Consistency of the Single Calculus Chain Optical Products with Archived Measurements from an EARLINET Lidar Station
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Instrumentation and Tools
2.1. Thessaloniki Lidar System
2.2. Thessaloniki Aerosol Lidar Algorithm-Thalia
2.3. SCC Structure Overview
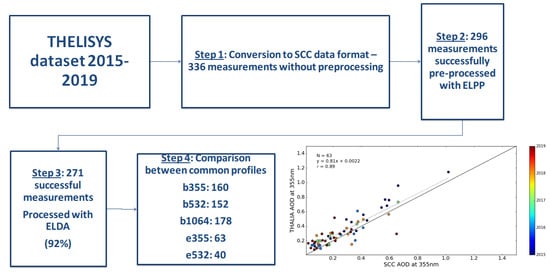
2.4. Dataset Overview
2.5. Selection of the Threshold Values for the Calculation of the Optical Products Derived by Scc
- The lowest height for the reference height to be searched (Lowest Height in meters)
- The maximum height for the reference height to be searched (Top Height in meters)
- The width of the reference height interval (the average value within this calibration window and its standard deviation are used to estimate the calibration factor and its statistical uncertainty—the backscatter calibration window width in meters with typical values of 0.5 or 1 km)
- The backscatter ratio, ranging from 1 to 1.4 (depending on the wavelength)
2.6. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity Studies
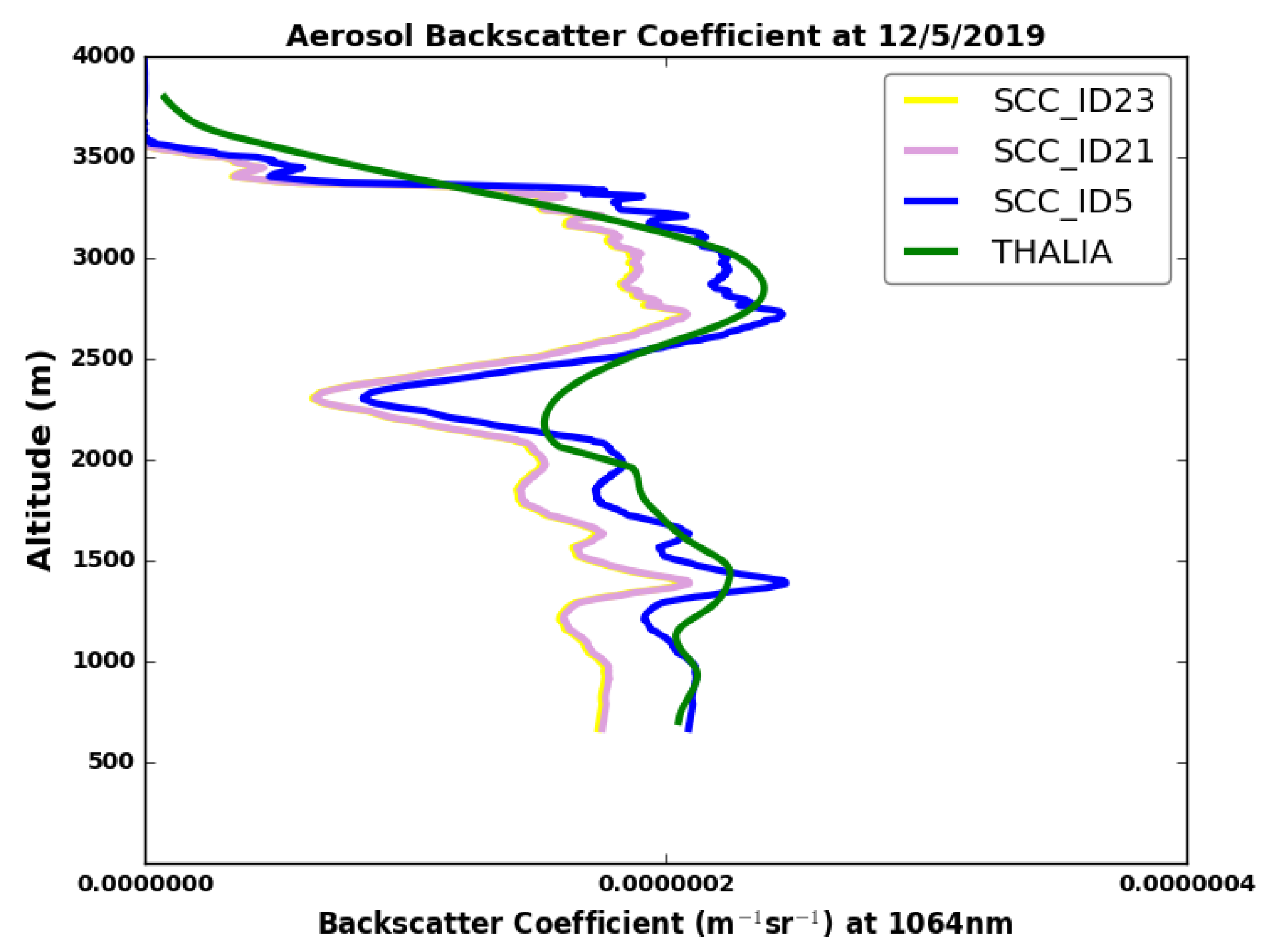
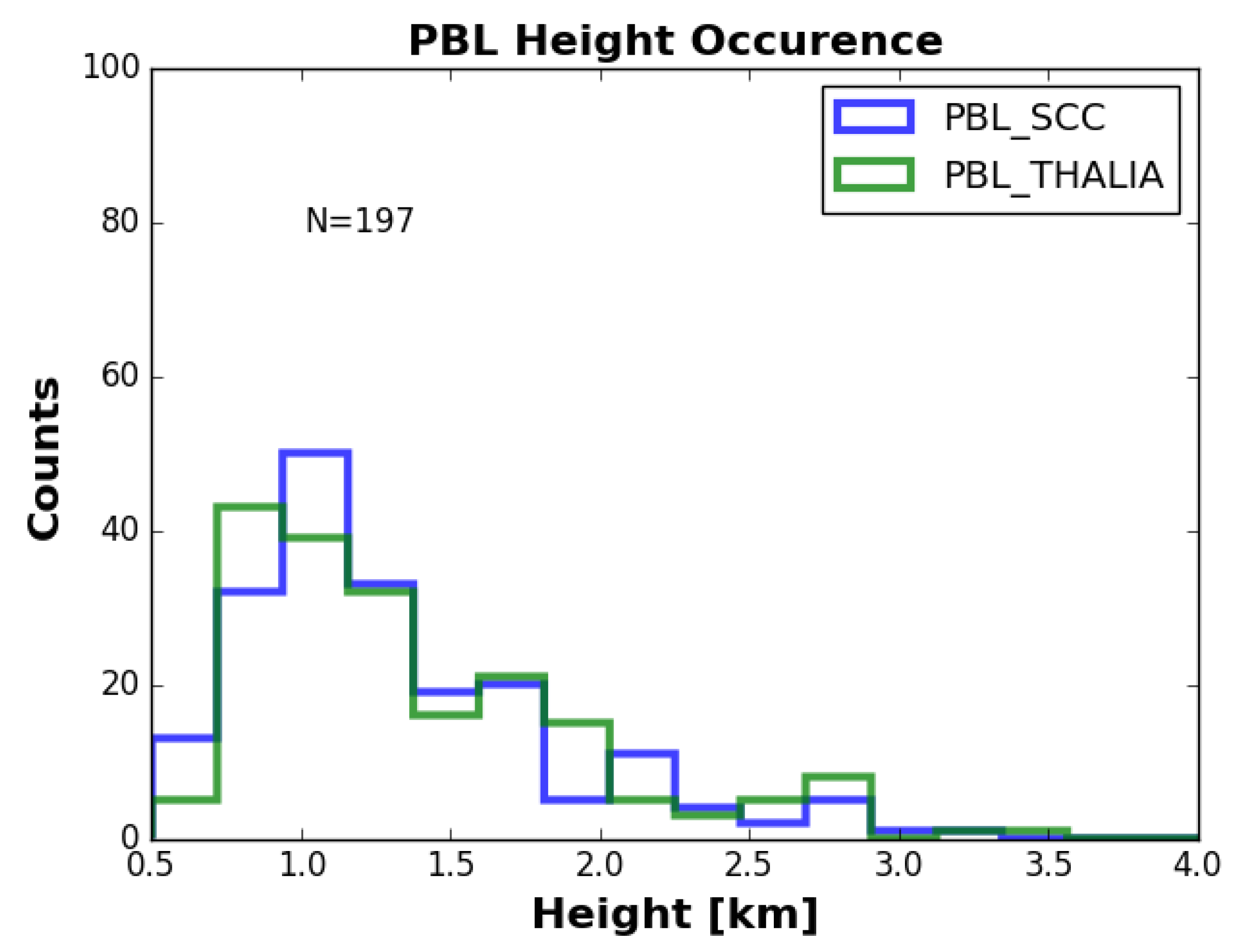
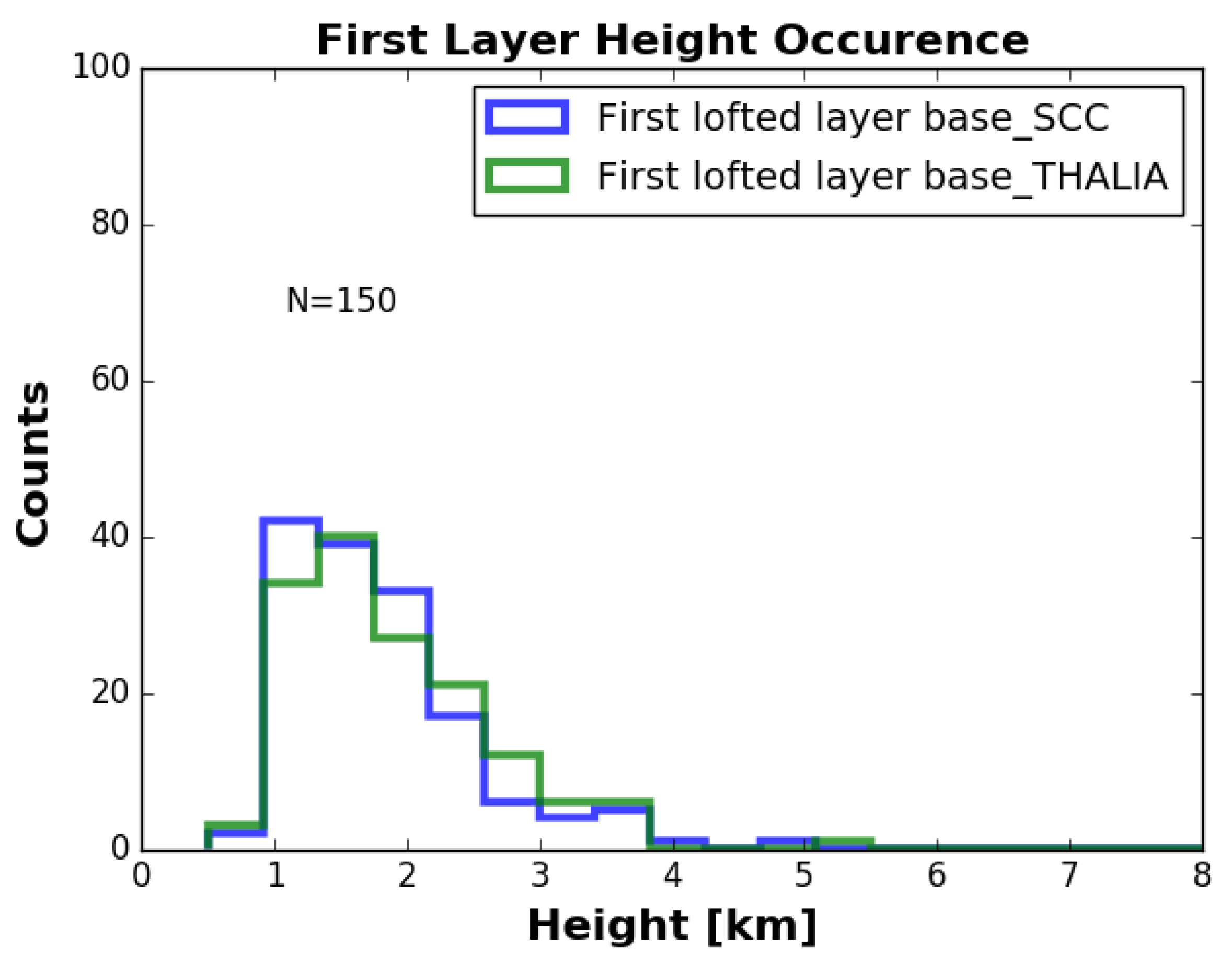
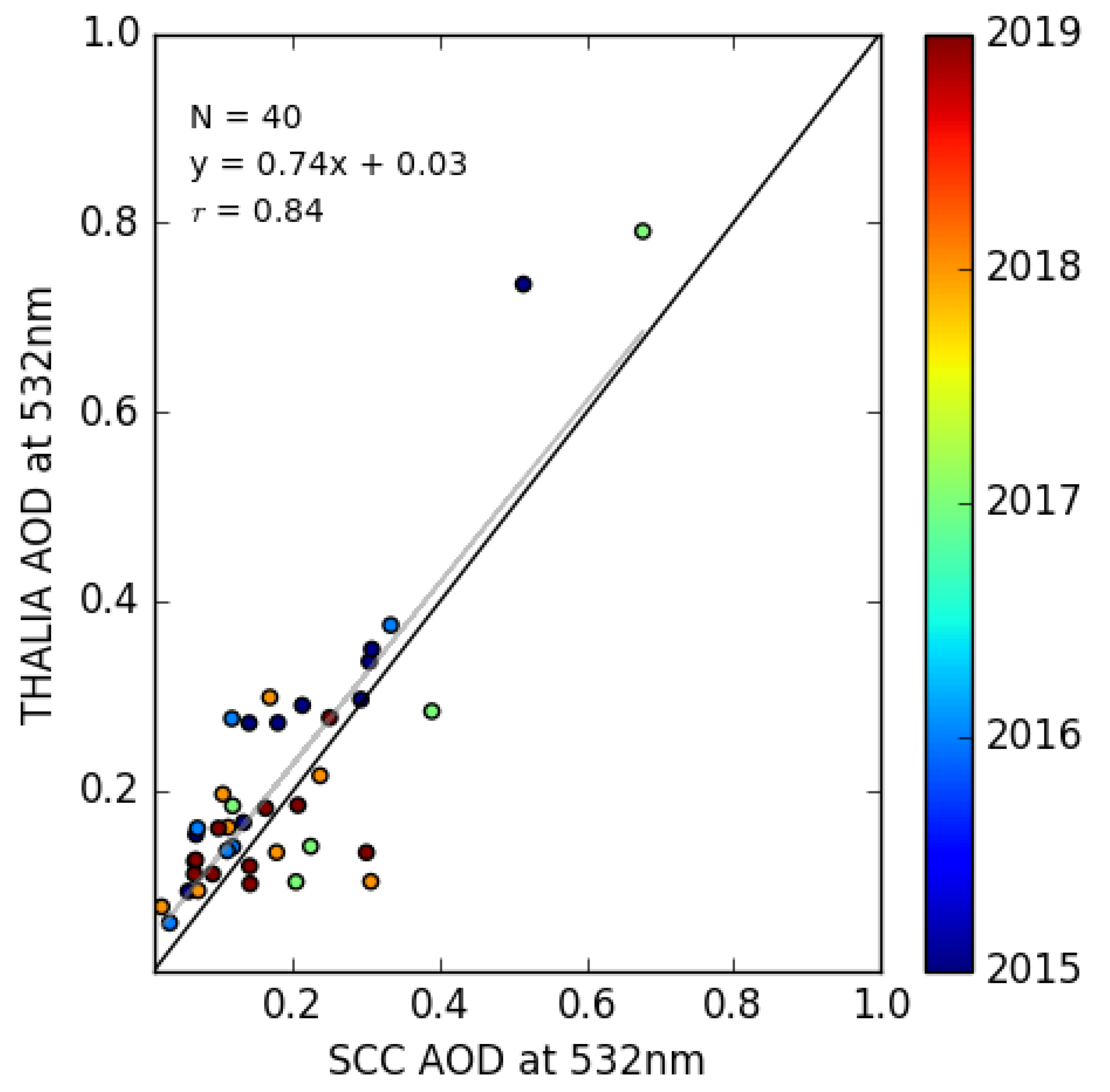
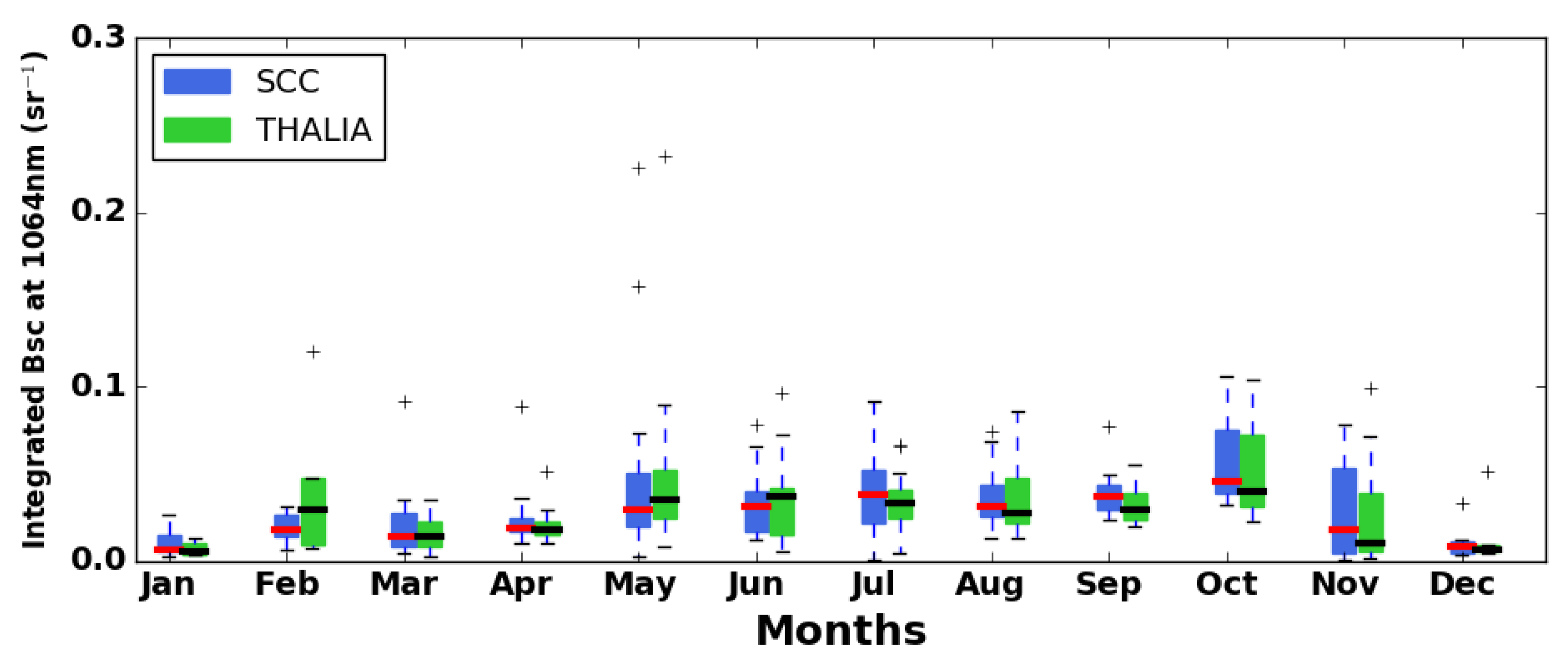
3.2. Columnar Analysis-Geometrical Properties
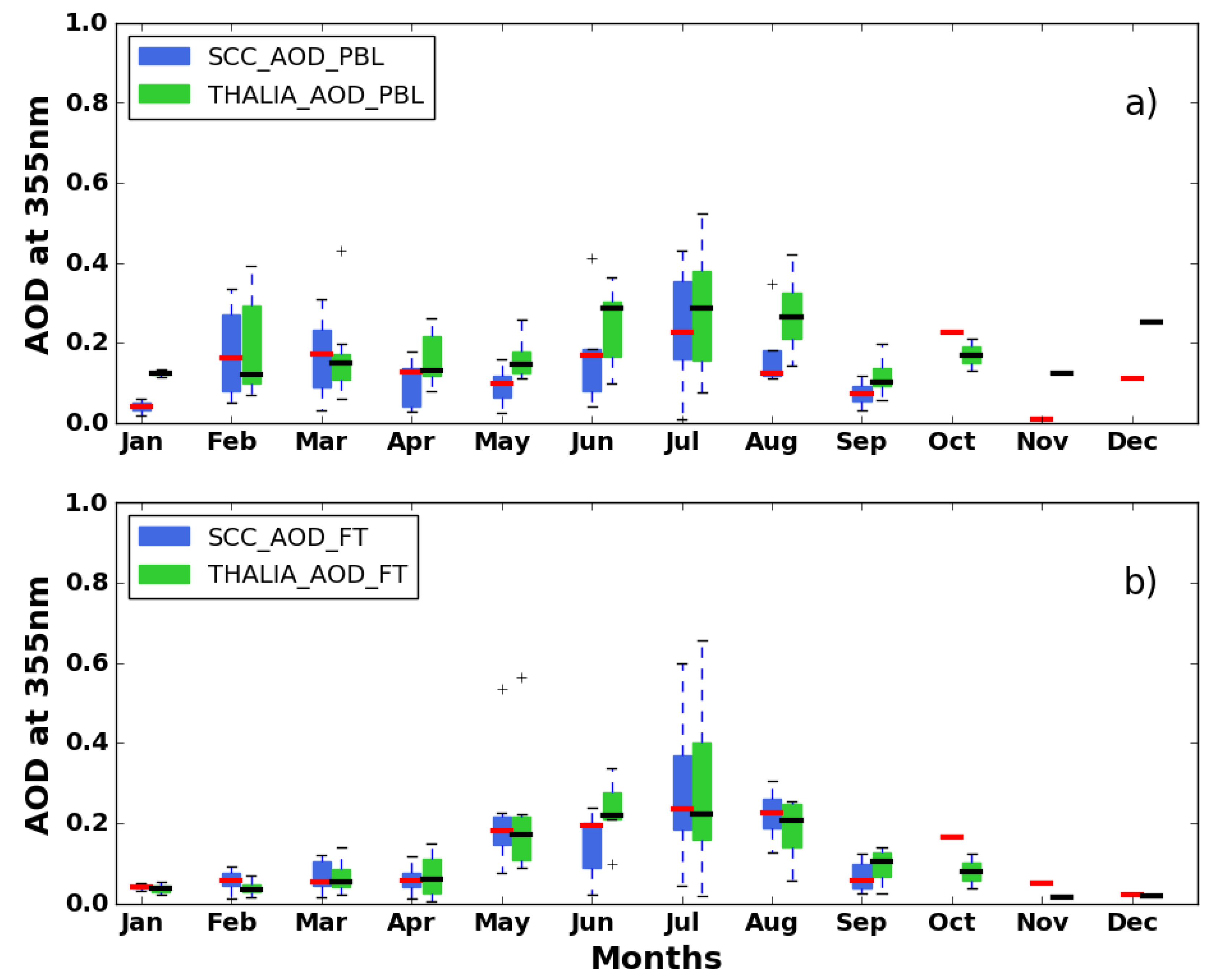
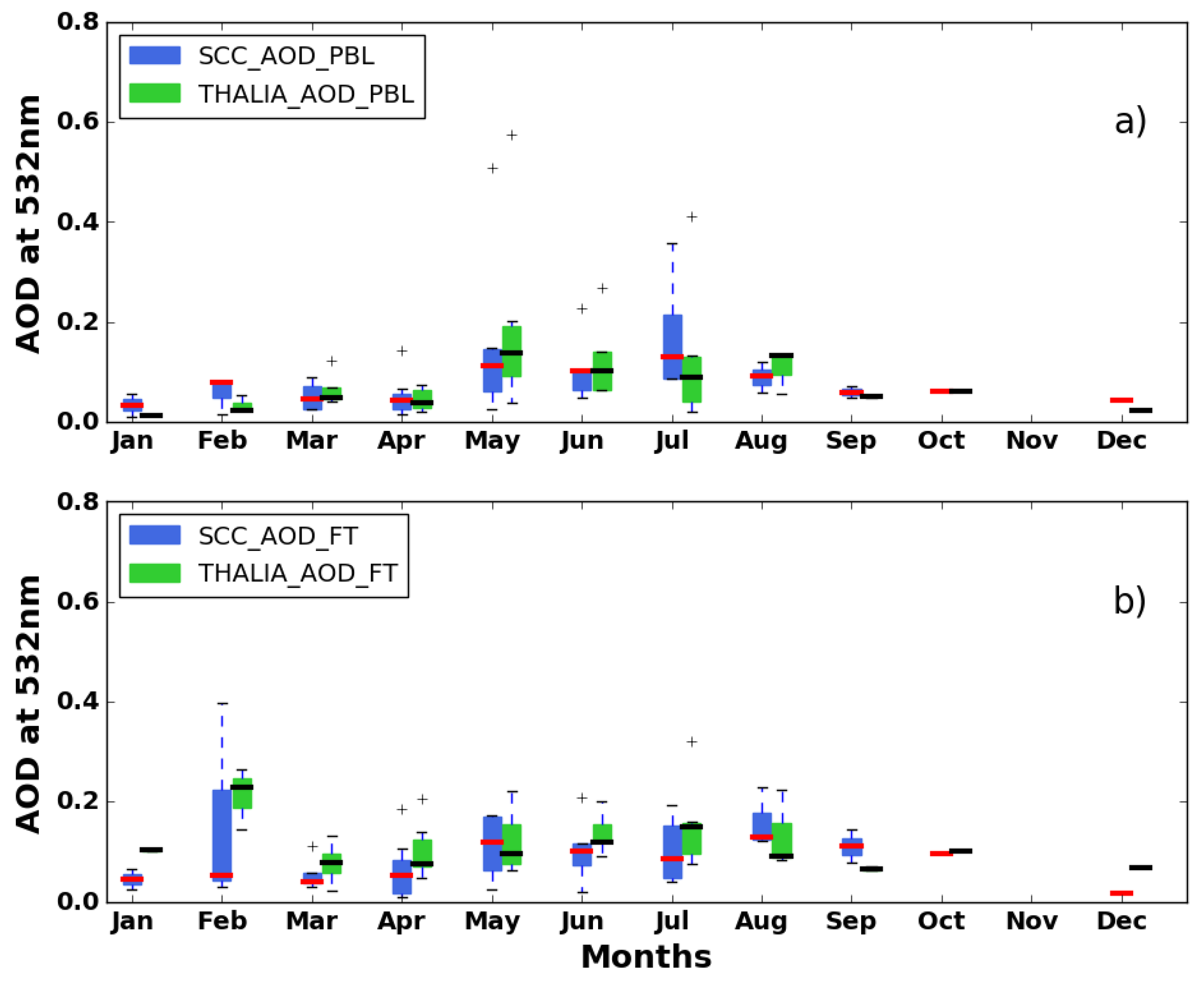
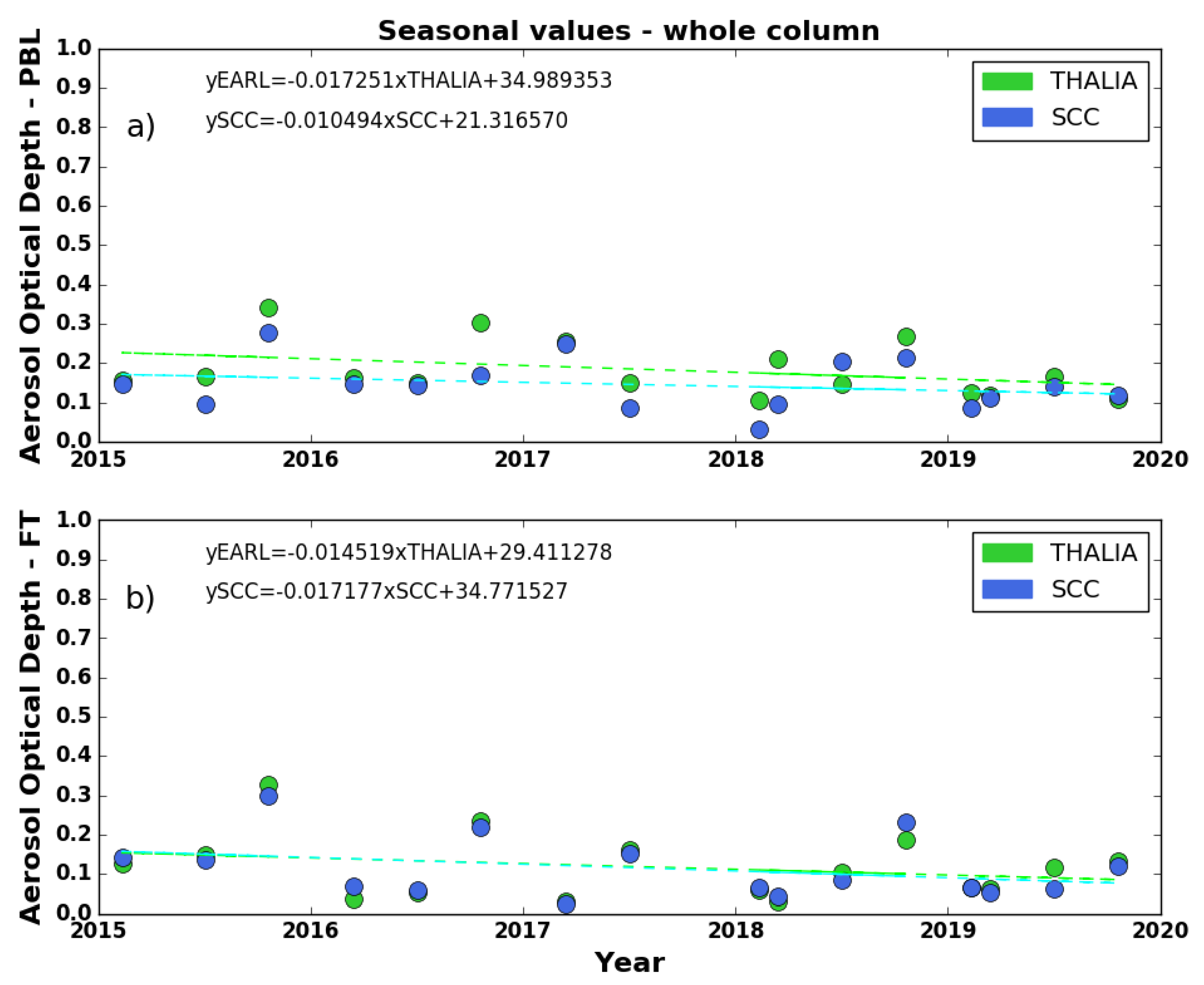
3.3. Seasonal Cycles-Optical Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papagiannopoulos, N.; Mona, L.; Amodeo, A.; D’Amico, G.; Gumà Claramunt, P.; Pappalardo, G.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Amiridis, V.; Kokkalis, P.; et al. An automatic observation-based aerosol typing method for EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15879–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, D.; Vasilescu, J.; Talianu, C.; Binietoglou, I.; Nicolae, V.; Andrei, S.; Antonescu, B. A neural network aerosol-typing algorithm based on lidar data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14511–14537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Hünerbein, A.; Horn, S.; Kanitz, T.; Donovan, D.; van Zadelhoff, G.-J.; Daou, D.; Fischer, J.; et al. HETEAC: The Aerosol Classification Model for Earth-CARE. EPJ Web Conf. 2016, 119, 01–004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Tsekeri, A.; Wandinger, U.; Schwarz, A.; Giannakaki, E.; Mamouri, R.; Kokkalis, P.; Binietoglou, I.; Solomos, S.; et al. LIVAS: A 3-D multi-wavelength aerosol/cloud database based on CALIPSO and EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7127–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Esselborn, M.; Weinzierl, B.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; Petzold, A. Aerosol classification by airborne high spectral resolution lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W.; Rogers, R.R.; Obland, M.D.; Butler, C.F.; Cook, A.L.; Harper, D.B.; Froyd, K.D. Aerosol classification using airborne High Spectral Resolution Lidar measurements—Methodology and examples. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosenberg, J.; Matthias, V.; Amodeo, A.; Amiridis, V.; Ansmann, A.; Baldasamo, J.M.; Balin, I.; Balis, D.; Bockmann, C.; Boselli, A.; et al. EARLINET: A European Aerosol Research Lidar Network to Establish an Aerosol Climatology. Rep. Max-Planck-Inst. Meteorol. 2003, 348, 16–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pappalardo, G.; Amodeo, A.; Apituley, A.; Comeron, A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; et al. EARLINET: Towards an advanced sustainable European aerosol lidar network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2389–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Freudenthaler, V.; Baars, H.; Amodeo, A.; Engelmann, R.; Mattis, I.; Groß, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Giunta, A.; D’Amico, G.; et al. EARLINET instrument intercomparison campaigns: Overview on strategy and results. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1001–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Mona, L.; D’Amico, G.; Wandinger, U.; Adam, M.; Amodeo, A.; Ansmann, A.; Apituley, A.; Alados Arboledas, L.; Balis, D.; et al. Four-dimensional distribution of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull volcanic cloud over Europe observed by EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4429–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Haarig, M.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Hanssen, I.; Gausa, M.; Pietruczuk, A.; Szkop, A.; et al. The unprecedented 2017–2018 stratospheric smoke event: Decay phase and aerosol properties observed with the EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15183–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Amodeo, A.; Baars, H.; Binietoglou, I.; Freudenthaler, V.; Mattis, I.; Wandinger, U.; Pappalardo, G. EARLINET Single Calculus Chain-overview on methodology and strategy. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4891–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Amodeo, A.; Mattis, I.; Freudenthaler, V.; Pappalardo, G. EARLINET Single Calculus Chain-technical-Part 1: Pre-processing of raw lidar data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattis, I.; D’Amico, G.; Baars, H.; Amodeo, A.; Madonna, F.; Iarlori, M. EARLINET Single Calculus Chain-technical-Part 2: Calculation of optical products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3009–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; Binietoglou, I.; Baars, H.; Mona, L.; Amato, F.; Kokkalis, P.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Soupiona, O.; Voudouri, K.A. Earlinet single calculus chain: New products overview. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 176, 09014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sartelet, K.N.; Bocquet, M.; Chazette, P.; Sicard, M.; D’Amico, G.; Léon, J.F.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Augustin, P.; et al. Assimilation of lidar signals: Application to aerosol forecasting in the western Mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12031–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, M.; D’Amico, G.; Comerón, A.; Mona, L.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amodeo, A.; Baars, H.; Baldasano, J.M.; Belegante, L.; Binietoglou, I.; et al. EARLINET: Potential operationality of a research network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4587–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Siomos, N.; Giannakaki, E.; Amiridis, V.; D’Amico, G.; Balis, D.S. Comparison of aerosol backscatter and extinction profiles based on the earlinet database and the single calculus chain for Thessaloniki Greece (2001–2014). EPJ Web Conf. 2016, 119, 23024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Siomos, N.; Giannakaki, E.; Amiridis, V.; D’Amico, G.; Balis, D. Long-Term Comparison of Lidar Derived Aerosol Optical Depth Between Two Operational Algorithms and Sun Photometer Measurements for Thessaloniki, Greece. In Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siomos, N.; Balis, D.S.; Voudouri, K.A.; Giannakaki, E.; Filioglou, M.; Amiridis, V.; Papayannis, A.; Fragkos, K. Are EARLINET and AERONET climatologies consistent? The case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11885–11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Siomos, N.; Michailidis, K.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Mona, L.; Cornacchia, C.; Nicolae, D.; Balis, D. Comparison of two automated aerosol typing methods and their application to an EARLINET station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10961–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Wandinger, U.; Mona, L.; Hiebsch, A.; Mattis, I.; Amodeo, A.; Ansmann, A.; Seifert, P.; Linne, H.; Apituley, A.; et al. EARLINET correlative measurements for CALIPSO: First intercomparison results. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00H19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Pailleux, J.; Källén, E.; Vaughan, J.M.; Isaksen, L.; Flamant, P.; Wergen, W.; Andersson, E.; Schyberg, H.; Culoma, A.; et al. The atmospheric dynamics mission for global wind field measurement. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, V.; Freudenthaler, V.; Amodeo, A.; Balin, I.; Balis, D.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovsky, A.; Chourdakis, G.; Comeron, A.; Delaval, A.; et al. Aerosol lidar intercomparison in the framework of the EARLINET project 1. Instruments Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenthaler, V. About the effects of polarising optics on lidar signals and the 190-calibration. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2016, 9, 4181–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basart, S.; Pérez, C.; Nickovic, S.; Cuevas, E.; Bal-dasano, J. Development and evaluation of the BSC-DREAM8b dust regional model over Northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Tellus B 2012, 64, 18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Wandinger, U.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C.; Michaelis, W. Independent measurement of extinction and backscatter profiles in cirrus clouds by using a combined Raman elastic-backscatter lidar. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A. Experimental determination of the lidar overlap profile with Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckmann, C.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Amiridis, V.; Boselli, A.; Delaval, A.; Tomasi, F.D.; Frioud, M.; Grigorov, I.V.; et al. Aerosol lidar in tercomparison in the framework of the EARLINET project.2.Aerosol backscatter algorithms. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Giannakaki, E.; Komppula, M.; Balis, D. Variability in cirrus cloud properties using a PollyXT Raman lidar over high and tropical latitudes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4427–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D. Continuous monitoring of the boundary-layer top with lidar. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 7281–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, I.; Bais, A.F.; Fragkos, K.; Meleti, C.; Tourpali, K.; Zempila, M.M. Short- and long-term variability of spectral solar UV irradiance at Thessaloniki, Greece: Effects of changes in aerosols, total ozone and clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ELPP | Selection |
| Integration time | 3600 (s) |
| Vertical resolution | 15 (m) |
| ELDA | Selection |
| Elastic backscatter method | Klett |
| Extinction method | non-weighted linear fit |
| Low range error threshold | 10%:0.1 |
| High range error threshold | 10%:0.1 |
| Detection limit (for backscatter profiles) | (m−1sr−1) |
| Detection limit (for extinction profiles) | (m−1) |
| Backscatter calibration interval | Range: 3000–12,000 (m) |
| Backscatter calibration window width | 0.5 (km) |
| Backscatter calibration value in terms of backscatter ratio (355 nm and 532 nm) | 1.0 |
| Backscatter calibration value in terms of backscatter ratio (1064 nm) | 1.23 |
| ID5 | Values |
| Backscatter calibration interval | Range: 3000–12,000 (m) |
| Backscatter calibration window width | 0.5 (km) |
| Backscatter calibration value in terms of backscatter ratio | 1.23 |
| ID21 | Values |
| Backscatter calibration interval | Range: 5000–10,000 (m) |
| Backscatter calibration window width | 0.5 (km) |
| Backscatter calibration value in terms of backscatter ratio | 1.01 |
| ID23 | Values |
| Backscatter calibration interval | Range: 2000–12,000 (m) |
| Backscatter calibration window width | 0.5 (km) |
| Backscatter calibration value in terms of backscatter ratio | 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voudouri, K.A.; Siomos, N.; Michailidis, K.; D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; Balis, D. Consistency of the Single Calculus Chain Optical Products with Archived Measurements from an EARLINET Lidar Station. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233969
Voudouri KA, Siomos N, Michailidis K, D’Amico G, Mattis I, Balis D. Consistency of the Single Calculus Chain Optical Products with Archived Measurements from an EARLINET Lidar Station. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233969
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoudouri, Kalliopi Artemis, Nikolaos Siomos, Konstantinos Michailidis, Giuseppe D’Amico, Ina Mattis, and Dimitris Balis. 2020. "Consistency of the Single Calculus Chain Optical Products with Archived Measurements from an EARLINET Lidar Station" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233969
APA StyleVoudouri, K. A., Siomos, N., Michailidis, K., D’Amico, G., Mattis, I., & Balis, D. (2020). Consistency of the Single Calculus Chain Optical Products with Archived Measurements from an EARLINET Lidar Station. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233969