Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality in the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China: Observation and Analysis from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery and Panel Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Nighitime Light Imagery and Pre-Processing
2.3. Measurement of Urban Sprawl Dynamics
2.3.1. Urban Expansion Rate Index
2.3.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse
2.3.3. Rank-Size Rule Model
2.4. Urbanization Quality Assessment
2.4.1. Establishment of an Assessment System for Urbanization Quality
2.4.2. Entropy Weight Model
2.5. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Urban Sprawl
3.1.1. Dynamic Change of Total Nighttime Light Inventory
3.1.2. Rate, Intensity, and Pattern of Urban Sprawl
3.1.3. City Rank-Size Distribution Change of Urban Agglomeration System
3.2. Urbanization Quality of Urban Agglomeration
3.3. Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality
4. Discussion
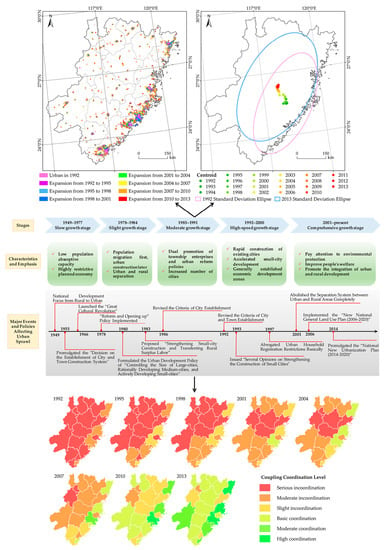
4.1. Urban Development Associated with State-Led Policies and Market-Oriented Land Reform
4.2. Lessons and Suggestions for WTSUA’s Further Urban Planning
4.3. Advantages and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D. How does sprawl differ across cities in China? A multi-scale investigation using nighttime light and census data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprowska, K.; Łaszkiewicz, E.; Kronenberg, J. Is urban sprawl linked to green space availability? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ma, W.; Wang, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, R.; Tao, Z. Identifying the internal structure evolution of urban built-up land sprawl (UBLS) from a composite structure perspective: A case study of the Beijing metropolitan area, China. Land Use Policy 2017, 62, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.L.; Lu, X.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Measurement of the eco-environmental effects of urban sprawl: Theoretical mechanism and spatiotemporal differentiation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, W.; Wu, W. Are social security policies for Chinese landless farmers really effective on health in the process of Chinese rapid urbanization? A study on the effect of social security policies for Chinese landless farmers on their health-related quality of life. Int. J. Equity Health 2014, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Da, H.; Wen, H.; Wang, Y. Spatial structure evolution of urban agglomerations and its driving factors in mainland china: From the monocentric to the polycentric dimension. Sustainability 2019, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y. Issues in China’s Urban Agglomeration Studies and New Exploration for China’s Urban Agglomeration Selection and Nurturing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z. Assessing urbanization quality using structure and function analyses: A case study of the urban agglomeration around Hangzhou Bay (UAHB), China. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ge, B.; Li, Y. Impacts of state-led and bottom-up urbanization on land use change in the peri-urban areas of Shanghai: Planned growth or uncontrolled sprawl? Cities 2017, 60, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijkamp, P.; Perrels, A. Sustainable Cities in Europe, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.H.; Ma, W.Q.; Qu, Y.B.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhou, D.Y. How does sprawl differ across urban built-up land types in China? A spatial-temporal analysis of the Beijing metropolitan area using granted land parcel data. Cities 2016, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, B.; Tousi, S.N. An explanation of urban sprawl phenomenon in Shiraz Metropolitan Area (SMA). Cities 2018, 73, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, P.; Yue, W.; Song, Y. Impacts of land finance on urban sprawl in China: The case of Chongqing. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Salarian, F. Urban sprawl on natural lands: Analyzing and predicting the trend of land use changes and sprawl in Mazandaran city region, Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatab, A.A.; Cavinato, M.E.R.; Lindemer, A.; Lagerkvist, C.J. Urban sprawl, food security and agricultural systems in developing countries: A systematic review of the literature. Cities 2019, 94, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J. From industrial toward ecological in China. Science 2012, 336, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, W. Analyzing the impact of urbanization quality on CO2 emissions: What can geographically weighted regression tell us? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Jin, H. Urban sprawl among Chinese cities of different population sizes. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, C.; Song, K.; Su, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhong, L.; Gao, Y. Analysis of coupling coordination variance between urbanization quality and eco-environment pressure: A case study of the west taiwan strait urban agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Zarzoso, I. The impact of urbanization on CO2 emissions: Evidence from developing countries. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, M.K.; Garg, P.K.; Khare, D. Monitoring and modelling of urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2008, 10, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahtahmassebi, A.R.; Song, J.; Zheng, Q.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.Y.; Pan, Y.; Moore, N.; Shahtahmassebi, G.; Haghighi, R.S.; et al. Remote sensing of impervious surface growth: A framework for quantifying urban expansion and re-densification mechanisms. Int. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 46, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonde, P.; Balamwar, S.; Ochawar, R.S. Urban sprawl detection and analysis using unsupervised classification of high resolution image data of Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust area in India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 17, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Netzband, M.; Fazal, S. Monitoring urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques of a fast growing urban center, India. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantakumar, L.N.; Kumar, S.; Schneider, K. Spatiotemporal urban expansion in Pune metropolis, India using remote sensing. Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, T.; Ding, K.; Wu, G. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban agglomerations in four major bay areas of USA, China and Japan from 1987 to 2017: Evidence from remote sensing images. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.J.; Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of urban land-use expansion: A case study of the yangtze river economic belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells-Quintana, D. Malthus living in a slum: Urban concentration, infrastructure and economic growth. J. Urban Econ. 2017, 98, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.R.; Yu, H.R.; Li, X. The spatial-temporal pattern analysis of city development in countries along the belt and road initiative based on nighttime light data. Geomat. Inform. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; He, C.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, Y. Detecting the 20 year city-size dynamics in China with a rank clock approach and DMSP/OLS nighttime data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, E.C.; Seto, K.C. Characterizing urban infrastructural transitions for the Sustainable Development Goals using multi-temporal land, population, and nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Elvidge, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, C.; Warner, T. Remote sensing of night-time light. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5855–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Cui, S.H. The characteristics in urbanization of economic region on west coast of Taiwan Strait. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 29, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Qian, Y.; Pickett, S.T.; Zhou, W. Urban mapping needs up-to-date approaches to provide diverse perspectives of current urbanization: A novel attempt to map urban areas with nighttime light data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 195, 103709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pei, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, Q.; Yue, J. Application of luojia 1-01 nighttime images for detecting the light changes for the 2019 spring festival in western cities, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guk, E.; Levin, N. Analyzing spatial variability in night-time lights using a high spatial resolution color Jilin-1 image–Jerusalem as a case study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 163, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City Application of Jilin 1 Nighttime Light Data. Available online: https://xw.qq.com/cmsid/20191110A04ICV00 (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; He, X.; Jendryke, M. A preliminary investigation of Luojia-1 night-time light imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Chen, T.; Ma, X.; Qu, L. A novel wrapper approach for feature selection in object-based image classification using polygon-based cross-validation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Soc. 2017, 14, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, R. Remote sensing monitoring and driving force analysis of urban expansion in Guangzhou City, China. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachowicz, M.; Liu, T. Finding spatial outliers in collective mobility patterns coupled with social ties. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1806–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shi, W.; Miao, Z. Confidence analysis of standard deviational ellipse and its extension into higher dimensional Euclidean space. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhou, J.; Pan, T.; Sun, Q.; Wu, M. Relationship of carbon emissions and economic growth in China’s construction industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živanović, Z.; Tošić, B.; Nikolić, T.; Gatarić, D. Urban System in Serbia-the Factor in the Planning of Balanced Regional Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W. Integrated analytic hierarchy process and its applications-a literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 186, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, H.D.; Yacob, M.R.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ishak, M.Y. Delphi method of developing environmental well-being indicators for the evaluation of urban sustainability in Malaysia. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.T.B.; Wu, D.D. Online banking performance evaluation using data envelopment analysis and principal component analysis. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F.; Prasher, S.O.; OzgaeZielinski, B.; Sliusarieva, A. Comparison of multiple linear and nonlinear regression, autoregressive integrated moving average, artificial neural network, and wavelet artificial neural network methods for urban water demand forecasting in montreal, Canada. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Ye, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Land fragmentation and variation of ecosystem services in the context of rapid urbanization: The case of Taizhou city, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk A. 2014, 28, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. Multi-criteria decision-making method based on a cross-entropy with interval neutrosophic sets. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 3598–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D. Assessment and forecast of Beijing and Shanghai’s urban ecosystem health. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.; Hu, M. Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy–resource–environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment-empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Wen, F. Coupling and coordination analysis of water resources-economy ecological environment in key provinces of “the Belt and Road”. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 52, 870–877. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Tao, X. Evolution and assessment on China’s urbanization 1960–2010: Under-urbanization or over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.F.; Huang, Y.Q. Uneven land reform and urban sprawl in China: The case of Beijing. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Measuring sprawl in large Chinese cities along the Yangtze river via combined single and multidimensional metrics. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Ng, C.N. Spatial and temporal dynamics of urban sprawl along two urban–rural transects: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 79, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P. Measuring urban sprawl and its drivers in large Chinese cities: The case of Hangzhou. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Q. Measuring urban sprawl in Beijing with geo-spatial indices. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigginton, N.S.; Fahrenkamp-Uppenbrink, J.; Wible, B.; Malakoff, D. Cities are the future. Science 2016, 352, 904–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Helkowski, J.H. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ren, Y. The reform of Hukou system in Chinese cities and the social inclusion of floating population. South China Popul. 2011, 26, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up land efficiency in urban China: Insights from the general land use plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Wen, Z.G. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.N. Historical evolution and enlightenment of Fujian’s governance strategy since the founding of the People’s Republic of China. Fujian Dangshi Yuekan 2007, 5, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Guanyu Jinyibu Tuijin Huji Zhidu Gaige de Yijian (Opinion on Further Advancing Reform of the Household Registration System). Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-07/30/content_8944.htm (accessed on 30 July 2014).
- Gu, S.; Li, Z. An institutional analysis of the process of urbanization in China from the bottom-up. Soc. Sci. China 2000, 194, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, S.; Ewing, R. A longitudinal study of changes in urban sprawl between 2000 and 2010 in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, W.B.; Pendall, R.; Nguyen, M.; Harrison, A. Who Sprawls Most? How Growth Patterns Differ Across the USA; Brookings Institution, Center on Urban and Metropolitan Policy: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.L.; Qiu, Y.L.; Ye, S.Z. Designation of new cities in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1998, 18, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Guldin, G.E. Urbanizing China. In The Development of Small Towns and their Role in the Modernization of China; Ma, R., Ed.; Greenwood Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 119–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kanbur, R.; Zhang, X. Fifty years of regional inequality in China: A journey through central planning, reform, and openness. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2005, 9, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S. Development and planning of small towns in China: Speculation, reassessment and prospect. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1997, 13, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. The Fourth Session of the Sixth National People’s Congress. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/test/2006-02/24/content_209830.htm (accessed on 24 February 2006).
- Wu, K.; Fang, C.L. The development process and basic pattern of China’s small towns since 1949 and its recent new situation. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 29, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z. Land acquisition compensation in post-reform China: Evolution, structure and challenges in Hangzhou. Land Use Policy 2015, 46, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of China. The National New Type Urbanization Plan (2014–2020). Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhuanti/xxczh/index.htm (accessed on 16 March 2014).
- Liu, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Da, B. Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, M. Urban spill over vs. local urban sprawl: Entangling land-use regulations in the urban growth of China’s megacities. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, D.Z.; Zeng, H. Modeling the dynamics of landscape structure in Asia’s emerging desakota regions: A case study in Shenzhen. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 53, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Province | City | Area (104 km2) | Population (Million Person) * | GDP (102 Billion-Yuan) * | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fujian | Fuzhou | 1.19 | 7.74 | 7.86 | FZ |
| Fujian | Xiamen | 0.18 | 4.11 | 4.79 | XM |
| Fujian | Putian | 0.40 | 2.90 | 2.24 | PT |
| Fujian | Sanming | 2.25 | 2.58 | 2.35 | SM |
| Fujian | Quanzhou | 1.11 | 8.70 | 8.47 | QZ |
| Fujian | Zhangzhou | 1.30 | 5.14 | 3.95 | ZZ |
| Fujian | Nanping | 2.59 | 2.69 | 1.79 | NP |
| Fujian | Longyan | 1.88 | 2.64 | 2.39 | LY |
| Fujian | Ningde | 1.29 | 2.91 | 1.94 | ND |
| Jiangxi | Yingtan | 0.36 | 1.28 | 0.82 | YT |
| Jiangxi | Shangrao | 2.30 | 6.81 | 2.21 | ST |
| Jiangxi | Ganzhou | 3.94 | 9.81 | 2.81 | GZ |
| Jiangxi | Fuzhou | 1.86 | 4.05 | 1.38 | FZa |
| Zhejiang | Wenzhou | 1.14 | 9.25 | 6.01 | WZ |
| Zhejiang | Quzhou | 0.88 | 2.21 | 1.47 | QZa |
| Zhejiang | Lishui | 1.67 | 2.70 | 1.39 | LS |
| Guangdong | Shantou | 0.22 | 5.64 | 2.51 | ST |
| Guangdong | Chaozhou | 0.32 | 2.66 | 1.07 | CZ |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | 1.56 | 4.38 | 1.11 | MZ |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | 0.54 | 6.09 | 2.15 | JY |
| Purpose | First-Grade Index | Basic Index | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization Quality | Eco-environment Status | X1 | Per capita water resources (m3/person) |
| X2 | Per capita land area (hm2/person) | ||
| X3 | Per capita gas supply volume (m3/person) | ||
| X4 | Per capita green areas (m2) | ||
| X5 | Treatment rate of domestic sewage (%) | ||
| X6 | Landfill rate for urban waste (%) | ||
| Social Well-being Level | X7 | Proportion of built-up area to total area (%) | |
| X8 | Per capita urban road area in municipal district (m2) | ||
| X9 | Per capita public library holdings (volume) | ||
| X10 | Proportion of science and technology expenditure to GDP (%) | ||
| X11 | Proportion of educational expenditure to GDP (%) | ||
| X12 | Number of teachers per 1000 students (unit) | ||
| X13 | Per capita housing (m2/person) | ||
| X14 | Number of medical beds per 1000 persons (unit) | ||
| X15 | Registered urban unemployment rate (%) | ||
| X16 | Number of buses per 1000 persons (unit) | ||
| Econo-demographic Development | X17 | Proportion of population in municipal district to total population (%) | |
| X18 | Population density in municipal district (person/km2) | ||
| X19 | Proportion of secondary and tertiary industry employment to total employment (%) | ||
| X20 | Per capita investment in fixed assets (Yuan/person) | ||
| X21 | Per capita GDP (Yuan/person) | ||
| X22 | Per capita GDP in the secondary and tertiary industry (Yuan/person) | ||
| X23 | GDP (100 million yuan) | ||
| X24 | Per capita disposable income of urban residents (Yuan) | ||
| X25 | Total retail sales of consumer goods (100 million yuan) | ||
| X26 | Proportion of secondary and tertiary industry GDP to total GDP (%) | ||
| X27 | Per capita local government fiscal revenue (Yuan) | ||
| X28 | Financial institution deposits at year-end (100 million Yuan) | ||
| Coordination Level | Coupling Coordination Degree | Coupling State | Coordination Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serious incoordination | [0.0, 0.4] | Low coupling phase | Serious disparity exists between urban expansion extent and urbanization quality level. The urban system development is degenerating. |
| Moderate incoordination | (0.4, 0.5] | Low coupling phase | Moderate disparity exists between urban expansion extent and urbanization quality level. It is basically acceptable in the short term. |
| Slight incoordination | (0.5, 0.6] | Antagonism phase | Slight disparity exists between urban expansion extent and urbanization quality level. It is acceptable in the short term. |
| Basic coordination | (0.6, 0.7] | Running-in phase | Urban expansion extent is basically synchronized with urbanization quality level. |
| Moderate coordination | (0.7, 0.8] | Running-in phase | Urban expansion extent is moderately synchronized with urbanization quality level, and it is ideal. |
| High coordination | (0.8, 1.0] | High coupling phase | Urban expansion extent is highly synchronized with urbanization quality level, and it is the most ideal. |
| City Type | City Name | 1992–1999 | 1999–2006 | 2006–2013 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Change Area/km2 | Total UERI/% | Change Area/km2 | UERI/% | Total Change Area/km2 | Total UERI/% | Change Area/km2 | UERI/% | Total Change Area/km2 | Total UERI/% | Change Area/km2 | UERI/% | ||
| Central City | WZ | 2661.07 | 46.46 | 616.77 | 132.24 | 2092.83 | 8.59 | 468.75 | 9.80 | 4313.86 | 11.06 | 966.44 | 11.98 |
| FZ | 301.39 | 23.20 | 332.05 | 9.74 | 1388.02 | 24.21 | |||||||
| QZ | 995.42 | 87.84 | 726.28 | 8.97 | 1183.12 | 8.97 | |||||||
| XM | 286.47 | 24.86 | 353.35 | 11.19 | 288.91 | 5.13 | |||||||
| ST | 461.02 | 27.49 | 212.40 | 4.33 | 487.38 | 7.63 | |||||||
| Noncentral City | PT | 1555.06 | 62.63 | 175.51 | 72.01 | 1661.61 | 12.42 | 139.15 | 9.45 | 6520.78 | 26.07 | 542.05 | 22.16 |
| SM | 82.27 | 32.52 | 64.55 | 7.79 | 395.06 | 30.85 | |||||||
| ZZ | 245.29 | 63.28 | 188.44 | 8.95 | 1083.43 | 31.64 | |||||||
| NP | 61.77 | 48.04 | 38.11 | 6.79 | 387.64 | 46.83 | |||||||
| LY | 93.85 | 69.11 | 103.05 | 13.00 | 374.41 | 24.73 | |||||||
| ND | 70.92 | 331.95 | 21.31 | 4.11 | 355.10 | 53.24 | |||||||
| YT | 32.47 | 204.69 | 45.31 | 18.64 | 147.34 | 26.30 | |||||||
| SR | 33.91 | 58.41 | 124.08 | 42.00 | 470.08 | 40.39 | |||||||
| GZ | 40.87 | 27.04 | 264.15 | 60.42 | 609.95 | 26.68 | |||||||
| FZa | 15.14 | 142.86 | 76.56 | 65.67 | 357.50 | 54.79 | |||||||
| QZa | 72.81 | 38.50 | 85.55 | 12.24 | 326.44 | 25.16 | |||||||
| LS | 49.81 | 236.00 | 122.96 | 33.25 | 420.47 | 34.17 | |||||||
| CZ | 188.54 | 50.74 | 205.76 | 12.17 | 206.32 | 6.59 | |||||||
| MZ | 128.13 | 61.69 | 82.73 | 7.49 | 238.90 | 14.19 | |||||||
| JY | 263.80 | 87.74 | 99.91 | 4.65 | 606.08 | 21.29 | |||||||
| All cities | 4216.13 | 51.35 | 3754.44 | 9.95 | 10,834.64 | 16.92 | |||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.; Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Ren, C.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lei, S.; Fu, W. Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality in the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China: Observation and Analysis from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery and Panel Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193217
Lu C, Li L, Lei Y, Ren C, Su Y, Huang Y, Chen Y, Lei S, Fu W. Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality in the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China: Observation and Analysis from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery and Panel Data. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Chunyan, Lin Li, Yifan Lei, Chunying Ren, Ying Su, Yufei Huang, Yu Chen, Shaohua Lei, and Weiwei Fu. 2020. "Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality in the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China: Observation and Analysis from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery and Panel Data" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193217
APA StyleLu, C., Li, L., Lei, Y., Ren, C., Su, Y., Huang, Y., Chen, Y., Lei, S., & Fu, W. (2020). Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urban Sprawl and Urbanization Quality in the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China: Observation and Analysis from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Imagery and Panel Data. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193217