Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
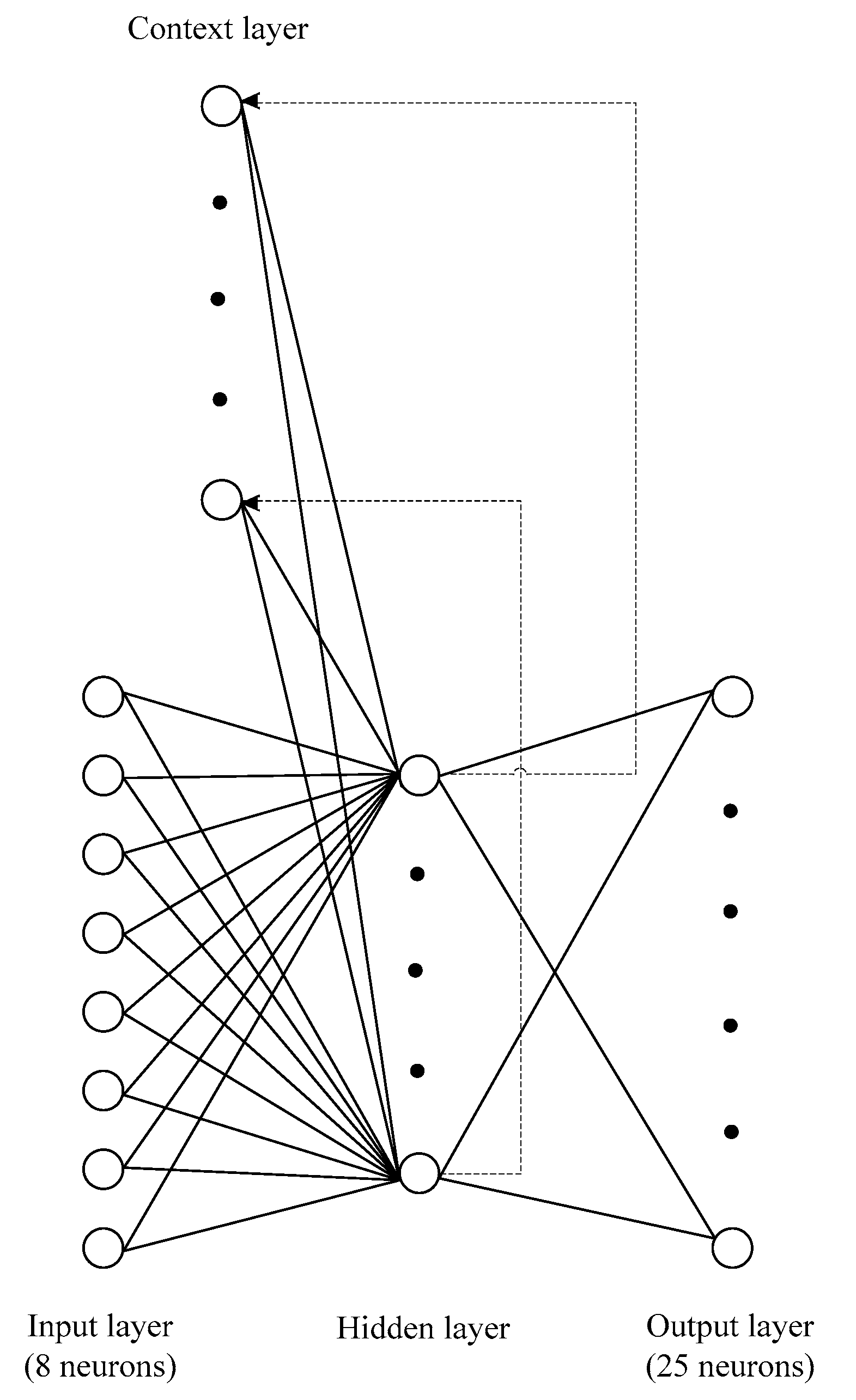
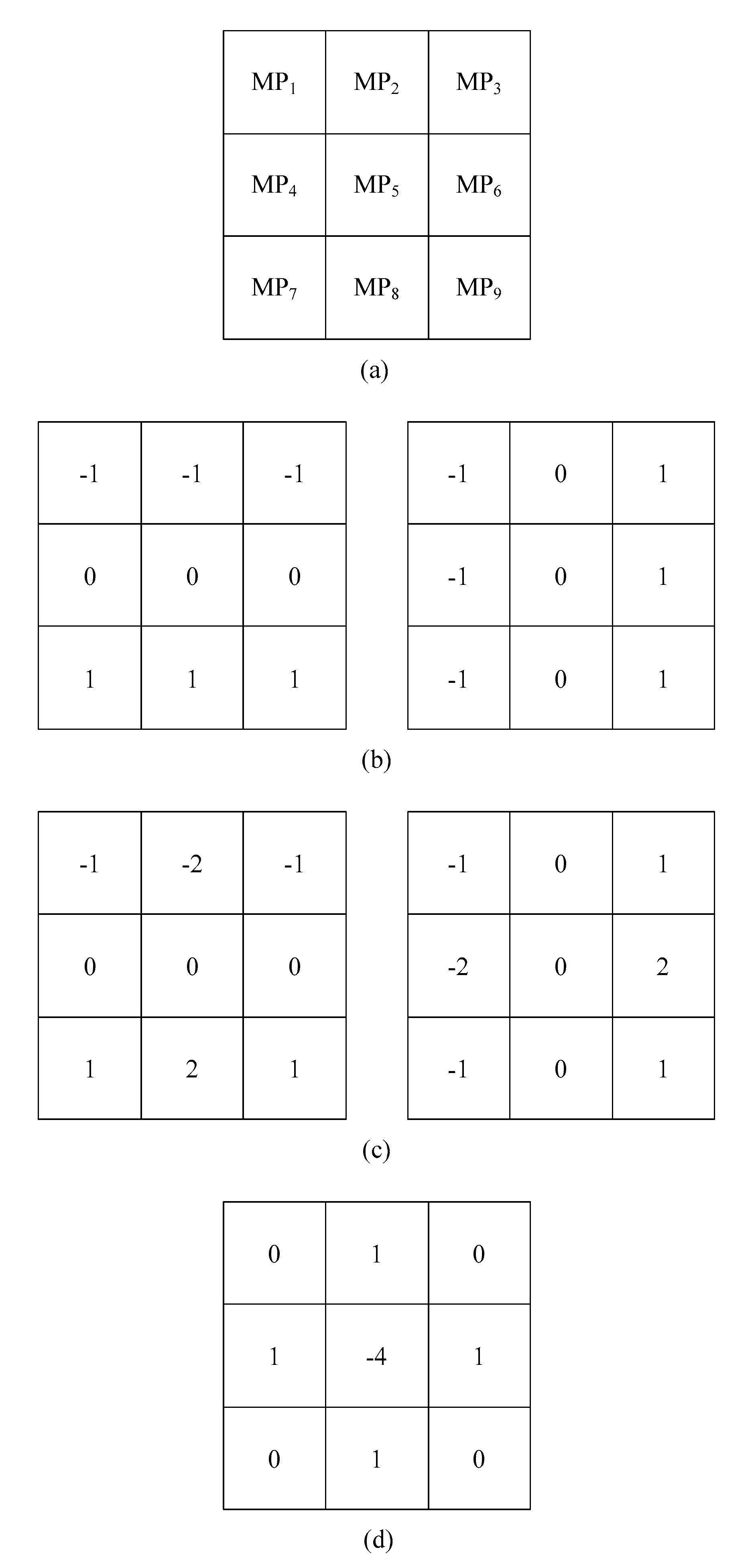
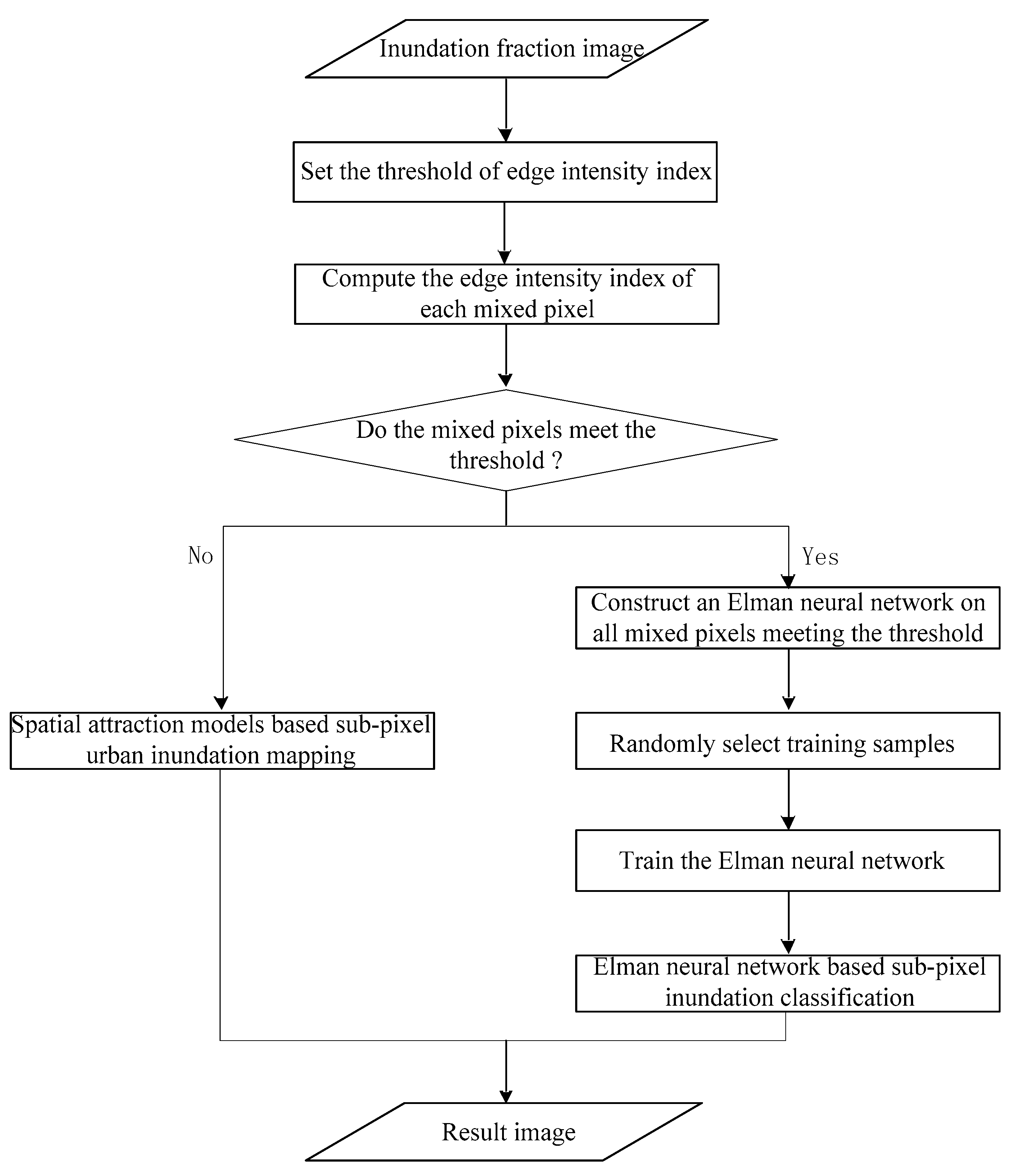
2. Methodology
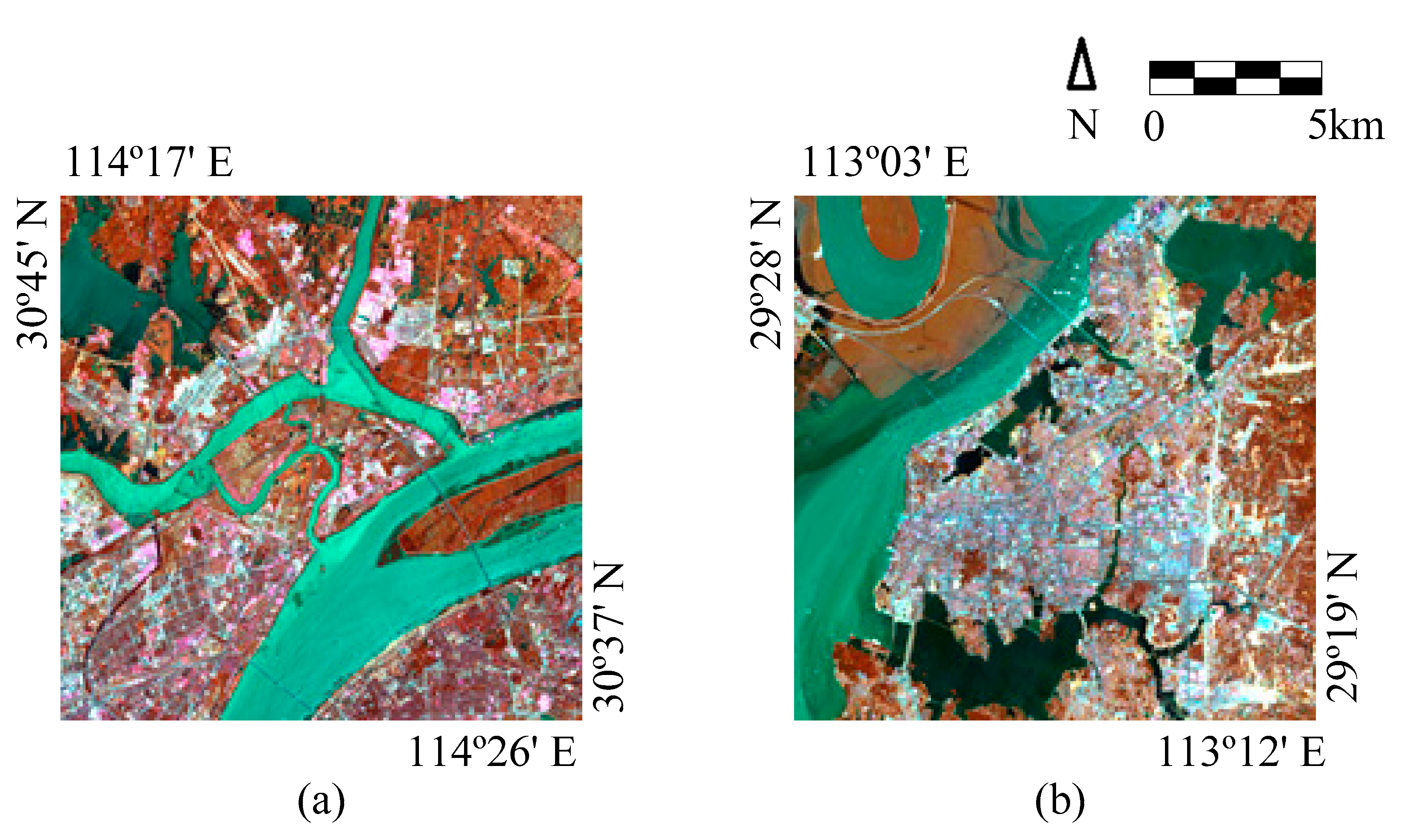
3. Case Study
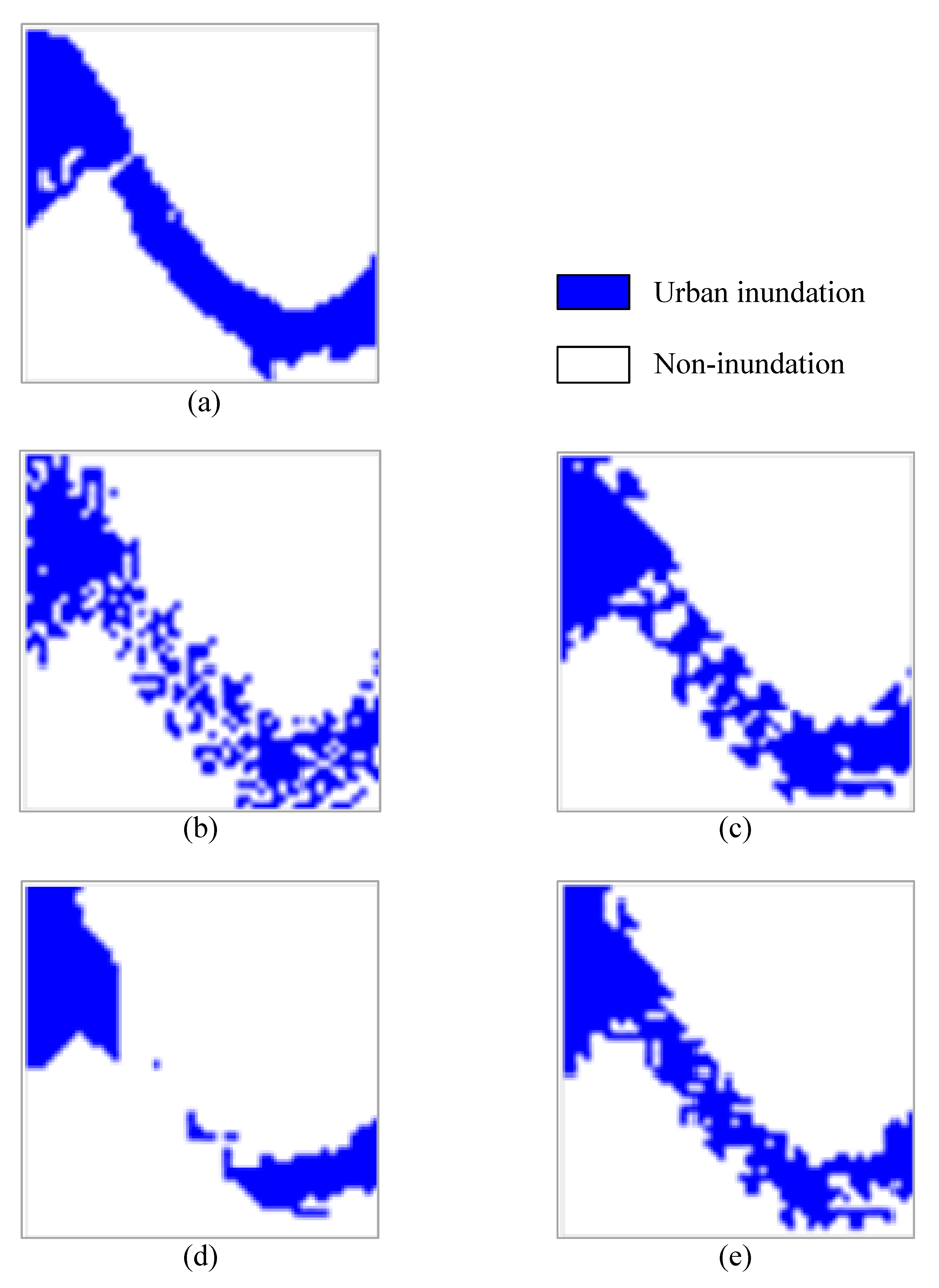
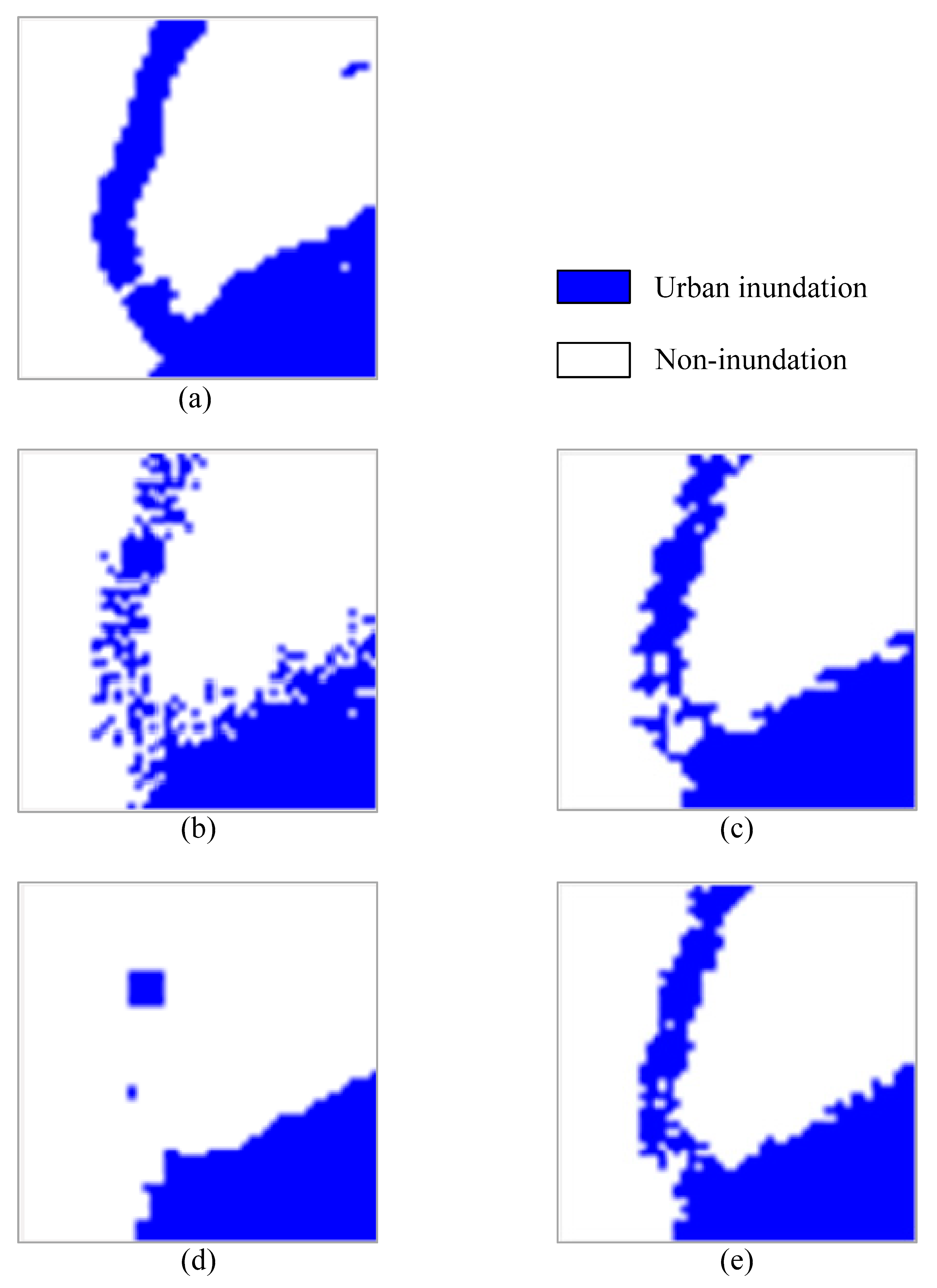
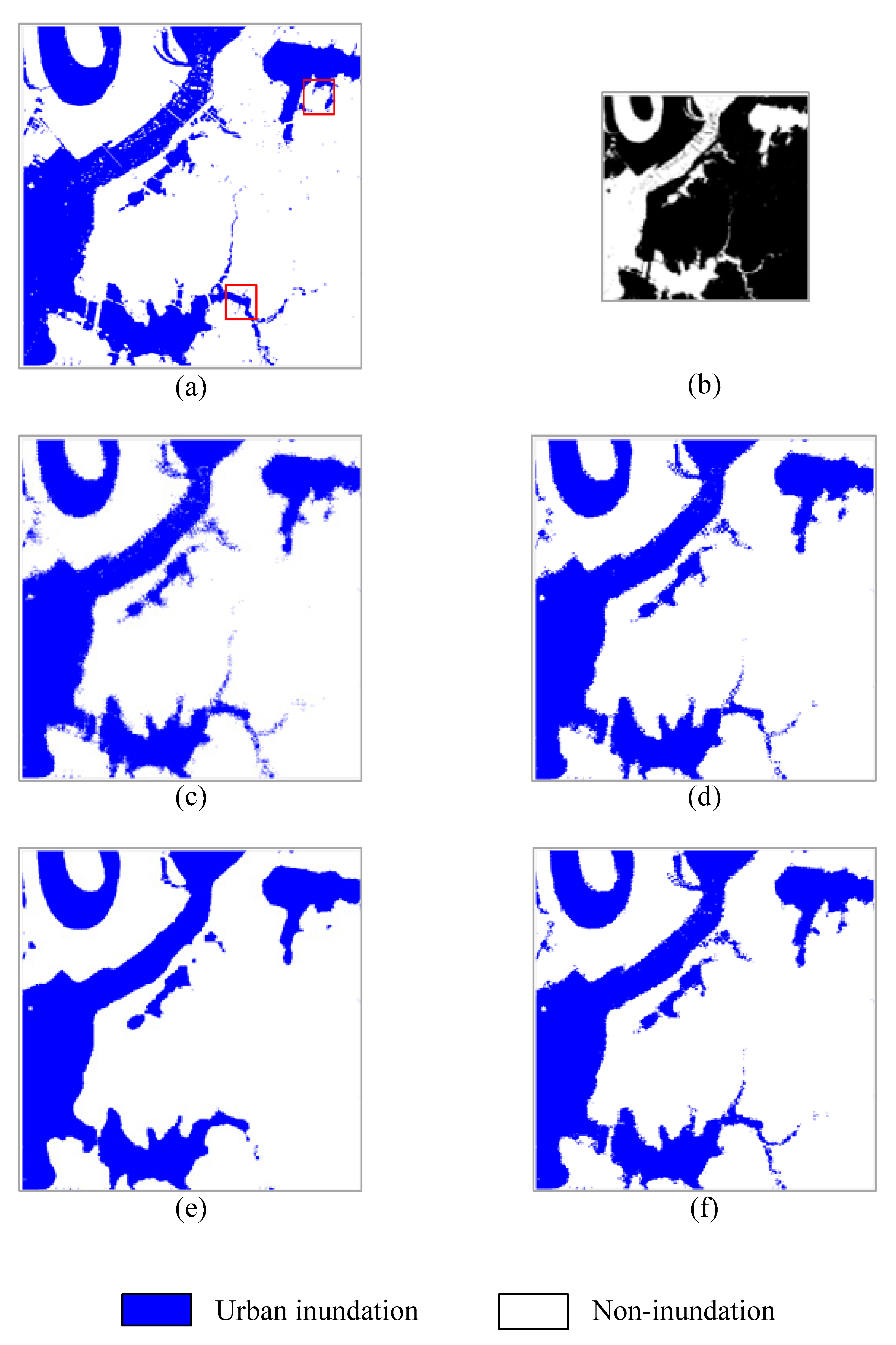
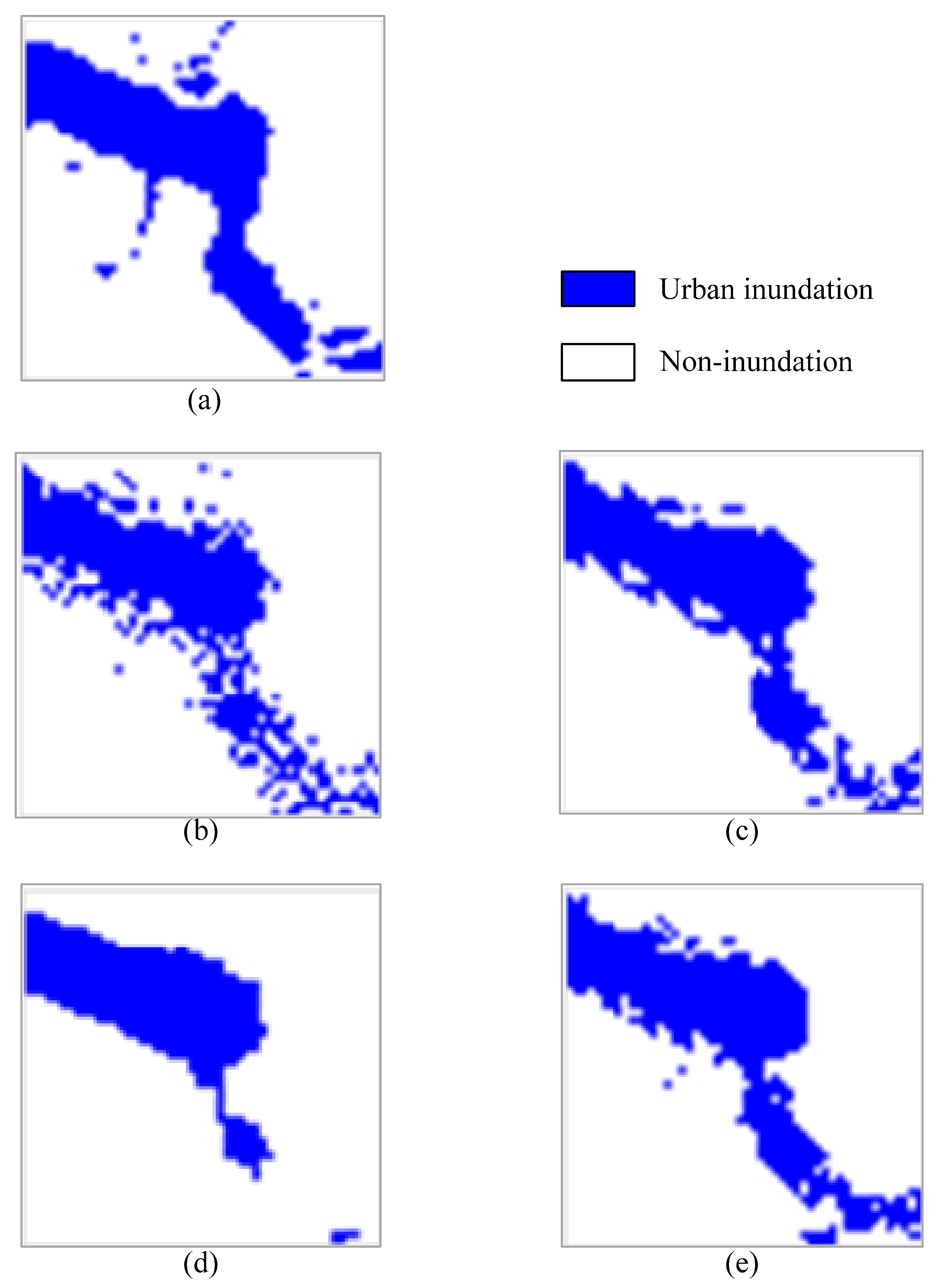
3.1. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.2. Summary
4. Discussion
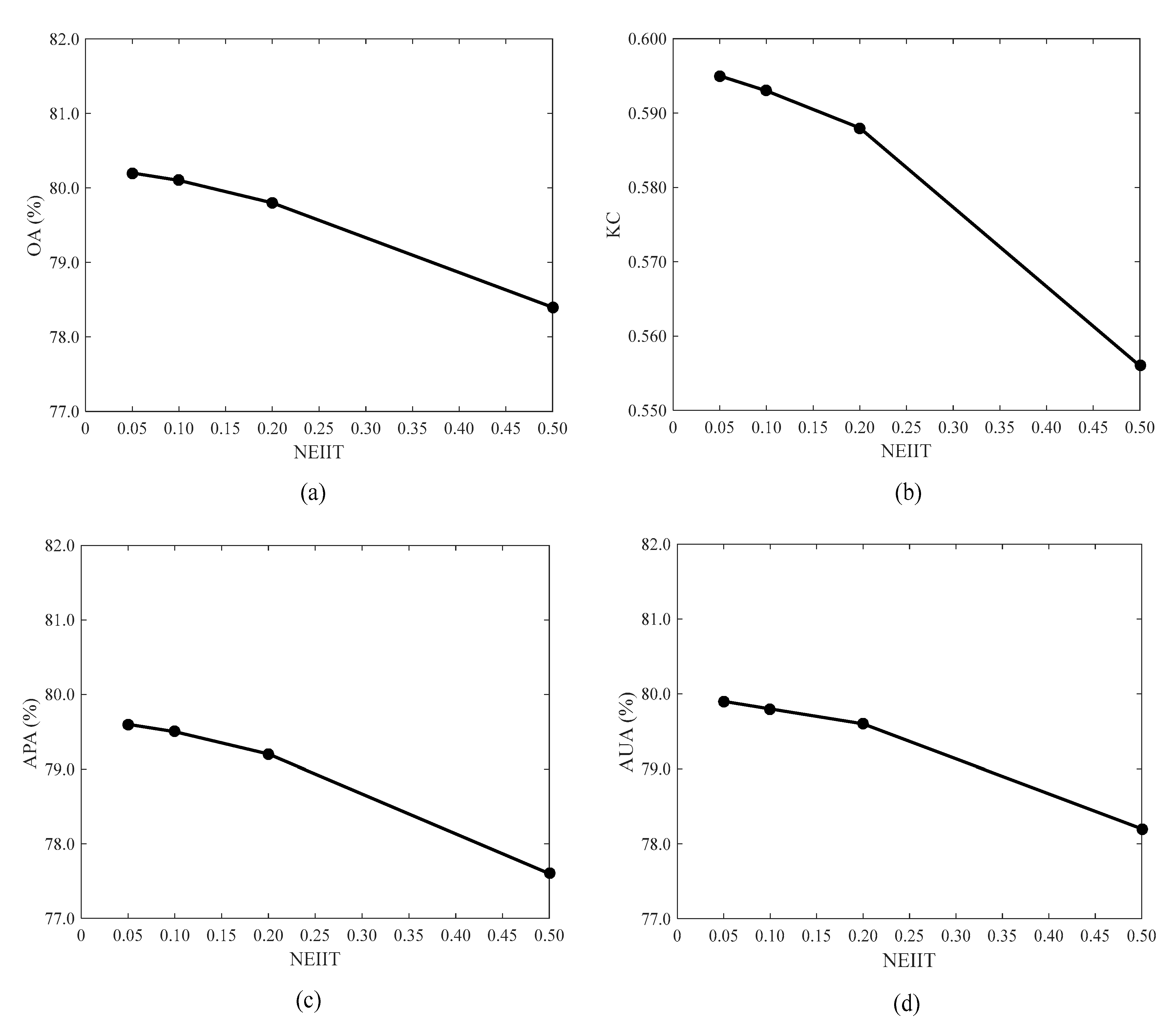
4.1. Effects of Normalized Edge Intensity Index (NEII) Threshold in Spatial Attraction Models and Elman Neural Network Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping (SAMENN-SUIM)
4.2. Repeated Tests
4.3. Effects of the Neuron Number of Hidden Layer in SAMENN-SUIM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Martinis, S.; Wieland, M. Urban flood mapping with an active self-learning convolutional neural network based on TerraSAR-X intensity and interferometric coherence. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertilsson, L.; Wiklund, K.; Tebaldi, I.D.; Rezende, O.M.; Verol, A.P.; Miguez, M.G. Urban flood resilience—A multi-criteria index to integrate flood resilience into urban planning. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; ten Veldhuis, M.C.; Schleiss, M.; Bouwens, C.; van de Giesen, N. Critical rainfall thresholds for urban pluvial flooding inferred from citizen observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Shafique, M.; Khattak, M.S. Flood hazard assessment and mapping of River Swat using HEC-RAS 2D model and high-resolution 12-m TanDEM-X DEM (WorldDEM). Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.; Teeuw, R. A methodology for urban micro-scale coastal flood vulnerability and risk assessment and mapping. Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeneghetti, A.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Tarpanelli, A. Preface: Remote sensing for flood mapping and monitoring of flood dynamics. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Song, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, B.; Xu, S.; Kong, F.; Jiang, X. Flood risk assessment and mapping based on a modified multi-parameter flood hazard index model in the Guanzhong Urban Area, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Di, L.; Tang, J.; Yu, E.; Zhang, C.; Rahman, M.S.; Shrestha, R.; Kang, L. Improvement and validation of NASA/MODIS NRT global flood mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, A.; Whaley, R.; Corston, K.; Kenny, F. Identifying historic river ice breakup timing using MODIS and Google Earth Engine in support of operational flood monitoring in Northern Ontario. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichet, N.; Kawamura, K.; Trong, D.P.; On, N.V.; Gong, Z.; Lim, J.; Khom, S.; Bunly, C. MODIS-Based investigation of flood areas in Southern Cambodia from 2002–2013. Environments 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genitha, C.H.; Vani, K. A hybrid approach to super-resolution mapping of remotely sensed multi-spectral satellite images using genetic algorithm and Hopfield neural network. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Hao, S.; Wang, L. Improving remote sensing image super-resolution mapping based on the spatial attraction model by utilizing the pansharpening technique. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Leung, H. Subpixel land cover mapping based on a new spatial attraction model with spatial-spectral information. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6444–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Foody, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Ling, F. Optimal endmember-based super-resolution land cover mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tong, X.; Plaza, A.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L. A new spectral-spatial sub-pixel mapping model for remotely sensed hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6763–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Liu, R.; Lu, B.; Meng, L. Enhanced super-resolution mapping of urban floods based on the fusion of support vector machine and general regression neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Integrating a scale-invariant feature of fractal geometry into the Hopfield neural network for super-resolution mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8933–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, P.V.; Herrmann, I.; Budhiraju, K.M.; Karnieli, A. Convolutional network architectures for super-resolution/sub-pixel mapping of drone-derived images. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 88, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H. An improved Elman neural network with piecewise weighted gradient for time series prediction. Neurocomputing 2019, 359, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Ren, W. Remaining useful life prediction of ultrasonic motor based on Elman neural network with improved particle swarm optimization. Measurement 2019, 143, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xia, L.; Wang, C. Maneuvering target tracking using simultaneous optimization and feedback learning algorithm based on Elman neural network. Sensors 2019, 19, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Lokesh, S.; Devi, M.R. An efficient Elman neural network classifier with cloud supported internet of things structure for health monitoring system. Comput. Netw. 2019, 151, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, S. A novel optimized GA-Elman neural network algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gong, S.; Han, G.; Wang, M.; Jin, A. Pruning Elman neural network and its application in bolt defects classification. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 1847–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks, Inc. Available online: https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/ (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Lu, K.; Hong, C.; Xu, Q. Recurrent wavelet-based Elman neural network with modified gravitational search algorithm control for integrated offshore wind and wave power generation systems. Energy 2019, 170, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.G.B.; Rueda, R.; Cuellar, M.P.; Pegalajar, M.C. Energy consumption forecasting based on Elman neural networks with evolutive optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 92, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hong, C. A new Elman neural network-based control algorithm for adjustable-pitch variable-speed wind-energy Conversion Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, S. Elman neural network optimized by firefly algorithm for forecasting China’s carbon dioxide emissions. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2019, 7, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, P.; Zhong, P. A hybrid model for real-time probabilistic flood forecasting using Elman neural network with heterogeneity of error distributions. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4027–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, J.; Pan, J. A digester temperature prediction model based on the Elman neural network. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2017, 33, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, J.; Rasekhi, J. Traffic signal prediction using Elman neural network and particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Eng. 2016, 29, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dhafian, B.; Ahmad, I.; Hussain, M.; Imran, M. Improving the security in healthcare information system through Elman neural network based classifier. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2017, 7, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, W.; Niu, H. Financial time series prediction using Elman recurrent random neural networks. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 4742515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASA. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/landsat/overview/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, R.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ge, Q. Continuous monitoring of lake dynamics on the Mongolian Plateau using all available Landsat imagery and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Huang, H.; Boschetti, L.; Giglio, L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, Z. Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 burned area mapping—A combined sensor multi-temporal change detection approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Ling, F.; Yue, L. Automatic semi-global artificial shoreline subpixel localization algorithm for landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zou, Z.; Hou, L.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Doughty, R.B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Mapping coastal wetlands of China using time series Landsat images in 2018 and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehman, S.V.; Foody, G.M. Key issues in rigorous accuracy assessment of land cover products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.; Chen, C.; Fang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y. Permanent disappearance and seasonal fluctuation of urban lake area in Wuhan, China monitored with long time series remotely sensed images from 1987 to 2016. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8484–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasanen, A.; Virtanen, T. Data and resolution requirements in mapping vegetation in spatially heterogeneous landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 111207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, D.C.; Chang, C. Fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Methods | Wuhan | Yueyang | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | KC | APA (%) | AUA (%) | OA (%) | KC | APA (%) | AUA (%) | |
| BPNN-SUIM | 72.9 | 0.446 | 72.2 | 72.5 | 72.8 | 0.455 | 72.7 | 72.9 |
| SVM-SUIM | 78.9 | 0.572 | 78.7 | 78.5 | 77.7 | 0.553 | 77.6 | 77.7 |
| SAM-SUIM | 78.3 | 0.553 | 77.3 | 78.2 | 77.2 | 0.543 | 77.1 | 77.5 |
| SAMENN-SUIM | 80.1 | 0.593 | 79.5 | 79.8 | 78.8 | 0.576 | 78.8 | 78.8 |
| Test | OA (%) | KC | APA (%) | AUA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 79.7 | 0.586 | 79.2 | 79.4 |
| 5 | 79.9 | 0.588 | 79.3 | 79.6 |
| 10 | 79.6 | 0.582 | 79.0 | 79.4 |
| 20 | 80.0 | 0.590 | 79.4 | 79.7 |
| Min | 79.6 | 0.582 | 79.0 | 79.4 |
| Max | 80.1 | 0.593 | 79.5 | 79.8 |
| Mean | 79.8 | 0.588 | 79.3 | 79.6 |
| SD | 0.135 | 0.003 | 0.167 | 0.139 |
| NN | OA (%) | KC | APA (%) | AUA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 79.7 | 0.586 | 79.2 | 79.4 |
| 25 | 80.1 | 0.593 | 79.5 | 79.8 |
| 50 | 79.9 | 0.589 | 79.3 | 79.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Meng, L.; Huang, C.; Shi, K. Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132068
Li L, Chen Y, Xu T, Meng L, Huang C, Shi K. Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(13):2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132068
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Linyi, Yun Chen, Tingbao Xu, Lingkui Meng, Chang Huang, and Kaifang Shi. 2020. "Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping" Remote Sensing 12, no. 13: 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132068
APA StyleLi, L., Chen, Y., Xu, T., Meng, L., Huang, C., & Shi, K. (2020). Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping. Remote Sensing, 12(13), 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12132068











