Co-Seismic Deformation and Fault Slip Model of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran–Iraq Earthquake Inferred from D-InSAR Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
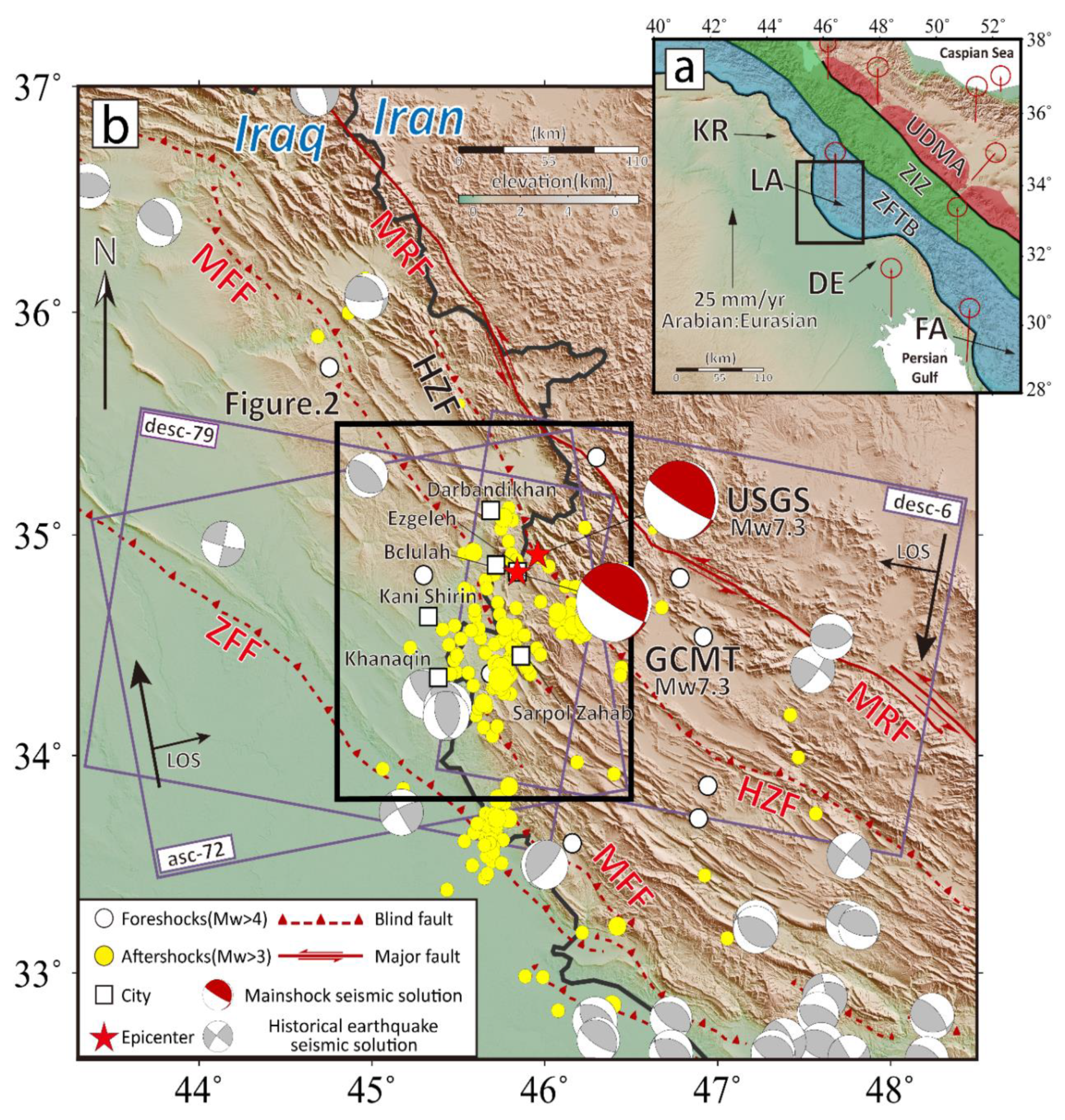
1.1. The Darbandikhan Earthquake
1.2. Tectonic Setting
2. InSAR Measurements
2.1. SAR Interferometry
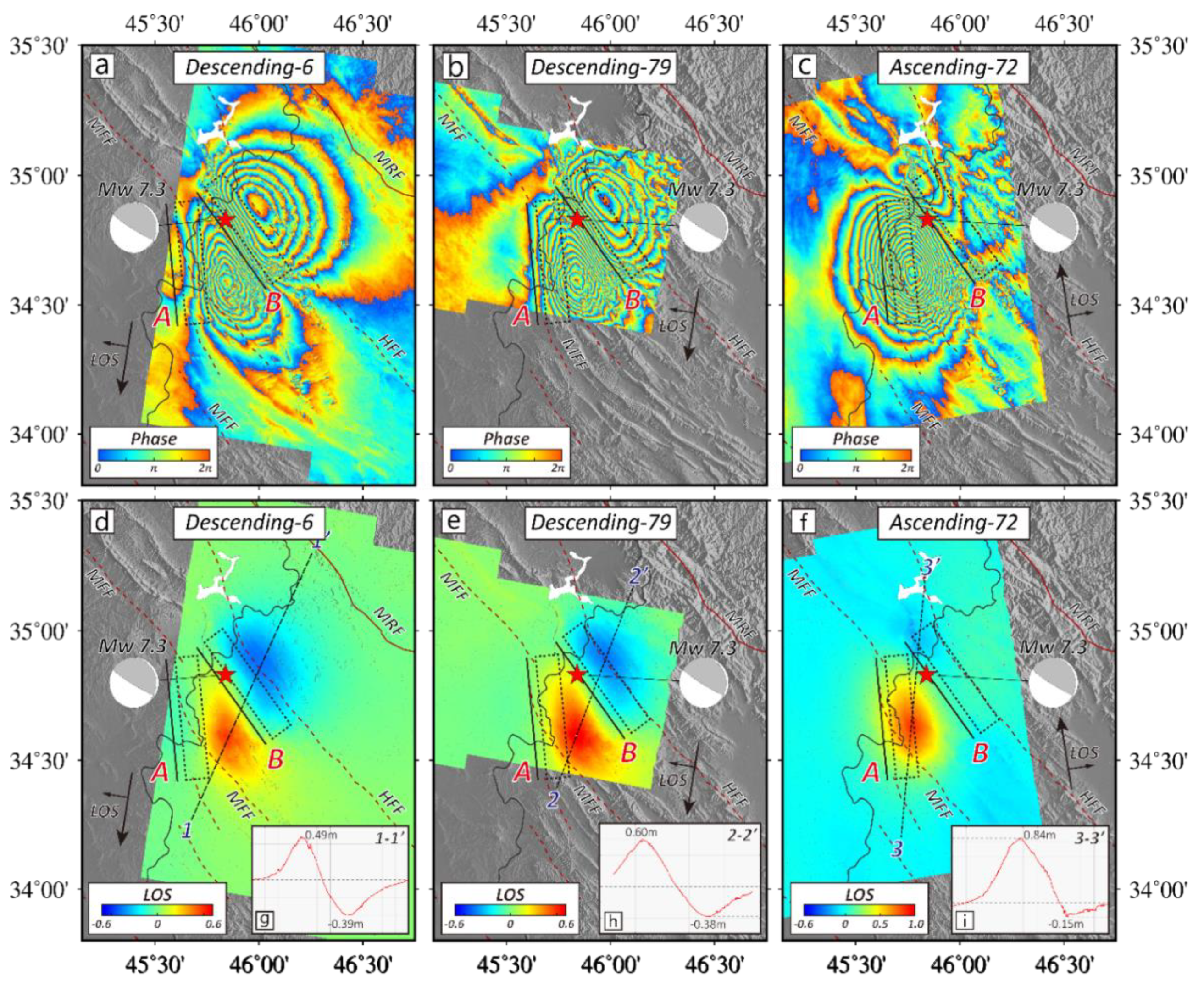
2.2. Coseismic Interferograms
3. Determination of the Three-Dimensional (3D) Coseismic Displacement Field
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Analysis on the 3D Co-Seismic Deformation Field
4. Fault Slip Distribution Inversion
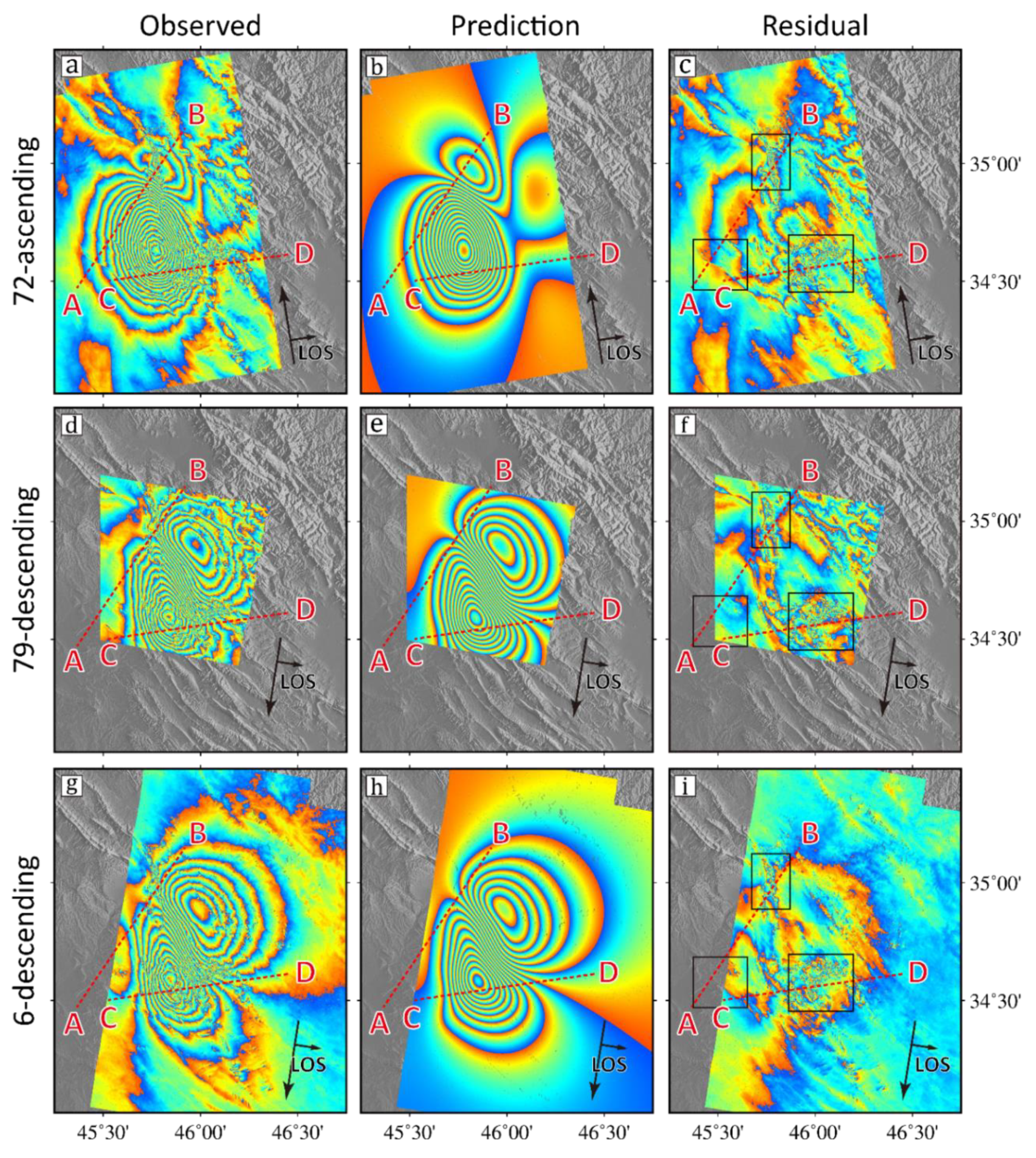
4.1. Inversion Method
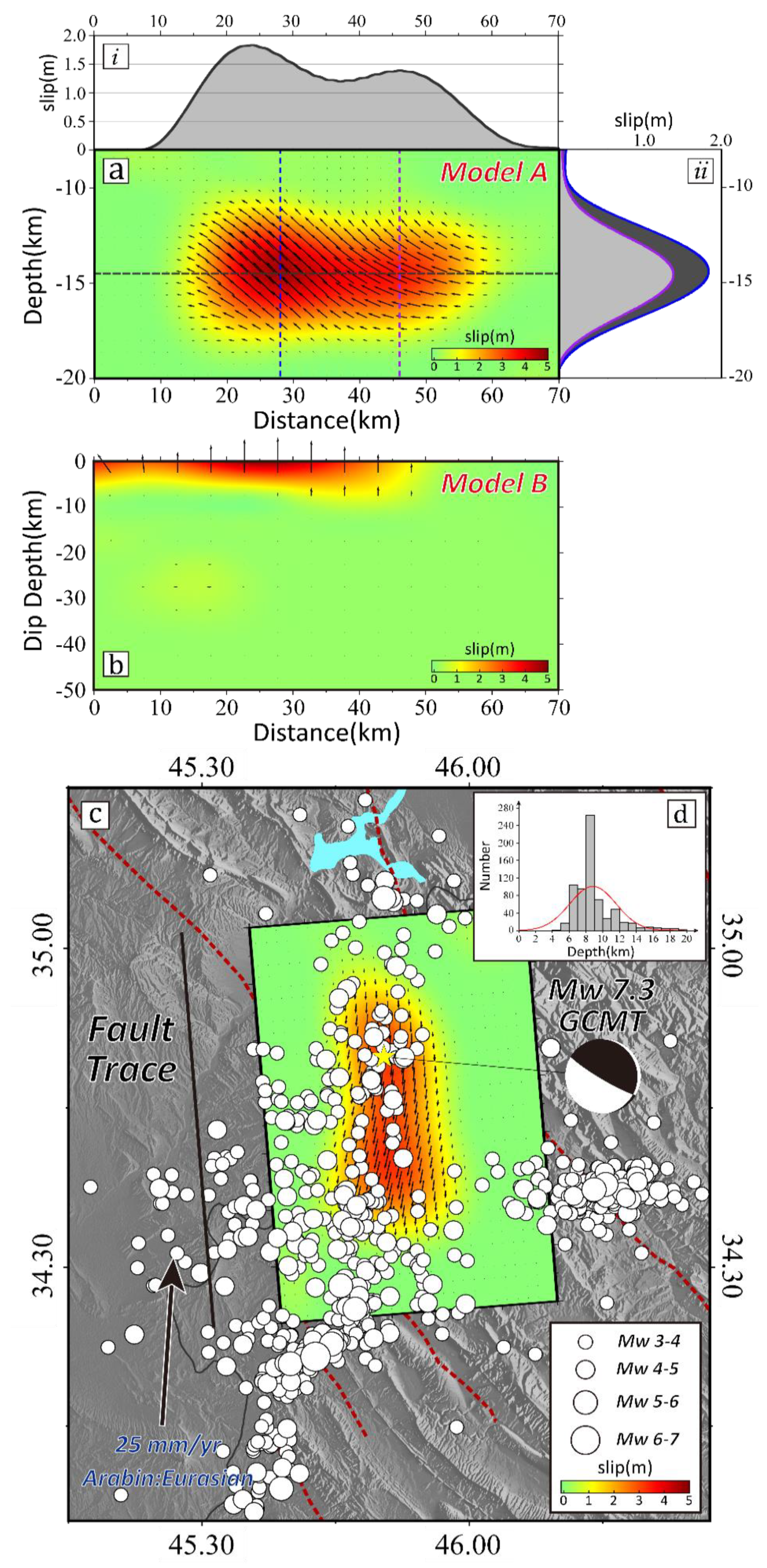
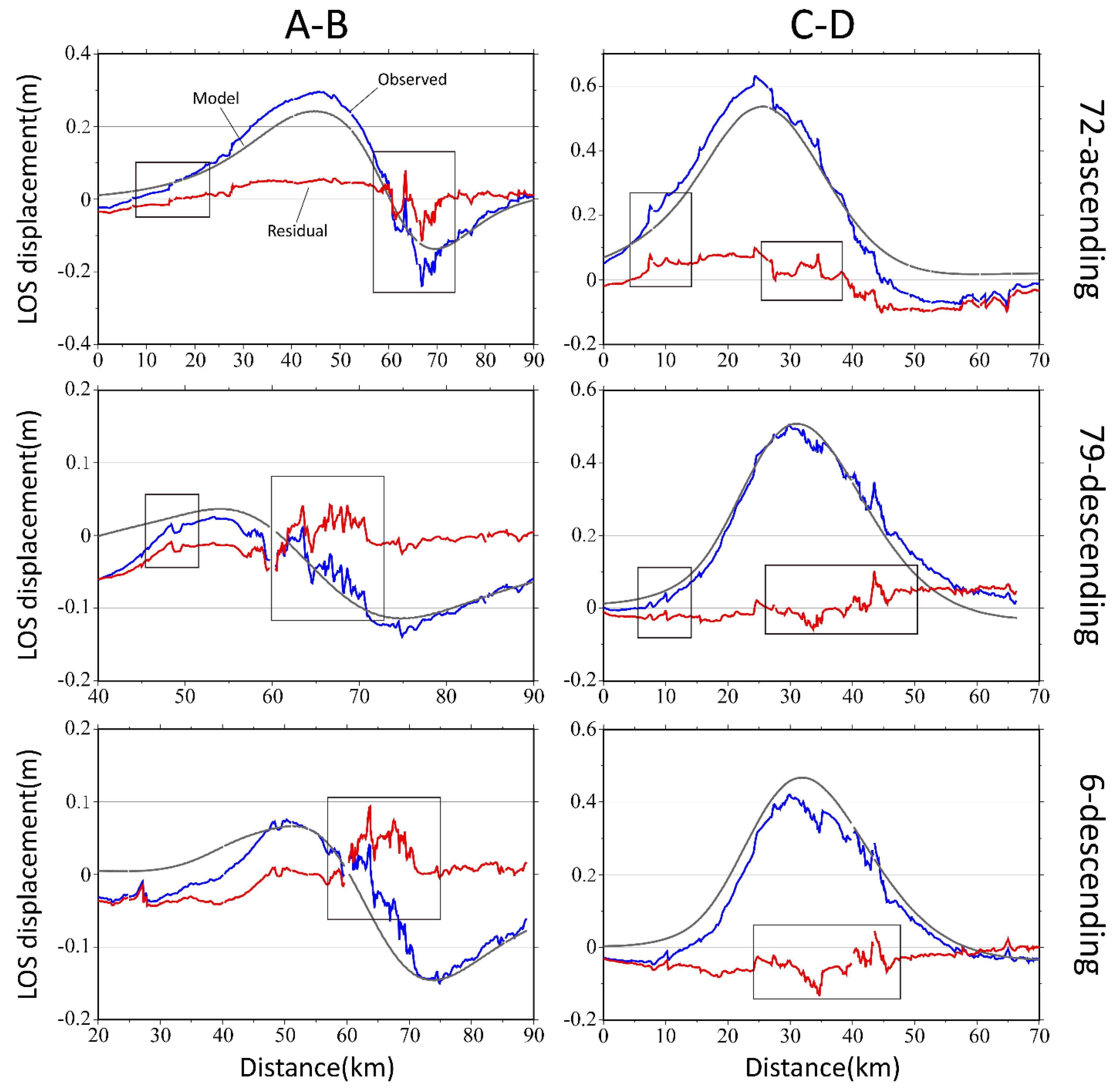
4.2. Distribution of Coseismic Slip
5. Discussion
5.1. Determination of the Seismogenic Fault
5.2. Oblique Thrusting and Its Implication of the Darbandikhan Earthquake
5.3. The Relationship Between the Master Blind Thrust and Surface Fold
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zare, M.; Kamranzad, F.; Parcharidis, I.; Tsironi, V. Preliminary Report of Mw7.3 Sarpol-E Zahab, Iran Earthquake on November 12, 2017; International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES): Tehran, Iran, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vernant, P.; Nilforoushan, F.; Hatzfeld, D.; Abbassi, M.R.; Vigny, C.; Masson, F.; Nankali, H.; Martinod, J.; Ashtiani, A.; Bayer, R.; et al. Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahryar Solaymani Azad, N.; Moradi, S.M.; Ajhdari, A.; Youssefi, T.; Mashal, M.; Roustaie, M. Preliminary Report on Geological Features of the Ezgaleh-Kermanshah Earthquake; Geological Survey of Iran Seismotectonics & Seismology Department: Tehran, Iran, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Morishita, Y.; Yarai, H.; Fujiwara, S. InSAR-derived crustal deformation and reverse fault motion of the 2017 Iran–Iraq Earthquake in the Northwest of the Zagros Orogenic Belt. Bull. Geospat. Inf. 2018, 66, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, G. Retrieving threedimensional co-seismic deformation of the 2017 Mw7.3 Iraq earthquake by multi-sensor SAR images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, W.D.; Brengman, C.M.J.; Li, S.; Peterson, K.E. Ramp-flat basement structures of the Zagros Mountains inferred from co-seismic slip and afterslip of the 2017 Mw7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran/Iraq earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 496, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Samsonov, S.; Almeida, R.; Yassaghi, A.; Li, J.; Qiu, Q.; Li, P.; Zheng, W. Geodetic Constraints of the 2017 M w 7.3 Sarpol Zahab, Iran Earthquake, and its implications on the structure and mechanics of the Northwest Zagros Thrust-Fold Belt. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6853–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessami, K.; Jamali, F.; Tabassi, H. Active Faults of Iran; International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES): Tehran, Iran, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nissen, E.; Tatar, M.; Jackson, J.A.; Allen, M.B. New views on earthquake faulting in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt of Iran. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 186, 928–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Ge, L.; Metternicht, G.I.; Hay, A.; Ng, M.; Wang, H.; Zare, M.; Kamranzad, F. Coseismic deformation and source model of the 12 November 2017 MW 7.3 Kermanshah Earthquake (Iran–Iraq border) investigated through DInSAR measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R.; Jolivet, R.; Gonzalez, P.J.; Avouac, J.-P.; Hollingsworth, J.; Searle, M.P.; Stevens, V.L. Himalayan megathrust geometry and relation to topography revealed by the Gorkha earthquake. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 9, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanne, F.; Awan, A.; Madji, A.; Pêcher, A.; Latif, M.; Kausar, A.; Mugnier, J.L.; Khan, I.; Khan, N.A. Postseismic deformation in Pakistan after the 8 October 2005 earthquake: Evidence of afterslip along a flat north of the Balakot-Bagh thrust. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B07401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funning, G.J.; Parsons, B.; Wright, T.J.; Jackson, J.A.; Fielding, E.J. Surface displacements and source parameters of the 2003 Bam (Iran) earthquake from Envisat advanced synthetic aperture radar imagery. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, B09406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C. Gamma SAR processor and interferometry software. In Proceedings of the 3rd ERS Symposium, Florence, Italy, 14–21 March 1997. [Google Scholar]
- González, P.J.; Bagnardi, M.; Hooper, A.J.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Samsonov, S.V.; Wright, T.J. The 2014–2015 Eruption of Fogo Volcano: Geodetic Modeling of Sentinel-1 TOPS Interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9239–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A Novel Phase Unwrapping Method Based on Network Programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Rosen, P.A. A Generalized Phase Unwrapping Approach for Sparse Data. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Doin, M.-P.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G.; Cavalié, O.; Doubre, C. Corrections of stratified tropospheric delays in SAR interferometry: Validation with global atmospheric models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.; England, P.C.; Fielding, E.J. InSAR observations of low slip rates on the major faults of western Tibet. Science 2004, 305, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, H.; Stuefer, M.; Siegel, A.; Skvarca, P.; Eckstaller, A. Mass fluxes and dynamics of Moreno Glacier, Southern Patagonia Icefield. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Short, N.; Mattar, K.E.; Jezek, K.C. Velocities and flux of the Filchner ice shelf and its tributaries determined from speckle tracking interferometry. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 27, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmüller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Precision estimation of local offsets between pairs of SAR SLCs and detected SAR images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2005: IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 29 July 2005; Volume 7, pp. 4803–4805. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y. Surface Deformation Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Motagh, M.; Walter, T.R. Inversion of slip distribution from coseismic deformation data by a sensitivity-based iterative fitting (SBIF)method. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 13–18 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ainscoe, E.A.; Elliott, J.R.; Copley, A.; Craig, T.J.; Li, T.; Parsons, B.E.; Walker, R.T. Blind thrusting, surface folding, and the develop-ment of geological structure in the Mw 6.3 2015 Pishan (China) earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 122, 9359–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Liang, C.; Song, Y.T. Towards the application of seismogeodesy in central Italy: A case study for the 2016 August 24 Mw 6.1 Italy earthquake modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustaei, M.; Nissen, E.; Abbassi, M.; Gholamzadeh, A.; Ghorashi, M.; Tatar, M.; Yamini-Fard, F.; Bergman, E.; Jackson, J.; Parsons, B. The 2006 March 25 Fin earthquakes (Iran)—Insights into the vertical extents of faulting in the Zagros Simply Folded Belt. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciello, E.; Vergés, J.; Saura, E.; Casini, G.; Fernández, N.; Blanc, E.; Homke, S.; Hunt, D.W. Fold patterns and multilayer rheology of the Lurestan Province, Zagros Simply Folded Belt (Iran). J. Geol. Soc. 2009, 166, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzfeld, D.; Tatar, M.; Priestley, K.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M. Seismological constraints on the crustal structure beneath the Zagros Mountain belt (Iran). Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 155, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yielding, G.; Jackson, J.A.; King, G.C.P.; Sinvhal, H.; Vita-Finzi, C.; Wood, R.M. Relations between surface deformation, fault geometry, seismicity, and rupture characteristics during the El Asnam (Algeria) earthquake of 10 October 1980. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 56, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, M. Master “blind” thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: Active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics. Tectonophysics 1995, 241, 193–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, M.; Jackson, J. A reappraisal of earthquake focal mechanisms and active shortening in the Zagros mountains of Iran. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 156, 506–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Jackson, J.A.; Haynes, M.; Fielding, E.J.; England, P.C.; Clarke, P.J. Source parameters of the 1 October 1995 Dinar (Turkey) earthquake from SAR interferometry and seismic bodywave modelling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 172, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, E.; Ghorashi, M.; Jackson, J.; Parsons, B.; Talebian, M. The 2005 Qeshm Island earthquake (Iran)—A link between buried reverse faulting and surface folding in the Zagros Simply Folded Belt? Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzfeld, D.; Molnar, P. Comparisons of the kinematics and deep structures of the Zagros and Himalaya and of the Iranian and Tibetan plat-eaus and geodynamic implications. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.B.; Saville, C.; Blanc, E.J.-P.; Talebian, M.; Nissen, E. Orogenic plateau growth: Expansion of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau across the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt. Tectonics 2013, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J. Geodetic model of the 2015 April 25 Mw 7.8 Gorkha Nepal Earthquake and Mw 7.3 after-shock estimated from InSAR and GPS data. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 203, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, P.Z.; Zeng, L.S.; Li, Z.F.; Wang, W. Tectonic setting and general features of coseismic rupture of the 25 April, 2015 M w 7.8 Gorkha, Nepal earthquake. China Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 2640–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.J.; Zhang, G.H.; Wang, C.S.; Li, Y.C.; Qu, C.Y.; Song, X.G.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.H. Joint inversion for the spatial fault slip distribution of the 2015 Nepal Mw 7.9 earthquake based on InSAR and GPS observations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilinger, R.; McClusky, S.; Vernant, P.; Lawrence, S.; Ergintav, S.; Çakmak, R.; Ozener, H.; Kadirov, F.; Guliev, I.; Stepanyan, R.; et al. GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa- Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B05411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon, N. Problems of the relationship between surface structure and deep displacements illustrated by the Zagros Range. Geol. Soc. (Lond.) Spec. Publ. 2015, 3, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.A. Reactivation of basement faults and crustal shortening in orogenic belts. Nature 1980, 283, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherkati, S.; Letouzey, J.; Frizon de Lamotte, D. Central Zagros fold-thrust belt (Iran): New insights from seismic data, field observation, and sandbox modeling. Tectonics 2015, 25, TC4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F. New, improved version of the Generic Mapping Tools released, Eos Trans. AGU 1998, 79, 579. [Google Scholar]


| Source | Epicenter | Fault Plane 1 | Fault Plane 2 | Depth (km) | Mw | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Strike (°) | Dip (°) | Rake (°) | Strike (°) | Dip (°) | Rake (°) | |||
| USGS 1 | 45.96 | 34.91 | 351 | 16 | 137 | 122 | 79 | 78 | 21.5 | 7.3 |
| Global CMT 2 | 45.84 | 34.83 | 351 | 11 | 140 | 121 | 83 | 82 | 18.0 | 7.3 |
| Barnhart et al. (2018) 3 | 45.87 a | 34.65 a | 350 | 15 | 128 b | —— | —— | —— | 15.0 a | 7.3 |
| Feng et al. (2018) 3 | 45.86 a | 34.73 a | 353.5 | 14.5 | 135.6 b | —— | —— | —— | 14.5 a | 7.3 |
| InSAR (this study) | —— | —— | 355.5 | 17.5 | 135.5 b | —— | — | —— | 14.5 a | 7.2 |
| Track | Methods | Orbit Path | Data 1 | Data 2 | Heading (°) | Incidence (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | D-InSAR Offset-tracking | Ascending | 12 November 2017 | 17 November 2017 | 62 | 6 | −12.95 | 33.78 |
| 79 | D-InSAR | Descending | 17 November 2017 | 18 November 2017 | 56 | 6 | −166.96 | 33.97 |
| 6 | D-InSAR Offset-tracking | Descending | 17 November 2017 | 19 November 2017 | 15 | 12 | −167.02 | 33.86 |
| Parameter | Length (km) | Width (km) | Top Depth | Bottom Depth | Dip | Strike | Slip 1 | Rake 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InSAR | 70 | 35 | 8.5 | 20 | 17.5 | 355.5 | 3.6 | 135.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Shan, X.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Co-Seismic Deformation and Fault Slip Model of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran–Iraq Earthquake Inferred from D-InSAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212521
Huang Z, Zhang G, Shan X, Gong W, Zhang Y, Li Y. Co-Seismic Deformation and Fault Slip Model of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran–Iraq Earthquake Inferred from D-InSAR Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(21):2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212521
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zicheng, Guohong Zhang, Xinjian Shan, Wenyu Gong, Yingfeng Zhang, and Yanchuan Li. 2019. "Co-Seismic Deformation and Fault Slip Model of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran–Iraq Earthquake Inferred from D-InSAR Measurements" Remote Sensing 11, no. 21: 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212521
APA StyleHuang, Z., Zhang, G., Shan, X., Gong, W., Zhang, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Co-Seismic Deformation and Fault Slip Model of the 2017 Mw 7.3 Darbandikhan, Iran–Iraq Earthquake Inferred from D-InSAR Measurements. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212521





