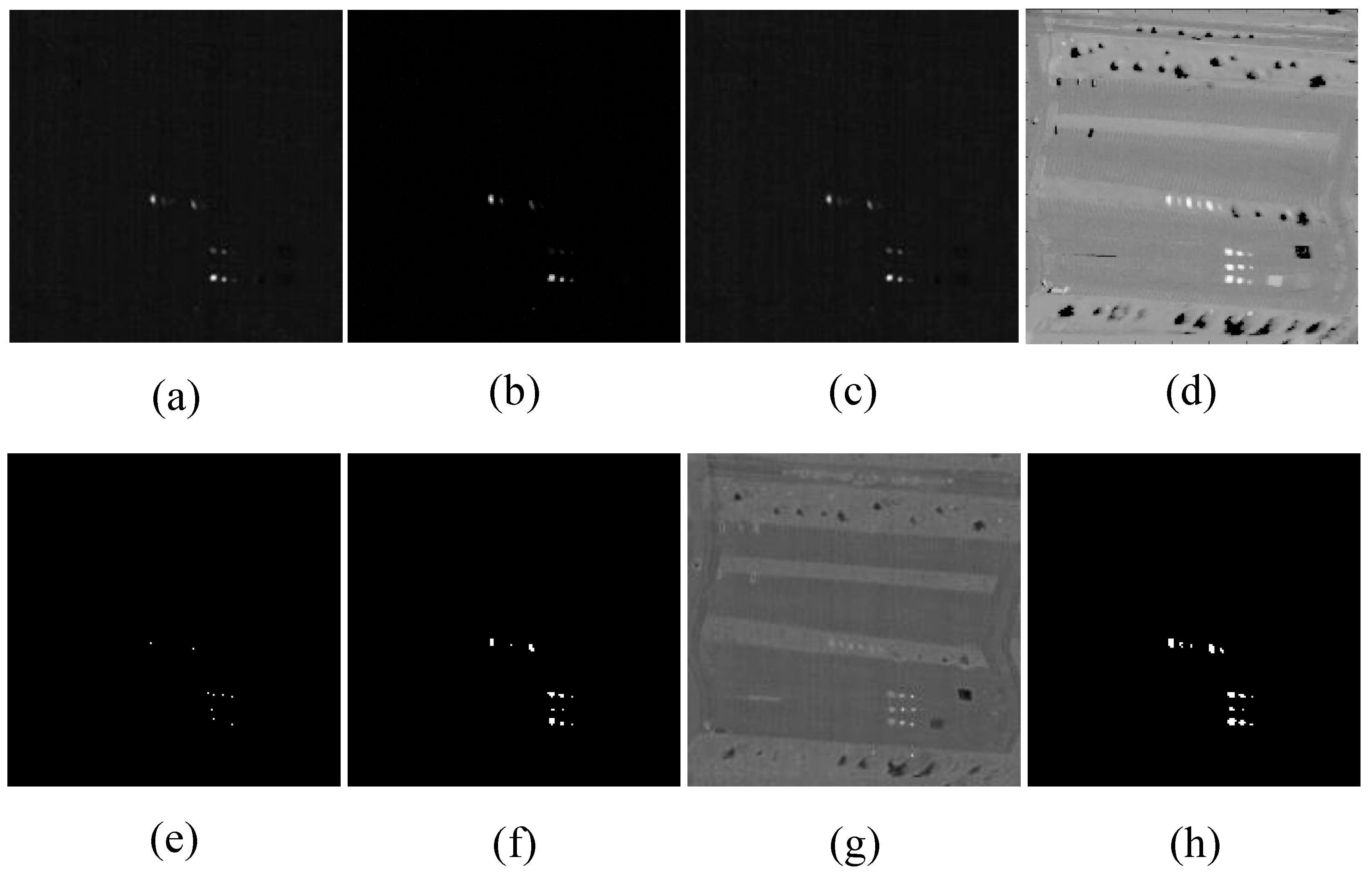
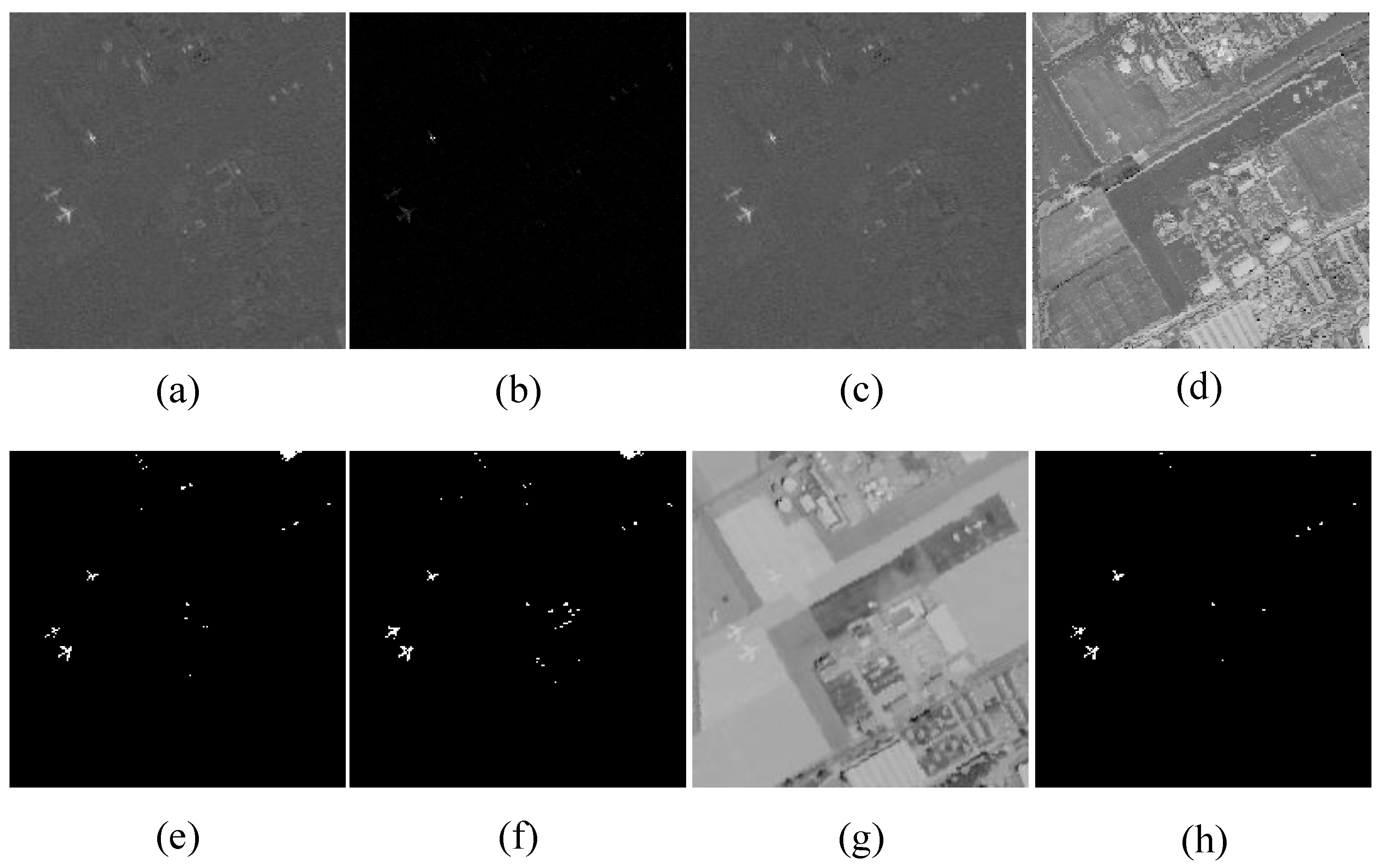
4.1. Hyperspectral Datasets
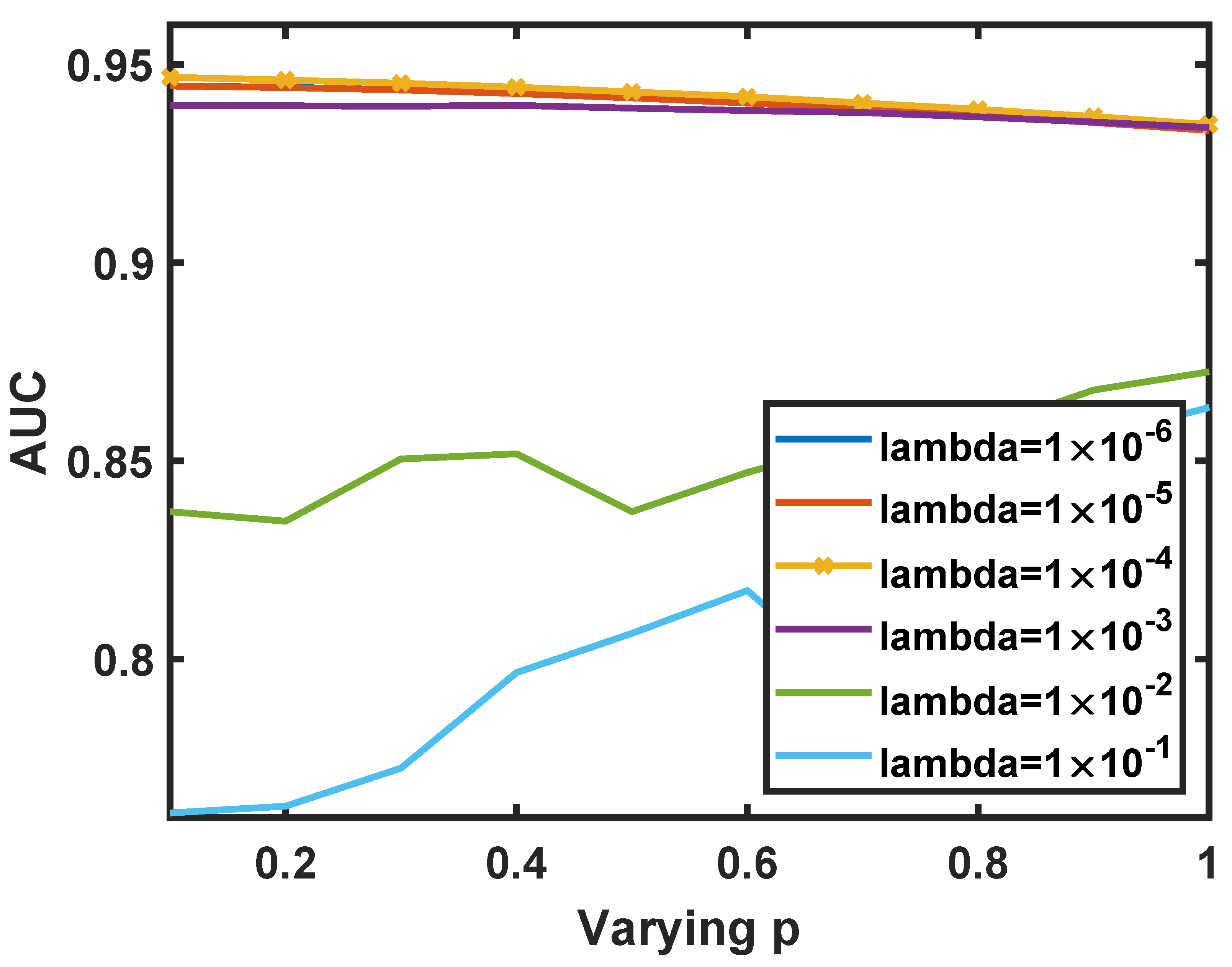
4.2. Parameters Analysis
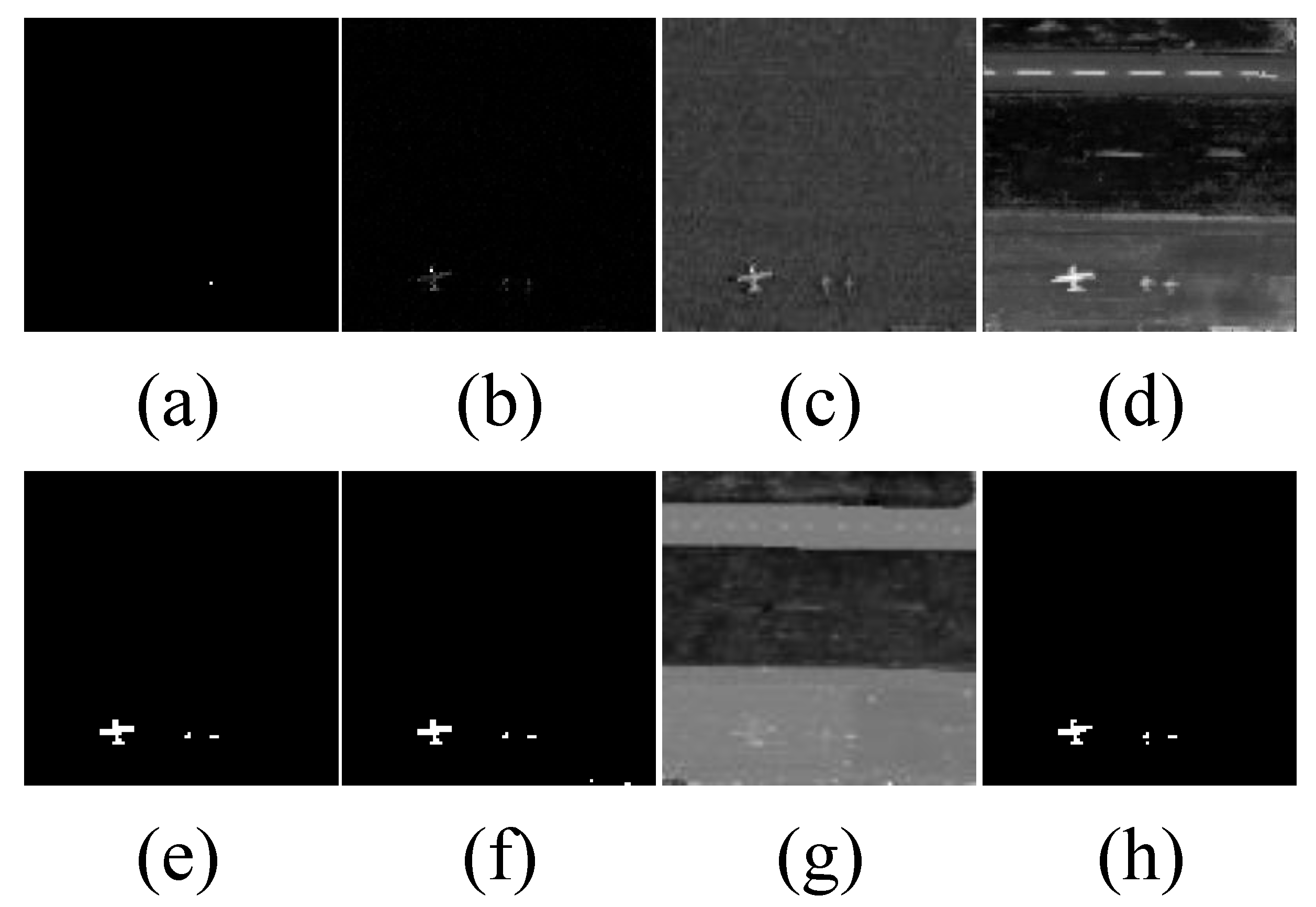
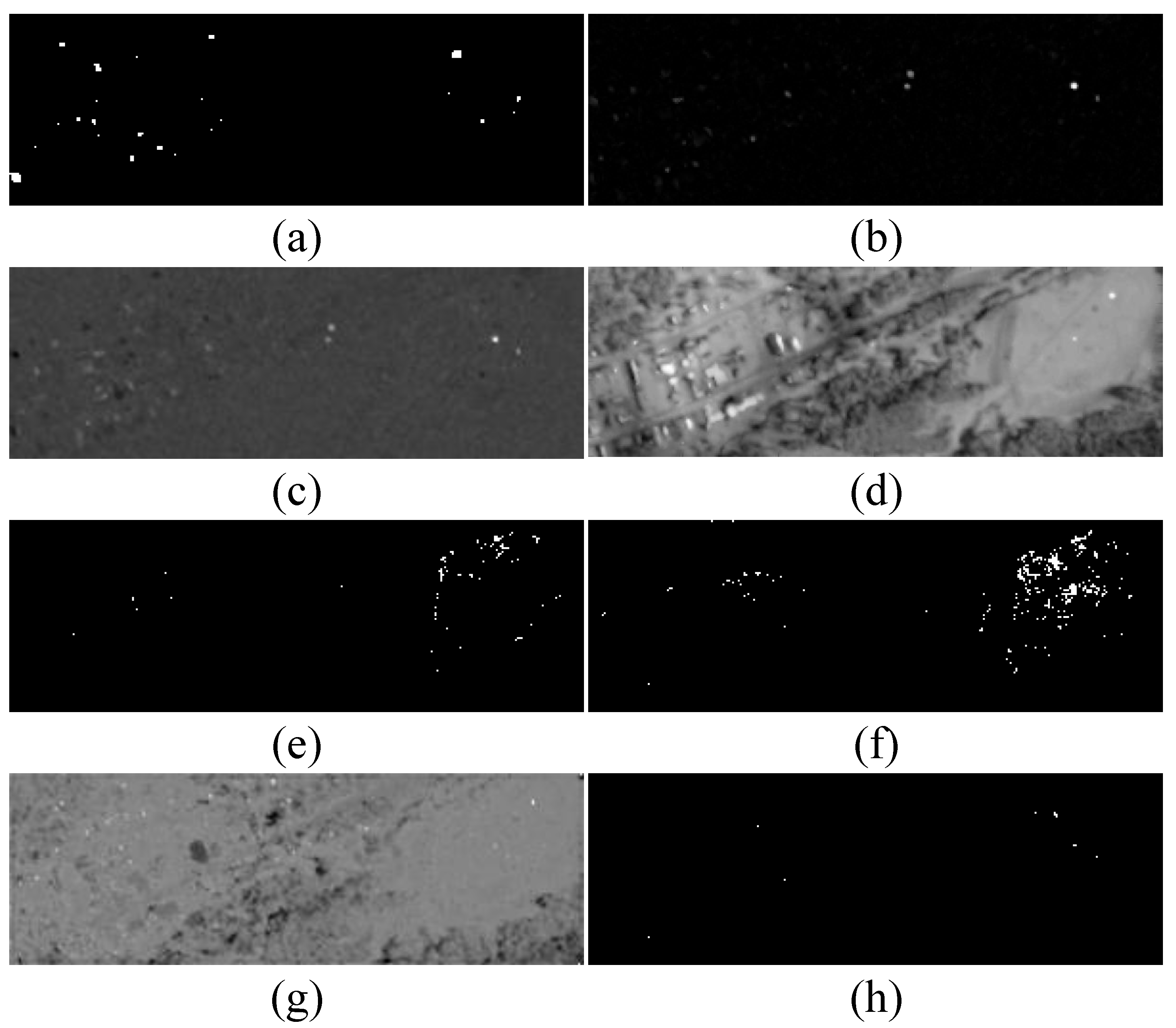
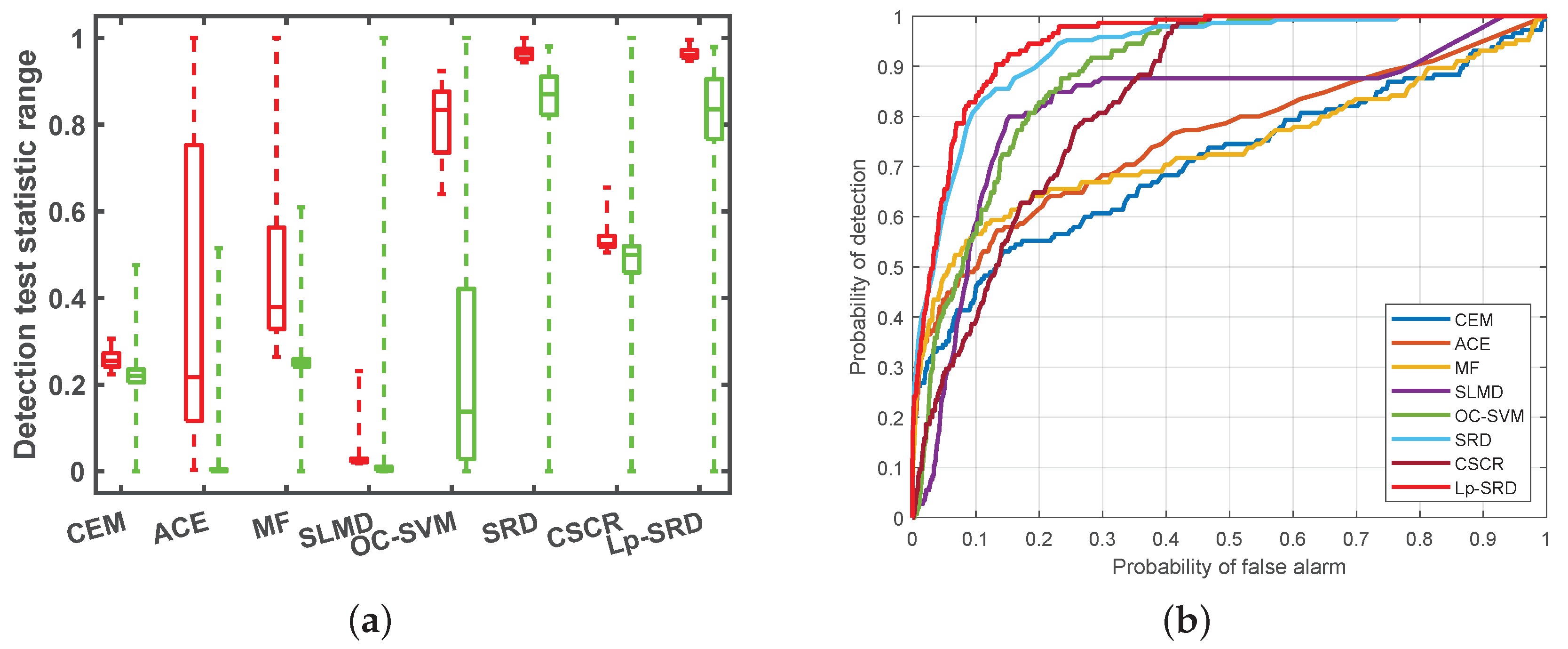
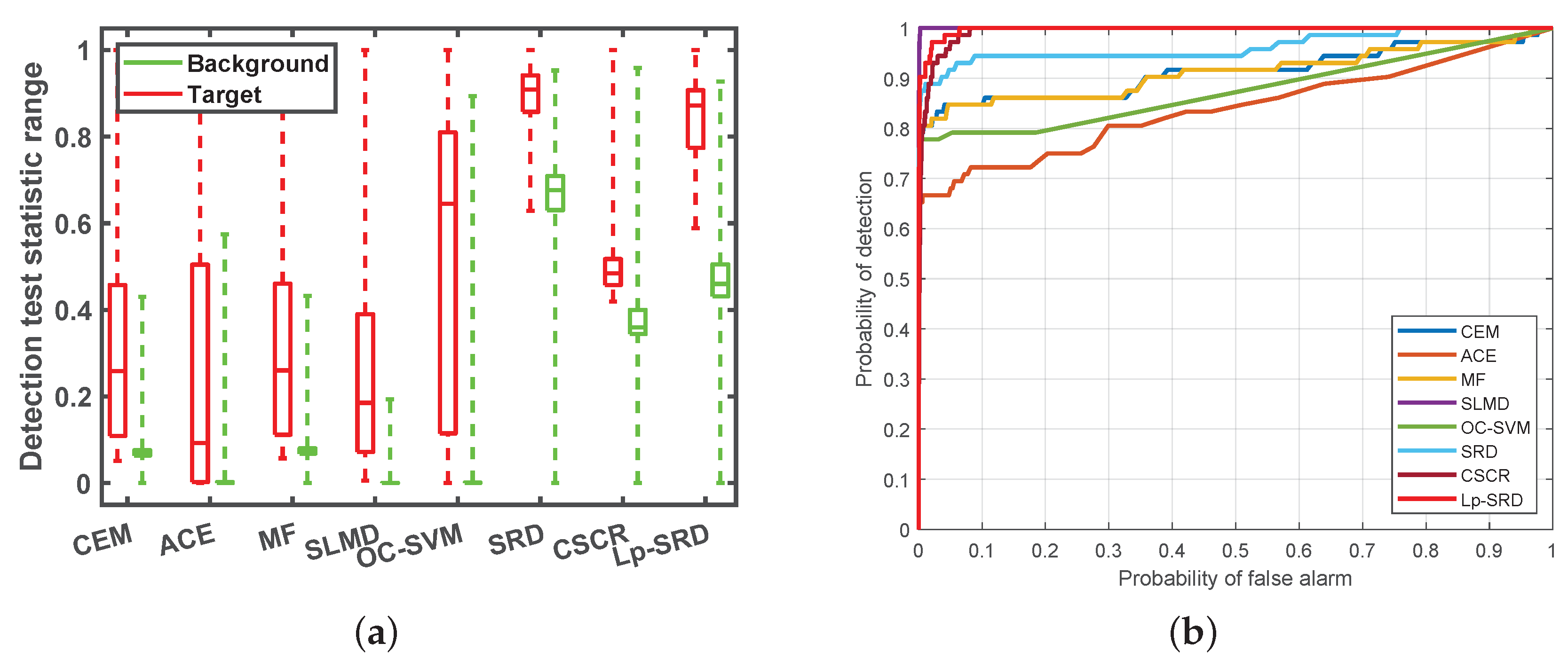
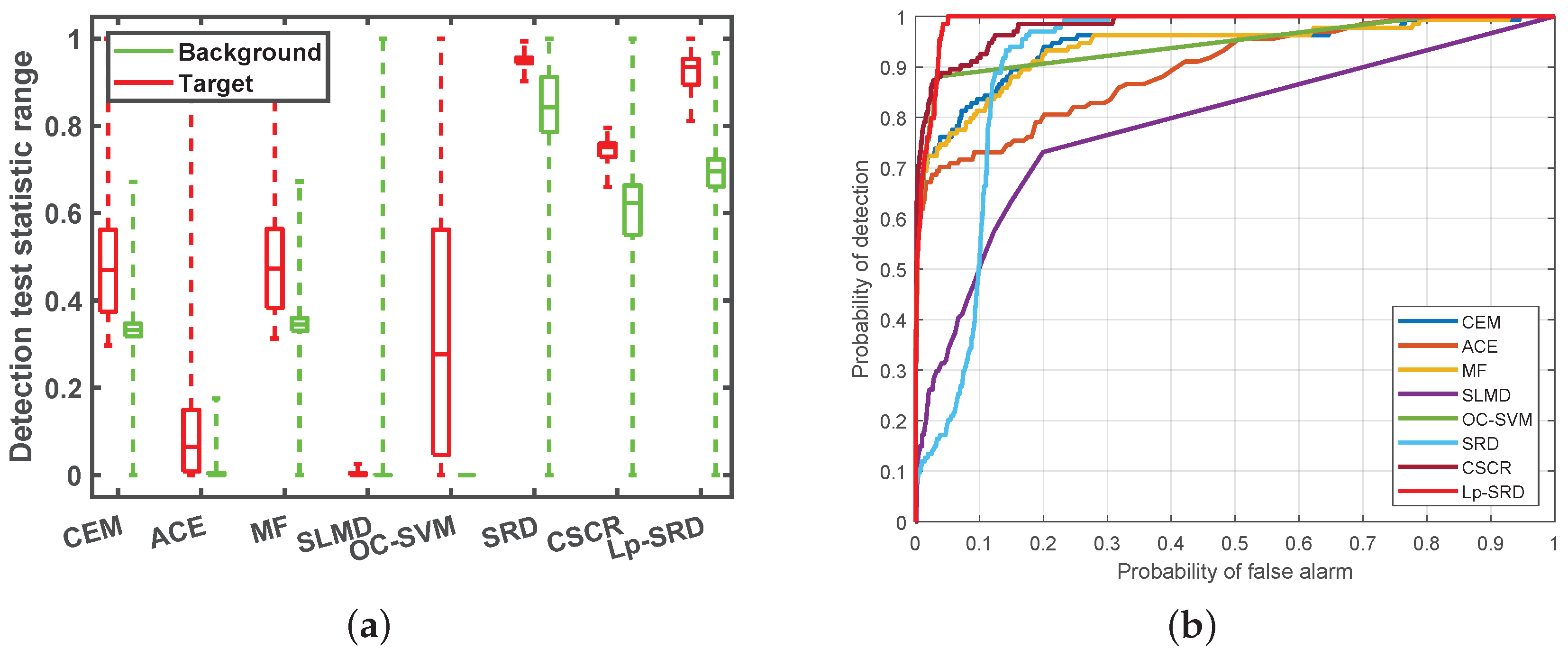
4.3. Detection Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schweizer, S.M.; Moura, J.M.F. Hyperspectral imagery: Clutter adaptation in anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2000, 46, 1855–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, B.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Jupp, D.L.; Pearlman, J.S. Preprocessing EO-1 Hyperion hyperspectral data to support the application of agricultural indexes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Du, Q.; Ran, Q.; Tao, R. HTD-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Target Detection in Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shang, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, H.; Song, M.; Chang, C.-I. Underwater Hyperspectral Target Detection with Band Selection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. A Survey of Sparse Representation: Algorithms and Applications. IEEE Access 2015, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D.; Huang, X.; Du, B. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Subpixel Target Detection Based on Supervised Metric Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4955–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. Hyperspectral Target Detection via Adaptive Joint Sparse Representation and Multi-Task Learning with Locality Information. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shi, Z. SparseCEM and SparseACE for Hyperspectral Image Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, L.C.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Song, M.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Chang, C.I. A Posteriori Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection for Unlabeled Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3091–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Li, H.C.; Song, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. Real-Time Constrained Energy Minimization for Subpixel Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2545–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Q. A survey on representation-based classification and detection in hyperspectral remote sensing imagery. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 83P2, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Zhao, X.D.; Li, W.; Li, H.C.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral anomaly detection by fractional fourier entropy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4920–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.C.; Theiler, J.; Roberts, D.A.; Borel, C.C. Clustering to improve matched filter detection of weak gas plumes in hyperspectral thermal imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, L.L.; Friedlander, B. Matched subspace detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2146–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, J.; Foy, B.R. EC-GLRT: Detecting Weak Plumes in Non-Gaussian Hyperspectral Clutter Using an Elliptically-Contoured Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Q. Collaborative representation for hyperspectral anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E. Partitioned correlation model for hyperspectral anomaly detection. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 123114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, J.A.; Bihl, T.J.; Bauer, K.W. Principal component reconstruction error for hyperspectral anomaly detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Simultaneous joint sparsity model for target detection in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Sparse representation for target detection in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. A sparse representation-based binary hypothesis model for target detection in hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D. Beyond the Sparsity-Based Target Detector: A Hybrid Sparsity and Statistics-Based Detector for Hyperspectral Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5345–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Prasad, S. Class-Dependent Sparse Representation Classifier for Robust Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2683–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, M.S.; Benhalouche, F.Z.; Deville, Y.; Djerriri, K.; Weber, C. Partial Linear NMF-Based Unmixing Methods for Detection and Area Estimation of Photovoltaic Panels in Urban Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, A.W.; Cheong, L.F.; Ovarlez, J.P. Sparse and Low-Rank Matrix Decomposition for Automatic Target Detection in Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5239–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B. Combined sparse and collaborative representation for hyperspectral target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 3904–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Hou, Z.; Wu, F.; Du, Q.; Chen, Y. Anomaly Detection for Hyperspectral Imagery Based on the Regularized Subspace Method and Collaborative Representation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Yang, A.Y.; Ganesh, A.; Sastry, S.S.; Ma, Y. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 31, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.S.; Olshausen, B.A.; Rozell, C.J. Learning sparse codes for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.Y.; Lin, Z.; She, Y.; Zhang, C. A comparison of typical lp minimization algorithms. Neurocomputing 2013, 119, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Candes, E.J.; Wakin, M.B.; Boyd, S.P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l1 minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2008, 14, 877–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodnitsky, I.F.; Rao, B.D. Sparse signal reconstruction from limited data using FOCUSS: A re-weighted minimum norm algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, D.; Fergus, R. Fast image deconvolution using hyper-Laplacian priors. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2009; pp. 1033–1041. [Google Scholar]
- She, Y. Thresholding-based iterative selection procedures for model selection and shrinkage. Electron. J. Stat. 2009, 3, 384–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, D. A generalized iterated shrinkage algorithm for non-convex sparse coding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D.; Huang, X. Sparse Transfer Manifold Embedding for Hyperspectral Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Ren, J.; Marshall, S. Improved sparse representation using adaptive spatial support for effective target detection in hyperspectral imagery. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8669–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, M. Sparse and Redundant Representations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. For most large underdetermined systems of linear equations the minimal l1-norm solution is also the sparsest solution. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. A J. Issued Courant Inst. Math. Sci. 2006, 59, 797–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofleitner, A.; Rabbani, T.; El-Ghaoui, L.; Bayen, A. Online Homotopy Algorithm for a Generalization of the LASSO. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 3175–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Dictionary-Based Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H. Robust patch-based sparse representation for hyperspectral image classification. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2017, 15, 1750028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, R.; Staneva, V. Restricted isometry properties and nonconvex compressive sensing. Inverse Probl. 2008, 24, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, R. Exact reconstruction of sparse signals via nonconvex minimization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2007, 14, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; Defrise, M.; De, M.C. An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. A J. Issued Courant Inst. Math. Sci. 2004, 57, 1413–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, N.M. Regularized spectral matched filter for target recognition in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2008, 15, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Li, J. Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection With Attribute and Edge-Preserving Filters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5600–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Kerekes, J.; Fairweather, I.; Crabtree, R. Development of a Web-Based Application to Evaluate Target Finding Algorithms. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; pp. II-915–II-918. [Google Scholar]
- Herweg, J.A.; Kerekes, J.P.; Weatherbee, O.; Messinger, D.; van Aardt, J.; Ientilucci, E.; Ninkov, Z.; Faulring, J.; Raqueño, N.; Meola, J. SpecTIR hyperspectral airborne rochester experiment data collection campaign. In Proceedings of the Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XVIII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23–27 April 2012; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; p. 839028. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.P. Hyperspectral anomaly detection via a sparsity score estimation framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Methods | CEM | ACE | MF | SLMD | OC-SVM | SRD | CSCR | Lp-SRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gulfport | 0.9154 | 0.9184 | 0.9371 | 0.9871 | 0.9852 | 0.9848 | 0.9908 | 0.9960 |
| HyMap | 0.7082 | 0.7554 | 0.7359 | 0.8182 | 0.8835 | 0.9303 | 0.8393 | 0.9468 |
| SpecTIR | 0.9124 | 0.8392 | 0.9115 | 0.9854 | 0.8757 | 0.9625 | 0.9932 | 0.9970 |
| San Diego | 0.9417 | 0.8961 | 0.9385 | 0.7880 | 0.7510 | 0.9590 | 0.9805 | 0.9899 |
| Methods | CEM | ACE | MF | SLMD | OC-SVM | SRD | CSCR | Lp-SRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gulfport | 0.1132 | 0.1538 | 0.1004 | 6.6481 | 0.0660 | 0.8232 | 3.0266 | 0.8816 |
| HyMap | 0.1715 | 0.3647 | 0.2236 | 6.5967 | 0.2423 | 2.3381 | 17.9000 | 4.8677 |
| SpecTIR | 0.1905 | 0.3688 | 0.2507 | 7.3971 | 0.1051 | 2.0856 | 8.0912 | 2.1889 |
| San Diego | 0.2916 | 0.6121 | 0.4352 | 12.2467 | 0.1522 | 2.8855 | 11.8767 | 3.6604 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Tao, R.; Ma, P. Adaptive Iterated Shrinkage Thresholding-Based Lp-Norm Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Imagery Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233991
Zhao X, Li W, Zhang M, Tao R, Ma P. Adaptive Iterated Shrinkage Thresholding-Based Lp-Norm Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Imagery Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233991
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaobin, Wei Li, Mengmeng Zhang, Ran Tao, and Pengge Ma. 2020. "Adaptive Iterated Shrinkage Thresholding-Based Lp-Norm Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Imagery Target Detection" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233991
APA StyleZhao, X., Li, W., Zhang, M., Tao, R., & Ma, P. (2020). Adaptive Iterated Shrinkage Thresholding-Based Lp-Norm Sparse Representation for Hyperspectral Imagery Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233991