Impacts of AOD Correction and Spatial Scale on the Correlation between High-Resolution AOD from Gaofen-1 Satellite and In Situ PM2.5 Measurements in Shenzhen City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Materials, and Methods
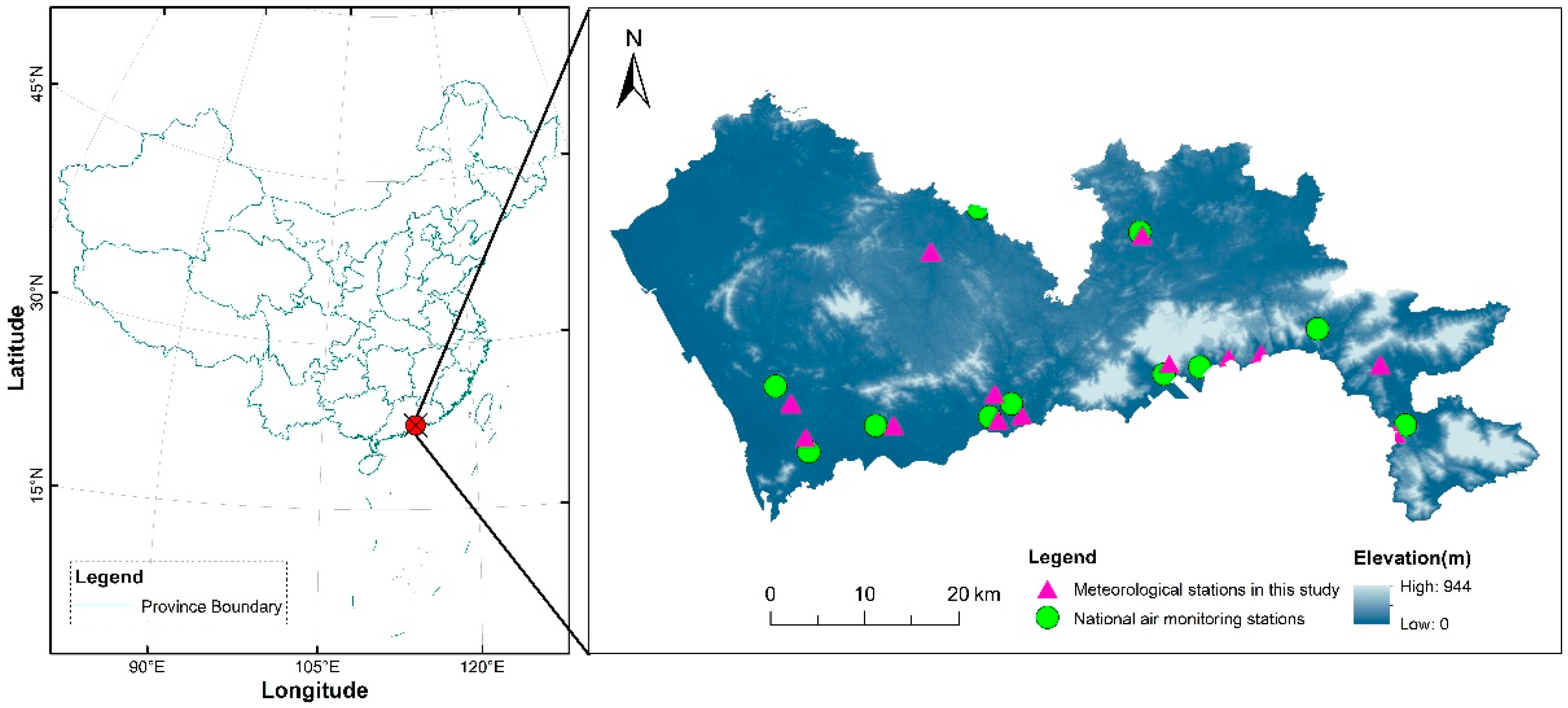
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data from the GF-1 Satellite
2.2.2. In Situ PM2.5 Measurement Data
2.2.3. Meteorological Station Data
2.2.4. Planet Boundary Layer Height Data
2.2.5. Terra MODIS 3-km DT AOD Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. GF-1 AOD Retrieval and Validation
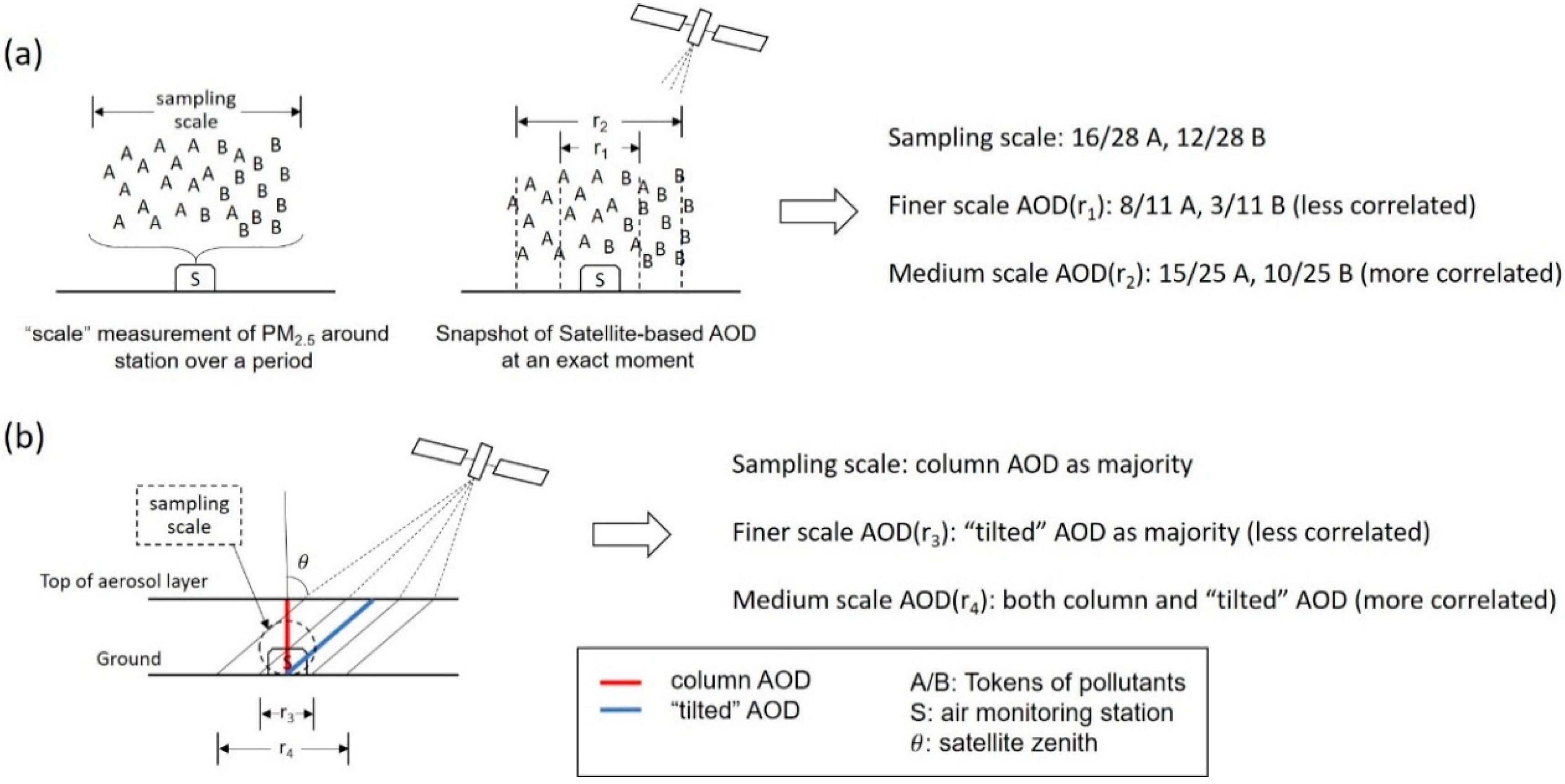
2.3.2. Extraction of AOD at Different Spatial Scales
2.3.3. Vertical and Humidity Corrections of AOD
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
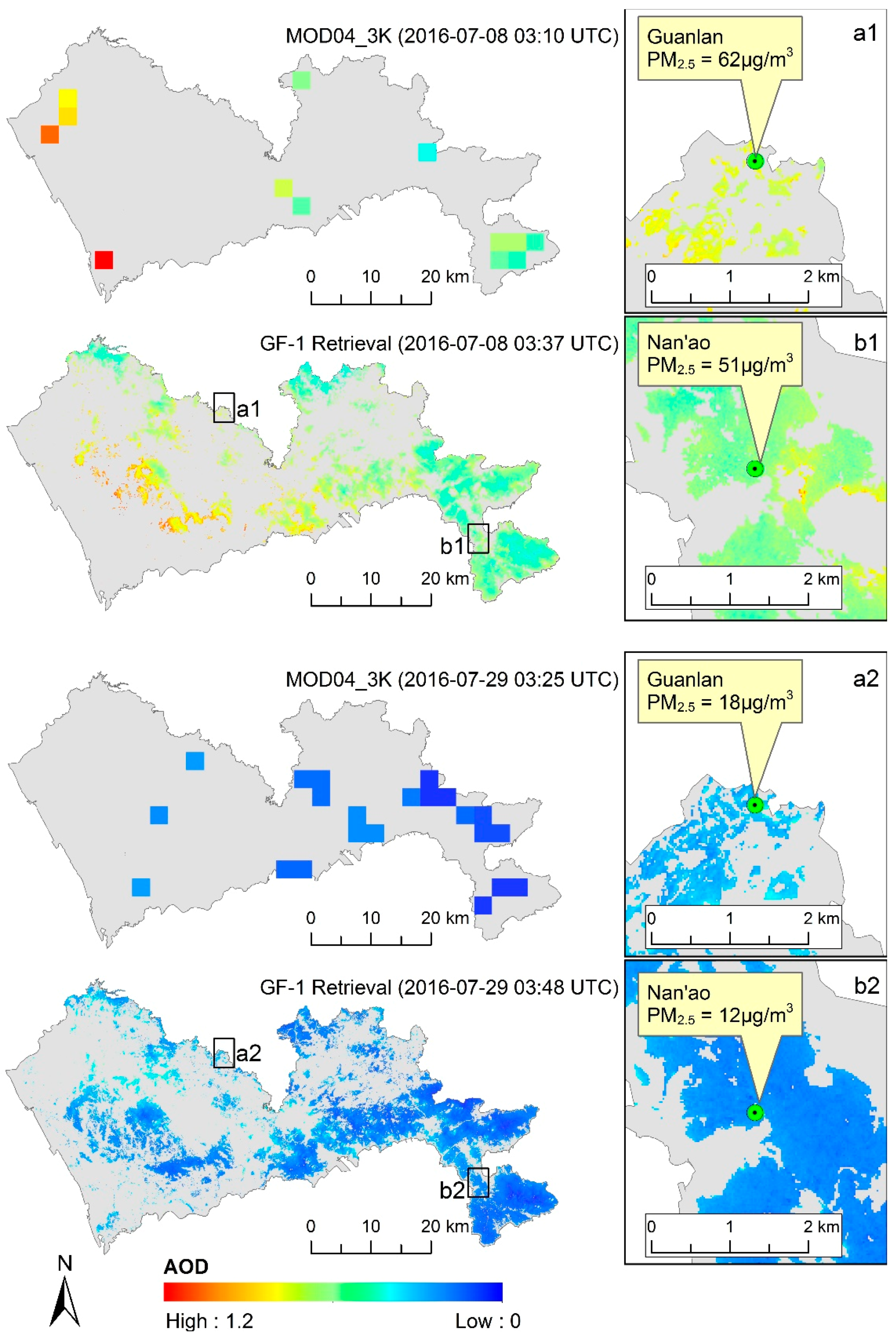
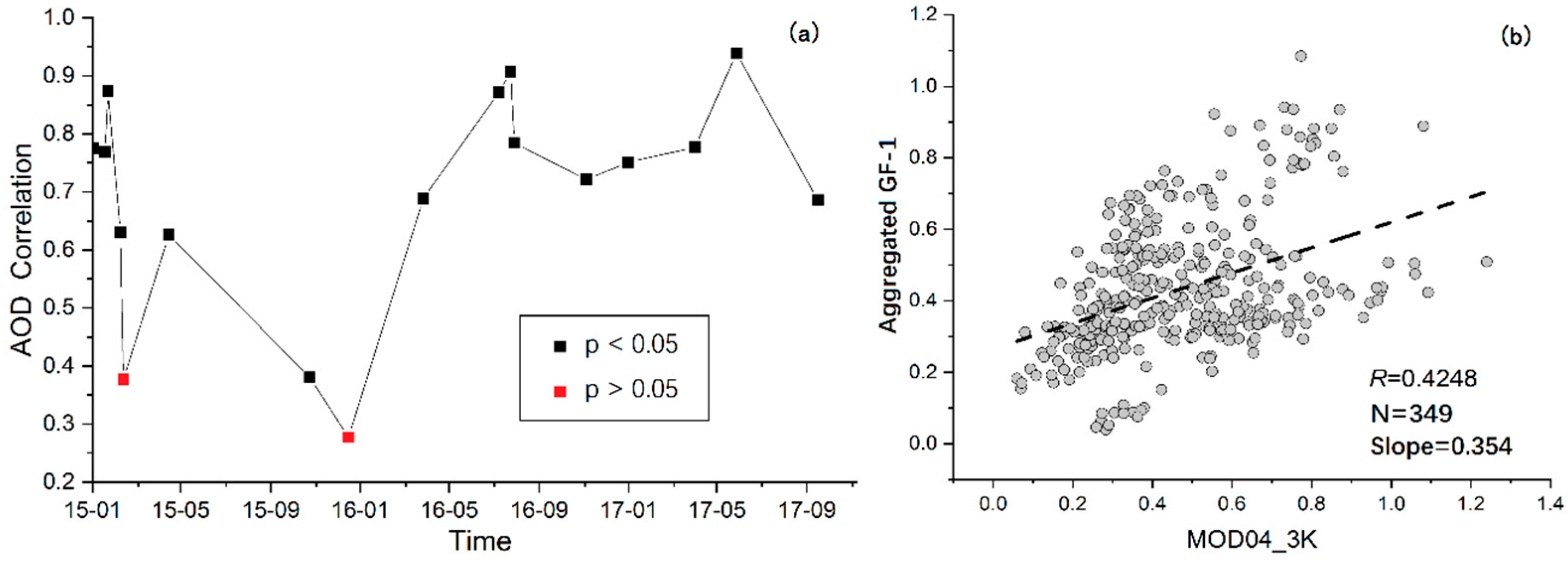
3.2. Retrieved and Validated GF-1 AOD
3.3. Pearson Correlation between GF-1 AOD and PM2.5 Concentrations
4. Discussion
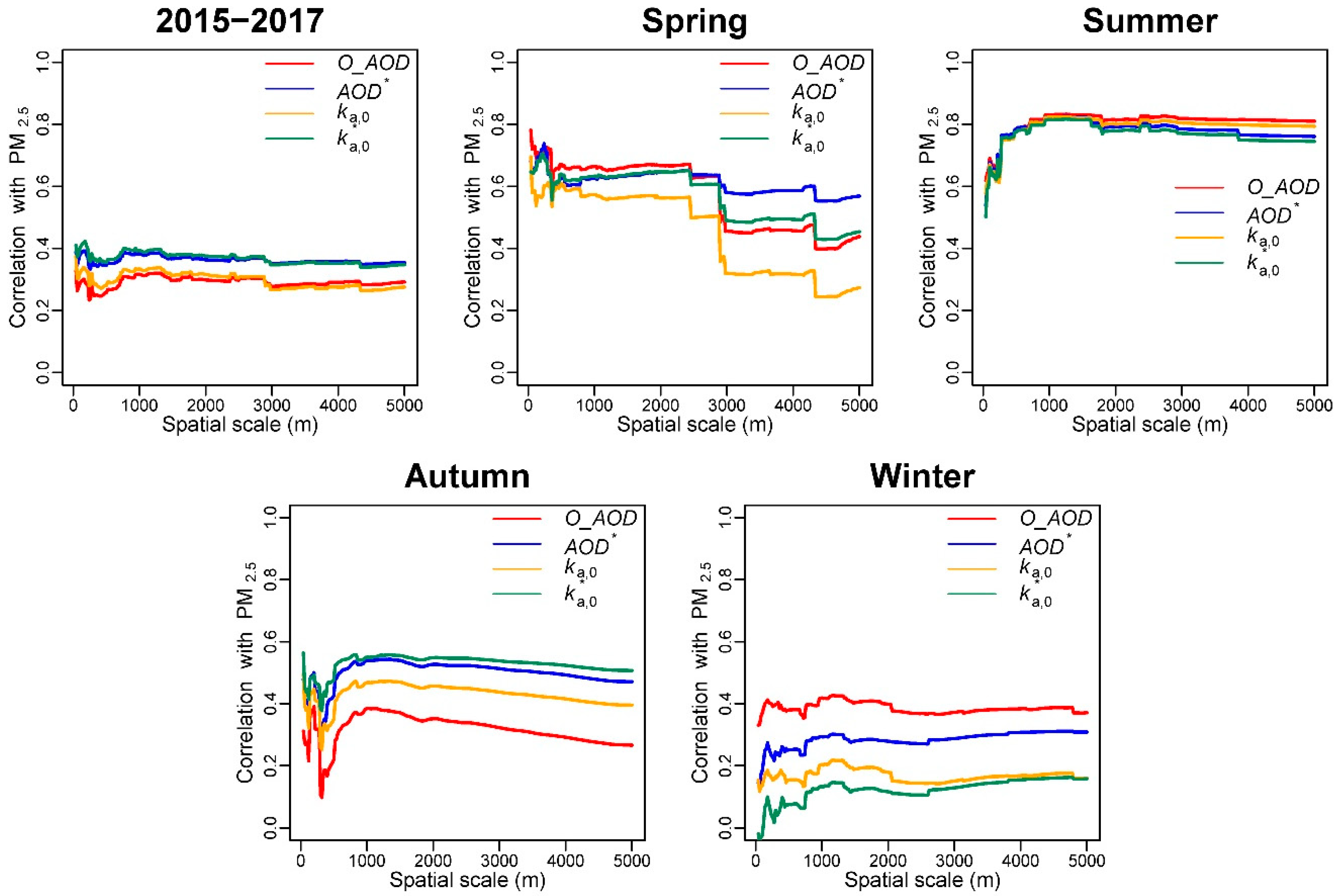
4.1. AOD Correction Effect on Correlations between AOD and PM2.5 Concentrations
4.2. Spatial Scale Effect on Correlations between AOD and PM2.5 Concentrations
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Mauderly, J.L.; Costa, D.L.; Wyzga, R.E.; Vedal, S.; Hidy, G.M.; Altshuler, S.L.; Marrack, D.; Heuss, J.M.; et al. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A.I.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease an Update to the Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Turner, M.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Krewski, D.; Brook, R.D. Relationships Between Fine Particulate Air Pollution, Cardiometabolic Disorders, and Cardiovascular Mortality. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 108–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.C.; Krewski, D.; Pope, C.A.I.; Chen, Y.; Gapstur, S.M.; Thun, M.J. Long-Term Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Lung Cancer in a Large Cohort of Never-Smokers. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Ho, K.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Han, J.; Xu, Z. Effect of chemical composition of PM2.5 on visibility in Guangzhou, China, 2007 spring. Particuology 2009, 7, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Tian, X. The impact of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on China’s agricultural production from 2001 to 2010. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Yi, S.; Kim, Y.P. Dry deposition fluxes of ambient particulate heavy metals in a small city, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, M.; Bagiroz, H.O. Sulfate dry deposition fluxes and overall deposition velocities measured with a surrogate surface. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 297, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Riemer, N.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Li, S. Urban heat island impacted by fine particles in Nanjing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.; Boucher, O. Estimates of the direct and indirect radiative forcing due to tropospheric aerosols: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanollahi, J.; Tzanis, C.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ramli, M.F.; Pirasteh, S. Development of the models to estimate particulate matter from thermal infrared band of Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, J.; Szykman, J.; Pierce, R.B.; Kittaka, C.; Neil, D.; Chu, D.A.; Remer, L.; Gumley, L.; Prins, E.; Weinstock, L.; et al. Improving national air quality forecasts with satellite aerosol observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote Sensing of Particulate Pollution from Space: Have We Reached the Promised Land? J Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Sendra, C. Algorithm for automatic atmospheric corrections to visible and near-IR satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 9, 1357–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Fallah-Adl, H.; Kalluri, S.; Jájá, J.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Townshend, J.R.G. An operational atmospheric correction algorithm for Landsat Thematic Mapper imagery over the land. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17173–17186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, B.; Bilal, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. Verification, improvement and application of aerosol optical depths in China Part I: Inter-Comparison of NPP-VIIRS and Aqua-MODIS. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 175, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z.; Du, L.; Gong, W. Validation of VIIRS AOD through a Comparison with a Sun Photometer and MODIS AODs over Wuhan. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, X. MODIS AOD sampling rate and its effect on PM2.5 estimation in North China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Si, M.; Li, W.; Wu, J. A multidimensional comparison between MODIS and VIIRS AOD in estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over a heavily polluted region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.; Li, G.; Gu, D.; Pan, X.; Liu, Y. MAIAC-based long-term spatiotemporal trends of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, L.; Alpert, P.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Chudnovsky, A. An example of aerosol pattern variability over bright surface using high resolution MODIS MAIAC: The eastern and western areas of the Dead Sea and environs. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Xue, Y.; Xu, H.; Guang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ai, J.; Jiang, S.; He, X. Validation and analysis of aerosol optical thickness retrieval over land. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 781–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovsky, A.A.; Kostinski, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Koutrakis, P. Spatial scales of pollution from variable resolution satellite imaging. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emili, E.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Popp, C.; Korkin, S.; Zebisch, M.; Wunderle, S.; Petitta, M. High spatial resolution aerosol retrieval with MAIAC: Application to mountain regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, L.; Strandgren, J.; Rozanov, V.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Wang, Y. A study of the impact of spatial resolution on the estimation of particle matter concentration from the aerosol optical depth retrieved from satellite observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7084–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandgren, J.; Mei, L.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y. Study of satellite retrieved aerosol optical depth spatial resolution effect on particulate matter concentration prediction. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 25869–25899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.H.; Chen, A.J.; Liu, G.R. An image-Based retrieval algorithm of aerosol characteristics and surface reflectance for satellite images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 3477–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Hui, G.; Gao, H. Modified DDV method of aerosol optical depth inversion over land surfaces from CBERS02B. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth for Chongqing using the HJ-1 satellite data. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Gu, X.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Wei, X.; Xiang, K.; Li, Y. High-Spatial-Resolution Aerosol Optical Properties Retrieval Algorithm Using Chinese High-Resolution Earth Observation Satellite I. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2016, 54, 5544–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q. Landsat 8-Based inversion methods for aerosol optical depths in the Beijing area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, W.; Li, W.; Li, J. Effects of Urban Landscape Pattern on PM2.5 Pollution—A Beijing Case Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 142449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Mao, F.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Estimation of ultrahigh resolution PM2.5 concentrations in urban areas using 160 m Gaofen-1 AOD retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Di, Q.; Koutrakis, P. Developing particle emission inventories using remote sensing (PEIRS). J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ho, H.C.; Xu, Y.; Ng, E. Improving satellite aerosol optical Depth-PM2.5 correlations using land use regression with microscale geographic predictors in a high-Density urban context. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; Homan, C.D.; Matthijsen, J. Comparison of spatial and temporal variations of aerosol optical thickness and particulate matter over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5304–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, L. Satellite-Based estimation of regional particulate matter (PM) in Beijing using vertical-and-RH correcting method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xiang, H. Impact and Suggestion of Column-to-Surface Vertical Correction Scheme on the Relationship between Satellite AOD and Ground-Level PM2.5 in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, J.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Lin, D.; et al. The Association between Air Pollution and Outpatient and Inpatient Visits in Shenzhen, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.C.; Li, R.R.; Flynn, L. The MODIS 2.1-mu m channel—Correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, K.; Ge, Q. Retrieval and Validation of Aerosol Optical Depth by using the GF-1 Remote Sensing Data. IOP Conf. Ser. 2017, 68, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcette, J.J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; van der Hage, J.C.H.; Ten Brink, H.M. Nephelometer derived and directly measured aerosol optical depth of the atmospheric boundary layer. Atmos. Res. 1996, 41, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, H. Estimation of surface-level PM2.5 concentration using aerosol optical thickness through aerosol type analysis method. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Pozzer, A.; Cao, C.X.; Lelieveld, J. Long-term (2001–2012) concentrations of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and the impact on human health in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5715–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Qu, Q.; Liu, S.X.; Li, X.; Zhong, P.Y.; Tau, J. Chemical Compositions in PM2.5 and Its Impact on Visibility in Summer in Pearl River Delta, China. Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 2758–2767, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Min, H.; Sun, T.; Lian, X.; Yun, L.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y. High time resolution observation and statistical analysis of atmospheric light extinction properties and the chemical speciation of fine particulates. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yun, H.; Gong, Z.; Li, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M. Source apportionment and secondary organic aerosol estimation of PM2.5 in an urban atmosphere in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Che, W.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, S. A highly resolved temporal and spatial air pollutant emission inventory for the Pearl River Delta region, China and its uncertainty assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5112–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, P.; Watson, J.; Chow, J.; Chen, A.; Sin, D.; Lau, A. Seasonal characteristics and regional transport of PM2.5 in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovsky, A.; Tang, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A critical assessment of high-resolution aerosol optical depth retrievals for fine particulate matter predictions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10907–10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, J. Satellite-derived high resolution PM2.5 concentrations in Yangtze River Delta Region of China using improved linear mixed effects model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Roy, D.P.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Huang, H. Evaluation of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A Aerosol Optical Depth Retrievals across Chinese Cities and Implications for Medium Spatial Resolution Urban Aerosol Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munchak, L.A.; Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.A.; Holben, B.N.; Schafer, J.S.; Hostetler, C.A.; Ferrare, R.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Applications over land in an urban/suburban region. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2013, 6, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keukelaere, L.; Sterckx, S.; Adriaensen, S.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Hunter, P.; Neil, C.; Van der Zande, D.; et al. Atmospheric correction of Landsat-8/OLI and Sentinel-2/MSI data using iCOR algorithm: Validation for coastal and inland waters. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Barbosa, C.; de Carvalho, L.; Jorge, D.; Lobo, F.; Novo, E. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Methods for Sentinel-2 MSI Images Applied to Amazon Floodplain Lakes. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 2015–2017 (N = 253) | Spring (N = 47) | Summer (N = 55) | Autumn (N = 42) | Winter (N = 109) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 concentrations (μg/m3) | mean | 43 | 29 | 32 | 36 | 56 |
| S.D. | 22.6 | 8.77 | 23.9 | 11.1 | 22.0 | |
| kurtosis | 2.29 | −0.28 | −1.38 | −0.96 | 3.20 | |
| skewness | 1.03 | −0.80 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 1.41 | |
| PBLH (m) | mean | 1032 | 1036 | 1197 | 1036 | 945 |
| S.D. | 177.8 | 133.0 | 52.64 | 117.1 | 195.3 | |
| kurtosis | −0.77 | −0.64 | −1.34 | −1.71 | −1.30 | |
| skewness | −0.62 | −0.71 | −0.40 | −0.15 | 0.02 | |
| RH (%) | mean | 50 | 48 | 59 | 57 | 44 |
| S.D. | 14.0 | 12.8 | 7.02 | 6.26 | 15.9 | |
| kurtosis | −0.46 | −0.74 | 0.97 | 0.80 | −0.91 | |
| skewness | −0.41 | 0.28 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 0.20 |
| O_AOD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | mean | 0.292 | 0.297 | 0.362 | 0.367 |
| S.D. | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.011 | 0.018 | |
| minimum | 0.234 | 0.264 | 0.334 | 0.340 | |
| maximum | 0.329 | 0.374 | 0.392 | 0.423 | |
| p values | mean | 2.18 × 10−4 | 5.76 × 10−5 | 6.61 × 10−6 | 2.80 × 10−6 |
| minimum | 1.10 × 10−6 | 2.53 × 10−7 | 2.94 × 10−9 | 8.65 × 10−10 | |
| maximum | 1.03 × 10−2 | 2.93 × 10−3 | 6.29 × 10−4 | 2.16 × 10−4 |
| Spatial Scales | O_AOD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40–1000 m | mean | 0.281 | 0.309 | 0.365 | 0.382 |
| S.D. | 0.026 | 0.024 | 0.018 | 0.020 | |
| C.V. | 9.25% | 7.77% | 4.93% | 5.23% | |
| 1020–2000 m | mean | 0.308 | 0.324 | 0.373 | 0.384 |
| S.D. | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.007 | |
| C.V. | 2.60% | 2.47% | 1.88% | 1.82% | |
| 2020–3000 m | mean | 0.298 | 0.306 | 0.363 | 0.371 |
| S.D. | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.007 | |
| C.V. | 2.34% | 3.92% | 1.10% | 1.88% | |
| 3020–4000 m | mean | 0.284 | 0.273 | 0.356 | 0.352 |
| S.D. | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| C.V. | 1.41% | 1.10% | 0.56% | 0.57% | |
| 4020–5000 m | mean | 0.288 | 0.272 | 0.353 | 0.346 |
| S.D. | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.005 | |
| C.V. | 1.39% | 2.21% | 0.85% | 1.45% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L.; Yao, F.; Peng, J. Impacts of AOD Correction and Spatial Scale on the Correlation between High-Resolution AOD from Gaofen-1 Satellite and In Situ PM2.5 Measurements in Shenzhen City, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192223
Wu J, Liang J, Zhou L, Yao F, Peng J. Impacts of AOD Correction and Spatial Scale on the Correlation between High-Resolution AOD from Gaofen-1 Satellite and In Situ PM2.5 Measurements in Shenzhen City, China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(19):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192223
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiansheng, Jingtian Liang, Liguo Zhou, Fei Yao, and Jian Peng. 2019. "Impacts of AOD Correction and Spatial Scale on the Correlation between High-Resolution AOD from Gaofen-1 Satellite and In Situ PM2.5 Measurements in Shenzhen City, China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 19: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192223
APA StyleWu, J., Liang, J., Zhou, L., Yao, F., & Peng, J. (2019). Impacts of AOD Correction and Spatial Scale on the Correlation between High-Resolution AOD from Gaofen-1 Satellite and In Situ PM2.5 Measurements in Shenzhen City, China. Remote Sensing, 11(19), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192223






