Abstract
Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (SAR, InSAR) is increasingly being used for deformation monitoring. Uncertainty in satellite state vectors is considered to be one of the main sources of errors in applications such as this. In this paper, we present frequency and spatial domain based algorithms to model orbital errors in InSAR interferograms. The main advantage of this method, when applied to the spatial domain, is that the order of the polynomial coefficient is automatically determined according to the features of the orbital errors, using K-cross validation. In the frequency domain, a maximum likelihood fringe rate estimate is deployed to resolve linear orbital patterns in strong noise interferograms, where spatial-domain-based algorithms are unworkable. Both methods were tested and compared with synthetic data and applied to historical Environmental Satellite Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ENVISAT ASAR) sensor and modern instruments such as Gaofen-3 (GF-3) and Sentinel-1. The validation from the simulation demonstrated that an accuracy of ~1mm can be obtained under optimal conditions. Using an independent GPS measurement that is discontinuous from the InSAR measurement over the Tohoku-Oki area, we found a 31.45% and 73.22% reduction in uncertainty after applying our method for ASAR tracks 347 and 74, respectively.
1. Introduction
The precise orbiting position information of space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems is of great significance in many Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) applications, especially in the case of ground motion monitoring [1,2,3]. The InSAR technique uses two sensors, carried on satellites, with slightly different incidence angles, to measure a displacement along the radar line-of-sight (LOS) between two SAR acquisitions. The theoretical accuracy can be as high as a centimeter to as low as a millimeter. This technique has been widely used to identify many geophysical processes that usually cause long-wavelength crustal deformation, including strain accumulation along locked continental faults, coseismic deformation caused by the occurrence of faulting in the lithosphere, and postseismic deformation caused by afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation [4,5,6].
The radar, the ground, and the intervening medium create a compound observing system; within this, there are several potential sources of errors that have a detrimental impact on the accuracy of InSAR measurements. In particular, satellite orbital errors [7], temporal and spatial decorrelation effects [8,9], atmospheric screens [10], and high-deformation gradients are the main limitations [11]. As far as orbital errors are concerned, they cause long-wavelength phase contributions to interferogram and are often referred to as ‘the phase ramp’. The pattern of the phase ramp usually depends on the satellite–state–vector error, especially on the radial and cross-track components of the orbital error [7]. The influence of orbital errors on the final accuracy of deformation products is largely contingent on the SAR instruments, i.e., the trajectory of the satellite orbit, the radar frequency, and the degree of overlap between the phase ramp and the deformation signals.
Several efforts have been made during the last two decades to mitigate the orbital error, and most of them start with spatial domain analyses of InSAR interferograms. A simple but very effective solution is de-ramping from the InSAR interferogram using a linear or quadratic surface fitting [3,12]. The phase ramp is either subtracted from the original phase or used to refine the spatial baseline to infer a revised interferogram [13,14]. Given a wrapped-phase pattern, the unwrapping operation is always required before fitting. The accuracy of the estimated coefficients in the polynomial model relies on the quality of the observations to be fitted. Error propagation in the unwrapping procedure over fast decorrelation areas with low coherence may distort the signal and, therefore, contribute to surface artifacts. To solve this problem, pixel offsets between bi-temporal-SAR data can be estimated using the cross-correlation algorithm; the baseline is then re-estimated to compensate for the residual phase in the interferogram [15]. Despite many efforts, the accuracy of the estimated offsets, from meter to decimeter, restricts the correction of the baseline components. Kohlhase et al. (2003) suggest counting the fringes caused by orbital errors according to phase gradients in differential interferograms and to adjust the trajectories of satellite orbits [16]. This does not work for coseismic scenes, where a stronger deformation causes dense fringes [7].
Advances related to orbital error correction refer to the time-series-SAR dataset. One such suggestion is to independently estimate the phase ramp on each interferogram using least squares scheme. To ensure consistency in the interferometric network, the polynomial coefficients are refined in a network sense by time-series inversions [17,18]. Considering the inseparability of phase ramp and long-wavelength deformation signals in the spatial dimension, the alternative is to estimate both deformation and orbital errors by exploiting spatio-temporal characteristics of both quantities [17,19]. However, resolving large, linear systems of algebraic equations, error propagation, and underdetermined problems have become the main challenges associated with these methods.
One promising alternative to separating long-wavelength displacement signals and orbit errors is to employ external data, for example, GPS measurement [20,21,22]. GPS displacements located in the SAR scene are projected onto the line-of-sight direction according to the incidence angle and the heading of the SAR geometry. The phase ramp is then estimated by minimizing the residuals between the InSAR interferogram and the phase inverted by the GPS. The final accuracy of the InSAR deformation product depends on the accuracy of the GPS measurements, the number of GPS stations and their spatial distribution.
In summary, the current problems of orbital error removal are two-fold. The first problem originates from the fact that all long-wavelength signals are treated as orbital errors during the correction without ancillary data. Although a few studies try to use wavelet-multiresolution analysis to classify the different components in the unwrapped interferogram automatically [23], the method is still empirical, as the number of levels of wavelet decomposition must be specified manually according to the features of the interferogram. The second problem involves robust regression. As stated in Reference [24], the model selection is subjective and relies on the distribution and the density of the targets showing high coherence, while errors in unwrapping are likely to mislead surface fitting. In fact, the method of estimating the phase ramp in the frequency domain may avoid the unwrapping error. However, few studies discuss using this method for orbital error correction. In the following section, we focus our analyses on the individual interferogram, as it is essential for time-series inversion and many geophysical applications.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we introduce the frequency and spatial domain based methods, respectively, from the image-processing viewpoint. In Section 3, the results and quantitative comparisons are presented using synthetic and real data. In Section 4, the feasibility of these methods, including their merits and faults, are investigated. In Section 5, conclusions are given.
2. Methods
2.1. Modeling Orbital Error in Frequency Domain
The fringe rate of long-wavelength signals in interferogram can be estimated by means of maximum likelihood (ML) frequency algorithms [25,26,27]. The idea is that the orbital error has a dominant term in its Fourier expansion. Assuming original interferogram I can be expressed as:
where , , , denote deformation phase, topographic phase, orbital ramp, and other phase components related to the atmosphere and decorrelation, respectively. is the differential interferogram. After atmospheric correction and/or phase filtering, we rewrite as a sinusoidal model:
where and denote the pixel index in radar coordinate, and are true fringe frequencies along range and azimuth direction, respectively, and is the residual phase.
The Fourier filter can be used to obtain the ML estimate of the average stripe rate in Equation (2). The peak location obtained by maximizing the 2D discrete Fourier transform (DFT) corresponds to the estimated frequencies and , respectively, and the phase at the DFT peak is approximate to . To better identify the exact frequencies, we increase the DFT frequency sampling by padding the signal in the window with enough zeros. The size of the padded zeros in both directions, and , can be determined by the Cramer-Rao bound of the variance of estimated frequency [26]:
where represents the signal-to-noise ratio, and are equivalent to each of the image sizes. The de-ramped interferogram can be obtained from the cross multiplication of the differential interferogram and the estimated phase ramp under the assumption , and .
The significant advantage of this method is its simple computation without the need for phase unwrapping and higher reliability over low-coherence areas (see Section 3.1). However, this method can only estimate the linear terms of orbital error. For non-linear fringe patterns, which are usually present in long-strip images, polynomial fitting in the spatial domain is recommended.
2.2. Modeling Orbital Error in Spatial Domain
The most popular method used in orbital-error correction is surface fitting with linear or quadratic models, using unwrapped phase observations. Its general form can be defined as [23]:
where is the polynomial model, and indicate the pixel index in radar coordinates. To solve the equation for the unknown coefficients , and , the least squares scheme is used. The solution can be written as:
where is the estimated vector in which the elements correspond to the coefficients in Equation (5). is the observations with size , and is the matrix containing the coordinates and . However, there are several drawbacks to using this method. Firstly, Equation (6) is not robust to abnormal values, such as unwrapping errors. In addition, the observations contribute to the equivalent weight without the consideration of the interferogram qualities. Secondly, the local deformation will contribute to the polynomial coefficients with the increase of the dimension in . Finally, the determination of the order of the polynomial model is not clear yet and is usually empirical. A more sophisticated method is therefore needed.
2.2.1. Preprocess: Multi-Looking and Manually Masking
An increase in looks can enhance the quality of long-wavelength signals and simultaneously mitigate the effect of the short-wavelength signals during the regression. On the other hand, the decreased dimension can reduce the computational burden for unwrapping and the iterative least squares scheme. For those regional deformation signals, manual masking should be undertaken. Although this step is simpler than wavelet decomposition [23], it is still effective without expert knowledge and computational complexity. In addition, masking is important for areas with a high phase gradient, where phase aliasing causes unexpected unwrapping errors [11].
2.2.2. Polynomial Model
For long-strip InSAR interferograms, it is difficult to use the linear or quadric models to incorporate orbit errors. A more general form is needed:
where and is the vector with the length and respectively, is coefficient matrix.
The parameters and should be carefully determined to prevent overfitting in terms of the spatial distribution of observations.
2.2.3. Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares Fitting
The main disadvantage of ordinary least squares is that there is a constant deviation in the errors. For observations with different coherence magnitudes, the method of weighted least squares should be used. Moreover, iterative behavior can be employed to reduce the influence of outliers on regression. We designed an iterative version for the least-squares solution according to the phase standard deviation (STD) and robust Bi-square weight. The modification of the parameter estimate in Equation (6) can be rewritten as:
In this paper, we define weight in two steps. The prior weight , defined by interferometric phase STD, can be simply written as [27]:
where is the looks and is the coherence observations. Compared with the coherence, phase STD is a more appropriate weight, as it takes looks into account. The function model Equation (9) is a close approximation to the complicated stochastic model when looks are greater than four [27]. After initial regression, the robust Bi-square weight , which minimizes a weighted sum of squares, is used during the iteration [28]:
where is least-squares residual for each observation from the previous iteration, is a tuning constant (4.685), and is the robust variance given by , where is the absolute deviation of the residuals from their median; is leverage that adjust the residuals. The total weight function , therefore, is:
where denotes the number of iterations. The iterations will stop if the fit converges (minimum change in coefficients <), or the maximum number of iterations allowed for fitting is reached (400).
2.2.4. Model Selection
The presence of the unwanted terms in Equation (7) and the overfitting lead to an unexpected bias or variance in interferograms. A trade-off should be made by taking advantage of K-cross validation, which has been widely used in machine learning [29]. Specifically, we obtained some test data from the same distribution and picked appropriate and in Equation (7) to minimize the same sum-of-squares difference that we used for fitting to the training data. This can be achieved by making several different splits in data . Each subsample is used once for testing, and the rest is used for training. The arrangement of this method is described as follows.
- Split data into subsamples with equivalent size .
- For , set validation data to be the subsample, and training data to be the other subsamples.
- Fit each model to and evaluate its performance on through weighted root-mean-square error (WRMSE).
- Pick and that leads to minimum WRMSE by averaging results.
Uniform sampling without replacement is used to separate data , and is set throughout this paper. Considering the different qualities of the validation data, we define WRMSE as:
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Data
In this section, the performance of the orbital-error corrections are evaluated and compared using a simulation. For notional convenience, we refer to the method in Equations (3) and (4) as DFT, and the method developed in Section 2.2 as adaptive ADP-Poly.
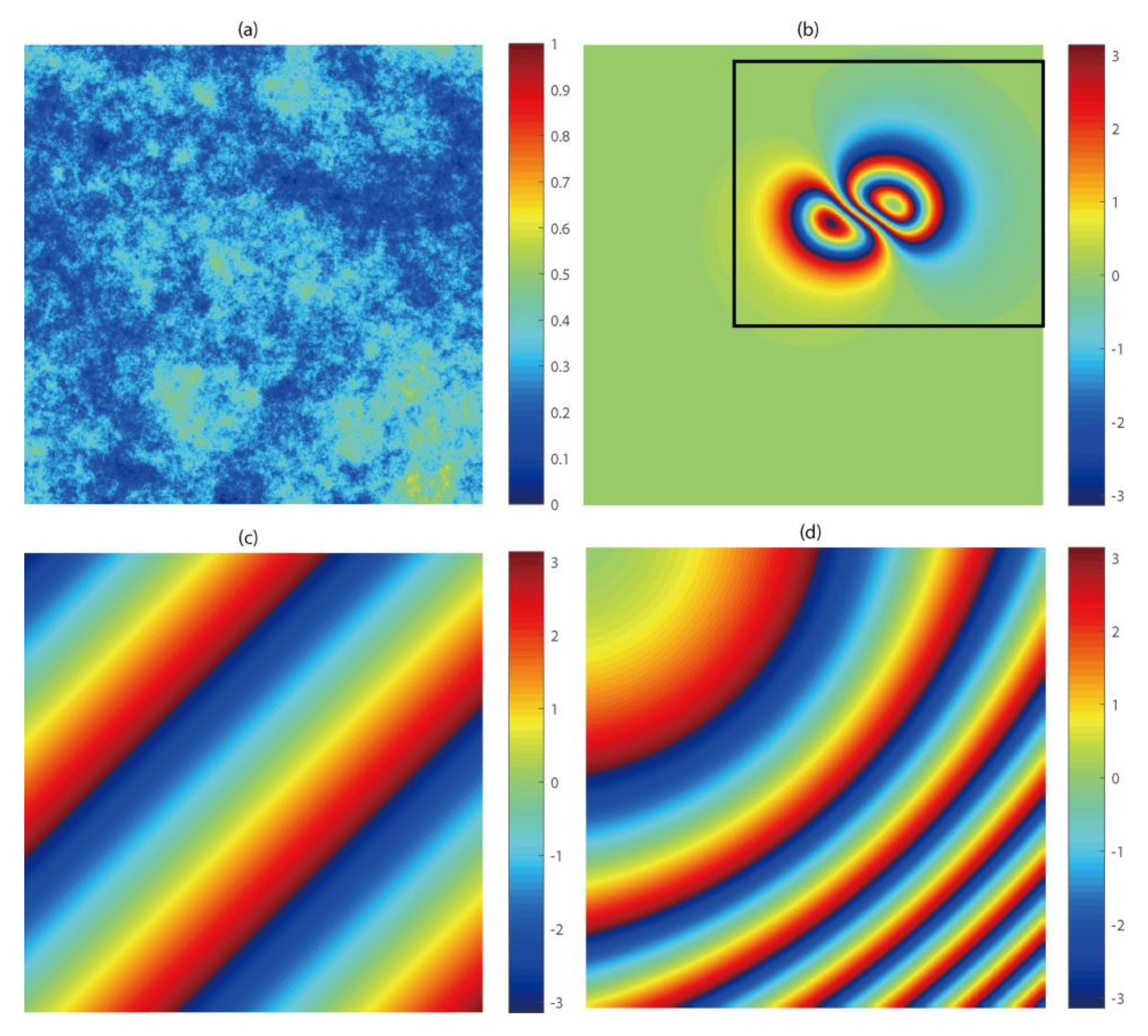
Three phase components, including deformation, random noise, and orbital errors were simulated according to the ENVISAT ASAR geometry. The surface deformation caused by a finite rectangular source was first simulated by the Okada 85 model [30] and then inverted to an interferometric phase (Figure 1b). To add phase noise, the coherence map was simulated under three principle sources of error, i.e., the Doppler, spatial, and temporal decorrelations [25,31], in which the temporal decorrelation was created using an isotropic-2D-fractal surface with a power law spectrum [32]. On the basis of the simulated coherence map under different looks (Figure 1a), the phase-STD map was obtained using the stochastic model (4.2.24) and (4.2.26) in [31]. The phase-noise map was finally generated using pointwise multiplication of the phase-STD map and the standard normal distributed random numbers. The linear and non-linear phase ramps were added to the orbital errors (Figure 1c,d). The combination of all components in synthetic interferograms is given in Figure 2.
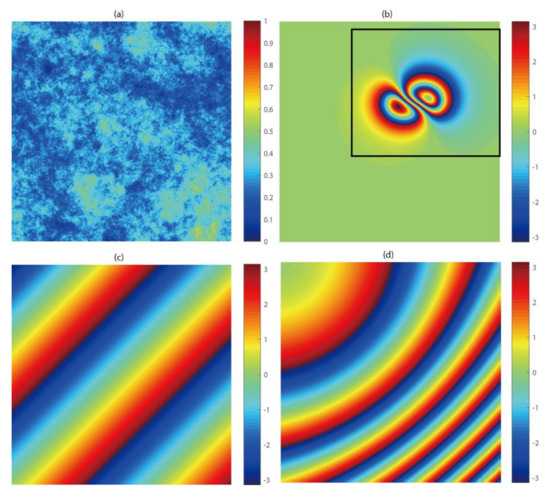
Figure 1.
Simulated InSAR parameters (a) coherence map; (b) noise-free differential interferogram. The black frame denotes the masked area for surface fitting in spatial domain; (c) linear orbital error and (d) nonlinear orbital error with non-uniform phase gradient.
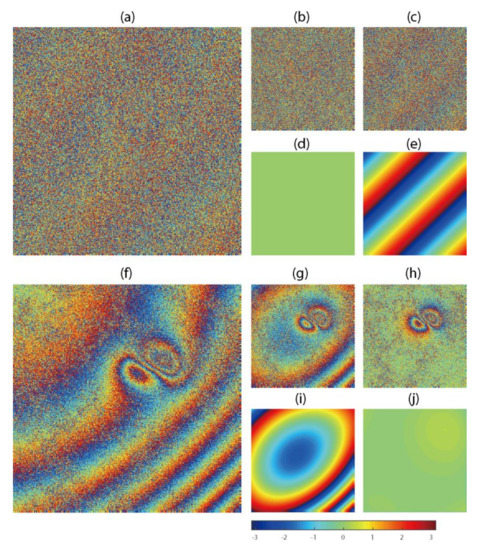
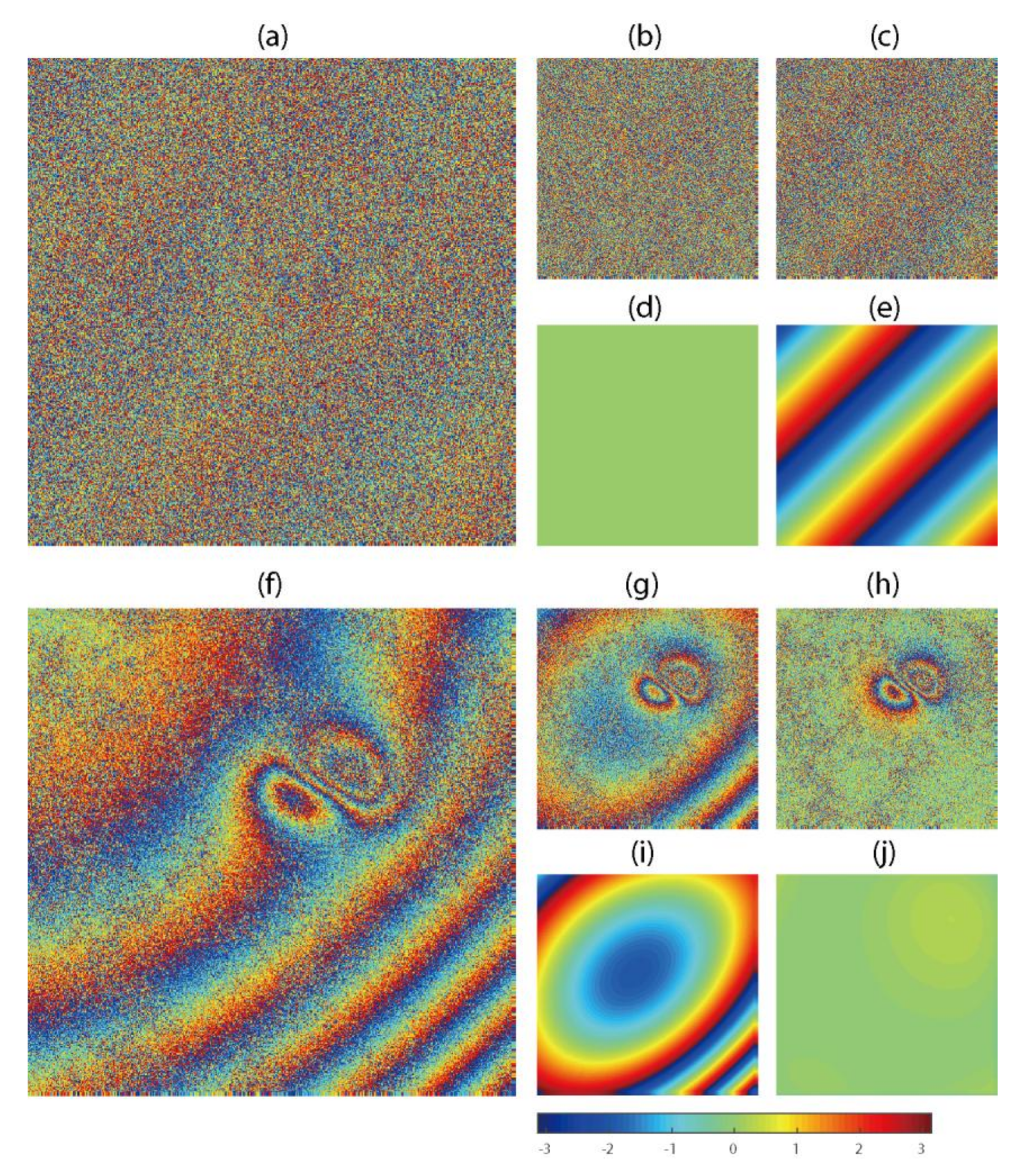
Figure 2.
Simulated linear and nonlinear orbit errors in InSAR interferograms. (a) noise added interferogram with averaged coherence and single look; (b) orbit-corrected interferogram using DFT; (c) orbit-corrected interferogram using ADP-Poly; the difference between truth and phase ramp estimated from DFT (d) and ADP-Poly (e); (f) noise added interferogram with averaged coherence and 2-looks; (g) orbit-corrected interferogram using DFT; (h) orbit-corrected interferogram using ADP-Poly; the difference between truth and phase ramp estimated from DFT (i) and ADP-Poly (j).
To test the methods over fast decorrelation areas, we adjusted the coherence magnitude to an average value of γ = 0.2 under single look, and then added the phase-noise to the interferogram in Figure 2a. Likewise, we set γ = 0.4 under 2-looks to test the capability of both methods on moderate noise scenes, as shown in Figure 2f. For the frequency–domain-based method, the DFT is applied to noisy interferograms directly, while adaptive Goldstein filtering driven by phase STD [33] and minimum cost–flow unwrapping [34] were used before ADP-Poly surface fitting.
Visually, ADP-Poly could not detect the phase ramp in very noisy scenes and left phase residuals in Figure 2c. By contrast, DFT accurately captured the linear phase ramp. The residual between the truth and estimate confirms the potential of using DFT without phase unwrapping (Figure 2d). When the quality of interferogram became better (Figure 2f), ADP-Poly showed its superior performance at detecting nonlinear features (Figure 2h), while DFT could not completely remove the error and left nonlinear residuals in the interferogram (Figure 2g).
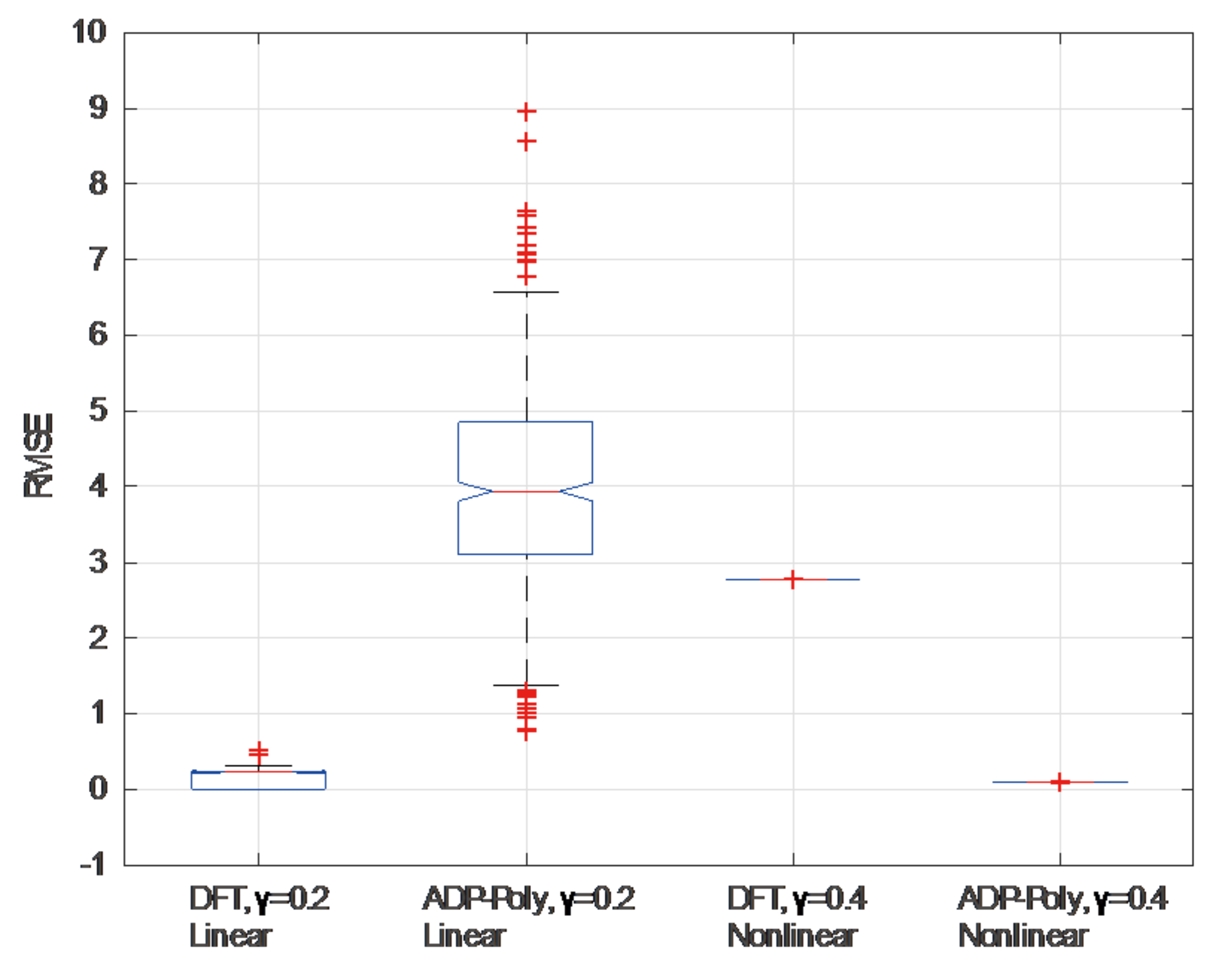
To make the results more statistically significant, we performed 500 simulations for each case and evaluated the phase residuals using root-mean-square error (RMSE). It can be seen from Figure 3 that DFT works well in linear orbital error correction over low coherence areas, and the averaged RMSE is up to 0.16 rad (4.99 rad for ADP-Poly). For nonlinear orbital features, ADP-Poly obtained RMSE of 0.10 rad (2.77 rad for DFT), which is equivalent to ~1 mm in deformation monitoring for C-band InSAR measurements.
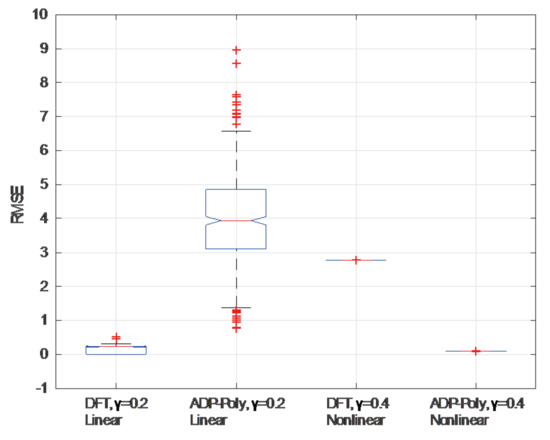
Figure 3.
Accuracy assessment for DFT and ADP-Poly under different noise degree and phase ramp patterns.
3.2. Real Data
Four SAR datasets, covering the Datong and Tohoku-Oki areas, were used to validate the methods of orbital error correction, respectively. The information for the interferogram is summarized in Table 1. The pre-processing includes the co-registration to subpixel accuracy with cross correlation algorithm, multi-looking (3 × 15 looks for ASAR data set along range and azimuth, 4 × 4 looks for GF-3 with stripmap model, 9 × 3 looks for Sentinel-1 with TOPSAR mode), the topography–component removal using the 90-m Shuttle Radar Topography Mission v. 4.1 digital elevation model, and the adaptive Goldstein filtering. The atmospheric delay is not considered any further due to the lack of the external data. For this paper, we assume that this component, together with orbital error, comprises the linear/nonlinear phase ramps.

Table 1.
ENVISAT ASAR acquisitions over Datong and Tohoku-Oki areas.*
3.2.1. Datong Area
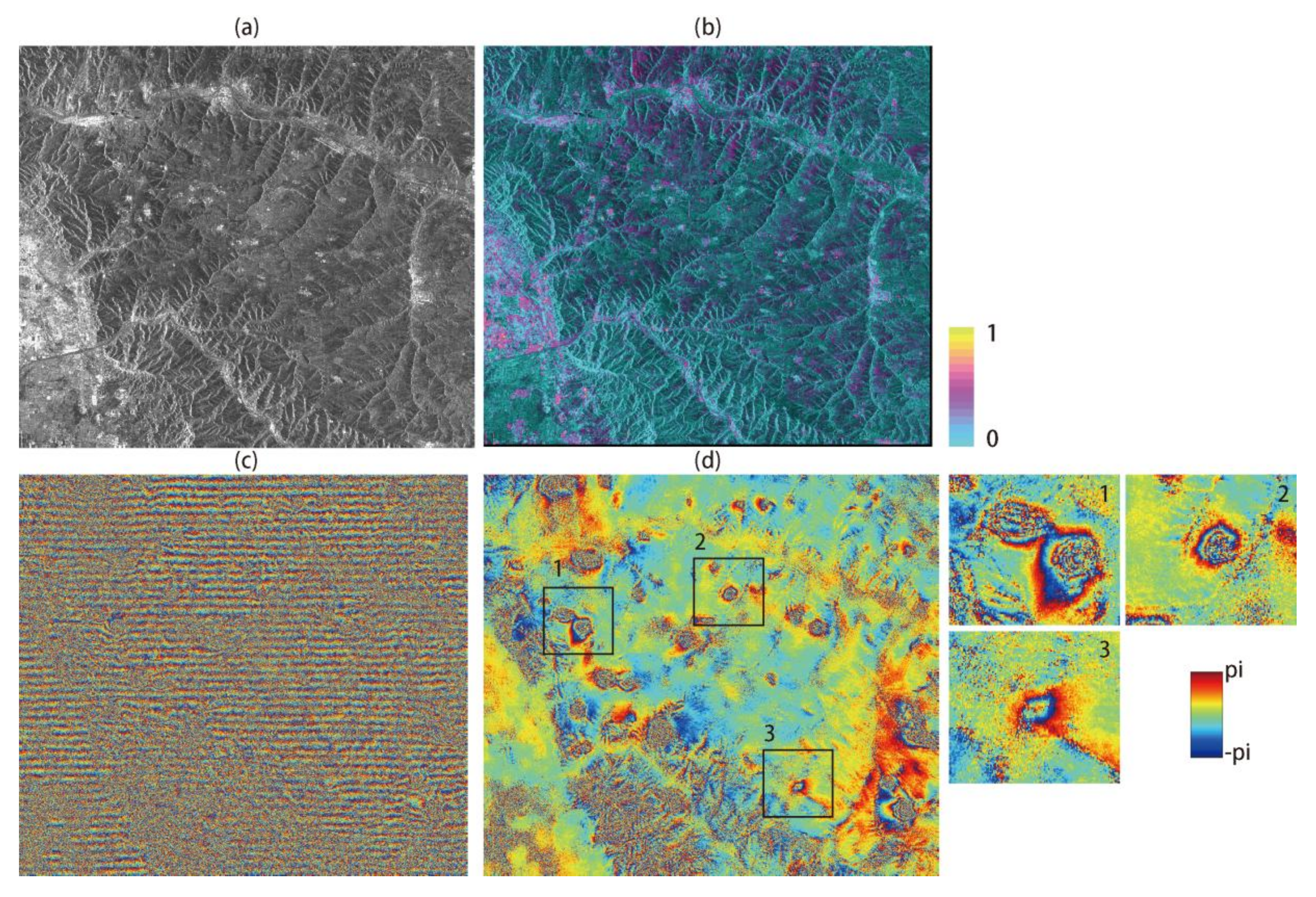
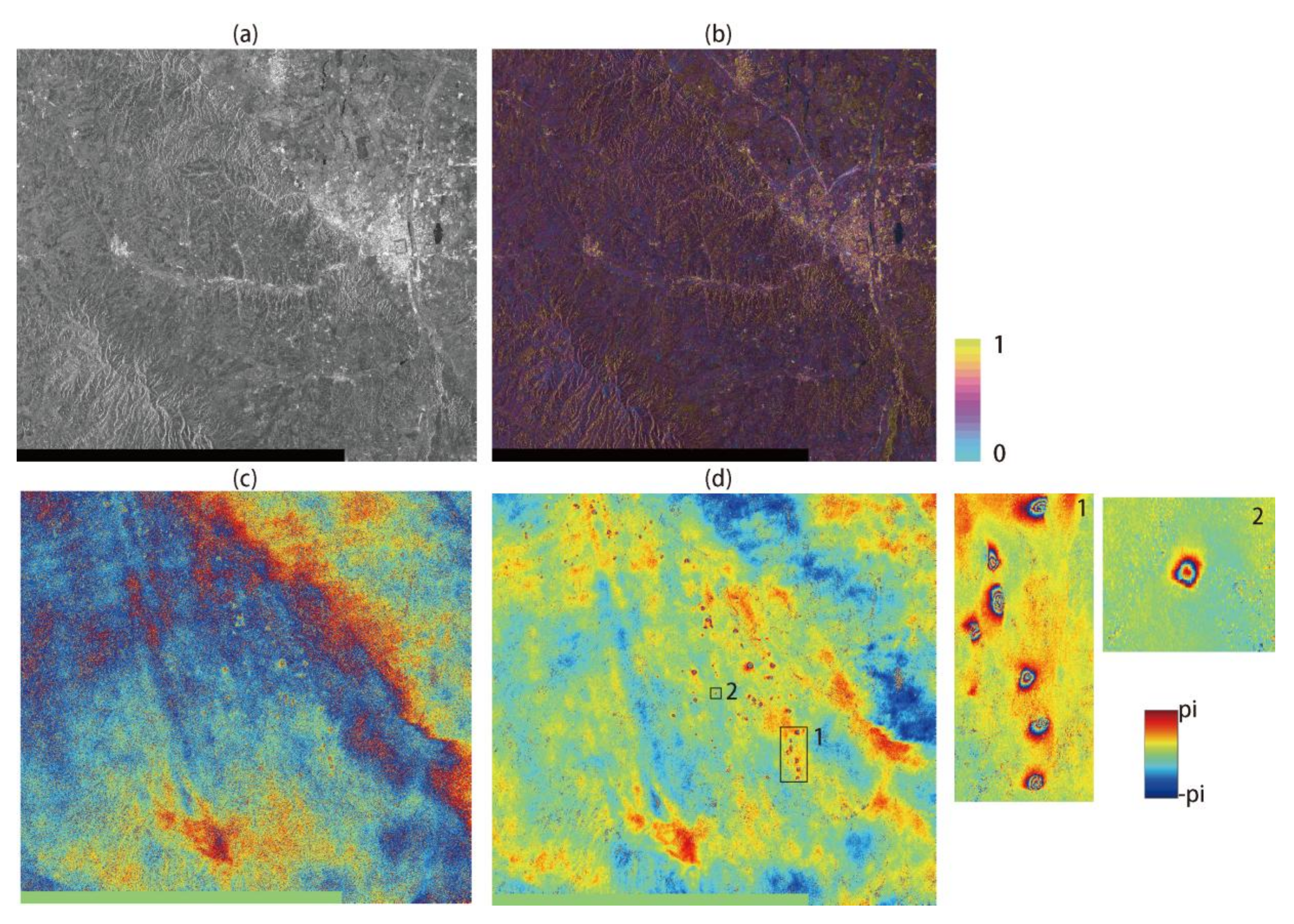
The deformation feature in the GF-3 interferogram is locally distributed because of the dynamics of land subsidence caused by underground mining activities over the Datong area, China. Errors in the GF-3 satellite state vectors can be observed in the differential interferogram (Figure 4c) and cause a linear phase ramp along the azimuth direction. Because of the relatively low coherence over the area (Figure 4b), we employed DFT to remove the long-wavelength signals (Figure 4d) without the phase unwrapping. The results in the amplified sub-regions (1–3) show that mining-related surface deformation could be monitored after removal of orbital errors. The multi-looking GF-3 SAR image is shown in Figure 4a.
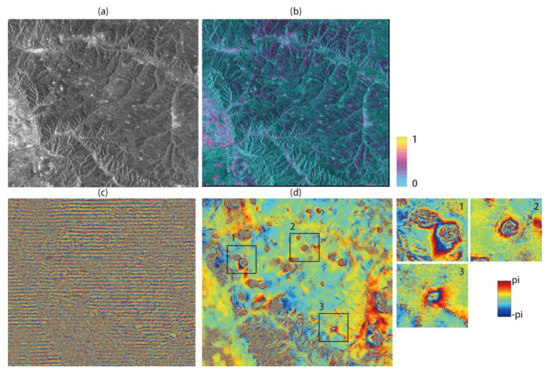
Figure 4.
Orbital error correction for GF-3 sensor over Datong area: (a) SAR intensity acquired on 1 April 2017; (b) corresponding coherence map; (c) original interferogram with linear phase ramp; (d) de-ramping interferogram estimated from DFT. The sub-image 1–3 corresponds to frames shown in Figure 4d.
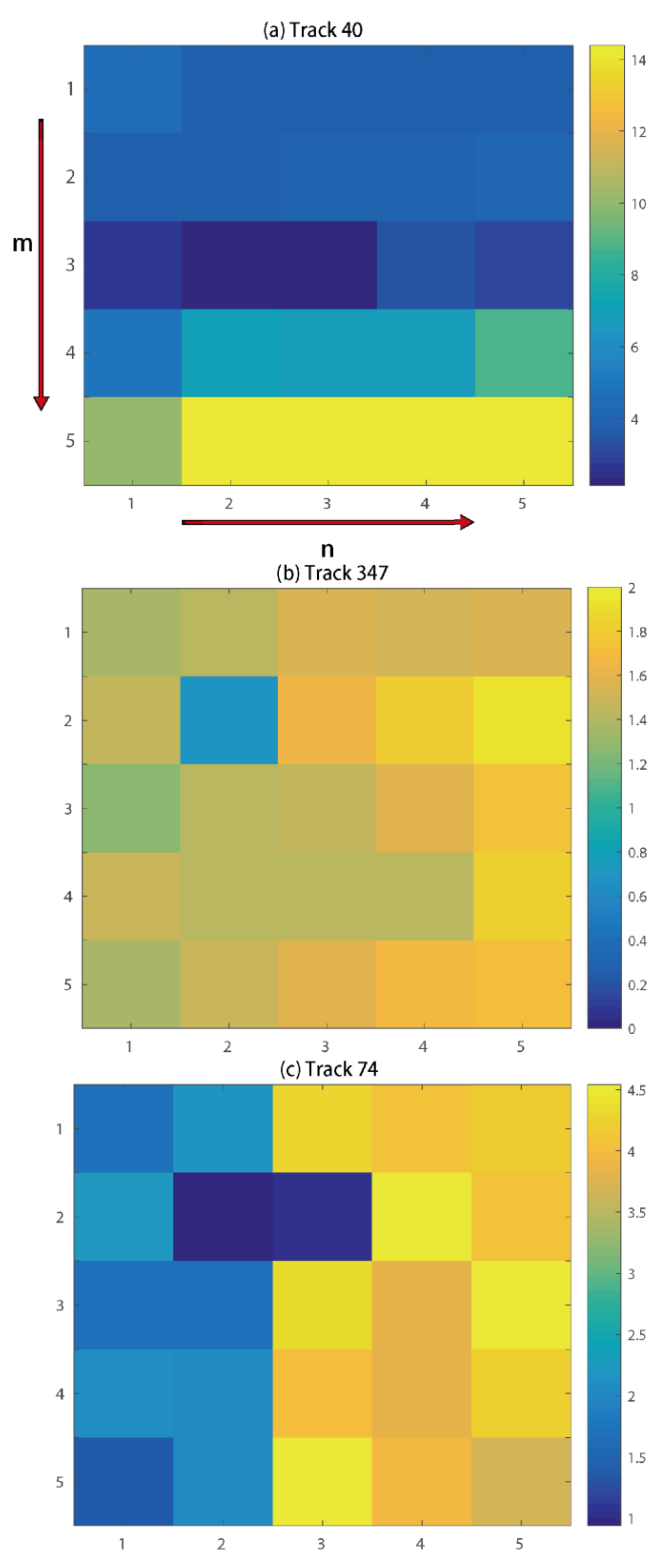
In contrast to GF-3, the better orbital qualities of Sentinel-1 instruments mitigate the phase ramp in the interferogram (Figure 5c). After burst and sub-swath merging, a nonlinear phase ramp with a relatively large spatial coverage can be observed in the upper right part of image. To remove the phase ramp, ADP-Poly is motivated by the high coherence magnitude (Figure 5b). A ten-fold cross validation was performed to select the optimal order of polynomial model. It can be seen from Figure 6a that the overfitting causes a larger bias for regression with the increase in order in polynomial, while the polynomial coefficient with n = 3 and m = 3 reaches the minimum WRMSE (2.15 rad, corresponding to ~9 mm). The final de-ramping interferogram is shown in Figure 5d, where the spatially distributed subsidence bowls can be clearly seen. The multi-looking sentinel-1 SAR image is shown in Figure 5a.
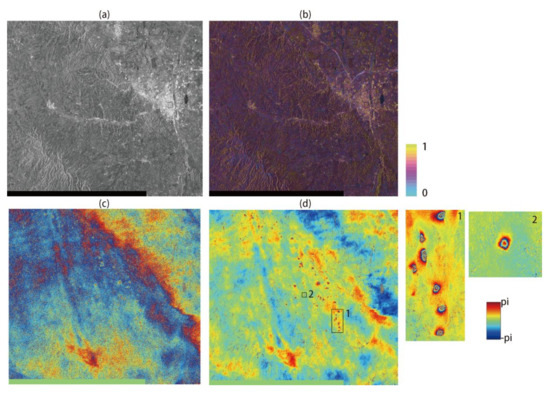
Figure 5.
Orbital error correction for Sentinel-1 sensor over Datong area: (a) SAR intensity acquired on 15 October 2015; (b) corresponding coherence map; (c) original interferogram with nonlinear phase ramp; (d) de-ramping interferogram estimated from ADP-Poly. The sub-image 1–2 corresponds to frames shown in Figure 5d.
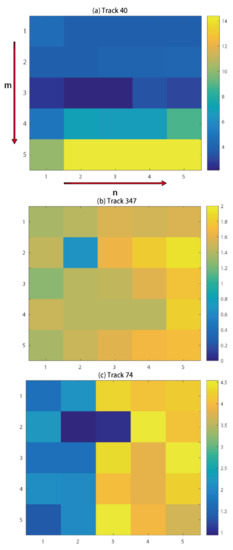
Figure 6.
Adaptive model selection of ADP-Poly for (a) track 40 (Sentinel-1); (b) track 347 (ASAR) and (c) track 74 (ASAR).
3.2.2. Tohoku-Oki Area
For long-wavelength displacement signals covering the whole image, external GPS measurements should be used to correct the displacement before phase-ramp estimation. To this end, GPS observations, including total 120 stations, were collected from the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) team at Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Caltech [20]. During the process, the GPS observations were first projected into the LOS direction using the central unit vector for east, north and vertical directions in descending ASAR (Table 2). Then, all GPS locations were transformed into radar coordinates. The nearest SAR neighbors, with respect to each GPS measurement, were averaged using 3 × 3 boxcar windows, and the weights were determined by means of averaged phase STD with a factor of 1/3. When the phase ramp fitted using ADP-Poly, 90% of the GPS observations located in each SAR track were used to correct the deformation in unwrapped InSAR interferogram, and the remaining 10% were used to evaluate the discrepancies between the GPS observations and the orbit-corrected InSAR coseismic measurements.

Table 2.
Deformation validation and RMSE before and after orbital error correction over Tohoku-Oki area.
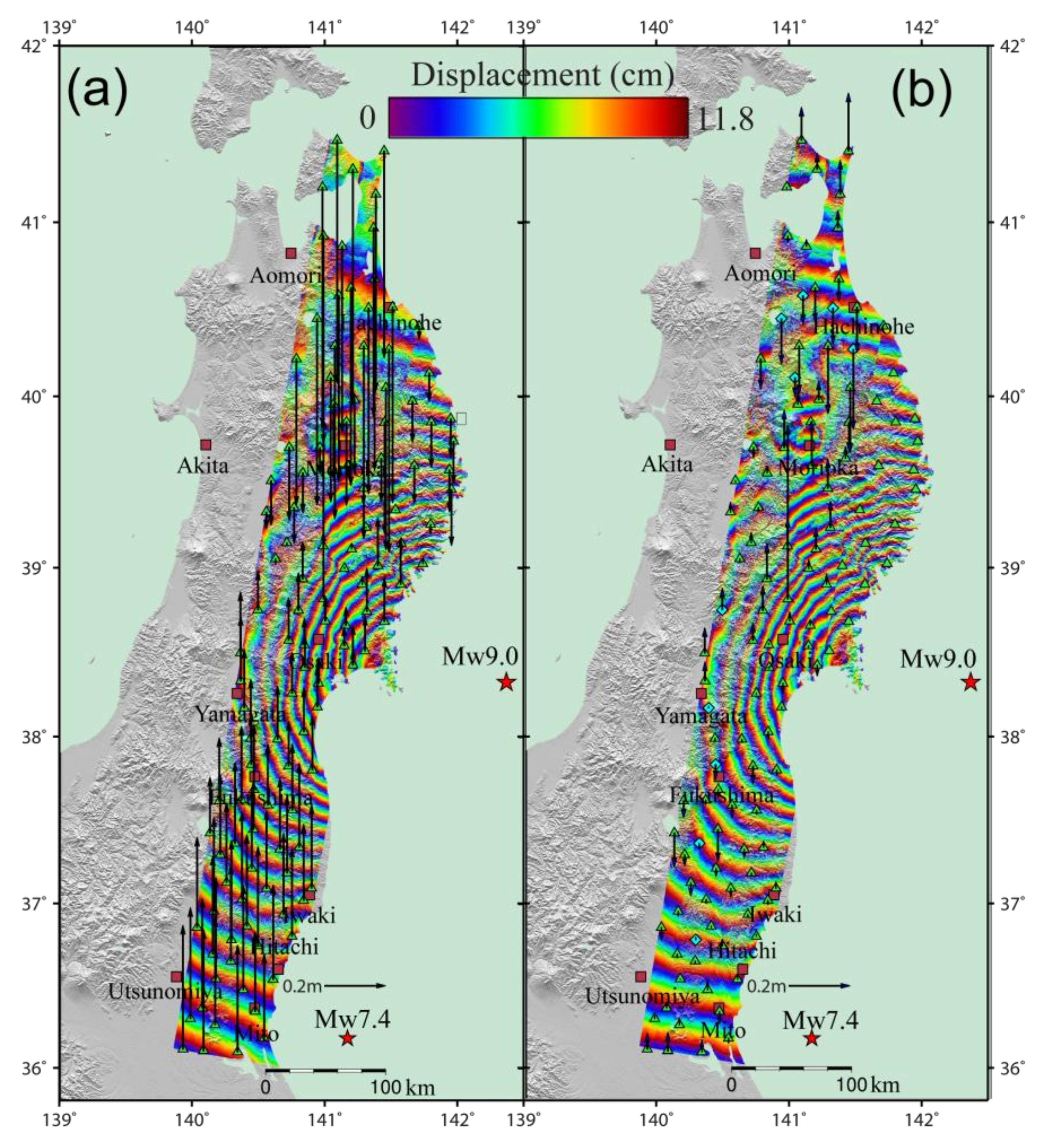
We present the results of before and after ADP-Poly orbital error correction in Figure 6 and Figure 7 and Table 2. It can be seen that ADP-Poly suggests a quadratic model to fit the ramps for both tracks (Figure 6b,c). The RMSE values, before and after the orbital error correction, are 35.55 cm and 9.52 cm for track 347, and 12.24 cm and 8.39 cm for track 74, respectively, demonstrating the usefulness of the ADP-poly method developed by the authors. After removal of phase ramp, the displacement caused by earthquakes is rewrapped to 11.8 cm for each fringe, as shown in Figure 7. As stated in previous studies [17,20,35], the discontinuity between GPS measurements and InSAR displacement can be attributed to unwrapping errors over very low coherence area and the aftershock and postseismic deformation that were not covered by the GPS observation period.
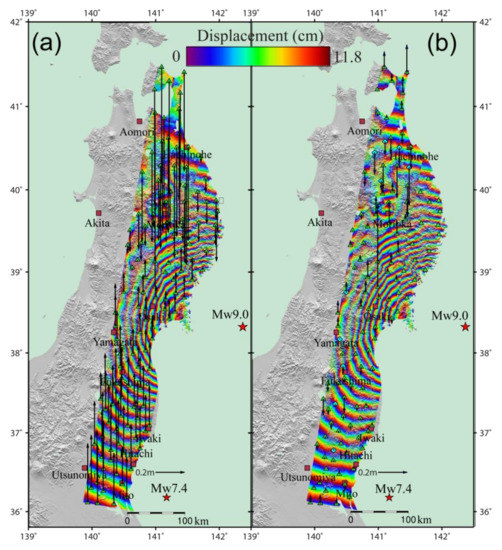
Figure 7.
Coseismic deformation interferograms generated using data from ASAR descending tracks 347 and 74, before (a) and after (b) orbital error correction. The locations of the cities (khaki square) and GPS stations (green triangle) that are used to remove the orbital errors. The arrows indicate the biases in the InSAR results as calculated from the GPS observations. Each color cycle represents 11.8 cm of LOS displacement toward or away from the satellite. The epicenters of the magnitude 9.0 main shock and a magnitude 7.4 aftershock are marked as red stars.
4. Discussion
Two methods of modeling orbital error in InSAR interferograms that deploy DFT and the polynomial model with adaptive order determination were presented. DFT is a robust estimator of linear components of the long-wavelength signals, even in strong noise environment. It transfers spatial phase ramps into the frequency spectrum and finds the fringe rate at the peak location of the Fourier transformation. The interpolation of the DFT of the interferogram can better identify the exact fringe rate. A significant advantage of this method is that phase wrapping is not required, and, therefore, the errors caused by the poor quality of the interferograms are avoided. For nonlinear fringe patterns, the polynomial model (ADP-Poly) can compensate for nonlinear components that cannot be estimated with DFT. The development of adaptive order determination for the polynomial model using K-cross validation ensures the model can follow the features of orbital errors more accurately. This step is missed in previous studies, which usually determine the order empirically.
Two problems in orbital error correction should be further pointed out. Firstly, the approach has no capacity to distinguish between orbital errors and long-wavelength atmospheric delays. To our knowledge, this is a common problem in most related studies [12,13,14,20,23]. We therefore made the assumption that the long-wavelength signal only represents the orbital error, implying that part of the tropospheric delay will also be removed from the interferogram. A good alternative is to remove the atmospheric delays prior to orbital error correction, for example, by using the Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service, applying the Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition model [34].
Secondly, manual masking is used to remove local deformation signals, leading to gaps in the local region, and so, no observation will yield contributions during de-ramping. To solve this problem, a deformation free interferogram can be inverted using a source geophysical model, e.g., Mogi’s formulation for an infinitesimal spherical source in an elastic half-space, by finding the global minimum in the misfit space using a simulated annealing algorithm [36]. To do this, General Inversion of Phase Technique, which estimates parameters in a quantitative model directly from the wrapped-phase data, can be employed [36].
5. Conclusions
This paper has explored orbital error correction in InSAR interferogram using frequency (DFT) and spatial domain (ADP-Poly) based methods. The results reveal that the modeling of orbital error should follow the features of fringe patterns and the quality of the interferogram. To detect linear features of orbital error, the method based on maximum likelihood fringe rate estimation should be deployed. The main advantage of this technique is that it is workable over fast decorrelation areas without the need of unwrapping. However, only linear components can be estimated using this method. For nonlinear features, ADP-Poly, which determines the order of polynomial automatically using K-cross validation, should be used. We evaluated both methods using historical and modern sensors, including ENVISAT ASAR, GF-3 and Sentinel-1. The experiments show that both historical and modern systems can benefit from our method to varying degrees, leading to clearer ground deformation signals, both locally and globally.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Guangcai Feng, from Central South University, for helping to collect GPS data and drawing Figure 7. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 41471373, the ESA-MOST Dragon 4 project under Grant 32248_2, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Surveying and Mapping Research Fund of Jiangsu Province JSCHKY201601. The GPS displacement data (Version 0.3) was provided by the ARIA team at JPL based on GPS data from the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. The ENVISAT ASAR raw data were supplied through the GEO Geohazards Supersite.
Author Contributions
Xin Tian designed and performed the experiments, and also wrote the article. Rakesh Malhotra revised the manuscript. Bing Xu performed GF-3 and Sentinel-1 data processing. Haoping Qi and Yuxiao Ma searched information about the data and contributed to the editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential sar interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in sar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, F.; Xiong, X.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Walter, T.R.; Weng, H.; Li, J. Overlapping post-seismic deformation processes: Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation following the 2011 Mw9.0 Tohoku (Japan) earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 196, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, A.; Hollingsworth, J.; Bergman, E. Constraints on fault and lithosphere rheology from the coseismic slip and postseismic afterslip of the 2006 Mw7.0 Mozambique earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Wen, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z. Time-dependent afterslip of the 2009 Mw6.3 Dachaidan earthquake (China) and viscosity beneath the qaidam basin inferred from postseismic deformation observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Insar uncertainty due to orbital errors. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 199, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, C.; Schmullius, C. Impact of tree species on magnitude of palsar interferometric coherence over siberian forest at frozen and unfrozen conditions. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-L.; Li, Z.-W.; Zhu, J.-J.; Feng, G.-C.; Long, J.-P. Atmospheric effects on insar measurements and their mitigation. Sensors 2008, 8, 5426–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhu, J.-J.; Feng, G. Modeling minimum and maximum detectable deformation gradients of interferometric sar measurements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.-W.; Wang, Q.-J.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J.-J.; Ding, X.-L. A refined strategy for removing composite errors of sar interferogram. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Peltzer, G.; Simons, M. Updated repeat orbit interferometry package released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2004, 85, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knedlik, S.; Loffeld, O.; Hein, A.; Arndt, C. A novel approach to accurate baseline estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’99), Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 254–256. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Berardino, P.; Bonano, M.; Euillades, L.D.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. Sbas-based satellite orbit correction for the generation of dinsar time-series: Application to radarsat-1 data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 5150–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhase, A.; Feigl, K.; Massonnet, D. Applying differential inSAR to orbital dynamics: A new approach for estimating ERS trajectories. J. Geod. 2003, 77, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.; Lu, Z.; Parsons, B. Multi-interferogram method for measuring interseismic deformation: Denali fault, Alaska. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, H.; Hanssen, R.F. Reliable estimation of orbit errors in spaceborne SAR interferometry. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1147–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.; Biggs, J. Interseismic slip rate of the northwestern Xianshuihe fault from inSAR data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; Omura, M. Calibration of an insar-derived coseimic deformation map associated with the 2011 Mw-9.0 Tohoku-oki earthquake. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Socquet, A.; Armijo, R.; Carrizo, D.; Genrich, J.; Simons, M. Andean structural control on interseismic coupling in the north Chile subduction zone. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourmelen, N.; Amelung, F.; Lanari, R. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar–GPS integration: Interseismic strain accumulation across the Hunter Mountain fault in the eastern California shear zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Walter, T.R. Estimating the effect of satellite orbital error using wavelet-based robust regression applied to inSAR deformation data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4600–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, H. Orbital Effects in Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zebker, H.A.; Chen, K. Accurate estimation of correlation in inSAR observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolini, U. 2-D phase unwrapping and instantaneous frequency estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z. Hybrid approach for unbiased coherence estimation for multitemporal inSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2459–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.W.; Welsch, R.E. Robust regression using iteratively reweighted least-squares. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1977, 6, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, B. The improvement for baran phase filter derived from unbiased inSAR coherence. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Yong, B.; Tian, X.; Malhotra, R.; Hu, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X. The potential of more accurate insar covariance matrix estimation for land cover mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping for large SAR interferograms: Statistical segmentation and generalized network models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsson, S.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Amelung, F. Fault slip distribution of the 1999 Mw7.1 Hector mine, California, earthquake, estimated from satellite radar and GPS measurements. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigl, K.L.; Thurber, C.H. A method for modelling radar interferograms without phase unwrapping: Application to the M 5 Fawnskin, California earthquake of 1992 December 4. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 176, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).