An Improved GPS-Inferred Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Using Terrain-Corrected Vertical Crustal Displacements Constrained by GRACE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Region and Data Description
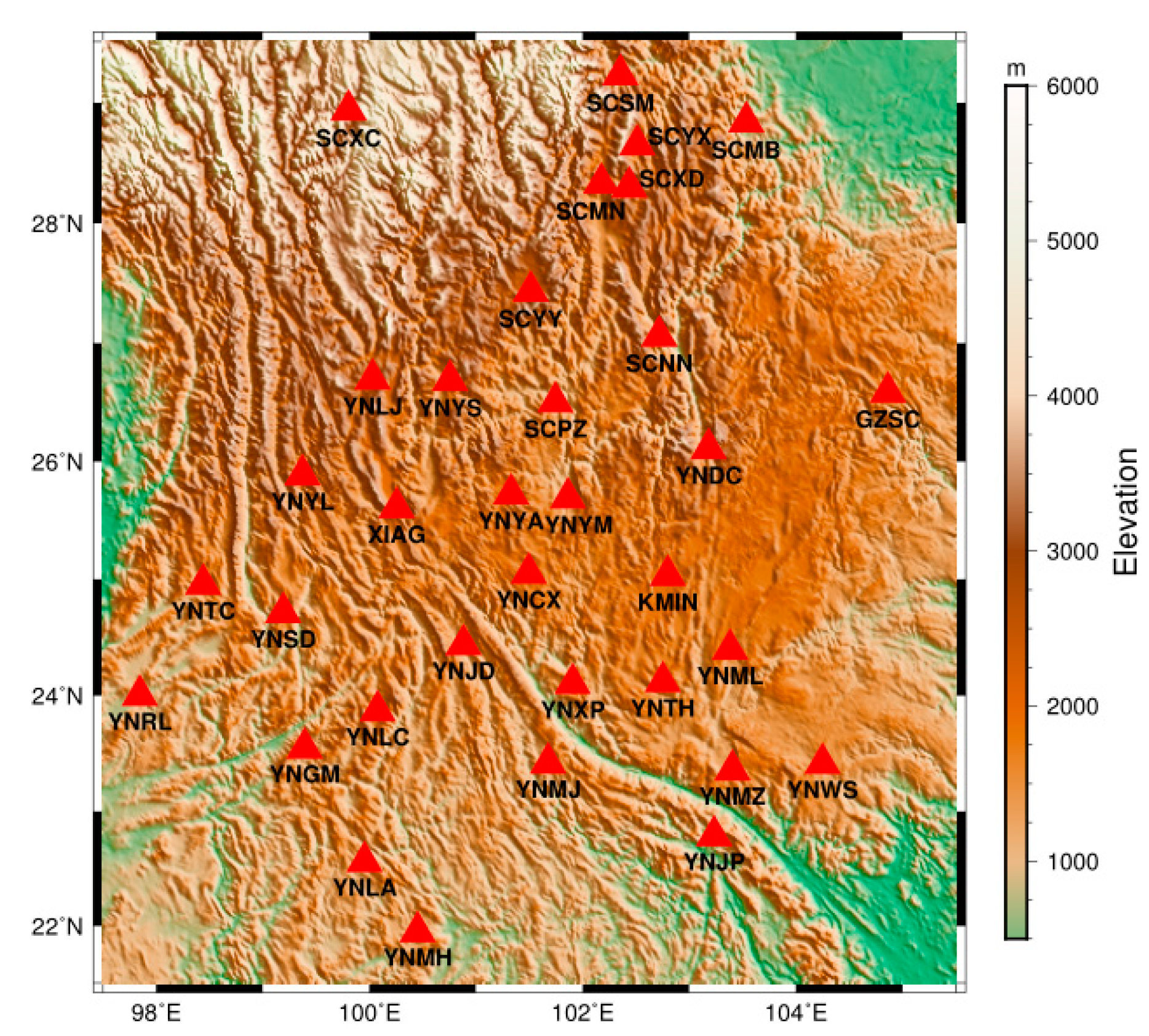
2.1. Southwest China
2.2. GPS VCD Data
2.3. GRACE and GLDAS TWS Data
3. Data Processing of GPS Time Series
3.1. GPS Data Preprocessing
3.2. GPS Data Post-Processing
4. TWS Inversion Model and Methodology from an Annual Variation of GPS VCD
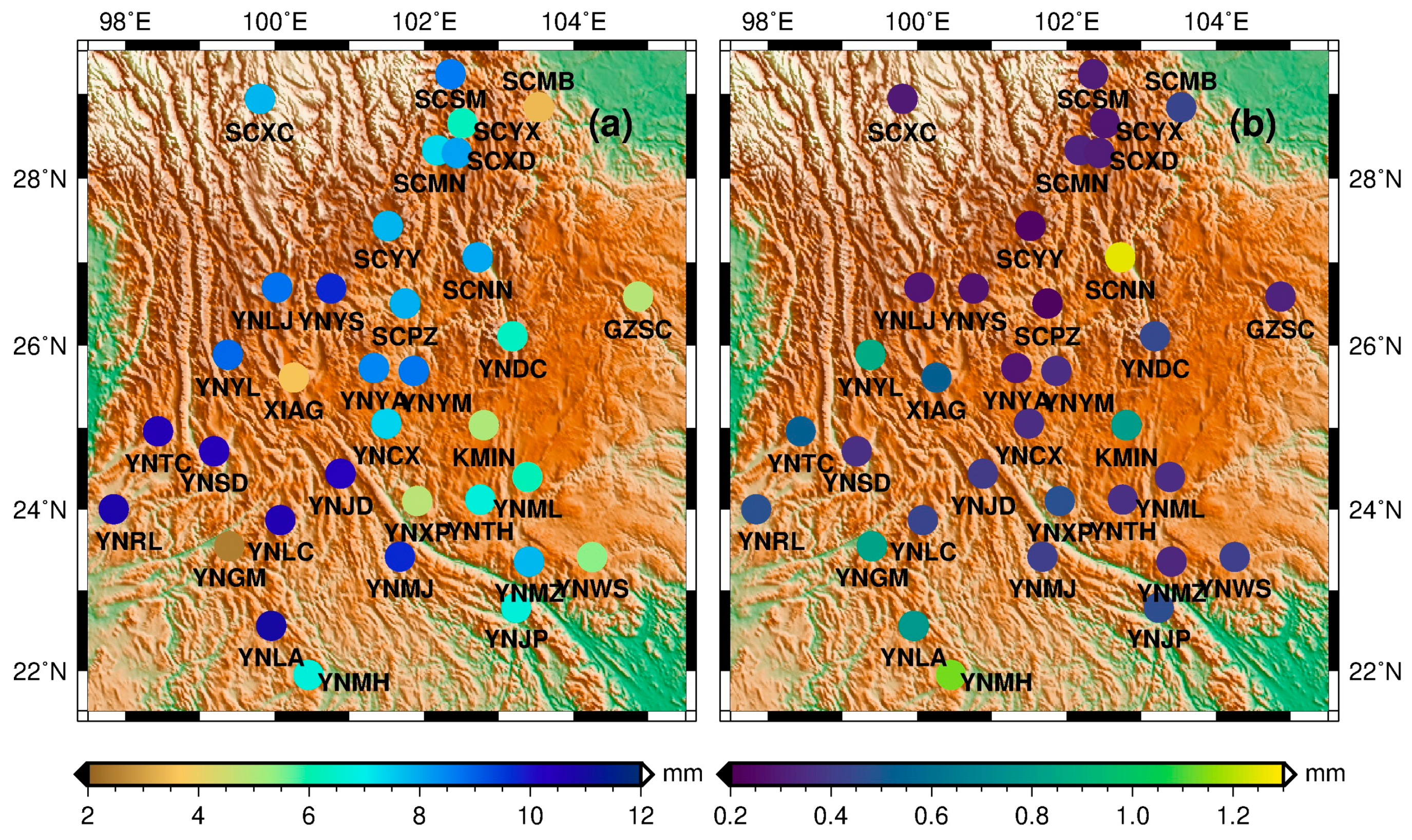
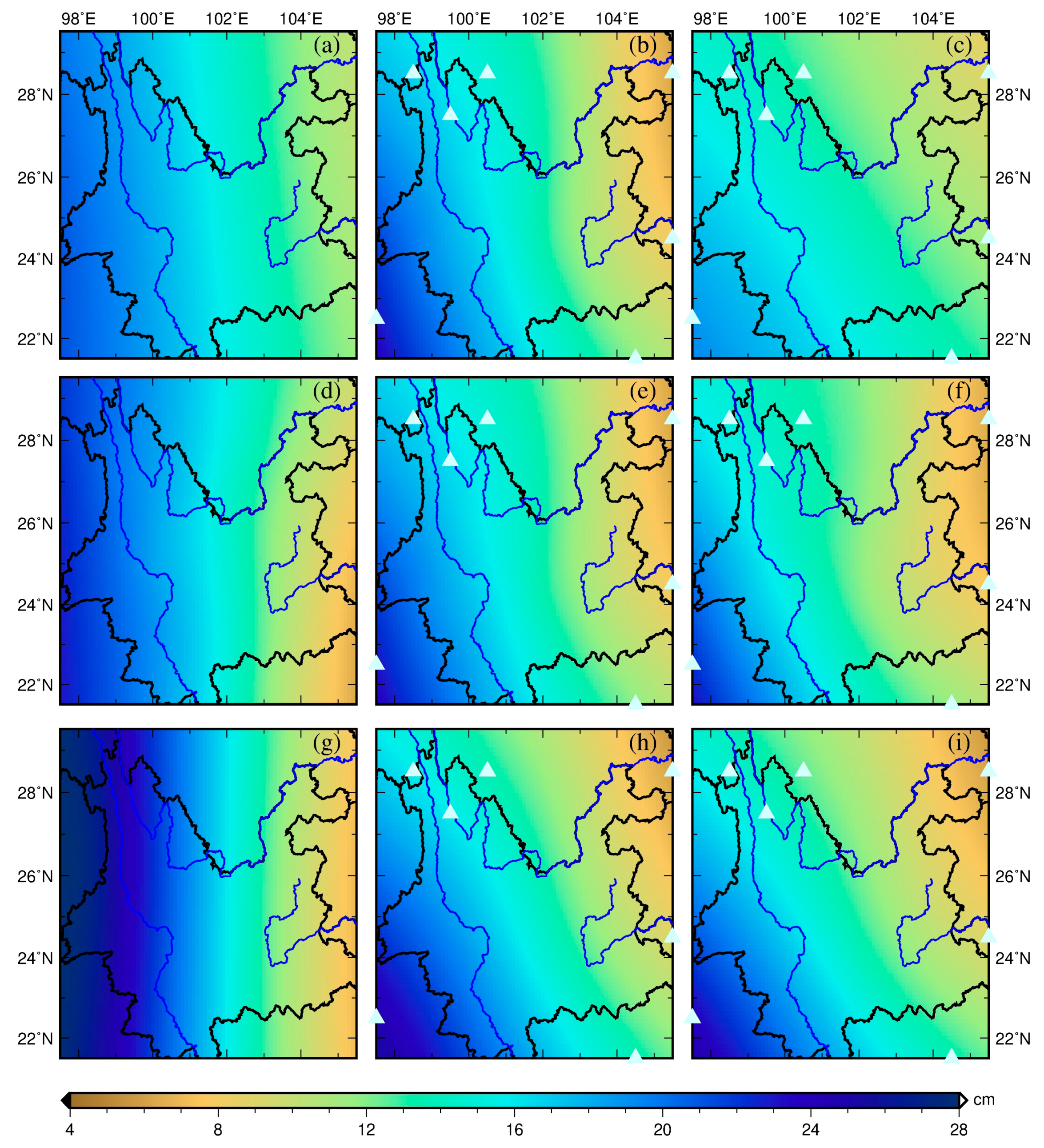
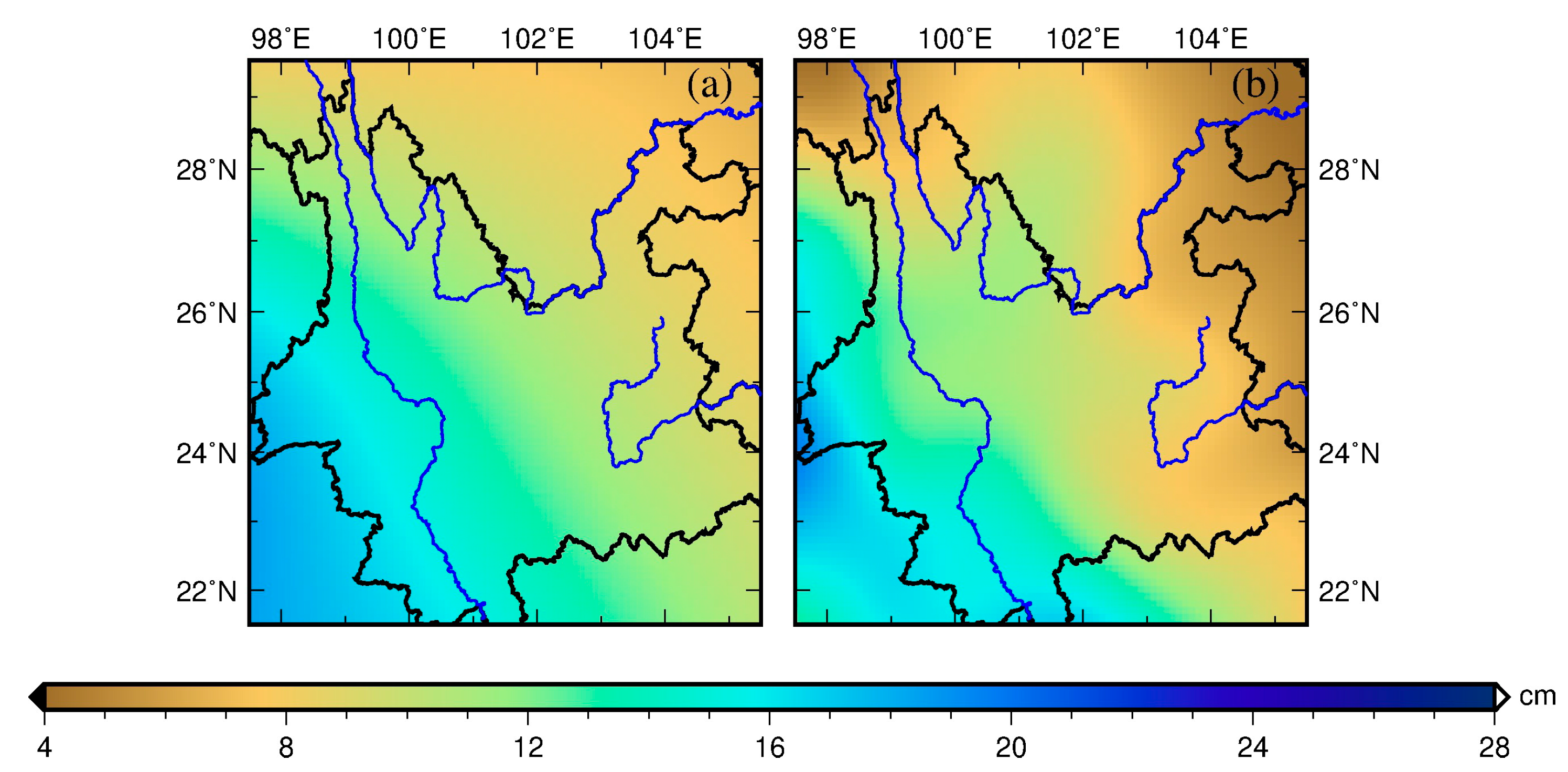
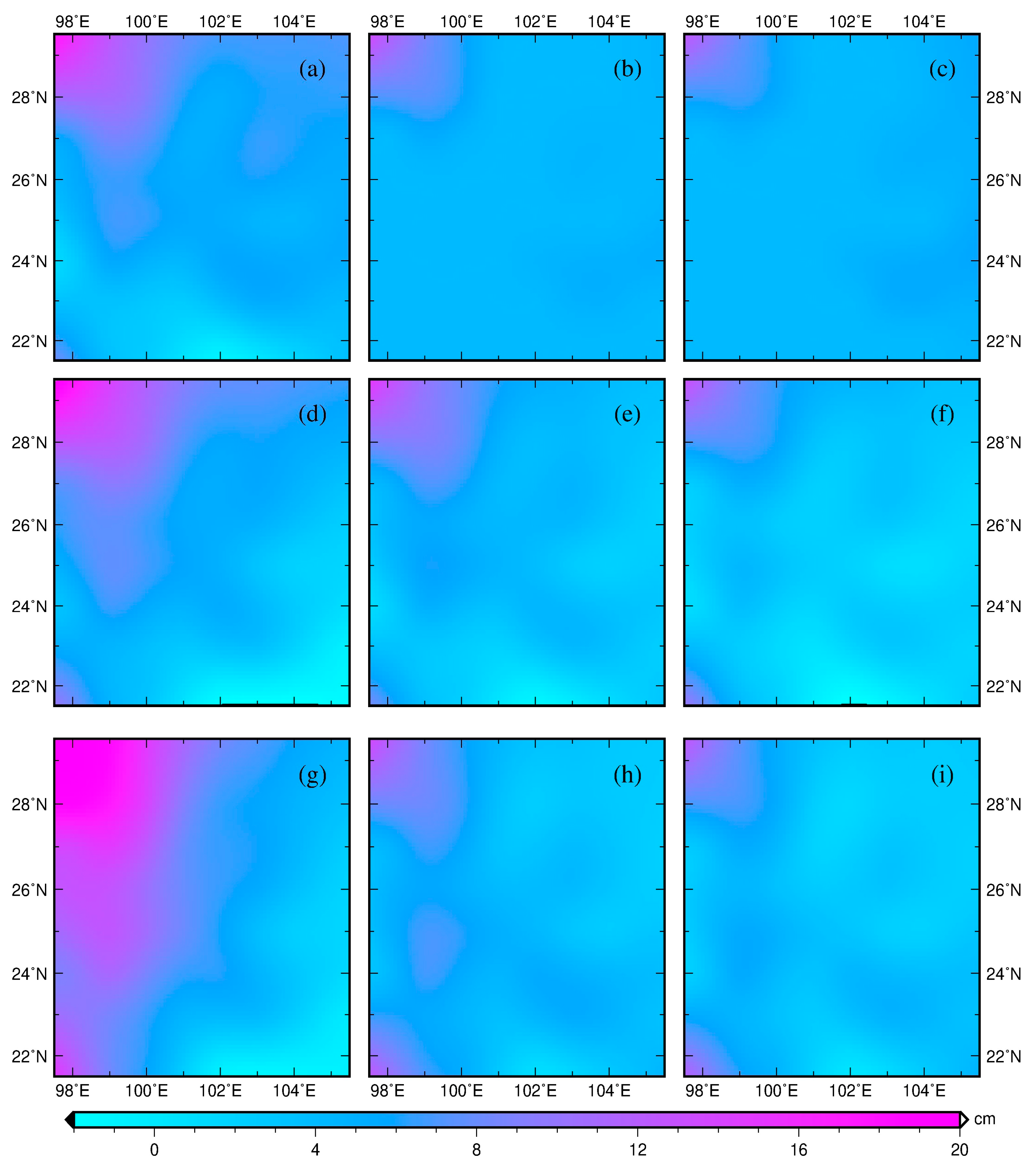
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, S.; Zhang, T. Terrestrial Water Storage Anomalies Associated with Drought in Southwestern USA from GPS Observations. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Fok, H.S.; Shum, C.K.; Li, Z. Earth surface deformation using GRACE and GPS techniques in the North China Plain. Sensors 2014, 14, 19861–19876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.G.; Feng, G.P. Large-scale variations of global groundwater from satellite gravimetry and hydrological models, 2002–2012. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 106, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argus, D.F.; Fu, Y.; Landerer, F.W. Seasonal variation in total water storage in California inferred from GPS observations of vertical motion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1971–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G.; Lavallée, D.; Clarke, P.; Nurutdinov, K. A new global mode of Earth deformation: Seasonal cycle detected. Science 2001, 294, 2342–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Milly, P.C.D.; Shmakin, A.B.; Blewitt, G.; Lavallée, D.; Larson, K.M. Crustal displacements due to continental water loading. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Alsdorf, D.; Kendrick, E.; Fortes, L.P.; Forsberg, B.; Smalley, R., Jr.; Becker, J. Seasonal fluctuations in the mass of the Amazon River system and Earth’s elastic response. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Elósegui, P.; Mitrovica, J.X.; Tamisiea, M.E. Climate-driven deformation of the solid Earth from GRACE and GPS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Lavallée, D. A comparison of annual vertical crustal displacements from GPS and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) over Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B03404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Freymueller, J.T.; Jensen, T. Seasonal hydrological loading in southern Alaska observed by GPS and GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckler, M.S.; Nooner, S.L.; Akhter, S.H.; Chowdhury, S.K.; Bettadpur, S.; Seeber, L.; Kogan, M.G. Modeling Earth deformation from monsoonal flooding in Bangladesh using hydrographic, GPS, and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B08407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, W.E. Deformation of the Earth by surface loads. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 761–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Argus, D.F.; Landerer, F.W. GPS as an independent measurement to estimate terrestrial water storage variations in Washington and Oregon. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Fok, H.S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Q. Potential seasonal terrestrial water storage monitoring from GPS vertical displacements: A case study in the lower three-rivers headwater region, China. Sensors 2016, 16, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.N. On the solution of ill-posed problems and the method of regularization. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1963, 151, 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, K.R. Maximum likelihood estimate of variance components. Bulletin Gæodésique 1986, 60, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R. Least-squares variance component estimation. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, H.S. Ocean Tides Modeling Using Satellite Altimetry. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Earth Sciences, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, D.M. The relationship between variable selection and data agumentation and a method for prediction. Technometrics 1974, 16, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M. Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1974, 36, 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Golub, G.H.; Heath, M.; Wahba, G. Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter. Technometrics 1979, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Likelihood and the Bayes procedure. Trab. Estad. Investig. Oper. 1980, 31, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P. Determination of surface gravity anomalies using gradiometric observables. Geophys. J. Int. 1992, 110, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 1992, 34, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C.; O’Leary, D.P. The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1993, 14, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, T.; Matsu’Ura, M. Geodetic data inversion using a Bayesian information criterion for spatial distribution of fault slip. Geophys. J. Int. 1992, 109, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahata, Y.; Yagi, Y.; Matsu’ura, M. Waveform inversion for seismic source processes using ABIC with two sorts of prior constraints: Comparison between proper and improper formulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funning, G.J.; Fukahata, Y.; Yagi, Y.; Parsons, B. A method for the joint inversion of geodetic and seismic waveform data using ABIC: Application to the 1997 Manyi, Tibet, earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. Joint inversion of GPS, InSAR and teleseismic data sets for the rupture process of the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal, earthquake using a generalized ABIC method. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, F.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Kikuchi, K. Multi-scale climate variability of the South China Sea monsoon: A review. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2009, 47, 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yin, X.A.; Yang, P.; Yang, Z.F. Assessment of contributions of climatic variation and human activities to streamflow changes in the lancang river, china. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2953–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Espinoza, J.C. Extreme seasonal droughts and floods in amazonia: Causes, trends and impacts. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, P.; Chen, H.; Cai, J.; Li, Z.; Chao, N.; Sneeuw, N. Annual variations of monsoon and drought detected by GPS: A case study in Yunnan, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Fan, D.; Wei, Y.; Yong, S. Seasonal crustal vertical deformation induced by environmental mass loading in mainland China derived from GPS, GRACE and surface loading models. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.J.; Zhang, R.; Tang, F.T.; Chen, T. Development of the Crustal Movement Observation Network of China and its Applications. Recent Dev. World Seismol. 2007, 2007, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Swenson, S. GRACE Monthly Land Water Mass Grids NETCDF Release 5.0. Ver. 5.0. PO. DAAC, CA, USA. 2012. Available online: https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/TELLUS_LAND_NC_RL05 (accessed on 12 July 2017).
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche, J.; Schmidt, R.; Petrovic, S.; Rietbroek, R. Decorrelated grace time-variable gravity solutions by gfz, and their validation using a hydrological model. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Huang, Y.; Deng, H.T.; Xu, S.Q.; Ning, J.S. Green’s Function of Earth’s Deformation as a Result of Atmospheric Loading. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 159, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, T.; King, R.; McClusky, S. GAMIT reference manual, release 10.4. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge. 2010. Available online: http://www-gpsg.mit.edu/~simon/gtgk/GAMIT_Ref.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2016).
- Dow, J.M.; Neilan, R.E.; Rizos, C. The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Métivier, L. ITRF2008: An improved solution of the international terrestrial reference frame. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.J.; King, M.A.; Moore, P.; Lavallée, D.A. Higher-order ionospheric effects on the GPS reference frame and velocities. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B03417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Werl, B.; Schuh, H. Troposphere Mapping Functions for GPS and Very Long Baseline Interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Operational Analysis Data. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B02406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Short note: A global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS conventions (2010); BUREAU INTERNATIONAL DES POIDS ET MESURES SEVRES (FRANCE), 2010. Available online: https://www.iers.org/SharedDocs/Publikationen/EN/IERS/Publications/tn/TechnNote36/tn36.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=1 (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; van Dam, T.; Ding, W. Comparative analysis of different environmental loading methods and their impacts on the GPS height time series. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collilieux, X.; Altamimi, Z.; Coulot, D.; Ray, J.; Sillard, P. Comparison of very long baseline interferometry, GPS, and satellite laser ranging height residuals from ITRF2005 using spectral and correlation methods. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, B12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Dam, T.V. Anomalous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. Gps Solutions 2008, 12, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.; Stewart, M. Aliased tidal signatures in continuous GPS height time series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, J.; Klos, A. On the significance of periodic signals in noise analysis of GPS station coordinates time series. GPS Solutions 2016, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, B. Effect of removing the common mode errors on linear regression analysis of noise amplitudes in position time series of a regional GPS network & a case study of GPS stations in Southern California. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Webb, F.; Prawirodirdjo, L.; Kedar, S.; Jamason, P. Spatiotemporal filtering using principal component analysis and Karhunen-Loeve expansion approaches for regional GPS network analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B03405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Bock, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, P.; Genrich, J. Southern California permanent GPS geodetic array: Spatial filtering of daily positions for estimating coseismic and postseismic displacements induced by the 1992 Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 18057–18070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Wahr, J.; Leuliette, E.; Dam, T.V.; Larson, K.M.; Francis, O. Geodetic measurements of postglacial adjustments in Greenland. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, B02402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.D.P.; Bock, Y.; Fang, P.; Jamason, P.; Nikolaidis, R.M.; Prawirodirdjo, L.; Miller, M.; Johnson, D.J. Error analysis of continuous GPS position time series. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, B03412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.S.; Fernandes, R.M.S.; Williams, S.D.P.; Bastos, L. Fast error analysis of continuous GNSS observations with missing data. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, M.; Liu, Y. Thermal effects on vertical displacement of GPS stations in China. Chin. J. Geophys 2010, 53, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Dong, D.; Ming, F.; Zhou, Y.; Na, W.; Feng, Z. Contributions of thermoelastic deformation to seasonal variations in GPS station position. GPS Solutions 2017, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, R.; Klemann, V.; Martinec, Z.; Tesauro, M. Applying local Green’s functions to study the influence of the crustal structure on hydrological loading displacements. J. Geodyn. 2015, 88, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Cheng, M.K.; Miyazaki, S. Anatomy of apparent seasonal variations from GPS-derived site position time series. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, B42075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, H.S.; Iz, H.B.; Schaffrin, B. Comparison of Four Geodetic Network Densification Solutions. Surv. Rev. 2009, 41, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, M.; Famiglietti, J. Downscaling GRACE remote sensing datasets to high-resolution groundwater storage change maps of California’s Central Valley. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Han, S.C. Statistical Downscaling of GRACE-Derived Groundwater Storage Using ET Data in the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5973–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
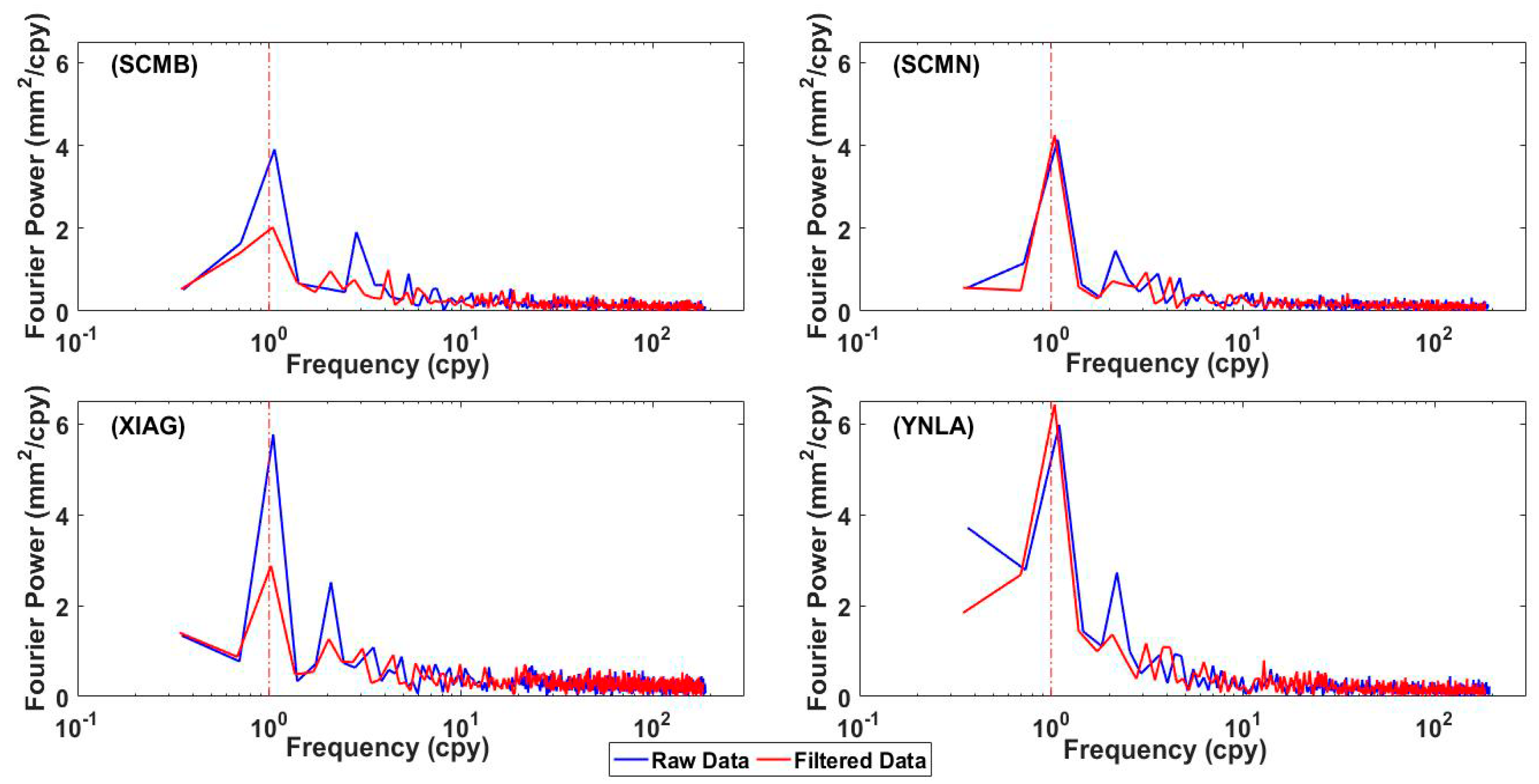
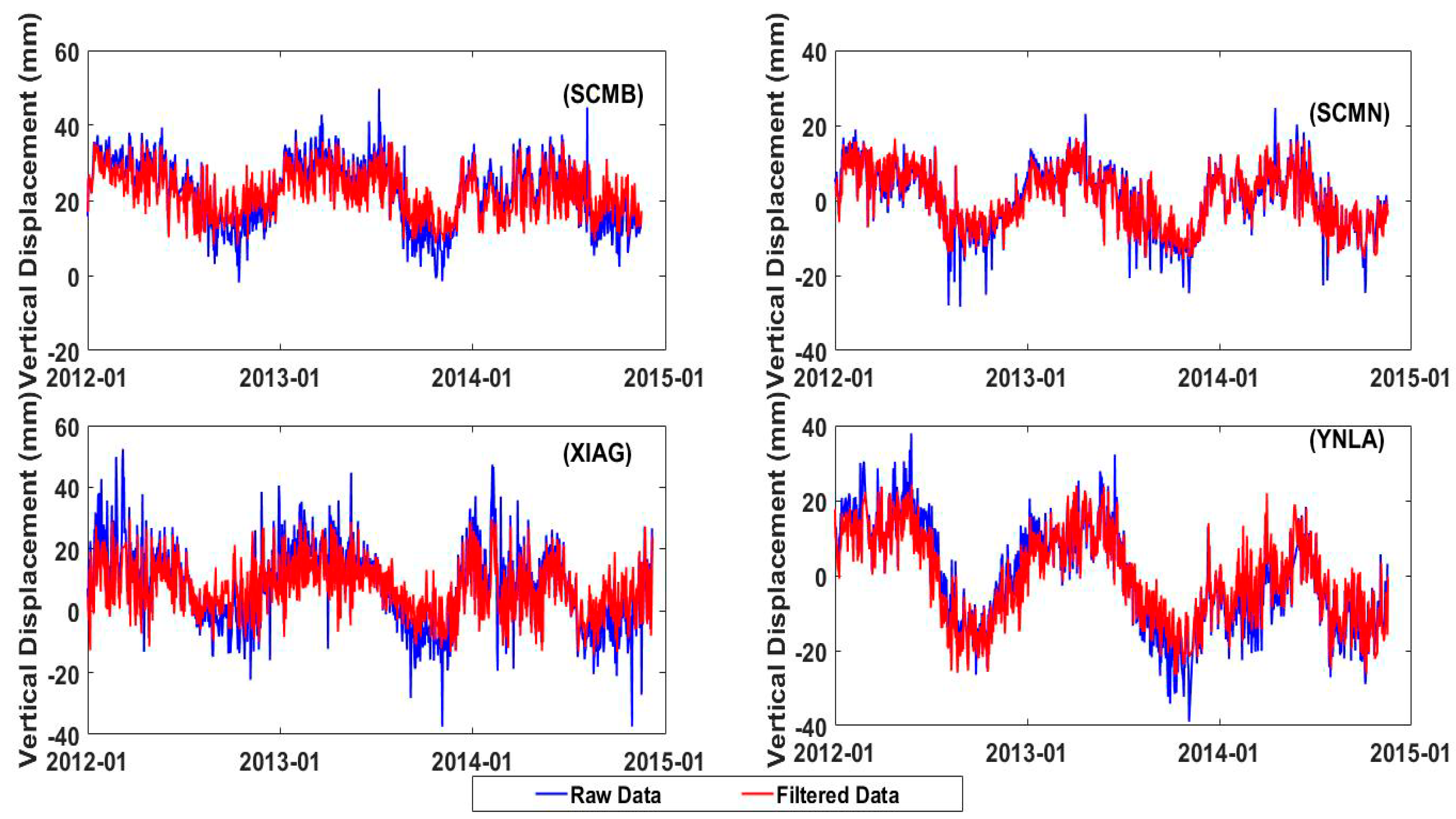
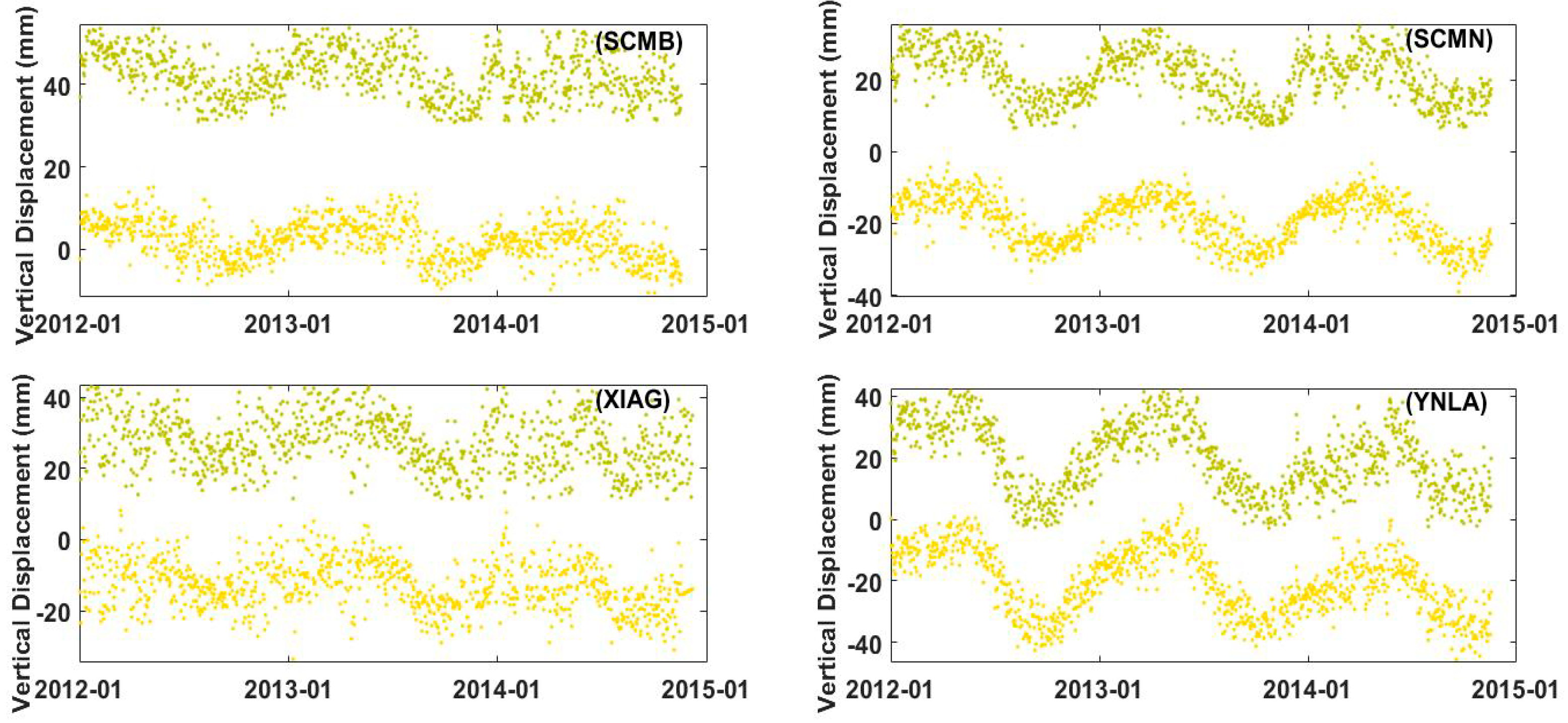
| RMS Error against GRACE (cm) | RMS Error against GLDAS (cm) | Mean Uncertainty (cm) | RMSR1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVCE | 7.76 | 8.92 | 0.46 | 1.08 |
| HVCE with TC | 7.13 | 8.27 | 0.42 | 1.04 |
| HVCE with SGDC | 3.50 | 4.89 | 0.13 | 1.45 |
| HVCE with SGDC and TC | 2.60 | 4.02 | 0.12 | 1.36 |
| TR | 4.63 | 6.11 | 0.42 | 1.44 |
| TR with TC | 3.53 | 5.05 | 0.29 | 1.41 |
| TR with SGDC | 3.17 | 4.73 | 0.14 | 2.00 |
| TR with SGDC and TC | 2.45 | 4.09 | 0.14 | 1.92 |
| ABIC | 5.14 | 6.35 | 0.43 | 1.90 |
| ABIC with TC | 3.76 | 5.01 | 0.41 | 1.83 |
| ABIC SGDC | 3.51 | 4.82 | 0.34 | 1.94 |
| ABIC SGDC and TC | 2.48 | 3.75 | 0.34 | 1.84 |
| HVCE | TR | ABIC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No constraint | 8.42 × 10−4 | 1.16 × 10−4 | 1.53 × 10−4 |
| TC | 8.42 × 10−4 | 1.16 × 10−4 | 1.77 × 10−4 |
| SGDC | 3.39 × 10−4 | 1.80 × 10−4 | 1.65 × 10−4 |
| SGDC and TC | 3.47 × 10−4 | 4.20 × 10−4 | 1.48 × 10−4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fok, H.S.; Liu, Y. An Improved GPS-Inferred Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Using Terrain-Corrected Vertical Crustal Displacements Constrained by GRACE. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121433
Fok HS, Liu Y. An Improved GPS-Inferred Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Using Terrain-Corrected Vertical Crustal Displacements Constrained by GRACE. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121433
Chicago/Turabian StyleFok, Hok Sum, and Yongxin Liu. 2019. "An Improved GPS-Inferred Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Using Terrain-Corrected Vertical Crustal Displacements Constrained by GRACE" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121433
APA StyleFok, H. S., & Liu, Y. (2019). An Improved GPS-Inferred Seasonal Terrestrial Water Storage Using Terrain-Corrected Vertical Crustal Displacements Constrained by GRACE. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121433






