Calibration of GLONASS Inter-Frequency Code Bias for PPP Ambiguity Resolution with Heterogeneous Rover Receivers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
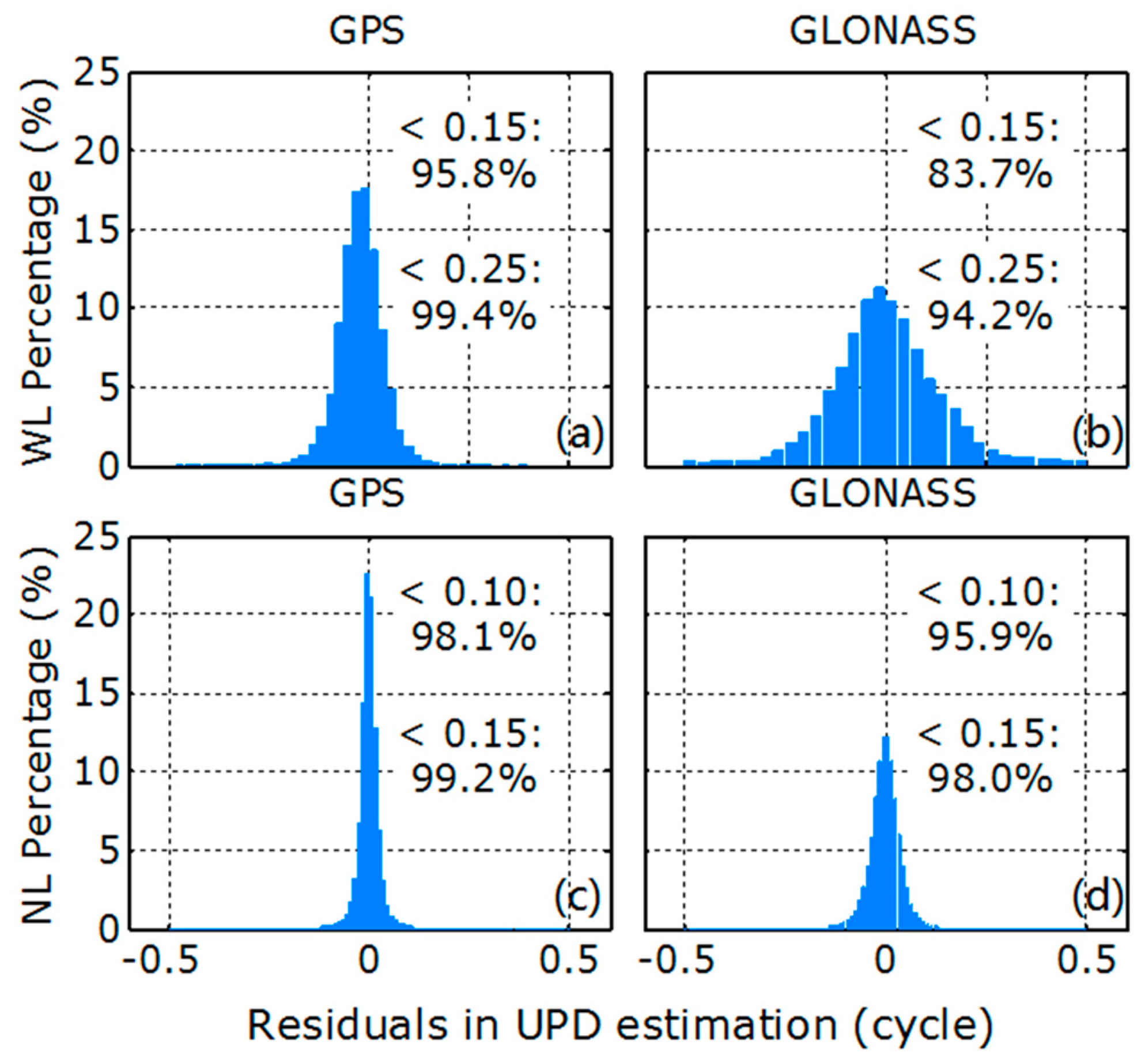
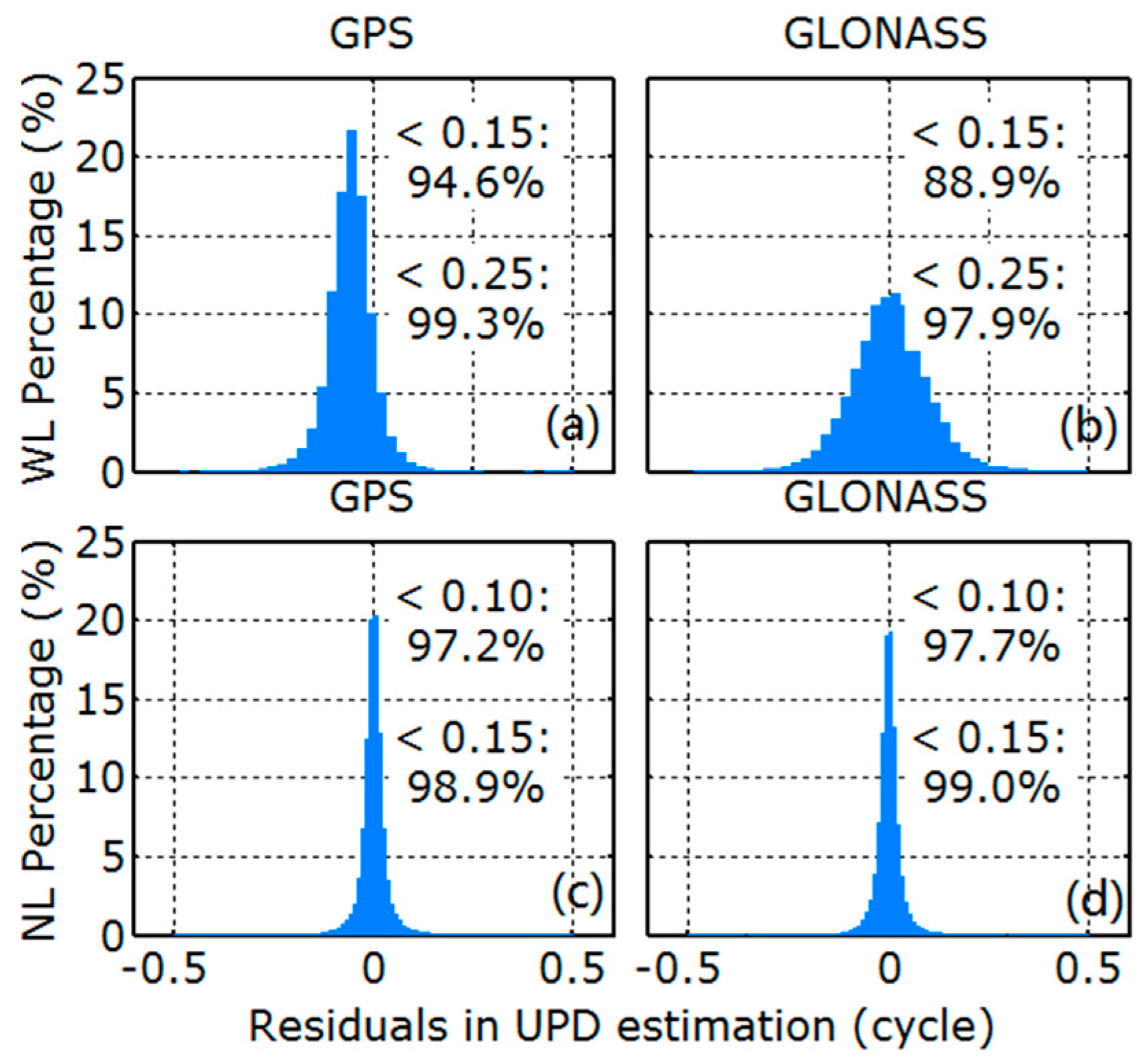
2.1. GLONASS UPD Estimation Strategy
2.2. Rover IFCB Correction Method
2.2.1. Correcting the Large Part
2.2.2. Correcting the Fractional Part
- (a)
- Select the ambiguity with the longest tracking arc, assume the WL IFCB residual is zero for the satellite, and fix the WL and NL ambiguities by rounding. The receiver UPD can thus be separated from all WL and NL float ambiguities.
- (b)
- Select another WL and NL ambiguity pair. First round down the WL ambiguity and if the corresponding NL ambiguity can be fixed, fix the WL ambiguity as the rounded-down value. If not, round up the WL ambiguity and if the corresponding NL ambiguity can be fixed, fix the WL ambiguity as the rounded-up value.
- (c)
- Repeat (b) for all remaining WL and NL ambiguity pairs.
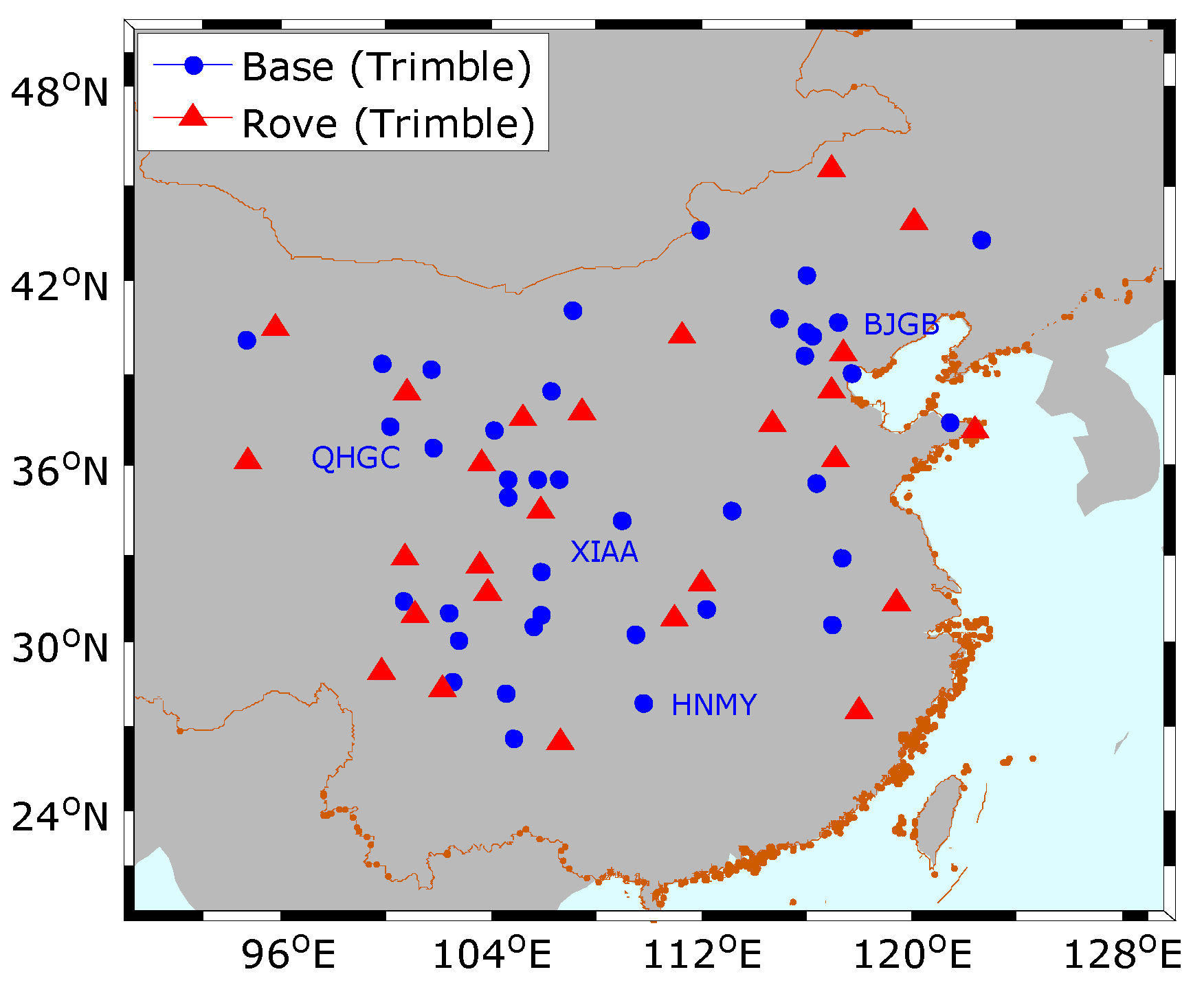
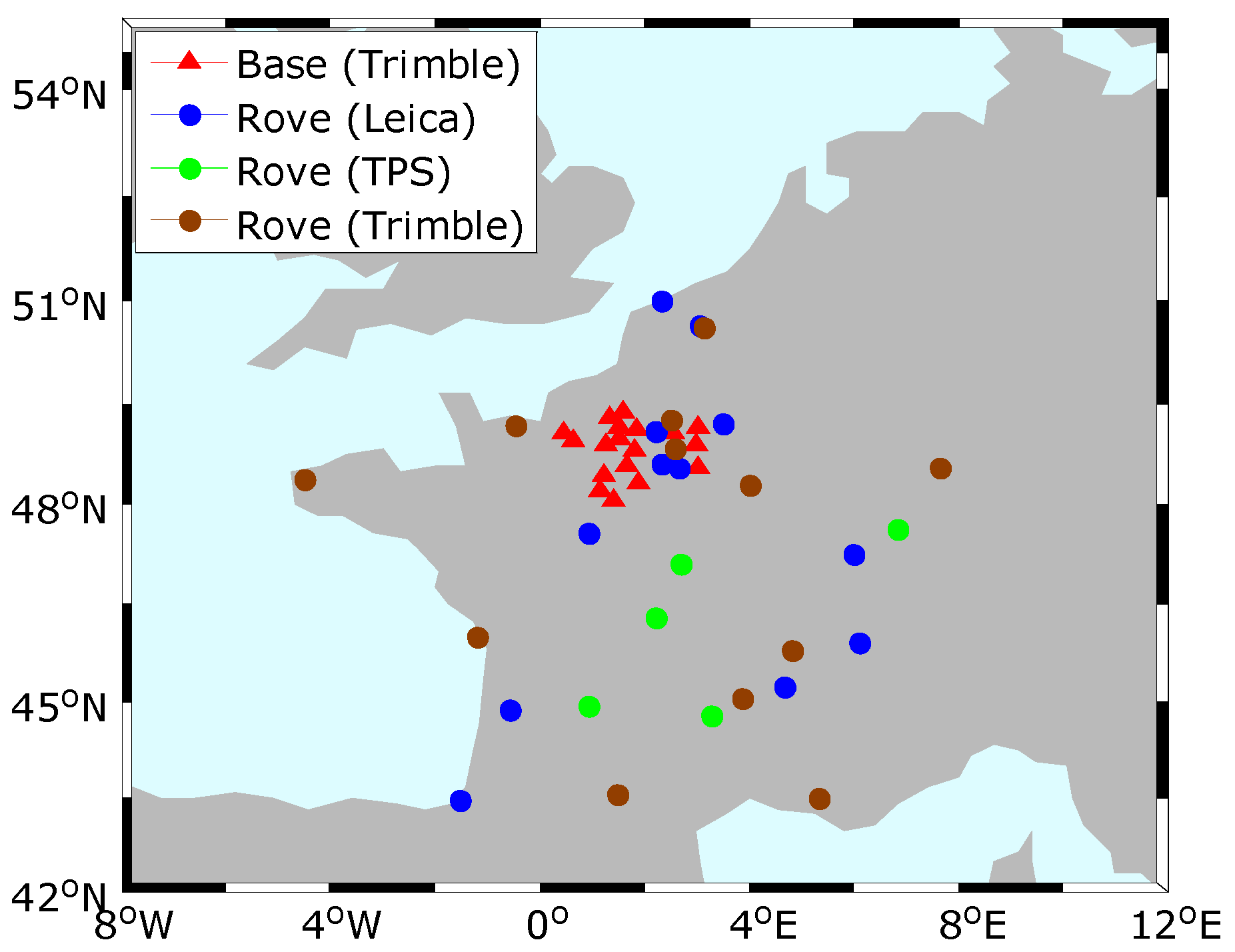
3. Data and Processing Strategy
4. Results and Validation
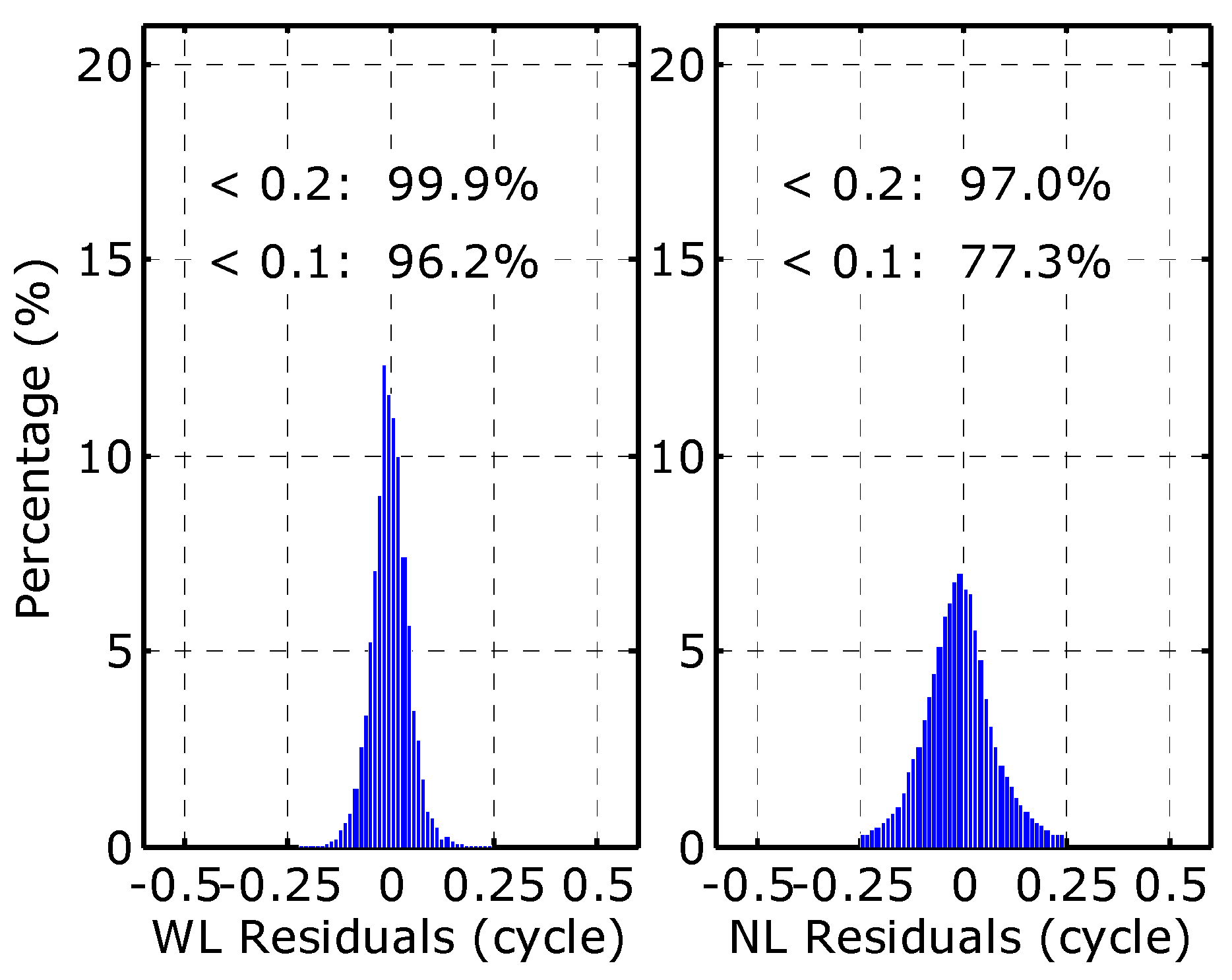
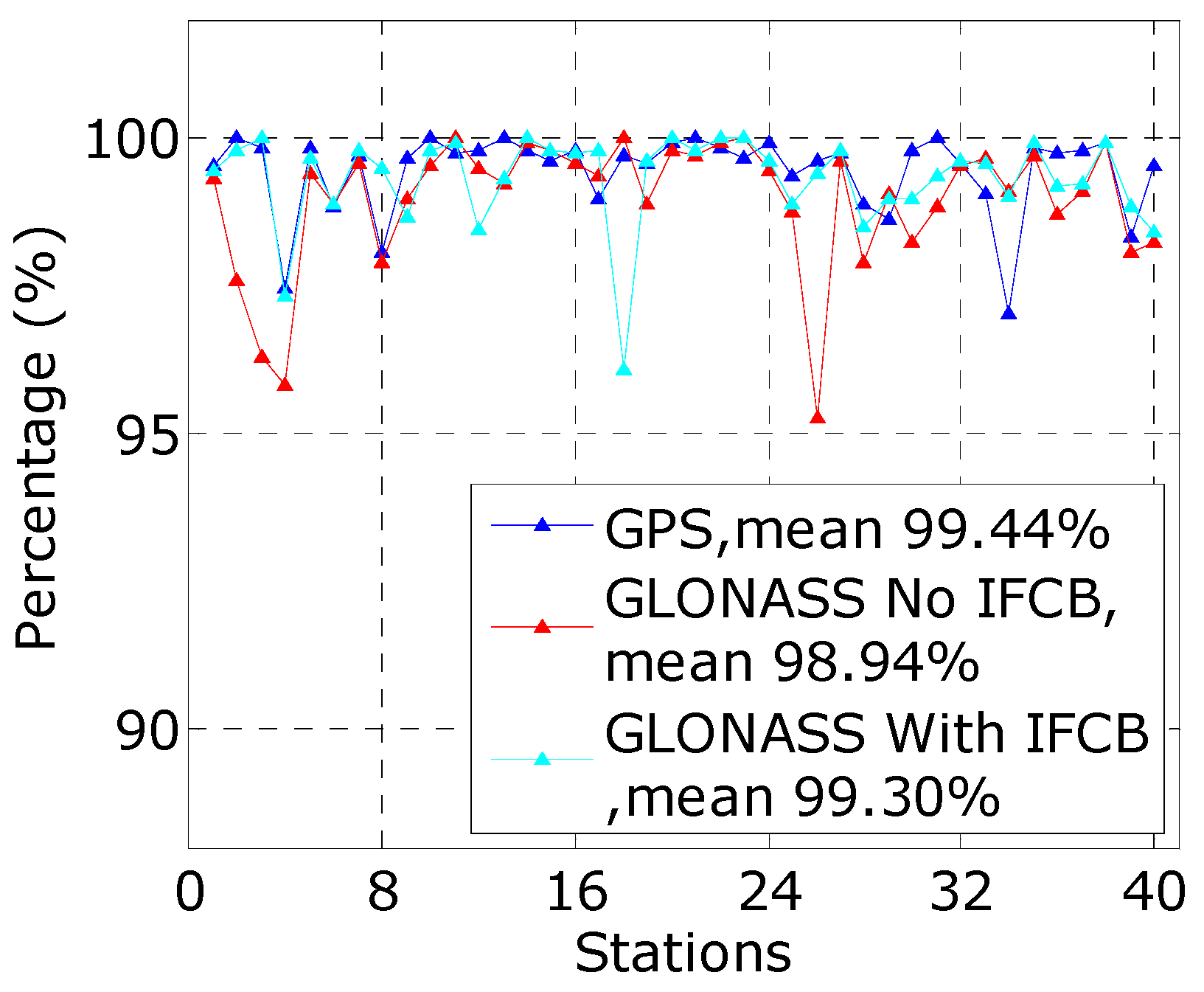
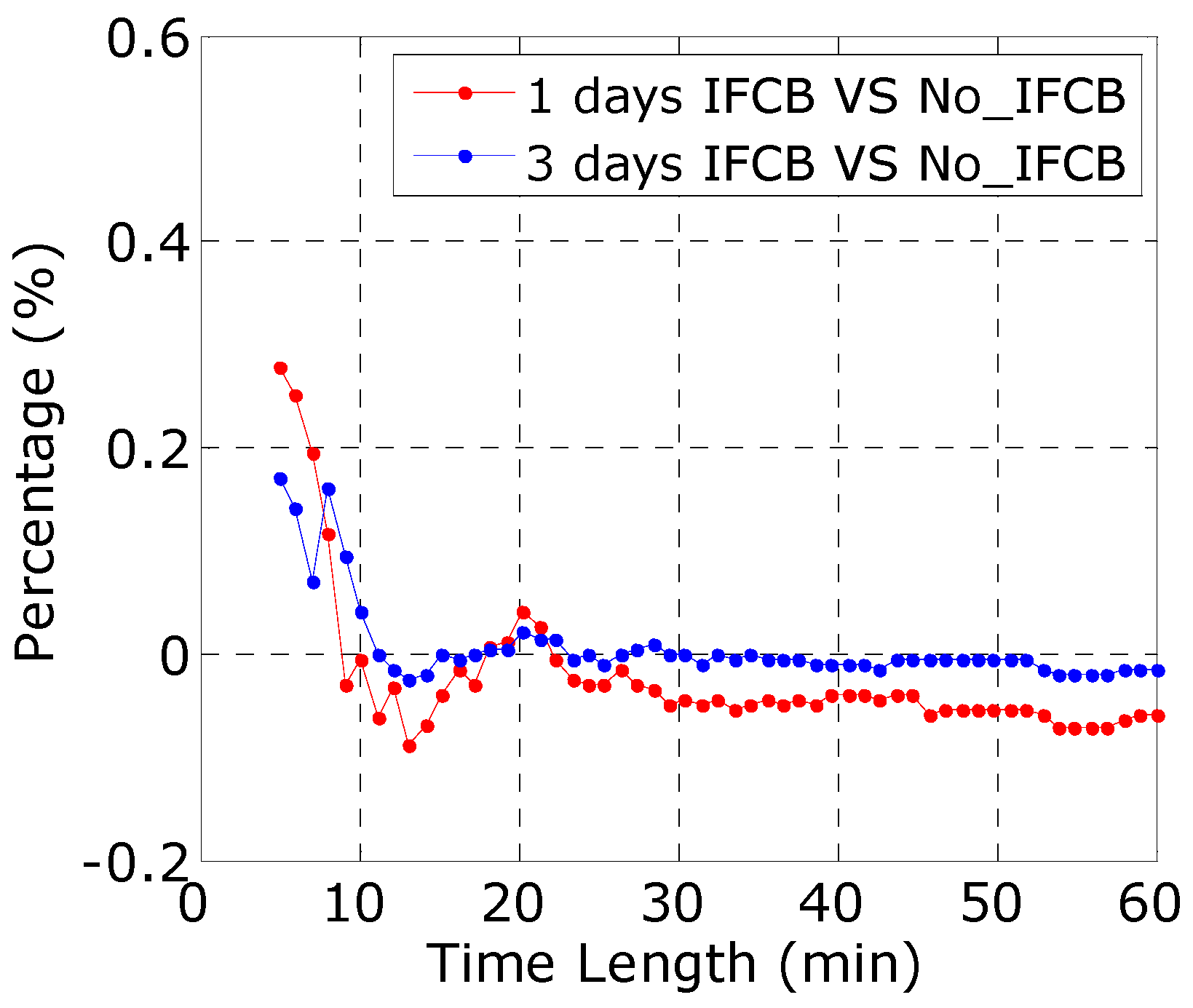
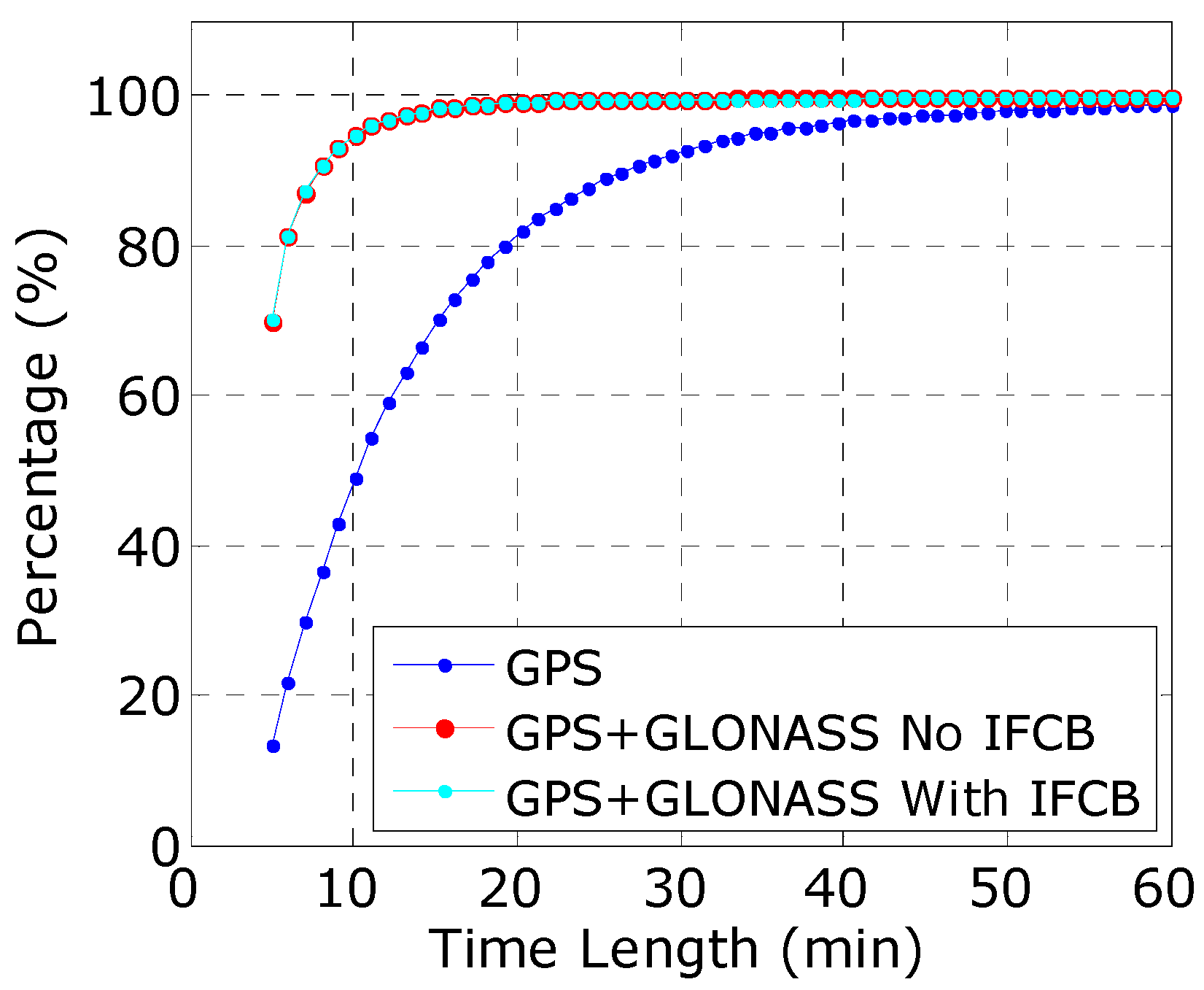
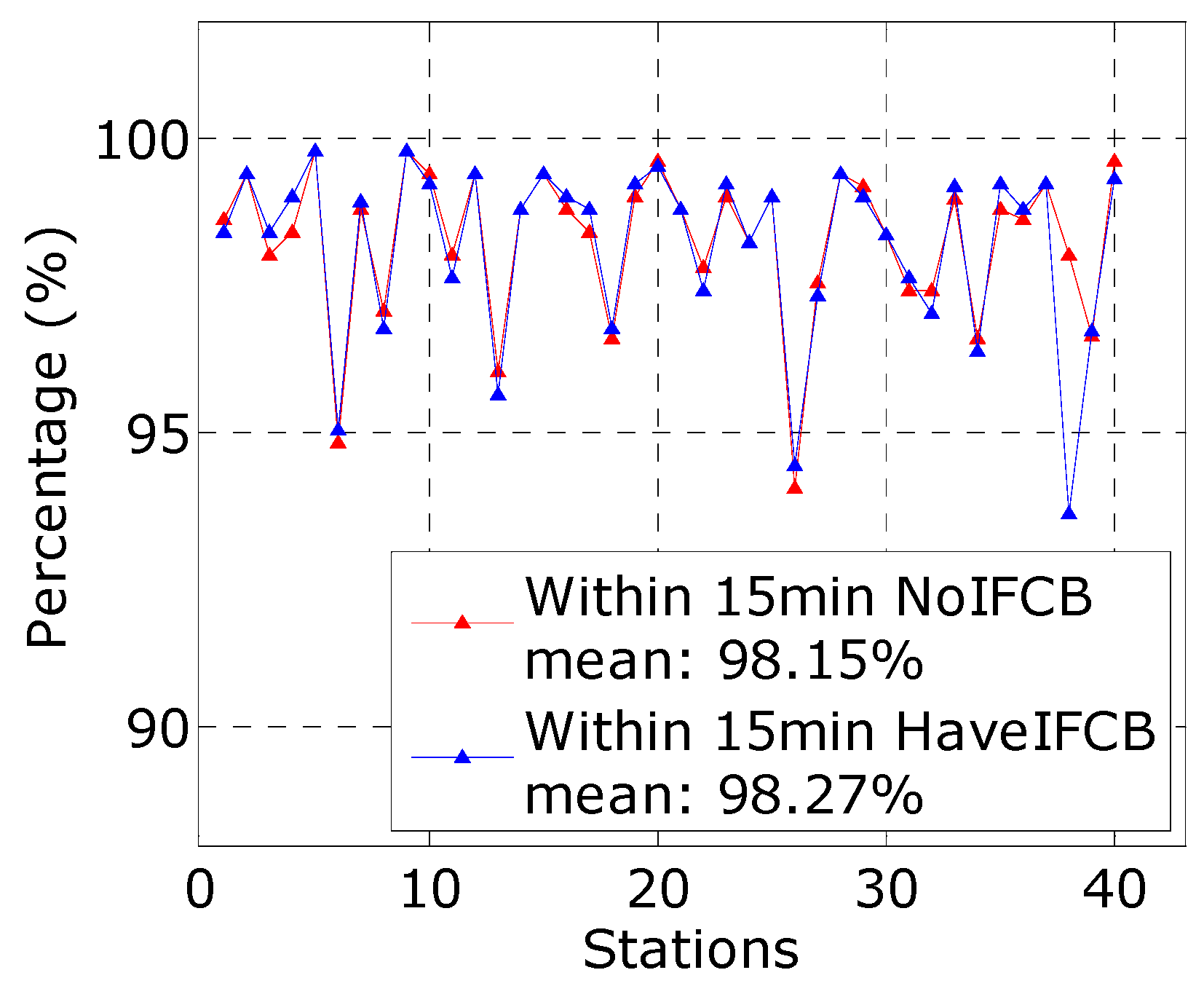
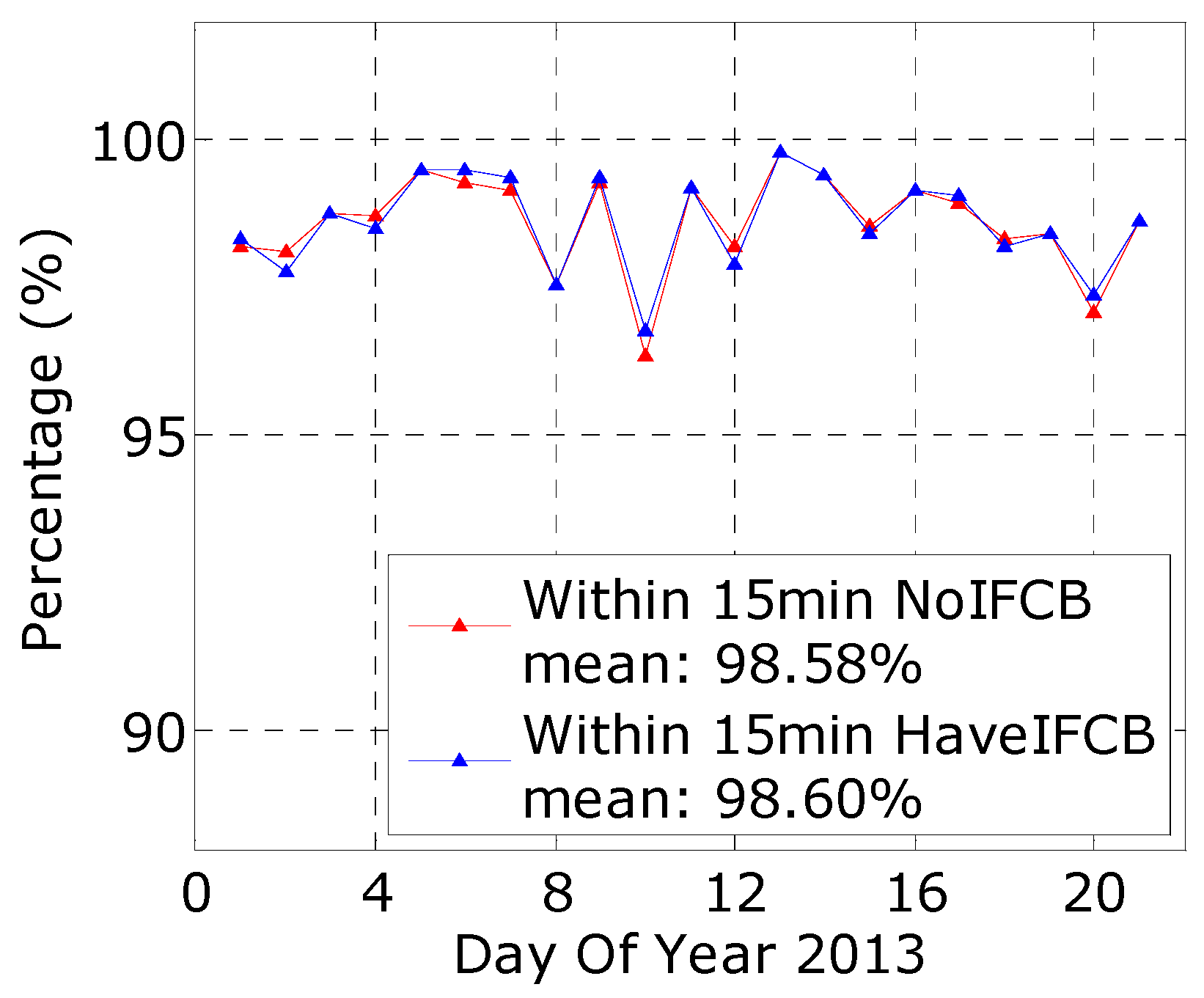
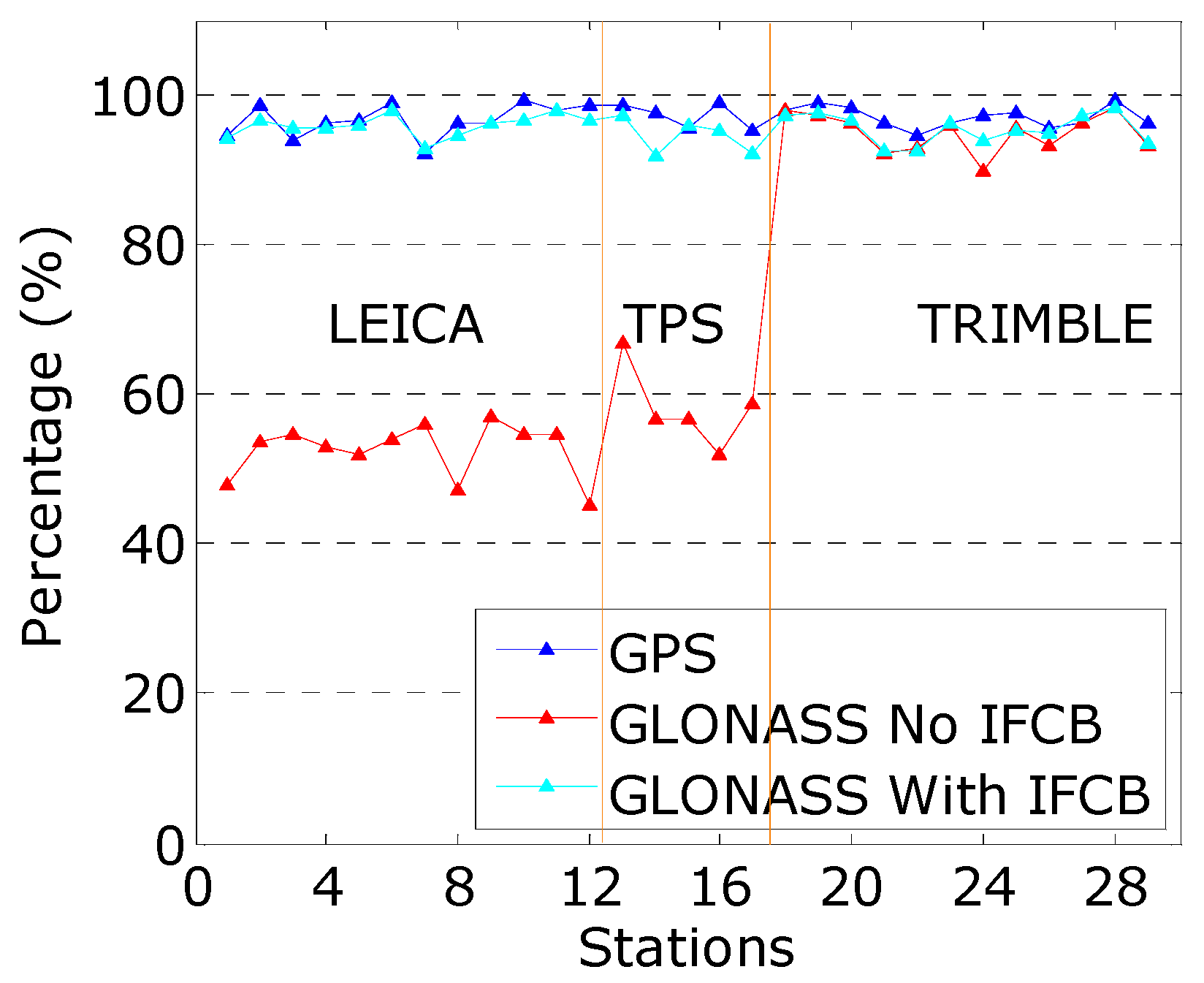
4.1. Assessment of Homogeneous Receivers
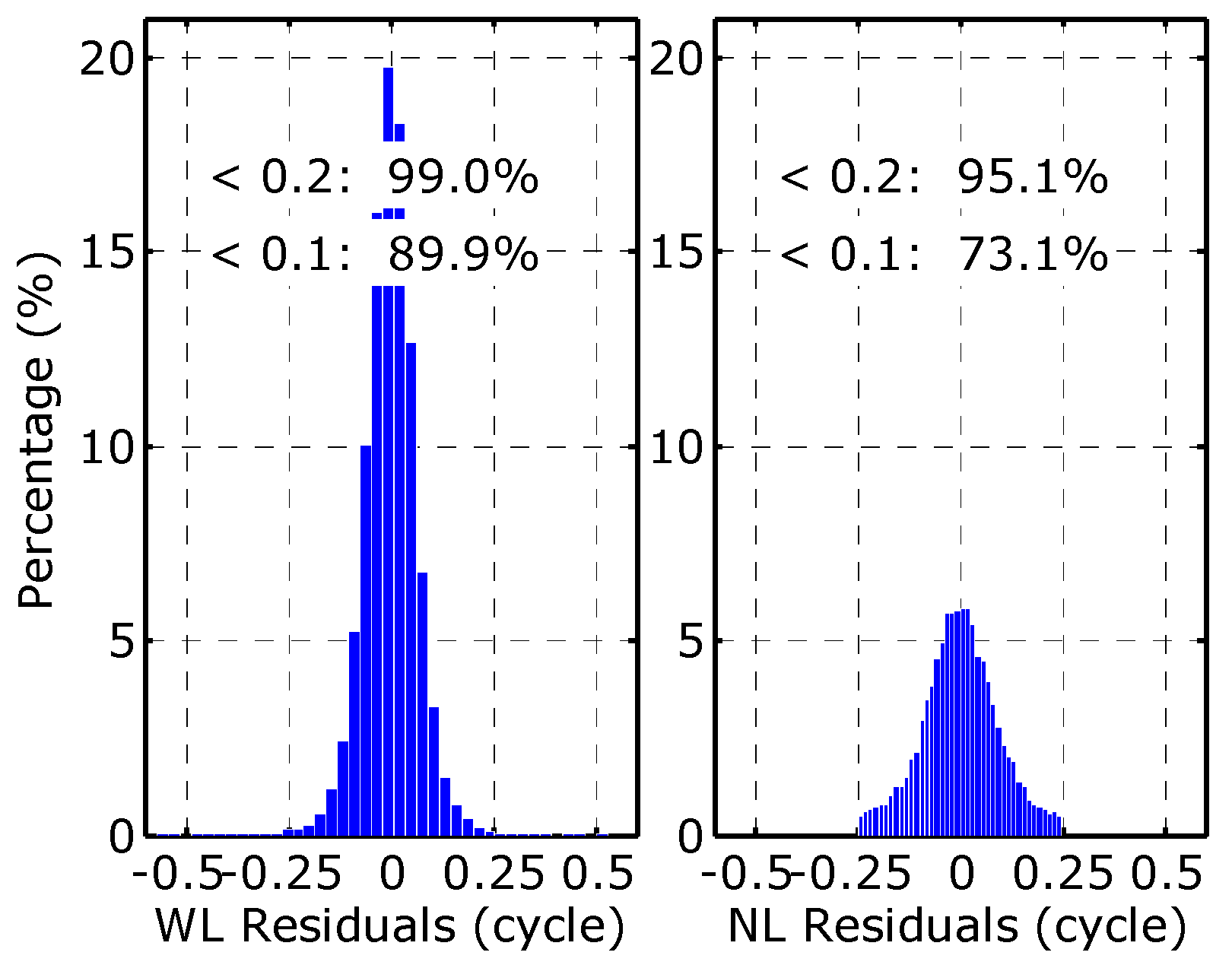
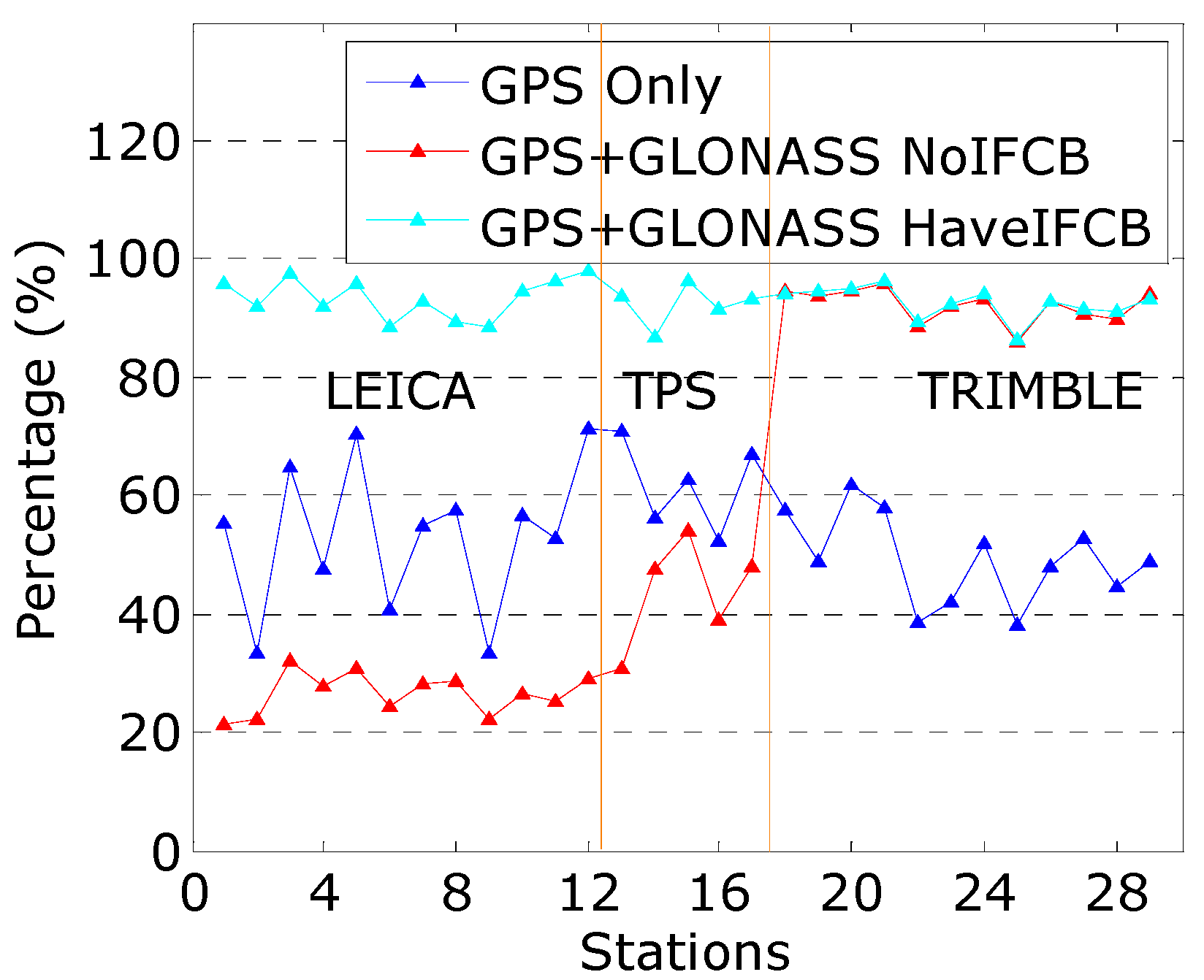
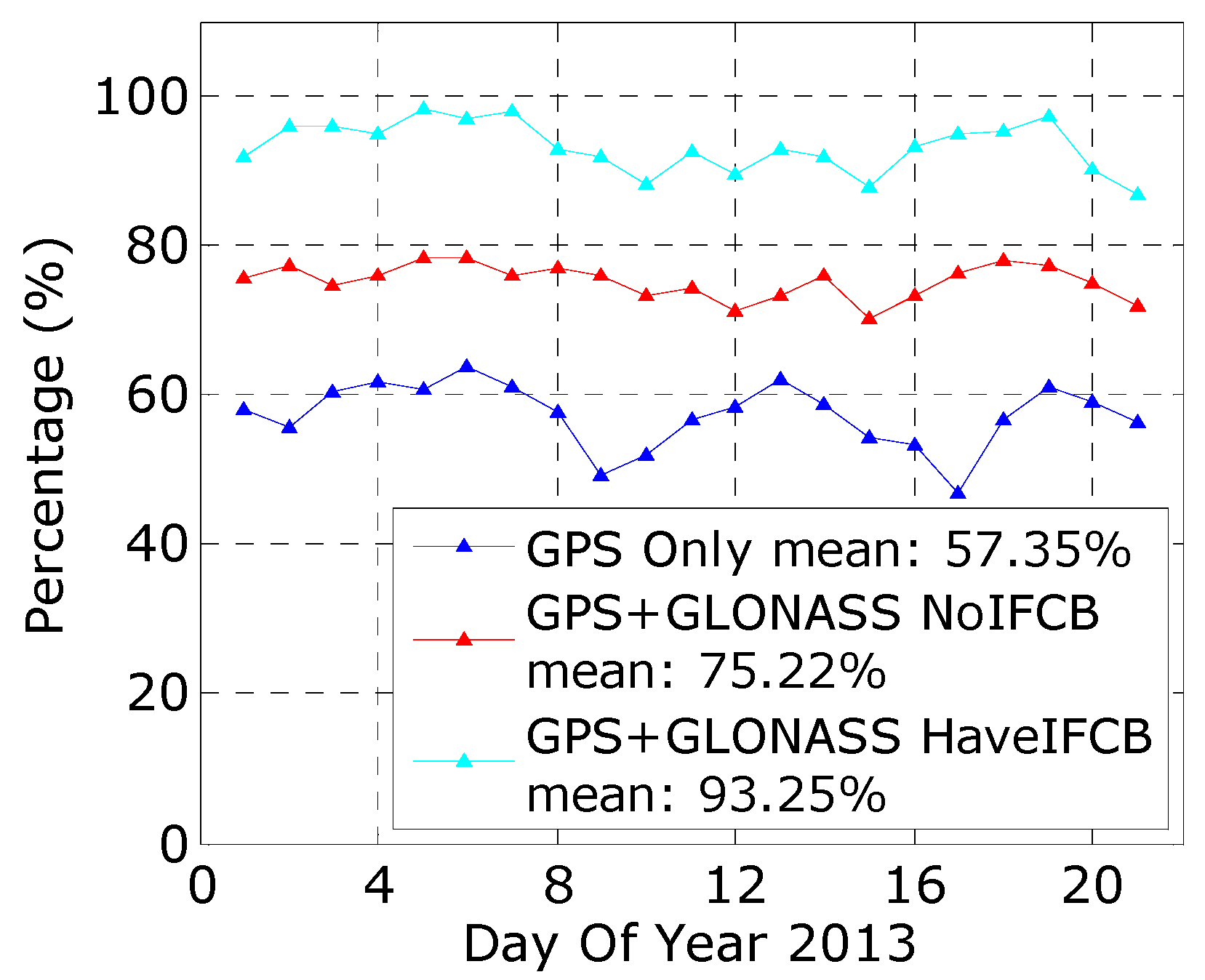
4.2. Assessment of Heterogeneous Receivers
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, M.J.; Nerem, R.S. GPS carrier phase AR using satellite-satellite single difference. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-1999, Nashville, TN, USA, 14–17 September 1999; pp. 1569–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Mervart, L.; Lukes, Z.; Rocken, C.; Iwabuchi, T. Precise Point Positioning with ambiguity resolution in real-time. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-2008, Savannah, GA, USA, 16–19 September 2008; pp. 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geodesy 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.; Lahaye, F.; Héroux, P.; Bisnath, S. Precise point positioning with AR using the decoupled clock model. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-2008, Savannah, GA, USA, 16–19 September 2008; pp. 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Laurichesse, D.; Mercier, F.; Berthias, J.P.; Broca, P.; Cerri, L. Integer ambiguity resolution on undifferenced GPS phase measurements and its application to PPP and satellite precise orbit determination. Navigation 2009, 56, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertiger, W.; Desai, S.D.; Haines, B.; Harvey, N.; Moore, A.W.; Owen, S.; Weiss, J.P. Single receiver phase ambiguity resolution with GPS data. J. Geodesy 2010, 84, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Teferle, F.N.; Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H. Towards PPP-RTK: Ambiguity resolution in real-time precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M. Regional reference network augmented precise point positioning for instantaneous ambiguity resolution. J. Geodesy 2011, 85, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. BeiDou phase bias estimation and its application in precise point positioning with triple-frequency observable. J. Geodesy 2015, 89, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegedor, J.; Liu, X.; Jong, K.; Goode, M.; Øvstedal, O.; Vigen, E. Estimation of Galileo Uncalibrated Hardware Delays for Ambiguity-Fixed Precise Point Positioning. Navigation 2016, 63, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Chen, D. Integrating GPS and BDS to shorten the initialization time for ambiguity-fixed PPP. GPS Solut. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felhauer, T. On the Impact of RF Front-end Group Delay Variations on GLONASS Pseudorange Accuracy. In Proceedings of the International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation 1997, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Reussner, N.; Wanninger, L. GLONASS Inter-frequency Biases and Their Effects on RTK and PPP Carrier phase Ambiguity Resolution. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-2011, Portland, Oregon, 19–23 September 2011; pp. 712–716. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninger, L. Carrier phase inter-frequency biases of GLONASS receivers. J. Geodesy 2012, 86, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F. Particle filter-based estimation of inter-frequency phase bias for real-time glonass integer ambiguity resolution. J. Geodesy 2015, 89, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaery, A.; Zhang, S.; Rizos, C. An enhanced calibration method of GLONASS inter-channel bias for GNSS RTK. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yi, W.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Xiang, Y. Impact of glonass pseudorange inter-channel biases on satellite clock corrections. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, D.; Tkachenko, M.; Tochilin, A. Statistical characterization of hardware biases in GPS + GLONASS receivers. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2000, Institute of Navigation, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–22 September 2000; pp. 817–826. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Takasu, T.; Kubo, N.; Yasuda, A. Evaluation and calibration of receiver inter-channel biases for RTK-GPS/GLONASS. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS-2010, Portland, Oregon, 21–24 September 2010; pp. 1580–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Leick, A.; Rizos, C.; Stewart, M.P. GPS and GLONASS integration: Modeling and ambiguity resolution issues. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, R. The synergism of GPS code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Satellite Doppler Positioning at Physical Sciences Laboratory of New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA, 8–12 February 1982; Volume 2, pp. 1213–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Melbourne, W.G. The case for ranging in GPS-based geodetic systems. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Wübbena, G. Software developments for geodetic positioning with GPS using TI-4100 code and carrier measurements. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Ye, S.; Zhang, R. Glonass phase bias estimation and its ppp ambiguity resolution using homogeneous receivers. GPS Solut. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banville, S. GLONASS ionosphere-free ambiguity resolution for precise point positioning. J. Geodesy 2016, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y. GLONASS fractional-cycle bias estimation across inhomogeneous receivers for PPP ambiguity resolution. J. Geodesy 2016, 90, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Shi, C. Rapid initialization of real-time PPP by resolving undifferenced GPS and GLONASS ambiguities simultaneously. J. Geodesy 2017, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Yao, Y. A method of undifferenced ambiguity resolution for GPS + GLONASS precise point positioning. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, Q. Rapid PPP Ambiguity Resolution Using GPS + GLONASS Observations. J. Geodesy 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Hajj, G.; Bertiger, W.; Lichten, S. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global mapping function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F.; Mercier, F.; Capdeville, H.; Soudarin, L. CNES-CLS IGS Analysis Centre products: Evaluation and recent improvements. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting. AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–18 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, H.; Brandl, M.; Chen, X.; Drescher, R.; Glocker, M.; Nardo, A.; Nitschke, M.; Salazar, D.; Weinbach, U.; Zhang, F. Towards the inclusion of Galileo and BeiDou/Compass satellites in Trimble CenterPoint RTX. In Proceedings of the 26th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2013), Nashville, TN, USA, 16–20 September 2013; pp. 1215–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, T.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Improving BDS integer ambiguity resolution using satellite-induced code bias correction for precise orbit determination. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Manufacturer | Receiver | Antenna | Dome | Firmware | Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Trimble | NETR5 | TRM55971.00 | NONE | 4.41 | 18 |
| Rover | Trimble (Sunnyvale, California, USA) | NETR5 | TRM55971.00 | NONE | 4.19 | 1 |
| 4.48 | 3 | |||||
| 4.42 | 3 | |||||
| NETR8 | TRM55971.00 | NONE | 4.48 | 1 | ||
| NETR9 | TRM57971.00 | NONE | 4.61 | 1 | ||
| 4.60 | 2 | |||||
| TRM59800.00 | NONE | 4.60 | 1 | |||
| Leica (Heerbrugg, Switzerland) | GR10 | LEIAS10 | NONE | 1.10 | 2 | |
| 2.00/4.007 | 1 | |||||
| GRX1200 + GNSS | LEIAR25 | LEIT | 7.8 | 1 | ||
| TPSCR.G3 | TPSH | 8.51 | 1 | |||
| GRX1200GGPRO | LEIAR25 | LEIT | 7.5 | 4 | ||
| 8.51 | 1 | |||||
| LEIAT504GG | LEIS | 2.62 | 1 | |||
| GX1230GG | LEIAT504GG | LEIS | 5.10 | 1 | ||
| TPS (Tokyo, Japan) | NETG3 | TPSCR.G3 | TPSH | 4.0 | 3 | |
| 3.4 | 2 |
| Time (min) | GPS Only (%) | GPS + GLONASS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No IFCB (%) | With IFCB (%) | ||
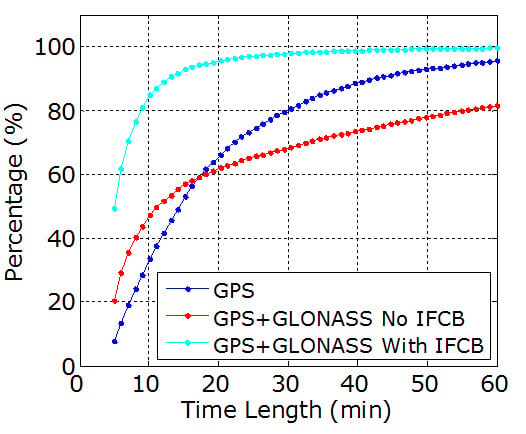
| 05 | 13.23 | 69.94 | 70.22 |
| 10 | 48.98 | 94.80 | 94.81 |
| 15 | 70.03 | 98.27 | 98.23 |
| Manufacture | GPS Only (%) | GPS + GLONASS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No IFCB (%) | With IFCB (%) | ||
| LEICA | 96.69 | 52.52 | 95.91 |
| TPS | 97.33 | 58.11 | 94.53 |
| TRIMBLE | 97.08 | 94.97 | 95.49 |
| Time (min) | GPS Only (%) | GPS + GLONASS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No IFCB (%) | With IFCB (%) | ||
| 05 | 7.43 | 20.41 | 49.14 |
| 10 | 33.52 | 47.14 | 84.88 |
| 15 | 52.92 | 56.92 | 92.86 |
| Manufacture | GPS Only (%) | GPS + GLONASS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No IFCB (%) | With IFCB (%) | ||
| LEICA | 53.19 | 26.51 | 93.44 |
| TPS | 61.83 | 43.90 | 92.34 |
| TRIMBLE | 49.18 | 92.15 | 92.58 |
| Solution Type | North | East | Up |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Only | 0.80 | 0.68 | 2.79 |
| GPS + GLONASS With IFCB | 0.66 | 0.60 | 2.45 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, Q. Calibration of GLONASS Inter-Frequency Code Bias for PPP Ambiguity Resolution with Heterogeneous Rover Receivers. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030399
Liu Y, Gu S, Li Q. Calibration of GLONASS Inter-Frequency Code Bias for PPP Ambiguity Resolution with Heterogeneous Rover Receivers. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanyan, Shengfeng Gu, and Qingquan Li. 2018. "Calibration of GLONASS Inter-Frequency Code Bias for PPP Ambiguity Resolution with Heterogeneous Rover Receivers" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030399
APA StyleLiu, Y., Gu, S., & Li, Q. (2018). Calibration of GLONASS Inter-Frequency Code Bias for PPP Ambiguity Resolution with Heterogeneous Rover Receivers. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030399