Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
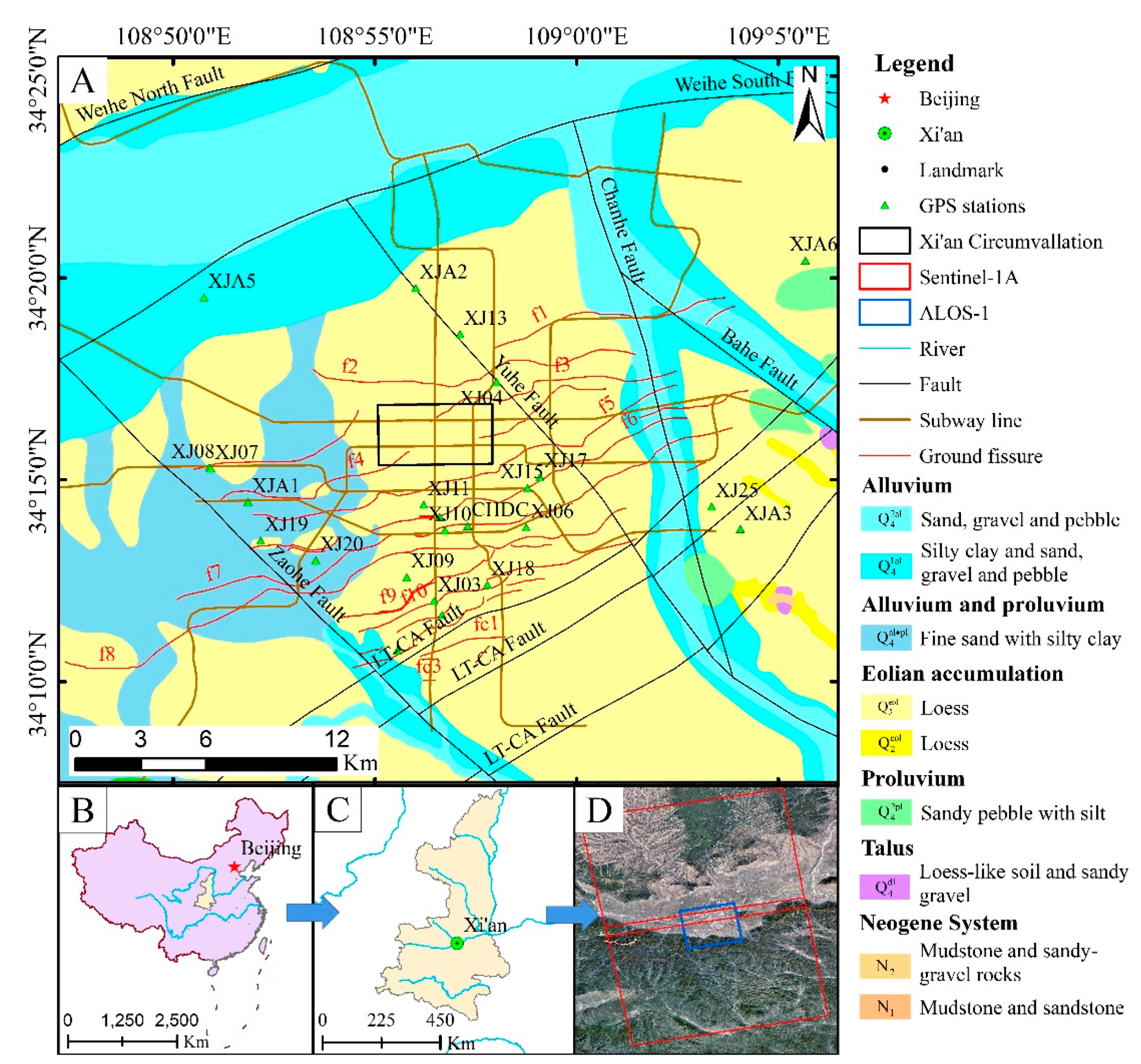
2. Study Area
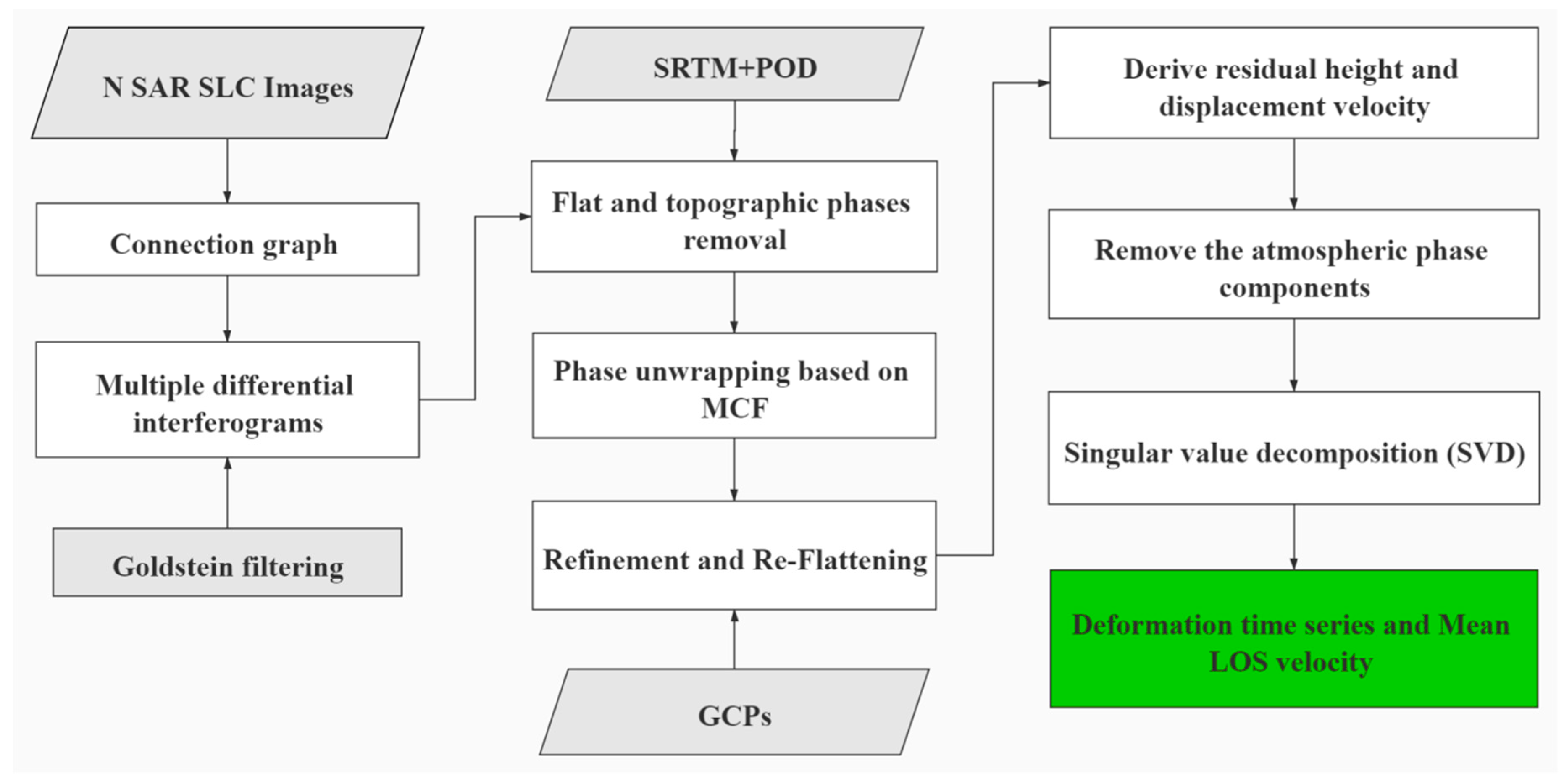
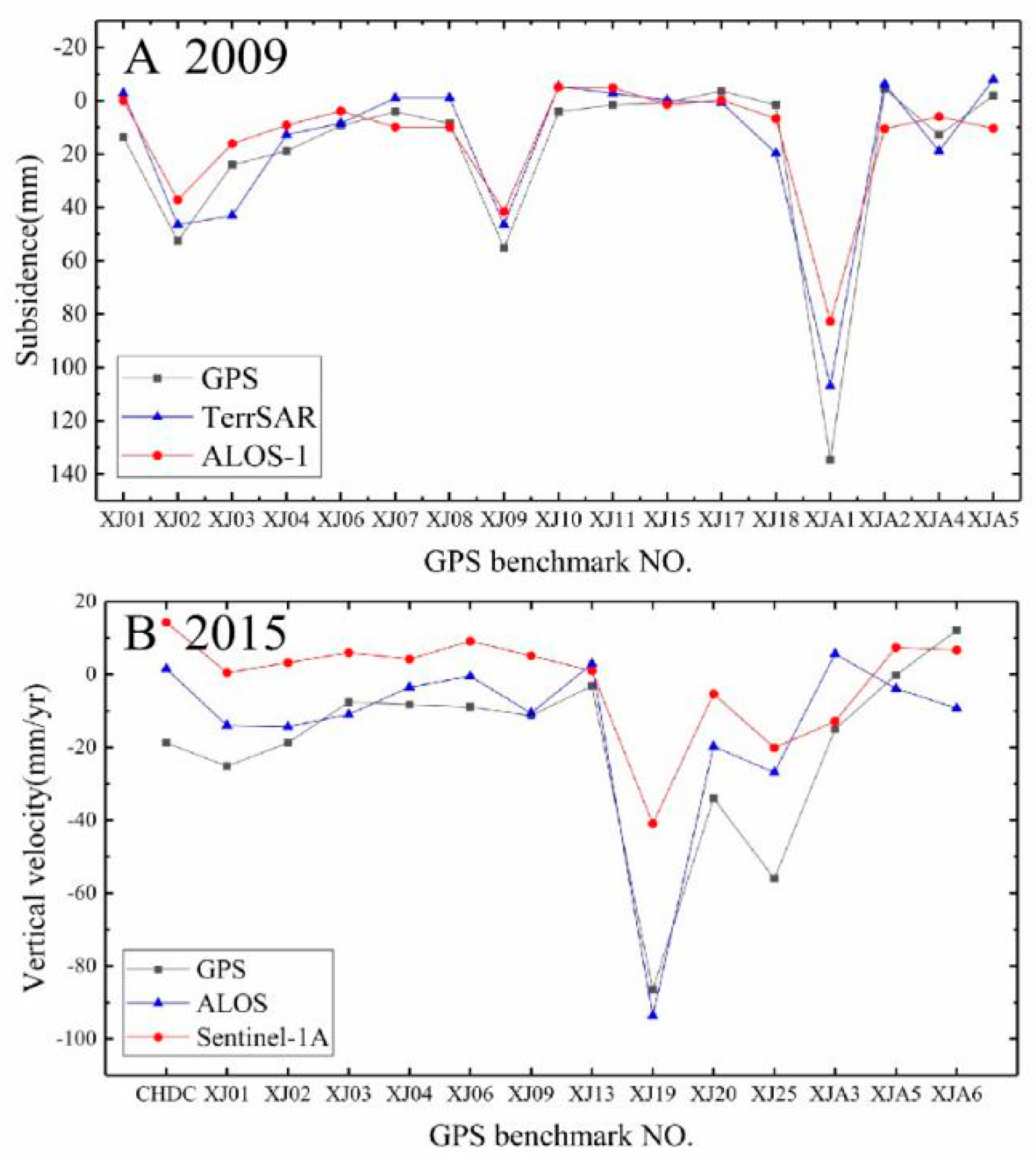
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
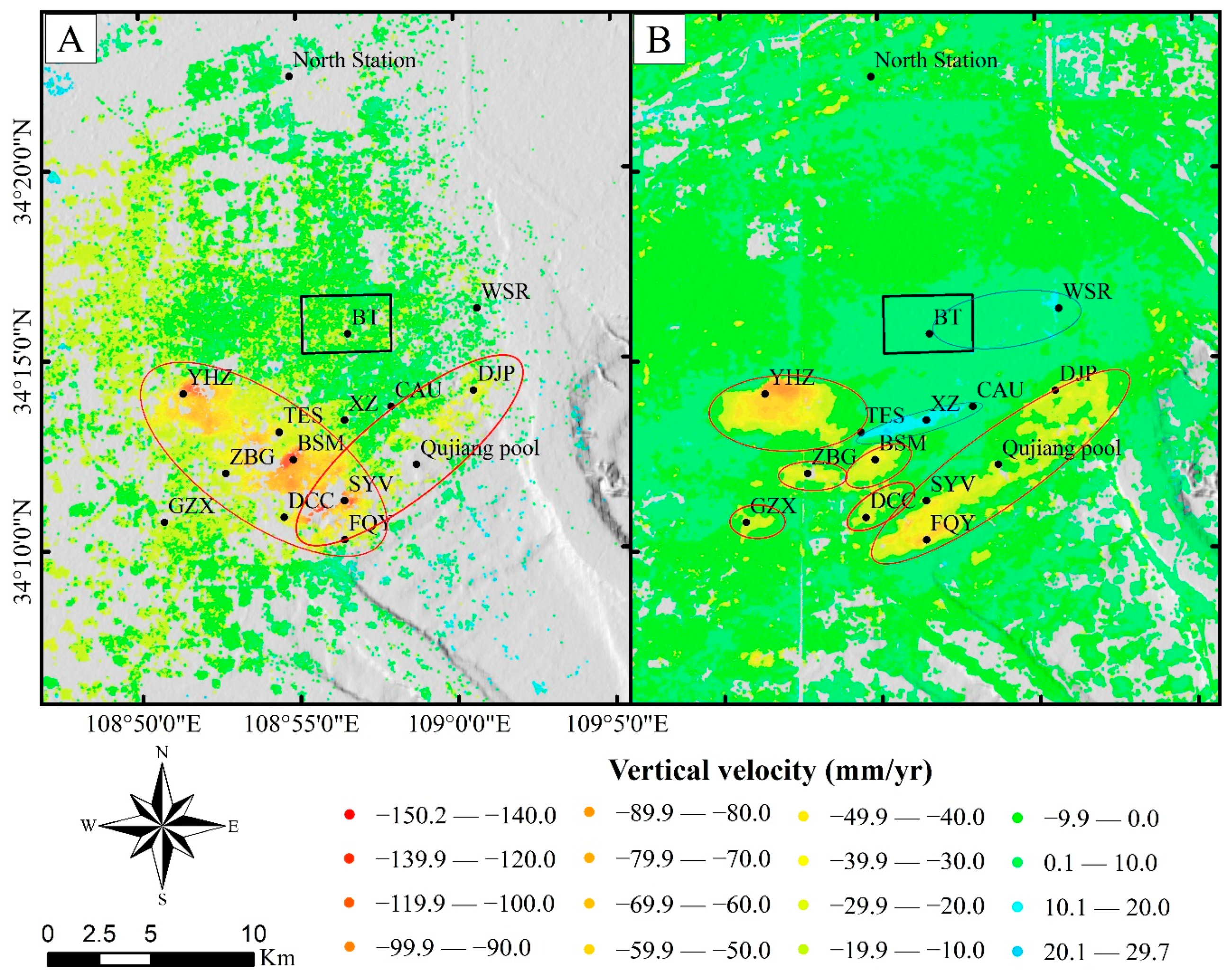
4.1. Spatial-Temporal Pattern of Land Subsidence from 2007–2019
4.2. Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound from 2007–2019
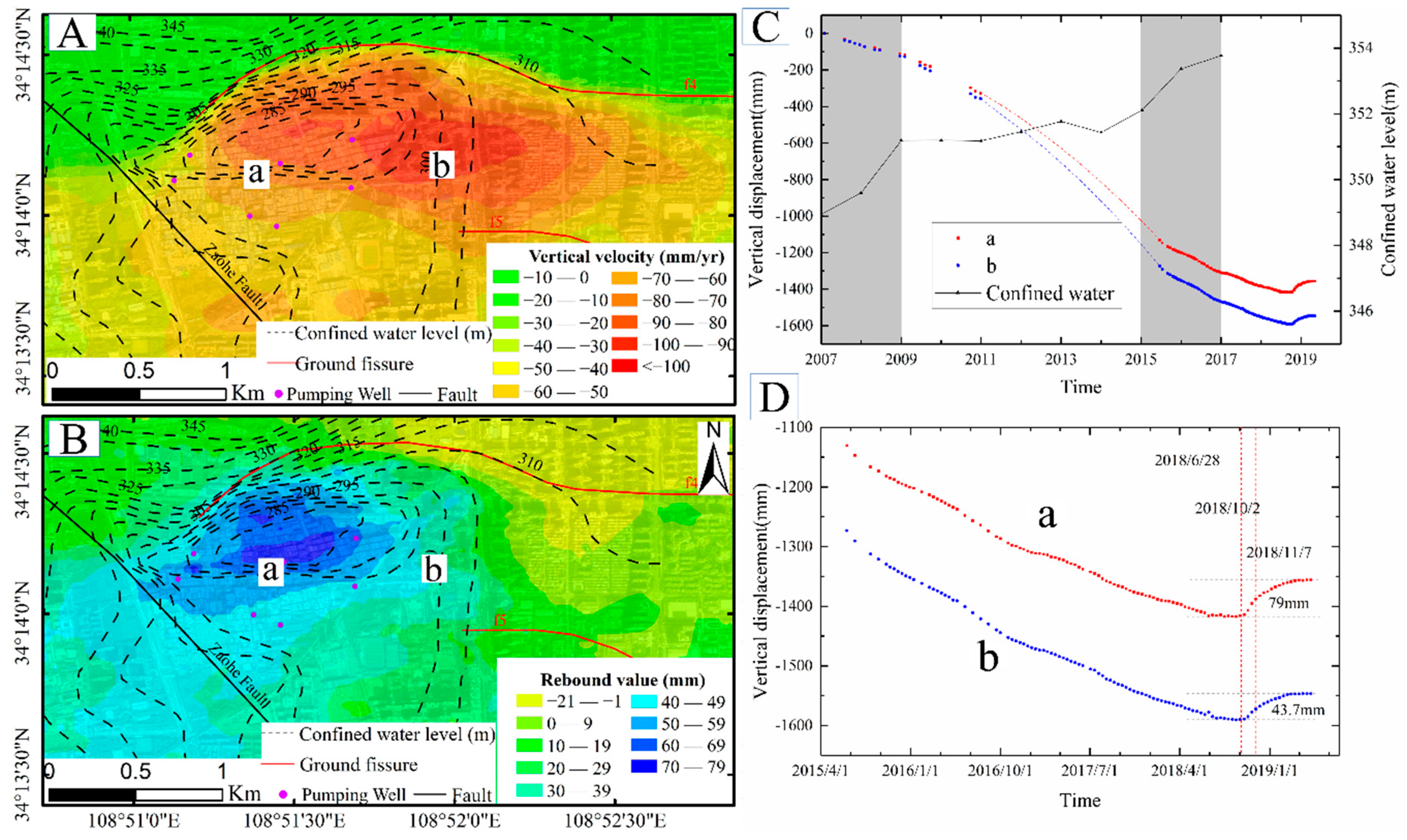
4.2.1. Land Subsidence in YHZ District
4.2.2. Land Subsidence in Beishanmen District
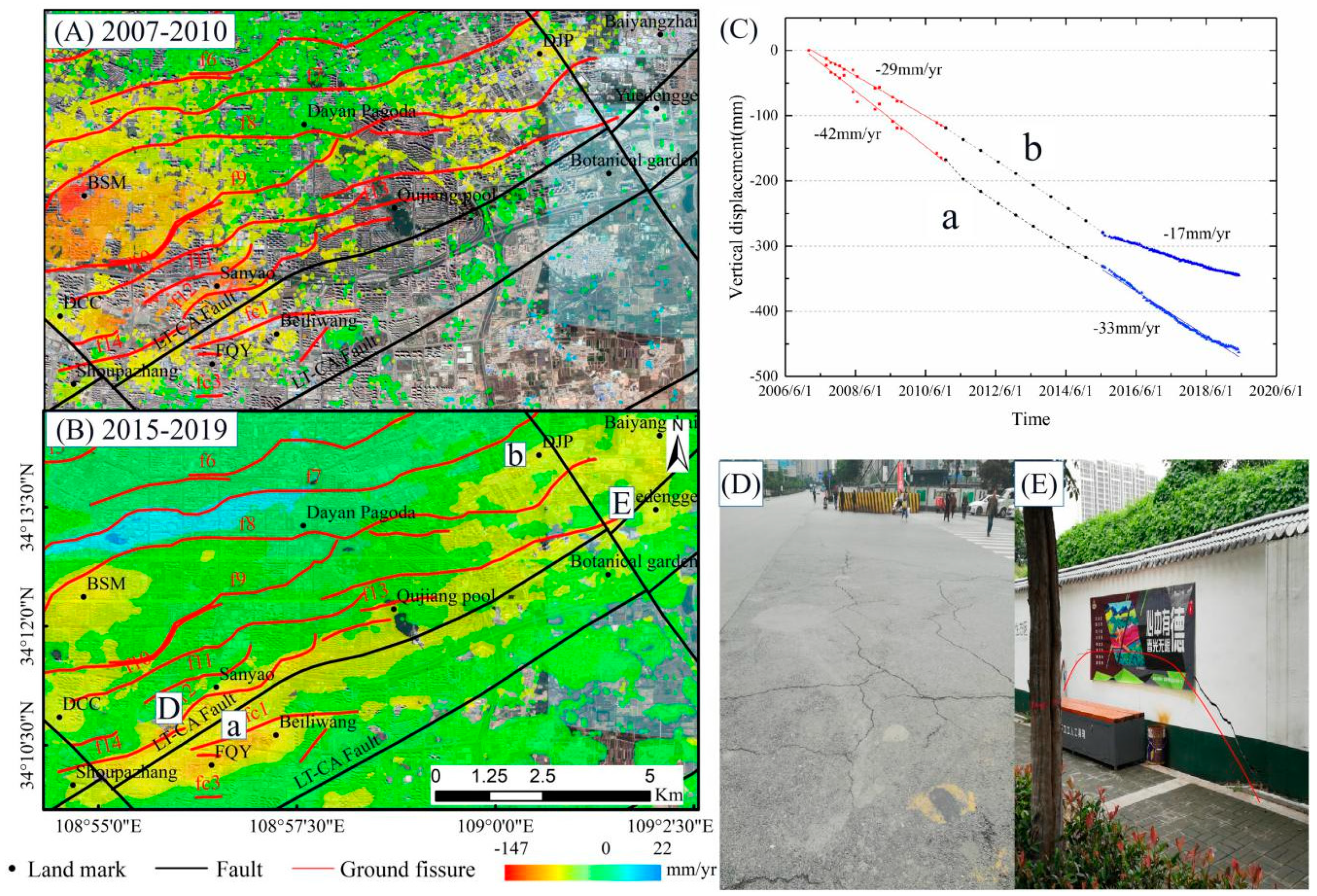
4.2.3. Land Subsidence in Fengqiyuan-Dengjiapo District
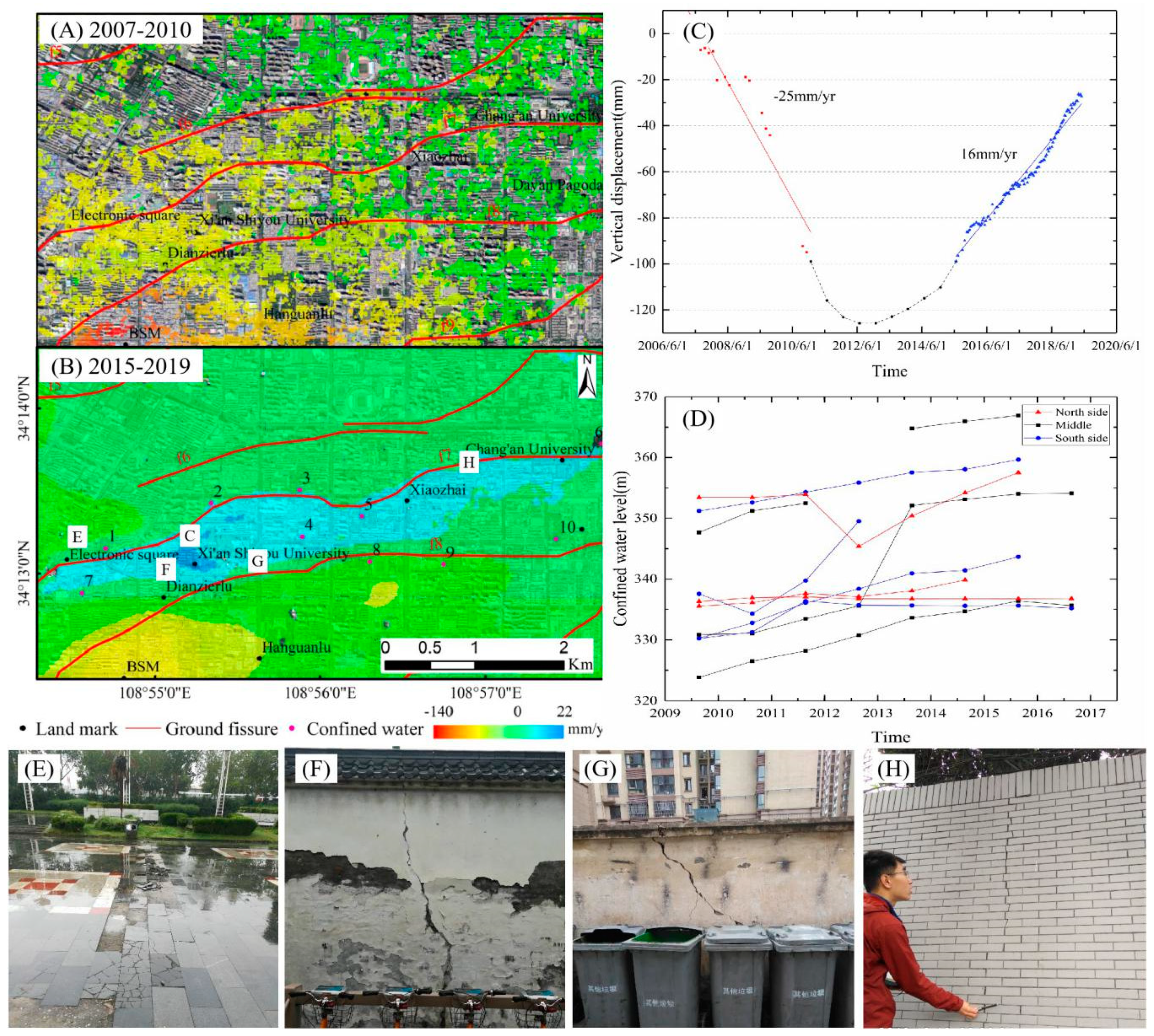
4.2.4. Land Rebound in The Electronic Square–Chang’an University District
5. Discussion
5.1. Driving Mechanism Analysis for Land Subsidence and Rebound Deformation
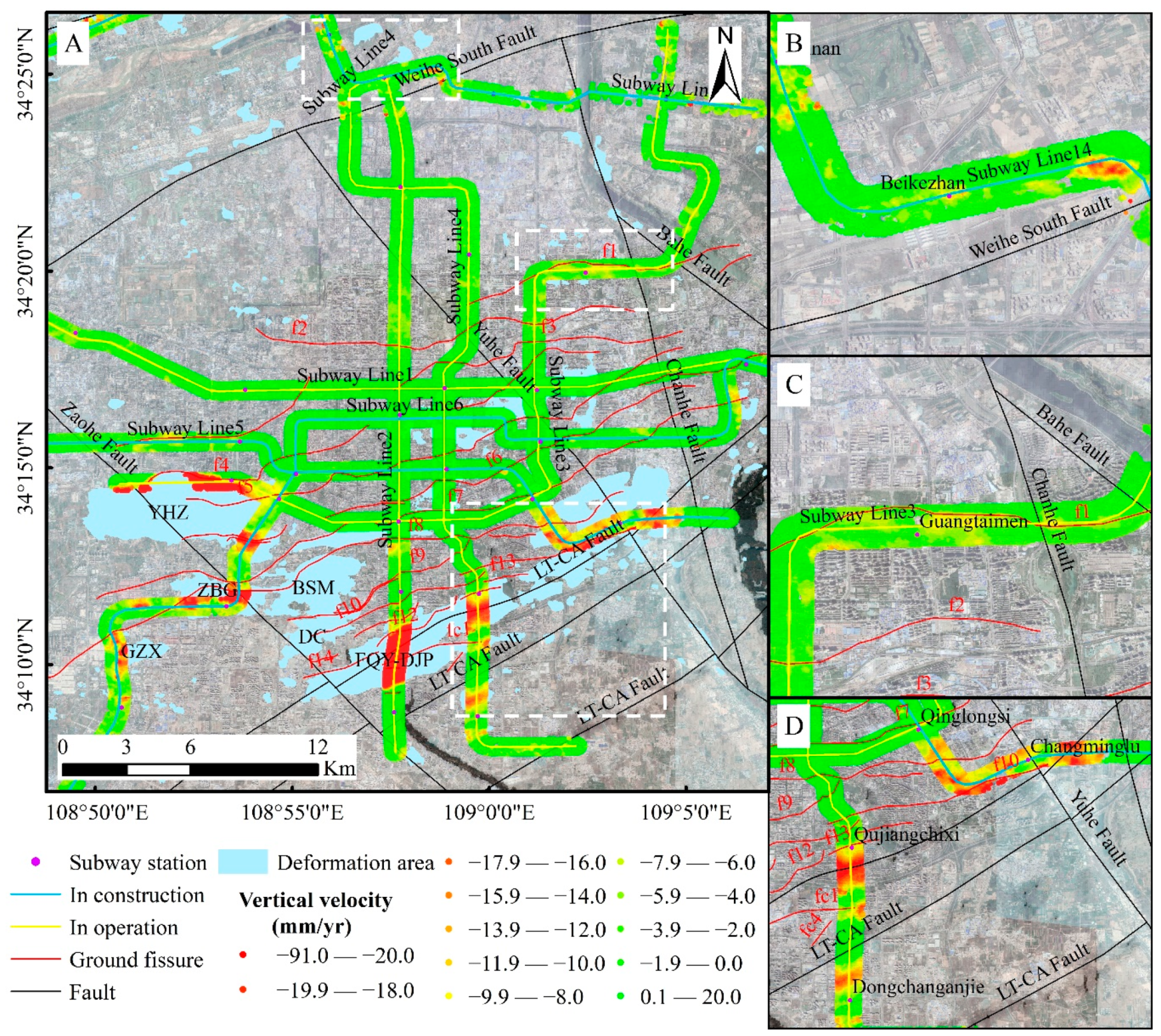
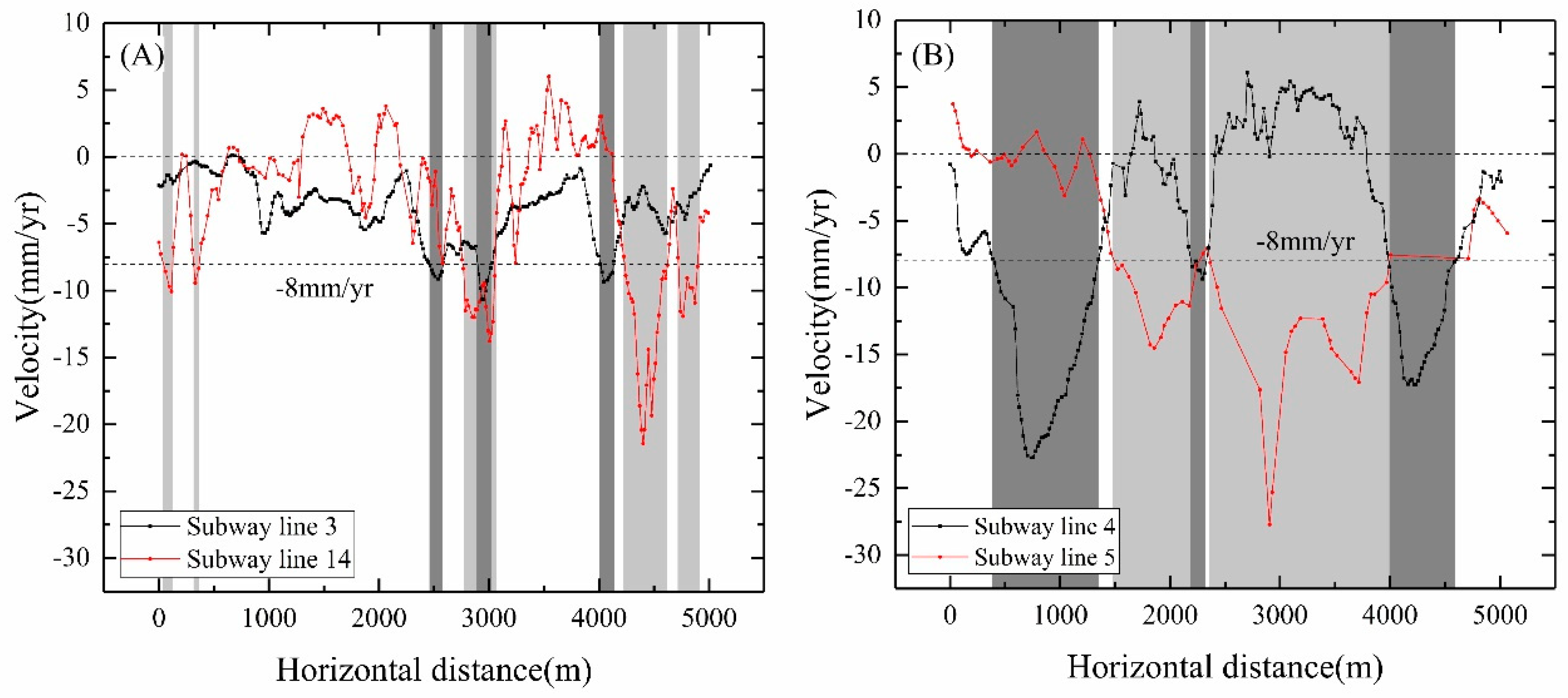
5.2. Analysis of Land Subsidence Along the Subway Line
5.3. Analysis of Land Subsidence and Rebound Trend
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Q. Land subsidence in China. Environ. Geol. 2005, 48, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, S.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, G. The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater with drawal in China. Nat. Hazards 2008, 45, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Lei, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Gao, M.; Guan, H.; Lv, W. Land subsidence lagging quantification in the main exploration aquifer layers in Beijing plain, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, A.; Abotalib, A.Z. Inferencing the land subsidence in the Nile Delta using Sentinel-1 satellites and GPS between 2015 and 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Zheng, Z. Analysis and prediction of ground fractures and surface subsidence hazard in Xi’an city using projection tracing. J. Eng. Geol. 1999, 7, 30–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Suo, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z. Land fracture and subsidence prevention in Xi’an. Quat. Sci. 2005, 25, 23–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, M. Sequential InSAR Time Series Deformation Monitoring of Land Subsidence and Rebound in Xi’an, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z. Research on spatial-temporal land deformation (2012–2018) over Xi’an, China, with Multi-Sensor SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, G. Characteristics of land subsidence, earth fissures and related disaster chain effects with respect to urban hazards in Xi’an, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, H.S.; Min, K.D.; Won, J.S. Satellite observation of coal mining subsidence by persistent scatter analysis. Eng. Geol. 2007, 92, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nolinear Subsidence Rate Estimation Using Permanent Scatterers in Differential SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Ruiz, A.M.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bastos, L.; Gil, A.J.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; Sanz de Galdeano, C. PS-InSAR processing methodologies in the detection of field surface deformation Study of the Granada basin (Central Betic Cordilleras, southern Spain). J. Geodyn. 2010, 49, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Solari, L.; Soldato, M.D.; Casagli, N. From picture to movie: Twenty years of ground deformation recording over tuscany region (Italy) with satellite insar. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Meng, X.; Wasowski, J.; Dijkstra, T.; Bovenga, F.; Xue, Y.; Wang, S. Ground instability detection using PS-InSAR in Lanzhou, China. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2014, 47, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, G. Detection of geohazards in the Bailong River Basin using synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Landslides 2016, 13, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Wen, D. Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.H. Sinking cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR detects rapid subsidence due to groundwater and gas extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z.; Yang, C.; Qi, X. Monitoring of land subsidence and ground fissures in Xian, China 2005-2006:mapped by SAR interferometry. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. Inferring Multi-dimensional Deformation Filed in Xi’an by Combining InSAR of Ascending and Descending Orbits with GPS Data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Land subsidence and ground fissures in Xi’an, China 2005-2012 revealed by multi-band InSAR time-series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ge, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D. Research on development characteristics and failure mechanism of land subsidence and ground fissure in Xi’an, monitored by using time-series SAR interferometry. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Q. Prediction of land subsidence and Its mitigation methods—A case study in the new urban district of Xi’an-Xianyang. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2013, 23, 115–118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, W. Computed Subsidence by Dislocation Model in Xi’an City. Northwestern Seismol. J. 2008, 30, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Teng, H. Numerical simulation and layerwise mark monitoring of land subsidence and ground fissures of typical section in Xi’an. Rock Soil Mech. 2014, 35, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Qu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, L.; Li, J. Influennce of groundwater exploitation on the land subsidence of Xi’an hightech zone. Prog. Geophys. 2018, 33, 1232–1238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Water Release Compaction Effect and Microstructure Change of Aquifer System in Xi’an. Northwestern Geol. 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yue, C.; Shi, J. Lowering of groundwater level and its negative environment effects in the area of Xi’an. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2005, 40, 100–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Su, S. Fractal Dimensions of Active Faults and Geologic Hazards in Weihe Basin. J. Northwest Univ. 1993, 23, 555–561. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colm, J.; Luke, B.; Alessandro, N. Environmental baseline monitoring for shale-gas development: Insights for monitoring ground motion using InSAR analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Bateson, L.B.; Jordan, C.J.; Dashwood, C. Simulating SAR geometric distortions and predicting Persistent Scatter densities for ERS-1/2 and ENVISAT C-band SAR and InSAR applications: Nationwide feasibility assessment to monitor the landmass of Great Britain with SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Agostini, A.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. A Procedure to Map Subsidence at the Regional Scale Using the Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) Technique. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10510–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Osmanoglu, B.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Dixon, T.H.; Avila-Olivera, J.A.; Garduno-Monroy, V.H.; DeMets, C.; Wdowinski, S. Monitoring land subsidence and its induced geological hazard with Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A case study in Morelia, Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, F.; Meng, X. Detetion of Land Subsidence Associated with Land Creation and Rapid Urbanization in the Chinese Loess Plateau Using Time Series InSAR: A Case Study of Lanzhou New District. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Q. Da preliminary study of Land Subsidence in the F4 Ground Fissure, Yuhuazhai area, Xi’an, China. J. Geol. Hazard Environ. Preserv. 2017, 28, 31–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaanxi Government Procurement Network. Available online: http://www.ccgp-shaanxi.gov.cn/noticeDetail.do?noticeguid=8a85be33667756bc0166806259b553c6 (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Xi’an Water Resources Center. Available online: https://www.meipian.cn/1yyjlr93 (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through cosmo-skymed persistent scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Hou, J.; Liang, J. Long-Term Land Subsidence Monitoring of Beijing (China) Using the Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) Technique. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3648–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving Spatio-Tmporal Development of Ground Subsidence Due to Subway Construction and Operation in Delta Regions with PS-InSAR Data: A Case Study in Guangzhou, Chins. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Fang, W.; Song, L.; Wang, F.; Zhu, X.; Jing, B.; Dong, X.; Zuo, Y. Analysis of the relationship among Geothermal water exploitation, Ground Subsidence and Ground Fissures in Xi’an city, China. Seismol. Geol. 2002, 24, 234–240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




| Parameters | ALOS-1 | Sentinel-1A |
|---|---|---|
| Band | L | C |
| Wavelength (cm) | 23.5 | 5.63 |
| Incidence angle (°) | 38.7 | 33.8 |
| Track | 464 | 84 |
| Polarization | VV | VV |
| Number of images used | 16 | 186 |
| Orbit Direction | Ascending | Ascending |
| Acquisition time | Jan 2007–Dec 2010 | Oct 2014–May 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, W.; Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W.; Chong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223756
Shi W, Chen G, Meng X, Jiang W, Chong Y, Zhang Y, Dong Y, Zhang M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223756
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Wei, Guan Chen, Xingmin Meng, Wanyu Jiang, Yan Chong, Yi Zhang, Ying Dong, and Maosheng Zhang. 2020. "Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223756
APA StyleShi, W., Chen, G., Meng, X., Jiang, W., Chong, Y., Zhang, Y., Dong, Y., & Zhang, M. (2020). Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Rebound over Xi’an in Western China Revealed by SBAS-InSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223756






