Recent Developments and Applications of Acoustic Infrasound to Monitor Volcanic Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
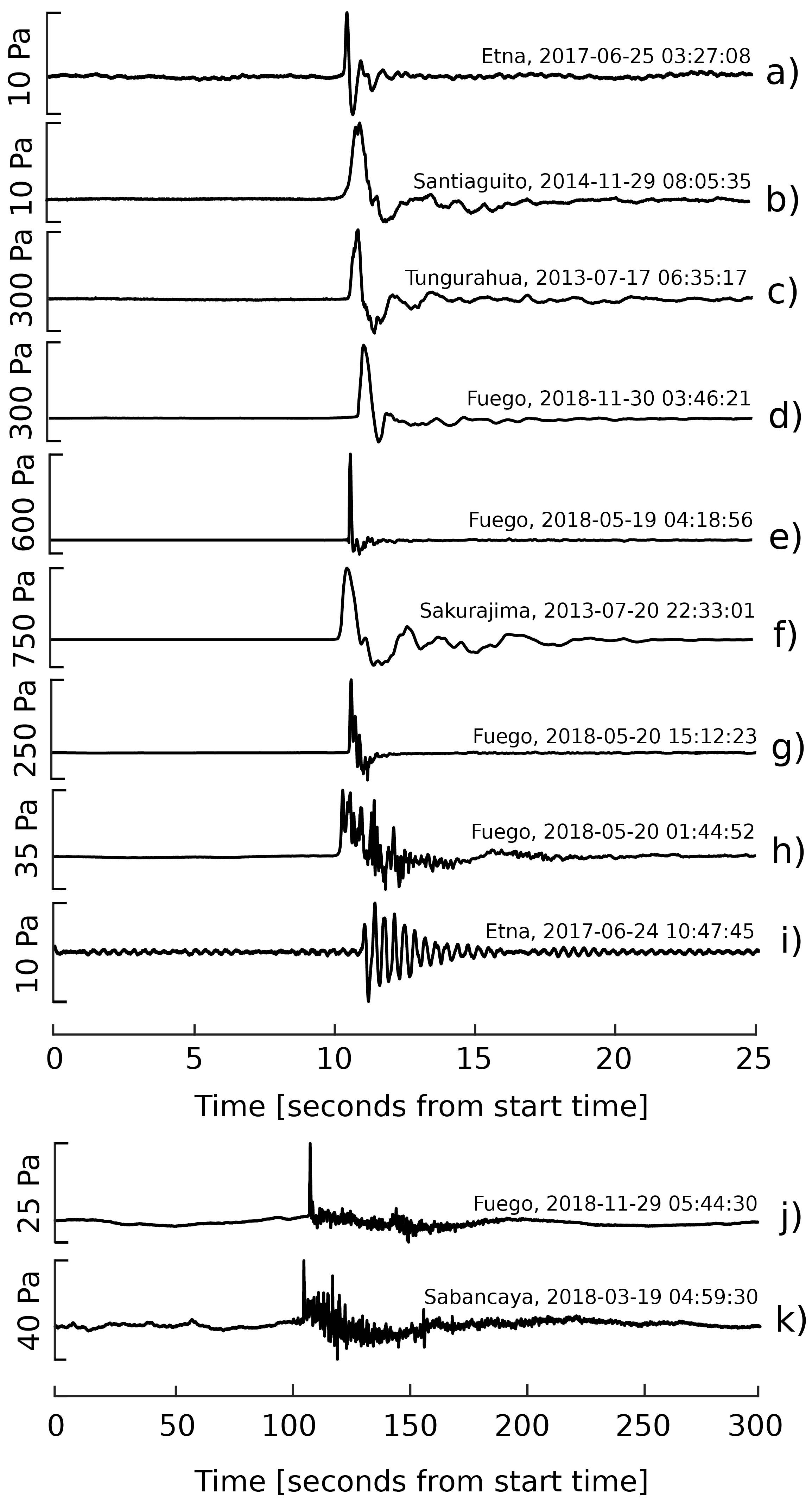
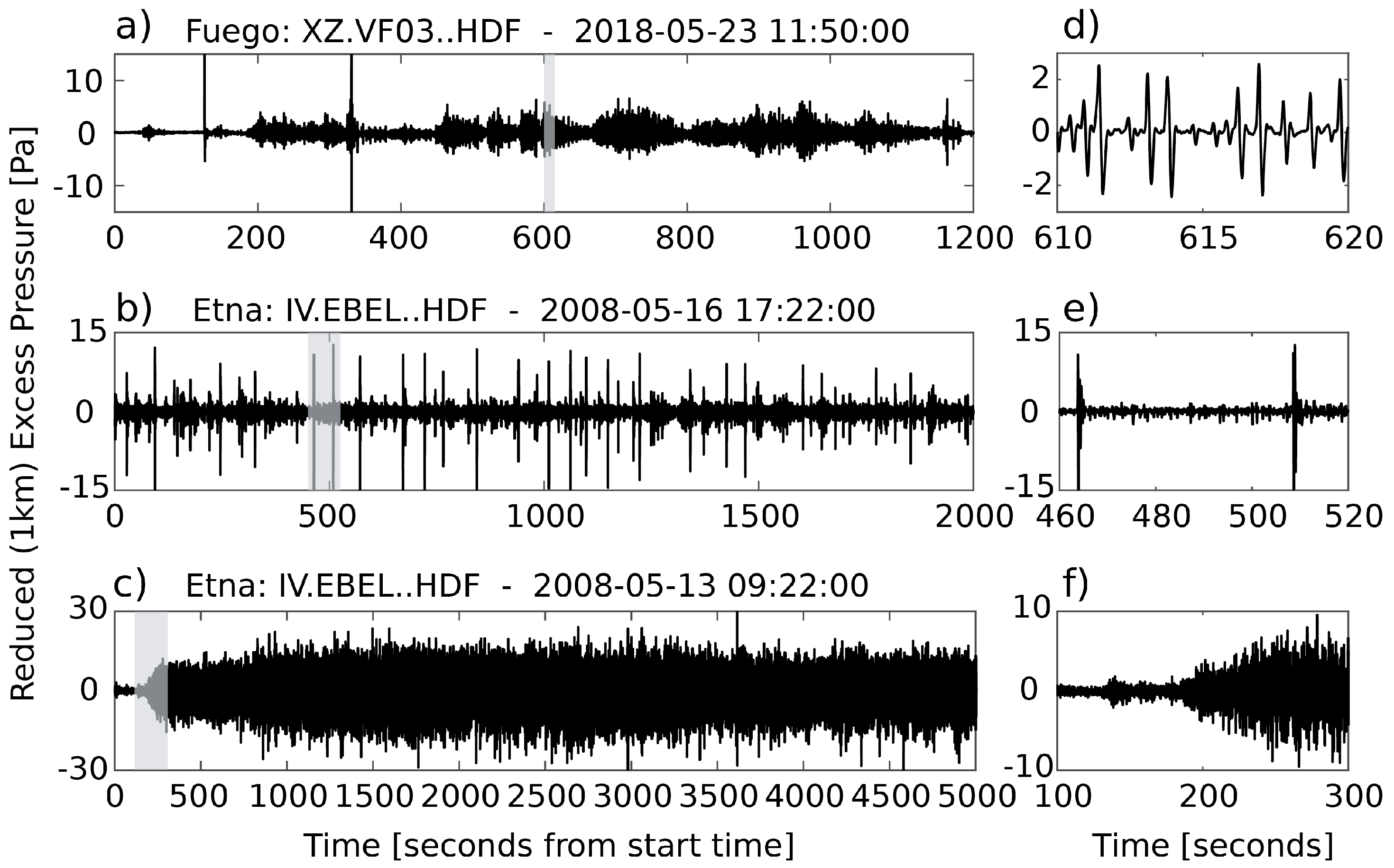
2. The Acoustic Fingerprint of Volcanoes
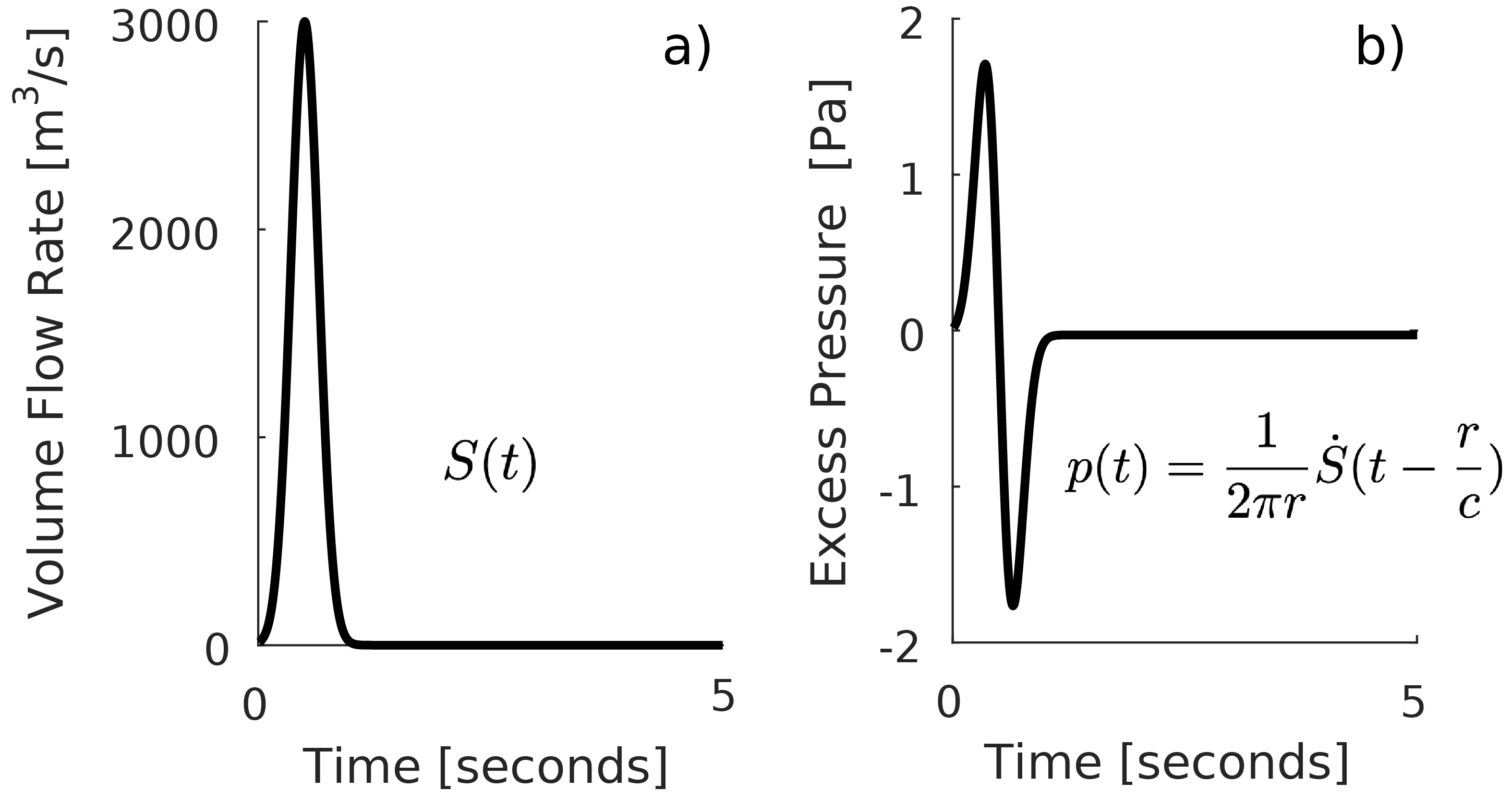
3. Linear Acoustic Theory and Multipole Acoustic Sources
4. Eruption Source Parameters and Their Potential Use in Ash Plume Modelling
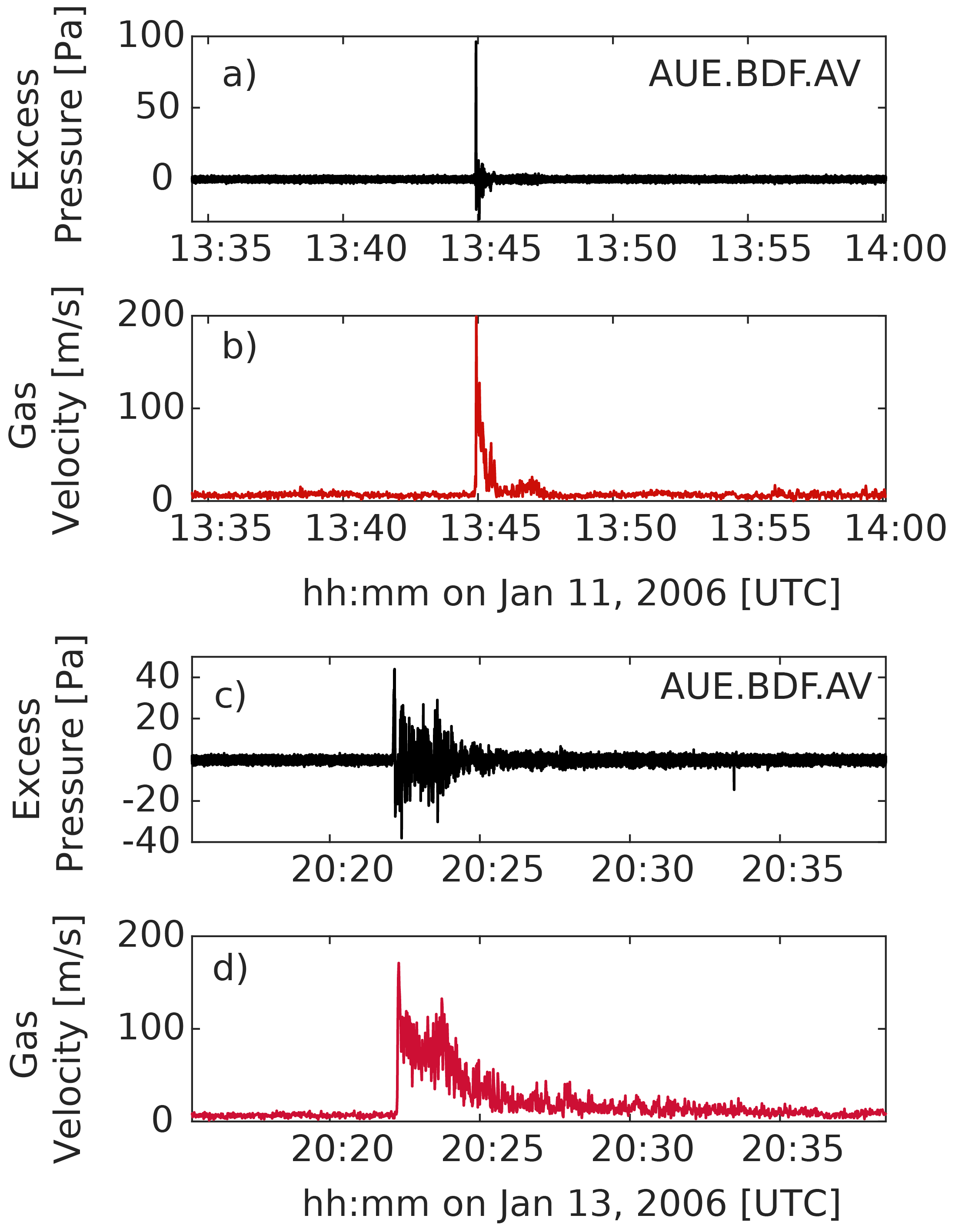
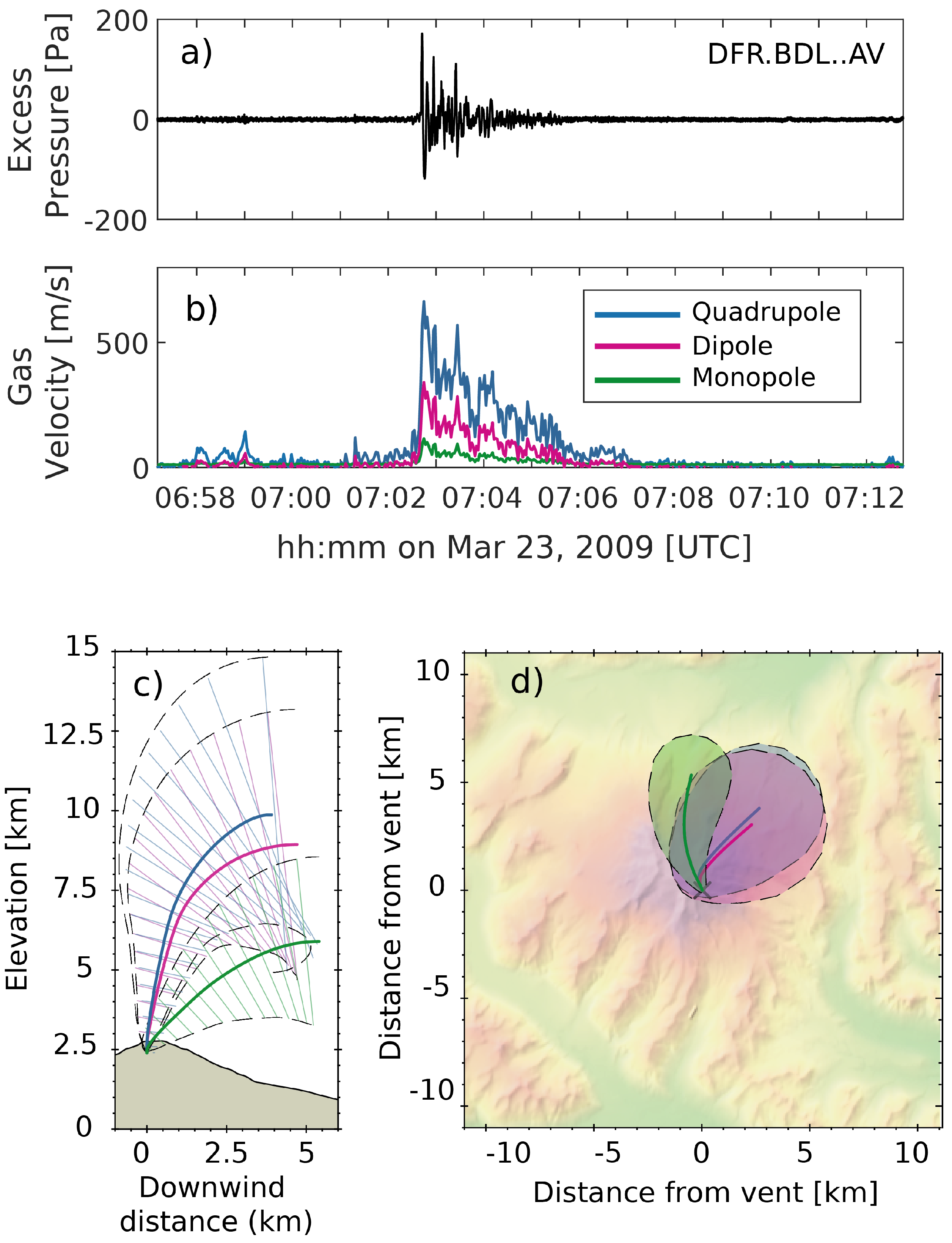
4.1. Fluid Flow Velocity from Acoustic Infrasound
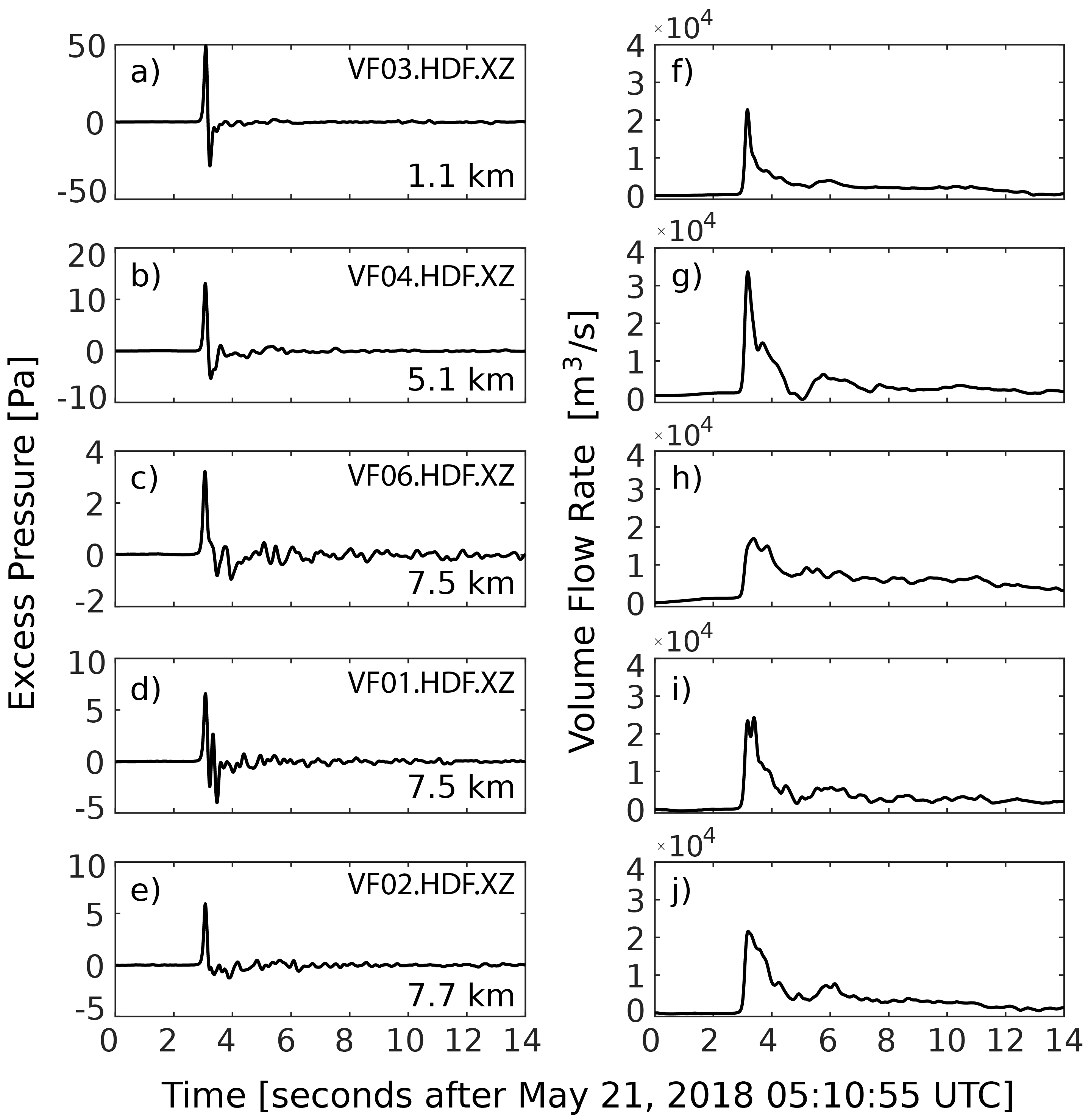
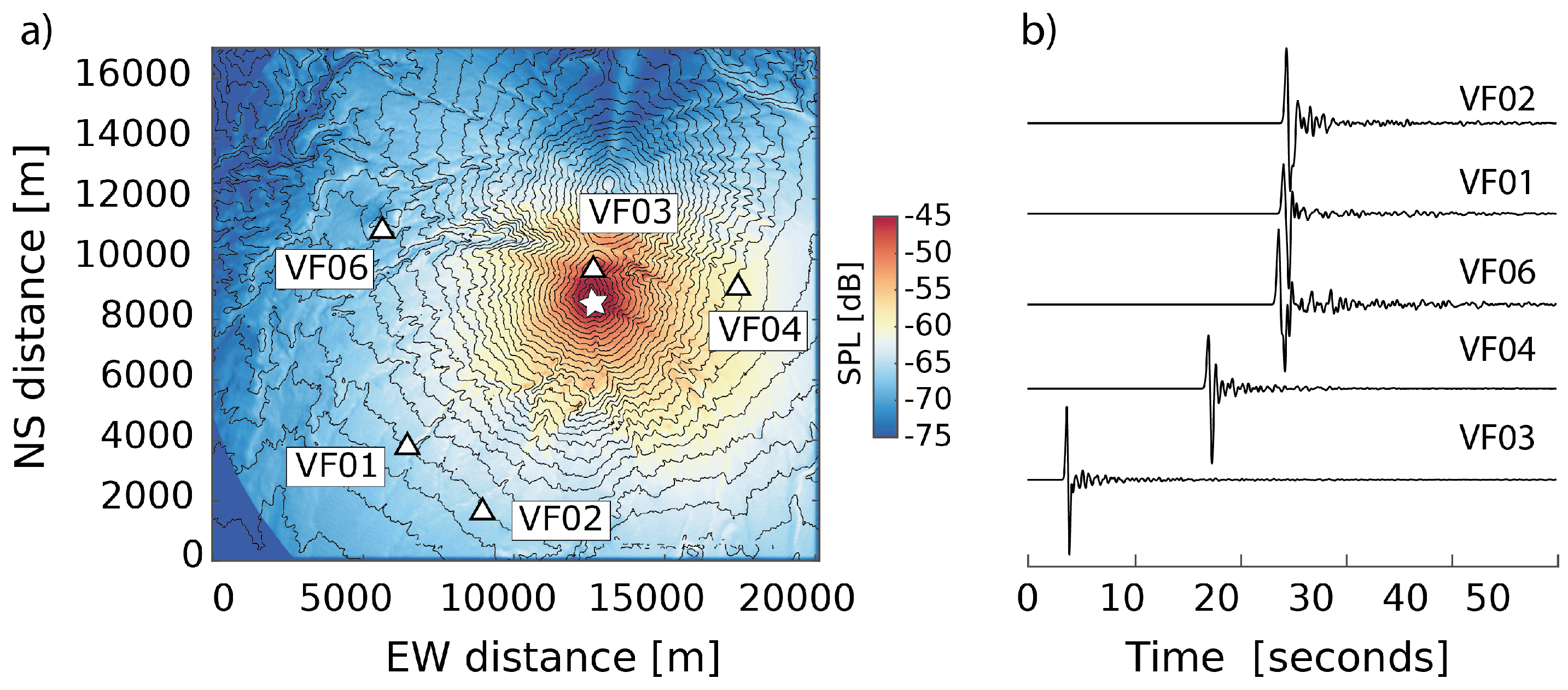
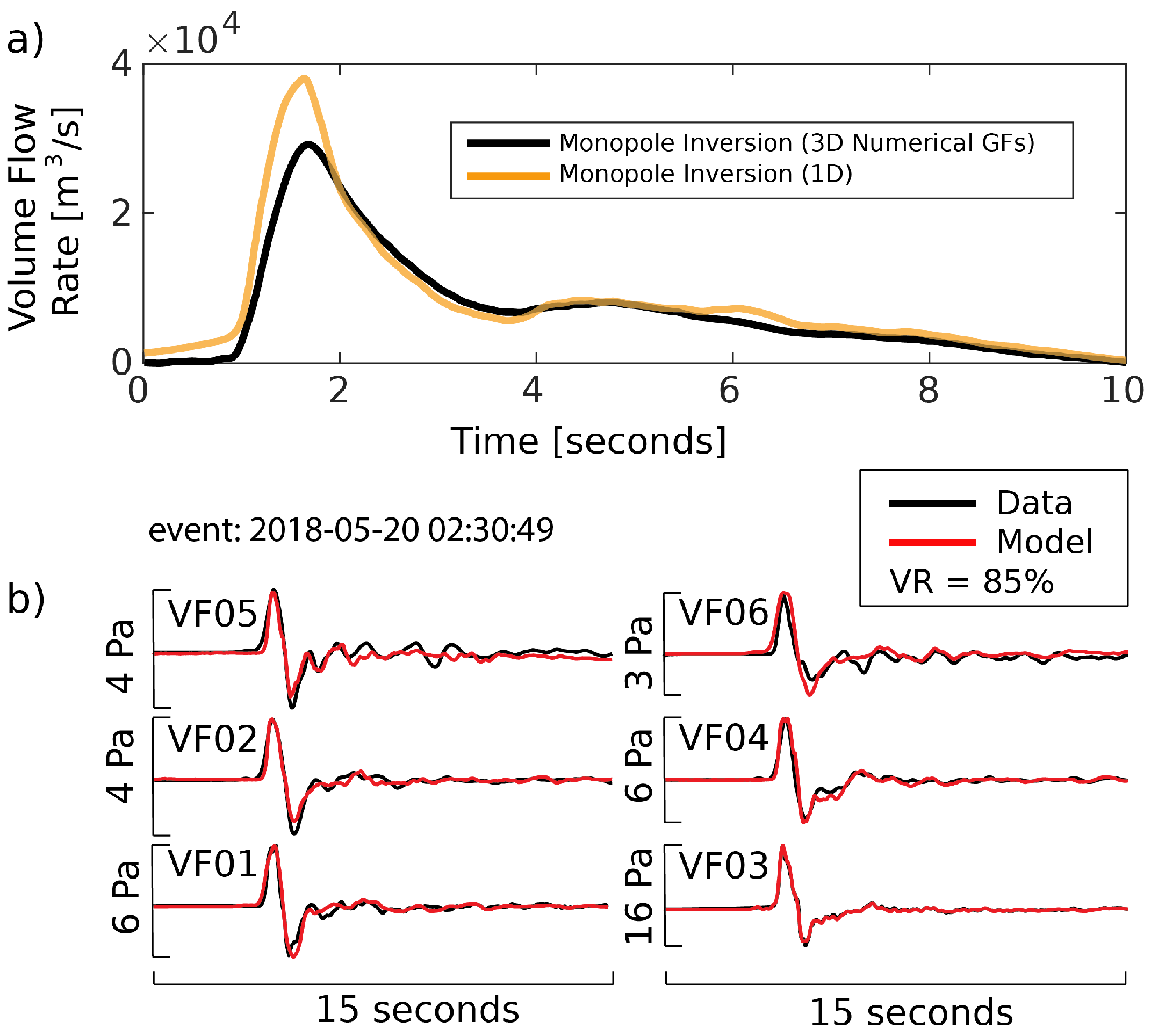
4.2. Acoustic Monopoles: Volume and Mass Flow Rate
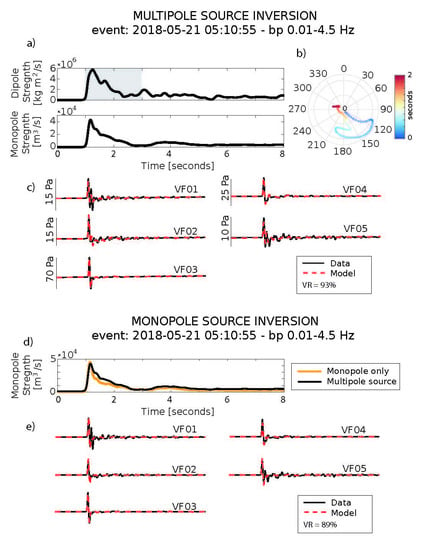
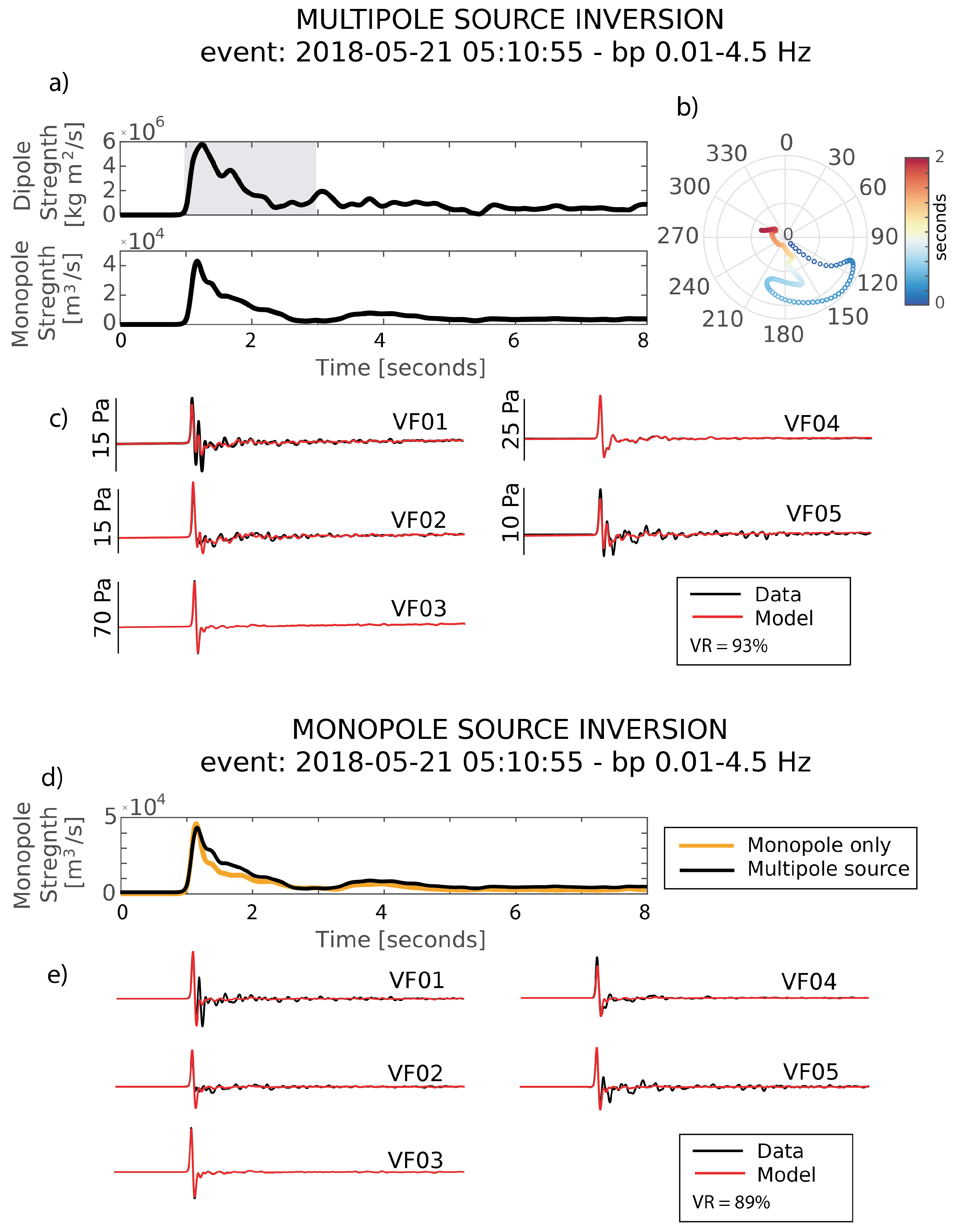
4.3. Acoustic Multipole Sources and Infrasound Waveform Inversion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matoza, R.S.; Fee, D.; Green, D.N.; Le Pichon, A.; Vergoz, J.; Haney, M.M.; Mikesell, T.D.; Franco, L.; Valderrama, O.A.; Kelley, M.R.; et al. Local, Regional, and Remote Seismo-acoustic Observations of the April 2015 VEI 4 Eruption of Calbuco Volcano, Chile. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 3814–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.K.; Jenkins, S.F.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Odbert, H.; Auker, M.R. Volcanic fatalities database: Analysis of volcanic threat with distance and victim classification. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.A.; Brantley, S.R.; Antolik, L.; Babb, J.L.; Burgess, M.; Calles, K.; Cappos, M.; Chang, J.C.; Conway, S.; Desmither, L.; et al. The 2018 rift eruption and summit collapse of Kilauea Volcano. Science 2019, 363, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report on Fuego (Guatemala). In Weekly Volcanic Activity Report; Sennert, S.K., Ed.; 2018; Available online: https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=342090June2018 (accessed on 30 May 2019).
- Mastin, L.G.; Guffanti, M.; Servranckx, R.; Webley, P.; Barsotti, S.; Dean, K.; Durant, A.; Ewert, J.W.; Neri, A.; Rose, W.I.; et al. A multidisciplinary effort to assign realistic source parameters to models of volcanic ash-cloud transport and dispersion during eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 186, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VAAC Operational Dispersion Model Configuration Snap Shot. Available online: https://www.wmo.int/aemp/sites/default/files/VAAC_Modelling_OperationalModelConfiguration-March2016_v3.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Dürig, T.; Gudmundsson, M.T.; Dioguardi, F.; Woodhouse, M.; Björnsson, H.; Barsotti, S.; Witt, T.; Walter, T.R. REFIR- A multi-parameter system for near real-time estimates of plume-height and mass eruption rate during explosive eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 360, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.S.J.; Bursik, M.I.; Carey, S.N.; Gilbert, J.S.; Glaze, L.; Sigurdsson, H.; Woods, A.W. Volcanic Plumes; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Settle, M. Volcanic eruption clouds and the thermal power output of explosive eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1978, 3, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Huang, T.C.; Watkins, N.D. The control of volcanic column heights by eruption energetics and dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1978, 83, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, M.; Fee, D.; Matoza, R. Volcano Acoustics. Modeling Volcanic Processes: The Physics and Mathematics of Volcanism; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, S.; Fee, D.; Haney, M.; Schneider, D. Detecting hidden volcanic explosions from Mt. Cleveland Volcano, Alaska with infrasound and ground-coupled airwaves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 21312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, M.; Fee, D.; Steffke, A.; McCormack, D.; Servranckx, R.; Bass, H.; Hetzer, C.; Hedlin, M.; Matoza, R.; Yepes, H.; Ramon, P. Capturing the Acoustic Fingerprint of Stratospheric Ash Injection. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fee, D.; Steffke, A.; Garces, M. Characterization of the 2008 Kasatochi and Okmok eruptions using remote infrasound arrays. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, K.; Ishihara, K.; Tahira, M. Infrasonic and seismic detection of explosive eruptions at Sakurajima volcano, Japan, and the PEGASAS-VE early-warning system. In First International Symposium on Volcanic Ash and Aviation Safety; Casadevall, T.J., Ed.; U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin: Seattle, WA, USA, 1994; Volume 2047, pp. 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Ripepe, M.; Marchetti, E.; Delle Donne, D.; Genco, R.; Innocenti, L.; Lacanna, G.; Valade, S. Infrasonic Early Warning System for Explosive Eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9570–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan-Auerbach, J.; Bellesiles, A.; Fernandes, J.K. Estimates of eruption velocity and plume height from infrasonic recordings of the 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 189, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripepe, M.; Bonadonna, C.; Folch, A.; Donne, D.D.; Lacanna, G.; Marchetti, E. Ash-plume dynamics and eruption source parameters by infrasound and thermal imagery: The 2010 Eyjafjallaj okull eruption. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 366, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, O.D.; De Angelis, S.; Lavallée, Y. Using infrasound to constrain ash plume rise. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2015, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergniolle, S.; Caplan-Auerbach, J. Basaltic thermals and Subplinian plumes: Constraints from acoustic measurements at Shishaldin volcano, Alaska. Bull. Volcanol. 2006, 68, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudron, C.; Taisne, B.; Garcés, M.; Alexis, L.P.; Mialle, P. On the use of remote infrasound and seismic stations to constrain the eruptive sequence and intensity for the 2014 Kelud eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6614–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoza, R.S.; Vergoz, J.; Le Pichon, A.; Ceranna, L.; Green, D.N.; Evers, L.G.; Ripepe, M.; Campus, P.; Liszka, L.; Kvaerna, T.; Kjartansson, E.; Höskuldsson, Á. Long-range acoustic observations of the Eyjafjallajökull eruption, Iceland, April–May 2010. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.N.; Evers, L.G.; Fee, D.; Matoza, R.S.; Snellen, M.; Smets, P.; Simons, D. Hydroacoustic, infrasonic and seismic monitoring of the submarine eruptive activity and sub-aerial plume generation at South Sarigan, May 2010. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 257, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Watson, L.M.; Palma, J.L.; Dunham, E.M.; Anderson, J.F. Forecasting the Eruption of an Open-Vent Volcano Using Resonant Infrasound Tones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Palma, J.L. Lahar infrasound associated with Volcán Villarrica’s 3 March 2015 eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6324–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, S.R.; Thompson, G.; Johnson, J.; De Angelis, S.; Fee, D. Seismic and Infrasonic Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1071–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Brogi, F.; Ripepe, M.; Bonadonna, C. Lattice Boltzmann modeling to explain volcano acoustic source. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, E.; Ripepe, M.; Delle Donne, D.; Genco, R.; Finizola, A.; Garaebiti, E. Blast waves from violent explosive activity at Yasur Volcano, Vanuatu. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5838–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoza, R.S.; Fee, D.; Lopez, T.M. Acoustic Characterization of Explosion Complexity at Sakurajima, Karymsky, and Tungurahua Volcanoes. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2014, 85, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Ripepe, M. Volcano infrasound: A review. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2011, 206, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fee, D.; Matoza, R.S. An overview of volcano infrasound: From hawaiian to plinian, local to global. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 249, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woulff, G.; McGetchin, T.R. Acoustic Noise from Volcanoes: Theory and Experiment. Geophys. J. Int. 1976, 45, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighthill, M.J. On sound generated aerodynamically I. General theory. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1952, 211, 564–587. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lees, J.M.; Ruiz, M. Acoustic multipole source model for volcanic explosions and inversion for source parameters. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.M.C.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics; International Series in Pure And Applied Physics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Lighthill, M.J. Waves in Fluids; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978; p. 504. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.S. Buoyancy Effects in Fluids; Cambridge Monographs on Mechanics, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, G.A. Optimum Formulas for Buoyant Plume Rise. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 265, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, M.J.; Hogg, A.J.; Phillips, J.C.; Sparks, R.S.J. Interaction between volcanic plumes and wind during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption, Iceland. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.J.; Hoblitt, R.P. Doppler weather radar observations of the 2009 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 259, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B. Volcanic eruptions observed with infrasound. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Lees, J.M. Sound produced by the rapidly inflating Santiaguito lava dome, Guatemala. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Miller, A.J.C. Application of the Monopole Source to Quantify Explosive Flux during Vulcanian Explosions at Sakurajima Volcano (Japan). Seismol. Res. Lett. 2014, 85, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacanna, G.; Ripepe, M. Influence of near-source volcano topography on the acoustic wavefield and implication for source modeling. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 250, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Fee, D.; Yokoo, A.; Lees, J.M. Acoustic source inversion to estimate volume flux from volcanic explosions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5243–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Aster, R.; Jones, K.R.; Kyle, P.; McIntosh, B. Acoustic source characterization of impulsive Strombolian eruptions from the Mount Erebus lava lake. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 177, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, S.; Lamb, O.D.; Lamur, A.; Hornby, A.J.; von Aulock, F.W.; Chigna, G.; Lavallée, Y.; Rietbrock, A. Characterization of moderate ash-and-gas explosions at Santiaguito volcano, Guatemala, from infrasound waveform inversion and thermal infrared measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6220–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lees, J.M. Finite-difference time-domain modeling of transient infrasonic wavefields excited by volcanic explosions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostashev, V.E.; Wilson, D.K.; Liu, L.; Aldridge, D.F.; Symons, N.P.; Marlin, D. Equations for finite- difference, time-domain simulation of sound propagation in moving inhomogeneous media and numerical implementation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fee, D.; Izbekov, P.; Kim, K.; Yokoo, A.; Lopez, T.; Prata, F.; Kazahaya, R.; Nakamichi, H.; Iguchi, M. Eruption mass estimation using infrasound waveform inversion and ash and gas measurements: Evaluation at Sakurajima Volcano, Japan. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 480, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.A. Solution of sparse rectangular systems using LSQR and CRAIG. BIT Numer. Math. 1995, 35, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, A.M.; Fee, D.; Matoza, R.S.; Jolly, A.D.; Kim, K.; Christenson, B.W.; Johnson, R.; Kilgour, G.; Garaebiti, E.; Austin, A.; et al. 3-D acoustic waveform simulation and inversion supplemented by infrasound sensors on a tethered weather balloon at Yasur Volcano, Vanuatu. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2017, New Orleans, LO, USA, 11–15 December 2017; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Moreno, A.; Iezzi, A.; Lamb, O.; Zuccarello, L.; Fee, D.; De Angelis, S. Assessment of eruption intensity using infrasound waveform inversion at Mt. Etna, Italy. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2017, New Orleans, LO, USA, 11–15 December 2017; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Angelis, S.; Diaz-Moreno, A.; Zuccarello, L. Recent Developments and Applications of Acoustic Infrasound to Monitor Volcanic Emissions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111302
De Angelis S, Diaz-Moreno A, Zuccarello L. Recent Developments and Applications of Acoustic Infrasound to Monitor Volcanic Emissions. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(11):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111302
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Angelis, Silvio, Alejandro Diaz-Moreno, and Luciano Zuccarello. 2019. "Recent Developments and Applications of Acoustic Infrasound to Monitor Volcanic Emissions" Remote Sensing 11, no. 11: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111302
APA StyleDe Angelis, S., Diaz-Moreno, A., & Zuccarello, L. (2019). Recent Developments and Applications of Acoustic Infrasound to Monitor Volcanic Emissions. Remote Sensing, 11(11), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111302