Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014
Abstract
1. Introduction
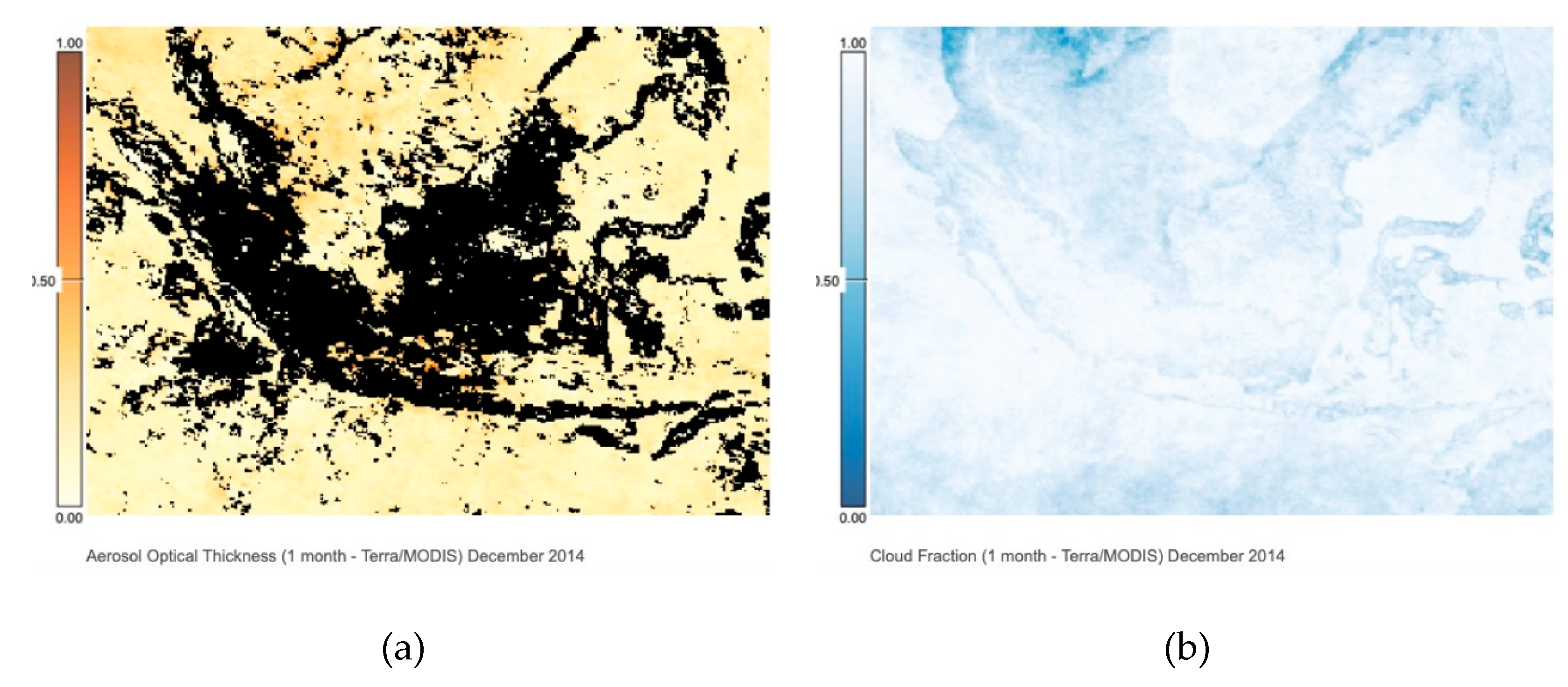
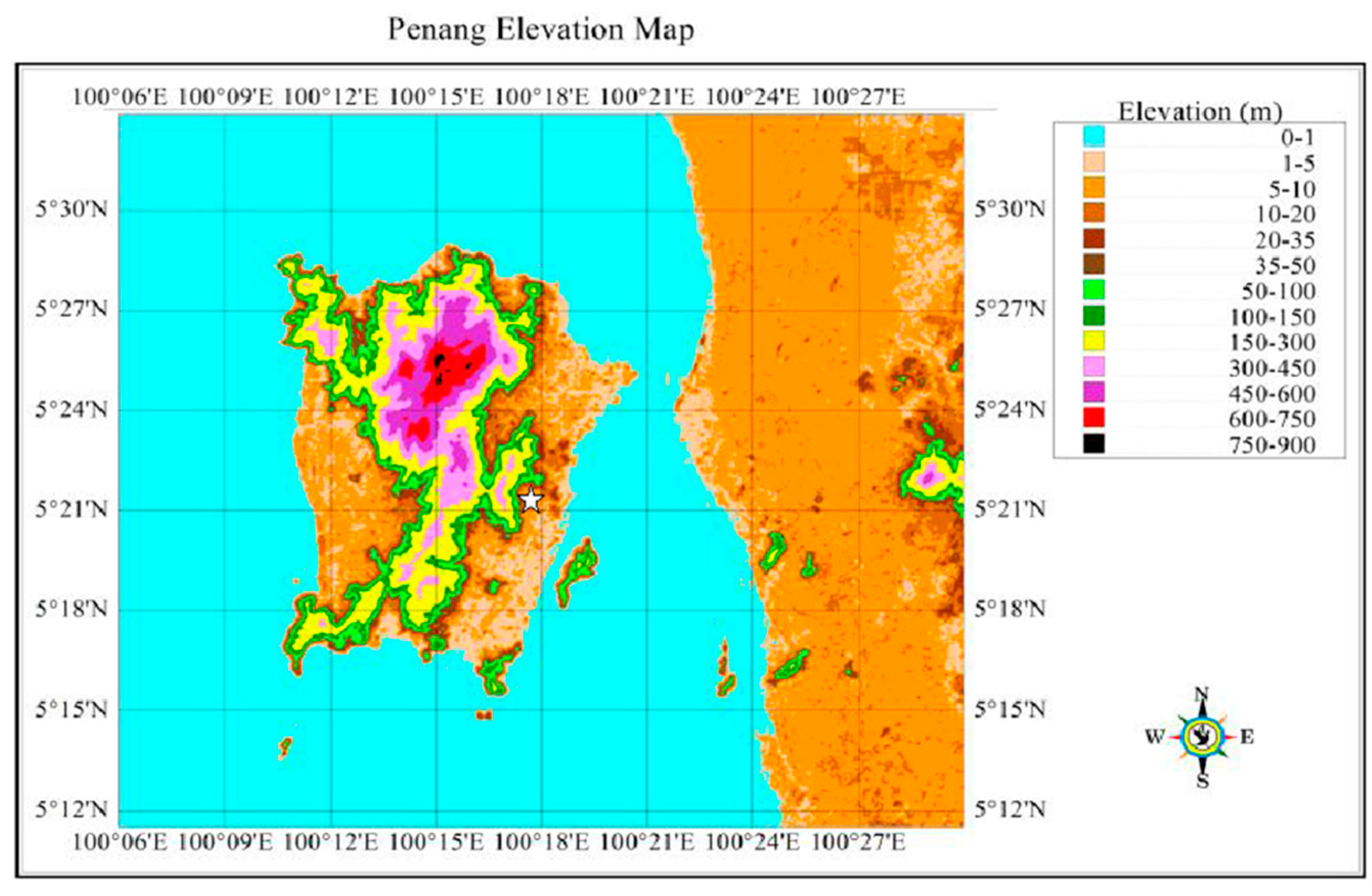
2. Study Area and Atmospheric Dynamics Analysis over the Observational Site
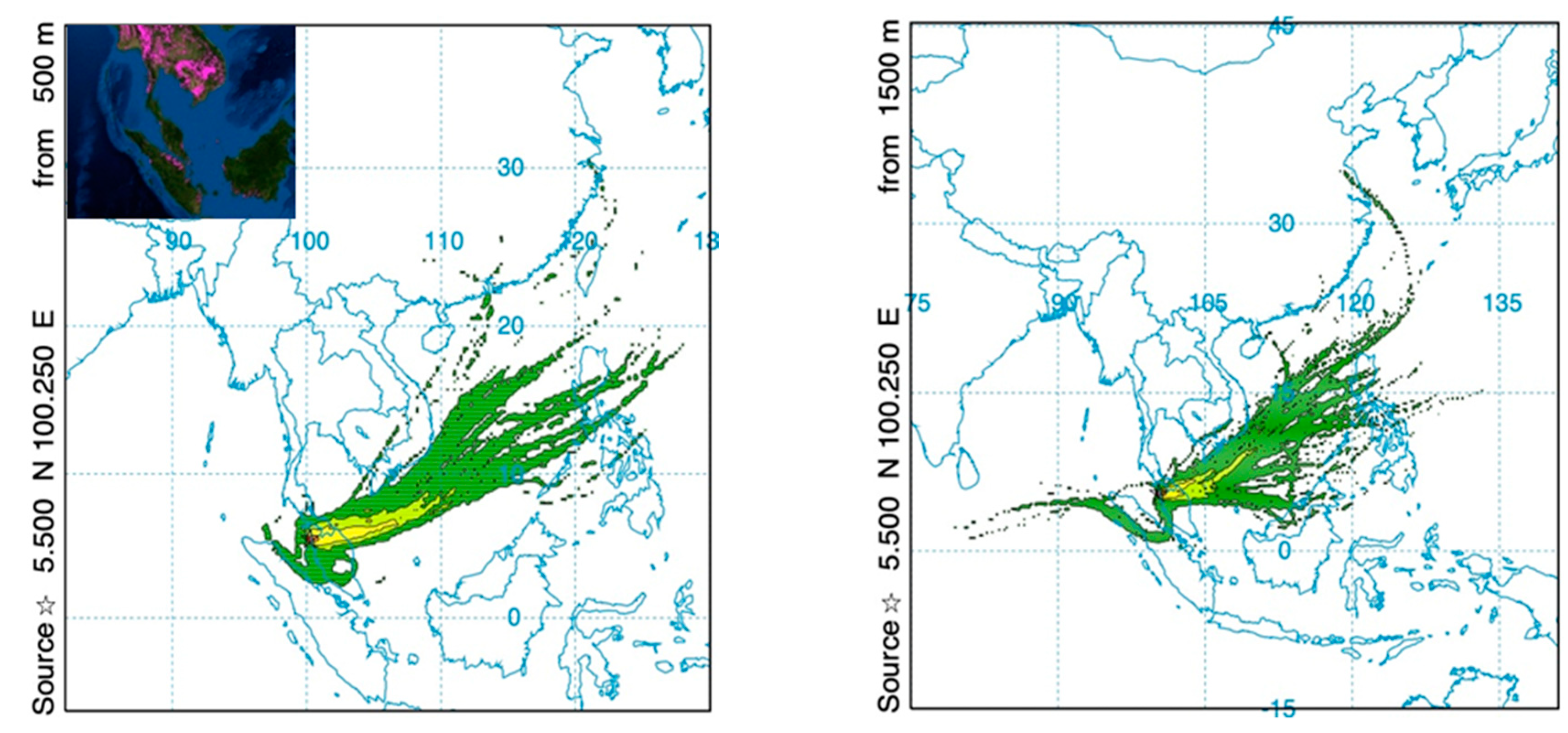
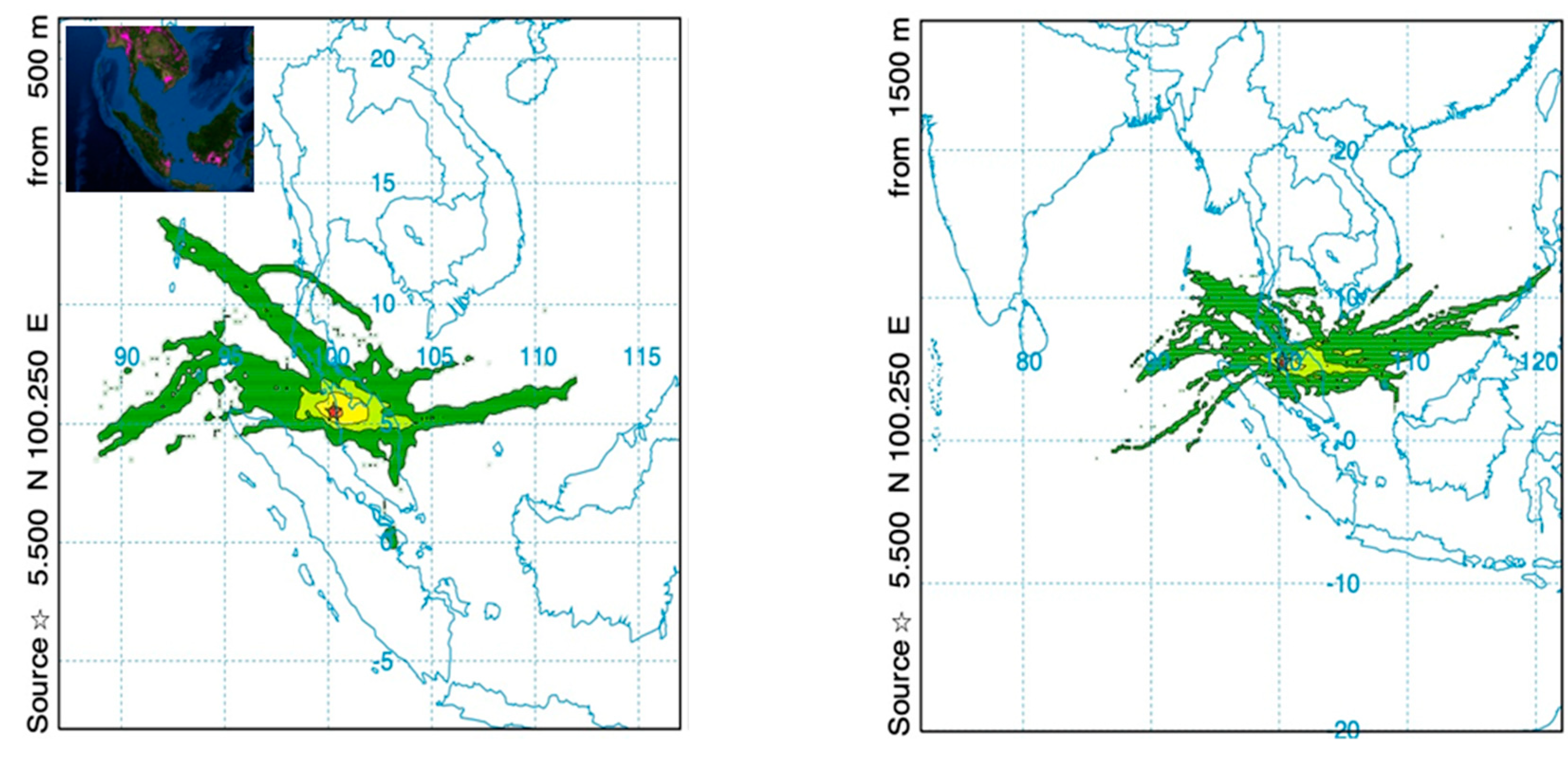
2.1. Back-Trajectory Analysis and Vertical Atmospheric Dynamics at Observational Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Raymetrics Lidar
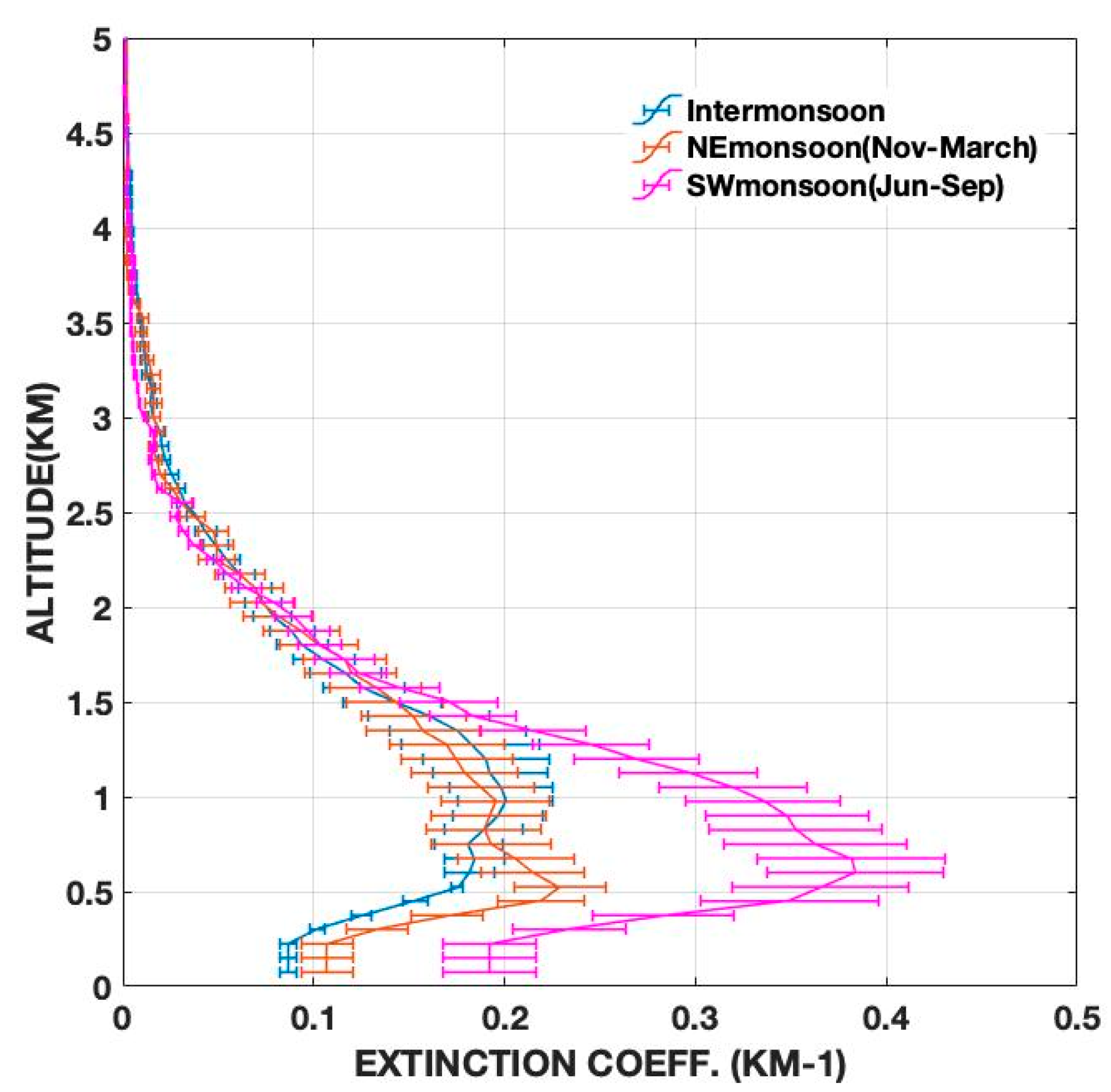
2014 Seasonally Averaged Atmospheric Extinction Coefficients
3.2. The Fu–Liou–Gu (FLG) Atmospheric Radiative Transfer Model
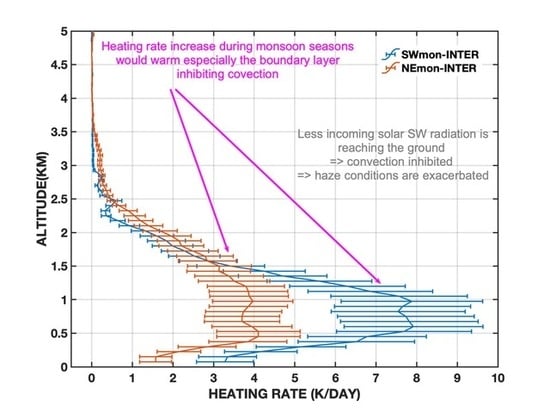
4. Results
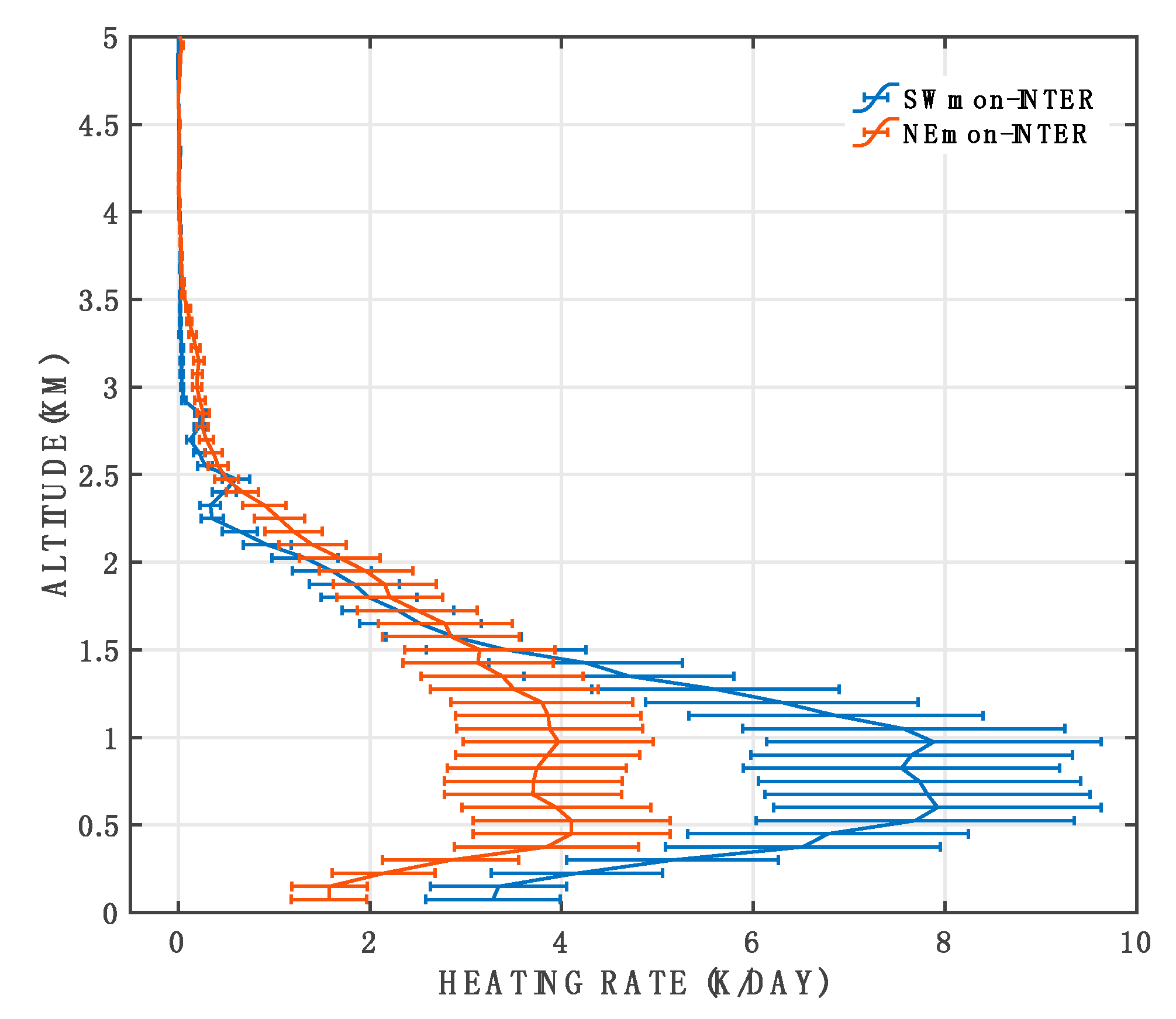
FLG RT Model Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, J.S.; Hyer, E.J.; Johnson, R.S.; Holben, B.N.; Yokelson, R.J.; Zhang, J.; Holz, R.E. Observing and Understanding the Southeast Asian Aerosol System by Remote Sensing: An Initial Review and Analysis for the Seven Southeast Asian Studies (7SEAS) Program. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 403–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Lagrosas, N.D.; Jonsson, H.H.; Reid, E.A.; Atwood, S.A.; Boyd, T.J.; Ghate, V.P.; Xian, P.; Posselt, D.J.; Simpas, J.B.; et al. Aerosol meteorology of Maritime Continent for the 2012 7SEAS southwest monsoon intensive study—Part 2: Philippine receptor observations of fine-scale aerosol behavior. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14057–14078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.D.; van der Werf, G.R.; Shen, S.S.P. Human amplification of drought-induced biomass burning in Indonesia since 1960. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J.; Liew, S.C. Degradation and development of peatlands in Peninsular Malaysia and in the islands of Sumatra and Borneo since 1990. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.E.F.; Siegert, J.O.; Rieley, H.D.V.; Boehm, A.; Jaya, S. Limin The amount of carbon released from peat and forest in Indonesia during 1997. Nature 2002, 420, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, G.; Ruecker, A.; Hindrichs, A.A. Hoffmann Increased damage from fires in logged forests during droughts caused by El Niño. Nature 2001, 414, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Xian, P.; Hyer, E.J.; Flatau, M.K.; Ramirez, E.M.; Turk, F.J.; Sampson, C.R.; Zhang, C.; Fukada, E.M.; Maloney, E.D. Multi-Scale Meteorological Conceptual Analysis of Observed Active Fire Hotspot Activity and Smoke Optical Depth in the Maritime Continent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2117–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.C.; Ge, J.; Wang, E.J.; Welton, A.; Bucholtz, E.J.; Hyer, E.A.; Reid, B.N.; Chew, S.; Liew, S.V.; Salinas, S.; et al. Applying Advanced Ground-Based Remote Sensing in the Southeast Asian Maritime Continent to Characterize Regional Proficiencies in Smoke Transport Modeling. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Di Girolamo, P. Principal Component Analysis Approach to Evaluate Instrument Performances in Developing a Cost-Effective Reliable Instrument Network for Atmospheric Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.; Hlavka, D.L.; Welton, C.J.; Flynn, E.J.; Turner, D.D.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S.; Hwang, I.H. Aerosol Lidar Observation at Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Program Sites: Instrument and Data Processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.J.; Campbell, J.R.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Scott, V.S. Global monitoring of clouds and aerosols using a network of micro-pulse lidar systems. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4153, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ciofini, M.; Lapucci, A.; Lolli, S. Diffractive optical components for high power laser beam sampling. J. Opt. A 2003, 5, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Delaval, A.; Loth, C.; Garnier, A.; Flamant, P.H. 0.355-micrometer direct detection wind lidar under testing during a field campaign in consideration of ESA’s ADM-Aeolus Mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Campbell, J.R.; Lewis, J.R.; Gu, Y.; Marquis, J.W.; Chew, B.N.; Liew, S.; Salinas, S.V.; Welton, E.J. Daytime Top-of-the-Atmosphere Cirrus Cloud Radiative Forcing Properties at Singapore. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2017, 56, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, P.E.; Devara, P.C.S.; Maheskumar, R.S.; Pandithurai, G.; Dani, K.K. Lidar Measurements of Aerosol Column Content in an Urban Nocturnal Boundary Layer. Atmos. Res. 1997, 45, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, D.; Mattis, I.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Dubovik, O.; Stohl, A. Saharan Dust over a Central European EARLINET-AERONET Site: Combined Observations with Raman Lidar and Sun Photometer. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Tsay, S.C.; Lin, N.H.; Chang, S.C.; Li, C.; Welton, E.J.; Kuo, C.C. Origin, transport, and vertical distribution of atmospheric pollutants over the northern South China Sea during the 7SEAS/Dongsha experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 78, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Wang, S.H.; Lin, N.H.; Tsay, S.C.; Lolli, S.; Chuang, M.T.; Yu, J.Y. Assessment of aerosol optical property and radiative effect for the layer decoupling cases over the northern South China Sea during the 7-SEAS/Dongsha Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.Y.; Hee, W.S.; Hwee, S.L.; Abdullah, K.; Tiem, L.Y.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Welton, E.J. Variation in daytime tropospheric aerosol via LIDAR and sunphotometer measurements in Penang, Malaysia. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1588, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Hee, W.S.; San Lim, H.; Jafri, M.Z.M.; Lolli, S.; Ying, K.W. Vertical Profiling of Aerosol Types Observed across Monsoon Seasons with a Raman Lidar in Penang Island, Malay. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Lau, N.C.; Johnson, R.H.; Wang, B.; Yasunari, T. The Global Monsoon System: Research and Forecast, 2nd ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, W.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Lucker, P.L.; Weimer, C. CALIPSO lidar description and performance assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Eck, T.F. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Qiu, Z.; Jäkel, E.; Lolli, S. A Simplified and Robust Surface Reflectance Estimation Method (SREM) for Use over Diverse Land Surfaces Using Multi-Sensor Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Barker, H.W.; Beljaars, A.; Ceccaldi, M.; Chepfer, H.; Clerbaux, N.; Fukuda, S. The EarthCARE satellite: The next step forward in global measurements of clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and radiation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Ricaud, P.; Zbinden, R.; Dulac, F. Atmospheric pollution over the eastern Mediterranean during summer—A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13233–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaysian Meteorological Department. 2013; Monsoon. Available online: http://www.met.gov.my/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=69&Itemid=160 (accessed on 19 August 2015).
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An Overview of the HYSPLIT_4 Modelling System for Trajectories, Dispersion, and Deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bahiyah, N.; Wahid, A.; Latif, M.T.; Suratman, S. Composition and source apportionment of surfactants in atmospheric aerosols of urban and semi-urban areas in Malaysia. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Hyer, E.J.; Chew, B.N. Aerosol transport model evaluation of an extreme smoke episode in Southeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Stable Analytical Inversion Solution for Processing Lidar Returns. Appl. Opt.. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolli, S. Rain Evaporation Rate Estimates from Dual-Wavelength Lidar Measurements and Intercomparison against a Model Analytical Solution. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Boselli, A.; Sasso, G.; Spinelli, S.; Wang, X. Optimization of the lidar optical design for measurement of the aerosol extinction vertical profile. EPJ Web Conf. 2019, 197, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wiegner, M.; Madonna, F.; Binietoglou, I.; Forkel, R.; Gasteiger, J.; Geiß, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Schäfer, K.; Thomas, W. What is the benefit of ceilometers for aerosol remote sensing? An answer from EARLINET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, J. The Extinction-to-Backscatter Ratio of Tropospheric Aerosol: A Numerical Study. J. Atnos. Ocean. Tech. 1998, 15, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrare, R.A.; Turner, D.D.; Brasseur, L.H.; Feltz, W.F.; Dubovik, O.; Tooman, T.P. Raman lidar measurements of the aerosol extinction-to-backscatter ratio over the Southern Great Plains. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20333–20347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselovskii, I.; Whiteman, D.N.; Korenskiy, M.; Suvorina, A.; Pérez-Ramírez, D. Use of rotational Raman measurements in multiwavelength aerosol lidar for evaluation of particle backscattering and extinction. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Wandinger, U.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C.; Michaelis, W. Independent measurement of extinction and backscatter profiles in cirrus clouds by using a combined Raman elastic-backscatter lidar. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo, P.; Ambrico, P.F.; Amodeo, A.; Boselli, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Spinelli, N. Aerosol observations by lidar in the nocturnal boundary layer. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 4585–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, E.J.; Voss, K.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Flatau, P.J.; Markowicz, K.; Campbell, J.R.; Johnson, J.E. Measurements of aerosol vertical profiles and optical properties during INDOEX 1999 using micropulse lidars. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Madonna, F.; Rosoldi, M.; Campbell, J.R.; Welton, E.J.; Lewis, J.R.; Gu, Y.; Pappalardo, G. Impact of varying lidar measurement and data processing techniques in evaluating cirrus cloud and aerosol direct radiative effects. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeffelin, F.; Angelini, Y.; Morille, G.; Martucci, S.; Frey, G.P.; Gobbi, S.; Lolli, C.D.; O’Dowd, L.; Sauvage, I.; Xueref-Rémy, B.; et al. Evaluation of Mixing-Height Retrievals from Automatic Profiling Lidars and Ceilometers in View of Future Integrated Networks in Europe. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2012, 143, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milroy, C.; Martucci, G.; Lolli, S.; Loaec, S.; Sauvage, L.; Xueref-Remy, I.; O’Dowd, C.D. An Assessment of Pseudo-Operational Ground-Based Light Detection and Ranging Sensors to Determine the Boundary-Layer Structure in the Coastal Atmosphere. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 929080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liou, K.N. On the correlated k-distribution method for radiative transfer in nonhomogeneous atmospheres. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 2139–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liou, K.N. Parameterization of the radiative properties of cirrus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liou, K.N.; Cribb, M.; Charlock, T.P.; Grossman, A. Multiple scattering parameterization in thermal infrared radiative transfer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ferrara, J.; Liou, K.N.; Mechoso, C.R. Parameterization of cloud–radiation processes in the UCLA general circulation model. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3357–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liou, K.N.; Ou, S.C.; Fovell, R. Cirrus cloud simulations using WRF with improved radiation parameterization and increased vertical resolution. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.H.; Muller, J.; Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C.; Tsang, T.; Gao, F.; Barnsley, M.J. MODIS BRDF/albedo product: Algorithm theoretical basis document version 5.0. MODIS Doc. 1999, 23, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.-J.; Morcrette, O.B. Estimates of aerosol radiative forcing from the MACC re-analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2045–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Koskinen, J.; De Leeuw, G.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Comparison of CALIOP level 2 aerosol subtypes to aerosol types derived from AERONET inversion data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.T.; Shine, K.P.; Forster, P.M. The semi-direct aerosol effect: Impact of absorbing aerosols on marine stratocumulus. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 130, 1407–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.C.P.J.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Emitter | |
|---|---|
| Pulsed Laser Source (Class IV Laser) | Nd:YAG (Quantel Ultra Series) |
| Wavelength | 355 nm |
| Energy/Pulse | 33.4 mJ |
| Pulse Duration | 5.04 ns |
| Repetition Rate | 20 Hz |
| Laser Beam Divergence | < 0.63 mrad |
| Near Field Beam Diameter | 33.7 mm |
| Receiver | |
| Telescope Type | Cassegrainian |
| Primary Diameter | 200 mm, Parabolic, F10 |
| Secondary Diameter | 47 mm diameter, obs: 100 mm |
| Transmitter–Receiver Distance | 162.5 mm |
| Field of View | 1.7 mrad (default, adjustable from 0.5 to 3 mrad) |
| Interference Filter Bandwidth | 1.1 nm @ 355 nm, 1 nm @ 376 nm, 0.88 nm @ 387 nm, 0.97 @ 408 nm |
| Detection Unit | |
| Transient Recorder | LICEL |
| Detection Channels | 2 channels for elastic backscattering 1 channel for Raman backscattering |
| Detectors | 3 PMTs |
| Detection Mode | Analog and photon counting (only photon for 376 nm) |
| Data Output | 2-D time-height cross sections, 3-D temporal evolution of any parameter, ASCII files |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lolli, S.; Khor, W.Y.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S. Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222660
Lolli S, Khor WY, Matjafri MZ, Lim HS. Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(22):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLolli, Simone, Wei Ying Khor, Mohd Zubir Matjafri, and Hwee San Lim. 2019. "Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014" Remote Sensing 11, no. 22: 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222660
APA StyleLolli, S., Khor, W. Y., Matjafri, M. Z., & Lim, H. S. (2019). Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sensing, 11(22), 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222660