Where We Live—A Summary of the Achievements and Planned Evolution of the Global Urban Footprint
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Global Urban Footprint—Pushing the Limits of Mapping Human Settlements from Space
2.1. Data Base and Processing Framework
2.1.1. Urban Footprint Processor
2.1.2. Data Management
2.1.3. Feature Extraction
2.1.4. Unsupervised Classification
2.1.5. Mosaicking
2.1.6. Automated Post-Editing
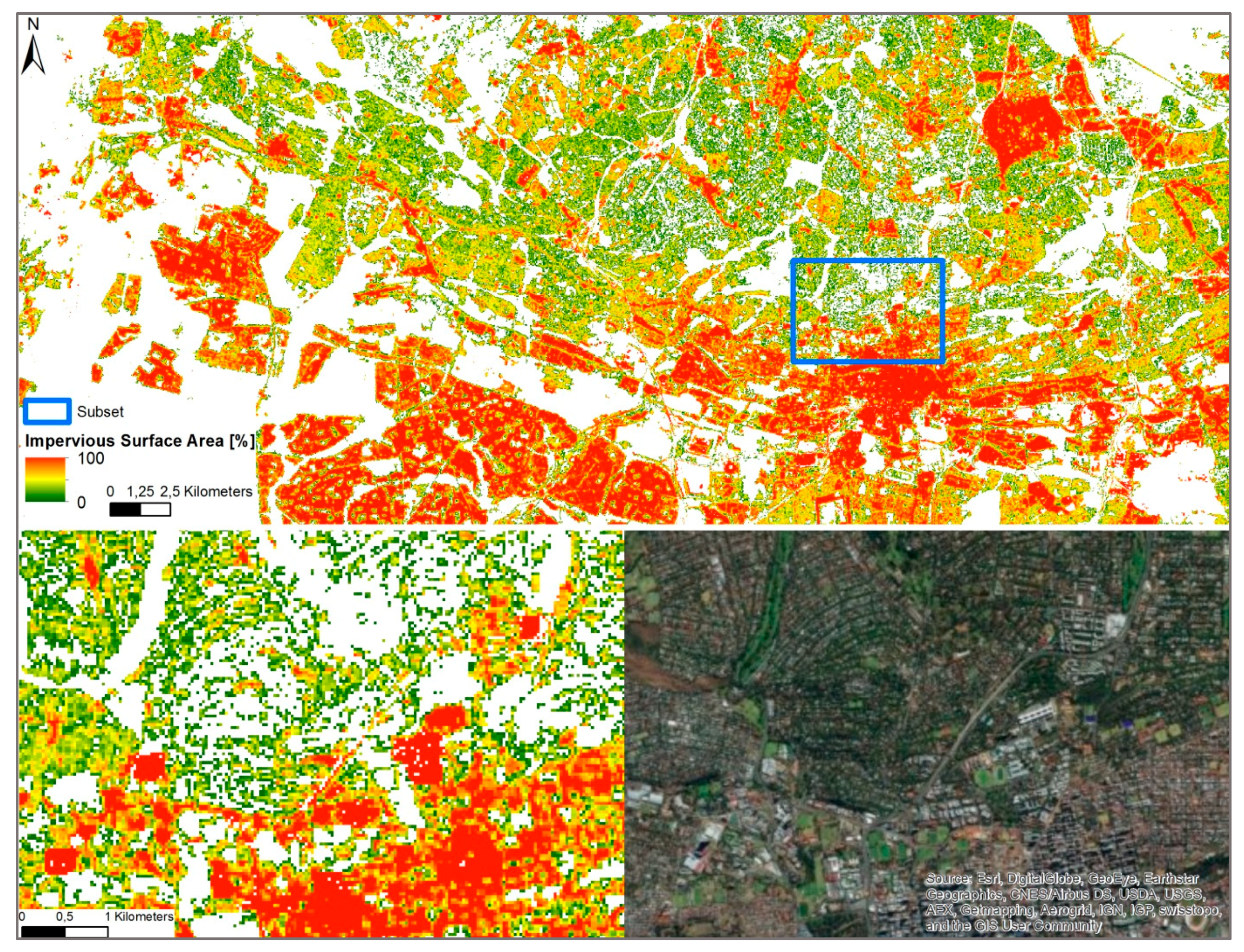
2.2. GUF Product Specification and Validation
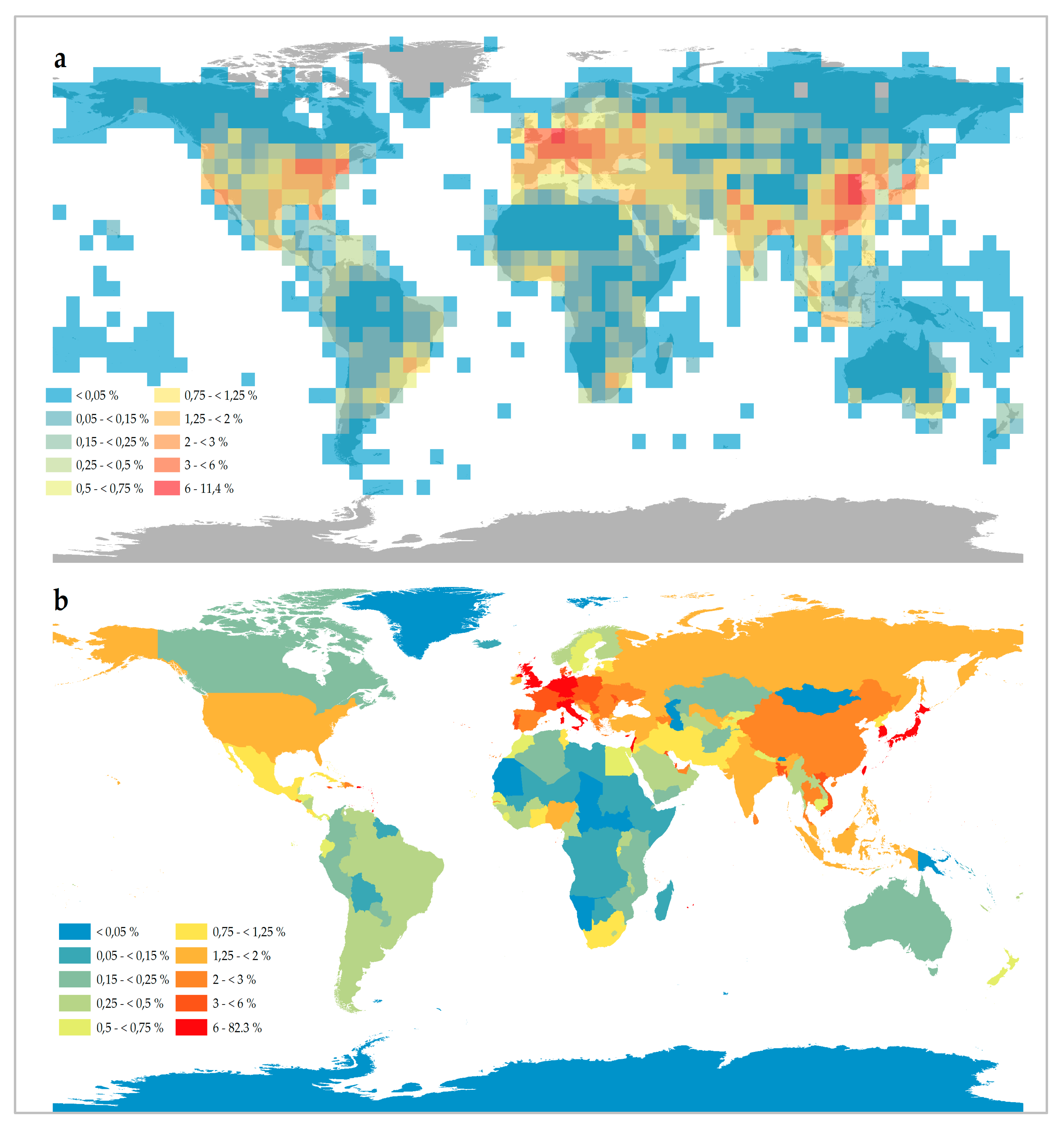
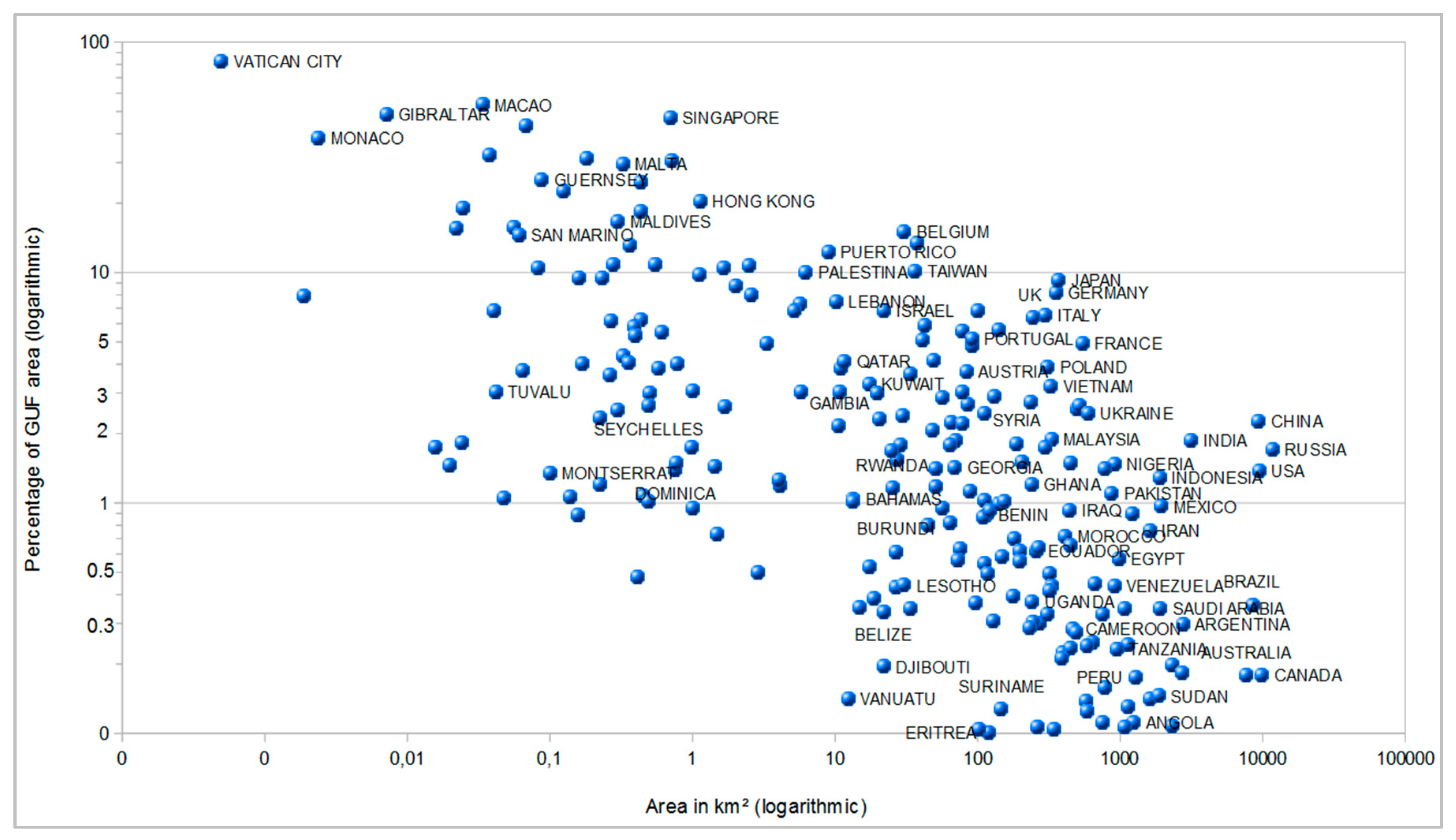
2.3. The State of Global Urbanization—First Figures Derived from the GUF Data
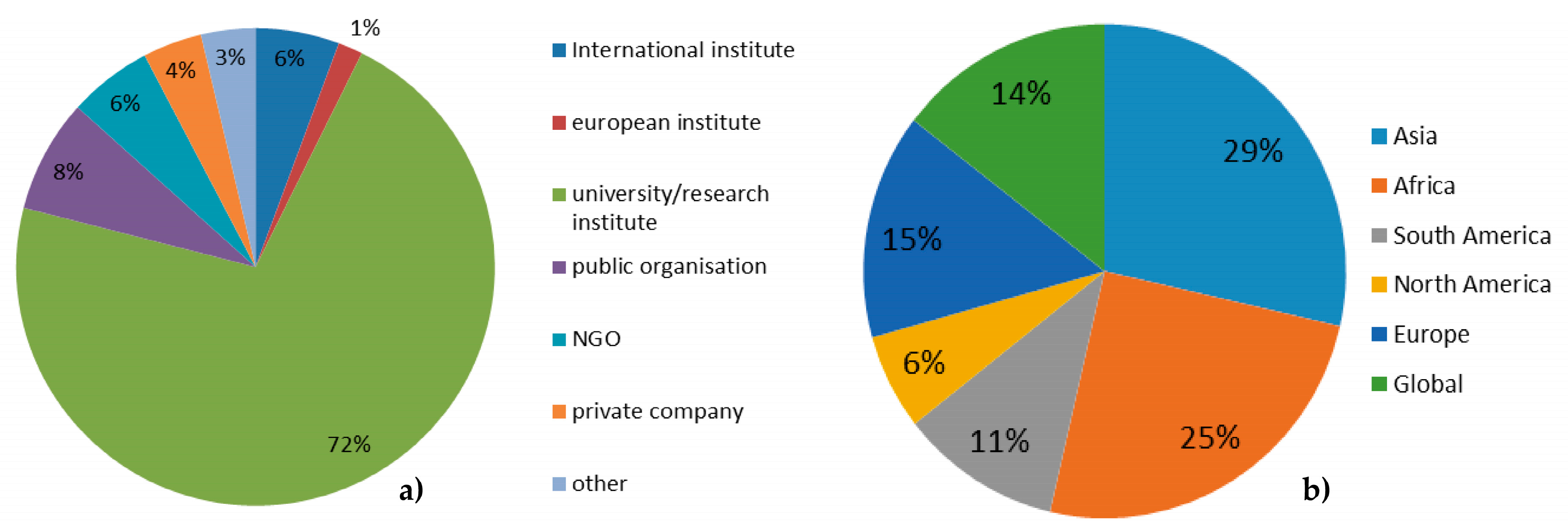
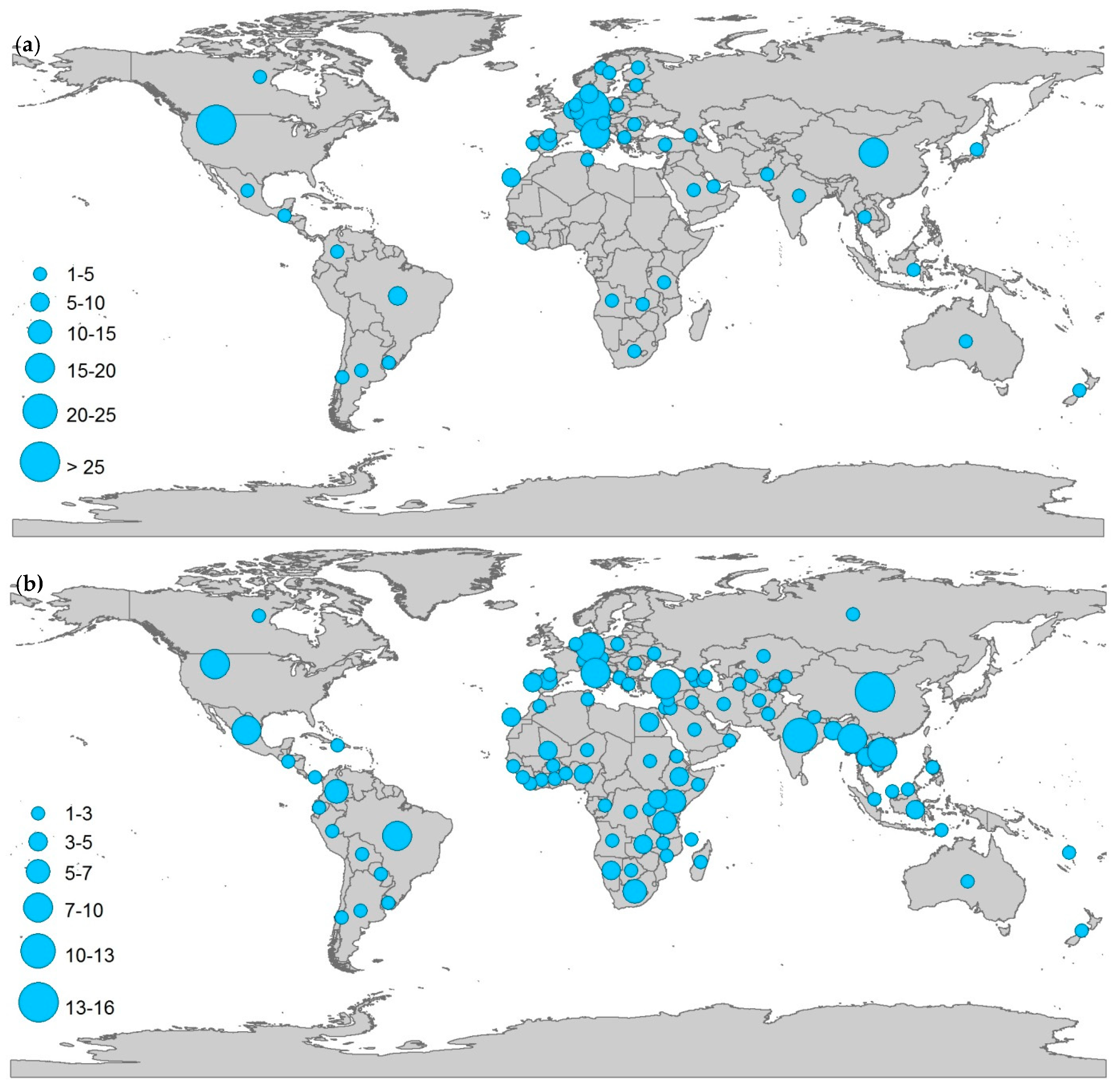
3. The User Perspective—Precise Data for Evidence-Based Planning and Decision Making
4. Evolution of the Product Portfolio and Future Updating Capability
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Human settlements, infrastructure and spatial planning. In Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 517. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; General Assembly United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- GPSC. Urban Sustainability Framework; Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC); World Bank: Washington DC, USA, 2018; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Bakar, A.H.; Cheen, K.S. A framework for assessing the sustainable urban development. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 85, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafakos, S.; Gianoli, A.; Tsatsou, A. Towards the development of an integrated sustainability and resilience benefits assessment framework of urban green growth interventions. Sustainability 2016, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützkendorf, T.; Balouktsi, M. Assessing a sustainable urban development: Typology of indicators and sources of information. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potere, D.; Schneider, A.; Angel, S.; Civco, D. Mapping urban areas on a global scale: Which of the eight maps now available is more accurate? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6531–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Jacob, A.; Gamba, P. Spaceborne sar data for global urban mapping at 30 m resolution using a robust urban extractor. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using modis 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arino, O.; Ramos Perez, J.J.; Kalogirou, V.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Van Bogaert, E. Global land cover map for 2009 (globcover 2009). PANGAEA 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, H.; Shao, X.; Iwao, K.; Shibasaki, R. An automated method for global urban area mapping by integrating aster satellite images and gis data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Lisini, G. A robust approach to global urban area extent extraction using ASAR Wide Swath Mode data. In Proceedings of the 2012 Tyrrhenian Workshop on Advances in Radar and Remote Sensing (TyWRRS), Naples, Italy, 12–14 September 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, M.; Pittore, M. Large-area settlement pattern recognition from landsat-8 data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Florczyk, A.; Freire, S.; Halkia, M.; Julea, A.; Kemper, T.; Soille, P.; Syrris, V. Operating Procedure for the Production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat Data of the Epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014; Joint Research Centre—European Commission: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Syrris, V.; Florczyk, A.J.; Soille, P.; Maffenini, L.; Burger, A.; Vasilev, V.; Rodriguez, D.; et al. Big earth data analytics on sentinel-1 and landsat imagery in support to global human settlements mapping. Big Earth Data 2017, 1, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using landsat images based on the google earth engine platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WUDAPT. World Urban Database and Assess Poatal Tools—Wudapt. Available online: http://www.wudapt.org/ (accessed on 22 May 2018).
- Bechtel, B.; Alexander, P.; Böhner, J.; Ching, J.; Conrad, O.; Feddema, J.; Mills, G.; See, L.; Stewart, I. Mapping local climate zones for a worldwide database of the form and function of cities. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Esch, T. Terrasar-x: How can high resolution Sar data support the observation of urban areas? In Proceedings of the ISPRS Conference 3rd International Symposium Remote Sensing and Data Fusion Over Urban Areas (URBAN 2005), Tempe, AZ, USA, 14–16 March 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Schlegel, I.; Tuan, V.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Varying scale and capability of envisat asar-wsm, terrasar-x scansar and terrasar-x stripmap data to assess urban flood situations: A case study of the mekong delta in can tho province. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5122–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift (2009–2010) over wuhan in central china revealed by terrasar-x insar analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Xu, X.; Dong, H.; Song, C.; Pu, F. Individual building extraction from terrasar-x images based on ontological semantic analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. Health diagnosis of major transportation infrastructures in shanghai metropolis using high-resolution persistent scatterer interferometry. Sensors 2017, 17, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissgerber, F.; Colin-Koeniguer, E.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Trouvé, N. 3d monitoring of buildings using terrasar-x insar, dinsar and polsar capacities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T. Automatisierte Analyse von Siedlungsflächen auf der Basis Höchstauflösender Radardaten (Automated Analysis of Urban Areas Based on High Resolution Sar Images). Ph.D. Dissertation, Bayerische Julius-Maximilians Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Esch, T.; Schenk, A.; Ullmann, T.; Thiel, M.; Roth, A.; Dech, S. Characterization of land cover types in terrasar-x images by combined analysis of speckle statistics and intensity information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1911–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Schenk, A.; Thiel, M. Monitoring of urban environments with terrasar-x data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2007, Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Esch, T.; Thiel, M.; Schenk, A.; Roth, A.; Muller, A.; Dech, S. Delineation of urban footprints from terrasar-x data by analyzing speckle characteristics and intensity information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Taubenböck, H.; Roth, A.; Heldens, W.; Felbier, A.; Thiel, M.; Schmidt, M.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Tandem-x mission—new perspectives for the inventory and monitoring of global settlement patterns. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Keil, M.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; Strano, E. Breaking new ground in mapping human settlements from space—The global urban footprint. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Felbier, A.; Roth, A.; Heldens, W.; Huber, M.; Schwinger, M.; Taubenbock, H.; Muller, A.; Dech, S. Urban footprint processor—Fully automated processing chain generating settlement masks from global data of the tandem-x mission. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Reißig, R.; Mikusch, E.; Reck, C. Processing management tools for earth observation products at DLR-DFD. In Data Systems in Aero-Space (DASIA); Agency, E.S., Ed.; European Space Agency: Nice, France, 2001; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Habermeyer, M.; Marschalk, U.; Roth, A. W42—A scalable spatial database system for holding digital elevation models. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fomferra, N.; Böttcher, M.; Zühlke, M.; Brockmann, C.; Kwiatkowska, E. Calvalus: Full-mission eo cal/val, processing and exploitation services. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5278–5281. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.; Chen, C.-J.; Lu, C.-J. A linear-time component-labeling algorithm using contour tracing technique. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2004, 93, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Üreyen, S.; Zeidler, J.; Metz–Marconcini, A.; Hirner, A.; Asamer, H.; Tum, M.; Böttcher, M.; Kuchar, S.; Svaton, V.; et al. Exploiting big earth data from space—First experiences with the timescan processing chain. Big Earth Data 2018, 2, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Üreyen, S.; Esch, T.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Zeidler, J.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Strano, E.; Gorelick, N. Exploiting satellite big data for outlining settlements globally—The world settlement footprint. 2015; Scientific Data in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Principles and Recommendations for Population and Housing Censuses, Revision 1; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Brown de Colstoun, E.C.; Tilton, J.C.; Tan, B. Global Human Built-up and Settlement Extent (Hbase) Dataset from Landsat; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2017.
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Marmanis, D.; Zeidler, J.; Elsayed, S.; Metz, A.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Dimensioning urbanization—An advanced procedure for characterizing human settlement properties and patterns using spatial network analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Himmler, V.; Schorcht, G.; Thiel, M.; Wehrmann, T.; Bachofer, F.; Conrad, C.; Schmidt, M.; Dech, S. Large-area assessment of impervious surface based on integrated analysis of single-date landsat-7 images and geospatial vector data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Marmanis, D.; Esch, T.; Felbier, A. A novel method for building height estmation using tandem-x data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4804–4807. [Google Scholar]
- Sibson, R. A brief description of natural neighbor interpolation. In Interpolating Multivariate Data; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google earth engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, M.; Kemper, T.; Geiß, C.; Esch, T.; Taubenböck, H. How good is the map? A multi-scale cross-comparison framework for global settlement layers: Evidence from central europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mück, M.; Klotz, M.; Taubenböck, H. Validation of the dlr global urban footprint in rural areas: A case study for Burkina Faso. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Dubai, UAE, 6–8 March 2017; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Group on Earth Observations. Global Urban Observation and Information. Available online: https://www.earthobservations.org/activity.php?id=125 (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- Group on Earth Observations. Geo Human Planet Initiative: Spatial Modeling of Impact, Exposure and Access to Resources. Available online: https://www.earthobservations.org/activity.php?id=119 (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- POPGRID. Popgrid—Data Collaborative Enhanced Population, Settlement and Infrastructure data. Available online: https://sites.google.com/ciesin.columbia.edu/popgrid (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- Esch, T.; Uereyen, S.; Asamer, H.; Hirner, A.; Marconcini, M.; Metz, A.; Zeidler, J.; Boettcher, M.; Permana, H.; Brito, F.; et al. Earth observation-supported service platform for the development and provision of thematic information on the built environment—The tep-urban project. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Dubai, UAE, 6–8 March 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]



| Kappa | OA% | PA% Settlement | PA% Non-Settlement | UA% Settlement | UA% Non-Settlement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GUF 0.4″ | 0.637 | 90.23 | 72.19 | 93.35 | 67.08 | 94.85 |
| GUF 2.8″ | 0.600 | 88.96 | 71.27 | 92.19 | 62.49 | 94.61 |
| GHSL | 0.472 | 87.98 | 45.31 | 95.77 | 66.18 | 90.55 |
| GL30 | 0.459 | 87.85 | 43.60 | 95.93 | 66.20 | 90.30 |
| MODIS500 | 0.246 | 84.84 | 22.71 | 96.19 | 52.11 | 87.20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esch, T.; Bachofer, F.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Marconcini, M.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Roth, A.; Üreyen, S.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; et al. Where We Live—A Summary of the Achievements and Planned Evolution of the Global Urban Footprint. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060895
Esch T, Bachofer F, Heldens W, Hirner A, Marconcini M, Palacios-Lopez D, Roth A, Üreyen S, Zeidler J, Dech S, et al. Where We Live—A Summary of the Achievements and Planned Evolution of the Global Urban Footprint. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060895
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsch, Thomas, Felix Bachofer, Wieke Heldens, Andreas Hirner, Mattia Marconcini, Daniela Palacios-Lopez, Achim Roth, Soner Üreyen, Julian Zeidler, Stefan Dech, and et al. 2018. "Where We Live—A Summary of the Achievements and Planned Evolution of the Global Urban Footprint" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060895
APA StyleEsch, T., Bachofer, F., Heldens, W., Hirner, A., Marconcini, M., Palacios-Lopez, D., Roth, A., Üreyen, S., Zeidler, J., Dech, S., & Gorelick, N. (2018). Where We Live—A Summary of the Achievements and Planned Evolution of the Global Urban Footprint. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060895







