An Improved Multi-Satellite Method for Evaluating Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Offset Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
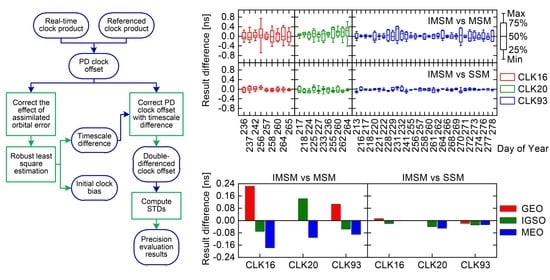
2. Method
2.1. Model of Real-Time BDS Clock Product
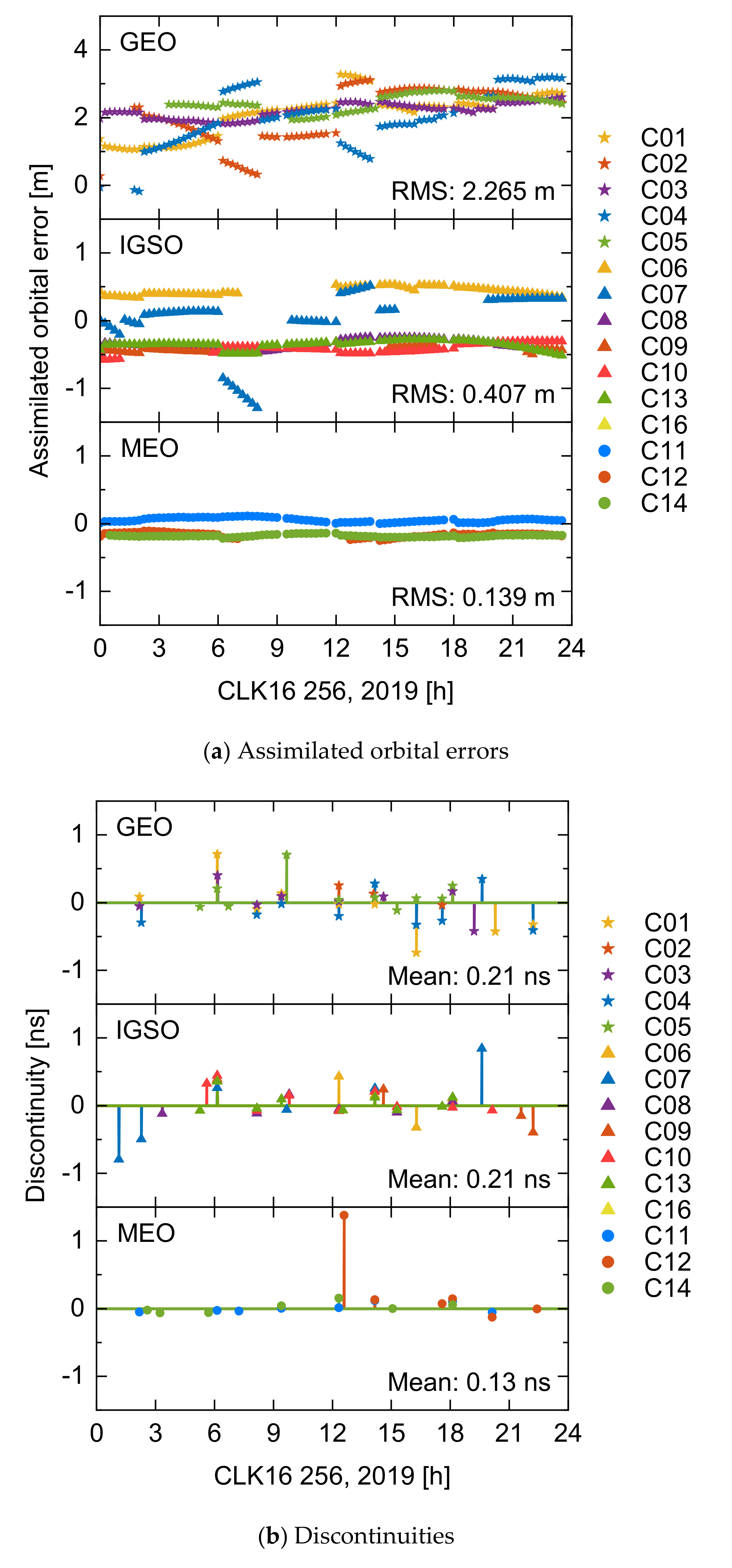
2.2. Effect of the Assimilated Orbital Errors
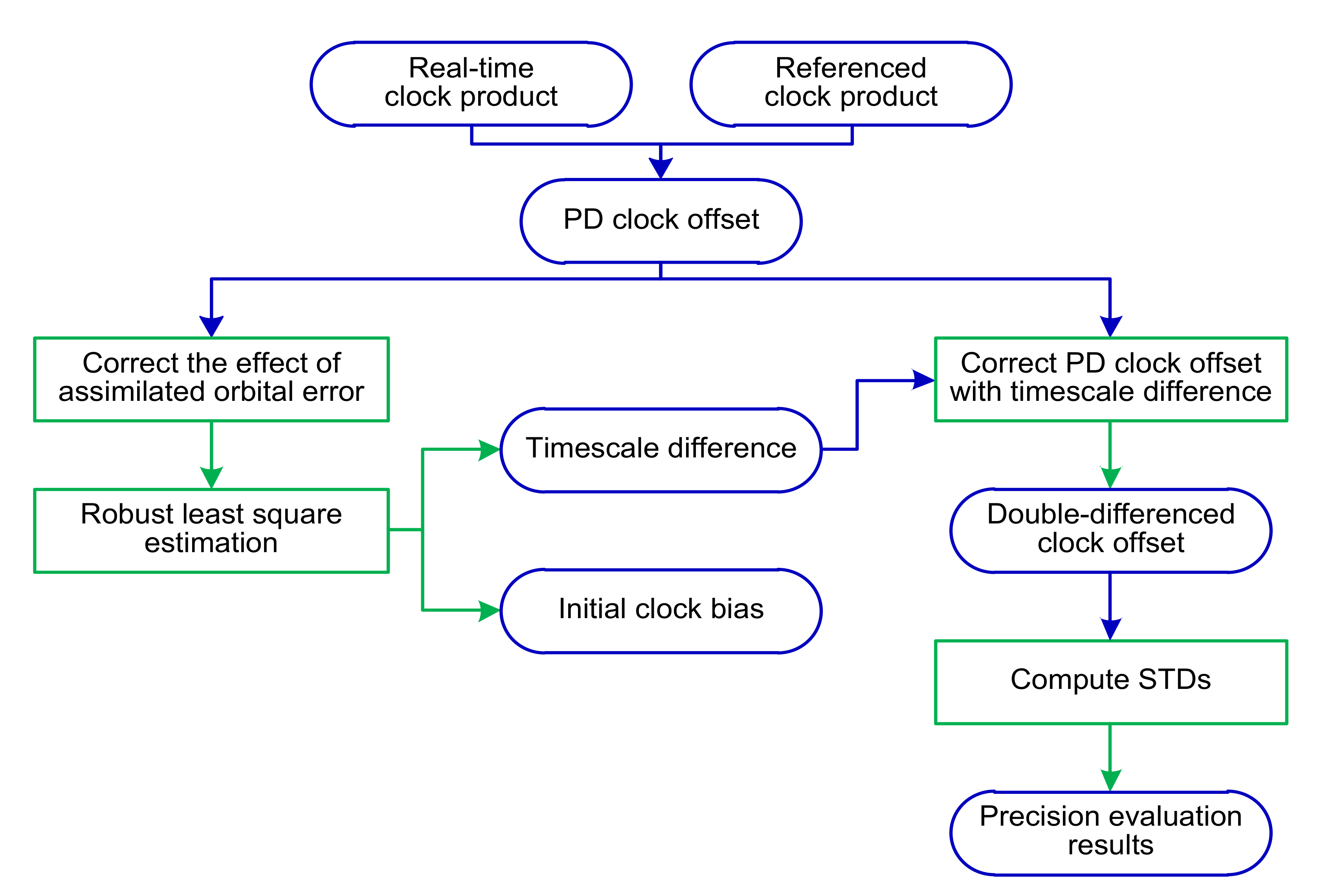
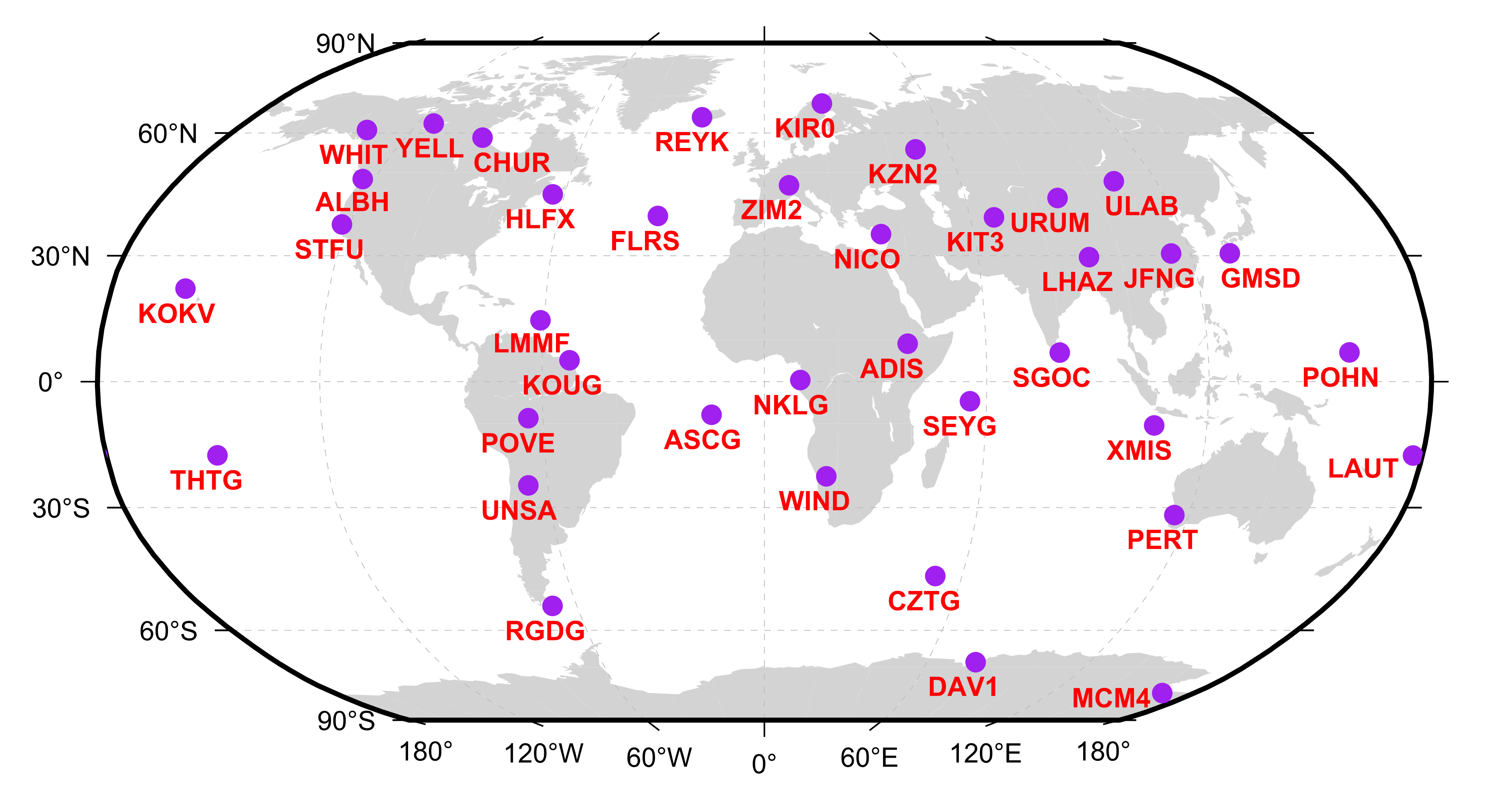
2.3. Precision Evaluation of BDS Real-time Clock Products
3. Results
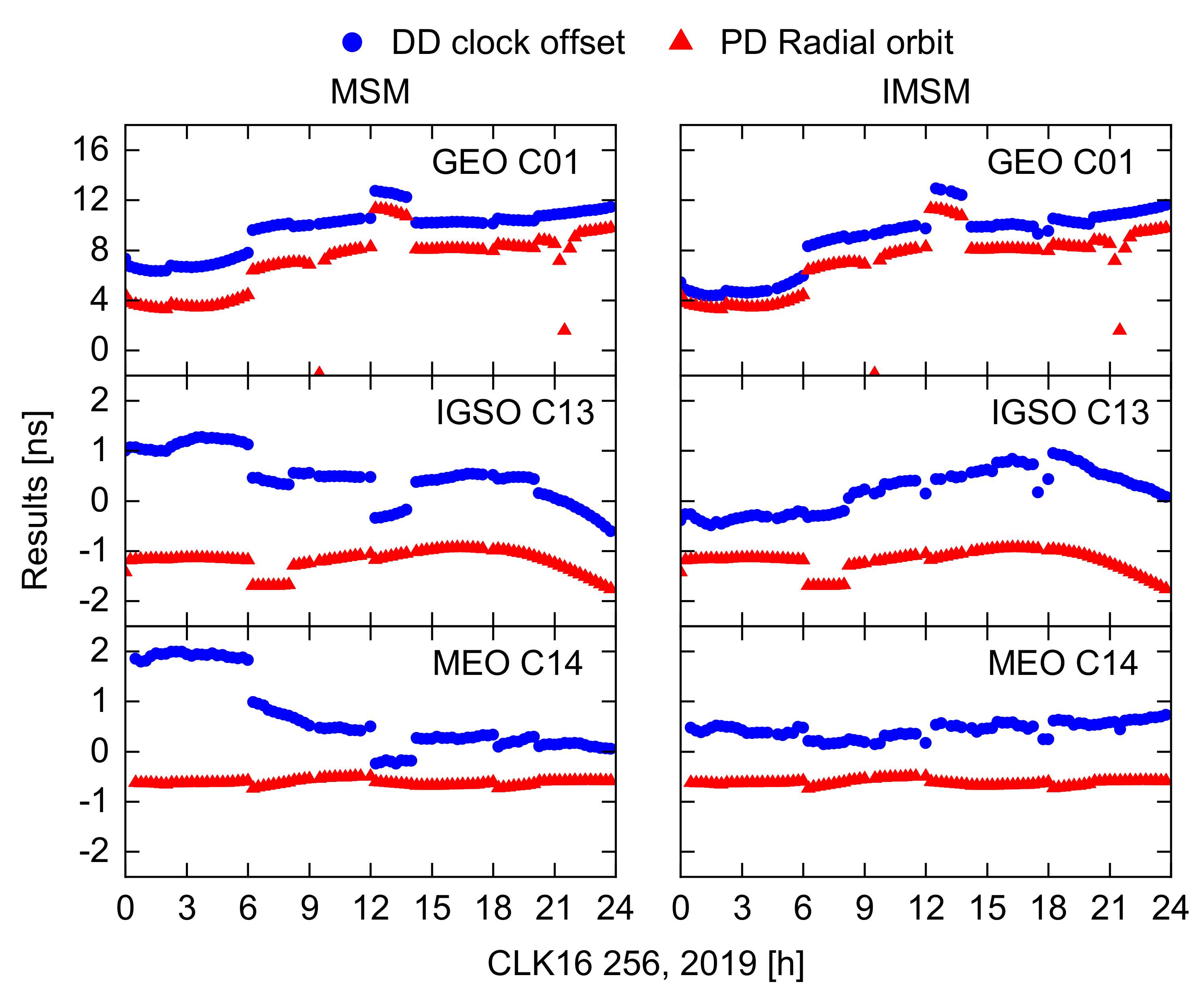
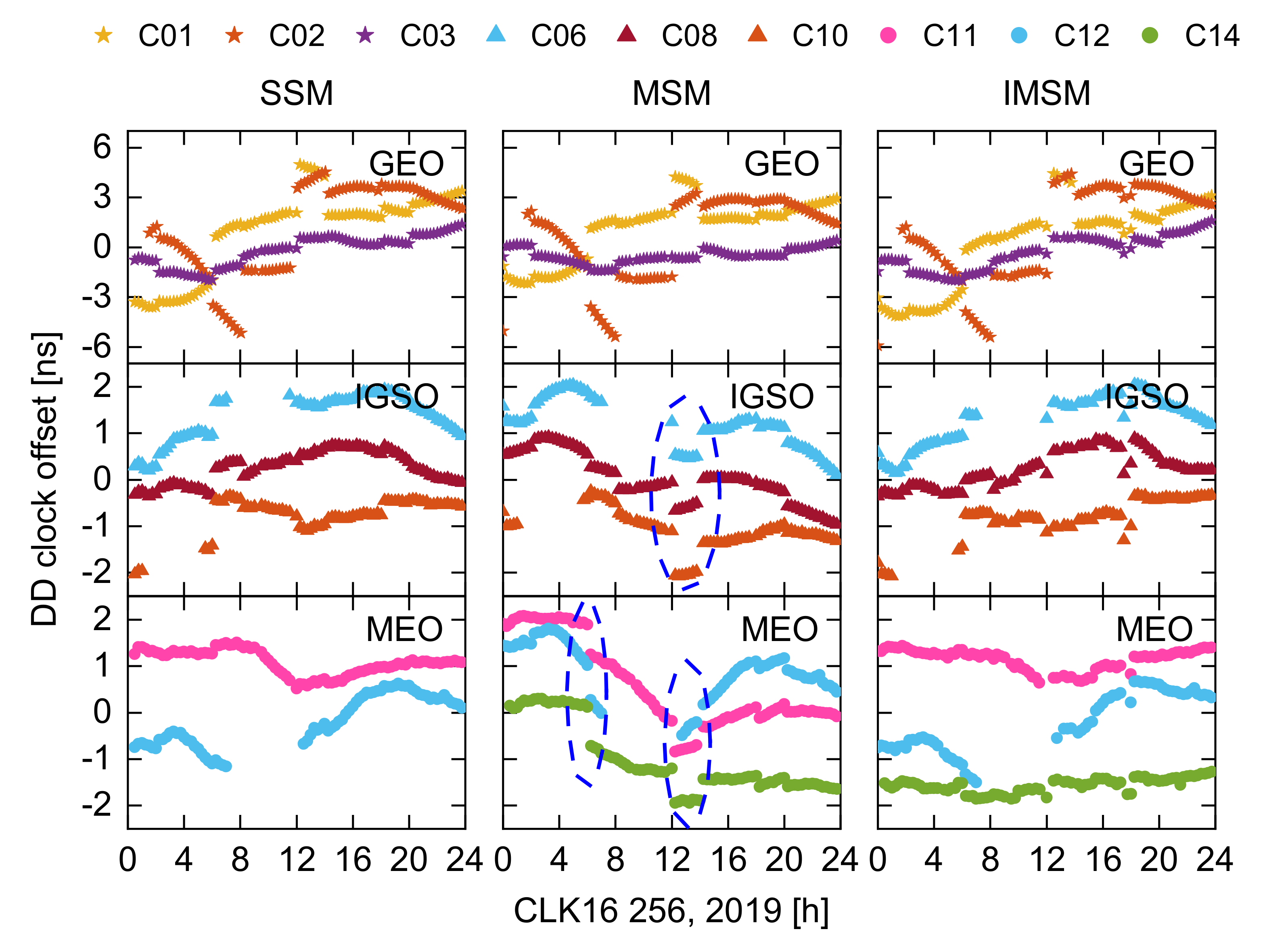
3.1. Effect Analysis of Assimilated Orbital Errors
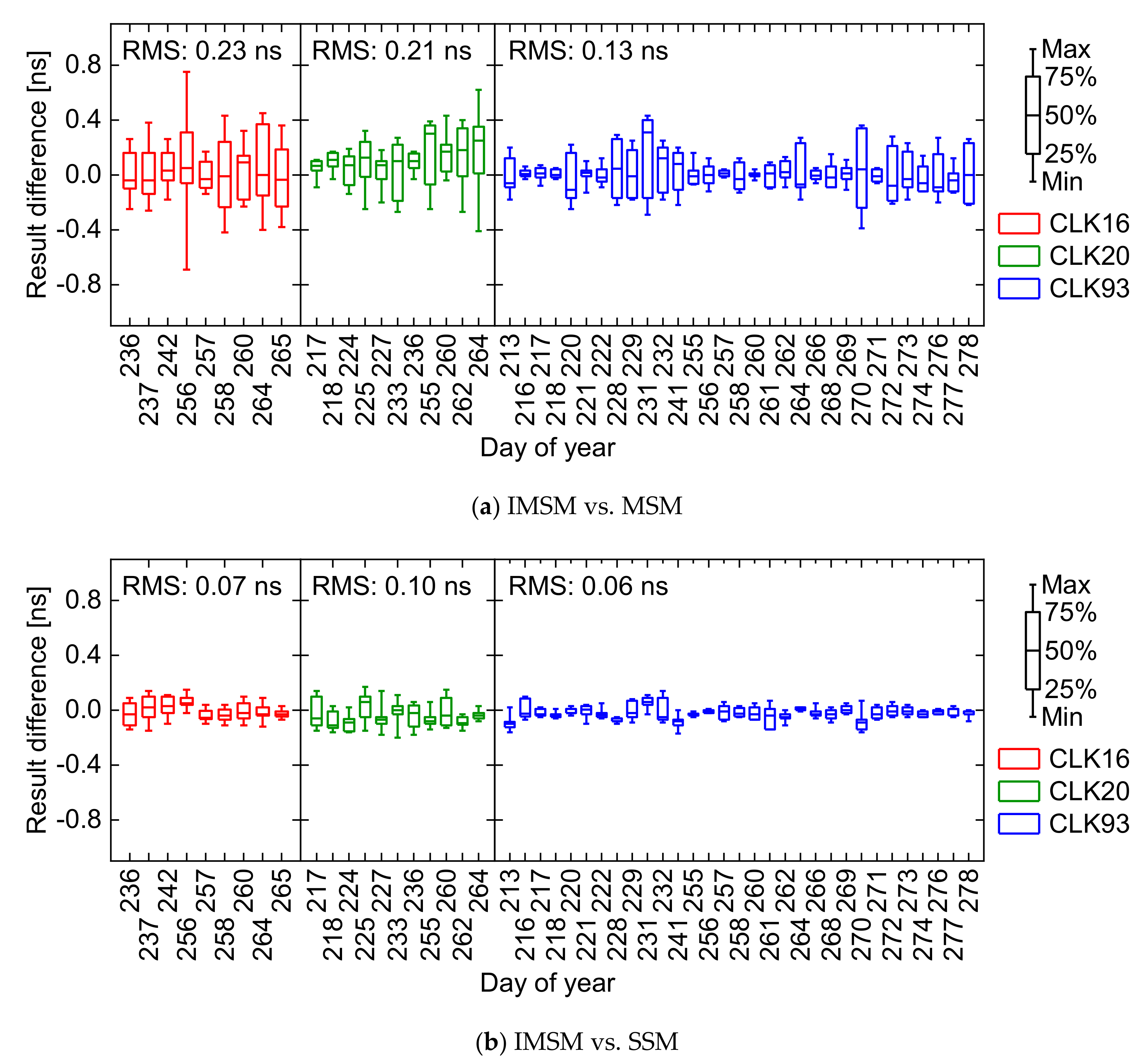
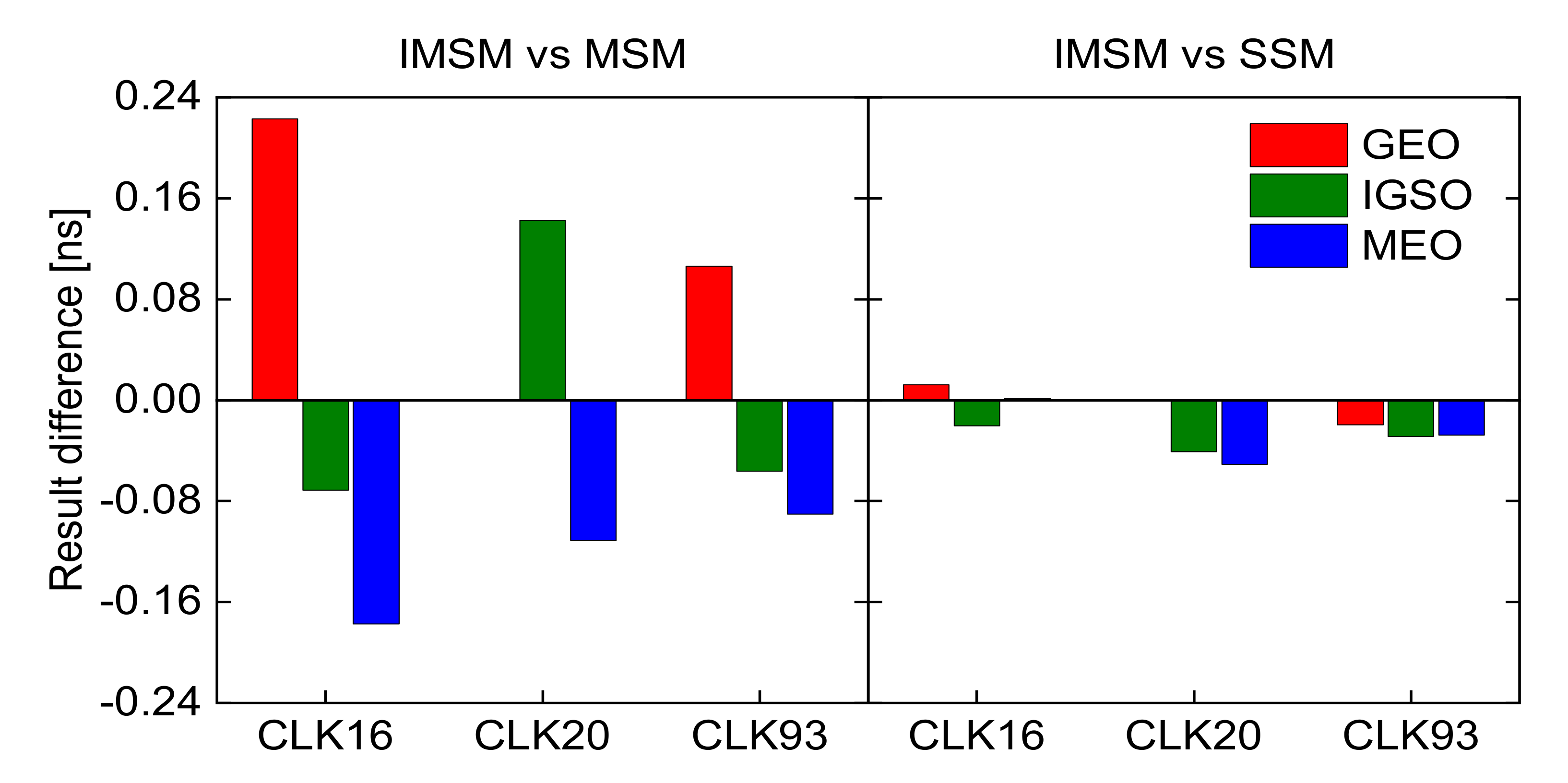
3.2. Comparison of Evaluation Results
3.3. Evaluation of Three Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Products
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdi, N.; Ardalan, A.A.; Karimi, R.; Rezvani, M.-H. Performance assessment of multi-GNSS real-time PPP over Iran. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2870–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Pan, L.; Kuang, K. Performance assessment of uncombined precise point positioning using Multi-GNSS real-time streams: Computational efficiency and RTS interruption. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 3133–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. Investigation of the performance of real-time BDS-only precise point positioning using the IGS real-time service. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L. Implementation and Analysis of Tightly Coupled Global Navigation Satellite System Precise Point Positioning/Inertial Navigation System (GNSS PPP/INS) with Insufficient Satellites for Land Vehicle Navigation. Sensors 2018, 18, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yuan, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, G. GPS real-time precise point positioning for aerial triangulation. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, T.; Qin, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Enhancing real-time precise point positioning time and frequency transfer with receiver clock modeling. GPS Solut. 2018, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, X.; Roberts, G.W.; Hancock, C.M.; De Ligt, H.; Guo, F. 1 Hz GPS satellites clock correction estimations to support high-rate dynamic PPP GPS applied on the Severn suspension bridge for deflection detection. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Yi, W.; Song, W.; Cao, C.; Chen, M. Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock offset products. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Ren, J.; Lou, Y.; Dai, X.; Fang, X. Long-term behavior and statistical characterization of BeiDou signal-in-space errors. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1907–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, H. Validation and Assessment of Multi-GNSS Real-Time Precise Point Positioning in Simulated Kinematic Mode Using IGS Real-Time Service. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. Assessment of Multiple GNSS Real-Time SSR Products from Different Analysis Centers. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F.; Prange, L.; Dach, R.; Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Montenbruck, O. Galileo orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P. Short-term analysis of GNSS clocks. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Bosy, J. IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, A.; Deo, M.; Kubo, N. Maintaining real-time precise point positioning during outages of orbit and clock corrections. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z. Quality assessment of CNES real-time ionospheric products. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Freeshah, M. Performance evaluation of real-time global ionospheric maps provided by different IGS analysis centers. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Qian, L.; Zeng, F.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, H. Real-time clock comparison and monitoring with multi-GNSS precise point positioning: GPS, GLONASS and Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierski, K.; Sośnica, K.; Hadas, T. Quality assessment of multi-GNSS orbits and clocks for real-time precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hao, J.; Liu, W.; Jiao, B.; Zhang, H.; Song, B. Performance Assessment of BDS Real-Time Precise Point Positioning Based on SSR Corrections. J. Surv. Eng. 2019, 145, 05019003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, K.L.; Ray, J.R.; Beard, R.L. Characterization of periodic variations in the GPS satellite clocks. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douša, J. The impact of errors in predicted GPS orbits on zenith troposphere delay estimation. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. The impact of orbital errors on the estimation of satellite clock errors and PPP. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Assessment of precise orbit and clock products for Galileo, BeiDou, and QZSS from IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX). GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurichesse, D.; Cerri, L.; Berthias, J.P.; Mercier, F. Real time precise GPS constellation and clocks estimation by means of a Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+ 2013, Nashville, TN, USA, 16–20 September 2013; pp. 1155–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Nischan, T.; Wickert, J. The GFZ real-time GNSS precise positioning service system and its adaption for COMPASS. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Dai, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Improving real-time clock estimation with undifferenced ambiguity fixing. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zha, J.; Zhao, C. An efficient undifferenced method for estimating multi-GNSS high-rate clock corrections with data streams in real time. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1435–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, F. Satellite clock estimation at 1 Hz for real-time kinematic PPP applications. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, W.; Yi, W.; Shi, C.; Lou, Y.; Guo, H. Research on a method of real-time combination of precise GPS clock corrections. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X. Robust Kalman filtering with constraints: A case study for integrated navigation. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Details/Strategies |
|---|---|
| Data period | Day of year 213–243 and 255–284, 2019 |
| Real-time products | Broadcast ephemeris + SSR corrections (WHU CLK16, DLR CLK20, CNES CLK93) Sample interval: 5 seconds Reference center: antenna phase center (APC) Software for data collecting: BKG Ntrip Caster (version 2.12.6) |
| Reference product | GFZ MGEX post-processed products Sample interval: 30 seconds Reference center: center of mass (CoM) |
| Clock product comparison | Resample interval: 30 seconds Reference center: APC. Satellite phase center offsets (PCO) are corrected using igs14_wwww.atx files that are specified in the GFZ SP3 file headers (wwww: week number). |
| Orbit | PRN | SSM | MSM | IMSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | C01 | 2.52 | 1.82 | 2.57 |
| C02 | 2.69 | 2.41 | 2.84 | |
| C03 | 0.94 | 0.45 | 1.04 | |
| C04 | 2.95 | 2.69 | 2.99 | |
| C05 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.95 | |
| mean | 1.99 | 1.63 | 2.08 | |
| IGSO | C06 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| C07 | 1.68 | 1.50 | 1.81 | |
| C08 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.38 | |
| C09 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.39 | |
| C10 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.43 | |
| C13 | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.43 | |
| mean | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.66 | |
| MEO | C11 | 0.26 | 0.94 | 0.25 |
| C12 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.64 | |
| C14 | \ | 0.75 | 0.17 | |
| mean | 0.41 | 0.76 | 0.35 |
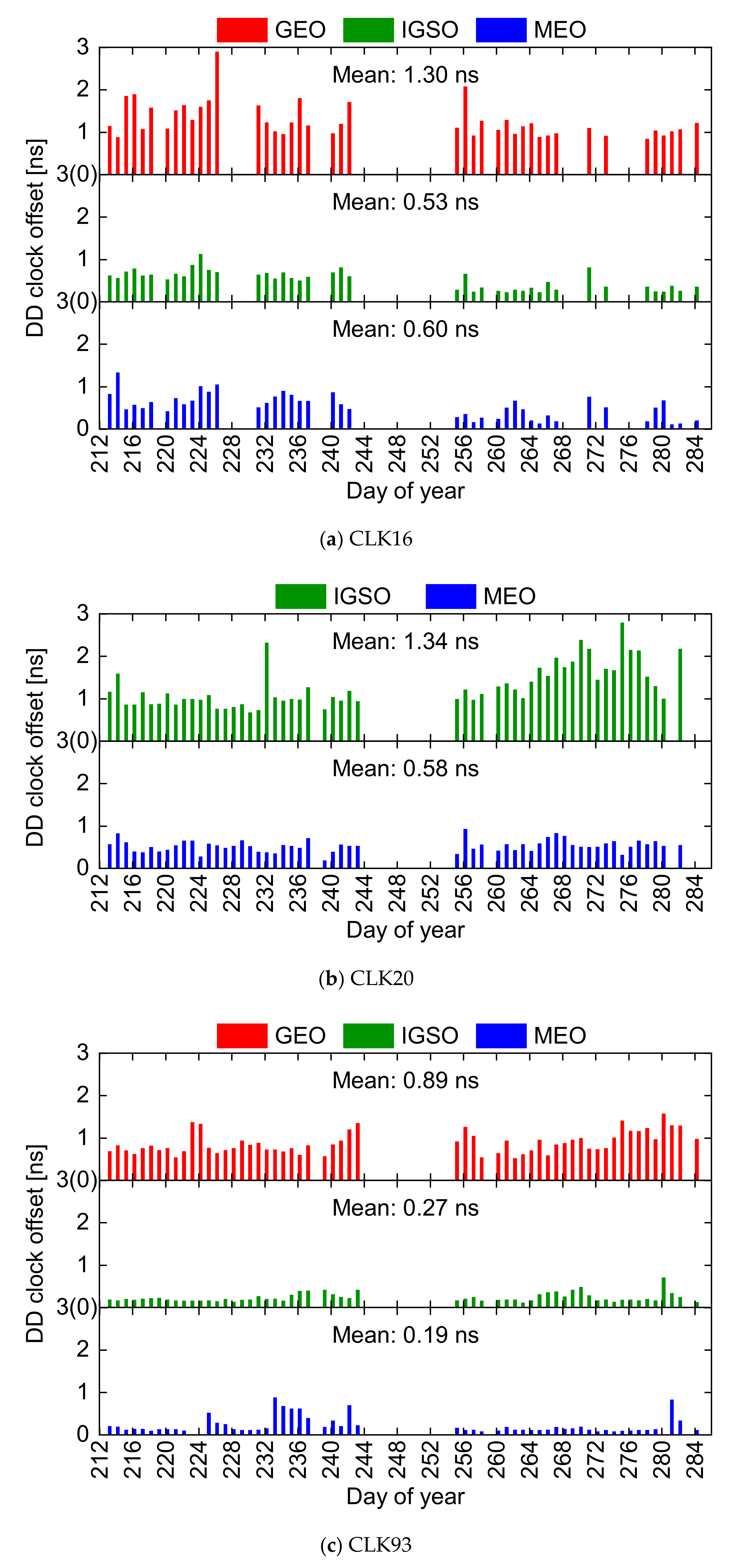
| Orbit | PRN | CLK16 | CLK20 | CLK93 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEO | C01 | 1.40 | \ | 0.72 |
| C02 | 1.22 | \ | 0.93 | |
| C03 | 1.15 | \ | 0.93 | |
| C04 | 1.49 | \ | 0.95 | |
| C05 | 1.24 | \ | 0.91 | |
| mean | 1.30 | \ | 0.89 | |
| IGSO | C06 | 0.54 | 1.21 | 0.27 |
| C07 | 0.63 | 1.11 | 0.28 | |
| C08 | 0.45 | 1.31 | 0.17 | |
| C09 | 0.47 | 1.86 | 0.41 | |
| C10 | 0.49 | 1.17 | 0.24 | |
| C13 | 0.50 | 1.19 | 0.22 | |
| C16 | 0.62 | 1.56 | \ | |
| mean | 0.53 | 1.34 | 0.27 | |
| MEO | C11 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.15 |
| C12 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.15 | |
| C14 | 0.71 | 0.58 | 0.28 | |
| mean | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Z.; Cai, C.; Pan, L.; Kuang, C. An Improved Multi-Satellite Method for Evaluating Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Offset Products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213638
Yuan Z, Cai C, Pan L, Kuang C. An Improved Multi-Satellite Method for Evaluating Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Offset Products. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213638
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Zhimin, Changsheng Cai, Lin Pan, and Cuilin Kuang. 2020. "An Improved Multi-Satellite Method for Evaluating Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Offset Products" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213638
APA StyleYuan, Z., Cai, C., Pan, L., & Kuang, C. (2020). An Improved Multi-Satellite Method for Evaluating Real-Time BDS Satellite Clock Offset Products. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3638. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213638