Comparison of Hyperspectral Versus Traditional Field Measurements of Fractional Ground Cover in the Australian Arid Zone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
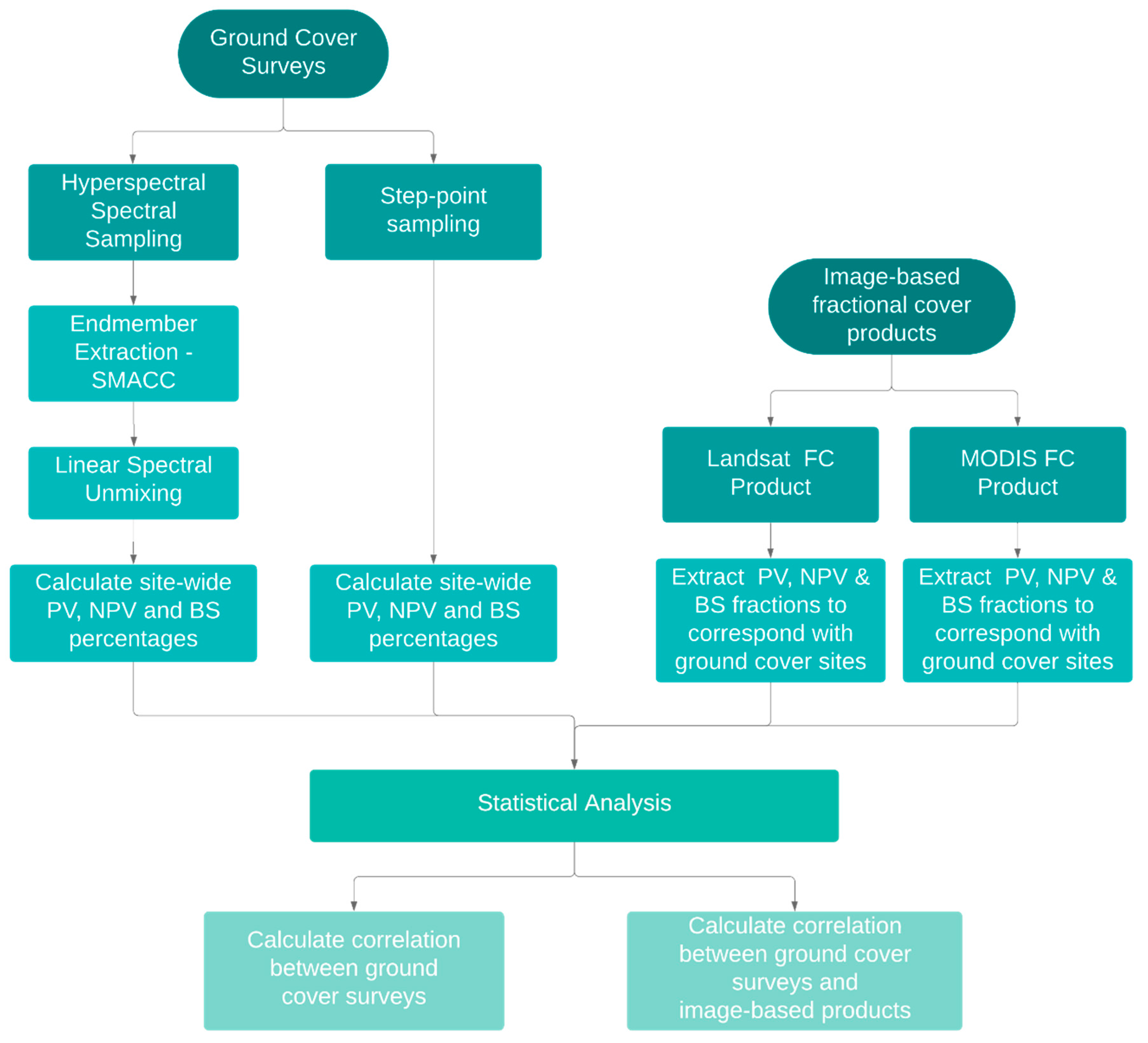
2. Materials and Methods
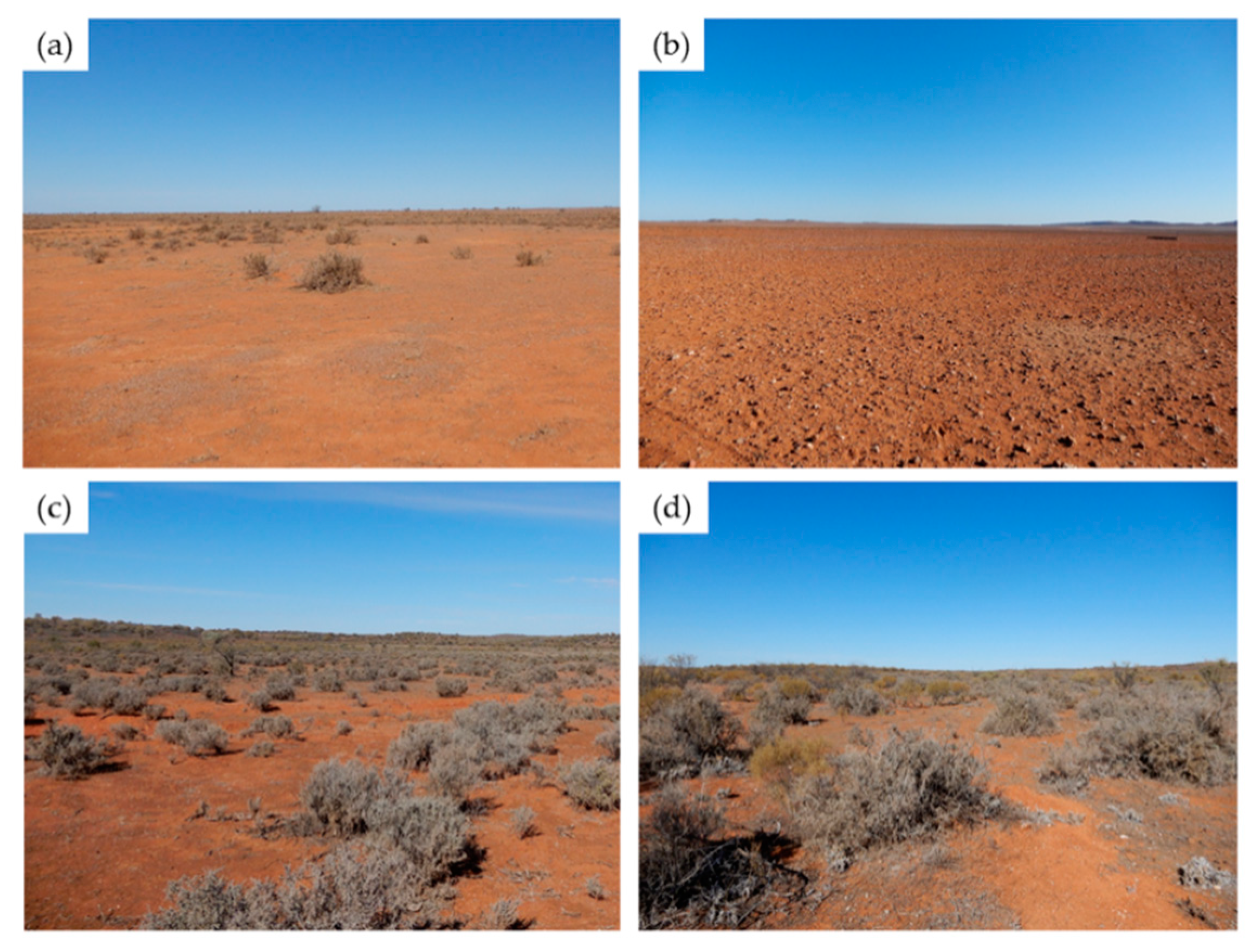
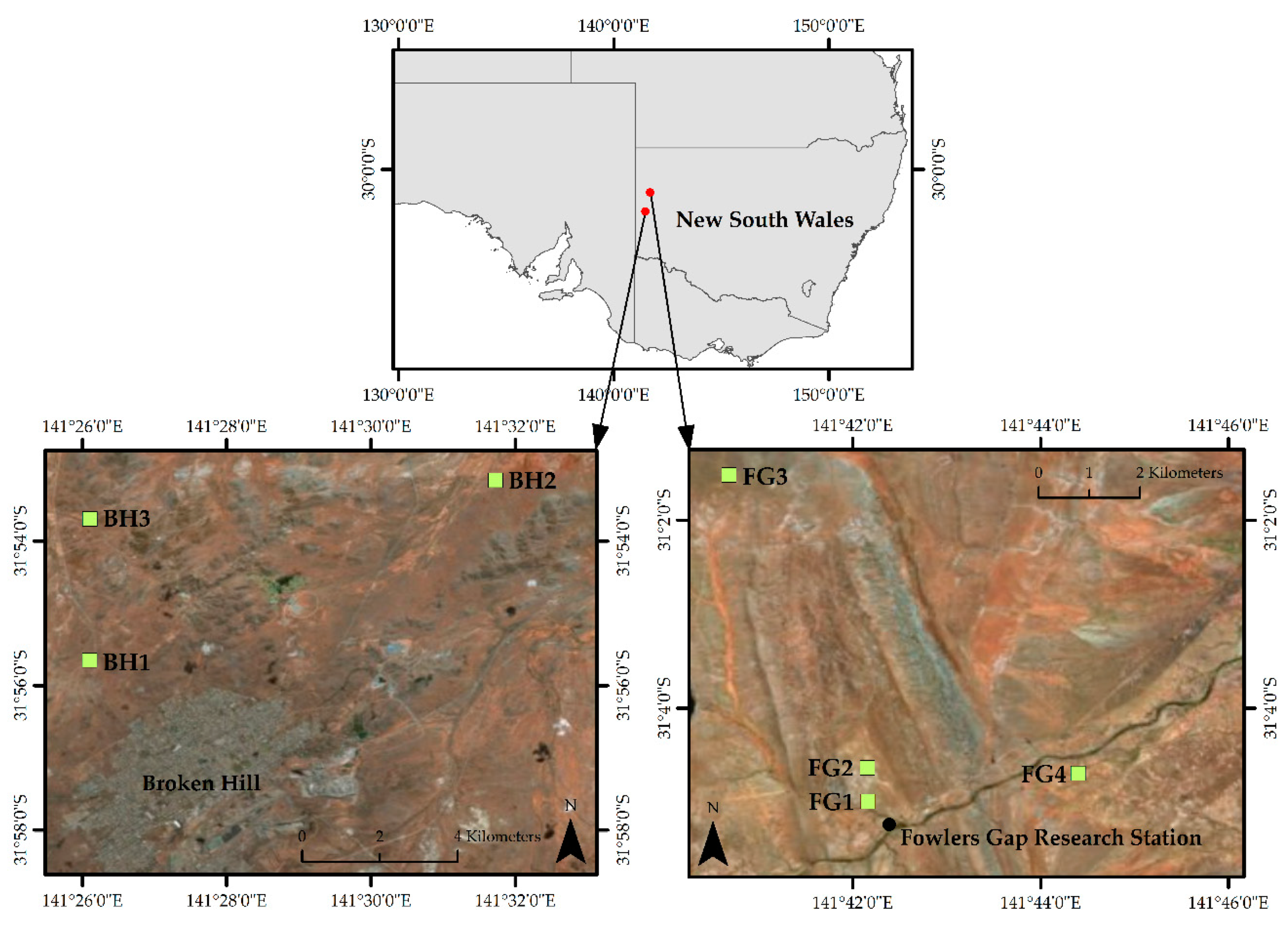
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground Cover Surveys
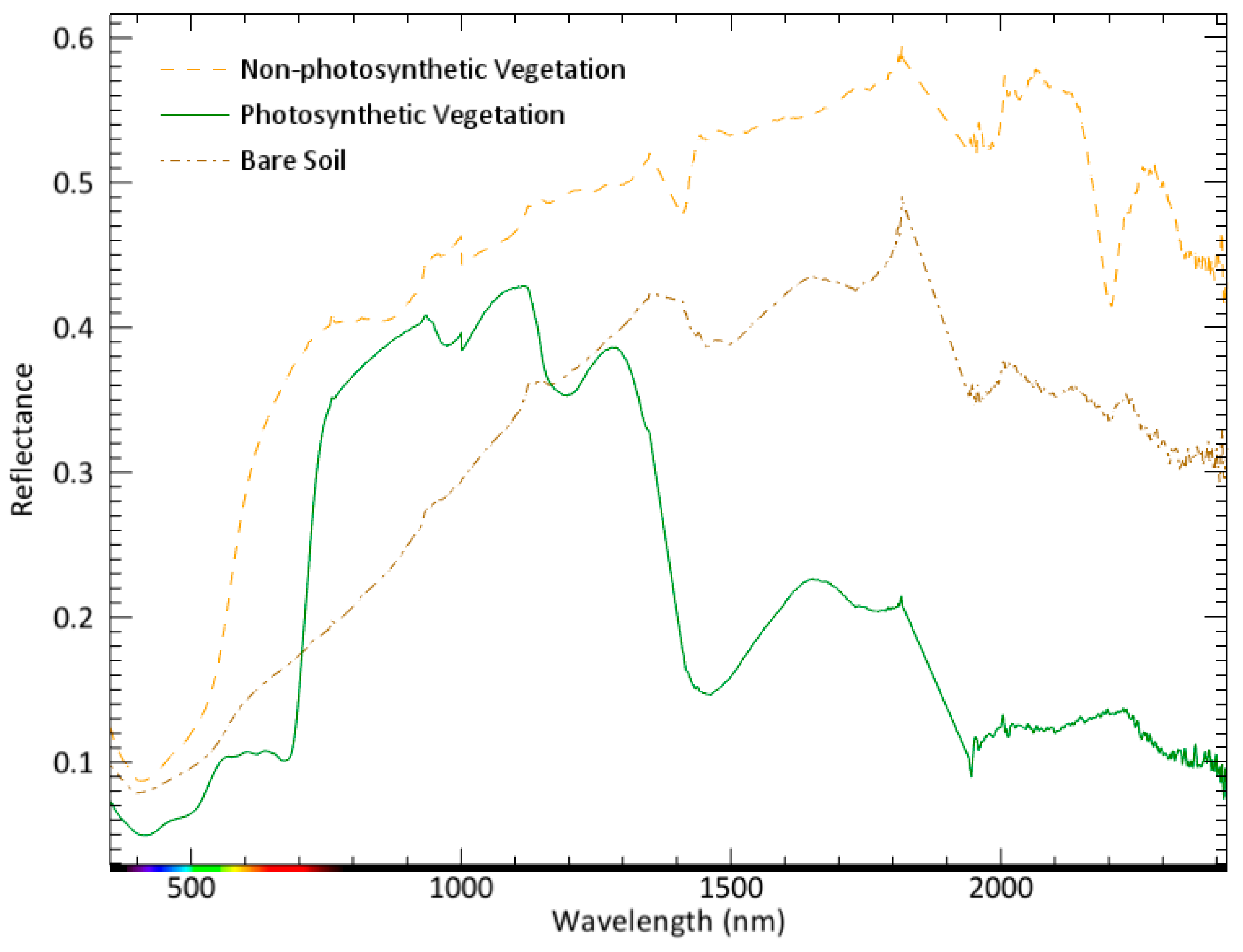
2.3. Endmember Extraction and Spectral Unmixing
2.4. Comparison to Image-Based Fractional Cover Products
2.5. Statistical Analysis
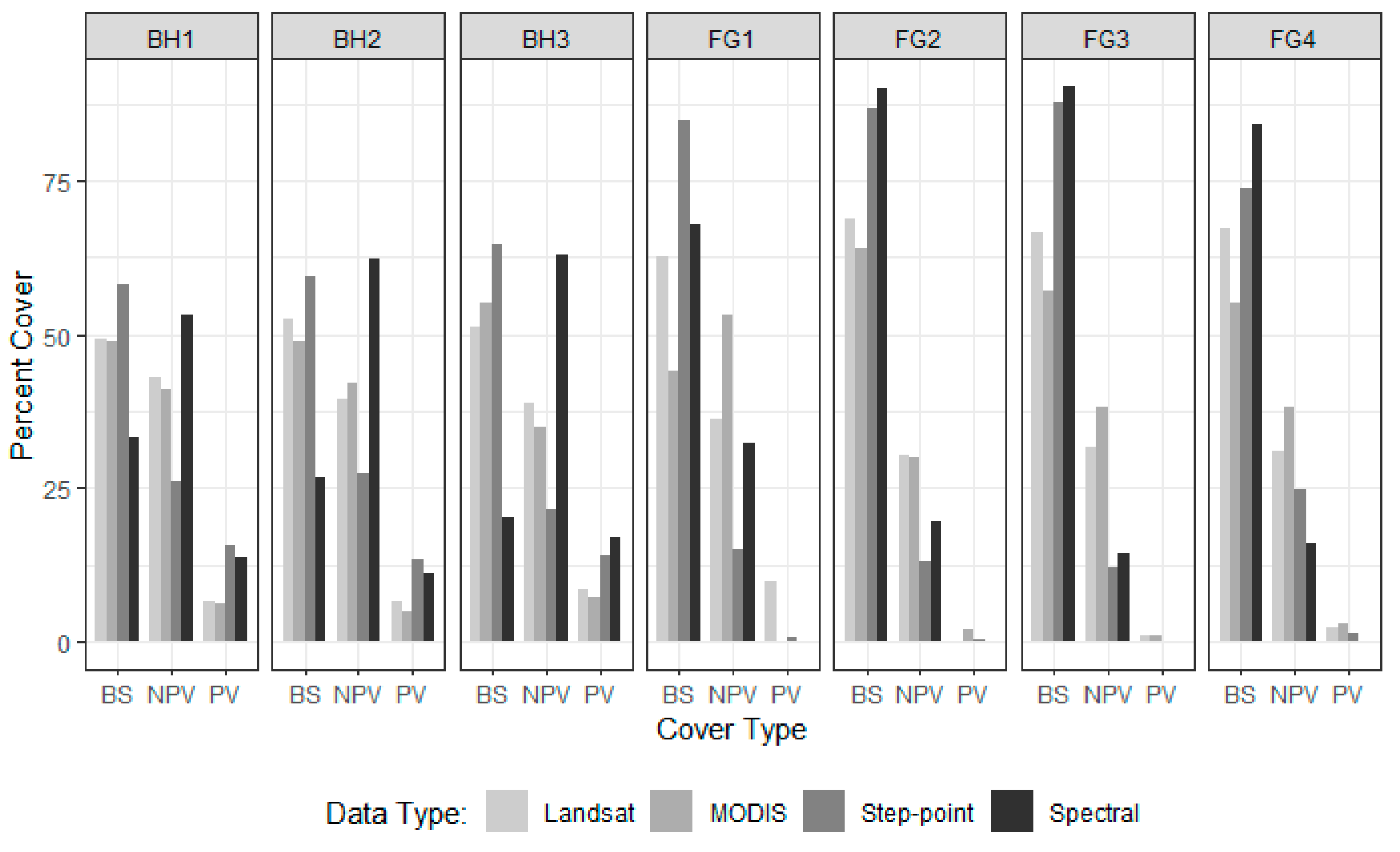
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Huete, A.; Yu, Q.; Coupe, N.R.; Davies, K.; Broich, M.; Ratana, P.; Beringer, J.; Hutley, L.B.; Cleverly, J.; et al. Spatial patterns and temporal dynamics in savanna vegetation phenology across the North Australian tropical transect. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.Y.; Deng, J.S.; Zheng, X.Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, K. Monitoring urban greenness dynamics using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintano, C.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Roberts, D.A. Multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (mesma) to map burn severity levels from Landsat images in mediterranean countries. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, M.T.; Mustard, J.F.; Melillo, J.M. Forest cover change in miombo woodlands: Modeling land cover of african dry tropical forests with linear spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Golian, S.; Karimi, D. Monitoring deforestation in Iran, Jangal-abr forest using multi-temporal satellite images and spectral mixture analysis method. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settle, J.; Drake, N. Linear mixing and the estimation of ground cover proportions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.O.; Ustin, S.L.; Adams, J.B.; Gillespie, A.R. Vegetation in deserts. I. A regional measure of abundance from multispectral images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 31, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Johnson, P.E. Spectral mixture modeling: A new analysis of rock and soil types at the viking lander 1 site. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 8098–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping Chaparral in the Santa Monica mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.S. Relative spectral mixture analysis—A multitemporal index of total vegetation cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. Geov1: Lai and fapar essential climate variables and fcover global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part 1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.; Cernicharo, J.; Lacaze, R.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Geov1: Lai, fapar essential climate variables and fcover global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part 2: Validation and intercomparison with reference products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, J.; Fisk, C.A.; Cox, J.W.; Anderson, S.J.; van Leeuwen, J. Modelling of THM formation potential and DOM removal based on drinking water catchment characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, R.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Hess, L.L. Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.B.; Crews, K.A.; Okin, G.S. Relating spatial patterns of fractional land cover to savanna vegetation morphology using multi-scale remote sensing in the Central Kalahari. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2082–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J.; Renzullo, L.J.; Barrett, D.J.; Marks, A.S.; Botha, E.J. Estimating fractional cover of photosynthetic vegetation, non-photosynthetic vegetation and bare soil in the Australian tropical savanna region upscaling the EO-1 Hyperion and MODIS sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Treitz, P.; Jelinski, D.; Miller, J.; Lafleur, P.; McCaughey, J.H. Image classification of a northern peatland complex using spectral and plant community data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, F.J.; Yang, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing of marsh species and plant vigour gradient in the New Jersey meadowlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 5209–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Oyarzabal, M.; Malthus, T.; McVicar, T.; Byrne, G.; Randall, L.; Stewart, J. Evaluation of the MODIS-Based Vegetation Fractional Cover Product; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2012; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lawley, E.F.; Lewis, M.M.; Ostendorf, B. Evaluating MODIS soil fractional cover for arid regions, using albedo from high-spatial resolution satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2028–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Montesano, P.; Nelson, R.; Sun, G.; Margolis, H.; Kerber, A.; Ranson, K. MODIS tree cover validation for the circumpolar taiga–tundra transition zone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.T.; Nickeson, J.E.; Davis, P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Woodcock, C.E.; Shabanov, N.; Hansen, M.; Cohen, W.B.; Oetter, D.R. High spatial resolution satellite observations for validation of MODIS land products: Ikonos observations acquired under the NASA scientific data purchase. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Moody, A. A comparison of methods for estimating fractional green vegetation cover within a desert-to-upland transition zone in central New Mexico, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarth, P.; Röder, A.S.M.; Denham, R. Tracking Grazing Pressure and Climate Interaction—The Role of Landsat Fractional Cover in Time Series Analysis. In Proceedings of the 15th Australasian Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry Conference, Alice Springs, Australia, 13–17 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Asner, G.P.; Heidebrecht, K.B. Spectral unmixing of vegetation, soil and dry carbon cover in arid regions: Comparing multispectral and hyperspectral observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3939–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.M. Numeric classification as an aid to spectral mapping of vegetation communities. Plant Ecol. 1998, 136, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkworth, R.; Perry, R.; Rossetti, C. A comparison of methods of estimating plant cover in an arid grassland community. J. Range Manag. 1962, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, F.G. An enhanced wheel-point method for assessing cover, structure and heterogeneity in plant communities. J. Range Manag. 1989, 42, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.A.; Love, R.M. The step-point method of sampling-a practical tool in range research. Rangeland Ecol. Manag. J. Range Manag. Arch. 1957, 10, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, J.; Schmidt, M.; Tindall, D.; Trevithick, R.; Scarth, P.; Stewart, J. Field measurement of fractional ground cover: A technical handbook supporting ground cover monitoring for Australia. ABARES Canberra ACT 2011, 1–58. Available online: https://daff.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/search/asset/1027474/0 (accessed on 12 July 2017).
- Trevithick, R.; Muir, J.; Denham, R. The effect of observer experience levels on the variability of fractional ground cover reference data. In Proceedings of the XXII Congress of the International Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Society, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, C.; Clarke, K.D.; Delean, S.; Lewis, M.M. Distinguishing photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic vegetation: How do traditional observations and spectral classification compare? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jupp, D.L.B.; Reddy, S.; Lymburner, L.; Mueller, N.; Tan, P.; Islam, A. An evaluation of the use of atmospheric and BRDF correction to standardize Landsat data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Fang, H.; Chen, M.; Shuey, C.J.; Walthall, C.; Daughtry, C.; Morisette, J.; Schaaf, C.; Strahler, A. Validating MODIS land surface reflectance and albedo products: Methods and preliminary results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Okin, G.S. Evaluation of spectral unmixing techniques using MODIS in a structurally complex savanna environment for retrieval of green vegetation, nonphotosynthetic vegetation, and soil fractional cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M. Discrimination of arid vegetation composition with high resolution casi imagery. Rangeland J. 2000, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Sparrow, B.; Leitch, E.; Foulkes, J.; Flitton, R.; Lowe, A.J.; Caddy-Retalic, S. Ausplots Rangelands Survey Protocols Manual; University of Adelaide Press: Adelaide, Australia, 2012; Available online: https://www.tern.org.au/AusPlots-Rangelands-Survey-Protocols-Manual-pg23944.html (accessed on 24 August 2016).
- Stern, H.; De Hoedt, G.; Ernst, J. Objective classification of Australian climates. Austr. Meteorol. Mag. 2000, 49, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Meteorology. Climate Statistics for Australian Locations—Summary Statistics Fowlers Gap AWS. 2019. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/averages/tables/cw_046128.shtml (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Mabbutt, J.A.; Burrell, J.P.; Corbett, J.R.; Sullivan, M.E. Land Systems of Fowlers Gap Station; University of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 1973; pp. 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Meteorology. Climate Statistics for Australian Locations—Summary Statistics Broken Hill Airport AWS. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/averages/tables/cw_047048.shtml (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Benson, J. Setting the Scene: The Native Vegetation of New South Wales; Background Paper; Native Vegetation Advisory Council: Sydney, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Analytical Spectral Devices. In Fieldspec 3 User Manual; ASD Inc.: Boulder, Colorado, 2008.
- Gruninger, J.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Hoke, M.L. The Sequential Maximum Angle Convex Cone (Smacc) Endmember Model; Spectral Sciences Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Gillespie, A.R. Imaging spectroscopy: Interpretation based on spectral mixture analysis. In Remote Geochemical Analysis: Elemental and Mineralogical Composition; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J. Calibration and validation of the Australian fractional cover product for MODIS collection 6. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoscience Australia. Fractional Cover (fc25) Product Description. 2015. Available online: https://d28rz98at9flks.cloudfront.net/79676/Fractional_Cover_FC25_v1_5.PDF (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Department of the Environment. Conservation Management Zones of Australia; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2015.

| Bare Soil | ||||
| Step-point | Spectral | |||
| rs | MAE | rs | MAE | |
| Step-point | ||||
| Spectral | 0.82 | 19.26 | ||
| MODIS | 0.58 | 20.31 | 0.56 | 26.43 |
| Landsat | 0.79 | 13.85 | 0.79 | 19.95 |
| Non-photosynthetic Vegetation | ||||
| Step-point | Spectral | |||
| rs | MAE | rs | MAE | |
| Step-point | ||||
| Spectral | 0.61 | 19.82 | ||
| MODIS | 0.43 | 19.62 | 0.16 | 19.61 |
| Landsat | 0.68 | 15.79 | 0.71 | 14.86 |
| Photosynthetic Vegetation | ||||
| Step-point | Spectral | |||
| rs | MAE | rs | MAE | |
| Step-point | ||||
| Spectral | 0.87 | 1.37 | ||
| MODIS | 0.86 | 4.24 | 0.91 | 4.21 |
| Landsat | 0.5 | 4.68 | 0.45 | 4.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fisk, C.; Clarke, K.D.; Lewis, M.M. Comparison of Hyperspectral Versus Traditional Field Measurements of Fractional Ground Cover in the Australian Arid Zone. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232825
Fisk C, Clarke KD, Lewis MM. Comparison of Hyperspectral Versus Traditional Field Measurements of Fractional Ground Cover in the Australian Arid Zone. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(23):2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232825
Chicago/Turabian StyleFisk, Claire, Kenneth D. Clarke, and Megan M. Lewis. 2019. "Comparison of Hyperspectral Versus Traditional Field Measurements of Fractional Ground Cover in the Australian Arid Zone" Remote Sensing 11, no. 23: 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232825
APA StyleFisk, C., Clarke, K. D., & Lewis, M. M. (2019). Comparison of Hyperspectral Versus Traditional Field Measurements of Fractional Ground Cover in the Australian Arid Zone. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232825






