Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET Data over East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
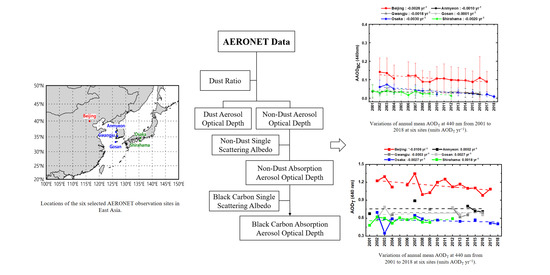
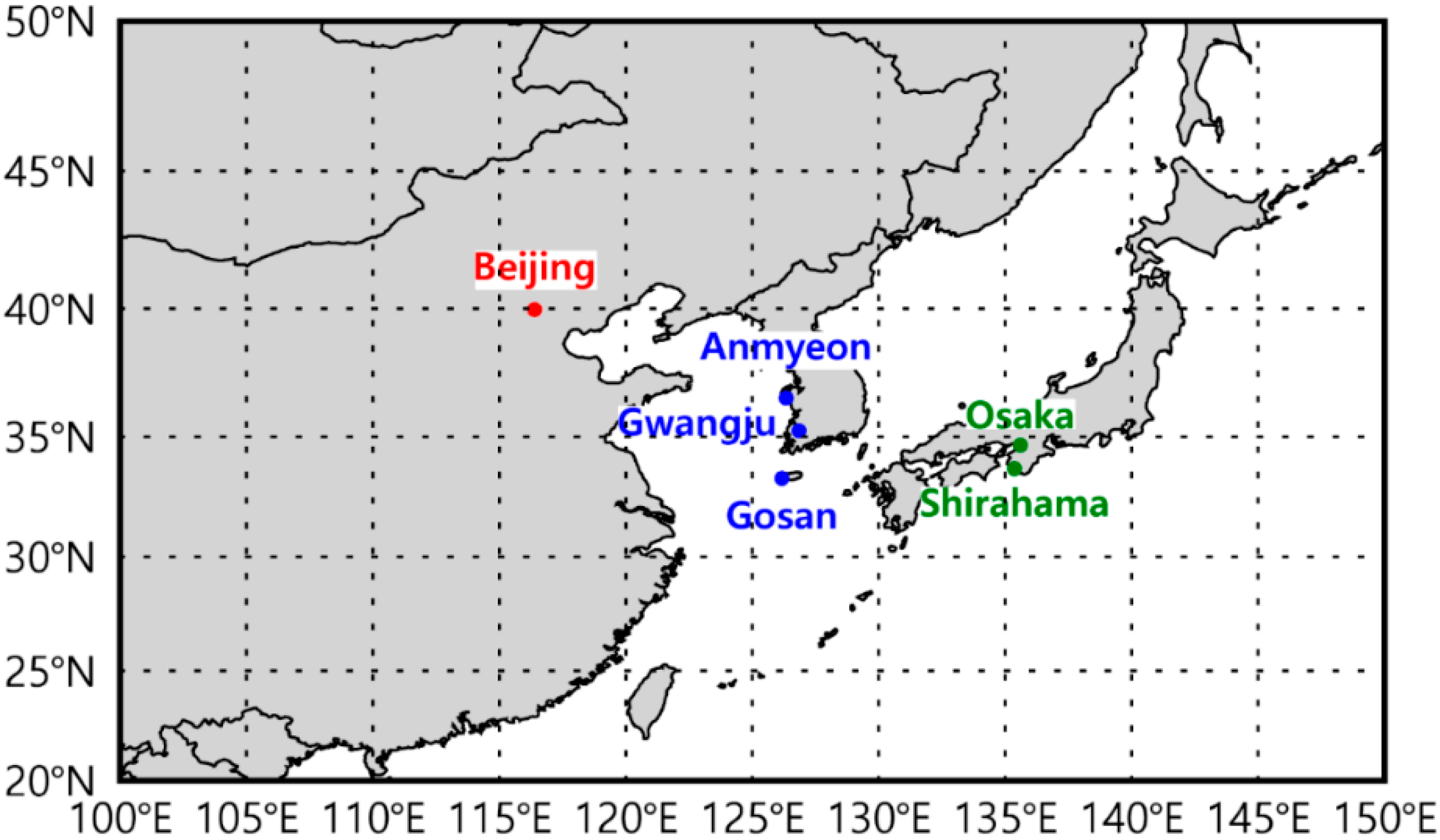
2.1. AERONET Version 3 Data and Sites
2.2. AAODBC Retrieval Methodology
2.3. Statistical Analysis
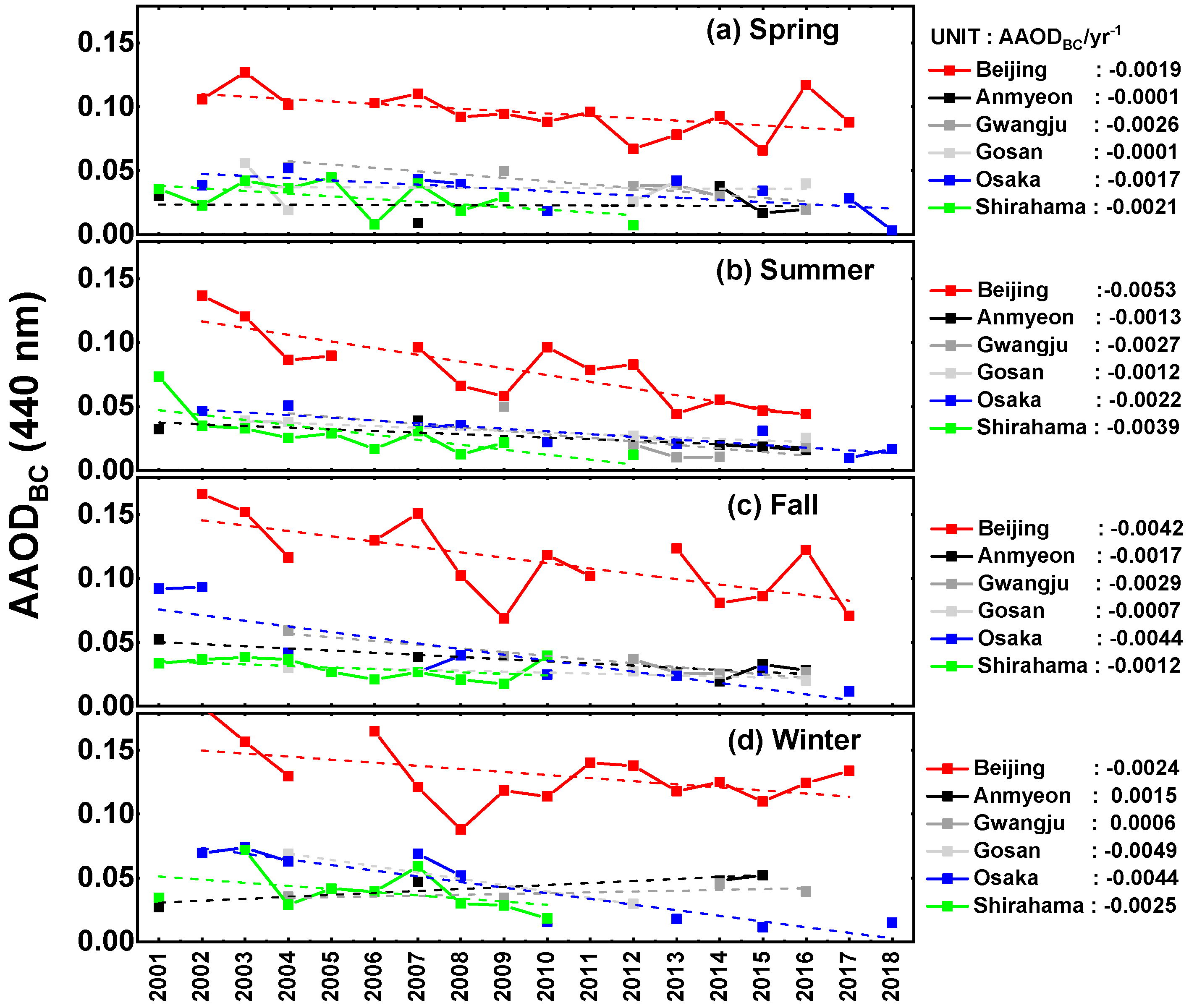
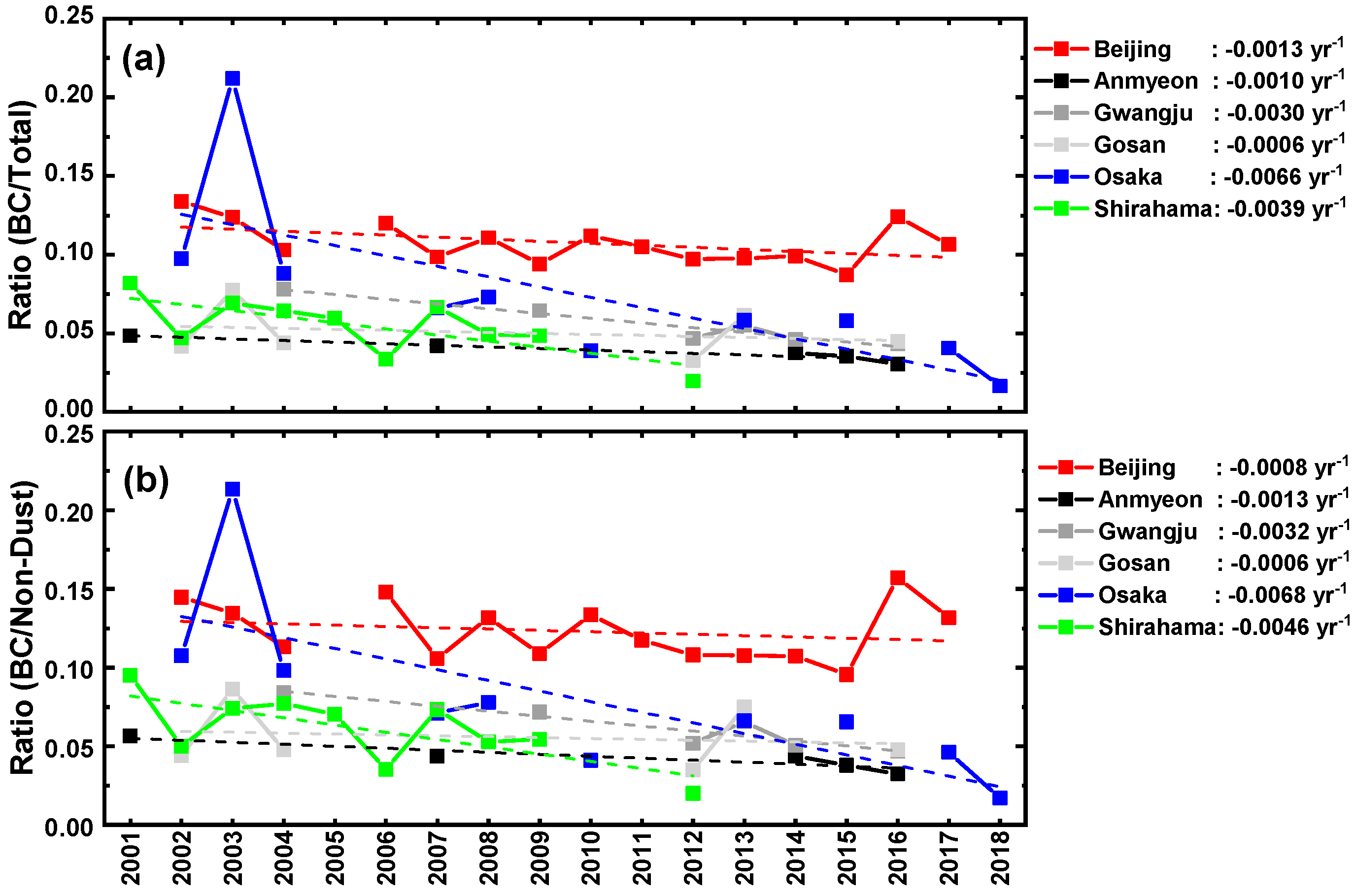
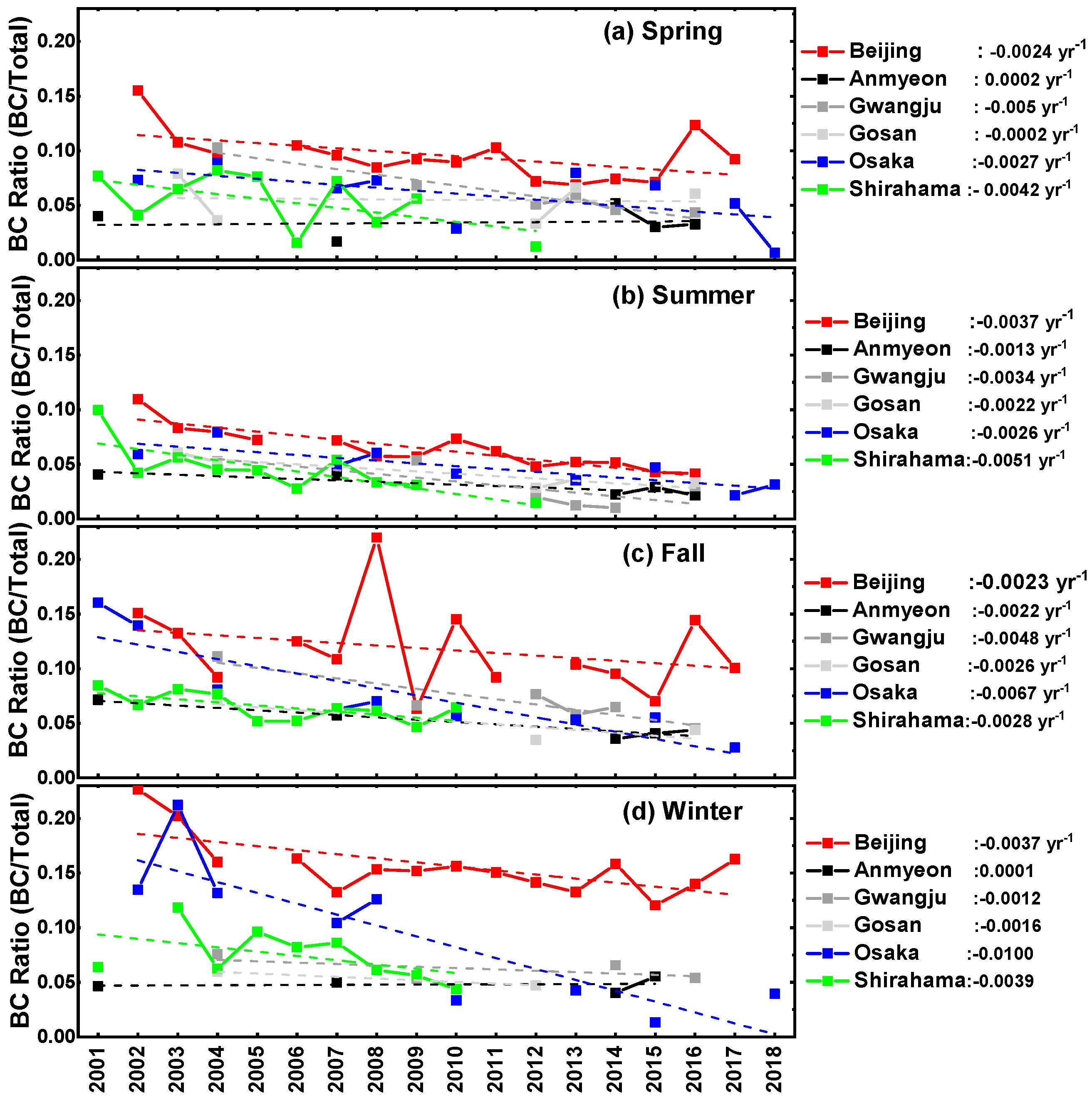
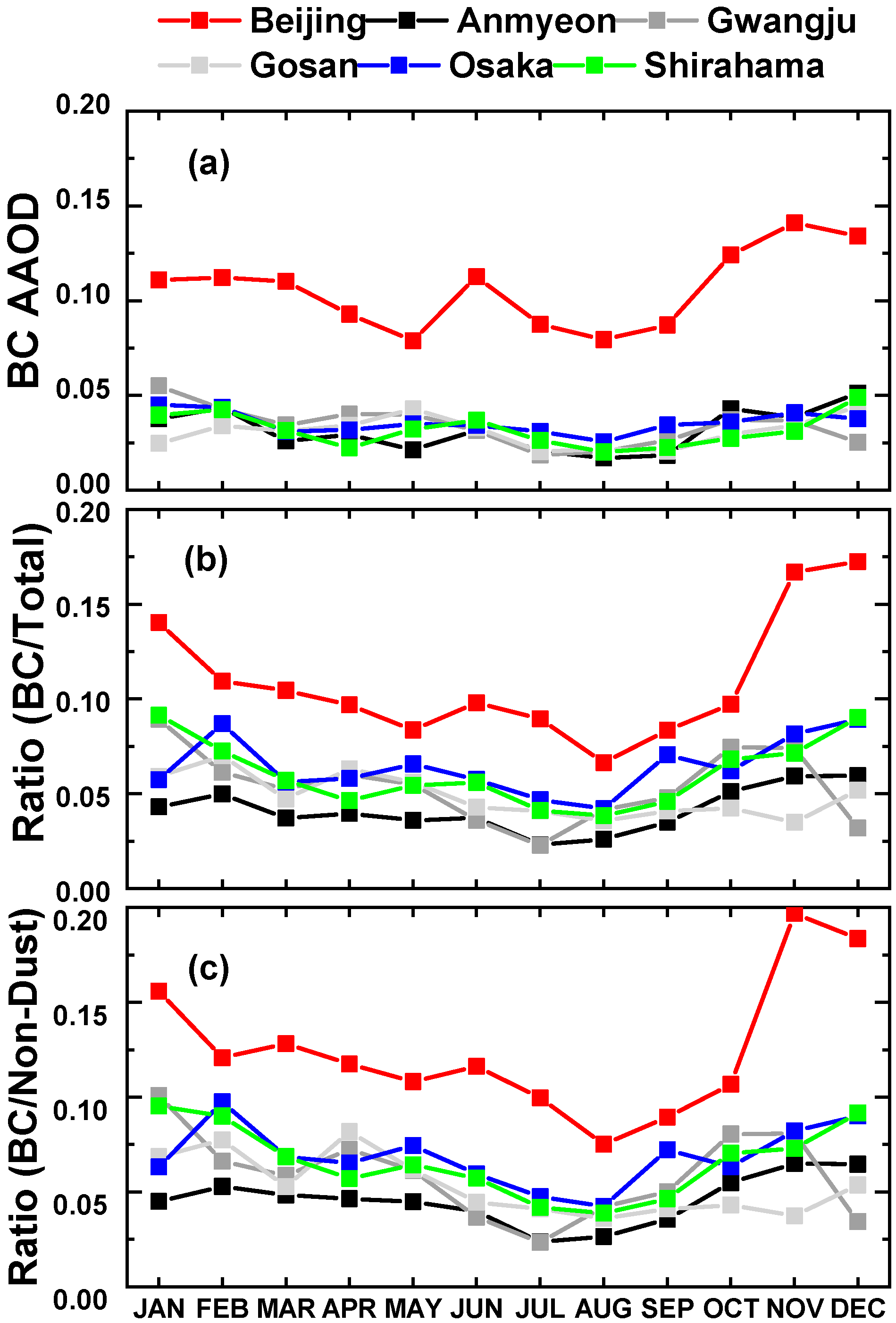
3. Results
3.1. Total Aerosol Optical Depth (AODT) and AAODBC
3.2. BC Ratio
3.3. Statistical Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; Shuai, Y.; Mao, Q. Study on the Influence of Aerosol Radiation Balance in One-Dimensional Atmospheric Medium UsingPn-Approximation Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, H.C.; Bhend, J. Causes of regional change-Aerosols. In Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin, 2nd ed.; Bolle, H.J., Menenti, M., Vesuvio, S.S.A., Rasool, I., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 6, pp. 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Sarangi, C.; Zhao, C.; Leung, R.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Yang, T.; Yang, B. Urbanization Effect on Winter Haze in the Yangtze River Delta Region of China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6710–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Shen, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, C. Anthropogenic Black Carbon Emission Increase during the Last 150 Years at Coastal Jiangsu, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, K.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, J.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; et al. Radiative absorption enhancement of dust mixed with anthropogenic pollution over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 7815–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black Carbon Emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, M.; Guo, S.; Du, Z.; Zheng, J.; Shang, D.; Zamora, M.L.; Zeng, L.; Shao, M.; Wu, Y.-S.; et al. Markedly enhanced absorption and direct radiative forcing of black carbon under polluted urban environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4266–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Huang, J.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Cen, K. A review on black carbon emissions, worldwide and in China. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Weber, R.J.; Song, Y.; Ke, Z.; Zou, Y. Modeling the global radiative effect of brown carbon: A potentially larger heating source in the tropical free troposphere than black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R.; Lacis, A.; Oinas, V. Global warming in the twenty-first century: An alternative scenario. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9875–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Ding, K.; Niu, X.; Nie, W.; Xu, Z.; Chi, X.; Wang, M.; et al. Effects of aerosol–radiation interaction on precipitation during biomass-burning season in East China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 10063–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Bergstrom, R.W.; Shinozuka, Y.; Clarke, A.D.; Decarlo, P.F.; Jimenez, J.L.; Livingston, J.M.; Redemann, J.; Dubovik, O.; Strawa, A. Absorption Angstrom Exponent in AERONET and related data as an indicator of aerosol composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-K.; Tesche, M.; Müller, D.; Noh, Y. Technical note: Absorption aerosol optical depth components from AERONET observations of mixed dust plumes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Clothiaux, E.E. Inferring black carbon content and specific absorption from AERONET retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 101, D10S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from sun and sky radiance measurements. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Munoz, O.; Veihelman, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle non-sphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-K.; Tesche, M.; Noh, Y.; Müller, D. Aerosol-type classification based on AERONET version 3 inversion products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3789–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzenberg, J. Size-segregated measurements of particulate elemental carbon and aerosol light absorption at remote artic locations. Atoms. Environ. 1982, 16, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kaercher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Schleicher, N.; Fricker, M.; Cen, K.; Liu, X.-L.; Kaminski, U.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.-F.; Norra, S. Long-term variation of black carbon and PM2.5 in Beijing, China with respect to meteorological conditions and governmental measures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, A.S.; Toon, O.B.; Stevens, D.E.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Ra-manathan, V.; Welton, E.J. Reduction of tropical cloudiness by soot. Science 2000, 288, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Minnis, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Satellite-based assessment of possible dust aerosols semi-direct effect on cloud water path over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Su, J.; Tang, Q.; Minnis, P.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Q. Taklimakan dust aerosol radiative heating derived from CALIPSO observations using the Fu-Liou radiation model with CERES constraints. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 9, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Jin, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.P. Seasonal variations in the light-absorbing properties of water-soluble and insoluble organic aerosols in Seoul, Korea. Atoms. Environ. 2016, 129, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Holben, B.; Zhang, G. Comparison of key absorption and optical properties between pure and transported anthropogenic dust over East and Central Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15501–15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Arao, K.; Uno, I.; Murayama, T.; Kagawa, N.; Aoki, K.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A. Continuous observations of Asian dust and other aerosols by polarization lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia. Geophys. Res. Atoms. 2004, 109, D19S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Freudenthaler, V.; Groß, S. Vertically resolved separation of dust and smoke over Cape Verde using multi-wavelength Raman and polarization lidars during Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment 2008. Geophys. Res. Atoms. 2009, 114, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Muller, D.; Gross, S.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Freudenthaler, V.; Weinzirl, B.; Veira, A.; Petzold, A. Optical and microphysical properties of smoke over Cape Verde inferred from multi-wavelength lidar measurements. TELLUS B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63B, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Müller, D.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Shimizu, A.; Sano, I.; Park, C.B. Depolarization ratios retrieved by AERONET sun–sky radiometer data and comparison to depolarization ratios measured with lidar. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6271–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Tesche, M.; Kim, K.; Kezoudi, M.; Tatarov, B.; Muller, D.; Noh, Y. On the spectral depolarization and lidar ratio of mineral dust provided in the AERONET version 3 inversion product. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12735–12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Vaughan, M.A.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hostetler, C.A. Separating mixtures of aerosol types in airborne High Spectral Resolution Lidar data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Hollrig, P.; Chin, M.; Fung, I.; Jacob, D.; Penner, J. Contribution of different aerosol species to the global aerosol extinction optical thickness: Estimates from model results. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 23895–23915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik, I.N.; Toon, O.B. Incorporation of mineralogical composition into models of the radiative properties of mineral aerosol from UV to IR wavelengths. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 9423–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wu, G.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, T.L.; Zhou, Q.Q. What is the real role of iron oxides in the optical properties of dust aerosols? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12159–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmuller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Aerosol light absorption and its measurement: A review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cao, J.; Ho, K.; Chen, L.W.A.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Chow, J.; Waston, J.; et al. The optical properties of urban aerosol in northern China: A case study at Xian. Atoms. Res. 2015, 160, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Shin, S.K.; Muller, D.; Shin, D.H. Influence of the vertical absorption profile of mixed Asian dust plumes on aerosol direct radiative forcing over East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Ramaswamy, V. Global sensitivity studies of the direct radiative forcing due to anthropogenic sulfate and black carbon aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, D6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, W. Light absorption carbonaceous particles: An investigative review. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 2007, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalizov, A.F.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, R. Enhanced light absorption and scattering by carbon soot aerosol internally mixed with sulfuric acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M. Seasonal variability of aerosol optical properties over Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4095–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Choi, I.J.; Yoon, S.C. A multi-year analysis of clear-sky aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing at Gosan, Korea (2001–2008). Atoms. Res. 2010, 95, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencal, S.; Kishcha, P.; Silva, A.M.D.; Elhacham, E.; Alpert, P. AOD distributions and trends of major aerosol species over a selection of the worlds most populated cities based on the 1st version of NASA’s MERRA aerosol reanalysis. Urban Clim. 2017, 20, 168–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, J.T. Spatio-temporal variations of optical properties of aerosols in East Asia measured by MODIS and relation to the ground-based mass concentrations observed in central Korea during 2001–2010. J. Atoms. Sci. 2014, 50, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Muller, D.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Shin, S. Estimation of radiative forcing by the dust and non-dust content in mixed East Asian pollution plumes on the basis of depolarization ratios measured with lidar. Atoms. Environ. 2012, 61, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. A comparison of dust properties between China continent and Korea, Japan in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5787–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kumar, K.R.; Zhao, T. The climatology of aerosol optical thickness and radiative effects in southeast Asia from 18-years of ground-based observations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Kim, S.W.; Park, R.J.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.S. Changes in column aerosol optical depth and ground-level particulate matter concentration over East Asia. Air Qual. Atoms. Health 2017, 11, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogacheva, L.; Leeuw, G.; Rodriguez, E.; Kolmonen, P.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexsandri, G.; Kourtidis, K.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of aerosols over China from two decades of multi-satellite observations- part 1: ATSR (1995–2011) and MODIS C6.1 (2000–2017). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11389–11407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, G.; Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kourtidis, K.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Amiridis, V.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Xue, Y.; et al. Two decades of satellite observations of AOD over mainland China using ATSR-2, AATSR and MODIS/Terra: Data set evaluation and large-scale patterns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tie, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Zhong, L.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Bi, X.; Deng, T. Effects of southeast Asia biomass burning on aerosols and ozone concentrations over the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. Atoms. Environ. 2008, 42, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Arimoto, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sheng, L.F.; Fu, G. Spatial distribution and inter annual variation of surface PM10 concentrations over eighty-six Chinese cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5641–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, C.L.; Ridely, D.A.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Drury, E.E. Satellite observations cap the atmospheric organic aerosol budget. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.M.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.M.; Qu, W.J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Carbonaceous aerosols in China: Top-down constraints on primary sources and estimation of secondary contribution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 28219–28272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tao, S. Inter annual variability of summertime aerosol optical depth over East Asia during 2000-2011: A potential influence from El Nino Southern Oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Characteristics of PM2.5 mass concentrations and Chemical species in urban and background areas of China: Emerging results from the CARE_China network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8849–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Pilot, E.; Yu, J.; Nie, C.; Holdaway, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Vardoulakis, S.; et al. Taking action on air pollution control in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebi (BTH) region: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Pollution Trends in China from 2000 to 2017: A multi-Sensor view from space. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Xu, X.; Che, H.; Tang, Z.; Gui, K.; An, L.; Lu, C.; Shi, G. Variation in MERRA-2 aerosol optical depth and absorption aerosol optical depth over China from 1980 to 2017. J. Atoms. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 186, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Taketani, F.; Zhu, C.; Choi, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Klimont, Z. Rapid reduction in black carbon emissions from China: Evidence from 2009-2019 observations on Fukue Island, Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6339–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.; Lim, S.; Fang, W.; Gustafsson, O.; Andersson, A.; Park, R.J.; Sheridan, P.J. Observation-based estimates of the mass absorption cross-section of black and brown carbon and their contribution to aerosol light absorption in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Oshima, N.; Kajino, M.; Mikami, R.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Verma, R.L.; Kajii, Y.; Kato, S.; Takami, A. Emisiions of black carbon in East Asia estimated from observations at a remote site in the East China Sea. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xie, S.D. Spatial and temporal variation of anthropogenic black carbon emissions in China for the period 1980–2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4825–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, H. Variation, sources and historical trend of black carbon in Beijing, China based on ground observation and MERRA-2 reanalysis data. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Shen, Z.X.; An, Z.S. Black carbon relationships with emissions and meteorology in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Jiang, F.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Zhu, B. Investigation on the direct radiative effect of fossil fuel black-carbon aerosol over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 104, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Chen, H.M.; Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, H.N.; Xie, M.; Chen, P.L.; Li, M.M.; et al. The direct effects of black carbon aerosols from different source sectors in East Asia in summer. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 5293–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, X.; Xie, T. The spatial and temporal distributions of absorbing aerosols over East Asia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.H.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagent, B.; Bond, T.; Angiola, A.; Van der gan, H.D.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, J.F.; Bond, T.C.; Eyring, V.; Granier, C.; Heil, A.; Klimont, Z.; Lee, D.; Liousse, C.; Mieville, A.; Owen, B.; et al. Historical (1850–2000) gridded anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of reactive gases and aerosols: Methodology and application. Atoms. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7017–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.E.; Lim, J.H.; Shim, J.M.; Kwon, J.-I.; Kim, I. Spring 2018 Asian Dust Events: Sources, transportation, and potential biogeochemical implications. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
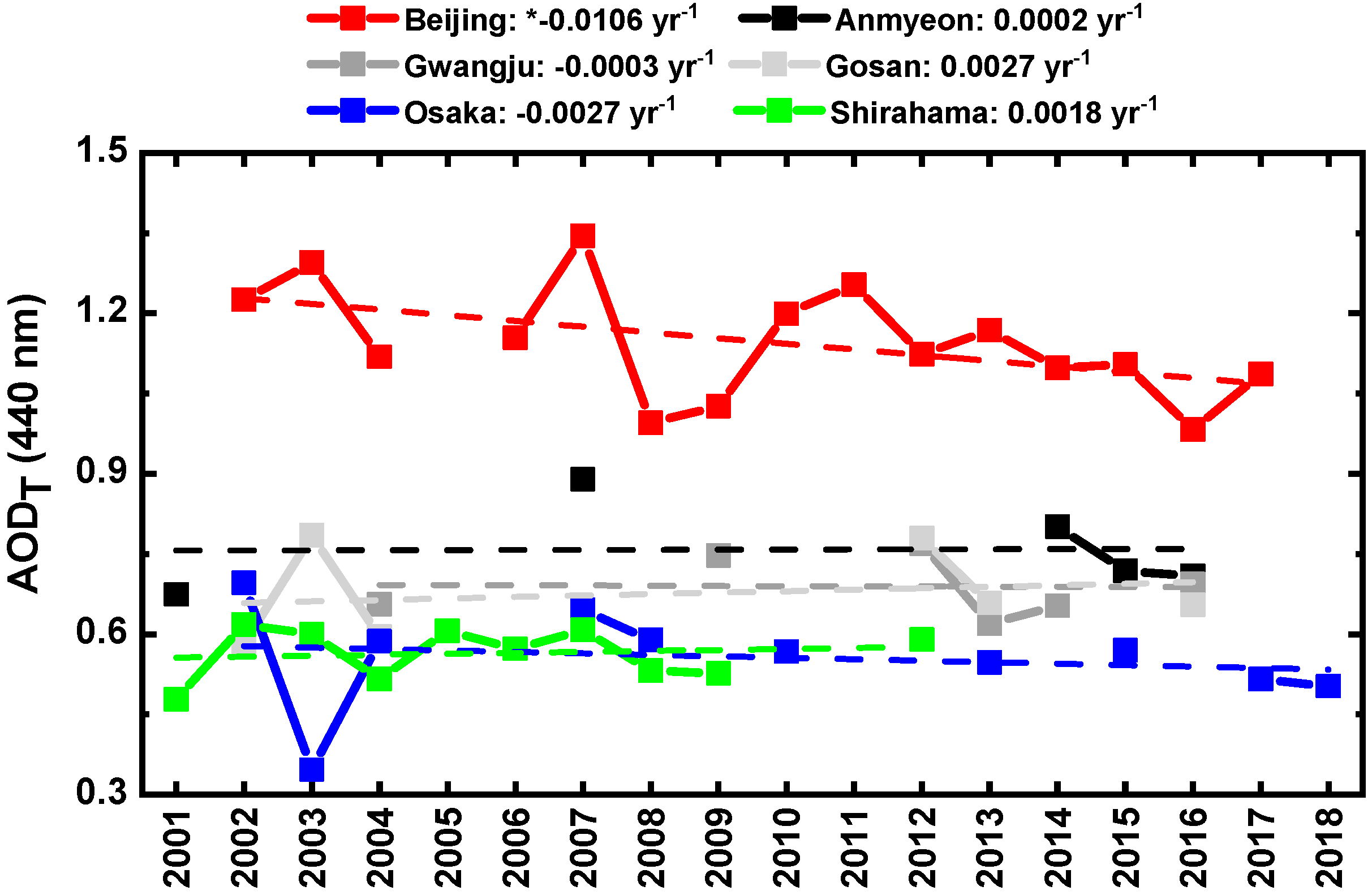
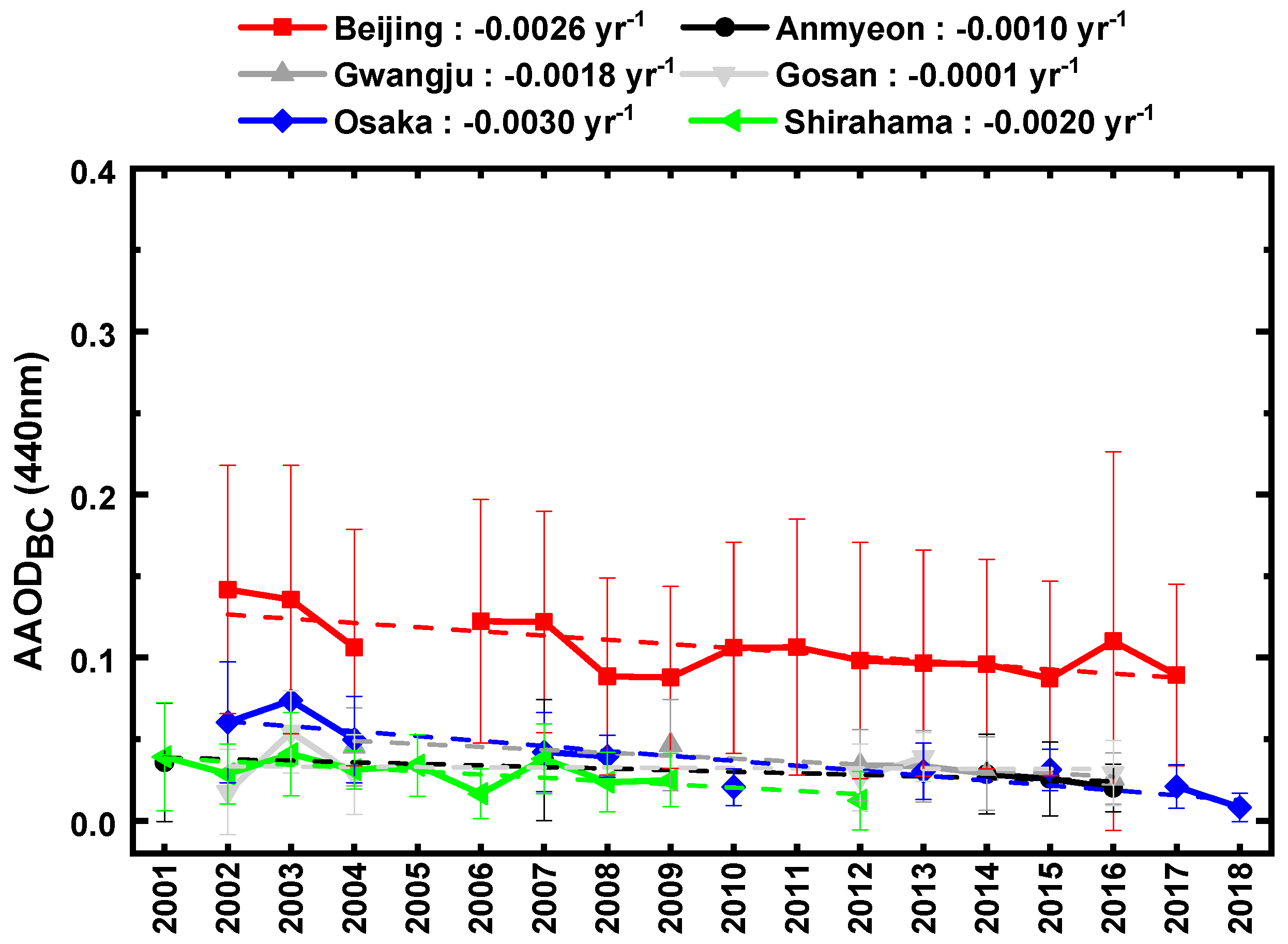
| Station | N | AODT (440 nm) (Mean ± SD) | AAODBC (440 nm) (Mean ± SD) | AAODBC Ratio (440 nm) (Mean ± SD) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Total | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Total | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | ||
| Beijing | 1313 | 1.15 ± 0.73 | 1.10 ± 0.65 | 1.43 ± 0.80 | 1.18 ± 0.80 | 0.96 ± 0.67 | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.09 ± 0.07 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 0.13 ± 0.08 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.15 ± 0.06 |
| Anmyeon | 240 | 0.74 ± 0.38 | 0.67 ± 0.30 | 0.78 ± 0.39 | 0.72 ± 0.37 | 0.94 ± 0.55 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| Gwangju | 267 | 0.70 ± 0.35 | 0.69 ± 0.31 | 0.84 ± 0.40 | 0.54 ± 0.18 | 0.80 ± 0.61 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.03 |
| Gosan | 113 | 0.69 ± 0.32 | 0.69 ± 0.32 | 0.72 ± 0.27 | 0.73 ± 0.39 | 0.63 ± 0.24 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.03 |
| Osaka | 300 | 0.58 ± 0.20 | 0.57 ± 0.19 | 0.64 ± 0.21 | 0.53 ± 0.20 | 0.53± 0.20 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.08 ± 0.07 |
| Shirahama | 296 | 0.57 ± 0.23 | 0.57 ± 0.22 | 0.65 ± 0.28 | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.51 ± 0.18 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.03 |
| Station | p-Value * |
|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.128 |
| Anmyeon | 0.358 |
| Gwangju | 0.023 |
| Gosan | 0.032 |
| Osaka | 0.00 |
| Shirahama | 0.016 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dehkhoda, N.; Noh, Y.; Joo, S. Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET Data over East Asia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213551
Dehkhoda N, Noh Y, Joo S. Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET Data over East Asia. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213551
Chicago/Turabian StyleDehkhoda, Naghmeh, Youngmin Noh, and Sohee Joo. 2020. "Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET Data over East Asia" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213551
APA StyleDehkhoda, N., Noh, Y., & Joo, S. (2020). Long-Term Variation of Black Carbon Absorption Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET Data over East Asia. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213551