Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. SONET Observations
2.2. Radiative Effect Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Multi-Year Average Aerosol Radiative Forcing and Efficiencies
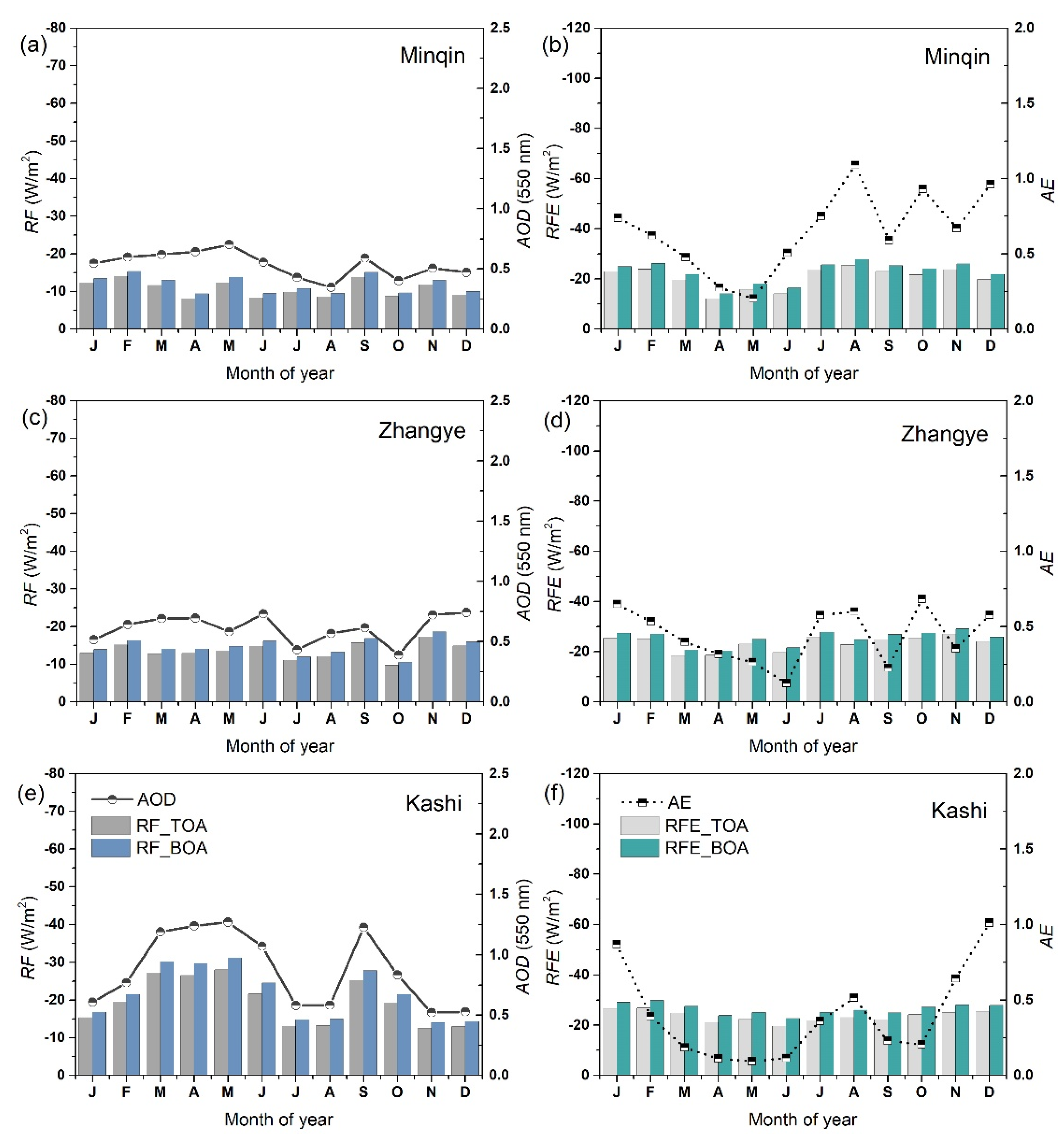
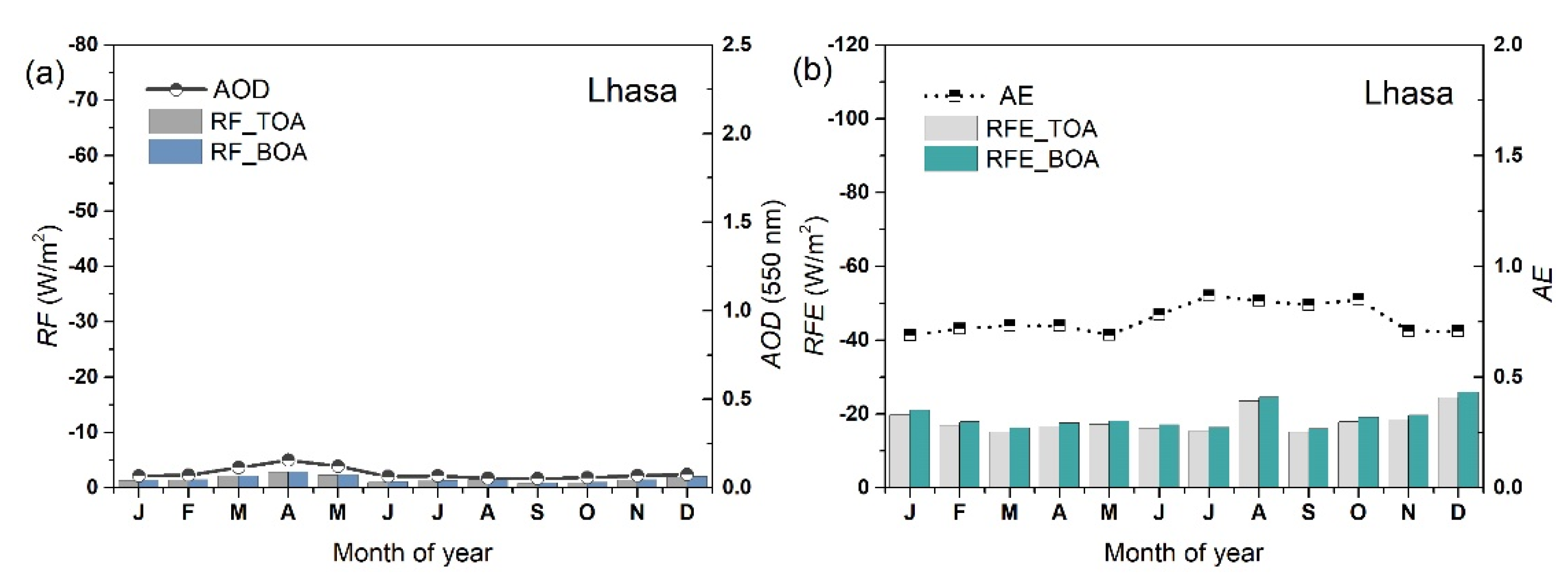
3.2. Annual Cycles of Aerosol Radiative Forcing and Efficiencies
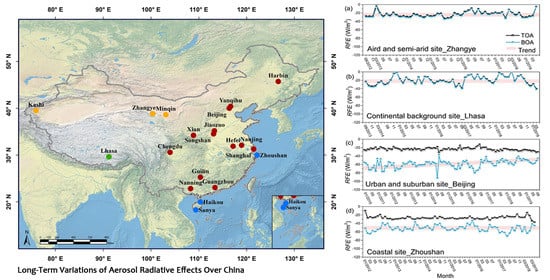
3.3. Long-Term Variations of Monthly Average Aerosol Radiative Forcing and Efficiencies
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamo, A.; Tafuro, A.M.; Kinne, S.; De Tomasi, F.; Perrone, M.R. Monthly-averaged anthropogenic aerosol direct radiative forcing over the Mediterranean based on AERONET aerosol properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6995–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkian, F.; Nicholson, S.E. Long-term variations of aerosol optical depth and aerosol radiative forcing over Iran based on satellite and AERONET data. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2018, 190, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.; Kang, C. Long-term trend of aerosol composition and direct radiative forcing due to aerosols over Gosan: TSP, PM10, and PM2.5 data between 1992 and 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6107–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmetwally, M.; Alfaro, S.C.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Favez, O.; Mohamed, Z.; Chatenet, B. Aerosol properties and associated radiative effects over Cairo (Egypt). Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzadeh, M.; Alam, K.; Abedini, Y.; Bidokhti, A.A.; Masoumi, A. Monthly and seasonal variations of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over Zanjan, Iran. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 164, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, O.; Diaz, J.P.; Exposito, F.J.; Diaz, A.M.; Dubovik, O.; Derimian, Y.; Dubuisson, P.; Roger, J. Shortwave radiative forcing and efficiency of key aerosol types using AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5129–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Olmo, F.J.; Lyamani, H.; Anton, M.; Quirantes, A.; Aladosarboledas, L. Aerosol radiative forcing during African desert dust events (2005–2010) over Southeastern Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 10331–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Won, J.; Omar, A.; Kim, S.W.; Sohn, B. Estimation of the radiative forcing by key aerosol types in worldwide locations using a column model and AERONET data. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6620–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendisch, M.; Hellmuth, O.; Ansmann, A.; Heintzenberg, J.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Eichler, H.; Muller, D.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Radiative and dynamic effects of absorbing aerosol particles over the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6405–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwirth, E.; Wendisch, M.; Ehrlich, A.; Heese, B.; Tesche, M.; Althausen, D.; Schladitz, A.; Muller, D.; Otto, S.; Trautmann, T. Spectral surface albedo over Morocco and its impact on radiative forcing of Saharan dust. Tellus B 2009, 61, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Chang, W.; Ou, Y.; Goloub, P.; Li, C.; Li, K.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wendisch, M. Aerosol solar radiative forcing near the Taklimakan Desert based on radiative transfer and regional meteorological simulations during the Dust Aerosol Observation-Kashi campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10845–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Holben, B.N.; Guo, Z. Investigating the aerosol optical and radiative characteristics of heavy haze episodes in Beijing during January of 2013. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 9884–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, K.T.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.S.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q.J. Comprehensive study of optical, physical, chemical, and radiative properties of total columnar atmospheric aerosols over China: An overview of sun–sky radiometer observation network (SONET) measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevasagullo, E. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Eck, T.F.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Cuevasagullo, E.; Blarel, L. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L.; Ding, N.; Xie, M.; Lu, M.; Zhang, F.; Duan, Y.; Zong, S. Analysis of aerosol radiative forcing over beijing under different air quality conditions using ground-based sun-photometers between 2013 and 2015. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhang, M.; Bilal, M.; Tao, M. Aerosol optical properties and associated direct radiative forcing over the Yangtze river basin during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Che, H.; Han, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Li, M.; Chen, P. The optical properties, physical properties and direct radiative forcing of urban columnar aerosols in the Yangtze river delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Letu, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Zou, J.; Fan, W. Haze optical properties from long-term ground-based remote sensing over Beijing and Xuzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Xu, H.; Cheng, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, W.; et al. Sun-sky radiometer observation network with the extension of multi-wavelength polarization measurements. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 19, 496–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.I.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Munoz, O.; Veihelmann, B. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Blarel, L.; Zhang, W.; Podvin, T.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Chen, H.; Holben, B.N. Improvements for ground-based remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol properties by additional polarimetric measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Blarel, L.; Wendisch, M. A method to calculate Stokes parameters and angle of polarization of skylight from polarized CIMEL sun/sky radiometers. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 149, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, O.; Diaz, A.M.; Exposito, F.J.; Diaz, J.P.; Dubovik, O.; Dubuisson, P.; Roger, J.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Derimian, Y. Validation of AERONET estimates of atmospheric solar fluxes and aerosol radiative forcing by ground-based broadband measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Vogelmann, A.M.; Ramanathan, V. Saharan dust aerosol radiative forcing measured from space. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2558–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Satheesh, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K. Aerosol radiative forcing due to enhanced black carbon at an urban site in India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 27-1–27-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchiazzi, P.; Yang, S.; Gautier, C.; Sowle, D. SBDART: A Research and teaching software tool for plane-parallel radiative transfer in the Earth’s atmosphere. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, E.T.; Artaxo, P.; Correia, A.L. Spatial variability of the direct radiative forcing of biomass burning aerosols and the effects of land use change in Amazonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J.P. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Schleicher, N.; Fricker, M.; Cen, K.; Liu, X.L.; Kaminski, U.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.F.; Norra, S. Long-term variation of black carbon and PM2.5 in Beijing, China with respect to meteorological conditions and governmental measures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Che, H.; Yi, Z. Long-term variation of black carbon aerosol in China based on revised aethalometer monitoring data. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
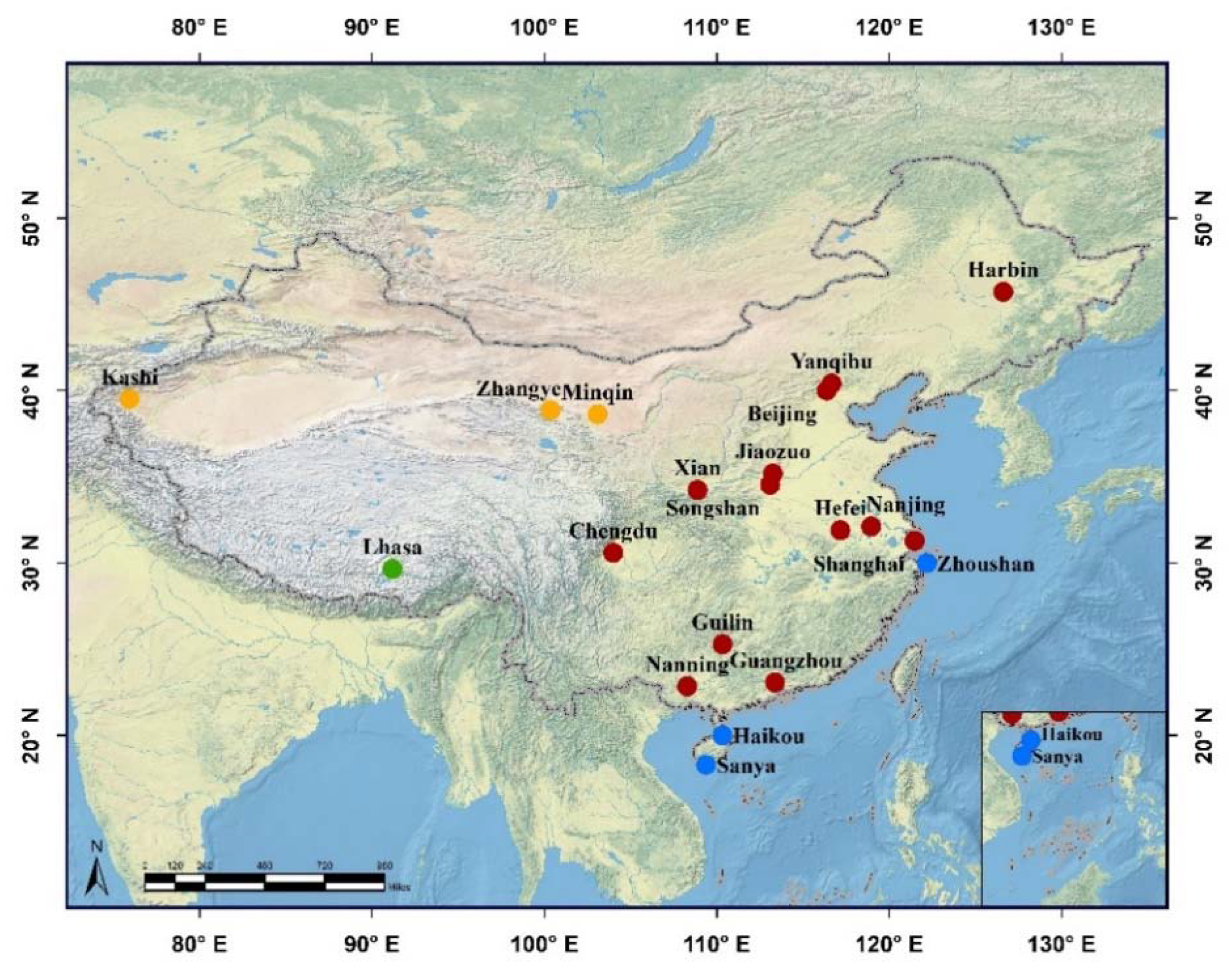
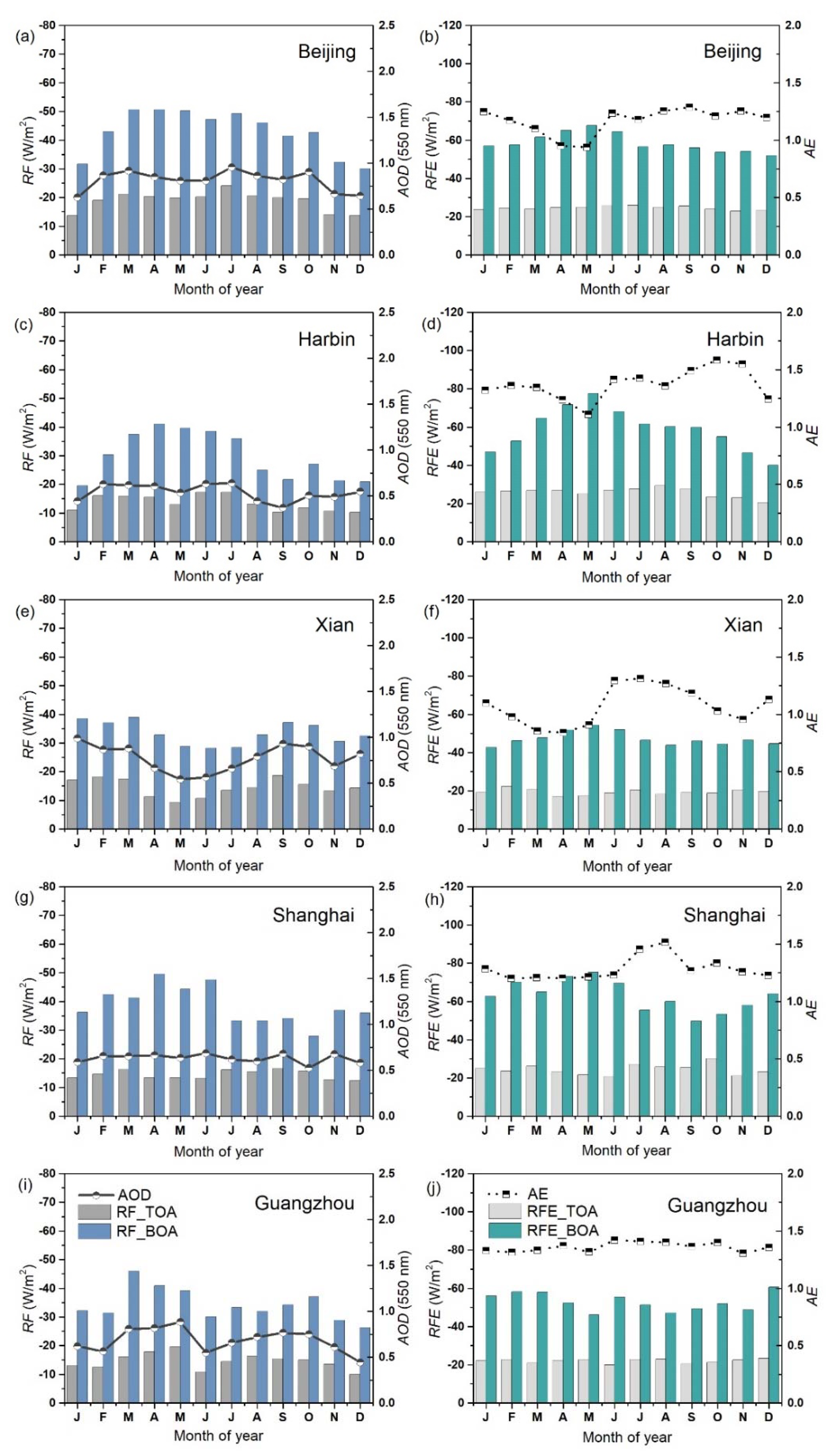
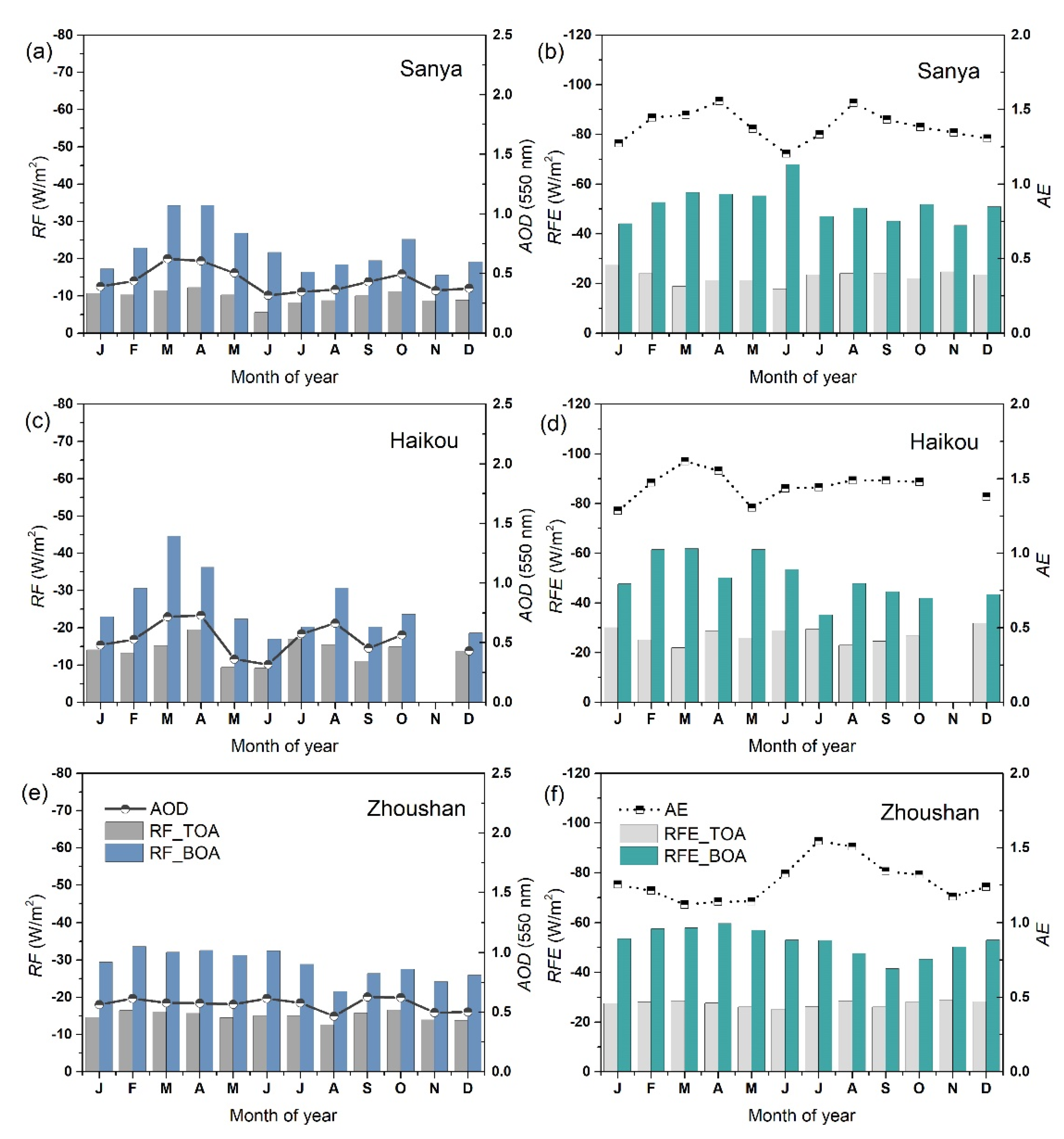
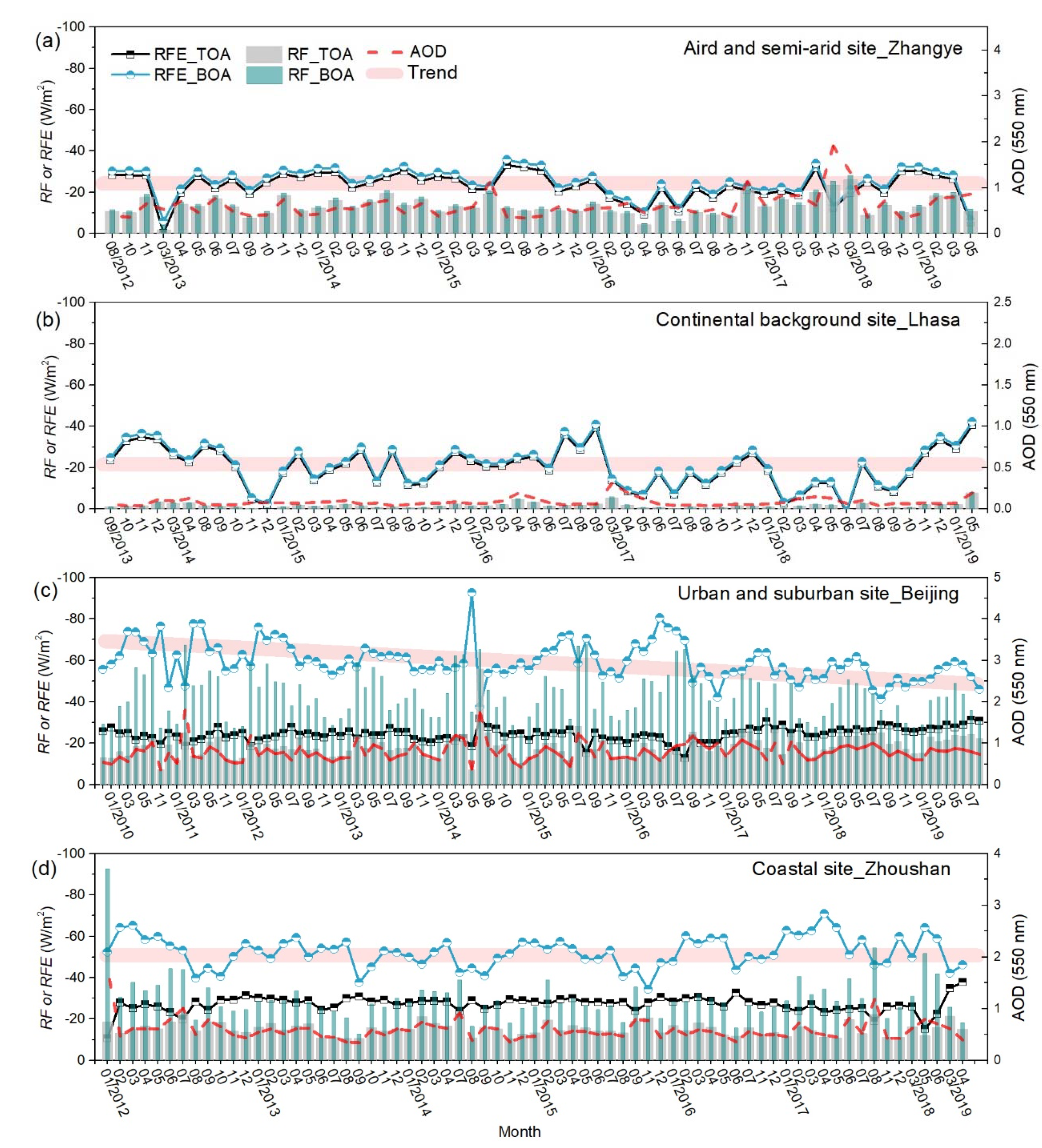
| Type | Station | Lon (˚E) | Lat (˚N) | Alt (m) | Time Period of Observation | Number of Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arid and semi-arid sites | Minqin | 103.0 | 38.6 | 1364.0 | February 2012–August 2019 | 191 |
| Zhangye | 100.3 | 38.8 | 1589.0 | August 2012–May 2019 | 157 | |
| Kashi | 75.9 | 39.5 | 1320.0 | September 2013–July 2019 | 264 | |
| continental background site | Lhasa | 91.2 | 29.6 | 3678.0 | September 2013–May 2019 | 906 |
| urban and suburban sites | Beijing | 116.3 | 40.0 | 59.0 | December 2009–August 2019 | 1058 |
| Yanqihu | 116.7 | 40.4 | 100.0 | December 2015–September 2019 | 289 | |
| Jiaozuo | 113.3 | 35.2 | 113.0 | June 2016–February 2018 | 233 | |
| Shanghai | 121.5 | 31.3 | 84.5 | March 2013–July 2019 | 437 | |
| Harbin | 126.6 | 45.7 | 223.0 | December 2013–April 2019 | 323 | |
| Hefei | 117.2 | 31.9 | 36.0 | January 2013–August 2019 | 550 | |
| Nanjing | 119.0 | 32.1 | 52.0 | May 2013–January 2019 | 461 | |
| Guangzhou | 113.4 | 23.1 | 28.4 | October 2011–May 2019 | 452 | |
| Songshan | 113.1 | 34.5 | 475.0 | December 2013–August 2019 | 560 | |
| Xian | 108.9 | 34.2 | 389.0 | May 2012–November 2017 | 578 | |
| Chengdu | 104.0 | 30.6 | 510.0 | June 2013–August 2019 | 354 | |
| Guilin | 110.3 | 25.3 | 160.4 | July 2017–August 2019 | 144 | |
| Nanning | 108.3 | 22.8 | 158.0 | November 2016–January 2019 | 102 | |
| coastal sites | Sanya | 109.4 | 18.3 | 28.9 | September 2014–August 2019 | 270 |
| Haikou | 110.3 | 20.0 | 22.0 | March 2014–March 2016 | 98 | |
| Zhoushan | 122.1 | 29.9 | 29.0 | January 2012–April 2019 | 409 |
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wavelengths | 0.2~4.0 µm | solar spectrum |
| aerosol properties | AOD (440, 675, 870, 1020 nm) | SONET daily average products |
| AE (440–870 nm) | ||
| SSA (440, 675, 870, 1020 nm) | ||
| g (440, 675, 870, 1020 nm) | ||
| atmospheric profiles | mid-latitude summer/ mid-latitude winter | depending on season |
| water vapor content | CWV | SONET daily average product |
| surface property | broadband surface albedo | MODIS surface albedo product |
| Site | Aerosol | RFTOA (W/m2) | RFBOA (W/m2) | RFETOA (W/m2) | RFEBOA (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arid and semi-arid sites | −14.9 ± 9 | −16.5 ± 10 | −22.2 ± 8 | −24.6 ± 8 | |
| Minqin | DU 1 | −10.7 ± 7 | −12.0 ± 7 | −18.5 ± 10 | −20.7 ± 10 |
| Zhangye | DU | −13.6 ± 8 | −14.8 ± 8 | −22.5 ± 9 | −24.5 ± 9 |
| Kashi | DU | −18.6 ± 11 | −20.7 ± 12 | −24.7 ± 5 | −27.5 ± 5 |
| continental background site | −1.6 ± 2 | −1.7 ± 2 | −18.0 ± 14 | −19.1 ± 15 | |
| Lhasa | CB 2 | −1.6 ± 2 | −1.7 ± 2 | −18.0 ± 14 | −19.1 ± 15 |
| urban and suburban sites | −15.4 ± 8 | −36.0 ± 16 | −22.6 ± 6 | −54.3 ± 14 | |
| Beijing | UI 3 | −18.7 ± 10 | −43.4 ± 18 | −24.3 ± 5 | −59.4 ± 14 |
| Yanqihu | UI | −16.8 ± 9 | −42.6 ± 17 | −21.5 ± 6 | −58.1 ± 15 |
| Jiaozuo | UI | −16.7 ± 10 | −38.7 ± 13 | −19.5 ± 5 | −51.3 ± 14 |
| Shanghai | UI+MR 4 | −14.0 ± 9 | −40.0 ± 22 | −23.9 ± 12 | −65.3 ± 22 |
| Harbin | UI | −14.0 ± 8 | −31.3 ± 15 | −25.8 ± 7 | −59.3 ± 16 |
| Hefei | UI | −14.1 ± 6 | −33.3 ± 12 | −23.1 ± 5 | −56.0 ± 12 |
| Nanjing | UI | −14.1 ± 6 | −34.2 ± 12 | −22.4 ± 4 | −56.0 ± 11 |
| Guangzhou | UI+MR | −14.2 ± 6 | −33.8 ± 13 | −22.0 ± 4 | −53.6 ± 11 |
| Songshan | UI+DU | −14.5 ± 7 | −29.6 ± 10 | −21.3 ± 6 | −44.8 ± 7 |
| Xian | UI+DU | −14.7 ± 8 | −33.9 ± 14 | −19.4 ± 5 | −46.8 ± 8 |
| Chengdu | UI | −15.9 ± 9 | −35.7 ± 14 | −20.2 ± 9 | −46.4 ± 11 |
| Guilin | UI | −14.3 ± 6 | −26.2 ± 10 | −26.5 ± 3 | −49.5 ± 9 |
| Nanning | UI | −14.2 ± 5 | −27.4 ± 9 | −26.2 ± 5 | −50.4 ± 8 |
| coastal sites | −13.6 ± 6 | −29.3 ± 12 | −25.3 ± 5 | −53.8 ± 10 | |
| Sanya | MR+UI | −10.9 ± 4 | −28.7 ± 13 | −21.4 ± 5 | −54.0 ± 9 |
| Haikou | MR+UI | −14.8 ± 5 | −30.2 ± 14 | −26.3 ± 5 | −51.7 ± 11 |
| Zhoushan | MR+UI | −15.0 ± 6 | −29.4 ± 11 | −27.7 ± 4 | −54.2 ± 10 |
| Site | Type | Quantity | Li et al. [14] (W/m2) | This Study (W/m2) | Absolute Difference (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhangye | Arid and semi-arid site | Time period | August 2012–October 2016 | August 2012–May 2019 | |
| RFETOA | −22.3 | −22.5 | 0.2 | ||
| RFEBOA | −24.4 | −24.5 | 0.1 | ||
| Lhasa | Continental background site | Time period | September 2013–September 2016 | September 2013–May 2019 | |
| RFETOA | −17.2 | −18.0 | 0.8 | ||
| RFEBOA | −18.7 | −19.1 | 0.4 | ||
| Beijing | Urban and suburban site | Time period | December 2009–November 2016 | December 2009–August 2019 | |
| RFETOA | −23.5 | −24.3 | 0.8 | ||
| RFEBOA | −62.4 | −59.4 | 3.0 | ||
| Zhoushan | Coastal site | Time period | January 2012–November 2016 | January 2012–April 2019 | |
| RFETOA | −29.3 | −27.7 | 1.6 | ||
| RFEBOA | −53.7 | −54.2 | 0.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Su, X.; Yang, L.; Ye, S.; Xu, H. Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203296
Li L, Li Z, Li K, Wang Y, Tian Q, Su X, Yang L, Ye S, Xu H. Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET). Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203296
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Zhengqiang Li, Kaitao Li, Yan Wang, Qingjiu Tian, Xiaoli Su, Leiku Yang, Song Ye, and Hua Xu. 2020. "Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET)" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203296
APA StyleLi, L., Li, Z., Li, K., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Su, X., Yang, L., Ye, S., & Xu, H. (2020). Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET). Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203296