1. Introduction
Sea surface salinity (SSS) is one of the most important parameters in marine dynamics and is closely related to large-scale ocean circulation and climate change [
1,
2]. SSS values can be effectively measured based on data from the Aquarius satellite. Electromagnetic radiation emissions from the sea surface can be measured in the form of equivalent brightness temperatures in Kelvin by the Aquarius satellite and then converted into SSS after applying corrections for various geophysical effects. The Aquarius satellite was launched in June 2011 by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) with the goal of providing monthly global SSS fields with a root mean squared difference (RMSD) of 0.2 psu over a spatial smoothing scale of 150 km [
3,
4]. The Aquarius satellite carries an L-band microwave radiometer (MWR) with a swath width of 390 km and an exact repeat orbit of 7 days.
The officially released standard Aquarius gridded SSS level 3 (L3) data products are generated from level 2 (L2) salinity data without any additional adjustments for climatology, reference model output or in situ data [
5]. To assess and validate the accuracy of the Aquarius gridded SSS fields, tests have been conducted in both global oceans and regional basins [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Official Aquarius version 5.0 products have been published, and the accuracy of the monthly L3 1° SSS fields has been estimated via a triple point analysis using individual matchups among Aquarius data, Argo float data and Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) data [
10,
11]. The triple point analysis results showed that the monthly average RMSD of the Aquarius L3 field data was 0.128 psu, whereas the mean RMSD between the weekly L3 analysis and the concurrent Argo float data was 0.247 psu. Garcia-Eidell et al. [
12] studied the spatial and temporal distributions of SSS data at high latitudes through a comparative analysis of the Aquarius weekly L3 polar-gridded products (version 5.0). The RMSD was 0.465 psu relative to the Coriolis Ocean database for ReAnalysis (CORA) 5.0 data. The accuracy of gridded SSS fields directly affects their application. To improve the utility of the gridded SSS fields, Melnichenko et al. [
13] used an optimal interpolation (OI) method to map the Aquarius L2 orbital SSS data. The orbital SSS data were first checked for quality according to quality flags. The weekly average OI SSS in the North Atlantic was calculated for the period from September 2011 to August 2013. The mean RMSD versus the Argo measurements was approximately 0.198. New weekly gridded SSS products on a nearly global 0.5° grid were also produced in 2016 [
14]. The overall RMSD values versus independent thermosalinograph (TSG) salinity data and concurrent Argo observations were approximately 0.20 psu and 0.18 psu, respectively.
The “radiometer_flags” dataset is a key quality flag dataset associated with the Aquarius L2 products and represents nonnominal data conditions for radiometer measurements [
15]. The Aquarius MWR does not measure the SSS directly; instead, it measures the microwave radiation signal emitted from the sea at 1–2 cm from the surface [
9], which may be influenced by marine environmental factors. For example, the influence of the wind speed on the L-band brightness temperature (TB) is approximately 0.2–0.3 K for a 1 m/s change in wind speed according to previous studies [
16,
17]. Furthermore, when the incidence angle increases from 20° to 50°, the sensitivity of TB to the wind speed decreases from 0.14 K/ms
−1 to −0.03 K/ms
−1 for V polarization and increase from 0.29 K/ms
−1 to 0.36 K/ms
−1 for H polarization [
18,
19]. In addition, rain drops have a great impact on TB because they induce freshening and roughness effects on the sea surface [
20]; especially under persistently rainy conditions with low winds, microwave measurements can strongly deviate from the real values [
21]. Significant errors also exist near coastal areas because of the contamination from the nearby land. The results of Li et al. [
22] show that the TB error is large when the distance to the coast (DC) is within 40 km and then decreases sharply from ∼60 to ∼4K, while with a further increase in DC from 40 to 400 km, the TB error decreases smoothly from ∼4 to ∼0.15 K. Therefore, the data quality is not constant under different conditions; consequently, orbital SSS data retrieved under different conditions should be treated differently. Although a number of studies have considered quality flags in the gridding procedure, these flags have been used only for data screening [
5,
14,
23].
The present paper aims mainly to improve the accuracy of gridded SSS data at smaller spatial and temporal scales by means of a newly proposed method: dual quality–distance weighting of the orbital SSS data based on quality flags. In this method, the orbital SSS data are processed according to quality flags with the goal of maximizing the utilization of unflagged data. In this study, near-global weekly 0.25° × 0.25° gridded SSS fields were constructed for September 2011 to May 2015. Additionally, the constructed SSS fields were compared with concurrent individual Argo buoy observations to verify the accuracy of the SSS fields.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 introduces the datasets used in this paper.
Section 3 describes the method and procedures. The results and verification are presented in
Section 4.
Section 5 offers a discussion, and
Section 6 concludes the paper.
4. Results and Verification
The weekly averaged near-global gridded SSS fields were calculated on a 0.25° × 0.25° grid using the three methods introduced above for the period of September 2011 to May 2015. The search radius used in this study was 150 km.
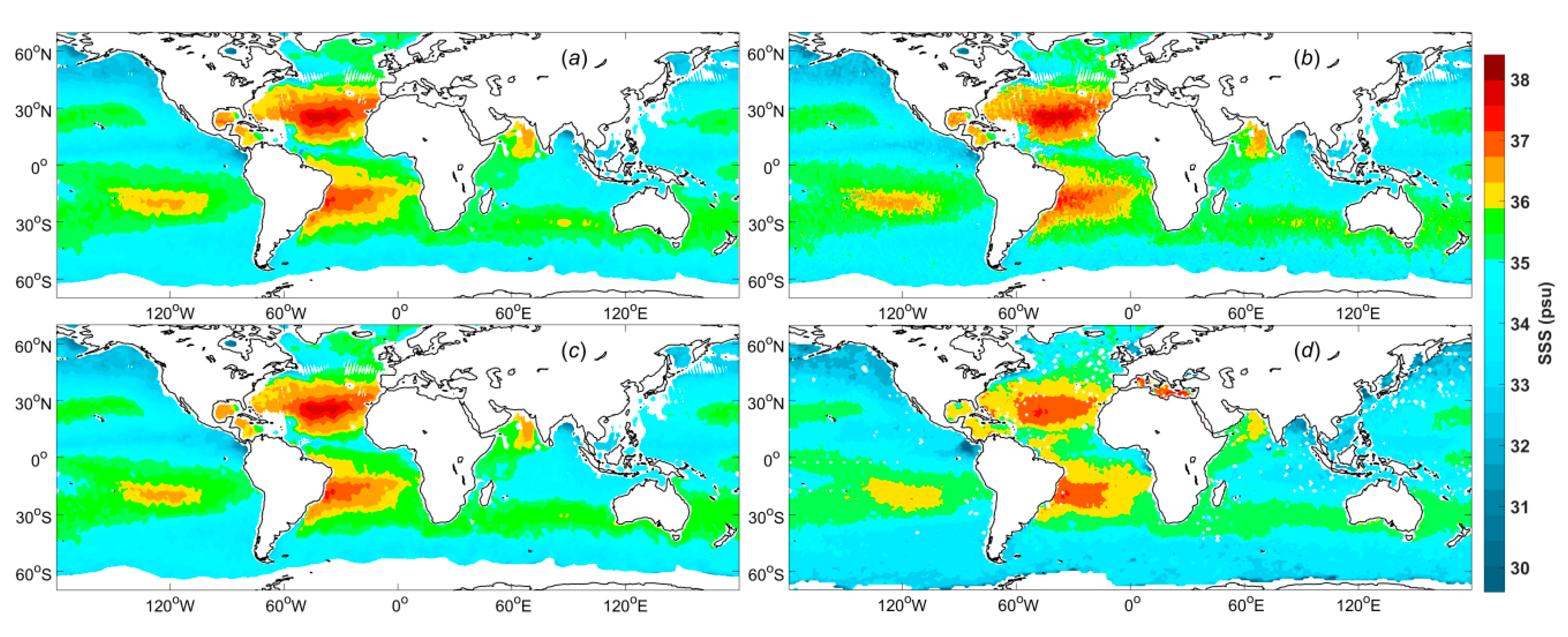
Figure 3a–c show the differences in the weekly Aquarius SSS fields constructed using the three interpolation methods for 2 July to 8 July 2013. For all three interpolation methods, the data were weighted in terms of both distance and data quality. Both WULF and WBLF are polynomial fitting methods, although these methods differ in the way they treat the independent variables.
Figure 3d shows the Aquarius SSS L3 product data provided by ADPS with a 1° × 1° spatial resolution.
Intuitively, there are obvious differences in smoothness and in the SSS values. The values for WAF, WULF and WBLF are all higher than those of the Aquarius SSS L3 product data in most regions. Although both WBLF (
Figure 3c) and WULF (
Figure 3b) are polynomial fitting methods, there are notable differences between their SSS maps. The WULF SSS map exhibits a slight sawtooth phenomenon, while the WBLF SSS field is very smooth. This difference may arise because WBLF considers the spatial distribution of the data, while WULF does not. Moreover, the SSS field for WAF (
Figure 3a) is slightly smoother than that for WBLF (
Figure 3c).
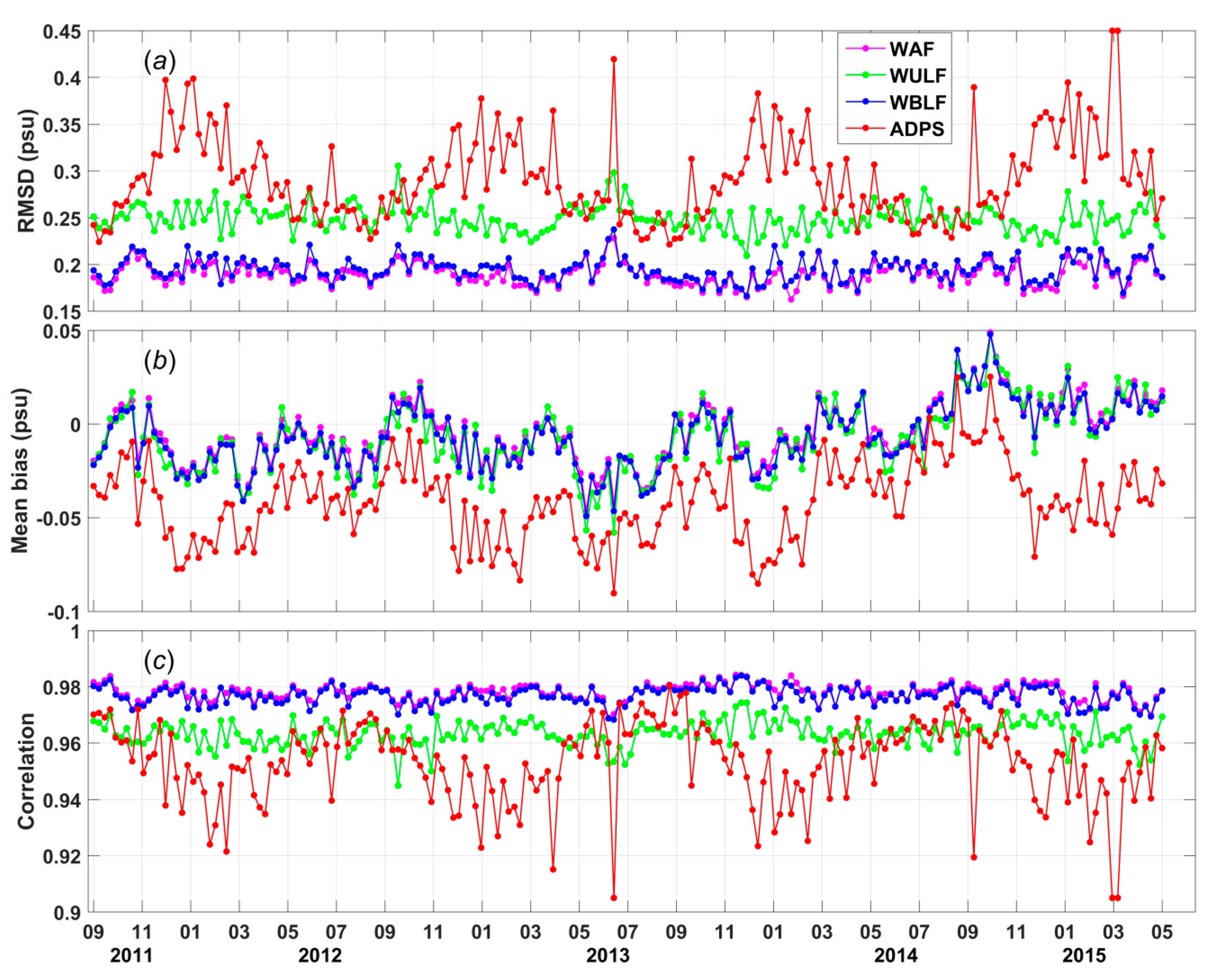
Comparisons between the individual Argo measurements and the SSS values calculated with the three interpolation methods are shown in
Figure 4. The magenta, green, blue and red curves are time series of the weekly RMSDs (
Figure 4a), biases (
Figure 4b) and correlations (
Figure 4c) of the results of WAF, WULF, and WBLF methods and the Aquarius L3 product data provided by ADPS. The analysis-to-buoy comparisons for the Aquarius L3 product data are presented here to answer the question of whether the new SSS fields are significantly more accurate than other Aquarius-derived SSS maps.
Significant differences are observed in the weekly RMSDs for the four analyses, as shown in
Figure 4a. The weekly RMSDs for the WAF method vary from 0.1625 to 0.2283 psu. Similar to the WAF method, the weekly RMSDs for the WBLF method vary from 0.1665 to 0.2374 psu. The weekly RMSDs for both the WAF and WBLF methods are much better than those of the ADPS product data, which vary from 0.2212 to 0.4499 psu. The weekly RMSDs for the WAF and WBLF analyses are smaller than 0.2 psu for most weeks; specifically, this is true for 153 and 139 weeks, respectively, during the 194-week comparison period. The weekly RMSDs for the WULF analysis, which vary from 0.2093 to 0.3054 psu, are larger than the weekly RMSDs for the other two methods. However, the seasonal signal, which is obvious in the ADPS product data, is effectively reduced by all proposed methods.
As illustrated in
Figure 4b, the WAF, WULF, and WBLF analyses can effectively reduce the biases but cannot completely eliminate them. These analyses may yield global bias time series that oscillate around zero. By contrast, the global bias time series for the ADPS product data are almost entirely less than zero, implying that most of the ADPS SSS data are fresher than the Argo buoy data.
The weekly correlations of the WAF and WBLF results with the Argo measurements take values of approximately 0.98 for nearly all weeks (
Figure 4c). The weekly correlation of the WULF results with the Argo measurements, which is approximately 0.96, is relatively small compared with those for the other two analyses. However, the weekly correlation of the ADPS product data with the Argo measurements is the worst, being as low as 0.9050 for some weeks.
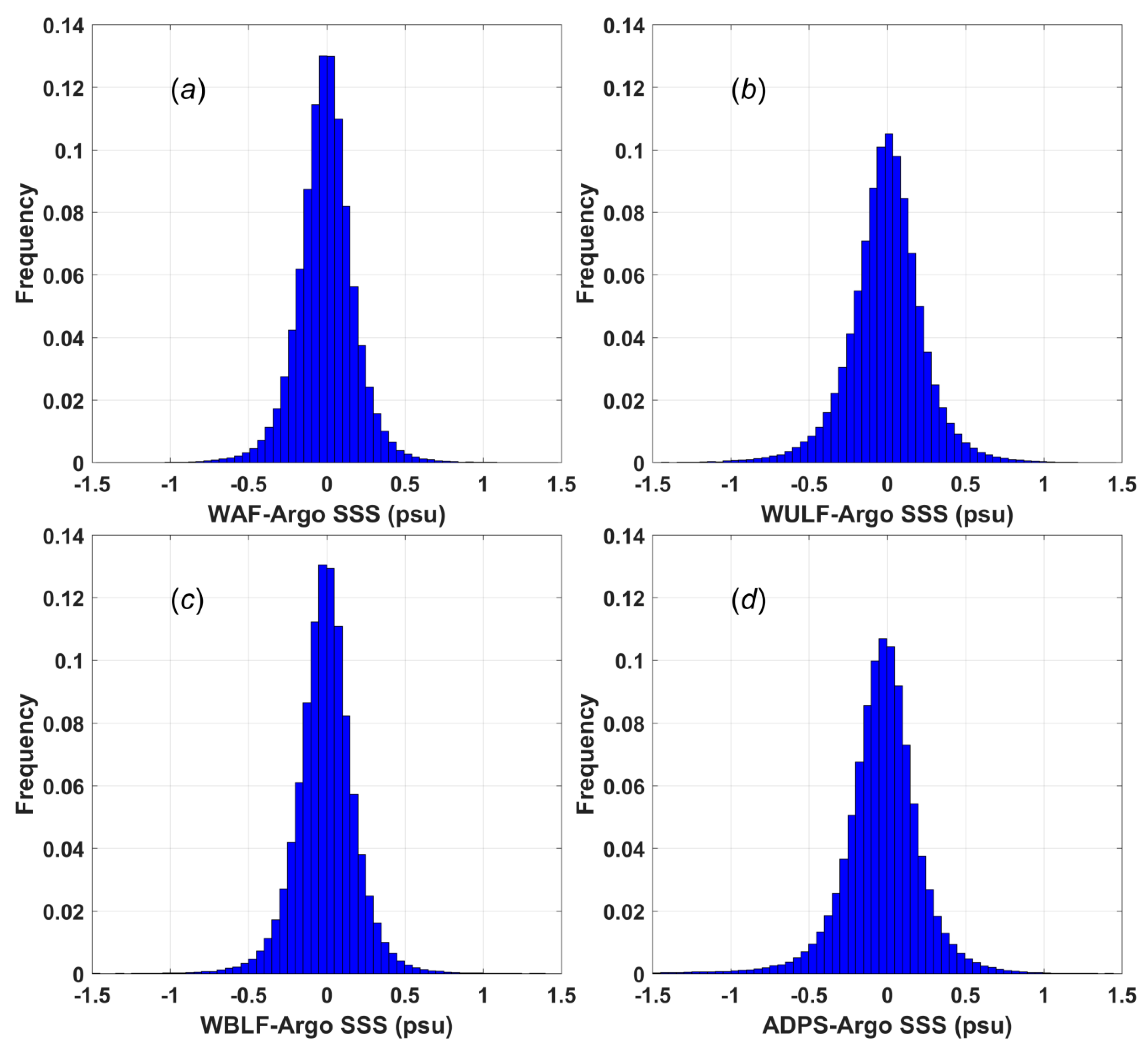
Histograms of the differences between the Argo data and the four types of SSS data are shown in
Figure 5. The percentages of the WAF SSS data (
Figure 5a) and the WBLF SSS data (
Figure 5c) that lie in the difference range from −0.1 psu to 0.1 psu are 48.97% and 48.32%, respectively; the corresponding percentage for the WULF SSS data is 39.91%, which is slightly smaller than that of 40.12% for the ADPS product data.
The number of outliers (defined here as points with differences greater than 0.5 psu) is approximately 1.98% for the WAF SSS data, 2.15% for the WBLF SSS data, 4.08% for the WULF SSS data and 5.45% for the ADPS product data. Notably, the number of data points falling within ±0.1 psu for the ADPS product data is slightly larger than that for the WULF SSS data. However, the ADPS product data also feature a larger population of values with large differences (>0.5 psu), which can significantly reduce the accuracy of the gridded SSS fields. Therefore, the overall accuracy of the ADPS products is worse than those of the other three types of SSS data. Note that the mean and RMSD values are presented in
Figure 6 below.
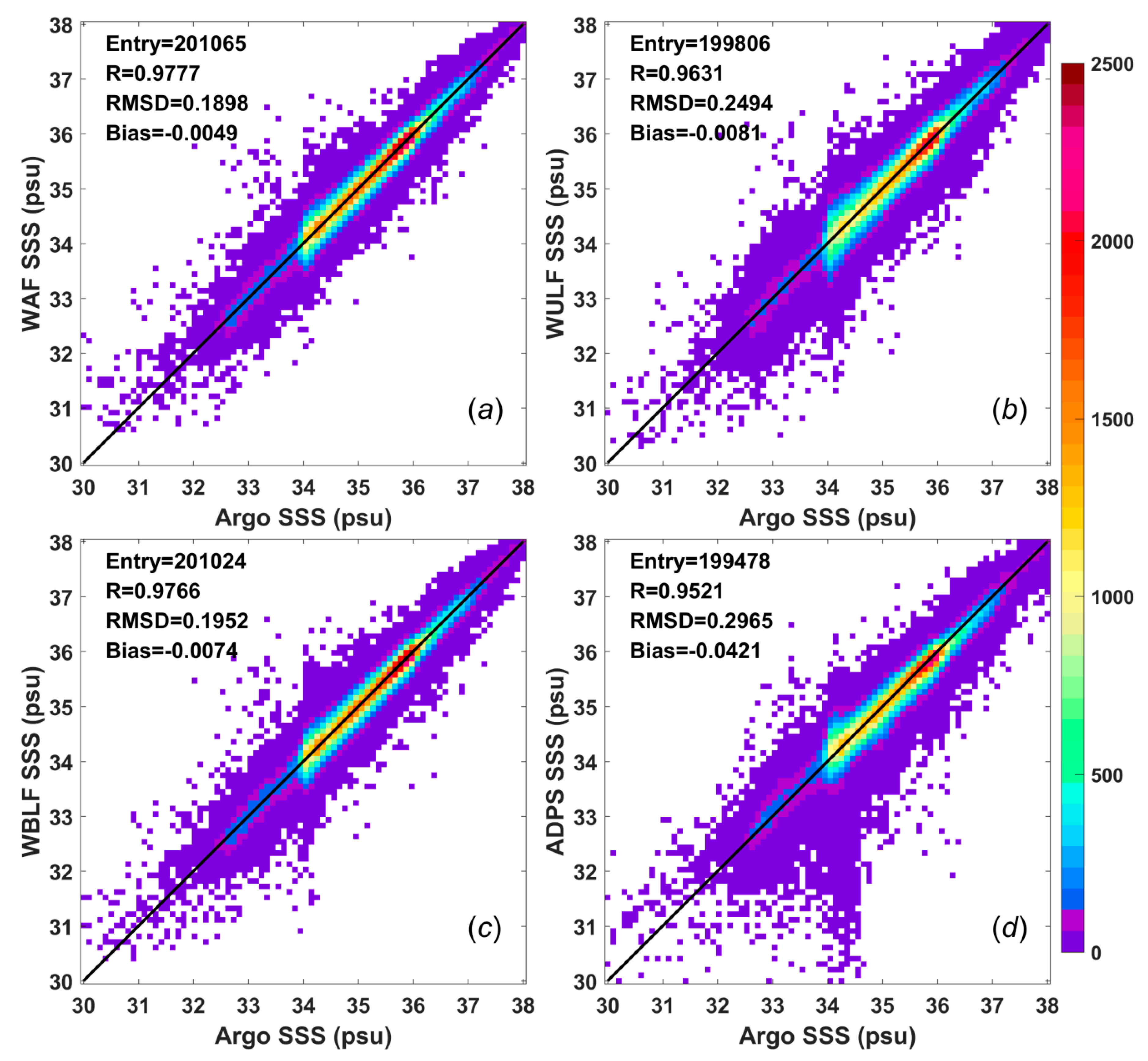
Scatter plots of the results of the Aquarius weekly SSS analyses and the collocated Argo buoy data between September 2011 and May 2015 were generated to determine how well the actual data points matched the collocated Argo data (
Figure 6). Theoretically, the numbers of collocated data, i.e., 200,065 for the WAF SSS analysis, 199,806 for the WULF SSS analysis, 200,024 for the WBLF SSS analysis and 199,478 for the ADPS product, should be the same. However, these values differ despite having the same duration because the numbers of missing values are different among the datasets.
The bias, which is defined as the Aquarius SSS value minus the Argo SSS value, is less than
psu for all three analyses proposed in this paper. The mean bias for the WAF method, which is the smallest bias among all three proposed analyses, is −0.0049 psu, and this value is much smaller than the bias of the L3 product, namely, −0.0421 psu. These negative values imply that the SSS estimates from the Aquarius data are fresher than the Argo data, whereas a positive value would indicate the opposite. The region in
Figure 6 with the highest density of points (red) for each of the WAF, WULF, and WBLF SSS analyses lies along the diagonal line. By contrast, the region with the highest density of points for the ADPS product is offset from the diagonal line, consistent with the relatively large negative bias; this pattern is also observed in
Figure 4b.
The correlation coefficients among the datasets were also calculated (
Figure 6). The plot of the WAF SSS data against the Argo SSS data shows that these two datasets have a very high correlation coefficient of 0.9777. The plot of the WBLF SSS data against the Argo SSS data exhibits a similar correlation coefficient of 0.9765. The plot of the WULF SSS data against the Argo SSS data yields a correlation coefficient of 0.9630, which is worse than those of the WAF and WBLF analyses but better than the correlation coefficient of 0.9521 found for the ADPS product. These results conform to the histograms shown in
Figure 5.
Figure 6 also shows that the L3 product has the largest mean RMSD of 0.2965 psu, which is consistent with the time series of weekly RMSDs shown in
Figure 4a. The mean RMSDs for the WAF and WBLF analyses are 0.1899 psu and 0.1952 psu, respectively, which are 0.1066 psu and 0.1013 psu smaller, respectively, than that for the ADPS product. The mean RMSD for the WULF analysis is 0.2495 psu, which is slightly smaller than that for the ADPS product.
5. Discussion
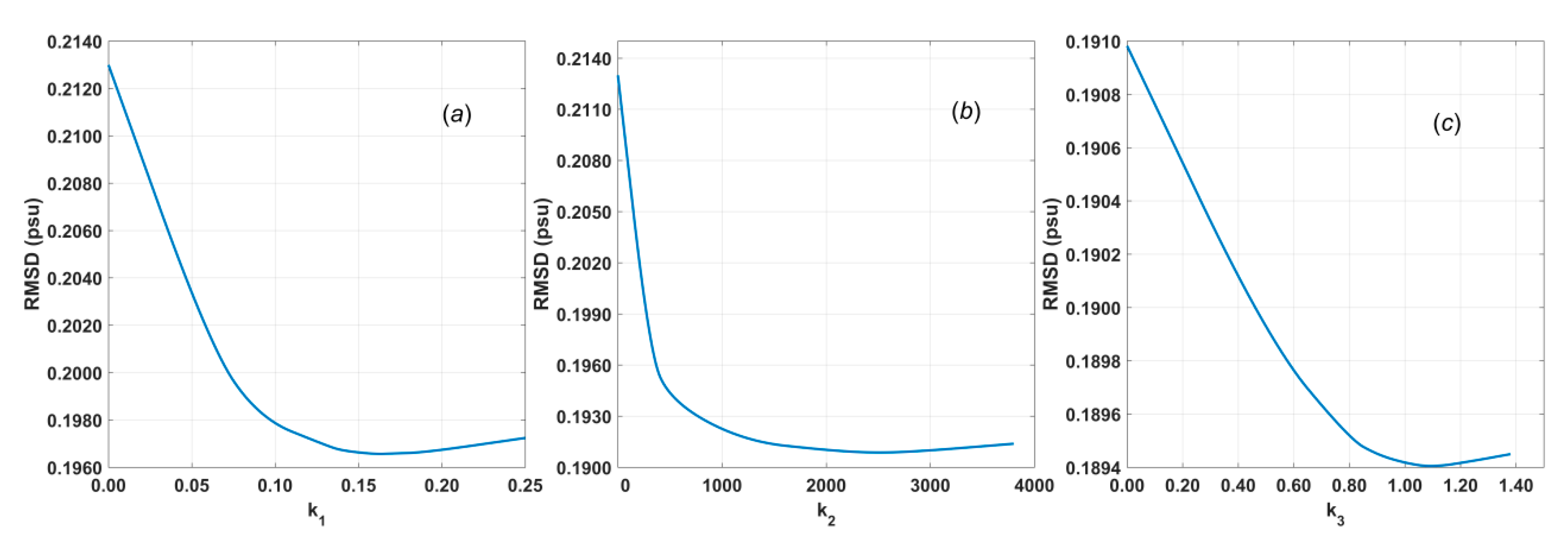
Among the interpolation methods, WAF is linear and the simplest method, whereas both WULF and WBLF are polynomial fitting methods. They all are widely used. The key differences between our methods and traditional methods lie in the weighting of the data. Although there are various weighting functions available, traditional methods treat only the distance as an independent variable, whereas we also consider the data quality. The improvement in the RMSD that is achieved through quality weighting is approximately ten times that achieved through distance weighting. Even when measurements with severe contamination have been discarded, moderate contamination may still exist. Therefore, results of higher accuracy can be obtained by assigning lower weights to data of lower quality. The results show that the accuracy of the output of our WAF method is improved by approximately 36% compared to the officially released weekly L3 products.
As shown in
Table 2, 14 conditions were used for dual quality–distance weighting in this study, which are not considered in traditional methods. The weight of each element in
(
Table 2) is related to its total influence on the RMSD as well as the frequency and distribution of occurrence of the corresponding condition. Considering the Gaussian function shown in Equation (4), the larger the weight of an element is, the smaller its contribution to the final result, and the more effective the elimination of its effect. Note that the total influence on the RMSD, i.e., the difference between
and
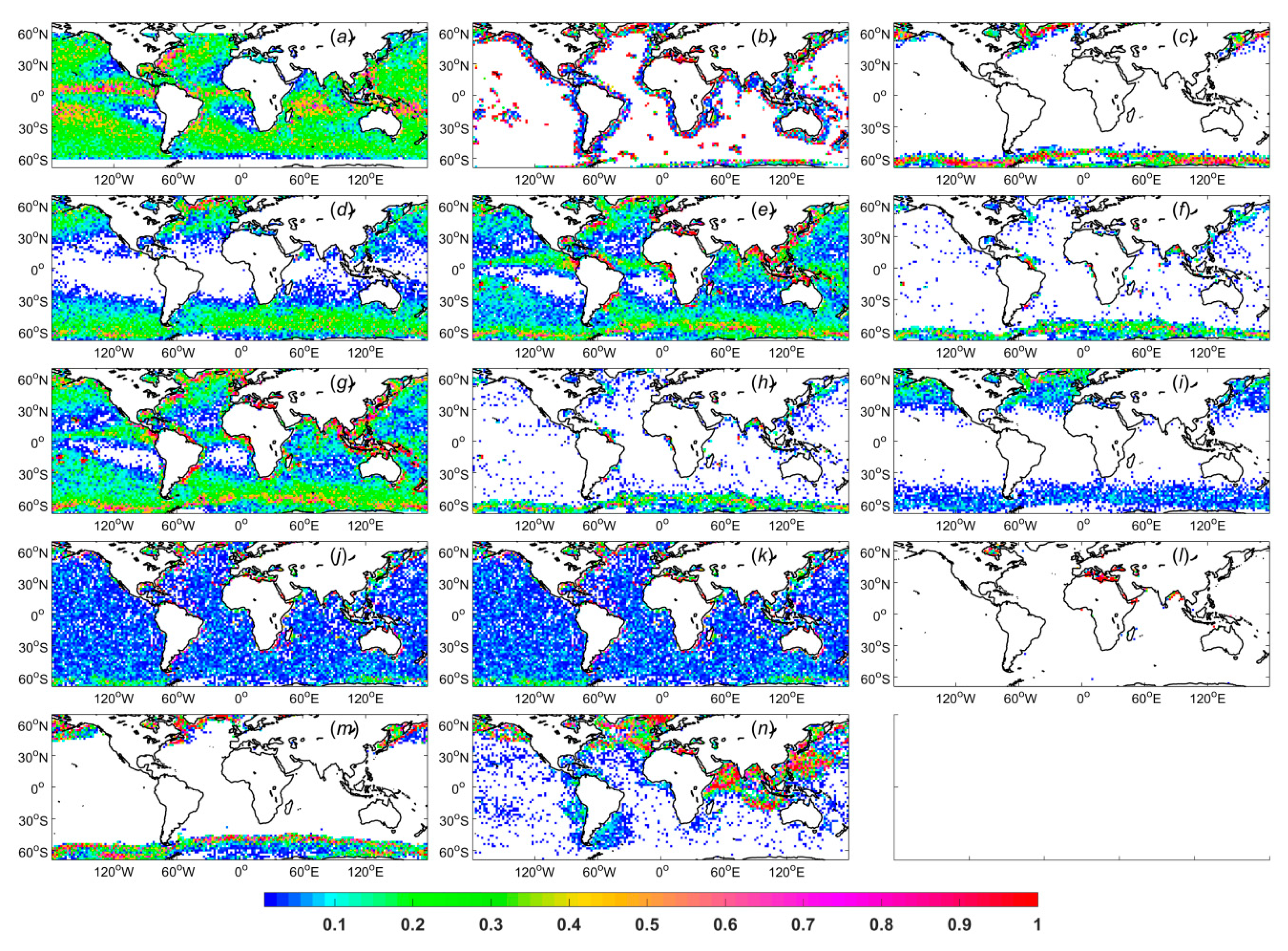
, may be very small because all conditions except the considered condition are still qualitatively weighted and thus have a dominant influence on the RMSD. The sum of the total influence on the RMSD exerted by all conditions should be equal to the difference between the RMSDs found with qualitative and quantitative quality weighting. The frequency of condition (g) (i.e., H moderate unusual brightness temperature) is the highest, at approximately 110336, whereas condition (l) (i.e., roughness correction failure) has the lowest frequency of 14399. Here, the frequency is calculated as the mean number of times that the corresponding element in
is flagged as 1 within one week. The distributions for each condition are displayed in
Figure 7, where conditions (a) to (n) correspond to those listed in
Table 2.
It can be seen from
Figure 7 and
Table 2 that although the difference between
and
for (g) is slightly larger than that for (j), the weight of (g) is smaller than that of (j) because the frequency of (g) is much higher than that of (j). Meanwhile, although the frequencies of (j) and (m) are almost the same, the weight of (j) is far larger than that of (m). By considering their distributions, it can be found that (m) features an obvious regional distribution, whereas (j) does not. Therefore, we can conclude that in this case, the distribution dominates the weighting process. The effects of the conditions without obvious regional distributions, i.e., (a), (e), (g), (j), and (k), can be significantly reduced, whereas the conditions with obvious regional distributions, i.e., (b), (c), (l), and (m), cannot be weighted effectively. This finding implies that as long as unflagged data exist in most areas where flagged data appear, the impact of those flagged data can be effectively eliminated, and vice versa.
Many conditions, such as wind contamination, sea ice contamination and cold water, have been considered for screening in the process of validation and transformation from L2 to L3 [
28,
29]. However, there are some conditions, such as unusual brightness temperatures and galactic contamination, which have not been used in any previous processing methods but also have great impact on the results. Hence, the results of this study should serve to remind readers of the importance of considering these conditions.
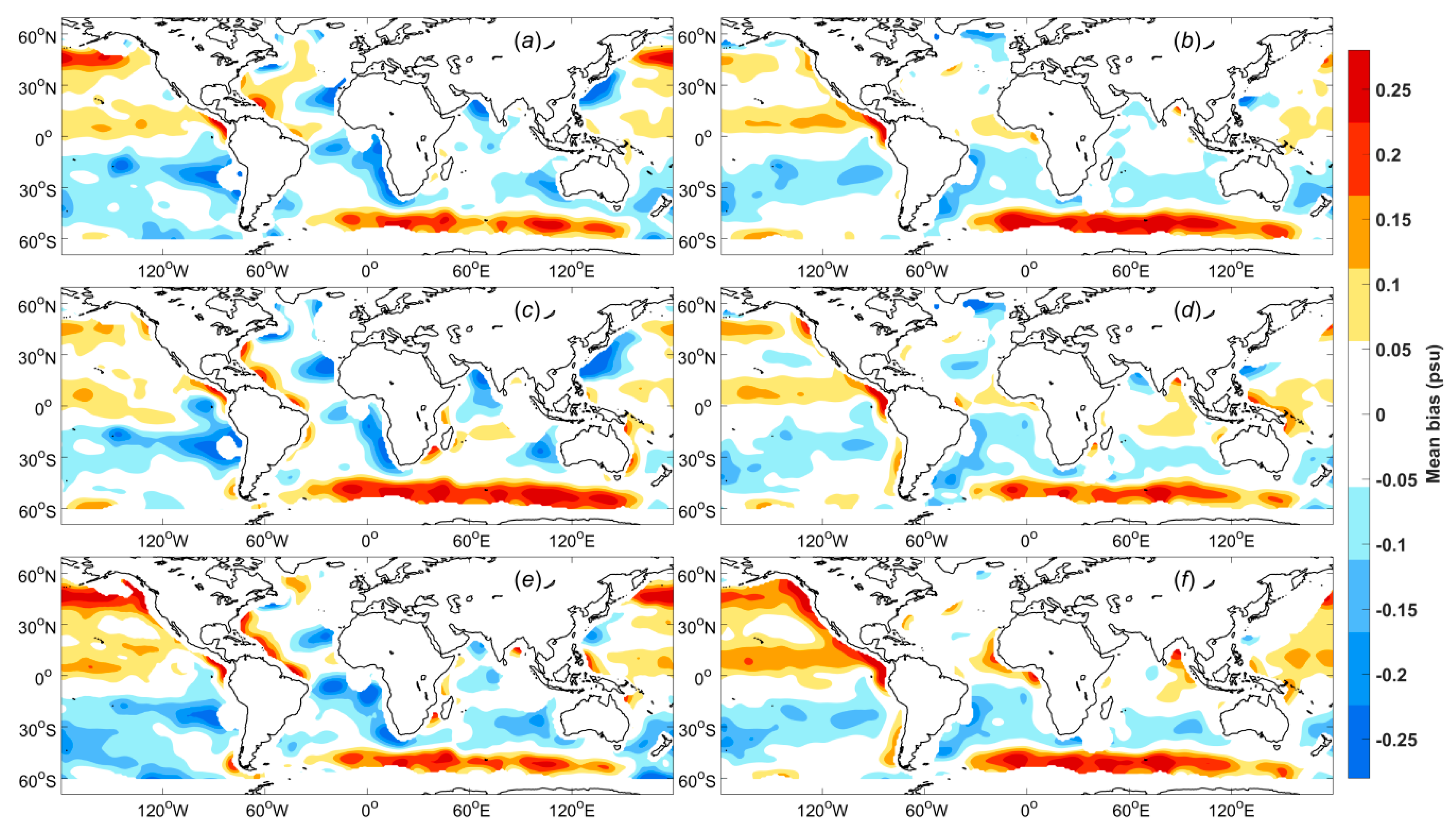
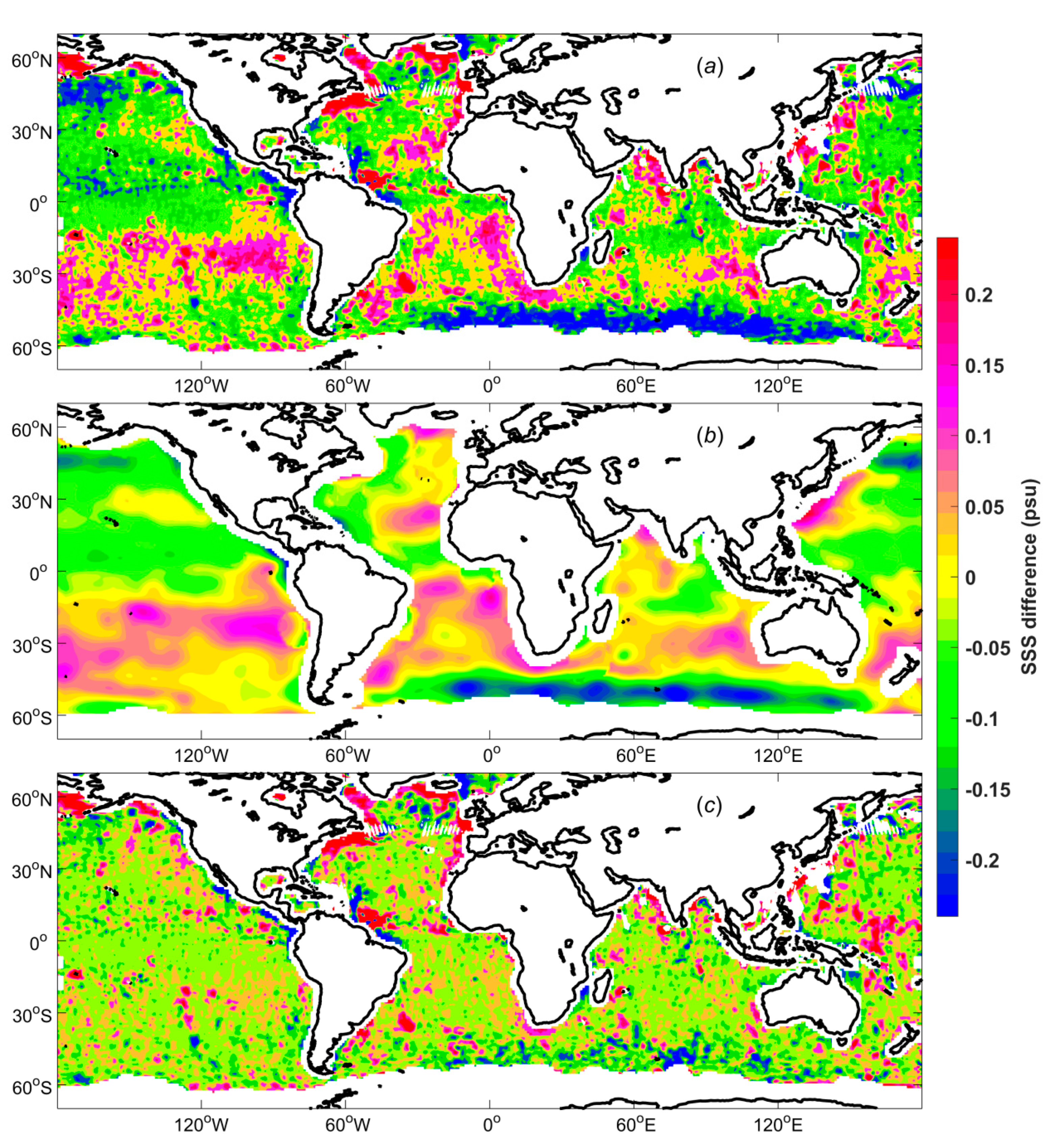
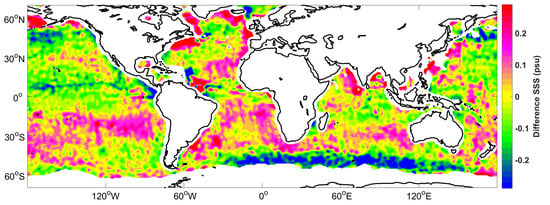
A map of the mean SSS differences between the WAF and ADPS products (WAF–ADPS) for the period of September 2011 to May 2015 is shown in
Figure 8. Obvious systematic biases are observed in the difference map, which are the result of the large-scale bias adjustment (
Figure 8b) as well as the weighting process (
Figure 8c). In particular, systematic differences are observed in many regions where salinity plays a critically important role in ocean dynamics. There are positive systematic biases in the South Temperate Zone, near near 30°S in the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans, which are mainly due to the large-scale bias adjustment. Negative systematic biases are observed in the North Pacific as well as the regions around 50°S in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans, which are also mainly caused by the large-scale bias adjustment. Most regions near a coast are characterized by positive systematic biases. By considering the distributions for each condition (
Figure 7), it can be found that for the five strongest influencing conditions, namely, (a), (j), (k), (e), and (g), high frequencies are also found in these near-coast regions. Because these regions show higher frequencies of these conditions, they should contribute less to the results than regions with lower frequencies do when weighted reasonably. Then, the results will be closer to the real values and show greater systematic biases with respect to the ADPS data, which do not include quality weighting. Positive systematic biases of approximately 0.2 psu are found in the Bay of Bengal, which are mainly caused by conditions (e), (g) and (n). There are also positive systematic biases of approximately 0.2 psu in the region near the Amazon River plume, which are mainly caused by conditions (a), (e), and (g). In the Labrador Sea, we can again see positive systematic biases of approximately 0.2 psu, which are mainly caused by conditions (b), (c), (g), (m), and (n). Negative systematic biases of approximately -0.2 psu are observed near 8°N in the Pacific Ocean, which are mainly caused by condition (a) in addition to the large-scale bias adjustment.
The Argo measurements should be treated as the ground truth. A previous study indicated that the salinity variation from the surface to a depth of 10 m is normally less than 0.1 psu, but when there is rain, the difference can be larger than 1 psu [
35]. In this study, most data with large differences were either screened out or reasonably weighted according to quality flags before being subjected to interpolation. When the Argo measurements are used to calculate the gridded fields, greater weights will be assigned to Aquarius SSS data whose values are closer to the Argo SSS values. Consequently, if the Argo SSS data are also used for validation, strong correlations may be found between the gridded SSS data and the Argo SSS data. Unfortunately, however, no adequate in situ data other than the Argo data are available. If possible, CTD or other in situ salinities should be used to calculate the gridded fields in future experiments.
The proposed methods have certain limitations. The weighting method proposed in this paper can be used only to eliminate the influence of conditions without obvious regional distributions. For a condition with an obvious regional distribution (such as cold water), the data cannot be effectively weighted. Moreover, a lack of coverage in the gridded SSS maps is observed in coastal regions and semi-enclosed seas, which mostly occurs because data with a large fraction of land contamination are discarded due to their low quality. In addition, a solid understanding of the physical basis of the proposed method is lacking because we have not found a unified standard for quantitatively evaluating the influence of different conditions. This shortcoming should be improved upon in future research.
Despite the aforementioned limitations, the results suggest that the proposed method shows good prospects in certain respects. First, the method can yield more accurate products at smaller spatial and temporal scales without small-scale noise. Second, the method can meet the demand for SSS analyses that are quantitatively consistent with existing in situ observations, such as those from Argo profile data. Additionally, the influences of different factors on salinity can be visualized and evaluated, thus serving as a reference for sensor design and reliability assessments of measurement results in the future.
6. Conclusions
A dual quality–distance weighting method is proposed in this paper. All types of nonnominal data conditions detected for the radiometer measurements of each block and beam are fully considered in our method. The key aspect of the method is the dual weighting of the data according to quality flags. By dual weighting the data in this way, the method can maximize the utilization of unflagged data while simultaneously minimizing unnecessary data loss.
The SSS satellite observations used in the study are officially released Aquarius L2 version 5.0 data. These data were first adjusted to eliminate large-scale systematic biases. In the weighting process, 14 data conditions were considered. Their geospatial distributions and influences on the SSS were visualized and evaluated. After the data were weighted, three popular interpolation methods, namely, WAF, WULF, and WBLF, were employed by setting a reasonable search radius. Weekly near-global gridded SSS fields were calculated on a 0.25° × 0.25° grid using all three methods for the period of September 2011 to May 2015. In addition, the officially released weekly Aquarius L3 global mapped version 5.0 SSS products provided by ADPS were considered for comparison.
To verify the accuracy of the results, error statistics were calculated by comparing individual Argo measurements with the SSS values obtained for a given week at the same locations by interpolating the corresponding Aquarius SSS maps. The accuracy of the WAF SSS data was found to be very similar to that of the WBLF SSS data. The accuracy of the results of these two methods is improved by approximately 36% and 34%, respectively, compared to the officially released weekly L3 products. The accuracy of the WULF SSS results is relatively poor but is still improved by approximately 16%.