Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example from a Red Soil from Israel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Samples and Laboratory Measurements
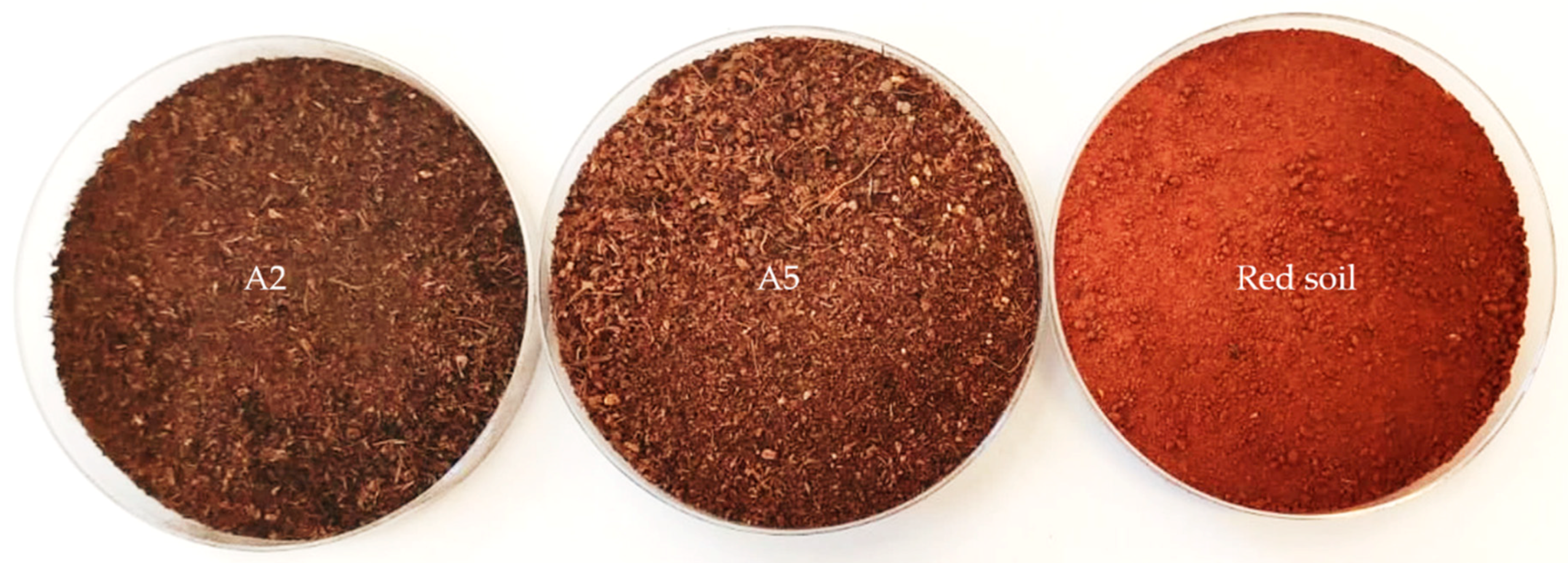
2.2. Artificial Sample Preparation I–Real OM–Soil Mixture (Authentic)
2.3. Spectral Measurements
2.4. Artificial Sample Preparation II–Spectral OM–Soil Mixture (Synthetic)
3. Results
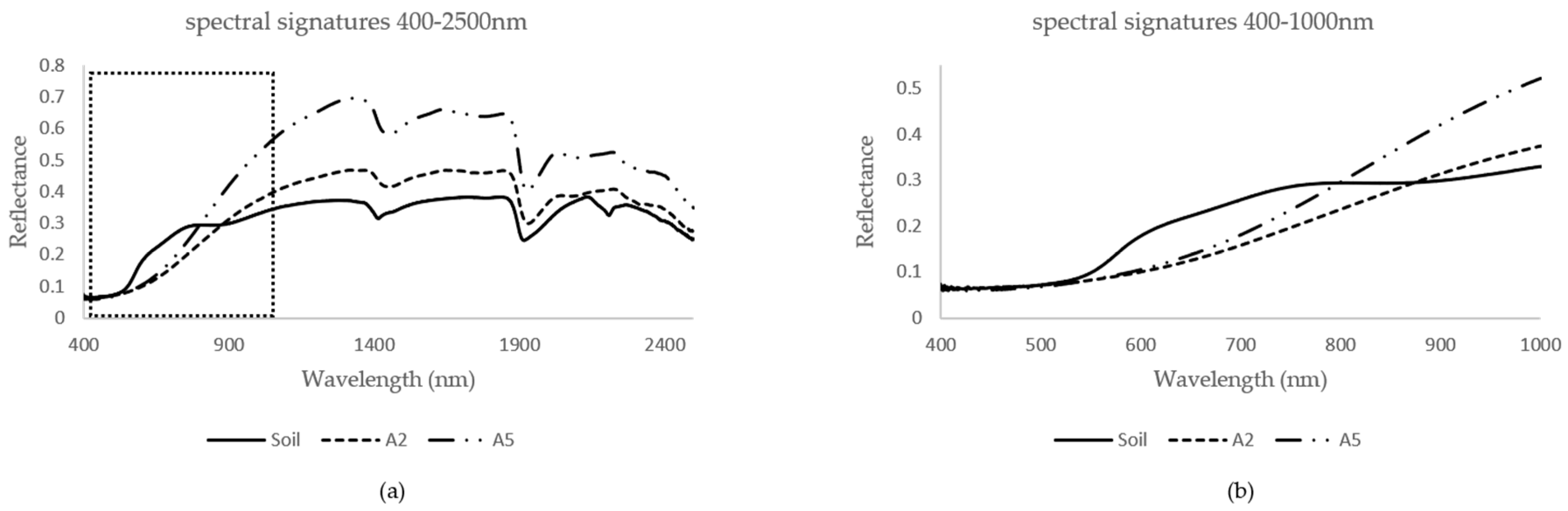
3.1. Pure Spectral Signatures of the OM and the Soil
3.2. Mixed Spectral Signatures: First Observation
3.3. Quantitative Effect of SOM Species on Iron-Oxide Spectral Features
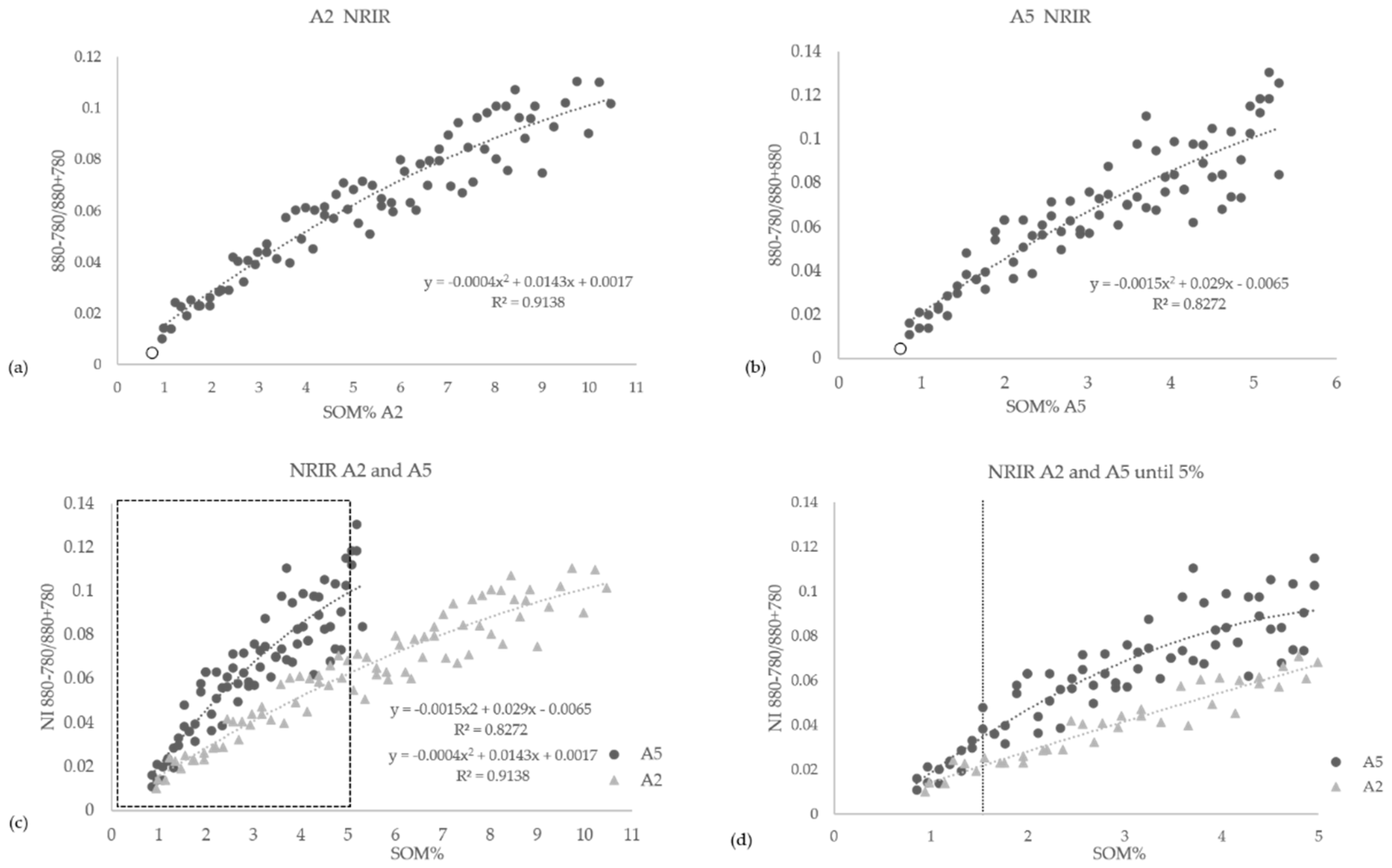
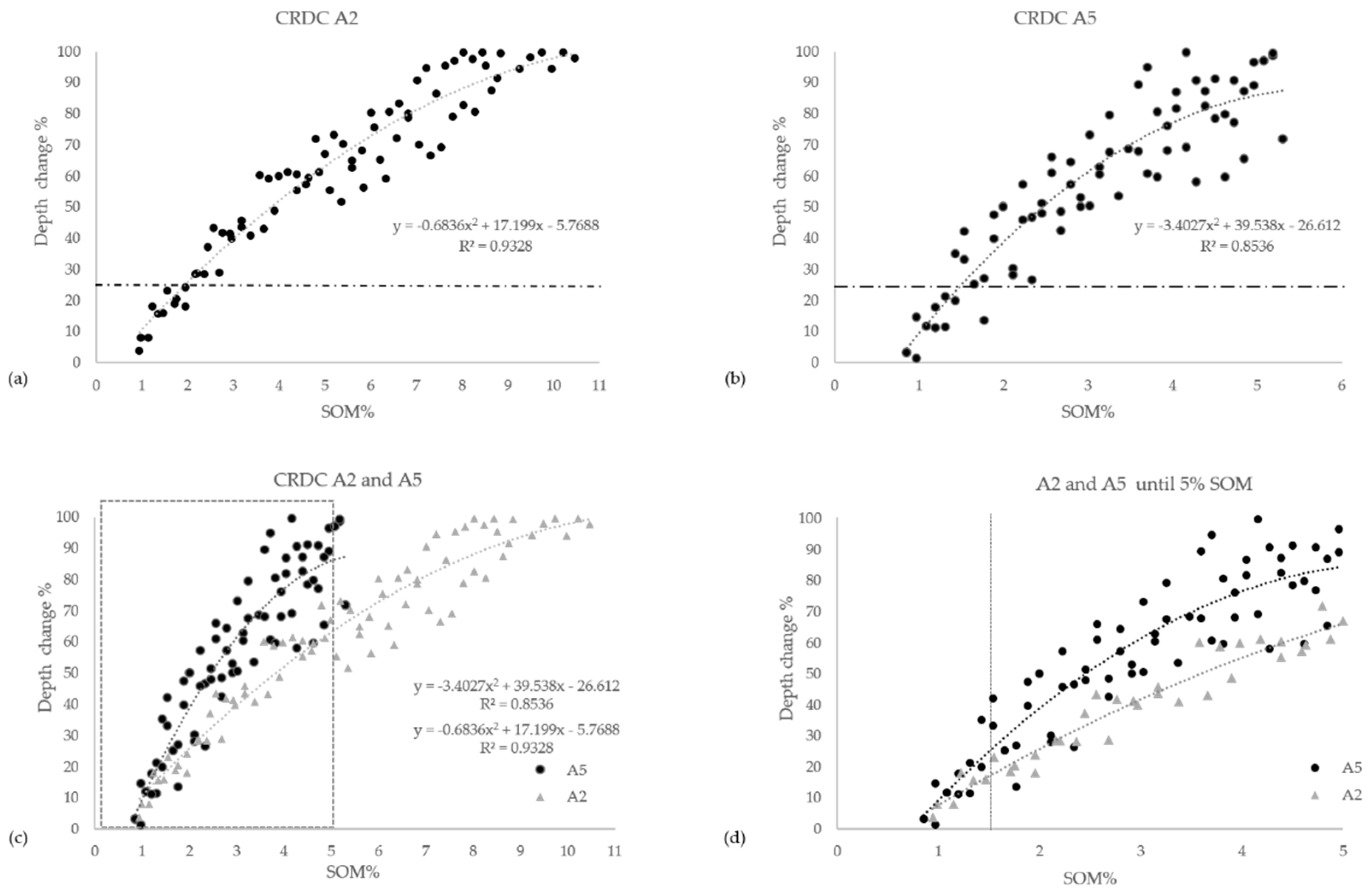
3.4. Iron-Oxide Indices and OM Effects with Increasing SOM Content
- (a)
- The spectral change at the maximum depth after CR at 880 nm by calculating the CR Depth Change (CRDC) according to:where Dpo is the original soil spectral depth [41] at 880 nm after applying the CR from 800–1000 nm, and Dps is the soil–OM mixture’s spectral depth at the same position with the same spectral manipulation.%CRDC = ((Dpo − Dps)/(Dpo))*100
- (b)
- The NRIR (Normalized Red Index Ratio) using wavelengths 880 nm and 780 nm, according to the equation:where R(880) and R(780) are the original reflectance values at these wavelengths for any given soil–OM mixture status. The masking effect of OM on the iron-oxide indices NRIR and CRDC was applied to all 160 mixture samples. The results are presented in Figure 6 and Figure 7.NRIR = (R(880) − R(780))/(R(880) + R(780))
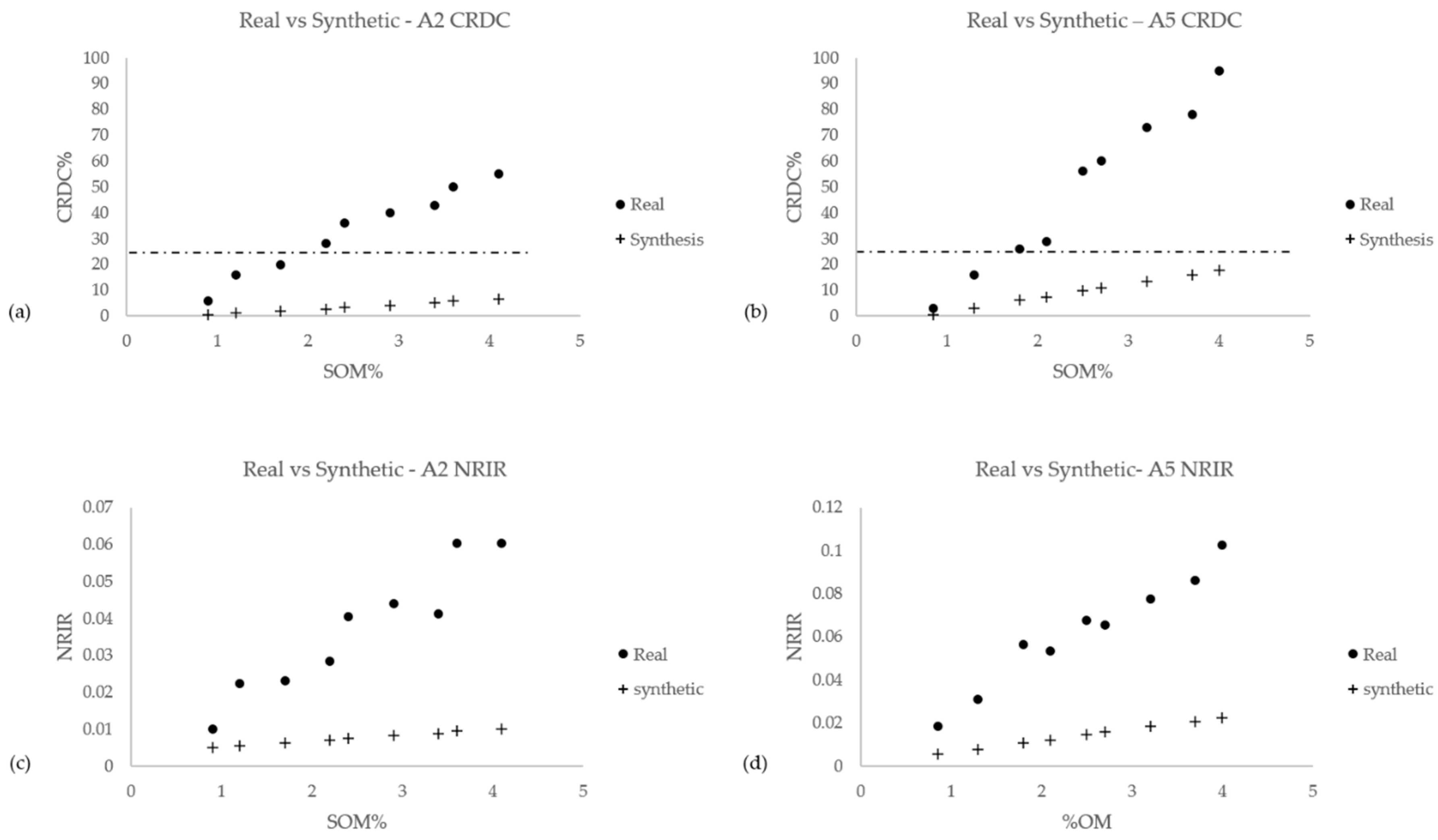
3.5. Artificial Soil–OM Mixtures: “Synthetic” Versus “Authentic”
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sukhdev Kayande, K.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Vinod Janse, P.; Kayte, J.N.; Ambedkar, B. Hyper spectral analysis of soil iron oxide using PLSR method: A review. Int. J. Future Rev. Comp. Sci. Commun. Eng. 2018, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Barrón, V.; Torrent, J. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of iron oxides. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1438–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Genú, A.M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Determination of soil attribute contents by means of reflected electromagnetic energy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4807–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E. Quantitative remote sensing of soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2002, 75, 173–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Levin, N.; Singer, A.; Karnieli, A.; Braun, O.; Kidron, G.J. Quantitative mapping of the soil rubification process on sand dunes using an airborne hyperspectral sensor. Geoderma 2006, 131, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W.; Lenhoff, A. Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: III Oxides and hydroxides. Mod. Geol. 1971, 2, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Stucki, J.W.; Bernard, A.; Goodman, U.S. Iron in Soils and Clay Minerals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arduino, E.; Barberis, E.; Ajmone Marsan, F.; Zanini, E.; Franchini, M. Iron oxides and clay minerals within profiles as indicators of soil age in Northern Italy. Geoderma 1986, 37, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA’s Earth Observing System. Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EVI-4) (EMIT on ISS). Available online: https://eospso.gsfc.nasa.gov/missions/earth-surface-mineral-dust-source-investigation-evi-4 (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Sørensen, L.K.; Dalsgaard, S. Determination of clay and other soil properties by near infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, H.L.; Cunningham, R.L.; Peterson, G.W. Spectral reflectance of selected Pennsylvania soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, M.F.; Kristof, S.J.; Johannsen, C.J.; Zachary, A.L. Effects of organic matter on the multispectral properties of soils. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1970, 79, 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, R.H.; Robinson, B.F.; McFee, W.H.; Peterson, J.B. Spectral Characteristics of Soils Related to the Interaction of Soil Moisture, Organic Carbon and Clay Content; LARS Information Note 081176; Laboratory Application of Remote Sensing, Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Karmanova, L.A. Effect of various iron compounds on the spectral reflectance and color of soils. Sov. Soil Sci. 1981, 13, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, E.R.; Baumgardner, M.F. Characteristic variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, T.L.; Baumgardner, M.F.; Franzmeier, D.P.; Stott, D.E.; Coster, D.C. High dimensional reflectance analysis of soil organic matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Tehrens, B. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Laboratory assessment of three quantitative methods for estimating the organic matter content of soils in China based on visible/near-infrared reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, J.; Bedidi, A.; Cervelle, B.; Pouget, M.; Flay, N. Visible spectrometric indices of hematite (Hm) and goethite (Gt) content in lateritic soils: The application of a Thematic Mapper (TM) image for soil-mapping in Brasilia, Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2835–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, X.; Peng, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Han, L.; Li, Y. Prediction of soil organic matter content in a litchi orchard of South China using spectral indices. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 123, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, Z.; Ji, W.; Wang, J. Influence of iron oxide on the spectral characteristics of organic matter. J. Remote Sens. (Yaogan Xuebao) 2013, 17, 1396–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, X. Removing the effects of iron oxides from Vis-NIR spectra for soil organic matter prediction. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.; Chabrillat, S.; Kaufmann, H.; Gfz, G.P.; Sensing, S.R. Preliminary analysis for soil organic carbon determination from spectral reflectance in the frame of the EU project DeSurvey. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation in the Assessment of Land Degradation and Desertification, Trier, Germany, 7–9 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Stuff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Galvao, L.S.; Vitorello, I. Role of organic matter in obliterating the effects of iron on spectral reflectance and colour of Brazilian tropical soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Inbar, Y.; Chen, Y. The reflectance spectra of organic matter in the visible near infrared and short-wave infrared region (400–2500 nm) during a control decomposition process. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmon, N.; Ben-Dor, E. An advanced analytical approach for spectral—Based modelling of soil properties. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2017, 7, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, O.P. Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clays Clay Miner. 1958, 7, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Banin, A. Determination of organic matter content in arid-zone soils using a simple “loss-on-ignition” method. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1989, 20, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining organic carbon in soils: Effect of variations in digestion conditions and of inorganic soil constituents. Soil Sci. 1934, 63, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogen, Y.; Neumann, C.; Chabrillat, S.; Goldshleger, N.; ben Dor, E. Evaluating the detection limit of organic matter using point and imaging spectroscopy. Geoderma 2018, 321, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Dor, E.; Ong, C.; Lau, I.C. Reflectance measurements of soils in the laboratory: Standards and protocols. Geoderma 2015, 245–246, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). USGS High Resolution Spectral Library. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/energy-and-minerals/mineral-resources-program/science/usgs-high-resolution-spectral-library?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- European Soil Data Centre (ESDAC). LUCAS: Land Use and Coverage Area frame Survey. Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/projects/lucas (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E. Spectral mixture modeling: A new analysis of rock and soil types at the Viking Lander 1 Site. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settle, J.J.; Drake, N.A. Linear mixing and the estimation of ground cover proportions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Haro, F.J.; Gilabert, M.A.; Meliá, J. Linear spectral mixture modelling to estimate vegetation amount from optical spectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 3373–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Escadafal, R. Assessment of biophysical soil properties through spectral decomposition techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladoni, M.; Bahrami, H.A.; Alavipanah, S.K.; Norouzi, A.A. Estimating soil organic carbon from soil reflectance: A review. Precis. Agric. 2010, 11, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Roush, T.L. Reflectance spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 6329–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N. Spectroscopy of Rocks and Minerals, and Principles of Spectroscopy; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeus, H.M.; Schaepman, M.E.; Kooistra, L.; Stevens, A.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; Spaargaren, O.S.P. Spectral reflectance-based indices for soil organic carbon quantification. Geoderma 2008, 145, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kissel, D.E.; West, L.T.; Adkins, W. Field-scale mapping of surface soil organic carbon using remotely sensed imagery. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, K.W.; Tripathi, N.K.; Honda, K.; Apisit, E. Analysis of vnir (400–1100 nm) spectral signatures for estimation of soil organic matter in tropical soils of Thailand. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhu, X.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Y. Spectroscopy-Based Soil Organic Matter Estimation in Brown Forest Soil Areas of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boul, S.W.; Southard, R.J.; Graham, R.C.; McDaniel, P.A. Soil Genesis and Classification; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hapke, B. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 3039–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Soil% | OM% | OM Added (g) | SOM% for Soil–A2 [(OM*0.81)+0.74] | SOM% for Soil–A5 [(OM*0.38)+0.74] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.7 | 0.3 | 0.105 | 0.98 | 0.85 |
| 2 | 99.4 | 0.6 | 0.210 | 1.23 | 0.97 |
| 3 | 99.1 | 0.9 | 0.315 | 1.47 | 1.08 |
| 4 | 98.8 | 1.2 | 0.420 | 1.71 | 1.20 |
| 5 | 98.5 | 1.5 | 0.525 | 1.96 | 1.31 |
| 6 | 98.2 | 1.8 | 0.630 | 2.20 | 1.42 |
| 7 | 97.9 | 2.1 | 0.735 | 2.44 | 1.54 |
| 8 | 97.6 | 2.4 | 0.840 | 2.68 | 1.65 |
| 9 | 97.3 | 2.7 | 0.945 | 2.93 | 1.77 |
| 10 | 97.0 | 3.0 | 1.050 | 3.17 | 1.88 |
| 11 | 96.7 | 3.3 | 1.155 | 3.41 | 1.99 |
| 12 | 96.4 | 3.6 | 1.260 | 3.66 | 2.11 |
| 13 | 96.1 | 3.9 | 1.365 | 3.90 | 2.22 |
| 14 | 95.8 | 4.2 | 1.470 | 4.14 | 2.34 |
| 15 | 95.5 | 4.5 | 1.575 | 4.39 | 2.45 |
| 16 | 95.2 | 4.8 | 1.680 | 4.63 | 2.56 |
| 17 | 94.9 | 5.1 | 1.785 | 4.87 | 2.68 |
| 18 | 94.6 | 5.4 | 1.890 | 5.11 | 2.79 |
| 19 | 94.3 | 5.7 | 1.995 | 5.36 | 2.91 |
| 20 | 94.0 | 6.0 | 2.100 | 5.60 | 3.02 |
| 21 | 93.7 | 6.3 | 2.205 | 5.84 | 3.13 |
| 22 | 93.4 | 6.6 | 2.310 | 6.09 | 3.25 |
| 23 | 93.1 | 6.9 | 2.415 | 6.33 | 3.36 |
| 24 | 92.8 | 7.2 | 2.520 | 6.57 | 3.48 |
| 25 | 92.5 | 7.5 | 2.625 | 6.82 | 3.59 |
| 26 | 92.2 | 7.8 | 2.730 | 7.06 | 3.70 |
| 27 | 91.9 | 8.1 | 2.835 | 7.30 | 3.82 |
| 28 | 91.6 | 8.4 | 2.940 | 7.54 | 3.93 |
| 29 | 91.3 | 8.7 | 3.045 | 7.79 | 4.05 |
| 30 | 91.0 | 9.0 | 3.150 | 8.03 | 4.16 |
| 31 | 90.7 | 9.3 | 3.255 | 8.27 | 4.27 |
| 32 | 90.4 | 9.6 | 3.360 | 8.52 | 4.39 |
| 33 | 90.1 | 9.9 | 3.465 | 8.76 | 4.50 |
| 34 | 89.8 | 10.2 | 3.570 | 9.00 | 4.62 |
| 35 | 89.5 | 10.5 | 3.675 | 9.25 | 4.73 |
| 36 | 89.2 | 10.8 | 3.780 | 9.49 | 4.84 |
| 37 | 88.9 | 11.1 | 3.885 | 9.73 | 4.96 |
| 38 | 88.6 | 11.4 | 3.990 | 9.97 | 5.07 |
| 39 | 88.3 | 11.7 | 4.095 | 10.22 | 5.19 |
| 40 | 88.0 | 12.0 | 4.200 | 10.46 | 5.30 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heller Pearlshtien, D.; Ben-Dor, E. Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example from a Red Soil from Israel. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121960
Heller Pearlshtien D, Ben-Dor E. Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example from a Red Soil from Israel. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(12):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121960
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeller Pearlshtien, Daniela, and Eyal Ben-Dor. 2020. "Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example from a Red Soil from Israel" Remote Sensing 12, no. 12: 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121960
APA StyleHeller Pearlshtien, D., & Ben-Dor, E. (2020). Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example from a Red Soil from Israel. Remote Sensing, 12(12), 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12121960







