Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methodology
2.1. Datasets
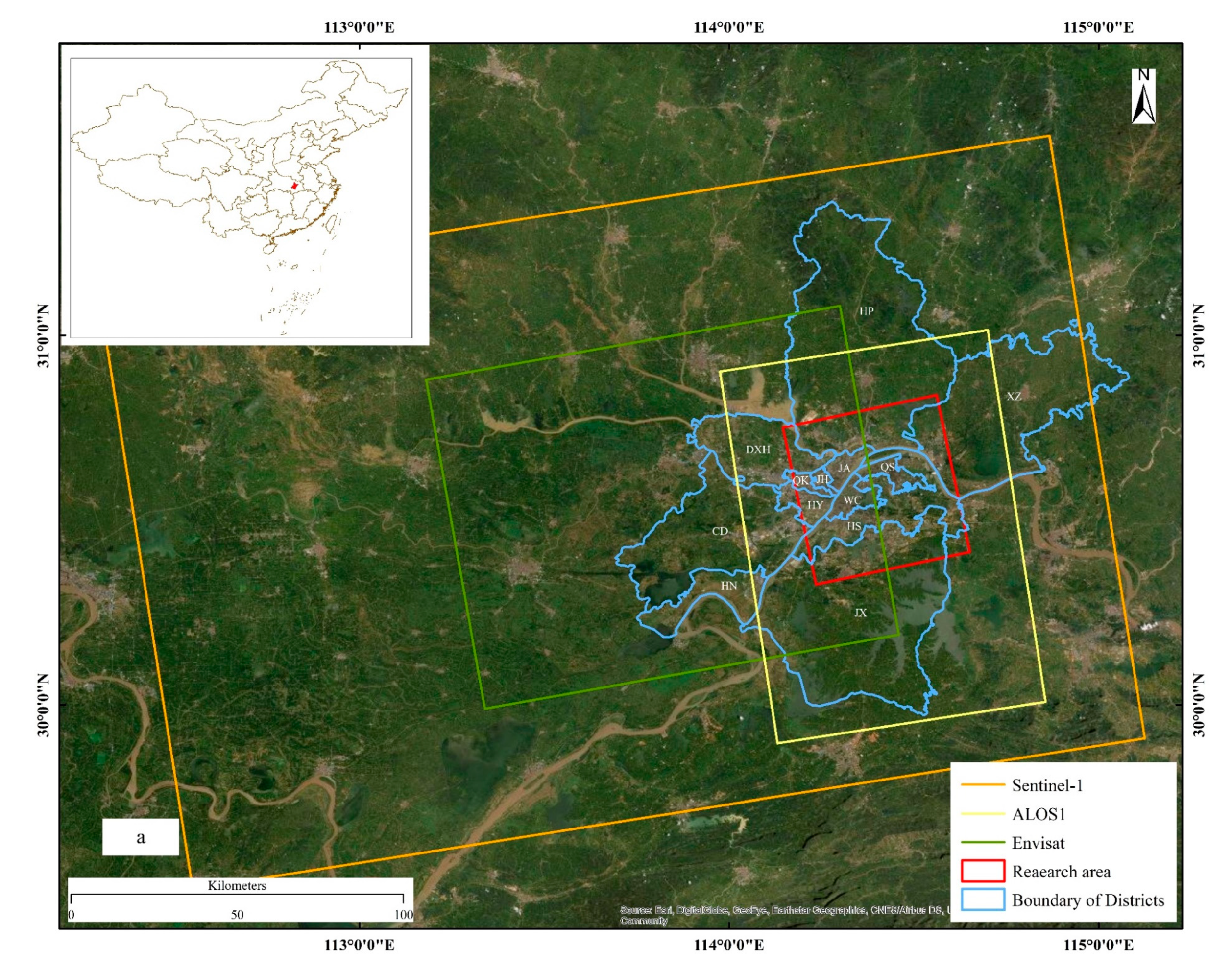
2.1.1. SAR Datasets
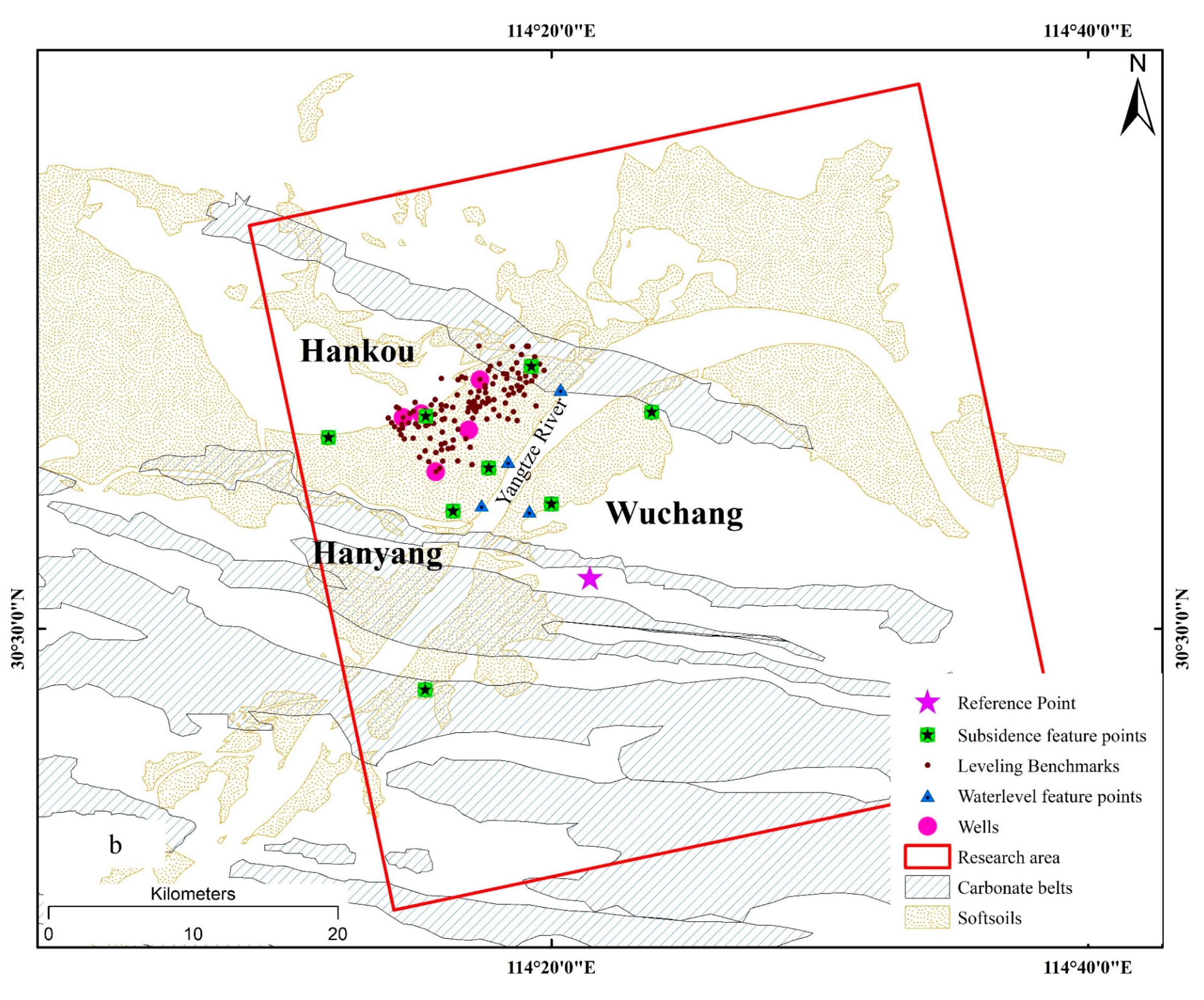
2.1.2. Leveling Observations, Groundwater Level, Yangtze River Water Levels Datasets
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. PS-InSAR Processing
2.2.2. SBAS-InSAR Processing
3. Results and Accuracy Assessment
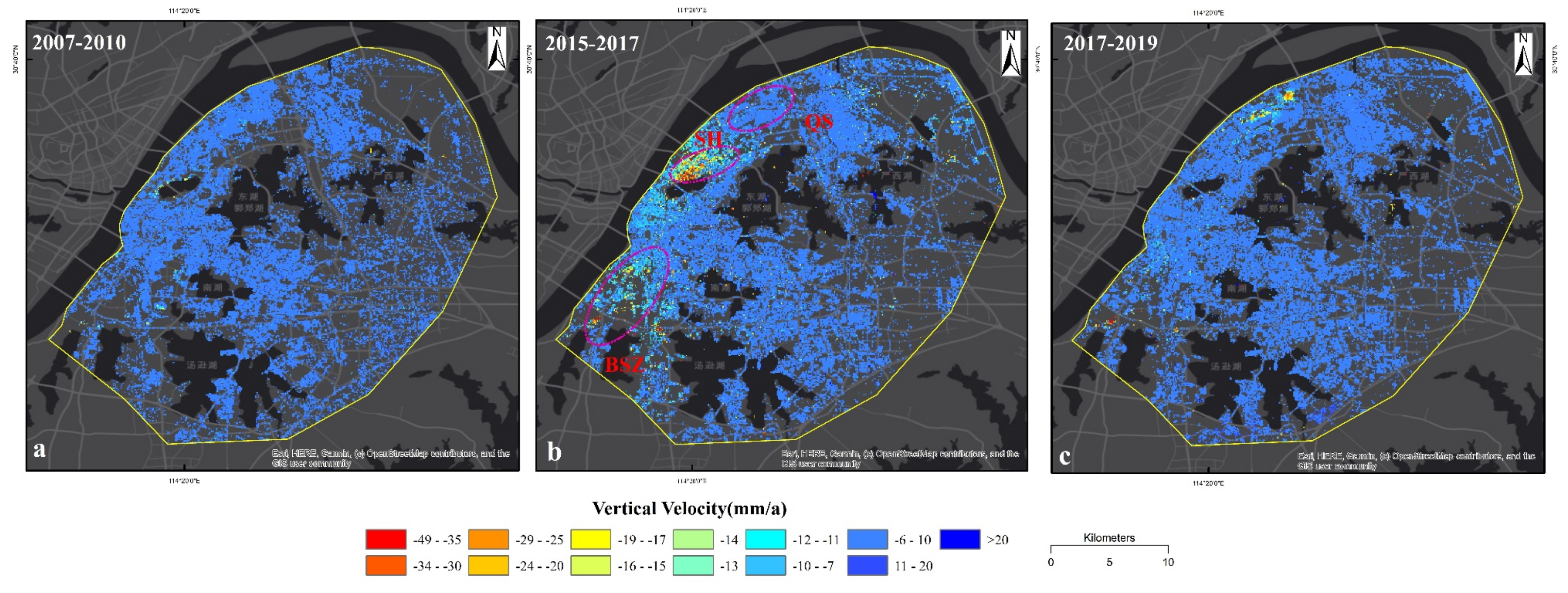
3.1. Velocity of Land Subsidence
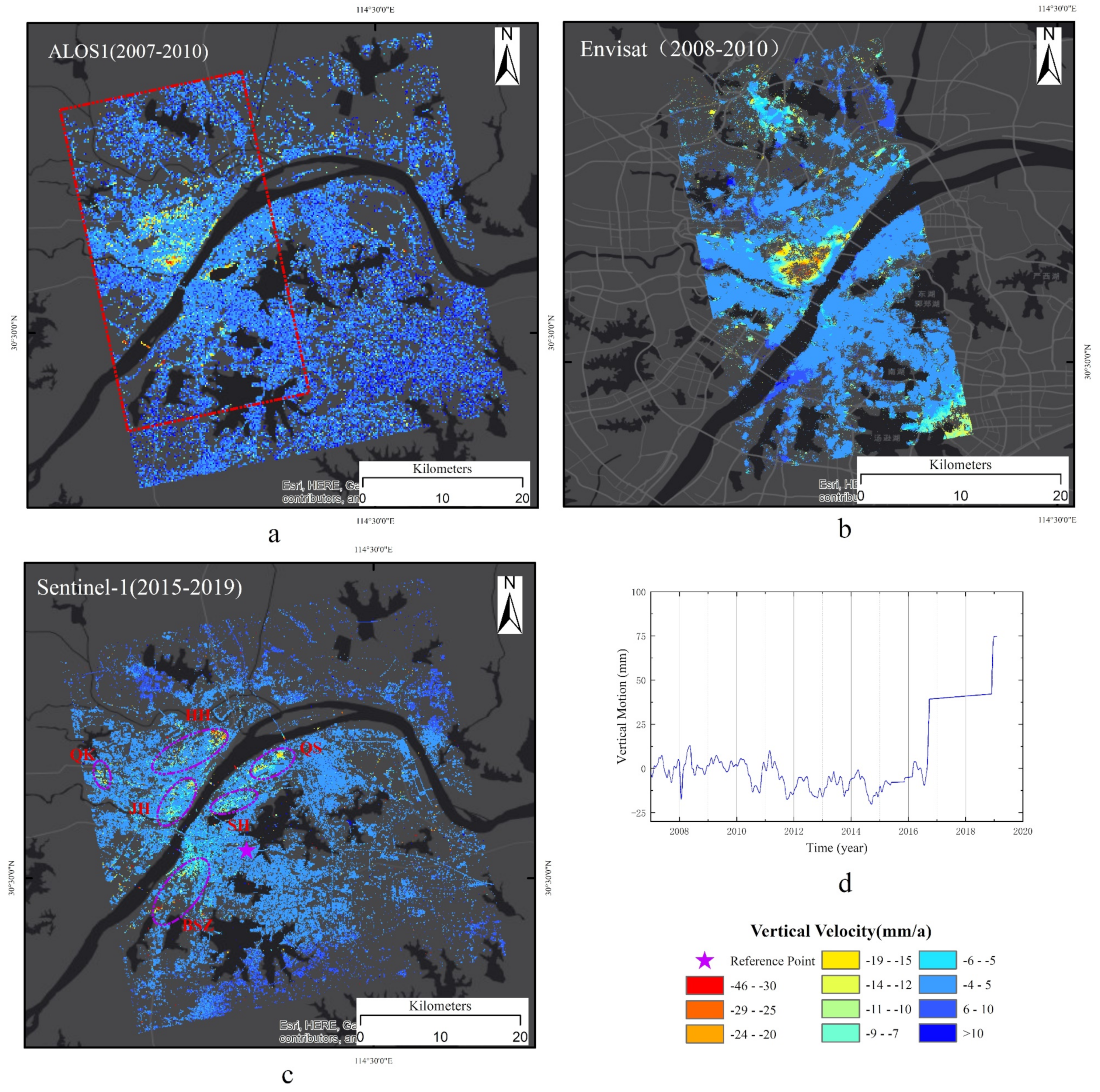
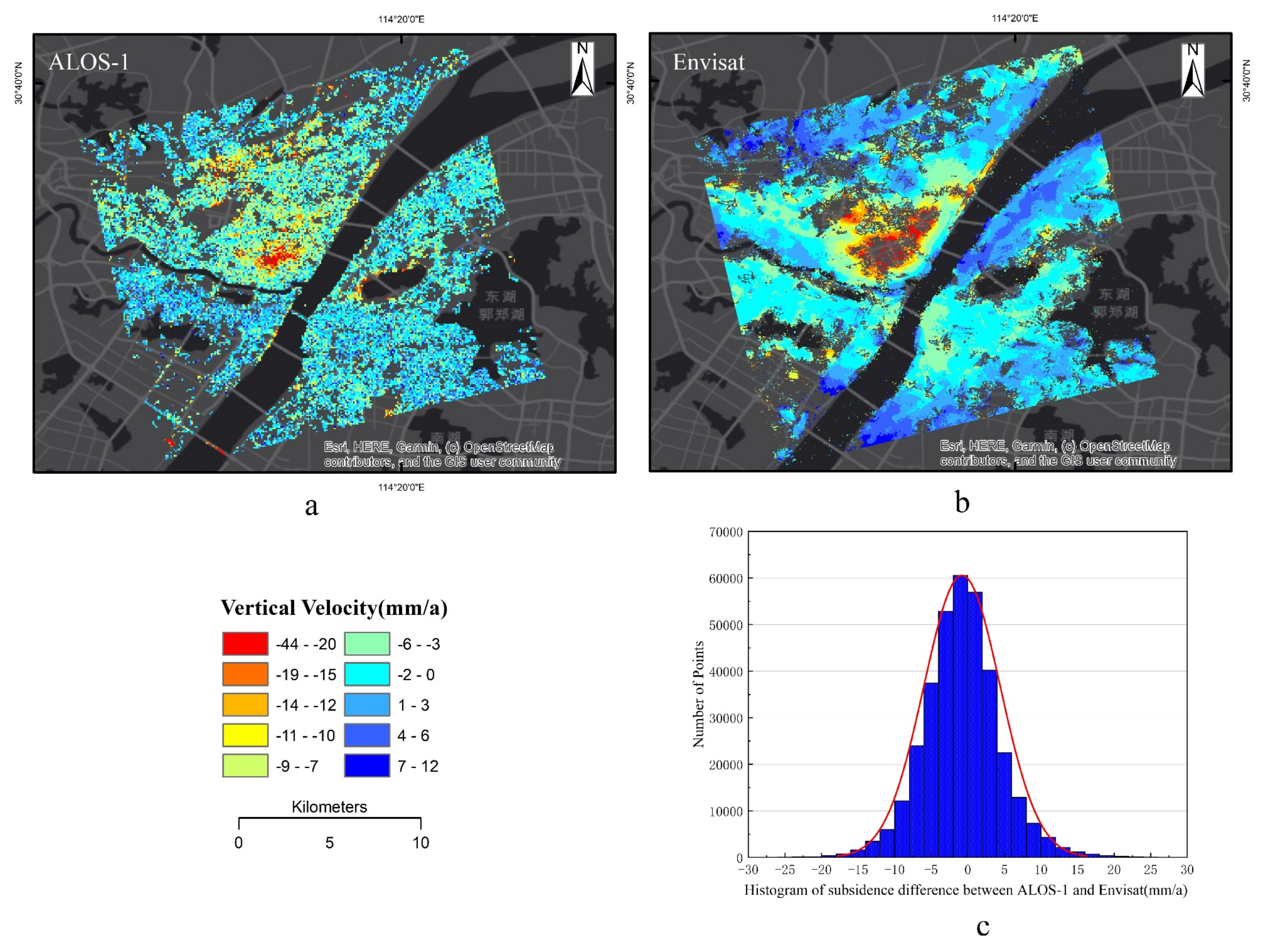
3.1.1. Land Subsidence Velocity with ALOS-1 and Envisat SAR Datasets from 2007 to 2010
3.1.2. Land Subsidence Velocity with Sentinel-1 Dataset from 2015 to 2019
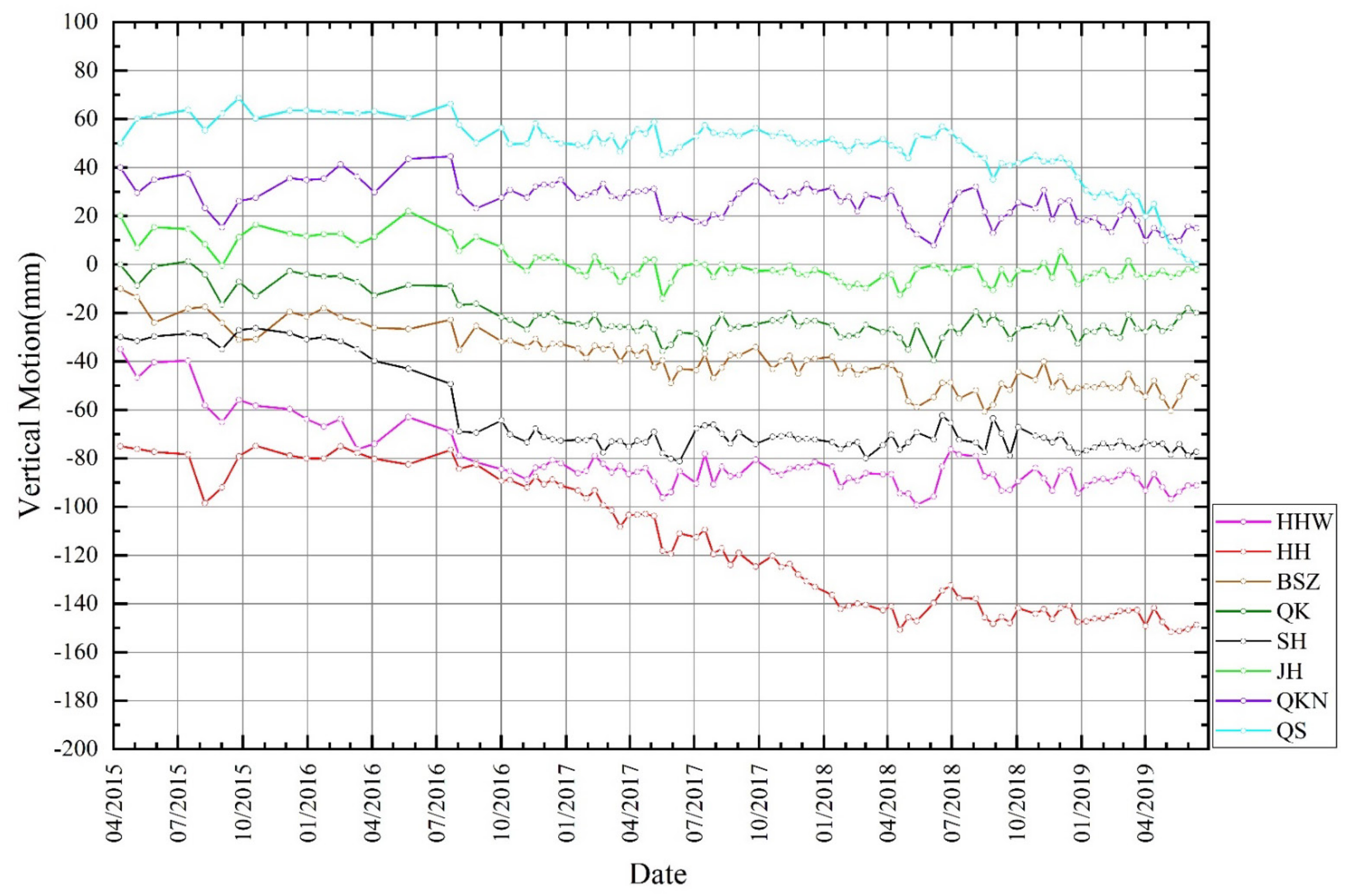
3.1.3. Time Series of Land Subsidence
3.2. InSAR Accuracy Assessment
4. Analysis
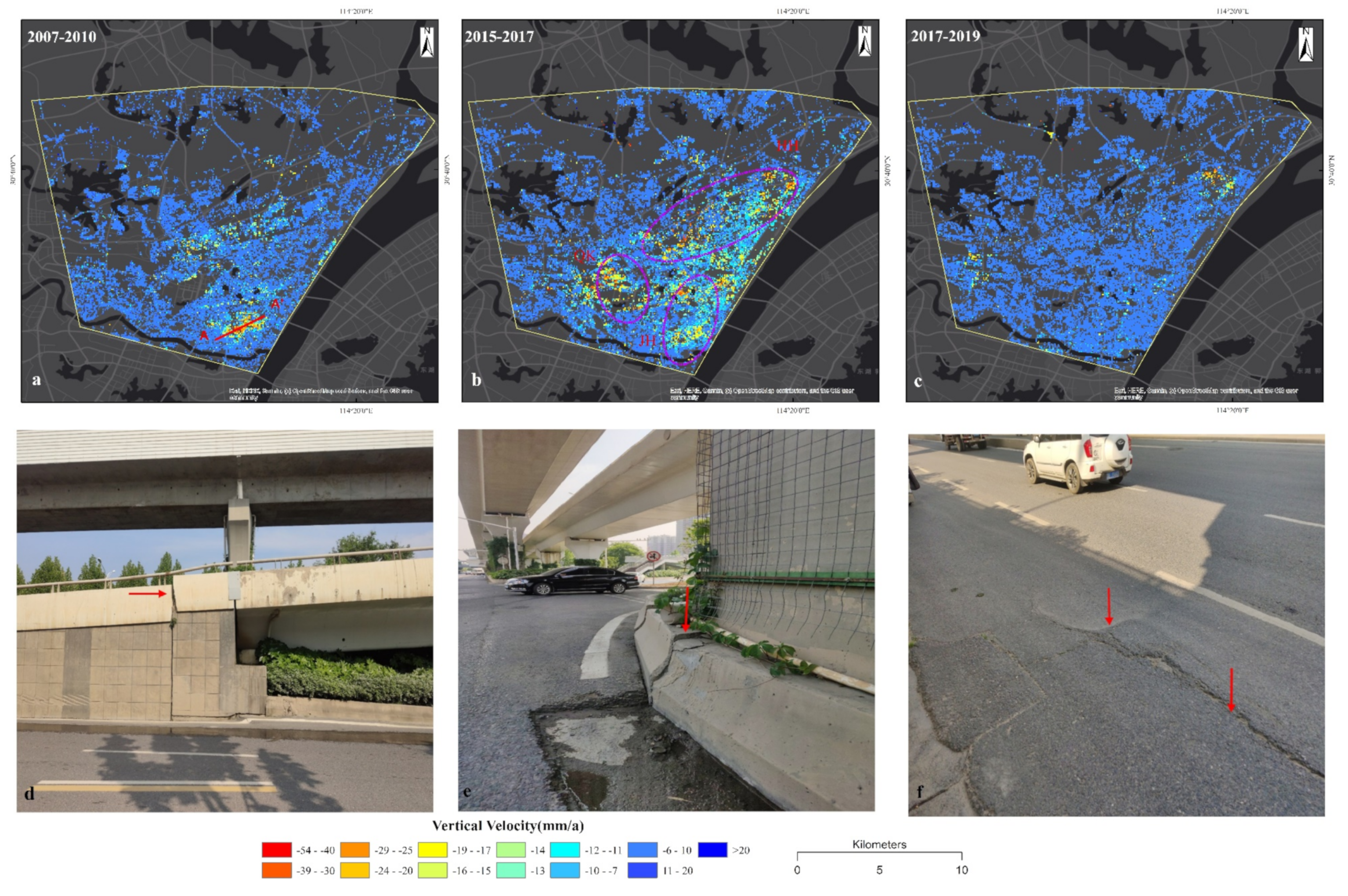
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Land Subsidence in Wuhan
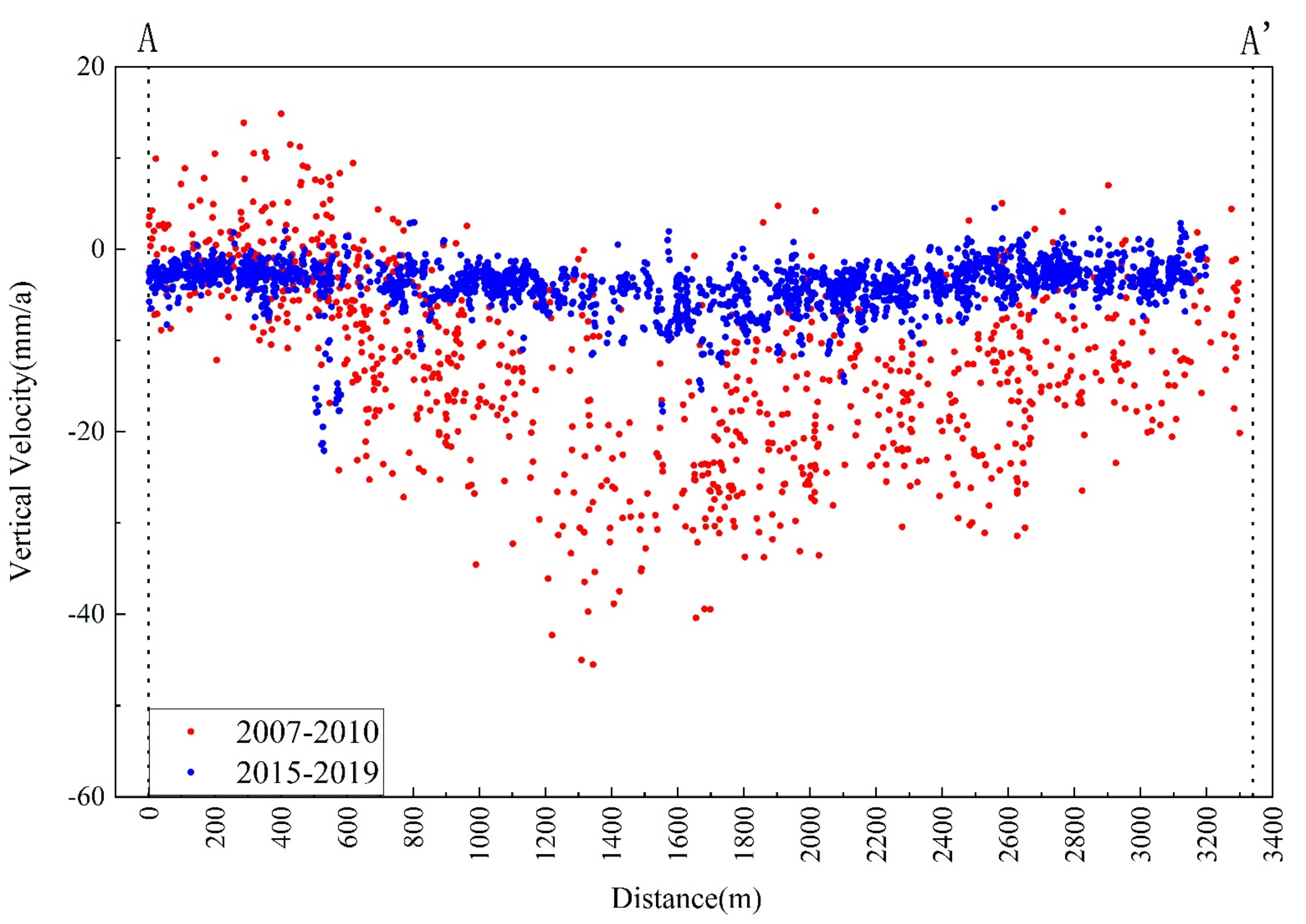
4.1.1. The Land Subsidence in Hankou
4.1.2. The Land Subsidence in Wuchang
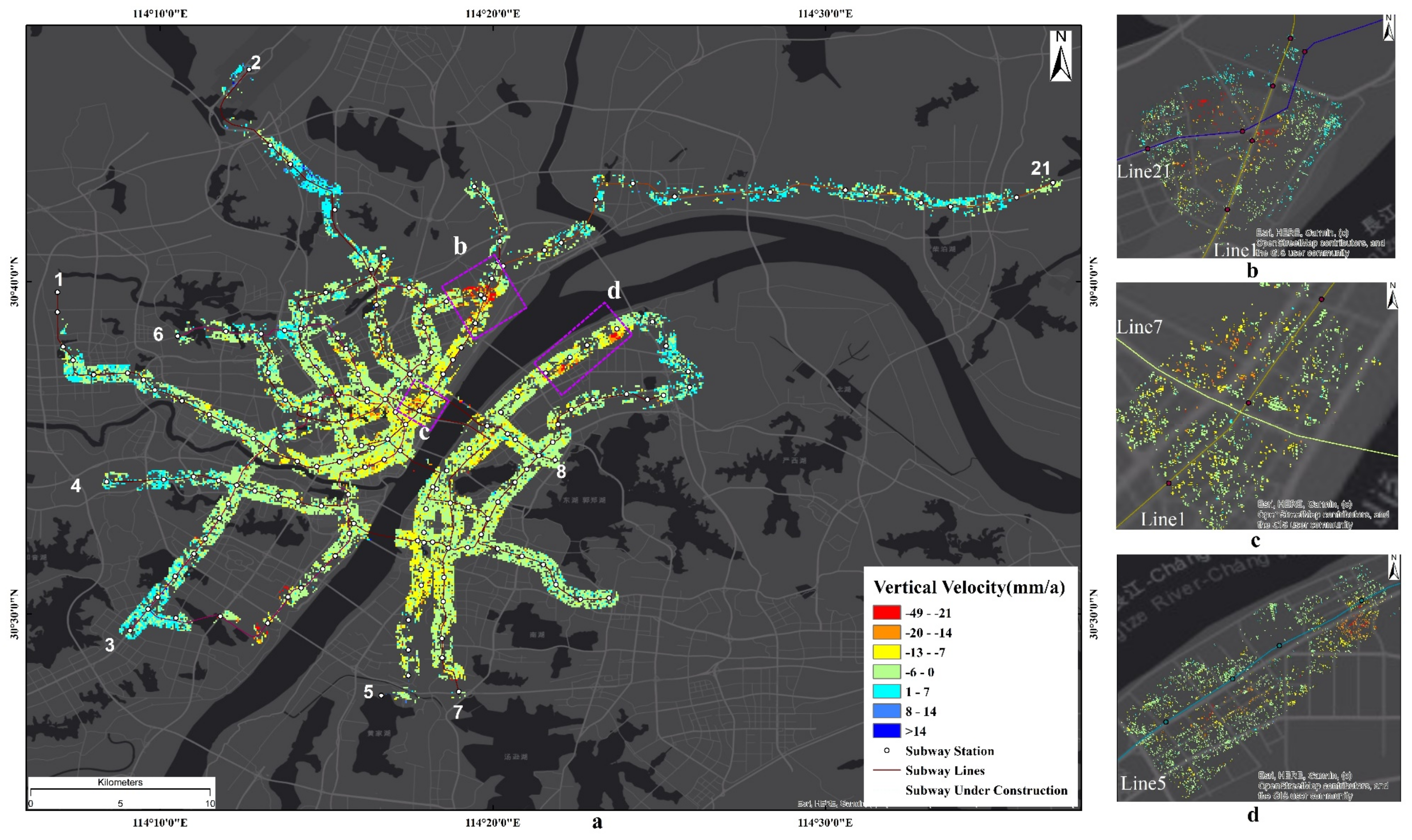
4.2. Land Subsidence Along Metro Lines
5. Discussion
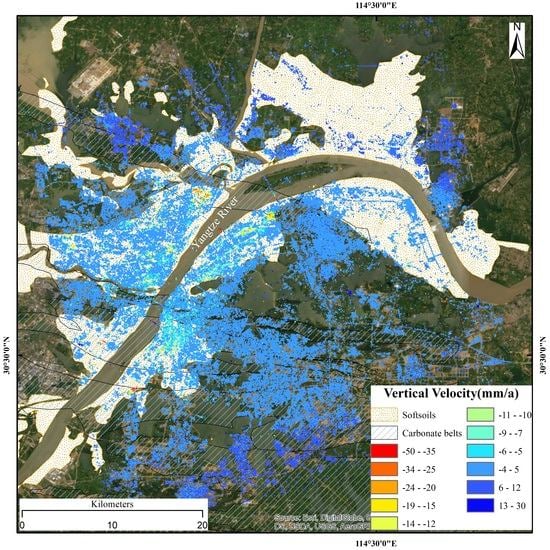
5.1. Correlation between Land Subsidence and Surface Geology
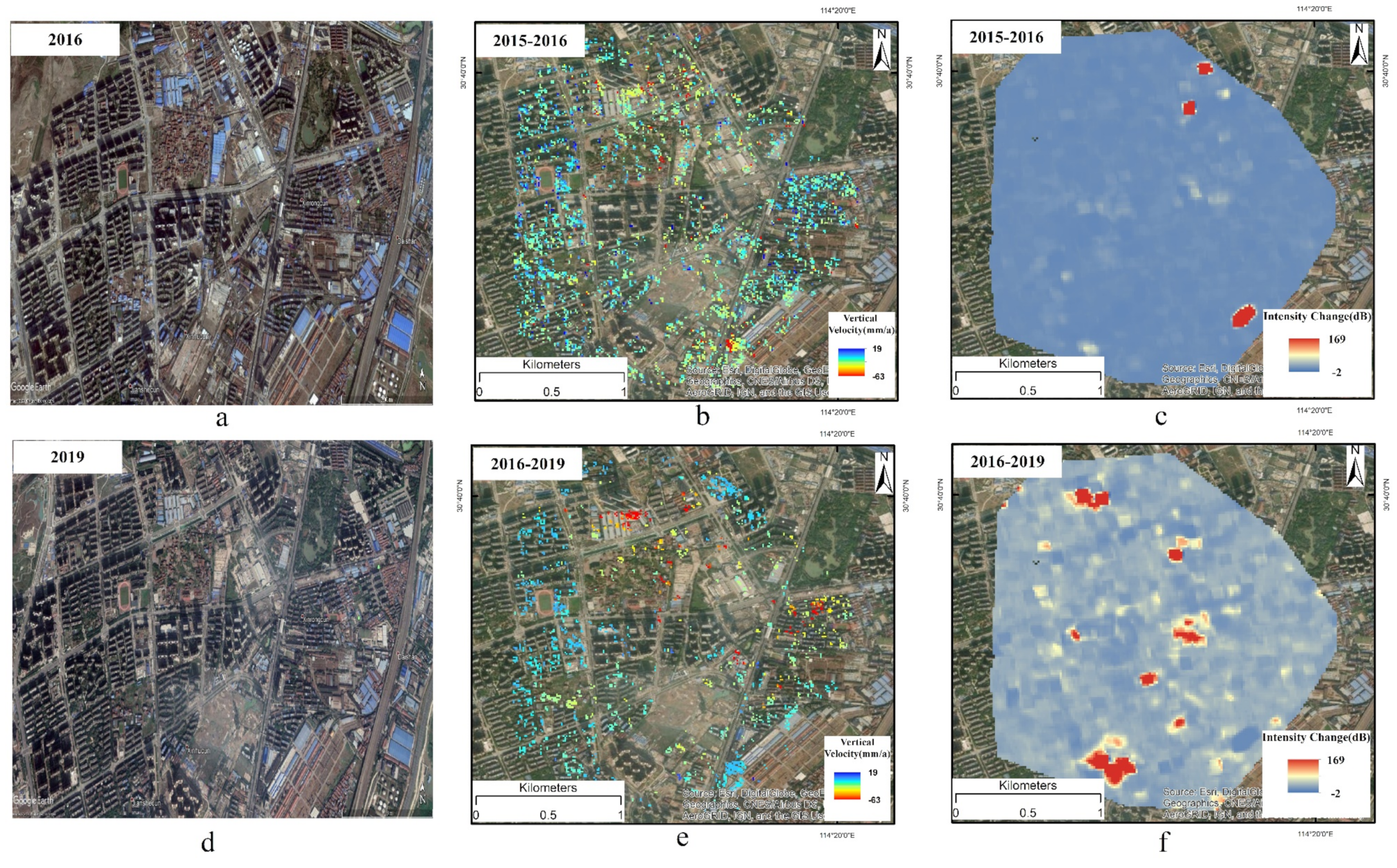
5.2. Correlation between Land Subsidence and Human Activity
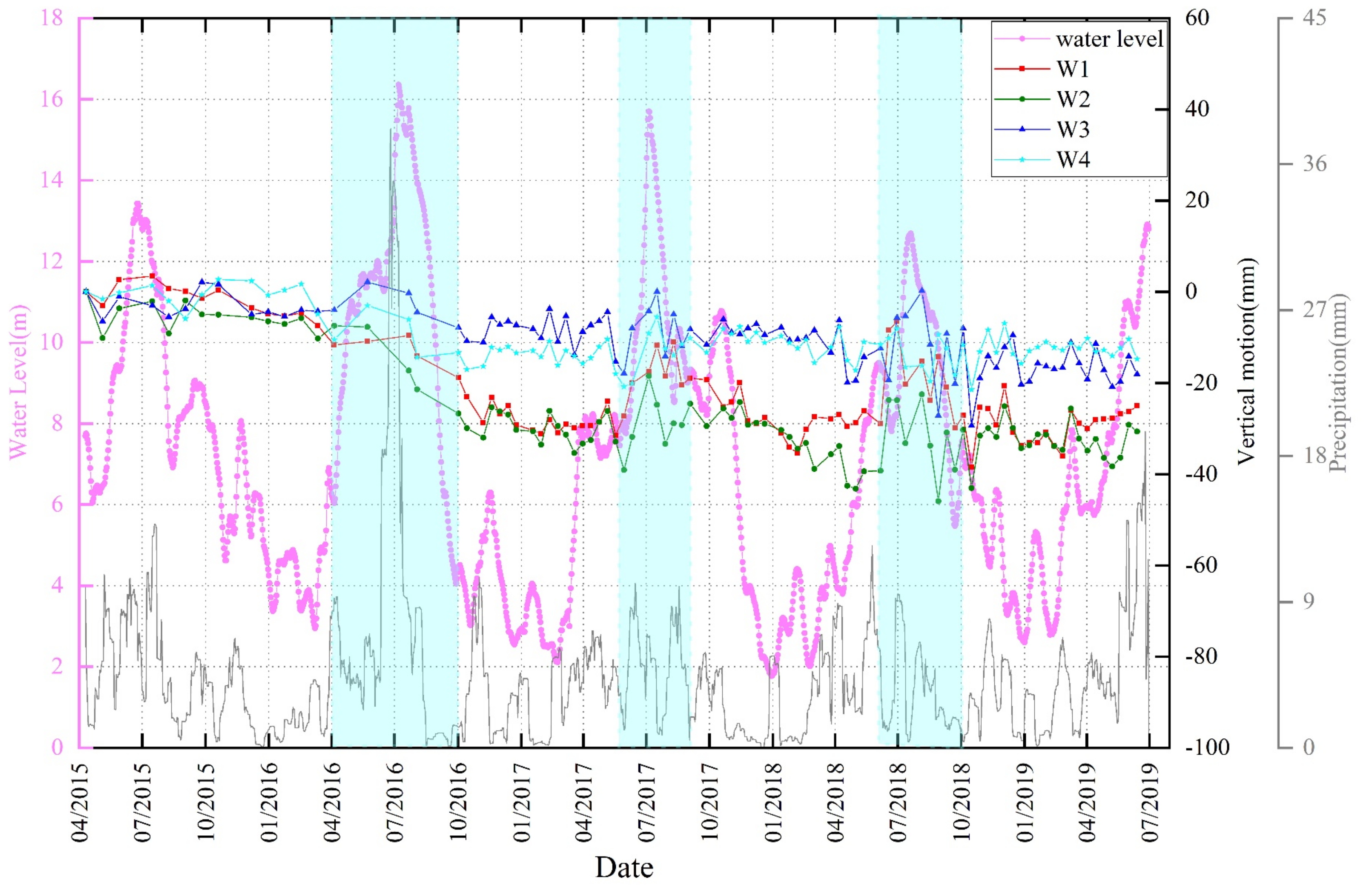
5.3. Correlation between Land Subsidence and Yangtze River Water Level
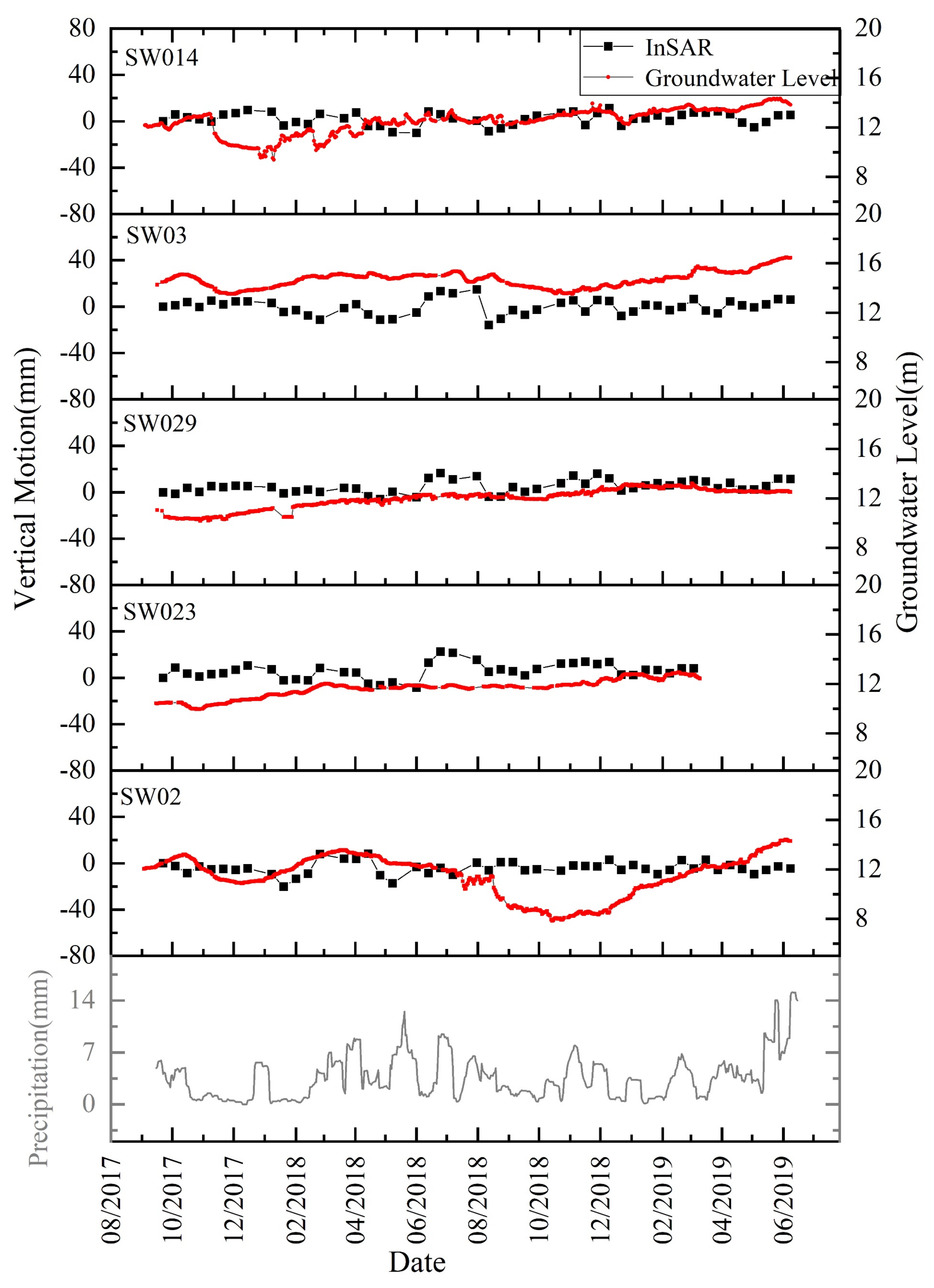
5.4. Correlation between Land Subsidence and Groundwater Levels
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Pei, S.; Jiao, J. Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou City, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Land subsidence and ground fissures in Xi’an, China 2005–2012 revealed by multi-band InSAR time-series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conacher, A.; Conacher, J.; Dragovich, D.; Maude, A. Rural Land Degradation in Australia; Oxford University Press: Melbourne, AUS, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, F.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bawden, G.W.; Kim, J.-W.; Zhao, C.; Qu, W. Mapping ground deformation over Houston–Galveston, Texas using multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, M.H.; Motagh, M. Ground surface response to continuous compaction of aquifer system in Tehran, Iran: Results from a long-term multi-sensor InSAR analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G. Mechanism Study and Hazard Assessment of Cover Karst Sinkholes in Wuhan City. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; He, Z.Z.; Yan, G.H.; Han, F.Y. Foundation pit dewatering and ground subsidence in binary structural stratum of Wuhan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 639, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. Research of features related to land subsidence and ground fissure disasters in the Beijing Plain. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, S.; Tang, H.; Peng, J. A GIS-based monitoring and early warning system for cover-collapse sinkholes in karst terrane in Wuhan, China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Gu, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, W. Characterization of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in the plain of Beijing city, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zheng, F.; Bai, J.; Wang, Y. Feasibility of land surface deformation monitoring by regional CORS. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2011, 28, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Fielding, E.; Patrick, M.R.; Trautwein, C.M. Estimating lava volume by precision combination of multiple baseline spaceborne and airborne interferometric synthetic aperture radar: The 1997 eruption of Okmok volcano, Alaska. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Galve, J.P.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Azañón, J.M.; Closson, D.; Caló, F.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Jabaloy, A.; Ruano, P.; Mateos, R.M.; Notti, D.; et al. Evaluation of the SBAS InSAR service of the European space Agency’s Geohazard Exploitation Platform (GEP). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, P.; Nikkhoo, M.; Samsonov, S.V.; Milillo, P.; Gil-Cruz, F.; Lazo, J. Source model for the Copahue volcano magma plumbing system constrained by InSAR surface deformation observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 5729–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, G.; Milillo, P.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Evaluation of InSAR monitoring data for post-tunnelling settlement damage assessment. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, G.; Magen, Y.; Nof, R.; Raz, E.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Shalev, E. InSAR measurements and viscoelastic modeling of sinkhole precursory subsidence: Implications for sinkhole formation, early warning, and sediment properties. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farolfi, G.; Del Soldato, M.; Bianchini, S.; Casagli, N. A procedure to use GNSS data to calibrate satellite PSI data for the study of subsidence: An example from the north-western Adriatic coast (Italy). Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Monitoring landslides and tectonic motions with the Permanent Scatterers Technique. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ma, P.; Wang, W. Urban infrastructure health monitoring with space multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 10, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 7, pp. 4362–4364. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Land subsidence in Taiyuan, China, monitored by InSAR technique with multisensor SAR datasets from 1992 to 2015. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer InSAR for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Kaufmann, J. Evolution of sinkholes over Wink, Texas, observed by high-resolution optical and SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-pass SAR interferometry with partially coherent targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Bai, J.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, F.; Vecchioli, F.; Wang, R.; Hu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, J. Ground deformations and building stability monitoring by COSMO-SkyMed PSP SAR interferometry: Results and validation with field measurements and surveys. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 6847–6850. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift (2009–2010) over wuhan in central china revealed by terrasar-X insar analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, M. Wuhan surface subsidence analysis in 2015–2016 based on sentinel-1a data by SBAS-inSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y. Monitoring land subsidence in Wuhan city (China) using the SBAS-InSAR method with radarsat-2 imagery data. Sensors 2019, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Perissin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. L-and X-band multi-temporal InSAR analysis of Tianjin subsidence. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7933–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to InSAR time series. JOSA A 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Lu, Z.; Kim, J.-W.; Zheng, W. Identify and monitor growth faulting using InSAR over northern Greater Houston, Texas, USA. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Peltzer, G.; Simons, M. Updated repeat orbit interferometry package released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2004, 85, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M.; Hanssen, R.F.; Perski, Z. Radar interferometry with public domain tools. In Proceedings of the FRINGE, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wegnüller, U.; Werner, C.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A.; Frey, O.; Santoro, M. Sentinel-1 support in the GAMMA software. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Zhu, Q.; Horgan, F.G.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment for tailings dams in Brumadinho of Brazil using InSAR time series approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plan on Prevention and Control of Geologic Disasters in Wuhan City. Wuhan Natural Resources and Planning Bureau. 2018. Available online: http://gtghj.wuhan.gov.cn/showjyh.asp?id=147594 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wei, R.; Yang, G.; Liu, C.; Jin, X.; Li, H. Analysis on spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of karst collapse and its influence factors in Wuhan City of Hubei Province. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2019, 30, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chunwu, R.; Guangzheng, L. CCTV Focus on the Settlement of the Building in Houhu of Wuhan. Available online: http://hb.ifeng.com/news/focus/detail_2013_10/14/1325441_0.shtml (accessed on 14 October 2013).
- Lambe, T.W.; Whitman, R.V. Soil Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.J. Consolidation and Settlement Analysis. In The Civil Engineering Handbook; CRC press: Boca Raton, USA, 2003; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.E. The progress of consolidation in a clay layer increasing in thickness with time. Geotechnique 1958, 8, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Feng, X.; Li, T.; Liang, M. Research on groundwater level variation and ground subsidence caused by foundation pit dewatering at the Wuhan first terrace. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2018, 45, 90–95. [Google Scholar]


| Study | Method | Dataset | Key Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bai et al. (2016) | SBAS-InSAR | 12 TerraSAR images (200910–201004) | (1) Cross-validation between InSAR and water level records of the Yangtze River. (2) Intensive municipal construction and industrial production are the main factors to land subsidence. (3) The subsidence areas associated with carbonate karst geology. |
| Xu (2016) | The fuzzy closeness degree and analytic hierarchy process | Geophysical survey, Well, Drilling (2009, 2014, 2015) | (1) The distribution of sinkhole in Wuhan. (2) The main factors of the sinkhole in Wuhan are natural factors and anthropogenic influence. |
| Costantini et al. (2016) | InSAR PSP approach | 45 Cosmo-SkyMed images (201306–201406) | (1) The standard deviation of the differences between the leveling and InSAR measurements is about 5 mm. (2) The average velocity of urban area from −80 mm/a to 40 mm/a. |
| Zhou et al. (2017) | SBAS-InSAR | 15 Sentinel-1 Images (201504–201604) | (1) The maximum subsidence has shifted from Wuguang to Houhu area. |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | SBAS-InSAR | 20 Radarsat-2 images (201510–201806) | (1) SBAS-based results conclude urban construction is a driving factor causing subsidence. |
| Sensor | ALOS-1 | Sentinel-1 | Envisat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band | L | C | C |
| Heading | −12.7 | −12.7 | −11.7 |
| Incidence angle | 38.75 | 39.25 | 22.8 |
| Track | 455 | 113 | 483 |
| Wavelength | 23.6 cm | 5.55 cm | 5.66 cm |
| Polarization | HH, HV | VV, VH | VV |
| Number of Scenes | 19 | 104 | 3 |
| Time range (yyyy-mm-dd) | 20070115–20101026 | 20150411–20190625 | 20081221, 20090125, 20100530 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Zou, J.; Lu, Z.; Qu, F.; Kang, Y.; Li, J. Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223788
Han Y, Zou J, Lu Z, Qu F, Kang Y, Li J. Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223788
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yakun, Jingui Zou, Zhong Lu, Feifei Qu, Ya Kang, and Jiangwei Li. 2020. "Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223788
APA StyleHan, Y., Zou, J., Lu, Z., Qu, F., Kang, Y., & Li, J. (2020). Ground Deformation of Wuhan, China, Revealed by Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223788