Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
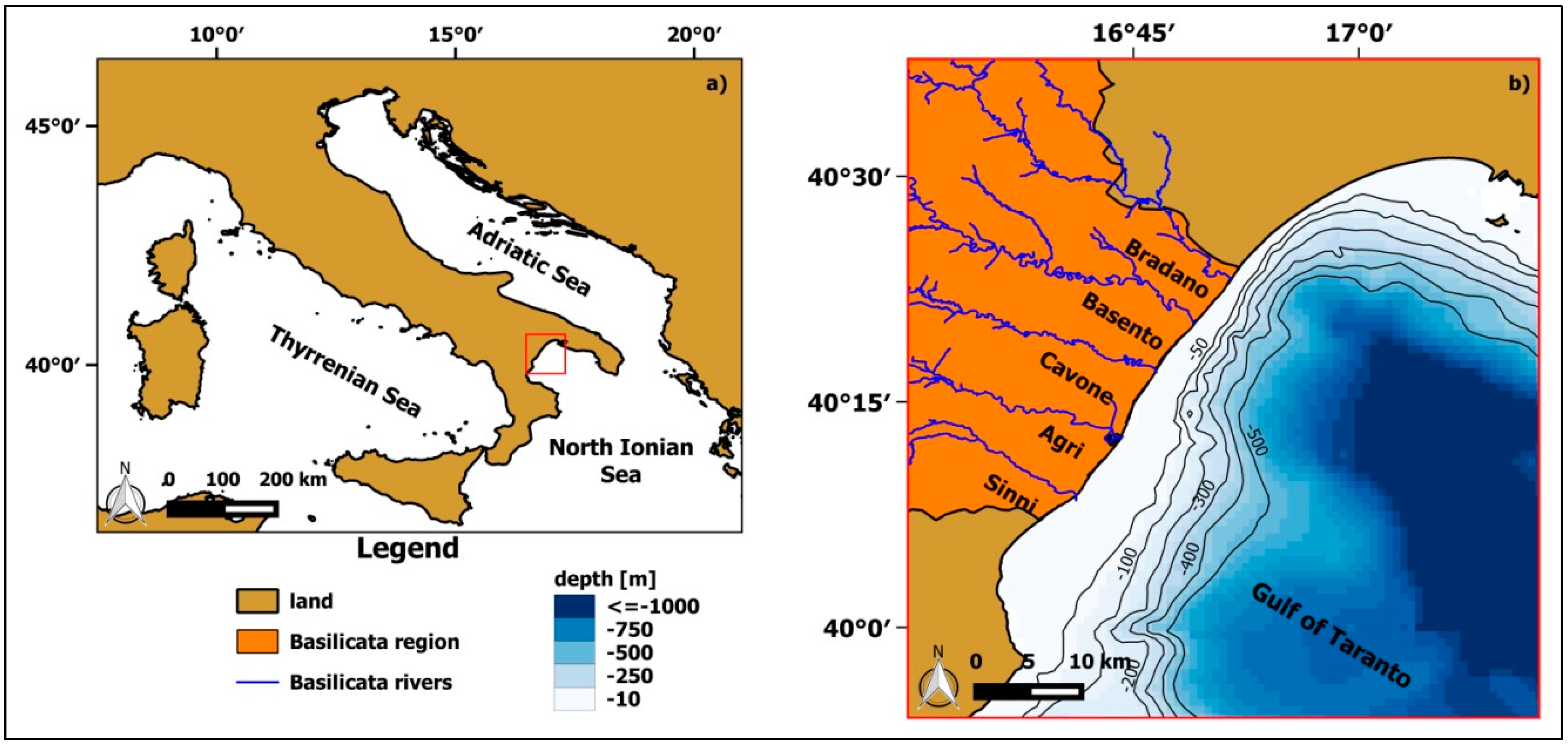
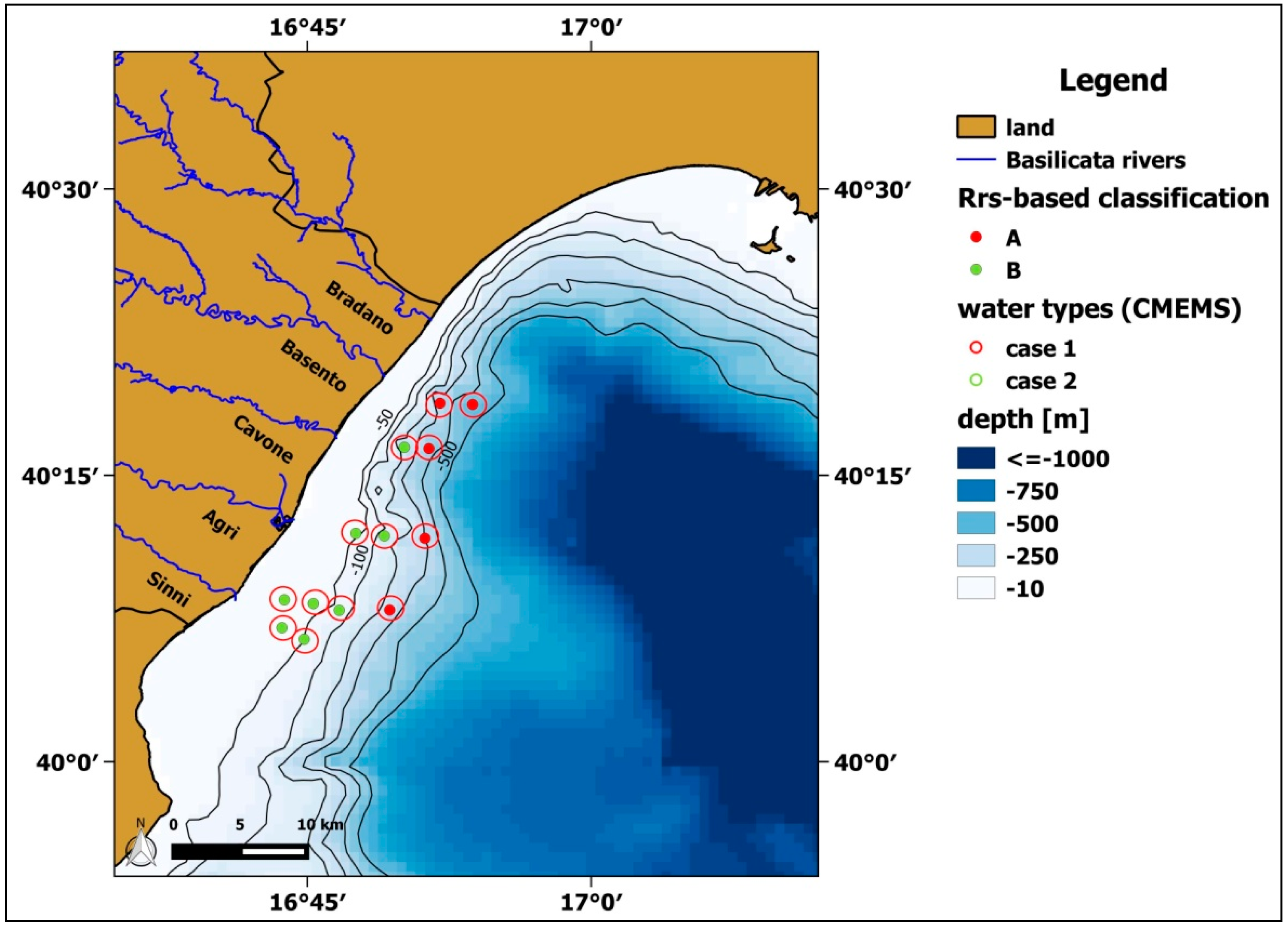
2.1. Study Area
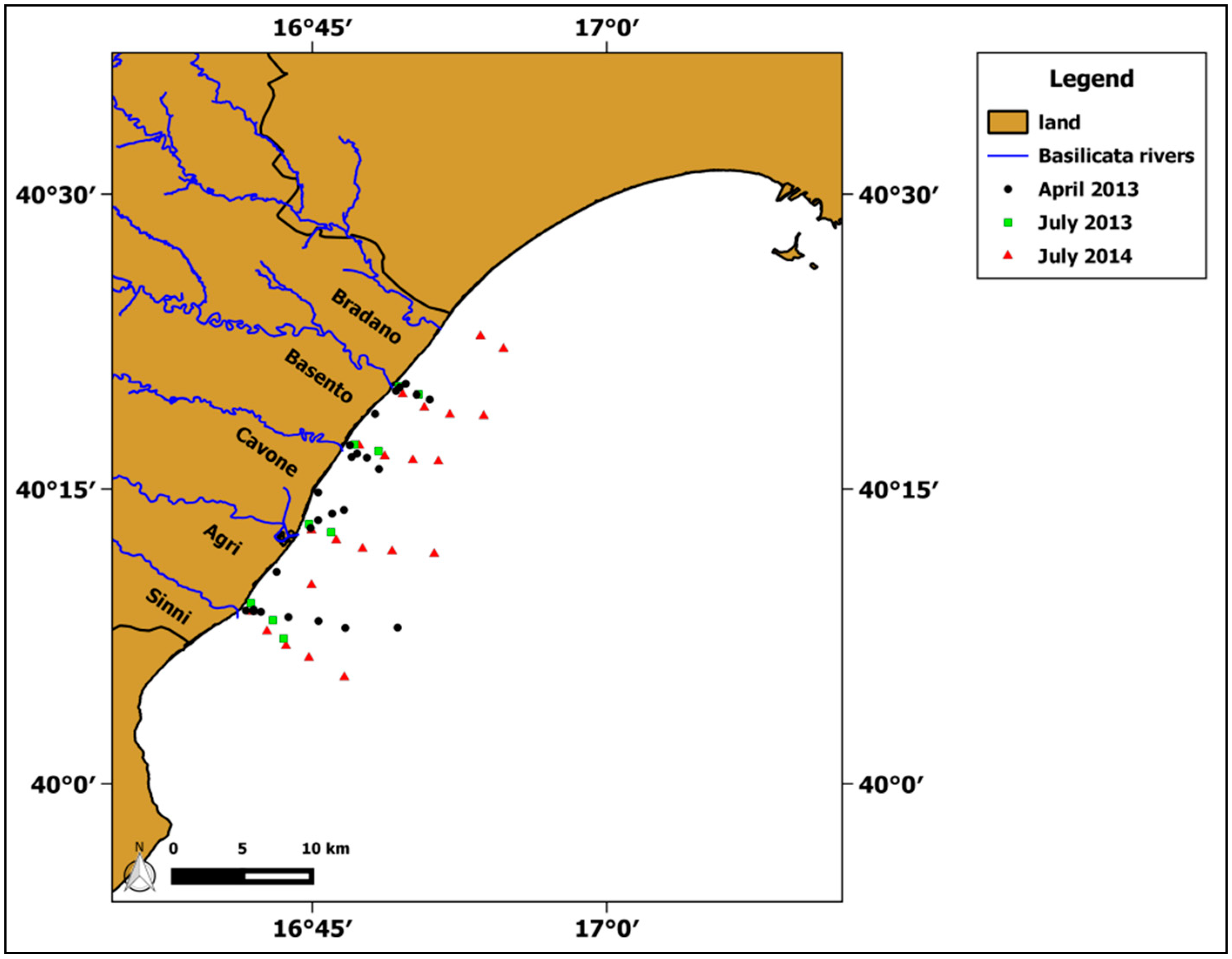
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
2.2.1. In Situ Chl-a and Absorption Spectra Analysis
2.2.2. In Situ Rrs(λ)
2.3. MODIS Satellite Data
MODIS Chl-a Algorithms: Med-OC3, GSM and GIOP
2.4. Chl-a Match-Up Analysis
3. Results
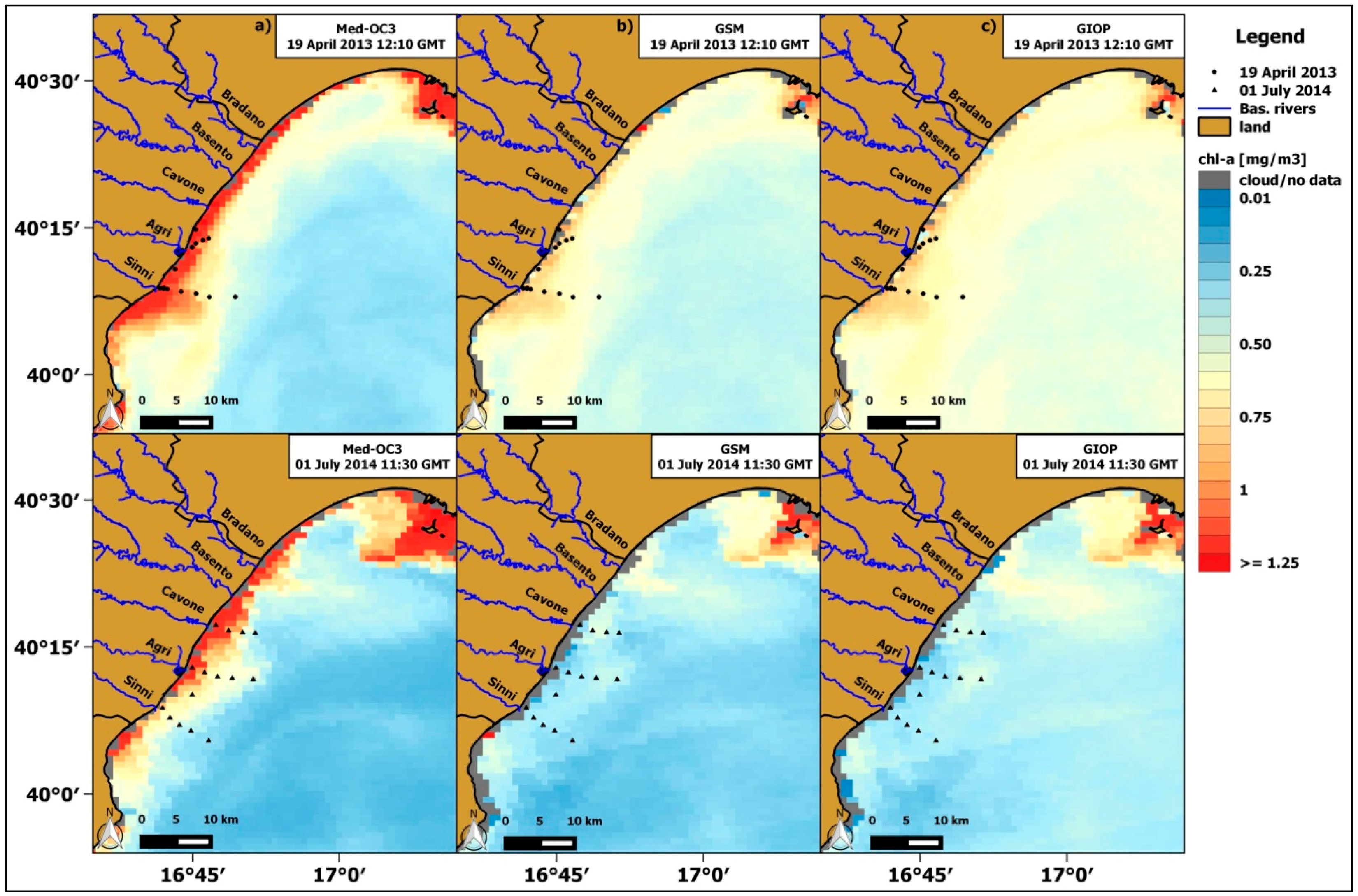
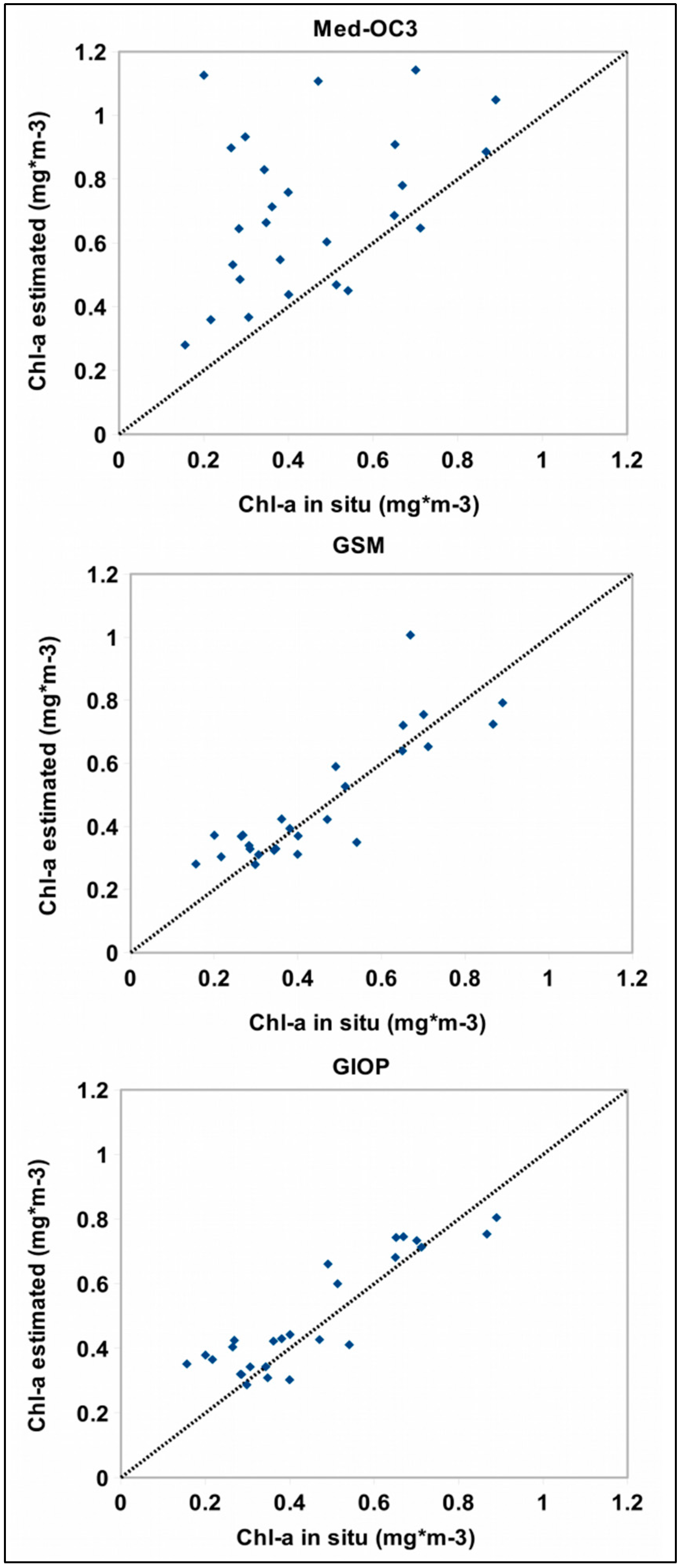
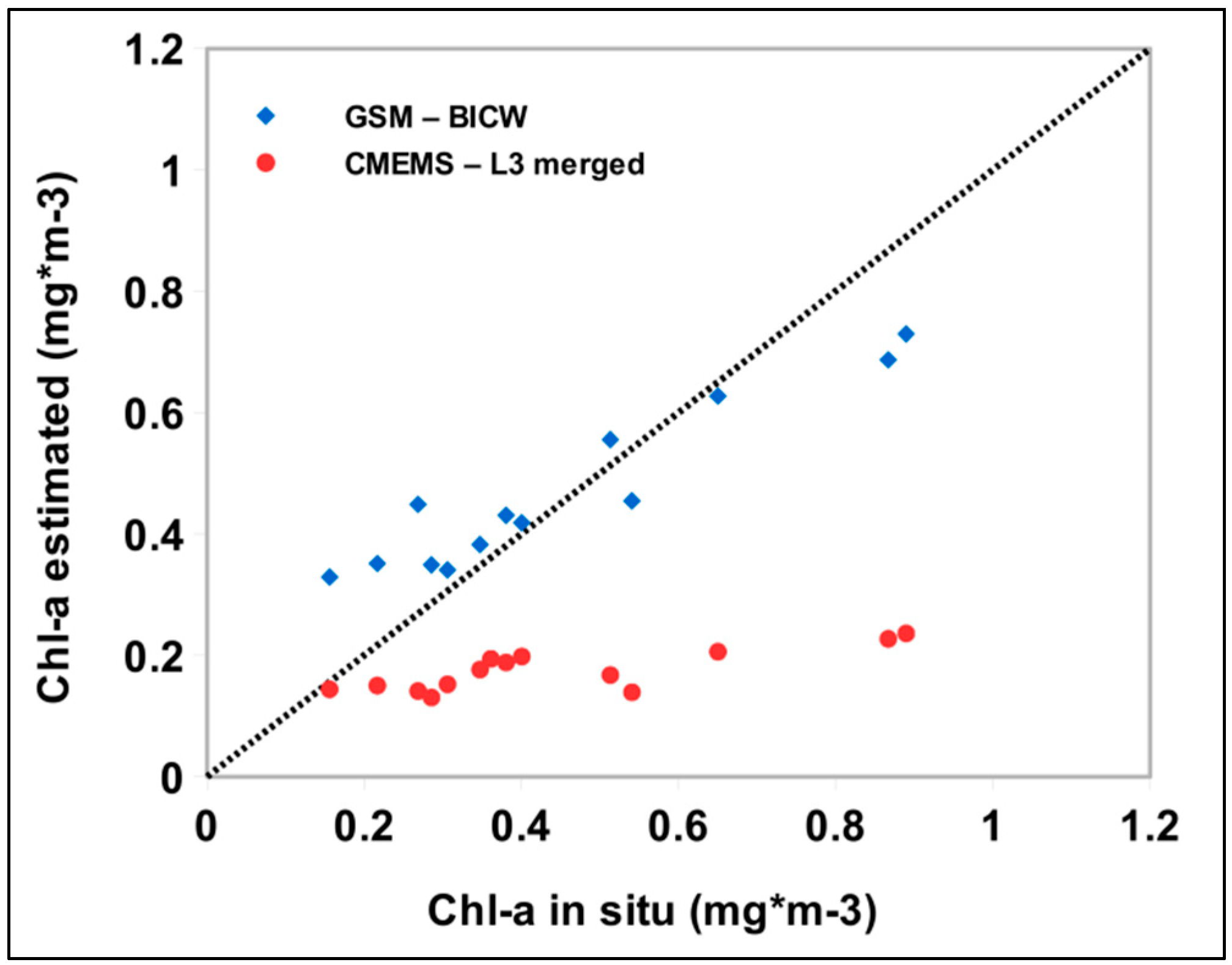
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of MODIS-Aqua Chl-a Algorithms
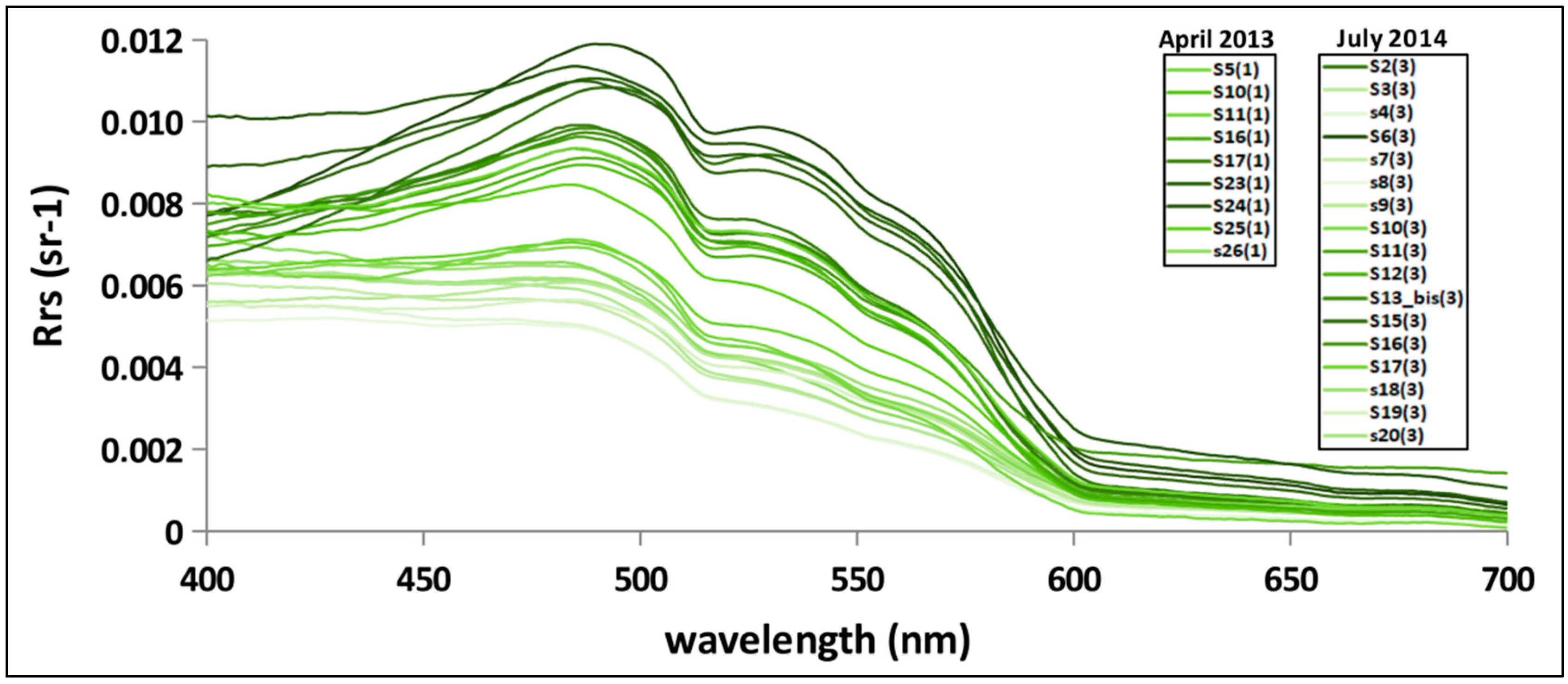
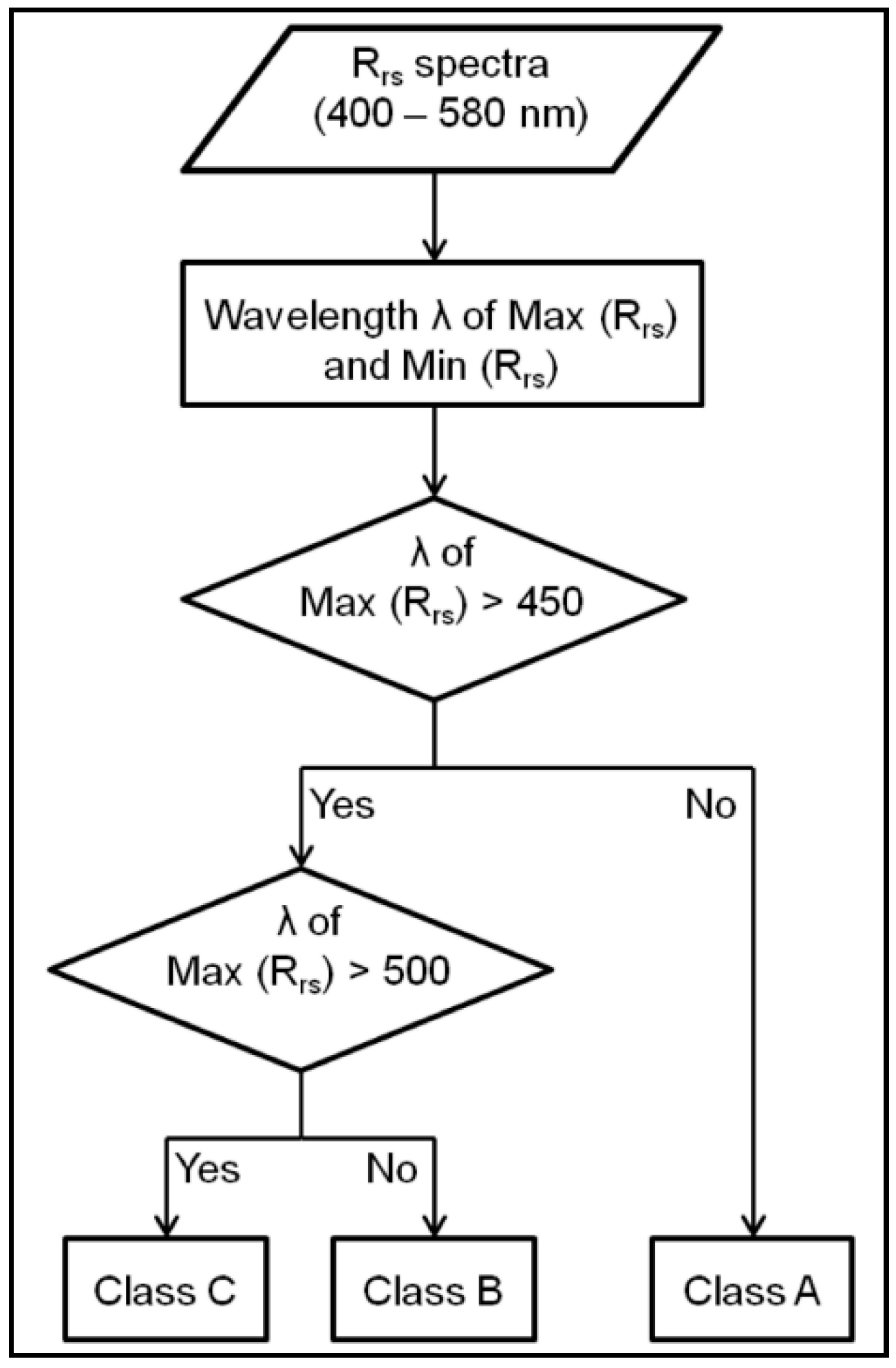
3.2. In Situ Rrs(λ) Spectra and Water Types Characterization
- Class A: Phytoplankton dominant waters, characterized by the spectral peak at about 400 nm.
- Class B: CDM dominant waters, with the maximum Rrs(λ) at approximately 490 nm.
- Class C: Mixed waters with no dominant bio-optical components, with a flat Rrs(λ) peak between 500–550 nm.
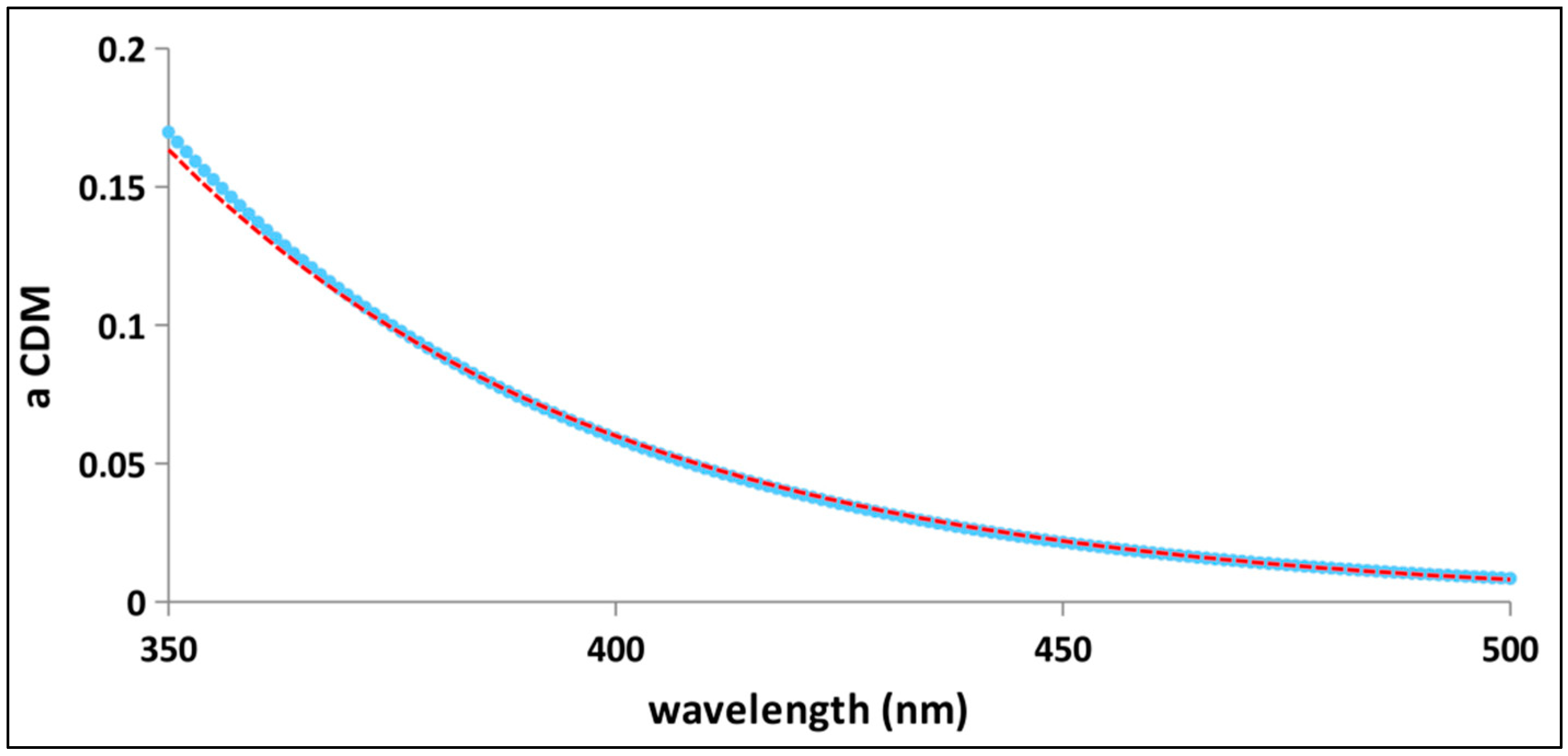
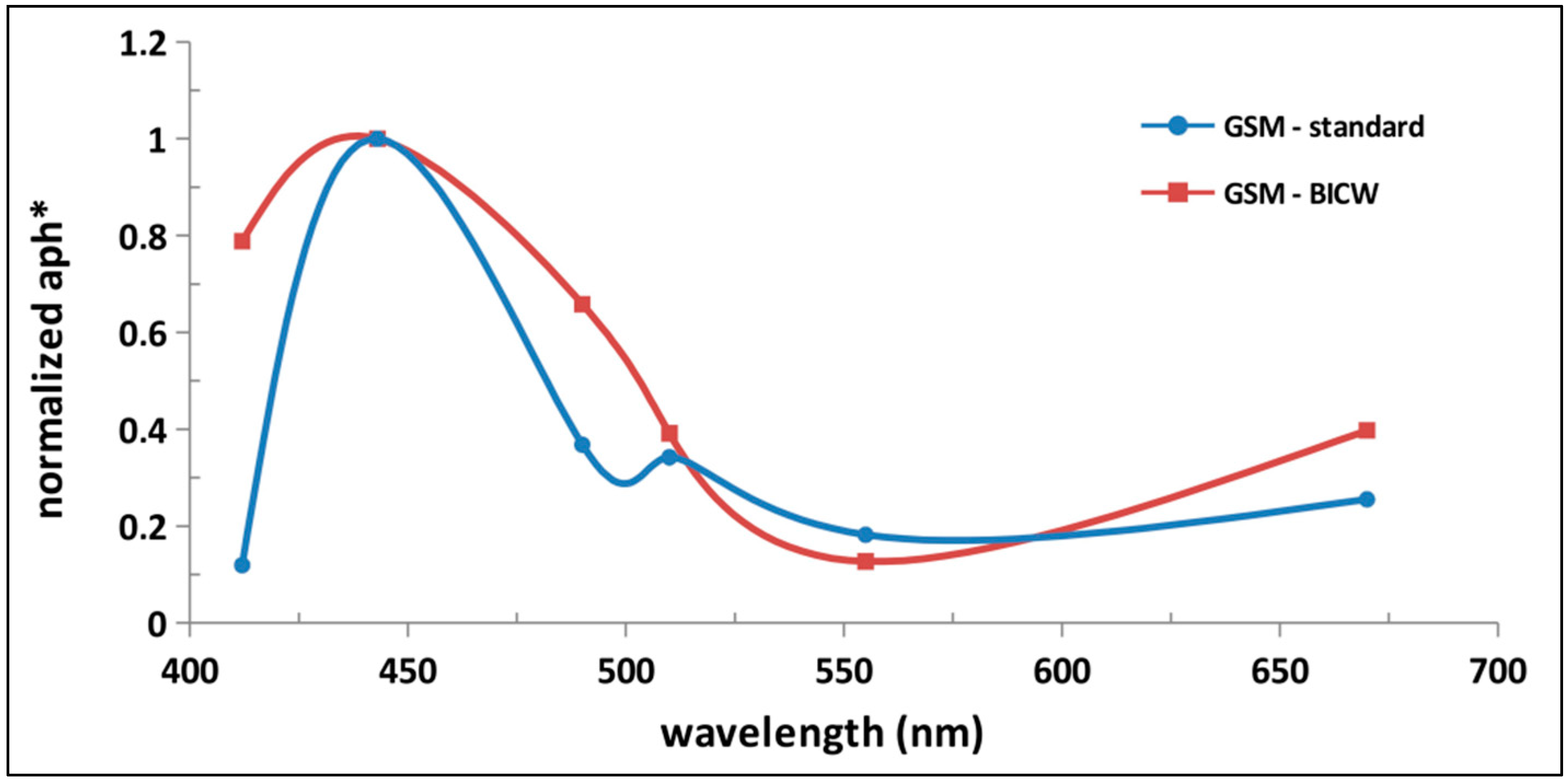
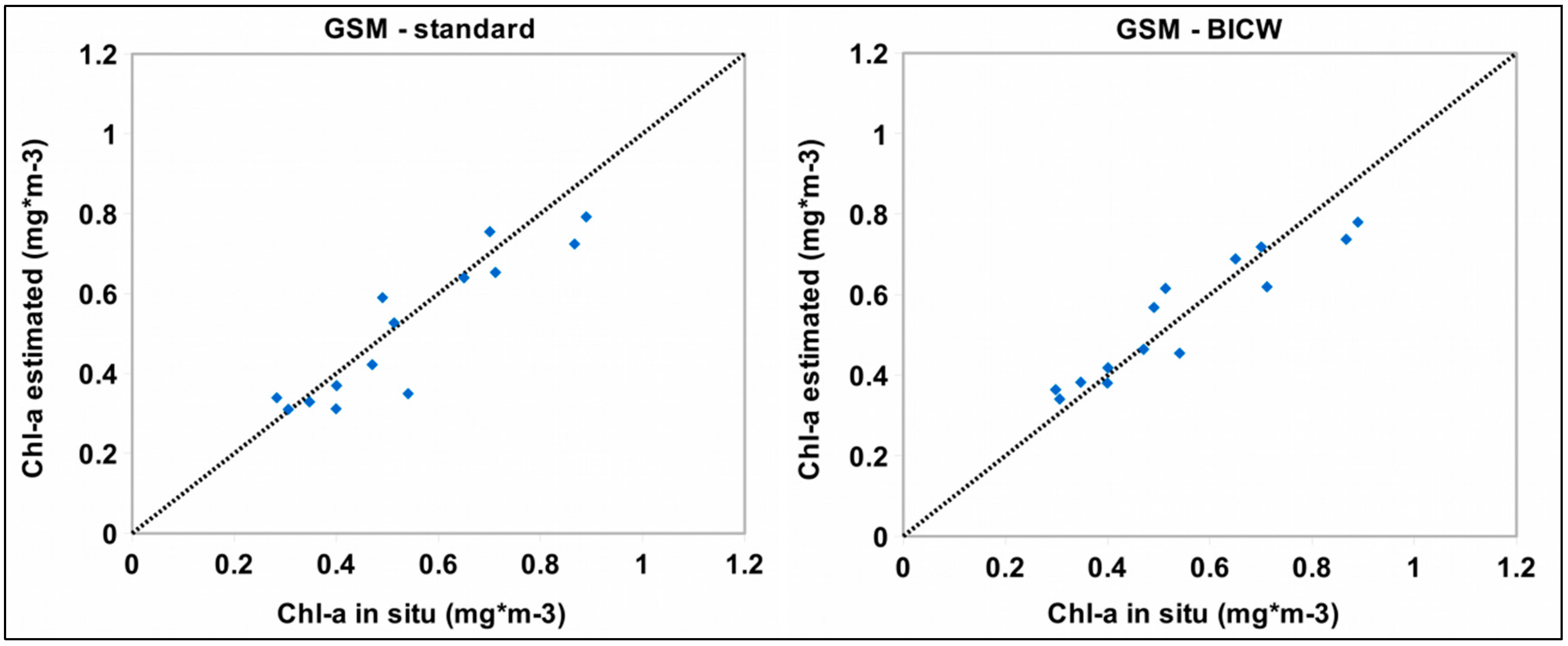
3.3. Local Scale Tuning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directive2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008, establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Di-rective). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Di Giacomo, P.M. Uncertainties and applications of satellite-derived coastal water quality products. Progr. Oceanogr. 2017, 159, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, S.; Icely, J.; Goela, P.C.; Del Valls, T.A.; Newton, A. Using remote sensing as a support to the implementation of the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive in SW Portugal. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 108, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, A.; Brassington, G.B. Operational Oceanography in the 21st Century; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, G.; Santoleri, R.; Vellucci, V.; d’Alcalà, M.R.; Marullo, S.; d’Ortenzio, F. The colour of the Mediterranean Sea: Global versus regional bio-optical algorithms evaluation and implication for satellite chlorophyll estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.; Sathyendranath, S.; Müller, D.; Brockmann, C.; Deschamps, P.Y.; Devred, E.; Doerffer, R.; Fomferra, N.; Franz, B.; Grant, M.; et al. The Ocean Colour Climate Change Initiative: III. A round-robin comparison on in-water bio-optical algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Garver, M.K.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.M. Perspectives on empirical approaches for ocean color remote sensing of chlorophyll in a changing climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17073–17078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; O’brien, M.C.; Siegel, D.A.; Toole, D.; Menzies, D.; Smith, R.C.; Muller, J.L.; Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; et al. SeaWiFS postlaunch calibration and validation analyses, part 3. NASA Tech. Memo. 2000, 206892, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, W.W.; Casey, N.W. Global and regional evaluation of the SeaWiFS chlorophyll data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoleri, R.; Volpe, G.; Marullo, S.; Nardelli, B.B. Open waters optical remote sensing of the Mediterranean Sea. In Remote Sensing of the European Seas; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ortenzio, F.; Marullo, S.; Ragni, M.; d’Alcalà, M.R.; Santoleri, R. Validation of empirical SeaWiFS algorithms for chlorophyll-a retrieval in the Mediterranean Sea: A case study for oligotrophic seas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Bosc, E.; Antoine, D. Algal biomass and sea surface temperature in the Mediterranean basin: Intercomparison of data from various satellite sensors, and implications for primary production estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darecki, M.; Stramski, D. An evaluation of MODIS and SeaWiFS bio-optical algorithms in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, O.; Arnone, R.A.; Bissett, W.P.; Dickey, T.D.; Davis, C.O.; Finkel, Z.; Oliver, M.; Moline, M.A. Watercolors in the coastal zone: what can we see? Biol. Sci. 2004, 144, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, J.P.; Carder, K.L. Estimating chlorophyll a concentrations from remote-sensing reflectance in optically shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, A.; Pascucci, S.; Betti, M.; Grilli, F.; Marini, M.; Pignatti, S.; Guicciardi, S. An Empirical Ocean Colour Algorithm for Estimating the Contribution of Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter in North-Central Western Adriatic Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, J. Global Bio-optical Algorithms for Ocean Color Satellite Applications: Inherent Optical Properties Algorithm Workshop at Ocean Optics XIX; Barga, Italy, 3–4 October 2008. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.J.; Barrow, T. A bio-optical algorithm for the remote estimation of the chlorophyll-a concentration in case 2 waters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Satellite estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration using the red and NIR bands of MERIS—The Azov sea case study. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C. Towards a unified approach for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in both terrestrial vegetation and turbid productive waters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoge, F.E.; Lyon, P.E. Satellite retrieval of inherent optical properties by linear matrix inversion of oceanic radiance models: An analysis of model and radiance measurement errors. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 16631–16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, S.A.; Siegel, D.A. Inherent optical property inversion of ocean color spectra and its biogeochemical interpretation 1. Time series from the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 18607–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Stramski, D. Estimation of the inherent optical properties of natural waters from the irradiance attenuation coefficient and reflectance in the presence of Raman scattering. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Boss, E.S.; Roesler, C. Uncertainties of inherent optical properties obtained from semianalytical inversions of ocean color. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 4074–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, T.J.; Moore, G.F.; Hirata, T.; Aiken, J. Semianalytical model for the derivation of ocean color inherent optical properties: Description, implementation, and performance assessment. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 8116–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. A generalized framework for modeling of inherent optical properties in ocean remote sensing applications. Proc. Ocean Opt. 2010, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Werdell, P.J.; Franz, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Feldman, G.C.; Boss, E.; Brando, V.E.; Dowell, M.; Hirata, T.; Lavender, S.J.; Lee, Z.; et al. Generalized ocean color inversion model for retrieving marine inherent optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carder, K.L.; Chen, F.R.; Lee, Z.P.; Hawes, S.K.; Kamykowski, D. Semianalytic Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectrometer algorithms for chlorophyll a and absorption with bio-optical domains based on nitrate-depletion temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 5403–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Peacock, T.G.; Davis, C.O.; Mueller, J.L. Method to derive ocean absorption coefficients from remote-sensing reflectance. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z. Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Monterey, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, S.L.; Dong, Q.; Hu, C.M.; Lin, G.; Li, Y.H.; Shang, S.P. On the consistency of MODIS chlorophyll—A products in the northern South China Sea. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Lotliker, A.A.; Miller, P.I.; Ashraf, P.M.; Kumar, T.S.; Suresh, T.; Ragavan, B.R.; Menon, H.B. Assessment of MODIS-Aqua chlorophyll-a algorithms in coastal and shelf waters of the eastern Arabian Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 65, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Polito, C.; Ciancia, E.; Coviello, I.; Doxaran, D.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. On the Potential of Robust Satellite Techniques Approach for SPM Monitoring in Coastal Waters: Implementation and Application over the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters Using MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarrese, R.; Chiaradia, M.T.; Tijani, K.; Morea, A.; Carlucci, R. ‘Chlorophyll a’ multi-temporal analysis in coastal waters with MODIS data. Rivista Italiana di Telerilevamento 2011, 43, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancia, E.; Coviello, I.; Di Polito, C.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. Investigating the chlorophyll-a variability in the Gulf of Taranto (North-western Ionian Sea) by a multi-temporal analysis of MODIS-Aqua Level 3/Level 2 data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 155, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ortenzio, F.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. On the trophic regimes of the Mediterranean Sea: A satellite analysis. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Nardelli, B.B.; Cipollini, P.; Santoleri, R.; Robinson, I.S. Seasonal to interannual phytoplankton response to physical processes in the Mediterranean Sea from satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayot, N.; D’Ortenzio, F.; d’Alcala, M.R.; Lavigne, H.; Claustre, H. Interannual variability of the Mediterranean trophic regimes from ocean color satellites. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Canora, F.; Pasquariello, G.; Spilotro, G. Shoreline variations and coastal dynamics: A space–time data analysis of the Jonian littoral, Italy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Auroux, C.; Mascle, J. The Gulf of Taranto (Southern Italy): Seismic stratigraphy and shallow structure. Mar. Geol. 1983, 51, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, F.; Sciarra, R.; Carniel, S.; Santoleri, R. Variability of Adriatic Sea coastal turbid waters from SeaWiFS imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchetto, M.; Boldrin, A.; Langone, L.; Miserocchi, S.; Tesi, T.; Foglini, F. Particle transport in the Bari canyon (southern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Geol. 2007, 246, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, P.; Guarnieri, A. A study of the hydrographic conditions in the Adriatic Sea from numerical modelling and direct observations (2000–2008). Ocean Sci. 2011, 7, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, A.G. A coupled wave-3-D hydrodynamics model of the Taranto Sea (Italy): A multiple-nesting approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, I.; Pinardi, N.; Coppini, G.; Oddo, P.; Lecci, R.; Mossa, M. Coastal ocean forecasting with an unstructured grid model in the southern Adriatic and northern Ionian seas. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Lyubartsev, V.; Cardellicchio, N.; Caporale, C.; Ciliberti, S.; Coppini, G.; de Pascalis, F.; Dialti, L.; Federico, I.; Filippone, M. Marine Rapid Environmental Assessment in the Gulf of Taranto: A multiscale approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2623–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Fenu, E.; Pinardi, N.; Bruciaferri, D.; Giacomelli, L.; Federico, I.; Coppini, G. A Structured and Unstructured grid Relocatable ocean platform for Forecasting (SURF). Deep Sea Res. Part II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2016, 133, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Pinardi, N.; Fenu, E.; Grandi, A.; Lyubartsev, V. Multi-nest high-resolution model of submesoscale circulation features in the Gulf of Taranto. Ocean Dyn. 2017, 67, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, G.; Pinardi, N.; Oddo, P.; Ciliberti, S.A.; Coppini, G. River runoff influences on the Central Mediterranean overturning circulation. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 1675–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autorità di Bacino della Basilicata. Available online: http://www.autoritadibacino.basilicata.it/adb/Pstralcio/pianoacque/Relazione_ottobre_2014.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Cavalli, R.M. Retrieval of Sea Surface Temperature from MODIS Data in Coastal Waters. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10260. Water Quality Measurement of Biochemical Parameters Spectrometric Determination of the Chlorophyll a Concentration; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; Wieland, J.; Stramska, M.; Mueller, J.L. Determination of spectral absorption coefficients of particles, dissolved material and phytoplankton for discrete water samples. Ocean Opt. Protoc. Satell. Ocean Color Sens. Valid. Rev. 2002, 3, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Sullivan, J.M.; Donaghay, P.L. Modeling the spectral shape of absorption by chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem. 2004, 89, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishino, M.; Okami, N.; Takahashi, M.; Ichimura, S. Light utilization efficiency and quantum yield of phytoplankton in a thermally stratified sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ViewSpec Pro Software Manual, ASD Inc. 2008. Available online: http://www.grss-ieee.org/lep4/project_materials_for_web/viewspecpro_manual.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Mueller, J.L.; Fargion, G.S.; McClain, C.R.; Mueller, J.; Brown, S.; Clark, D.; Johnson, B.; Yoon, H.; Lykke, K.; Flora, S. Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation Volume VI. In Special Topics in Ocean Optics Protocols; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- NASA’s Ocean Color Web. Available online: http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Gordon, H.R.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapucci, C.; Rella, M.A.; Brandini, C.; Ganzin, N.; Gozzini, B.; Maselli, F.; Luca, M.; Caterina, N.; Alberto, O.; Charles, T. Evaluation of empirical and semi-analytical chlorophyll algorithms in the Ligurian and North Tyrrhenian Seas. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.; Ovidio, F.; Rijkeboer, M. Atmospheric correction of SeaWiFS imagery for turbid coastal and inland waters. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Gentili, B. Diffuse reflectance of oceanic waters: Its dependence on Sun angle as influenced by the molecular scattering contribution. Appl. Opt. 1991, 30, 4427–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.; Gentili, B. Diffuse reflectance of oceanic water. II. Bidirectional aspects. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 6864–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multi-band quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricaud, A.; Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Claustre, H. Variability in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: Analysis and parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13321–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R package FDA. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/fda/fda.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Ye, H.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Shen, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. Spectral classification of the Yellow Sea and implications for coastal ocean color remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, M.; Piermattei, V.; Madonia, A.; Lacava, T.; Mainardi, U. T-FLaP advances: Instrumental and operative implementation. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2016, 9 (Suppl. 1), s185–s192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organelli, E.; Bricaud, A.; Gentili, B.; Antoine, D.; Vellucci, V. Retrieval of Colored Detrital Matter (CDM) light absorption coefficients in the Mediterranean Sea using field and satellite ocean color radiometry: Evaluation of bio-optical inversion models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Franz, B. Chlorophyll-a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: A novel approach based on three-band reflectance difference. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, A.; Harding, L.W., Jr.; Mallonee, M.E.; Adolf, J.E. Bio-optical model for Chesapeake Bay and the middle Atlantic bight. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, B.K.; Mouw, C.B.; Ciochetto, A.B. Characterizing CDOM Spectral Variability Across Diverse Regions and Spectral Ranges. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2018, 32, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, R.; Blough, N.V. Photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in natural waters: Kinetics and modeling. Mar. Chem. 2002, 78, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Hooker, S.B.; Bécu, G.; Gentili, B.; Tailliez, D.; Scott, A.J. Assessment of uncertainty in the ocean reflectance determined by three satellite ocean color sensors (MERIS, SeaWiFS and MODIS-A) at an offshore site in the Mediterranean Sea (BOUSSOLE project). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, A.M.; Lewis, M.R.; Cullen, J.J. Assessment of the relationships between domininant cell size in natural phytoplankton communities and spectral shape of the absorption coefficient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Claustre, H.; Ras, J.; Oubelkheir, K. Natural variability of phytoplanktonic absorption in oceanic waters: Influence of the size structure of algal populations. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, C11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organelli, E.; Nuccio, C.; Melillo, C.; Massi, L. Relationships between phytoplankton light absorption, pigment composition and size structure in offshore areas of the Mediterranean Sea. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2011, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, D.A.; Olson, R.J.; Wilson, W.H. Reflectance spectroscopy of marine phytoplankton. Part 1. Optical properties as related to age and growth rate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1979, 24, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramski, D.; Morel, A. Optical properties of photosynthetic picoplankton in different physiological states as affected by growth irradiance. Deep-Sea Res. 1990, 37, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Schuckmann, K.; Le Traon, P.Y.; Alvarez-Fanjul, E.; Axell, L.; Balmaseda, M.; Breivik, L.; Brewin, A.R.J.W.; Bricaud, C.; Drevillon, M.; Drillet, Y.; et al. The Copernicus marine environment monitoring service ocean state report. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2016, 9 (Suppl. 2), s235–s320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product User Manual. Available online: http://marine.copernicus.eu/documents/PUM/CMEMS-OC-PUM-009-ALL.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- D’Alimonte, D.; Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.F. Use of the novelty detection technique to identify the range of applicability of empirical ocean color algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.F.; Doyle, J.P.; Grossi, S.; van der Linde, D.; Targa, C.; Alberotanza, L. Coastal Atmosphere and Sea Time Series (CoASTS), Part 1: A Tower-Based Long-Term Measurement Program. NASA Tech. Memo. 2002, 19, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Uiboupin, R.; Arikas, A.; Vahter, K.; Paavel, B. Mapping Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument magery in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Alcântara, E.; Imai, N.; Rodrigues, T.; Bernardo, N. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration from optimizing a semi-analytical algorithm in productive inland waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Jakobsen, F.; Mercado, J.M.; Cortés, D.; Ramírez, T.; Salles, S.; Yebra, L. A new regional algorithm for estimating chlorophyll-a in the Alboran Sea (Mediterranean Sea) from MODIS-Aqua satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1431–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, A.I.; Schloss, I.R.; Almandoz, G.O.; Gagliardini, D.A. Evaluation of SeaWiFS and MODIS chlorophyll-a products in the Argentinean Patagonian continental shelf (38 S–55 S). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Otify, A.M. Evaluation of the physicochemical and chlorophyll-a conditions of a subtropical aquaculture in Lake Nasser area, Egypt. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Values | 18–19 April 2013 | 16 July 2013 | 1–2 July 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a (mg·m−3) | Min | 0.4905 | 0.1200 | 0.1559 |
| Max | 1.2009 | 1.0700 | 0.5407 | |
| Mean | 0.8000 | 0.3900 | 0.3306 | |
| Stdv | 0.1663 | 0.2727 | 0.0893 | |
| aph (440) (m−1) | Min | 0.0032 | 0.0025 | 0.0021 |
| Max | 0.0091 | 0.0114 | 0.0248 | |
| Mean | 0.0060 | 0.0053 | 0.0157 | |
| Stdv | 0.0013 | 0.0025 | 0.0055 | |
| aNAP (440) (m−1) | Min | 0.0032 | 0.0032 | 0.0032 |
| Max | 0.0091 | 0.0091 | 0.0091 | |
| Mean | 0.0060 | 0.0060 | 0.0060 | |
| Stdv | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 | |
| aCDOM (440) (m−1) | Min | 0.0061 | 0.0120 | 0.0100 |
| Max | 0.0306 | 0.0626 | 0.0700 | |
| Mean | 0.0165 | 0.0275 | 0.0233 | |
| Stdv | 0.0069 | 0.0159 | 0.0156 |
| λ (nm) | [m2mg−1] | S [nm−1] | η |
|---|---|---|---|
| 412 | 0.00665 | 0.0206 | 1.0337 |
| 443 | 0.05582 | ||
| 490 | 0.02055 | ||
| 510 | 0.01910 | ||
| 555 | 0.01015 | ||
| 670 | 0.01424 |
| Parameter | Empirical Relationship | Selected Values |
|---|---|---|
| A(λ) and B(λ) tabulated in [71] | ||
| S = 0.018 | ||
| η derived by Quasi Analytical Algorithm (QAA-v5) [70] |
| Algorithm | Adjusted R2 | p-Value | r | APD | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Med-OC3 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 1.81 | 84.11 % | 0.35 |
| GSM | 0.74 | <0.001 | 1.12 | 21.61 % | 0.10 |
| GIOP | 0.79 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 25.12 % | 0.09 |
| Parameter | Empirical Relationship | Adopted Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| λ | |||
| 412 | 0.04973 | ||
| 443 | 0.06336 | ||
| 490 | 0.04155 | ||
| 510 | 0.02471 | ||
| 555 | 0.00799 | ||
| 670 | 0.02507 | ||
| S | S = 0.0201 | ||
| η | η = 1.2031 | ||
| Algorithm | Adjusted R2 | p-Value | r | APD | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSM-standard | 0.82 | <0.001 | 0.95 | 12.12 % | 0.083 |
| GSM-BICW | 0.86 | <0.001 | 1.02 | 11.03 % | 0.070 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacava, T.; Ciancia, E.; Di Polito, C.; Madonia, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pergola, N.; Piermattei, V.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070987
Lacava T, Ciancia E, Di Polito C, Madonia A, Pascucci S, Pergola N, Piermattei V, Satriano V, Tramutoli V. Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070987
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacava, Teodosio, Emanuele Ciancia, Carmine Di Polito, Alice Madonia, Simone Pascucci, Nicola Pergola, Viviana Piermattei, Valeria Satriano, and Valerio Tramutoli. 2018. "Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070987
APA StyleLacava, T., Ciancia, E., Di Polito, C., Madonia, A., Pascucci, S., Pergola, N., Piermattei, V., Satriano, V., & Tramutoli, V. (2018). Evaluation of MODIS—Aqua Chlorophyll-a Algorithms in the Basilicata Ionian Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10070987












