Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
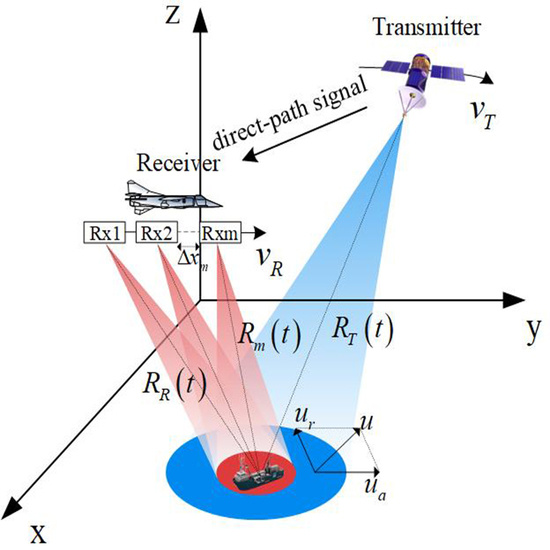
2. Geometry and Azimuth Signal Model for Moving Targets in GEO-SA-BiSAR
2.1. Geometry and Slant Range
2.2. Azimuth Multichannel Response Model
2.3. Doppler Bandwidth and PRF Analysis
3. Effects of the Target Velocity on Imaging Results
3.1. Effects on the Azimuth Multichannel Response
3.2. Effects on Imaging Results
4. Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction
4.1. Azimuth Doppler Spectrum Reconstruction
4.2. Moving Target Velocity Estimation
4.3. Moving Target Imaging in GEO-SA-BiSAR
5. Simulation Experiment
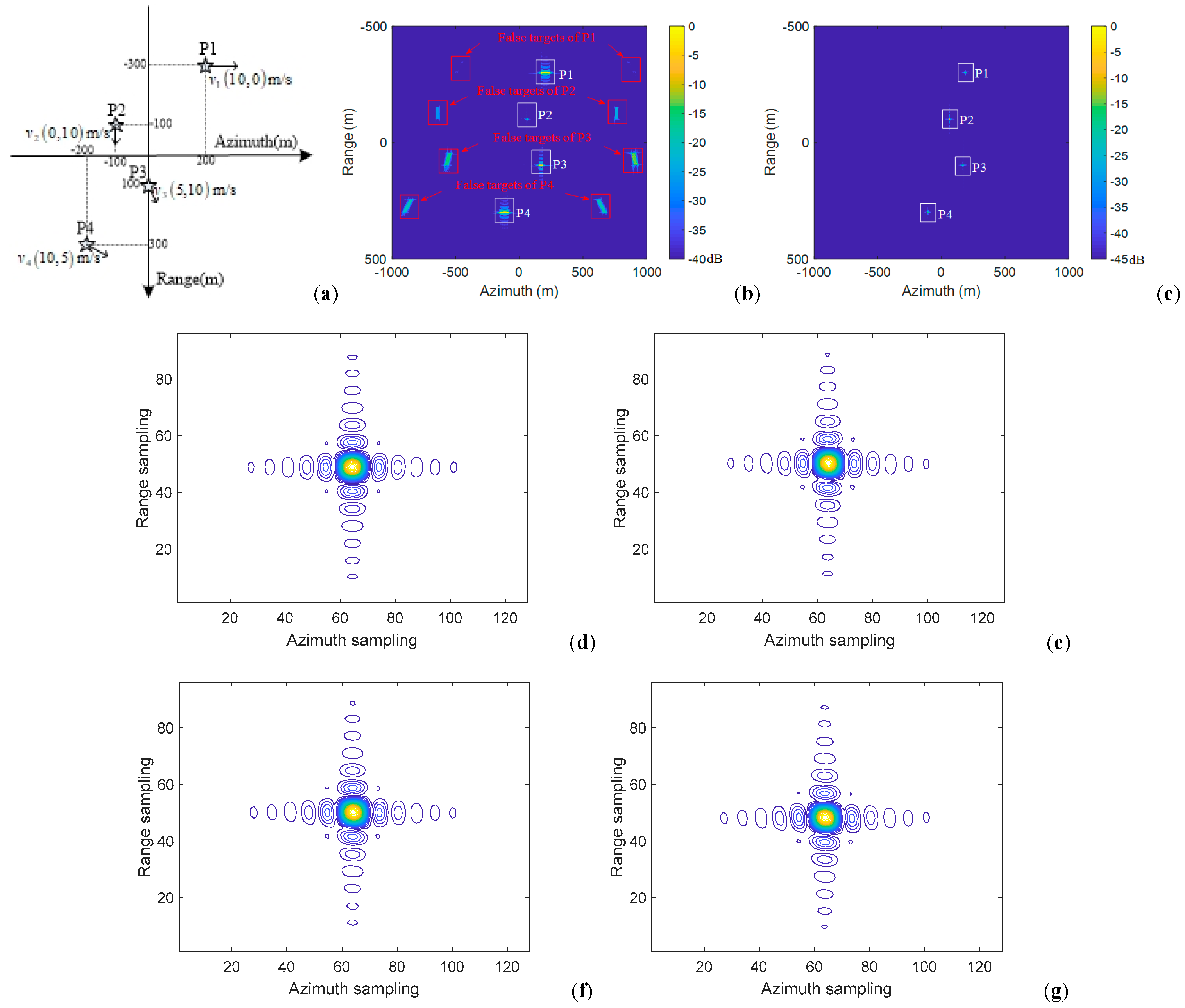
5.1. Simulation on Point Targets
5.2. Simulation of Distributed Targets
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyasu, K. Synthetic aperture radar in geosynchronous orbit. In Proceedings of the 1978 Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 15–19 March 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyasu, K. Conceptual Performance of a Satellite Borne, Wide Swath Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1981, 2, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyasu, K. Tutorial review of synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) with applications to imaging of the ocean surface. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyasu, K.; Pacelli, J.L. Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging from an Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, 21, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I. Tandem-L: A Highly Innovative Bistatic SAR Mission for Global Observation of Dynamic Processes on the Earth’s Surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Long, T.; Zeng, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z. The Accurate Focusing and Resolution Analysis Method in Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3548–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.; Mitchell, C.; Forte, B.; Holley, R.; Snapir, B.; Whittaker, P. System Design for Geosynchronous Synthetic Aperture Radar Missions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7750–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Pei, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. Inclined Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR: Performance Analysis and Mission Design. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ge, J. Resolution Calculation and Analysis in Bistatic SAR With Geostationary Illuminator. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wu, J.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, J. Geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Multichannel Bistatic SAR Imaging Using Weighted Fast Factorized Backprojection Method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Suo, Z.; Fang, C.; Chen, J. High-Resolution Wide-Swath Imaging of Spaceborne Multichannel Bistatic SAR with Inclined Geosynchronous Illuminator. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2380–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Z.; An, H.; Qu, J.; Yang, J. Azimuth Signal Multichannel Reconstruction and Channel ConFigureuration Design for Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Dekker, P.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Serra-Morales, P.; Sanz-Marcos, J. Phase Synchronization and Doppler Centroid Estimation in Fixed Receiver Bistatic SAR Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Hu, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, W.; Zhu, M.; Long, T. Extended NLCS Algorithm of BiSAR Systems With a Squinted Transmitter and a Fixed Receiver: Theory and Experimental Confirmation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 5019–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, A.; Cacoveanu, R.; Moldovan, A.; Rommen, B.; Datcu, M. COBIS: Opportunistic C-Band Bistatic SAR Differential Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3980–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G. Simultaneous High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR Imaging and Ground Moving Target Indication: Processing Approaches and System Concepts. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5015–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, N.; Krieger, G. Azimuth Phase Center Adaptation on Transmit for High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Li, S.; Xu, W. Investigation on Full-Aperture Multichannel Azimuth Data Processing in TOPS. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y. Processing of Multichannel Sliding Spotlight and TOPS Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4417–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Tan, W. Azimuth Phase Coding by Up and Down Chirp Modulation for Range Ambiguity Suppression. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143780–143791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Hu, J.; Huang, P.; Tan, W.; Dong, Y. Azimuth Phase Center Adaptive Adjustment upon Reception for High-Resolution Wide-Swath Imaging. Sensors 2019, 19, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J. A Two-Step Nonlinear Chirp Scaling Method for Multichannel GEO Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR Spectrum Reconstructing and Focusing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3713–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Huang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Han, K. Investigation of Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in High Resolution Wide Swath SAR. Sensors 2017, 17, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Yi, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Bao, Y. Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR Ground Moving Target Detection and Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qi, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Song, H. Accurate fourth-order doppler parameter estimation approach for geosynchronous SAR. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2012; 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 24–26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Rodon, J.; Broquetas, A.; Makhoul, E.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F. Nearly Zero Inclination Geosynchronous SAR Mission Analysis With Long Integration Time for Earth Observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Shu, B.; Yin, W.; Zeng, T.; Long, T. A Modified Frequency Domain Algorithm Based on Optimal Azimuth Quadratic Factor Compensation for Geosynchronous SAR Imaging. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, A. Generalized sampling expansion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1977, 24, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, N.; Villano, M.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Multichannel Azimuth Processing in ScanSAR and TOPS Mode Operation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.H. Focusing Bistatic Forward-Looking SAR With Stationary Transmitter Based on Keystone Transform and Nonlinear Chirp Scaling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, T.K.; Viet, T.V.; Pettersson, M.I. Suppression of Clutter in Multichannel SAR GMTI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. The Clutter Suppression Method of Airborne Multi-channel SAR-GMTI System. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2011, 30, 2831–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-X.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.-G.; Guo, R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Bao, Z. Robust Clutter Suppression and Moving Target Imaging Approach for Multichannel in Azimuth High-Resolution and Wide-Swath Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 687–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-B.; Liu, G.-S.; Gu, H.; Su, W.-M. Application of the fractional Fourier transform to moving target detection in airborne SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Keystone Transform Without Interpolation for SAR Ground Moving-Target Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Center frequency | 1.25 GHz |
| PRF | 180 Hz |
| Pulse bandwidth | 50 MHz |
| Integration time | 4.5 s |
| Eccentricity | 0 |
| Inclination | 60° |
| Right ascension of ascending node | 195.5° |
| Argument of perigee | 270° |
| Off nadir angle | 7° |
| Receiver height | 3 km |
| Slant range to scene center | 5 km |
| Receiver velocity | 300 m/s |
| Receiving channels | 3 |
| Receive sub-aperture length | 0.8 m |
| SCNR(dB) | −50 | −40 | −30 | −20 | −10 | 0 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRF = 170 Hz | Estimated velocity (m/s) | 14.93 | 13.37 | 12.39 | 10.85 | 10.42 | 10.33 | 10.23 |
| Deviation (m/s) | 4.93 | 3.37 | 2.39 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.23 | |
| Relative error | 49.3% | 33.7% | 23.9% | 8.5% | 4.2% | 3.3% | 2.3% | |
| PRF = 180 Hz | Estimated velocity (m/s) | 14.95 | 14.32 | 11.33 | 10.59 | 10.19 | 10.12 | 10.12 |
| Deviation (m/s) | 4.95 | 4.32 | 1.33 | 0.59 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |
| Relative error | 49.5% | 43.2% | 13.3% | 5.9% | 1.9% | 1.2% | 1.2% | |
| PRF = 190 Hz | Estimated velocity (m/s) | 15.68 | 5.27 | 8.01 | 10.73 | 10.12 | 10.11 | 10.04 |
| Deviation (m/s) | 5.68 | 4.73 | 1.99 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.04 | |
| Relative error | 56.8% | 47.3% | 19.9% | 7.3% | 1.2% | 1.1% | 0.4% | |
| Target Index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity (m/s) | −14 | −11 | −8 | −5 | −2 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 |
| Estimated velocity (m/s) | −14.19 | −11.11 | −7.91 | −5.12 | −1.89 | 1.15 | 4.15 | 7.11 | 10.17 | 13.14 |
| Deviation (m/s) | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.14 |
| Relative error | 1.4% | 1.0% | 1.1% | 2.4% | 5.5% | 15% | 3.7% | 1.5% | 1.7% | 1.1% |
| Method | Target | Azimuth | Range | MFTA (dB) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res(m) | PSLR(dB) | ISLR(dB) | Res(m) | PSLR(dB) | ISLR(dB) | |||
| Conventional | P1 | 59.55 | −26.30 | −26.37 | 2.64 | −13.01 | −9.77 | −44.43 |
| P2 | 1.06 | −11.26 | −7.65 | 2.70 | −13.46 | −10.19 | −21.95 | |
| P3 | 8.77 | −7.94 | −10.58 | 2.68 | −12.78 | −9.32 | −20.82 | |
| P4 | 17.99 | −5.10 | −4.15 | 2.66 | −13.25 | −9.86 | −25.04 | |
| Proposed | P1 | 0.83 | −13.25 | −10.01 | 2.64 | −13.22 | −9.92 | −68.89 |
| P2 | 0.80 | −13.07 | −10.14 | 2.69 | −13.48 | −10.19 | −56.68 | |
| P3 | 0.81 | −13.11 | −10.11 | 2.68 | −13.42 | −10.15 | −52.42 | |
| P4 | 0.83 | −13.26 | −10.09 | 2.67 | −13.34 | −10.07 | −47.56 | |
| Theoretical value | P1 | 0.81 | −13.26 | −9.80 | 2.66 | −13.26 | −9.80 | -- |
| P2 | 0.79 | −13.26 | −9.80 | 2.66 | −13.26 | −9.80 | -- | |
| P3 | 0.80 | −13.26 | −9.80 | 2.66 | −13.26 | −9.80 | -- | |
| P4 | 0.81 | −13.26 | −9.80 | 2.66 | −13.26 | −9.80 | -- | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Wei, Z.; Huang, P.; Tan, W.; Liu, B.; Gao, Z.; Dong, Y. Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111703
Xu W, Wei Z, Huang P, Tan W, Liu B, Gao Z, Dong Y. Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(11):1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111703
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wei, Zhengbin Wei, Pingping Huang, Weixian Tan, Bo Liu, Zhiqi Gao, and Yifan Dong. 2020. "Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR" Remote Sensing 12, no. 11: 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111703
APA StyleXu, W., Wei, Z., Huang, P., Tan, W., Liu, B., Gao, Z., & Dong, Y. (2020). Azimuth Multichannel Reconstruction for Moving Targets in Geosynchronous Spaceborne–Airborne Bistatic SAR. Remote Sensing, 12(11), 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12111703