Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
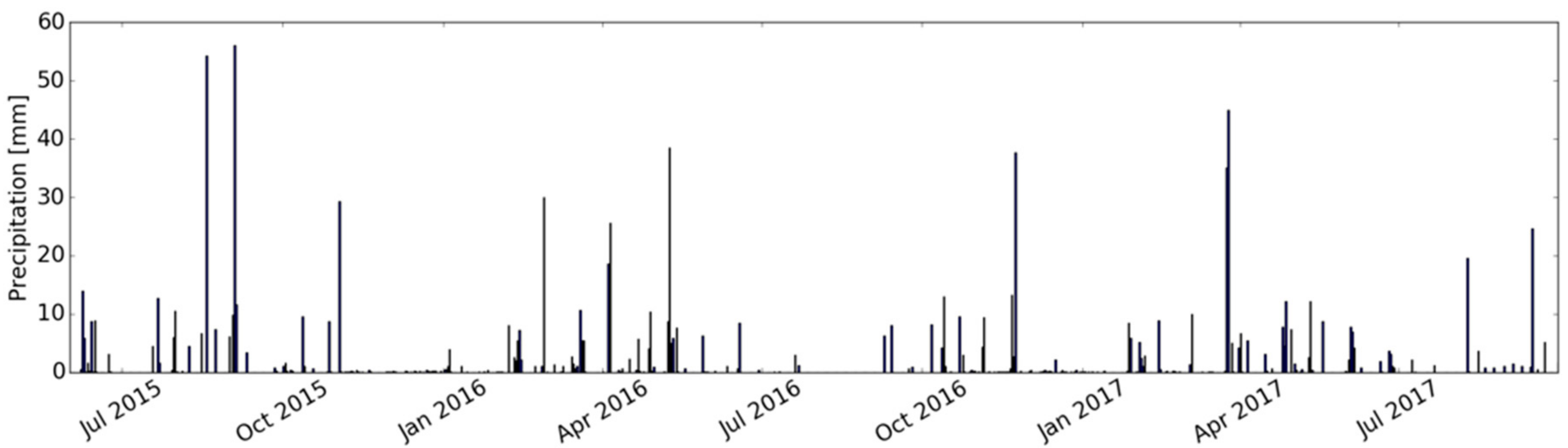
2. Database and Study Area
2.1. Database
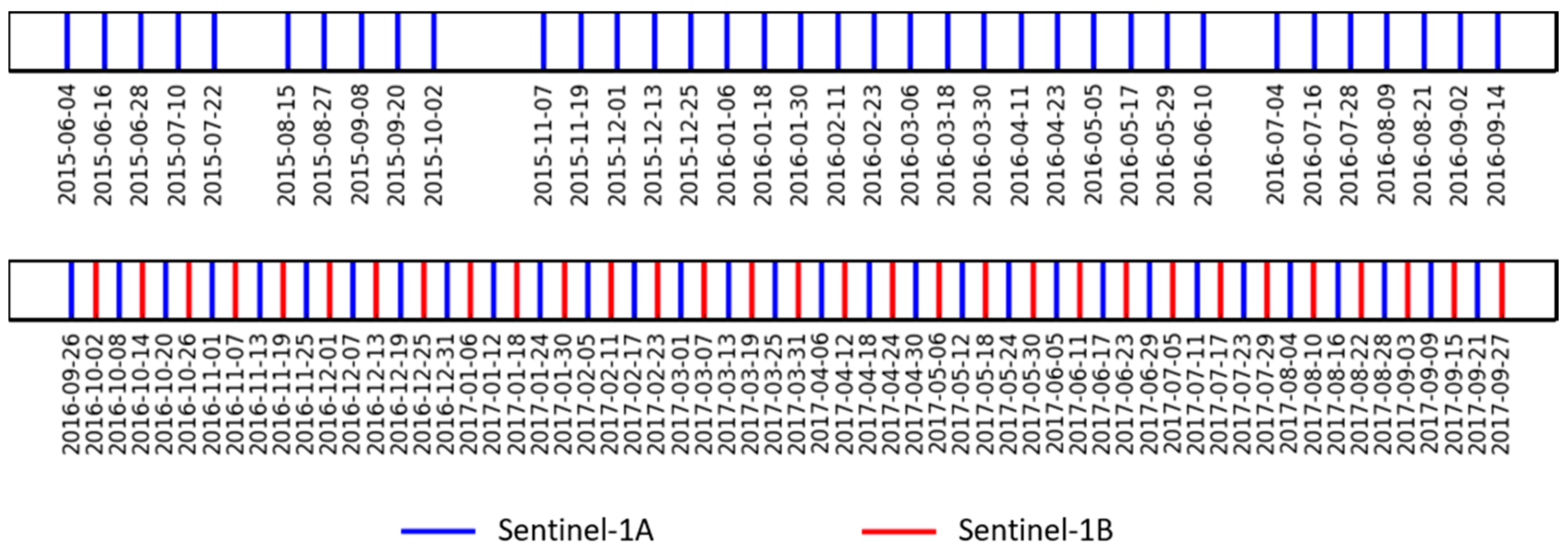
2.1.1. Sentinel-1 Data
- -
- Thermal noise removal
- -
- Radiometric calibration
- -
- Terrain correction using SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) DEM (Digital Elevation Model) at 30 m.
2.1.2. Ground Truth (SIGPAC)
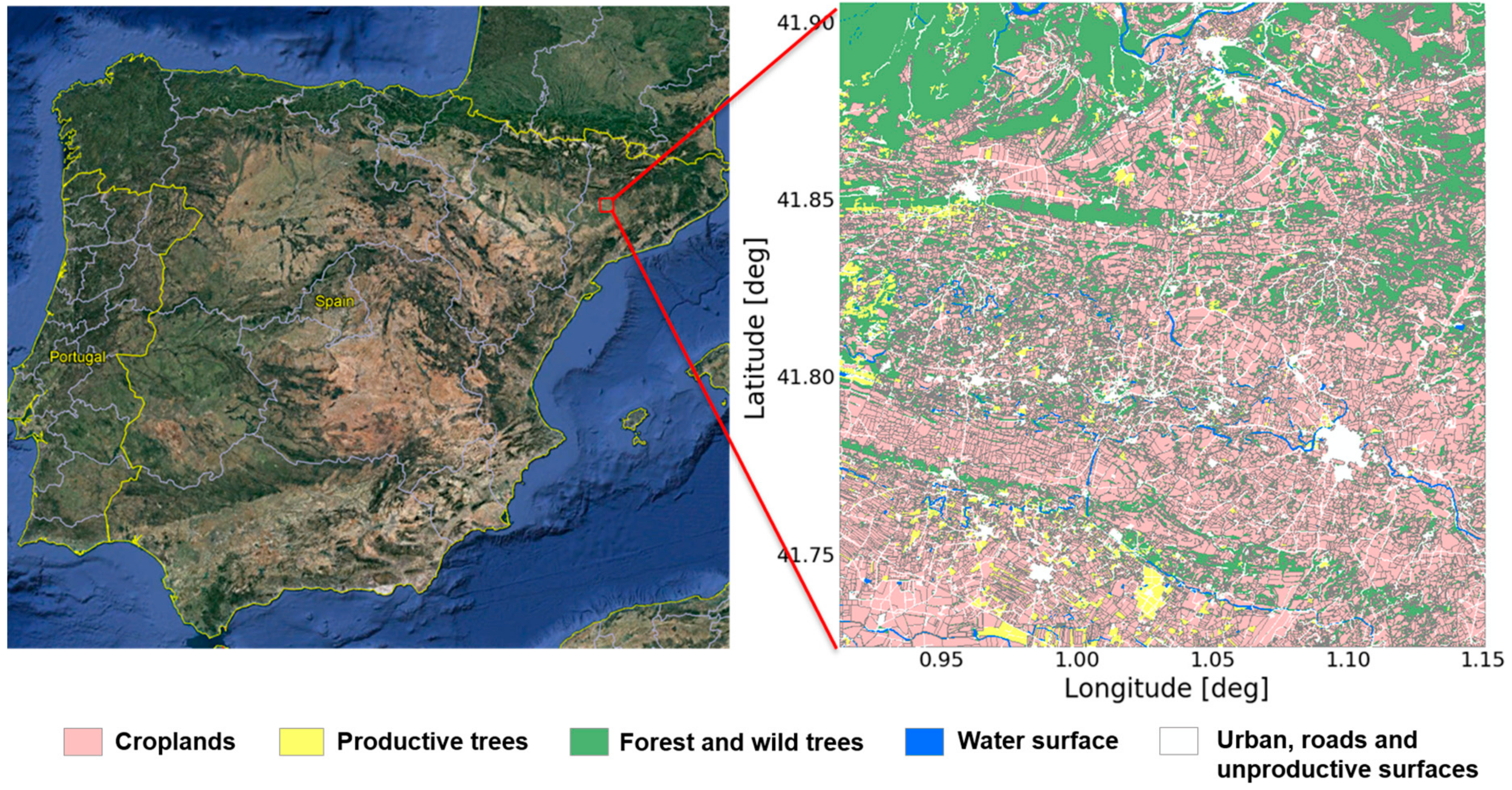
2.2. Study Area
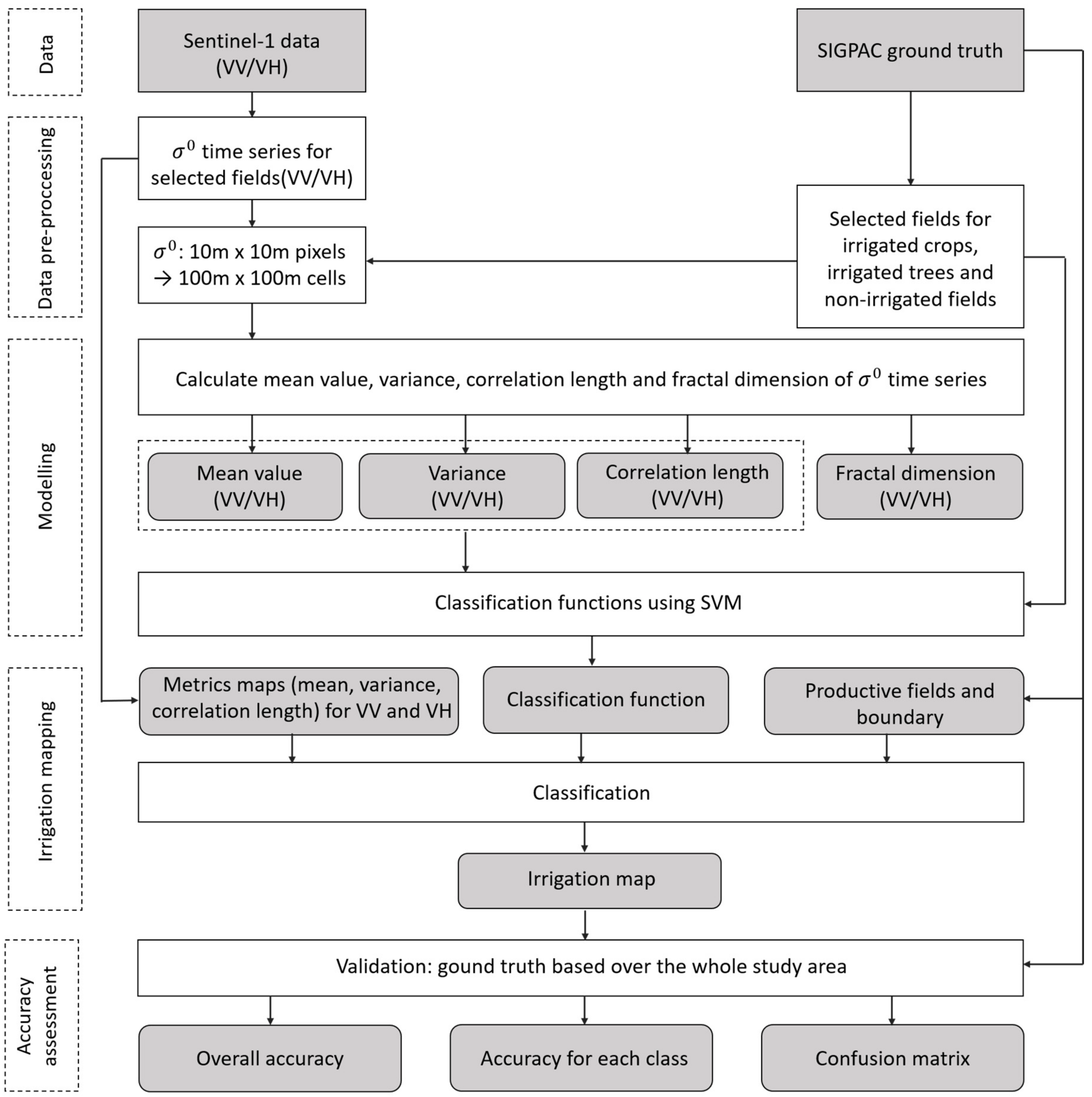
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
3.2. Analyzed Metrics
3.2.1. Mean Value of σ°
3.2.2. Signal Variance
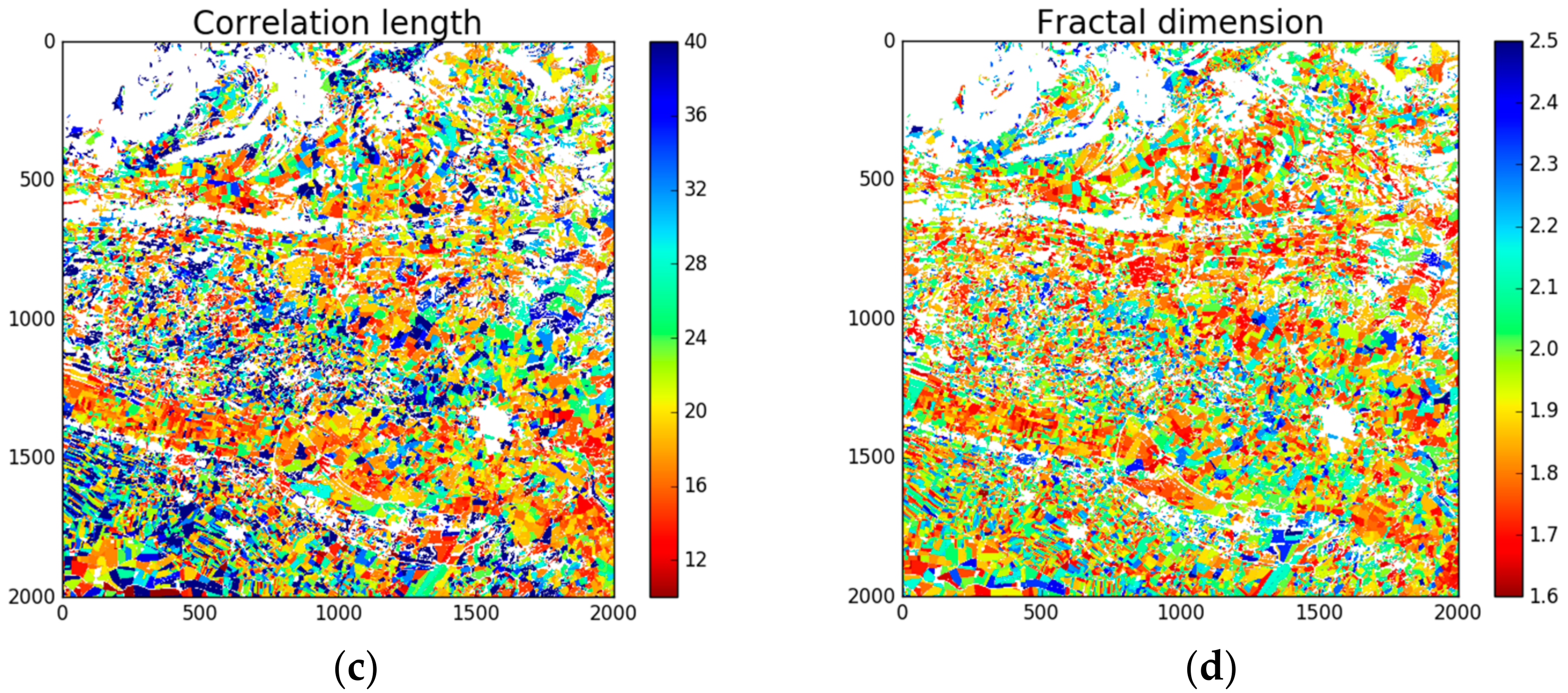
3.2.3. Signal Correlation Length
3.2.4. Fractal Dimension
3.3. Modeling
3.3.1. Support Vector Machine
3.3.2. Classification Function
3.4. Tree Classification
3.5. Random Forest (RF) Classification
4. Results and Validation
4.1. Metrics Mapping
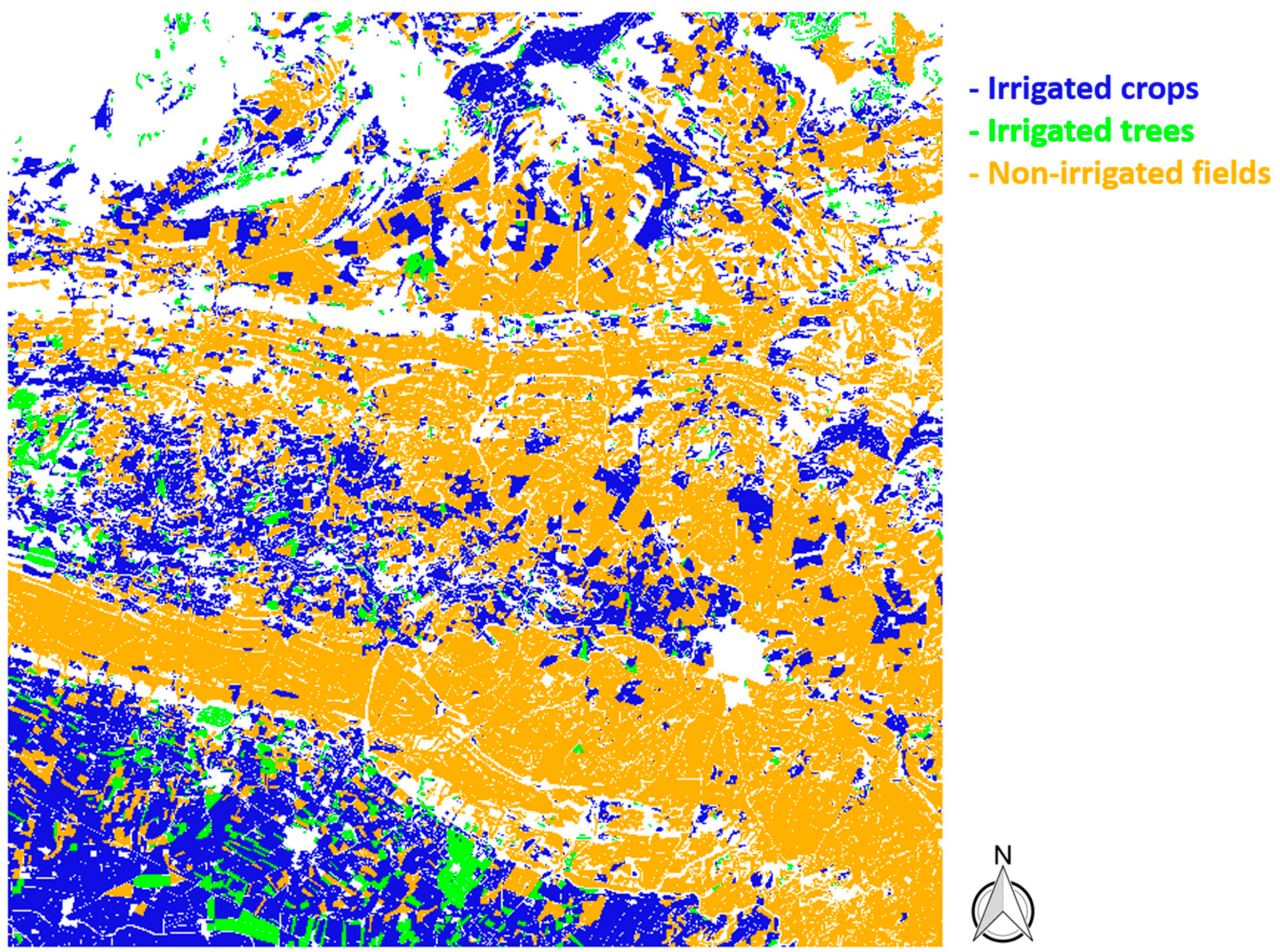
4.2. Classification Map
4.3. Validation
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleick, P.H. Global freshwater resources: Soft-path solutions for the 21st century. Science 2003, 302, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Meijer, S.; Cline, S.A. International Model for Policy Analysis of Agricultural Commodities and Trade (IMPACT): Model Description; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdogan, M.; Yang, Y.; Allez, G.; Cervantes, C. Remote Sensing of Irrigated Agriculture: Opportunities and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2274–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrou, M.; Page, M.L.; Chehbouni, A.; Simonneaux, V.; Er-Raki, S.; Jarlan, L.; Ouzine, L.; Khabba, S.; Chehbouni, G. Assessment of Equity and Adequacy of Water Delivery in Irrigation Systems Using Remote Sensing-Based Indicators in Semi-Arid Region, Morocco. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4697–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, V. Mixed Modeling and Multi-Resolution Remote Sensing of Soil Evaporation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Toulouse 3 Paul Sabatier (UT3 Paul Sabatier), Toulouse, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ambika, A.K.; Wardlow, B.; Mishra, V. Data descriptor: Remotely sensed high resolution irrigated area mapping in India for 2000 to 2015. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Magidi, J.; Nhamo, L.; Koppen, B. Mapping Irrigated Areas in the Limpopo Province, South Africa; IWMI Working Paper 172; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Schull, M.; Turral, H. Ganges and Indus river basin land use/land cover (LULC) and irrigated area mapping using continuous streams of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 95, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, C.M.; Belmonte, A.C. Irrigated crop area estimation using Landsat TM imagery in La Mancha, Spain. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, T.W.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Gumma, M.K.; Scott, C.A.; Parthasaradhi, G.R.; Turral, H.N. Irrigated area mapping in heterogeneous landscapes with MODIS time series, ground truth and census data, Krishna Basin, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4245–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheeravath, V.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Chandrakantha, G.; Noojipady, P.; Reddy, G.P.O.; Biradar, C.M.; Gumma, M.K.; Velpuri, M. Irrigated areas of India derived using MODIS 500 m time series for the years 2001–2003. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 65, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamthonkiat, D.; Honda, K.; Turral, H.; Tripathi, N.K.; Wuwongse, V. Discrimination of irrigated and rainfed rice in a tropical agricultural system using SPOT VEGETATION NDVI and rainfall data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2527–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draeger, W.C. Monitoring Irrigated Land Acreage Using LANDSAT Imagery: An Application Example. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–29 April 1977; pp. 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Thiruvengadachari, S. Satellite sensing of irrigation pattern in semiarid areas: An Indian study. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1981, 47, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Rundquist, D.C.; Richardo, H.; Carlson, M.P.; Cook, A. The Nebraska center-pivot inventory—An example of operational satellite remote sensing on a long term basis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1989, 55, 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, M.; Mamanpoush, A.; Gieske, A.; Miranzadeh, M.; Torabi, M.; Salemi, H.R. Crop and land cover classification in Iran using Landsat 7 imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4117–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M.; Gutman, G. A New Methodology to Map Irrigated Areas Using Multi-Temporal MODIS and Ancillary Data: An Application Example in the Continental US. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3520–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boken, V.K.; Hoogenboom, G.; Kogan, F.N.; Hook, J.E.; Thomas, D.L.; Harrison, K.A. Potential of using NOAA-AVHRR data for estimating irrigated area to help solve an inter-state water dispute. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Hideto, F.; Nelson, A.; Dheeravath, V.; Busia, D.; Rala, A. Mapping Irrigated Areas of Ghana Using Fusion of 30 m and 250 m Resolution Remote-Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M. Land Surface Remote Sensing in Continental Hydrology; ISTE Press: London, UK; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Morvan, A.L.; Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Chanzy, A. Soil moisture profile effect on radar signal measurement. Sensors 2008, 8, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguela, T.P.; Zribi, M.; Hasenauer, S.; Habets, F.; Loumagne, C. Analysis of surface and root-zone soil moisture dynamics with ERS scatterometer and the hydrometeorological model SAFRAN-ISBA-MODCOU at Grand Morin watershed (France). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Chahbi, A.; Shabou, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Duchemin, B.; Baghdadi, N.; Amri, R.; Chehbouni, A. Soil surface moisture estimation over a semi-arid region using ENVISAT ASAR radar data for soil evaporation evaluation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Gorrab, A.; Baghdadi, N. A new soil roughness parameter for the modelling of radar backscattering over bare soil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanelli, G.; Paloscia, S.; Zribi, M.; Chahbi, A. Sensitivity analysis of X-band SAR to wheat and barley leaf area index in the Merguellil Basin. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Dechambre, M. A new empirical model to retrieve soil moisture and roughness from C-band radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Cresson, R.; Pottier, E.; Aubert, M.; Zribi, M.; Jacome, A.; Benabdallah, S. A potential use for the C-band polarimetric SAR parameters to characterize the soil surface over bare agriculture fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3844–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.S.; Patel, P.; Manchanda, M.L.; Adiga, S. Use of multiincidence angle RADARSAT-1 SAR data to incorporate the effect of surface roughness in soil moisture estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1638–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, M.; Cumming, I. A modified empirical model for soil moisture estimation in vegetated areas using SAR data. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tomer, S.K.; Al Bitar, A.; Sekhar, M.; Zribi, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Sreelash, K.; Sharma, A.K.; Corgne, S.; Kerr, Y. Retrieval and Multi-scale Validation of Soil Moisture from Multi-temporal SAR Data in a Tropical Region. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8128–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N. Synergetic use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data for soil moisture mapping at 100 m resolution. Sensors 2017, 17, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Bazzi, H. Synergic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images for Operational Soil Moisture Mapping at High Spatial Resolution over Agricultural Areas. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbes, F.; Toan, T.L. Rice field mapping and monitoring with RADARSAT data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 745–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J.; Ross, S.; Brisco, B.; Brown, R.; Staples, G. Rice monitoring and production estimation using multitemporal RADARSAT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Andre, C.; Decharme, B. A Method for Soil Moisture Estimation in Western Africa Based on the ERS Scatterometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Srivastava, H.S.; Panigrahy, S.; Parihar, J.S. Comparative evaluation of the sensitivity of multi-polarized multi-frequency SAR backscatter to plant density. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacome, A.; Bernier, M.; Chokmani, K.; Gauthier, Y.; Poulin, J.; De Sève, D. Monitoring Volumetric Surface Soil Moisture Content at the La Grande Basin Boreal Wetland by Radar Multi Polarization Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4919–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazirh, A.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S.; Gao, Q.; Rivalland, V.; Malbeteau, Y.; Khabba, S.; Escorihuela, M.J. Retrieving surface soil moisture at high spatio-temporal resolution from a synergy between Sentinel-1 radar and Landsat thermal data: A study case over bare soil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweys, O.A.; Elwan, A.; Borham, T. Retrieving topsoil moisture using RADARSAT-2 data, a novel approach applied at the east of The Netherlands. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherboudj, I.; Magagi, R.; Berg, A.A.; Toth, B. Soil moisture retrieval over agricultural fields from multi-polarized and multi-angular RADARSAT-2 SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, M.; Kaartinen, H.; Hyyppä, J.; Laurila, H.; Kuittinen, R. The Use of ENVISAT Alternating Ploarization SAR Images in Agricultureal Monitoring in Compatison with RADARSAT-1 SAR Images. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, S.; Srivastava, H.S. Comparative evaluation of the sensitivity of multi-polarized SAR and optical data for various land cover classes. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS Geogr. 2016, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- INFORMACIÓ DE LES DADES SIGPAC. Available online: https://analisi.transparenciacatalunya.cat/api/views/w9bf-jejh/files/36948005-55ef-4003-826b-d01c17968ddf?download=true&filename=Dades_SIGPAC_2017.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- El Departament d’Agricultura, Ramaderia, Pesca i Alimentació (DARP)—Mapa Agricultura. Available online: http://sig.gencat.cat/visors/Agricultura.html (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Escorihuela, M.J.; Quintana-Segui, P. Comparison of remote sensing and simulated soil moisture datasets in mediterranean landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelson, R.A.; Krolik, J.H. The discrete correlation function—A new method for analyzing unevenly sampled variability data. Astrophys. J. 1988, 333, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. Fractals, Form, Chance and Dimension; W. H. Freeman and Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1977; p. 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, R.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Duchemin, B.; Gruhier, C.; Chehbouni, A. Analysis of vegetation behavior in a north African semi-arid region, using SPOT-Vegetation NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2568–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, G.; Gong, P.; Liang, S. Fractal analysis of remotely sensed images: A review of methods and applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4963–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menenti, M.; Azzali, S.; Vries, A.; Fuller, D.; Prince, S. Vegetation monitoring in southern Africa using temporal fourrier analysis of AVHRR/NDVI observations. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Remote Sensing in Arid and Semi-arid Regions, Lanzhou, China, 25–28 August 1993; Volume 3, pp. 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Havlin, S.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Golberger, A.L.; Ivanov, P.C.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. Application of statistical physics to heartbeat diagnosis. Physica A 1999, 274, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Lerner, A. Pattern recognition using generalized portrait method. Autom. Remote Control 1963, 24, 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K. The Random Subspace Method for Constructing Decision Forests. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K.; Hostetler, L. The estimation of the gradient of a density function, with applications in pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1975, 21, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift analysis and applications. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1197–1203. [Google Scholar]
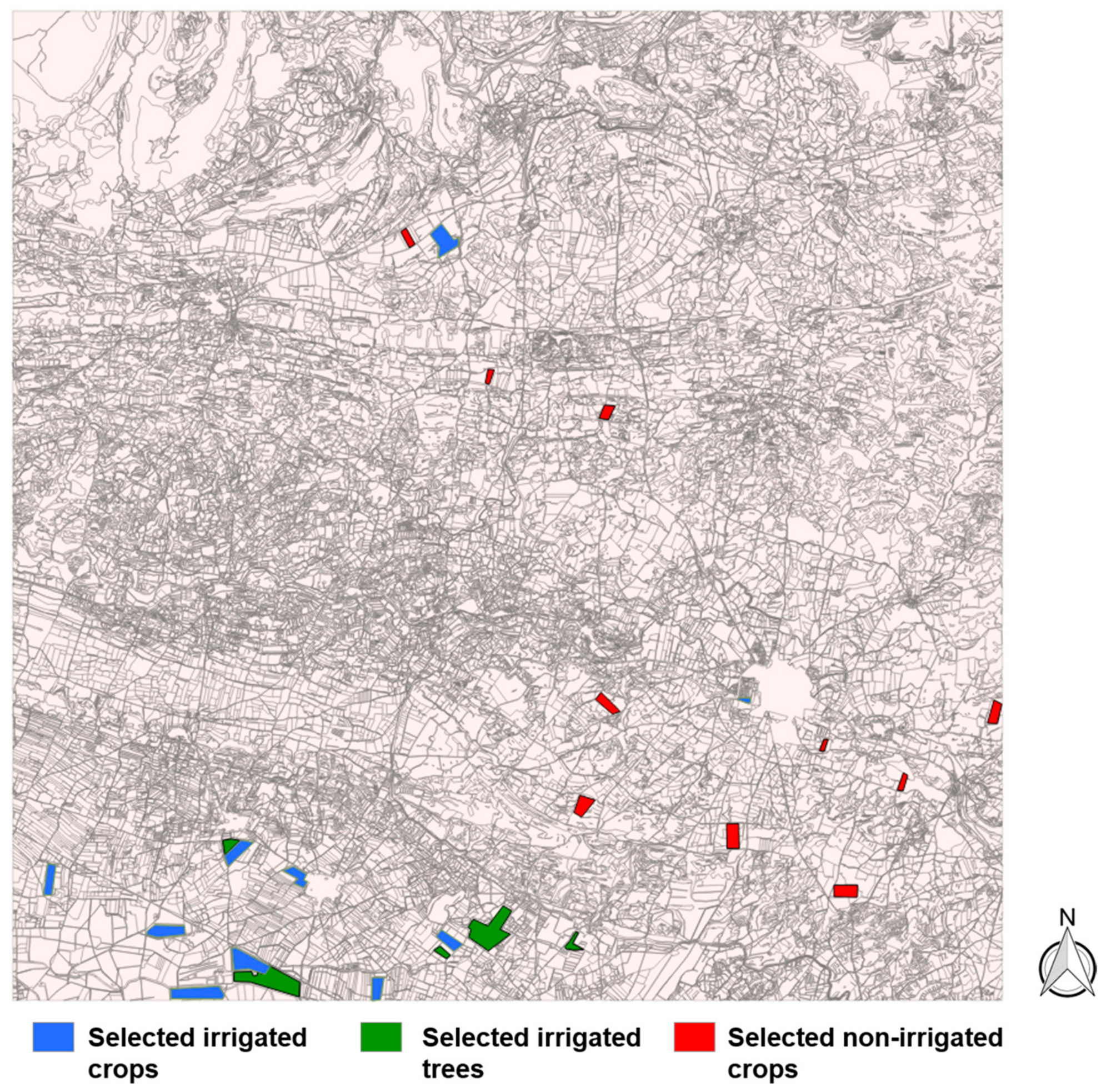


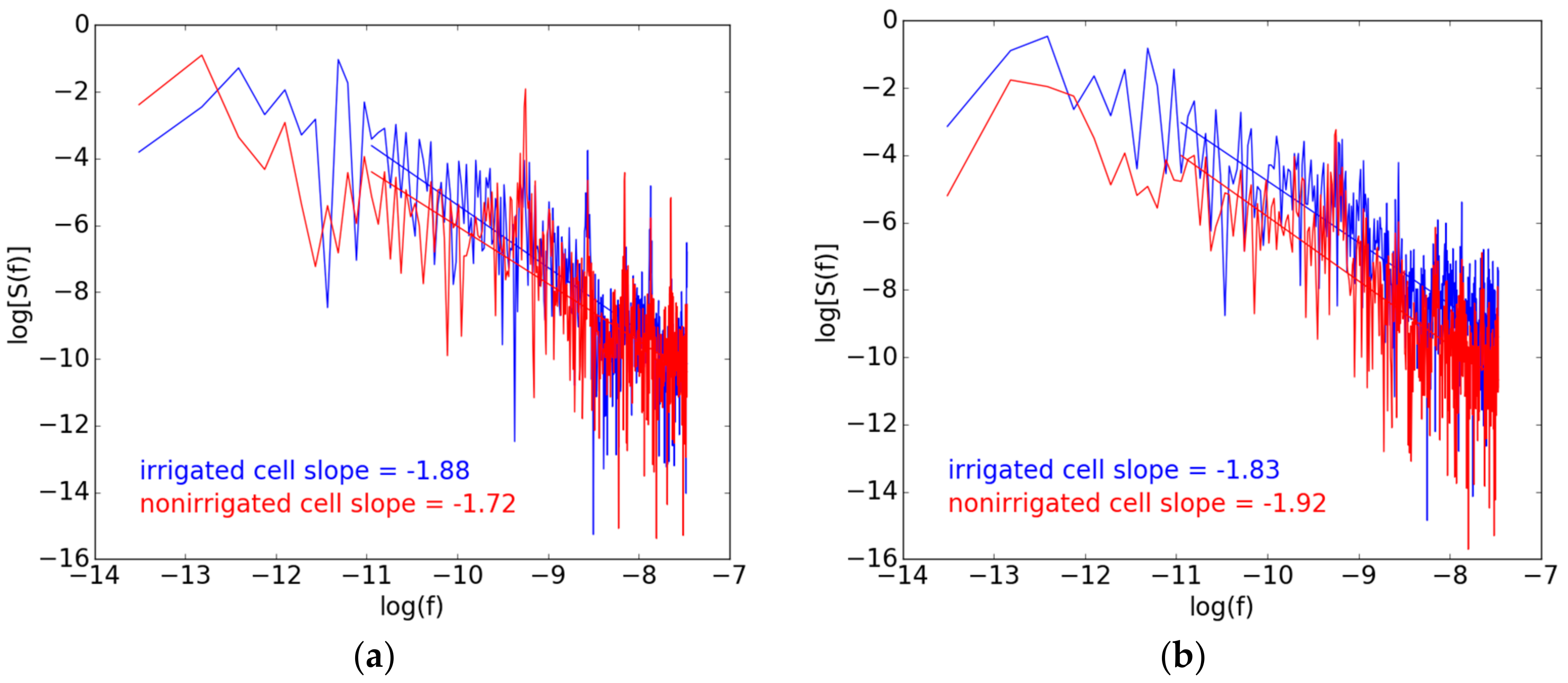
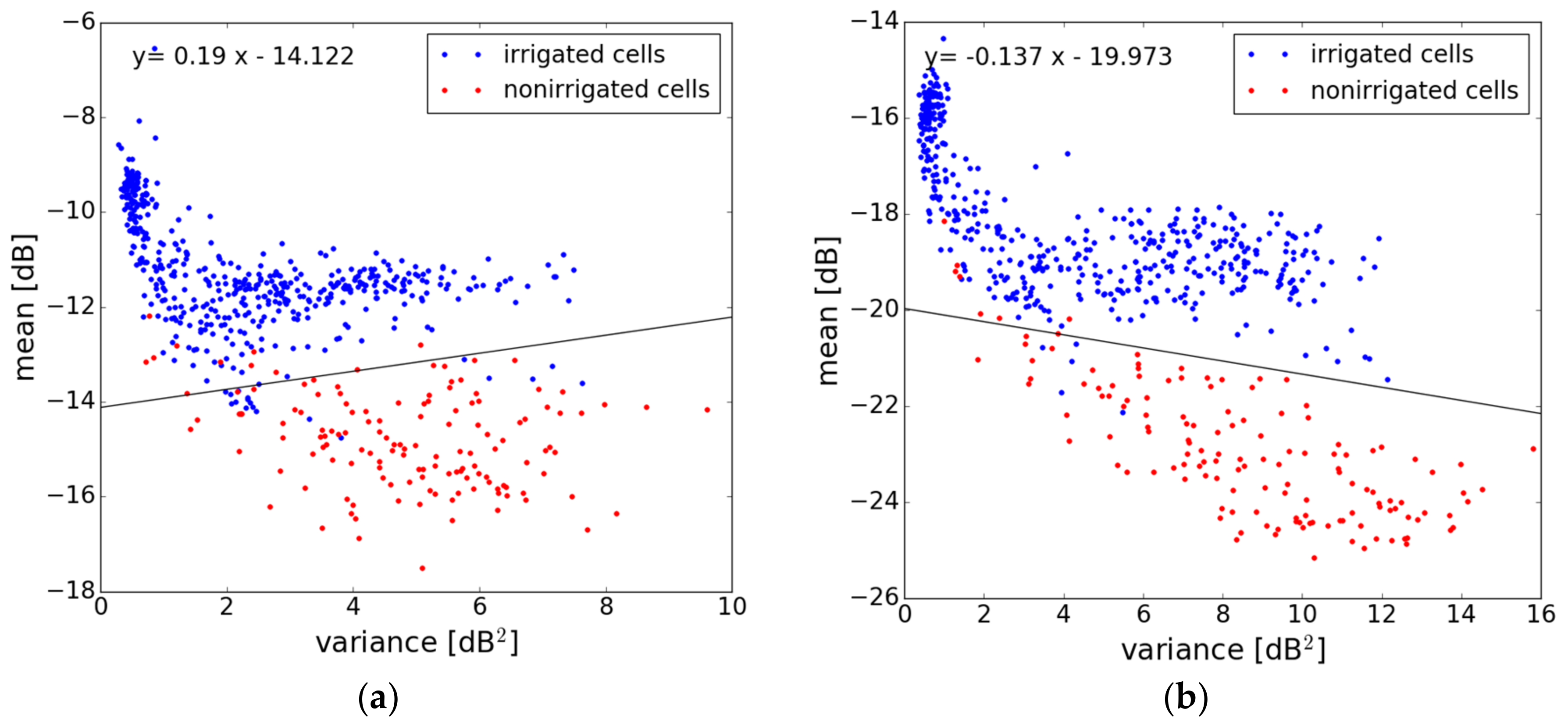
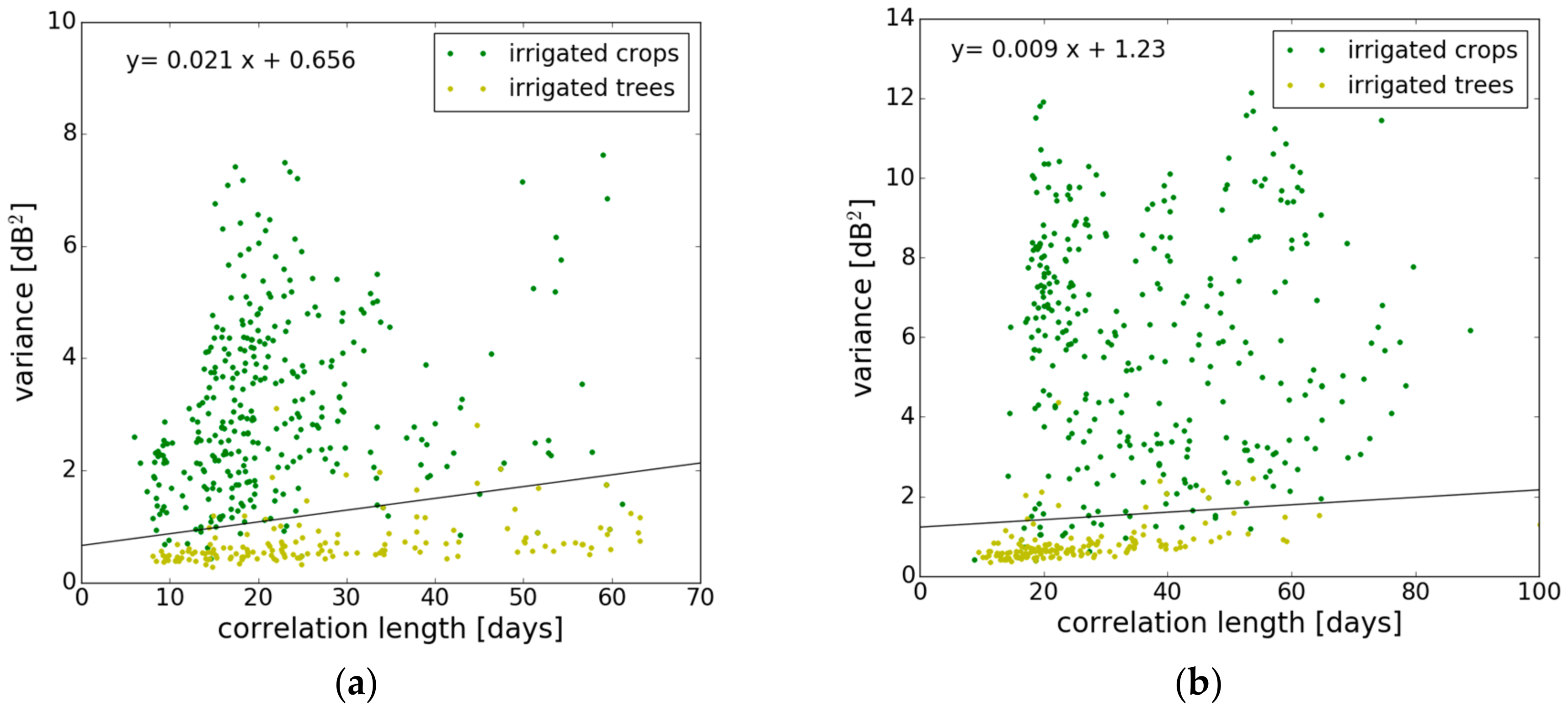

| Classes | Irrigated Crops | Irrigated Trees | Non-Irrigated Fields |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigated crops | 77.5% | 1.9% | 20.6% |
| Irrigated trees | 22.3% | 73.5% | 4.2% |
| Non-irrigated fields | 14.8% | 1.9% | 83.3% |
| Input Metrics | Mean (VV/VH) | Mean (VV/VH) + Variance (VV/VH) | Mean (VV/VH) + Variance (VV/VH) + Correlation Length (VV/VH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 80.9% | 81.9% | 82.2% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Segui, P.Q. Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091495
Gao Q, Zribi M, Escorihuela MJ, Baghdadi N, Segui PQ. Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(9):1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091495
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Qi, Mehrez Zribi, Maria Jose Escorihuela, Nicolas Baghdadi, and Pere Quintana Segui. 2018. "Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale" Remote Sensing 10, no. 9: 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091495
APA StyleGao, Q., Zribi, M., Escorihuela, M. J., Baghdadi, N., & Segui, P. Q. (2018). Irrigation Mapping Using Sentinel-1 Time Series at Field Scale. Remote Sensing, 10(9), 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10091495









