Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation and Effective Rainfall Using Gauge Observations, Satellite, and Gridded Climate Data for Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Colorado River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area of Study
2.2. Precipitation Products
2.2.1. TRMM-3B42
2.2.2. PRISM
2.2.3. Daymet
2.2.4. Weather Station Data Source
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Yang Correction for Gauge Precipitation Data
2.3.2. Bias Analysis with Statistical Indices
2.3.3. Bias Correction
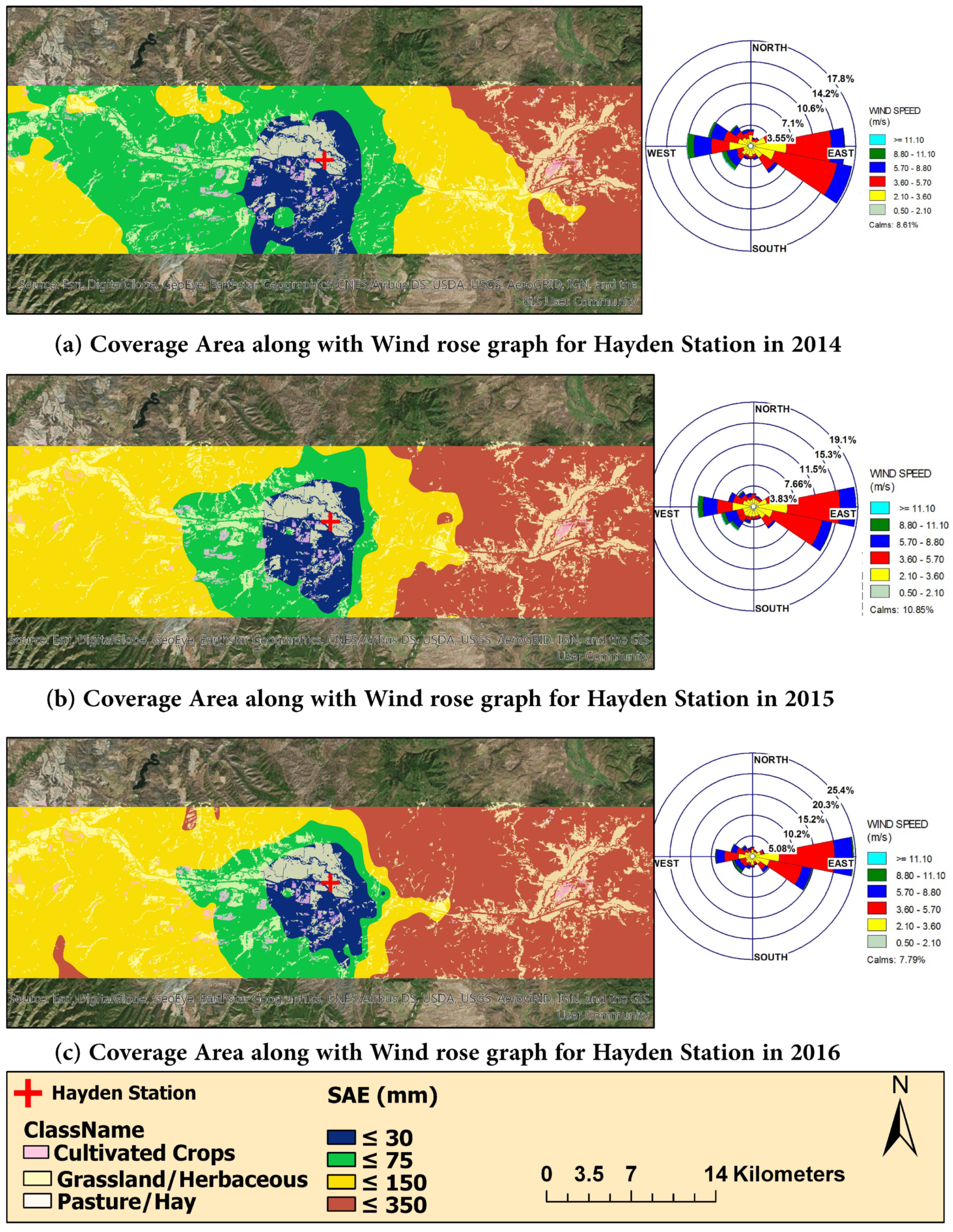
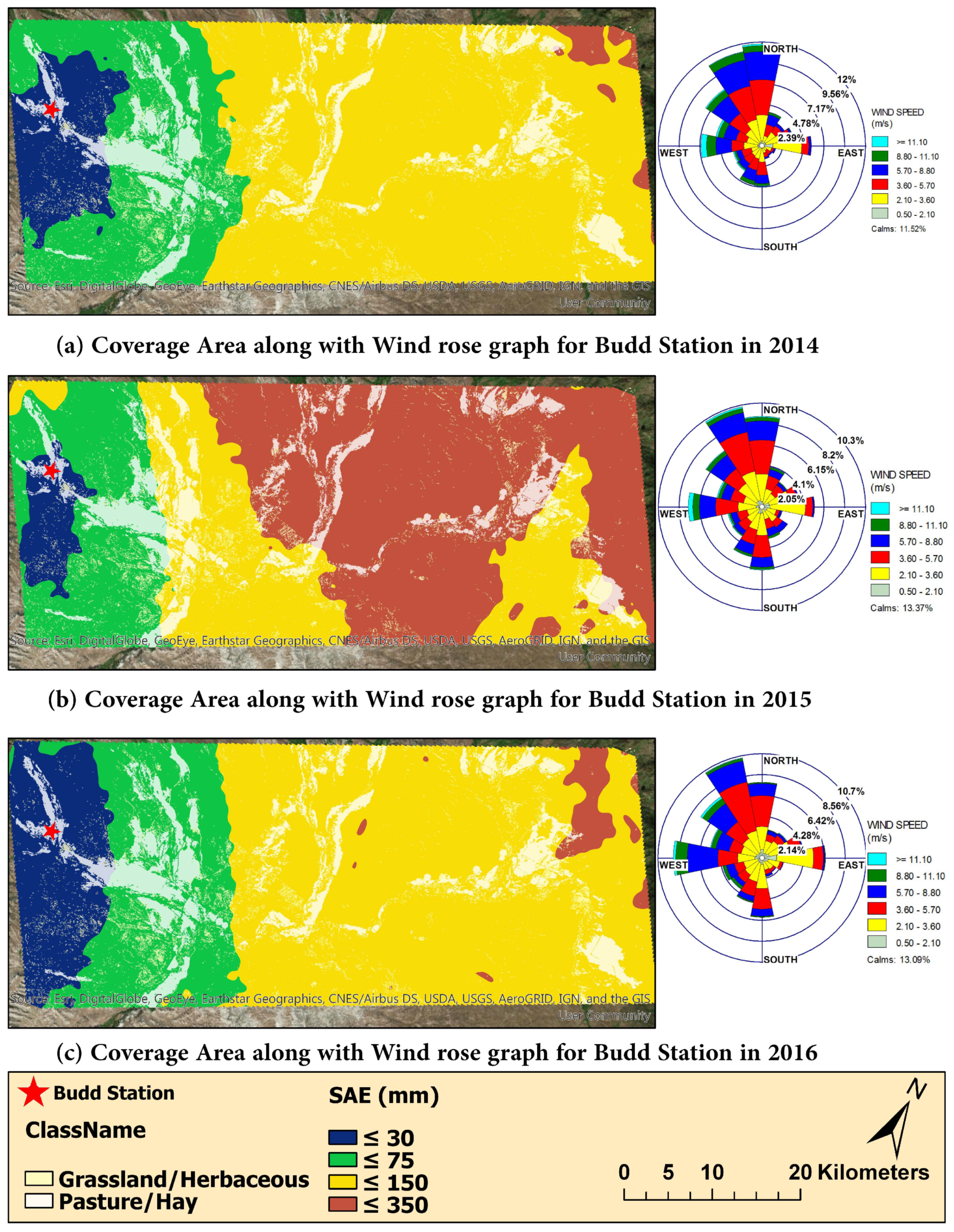
2.3.4. Gauge Coverage Area or Area of Influence
2.3.5. Effective Precipitation Using the USDA-SCS Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Precipitation Resolution Impact
3.2. Yang Correction
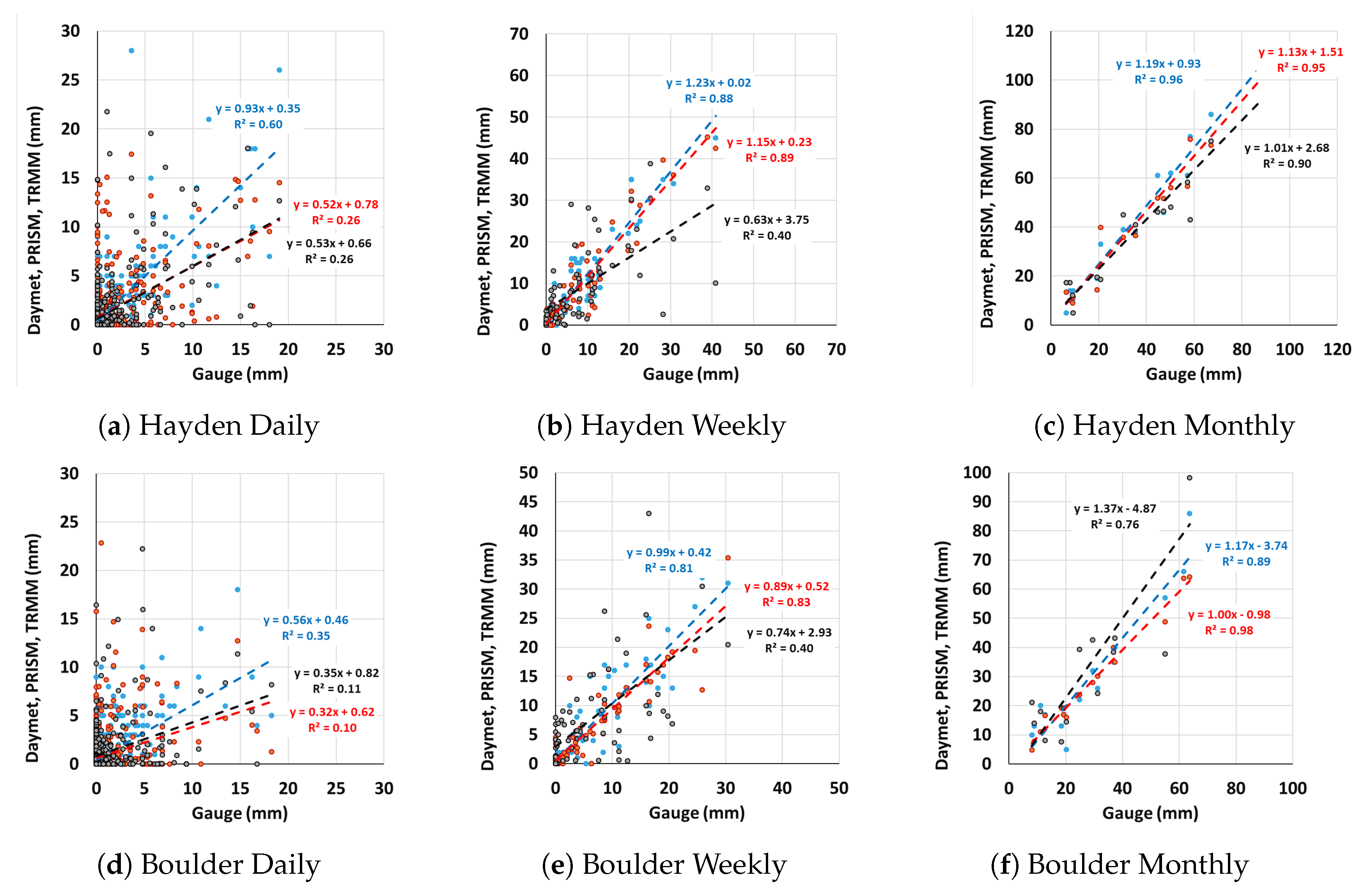
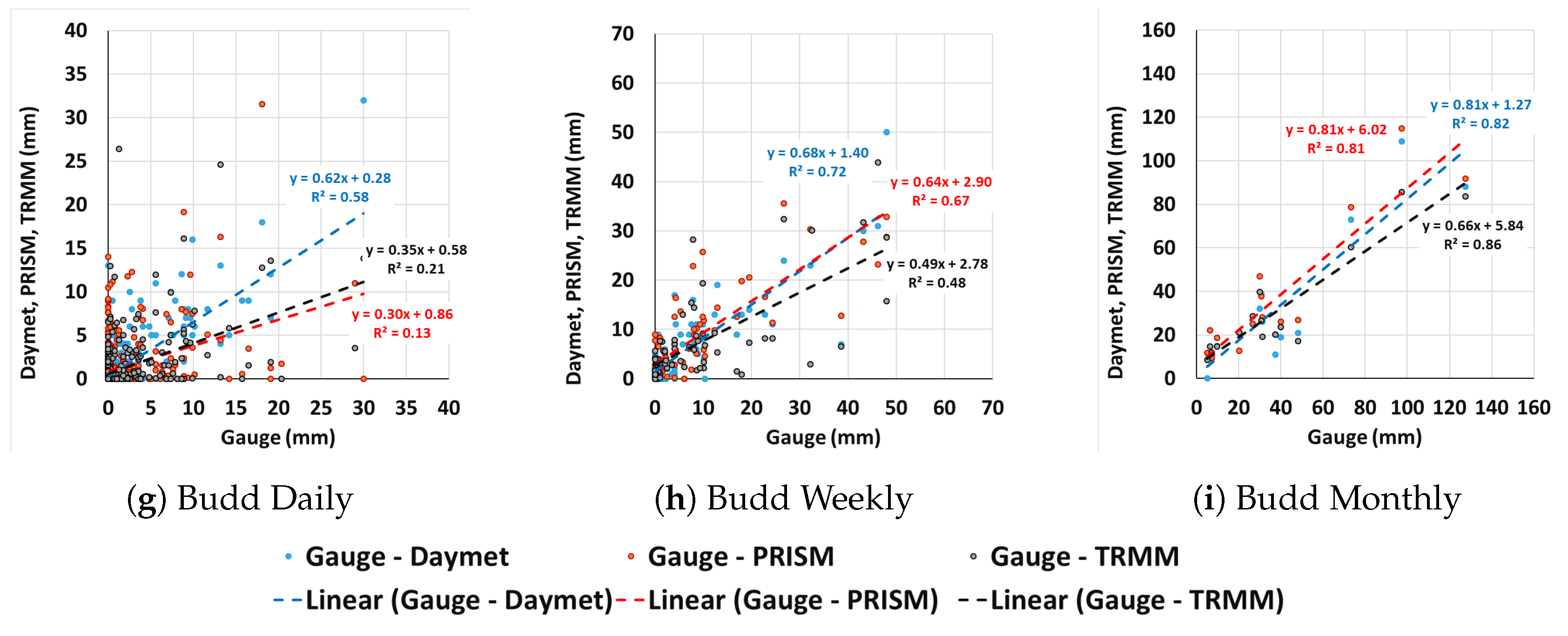
3.3. Spatial Precipitation Bias Analysis
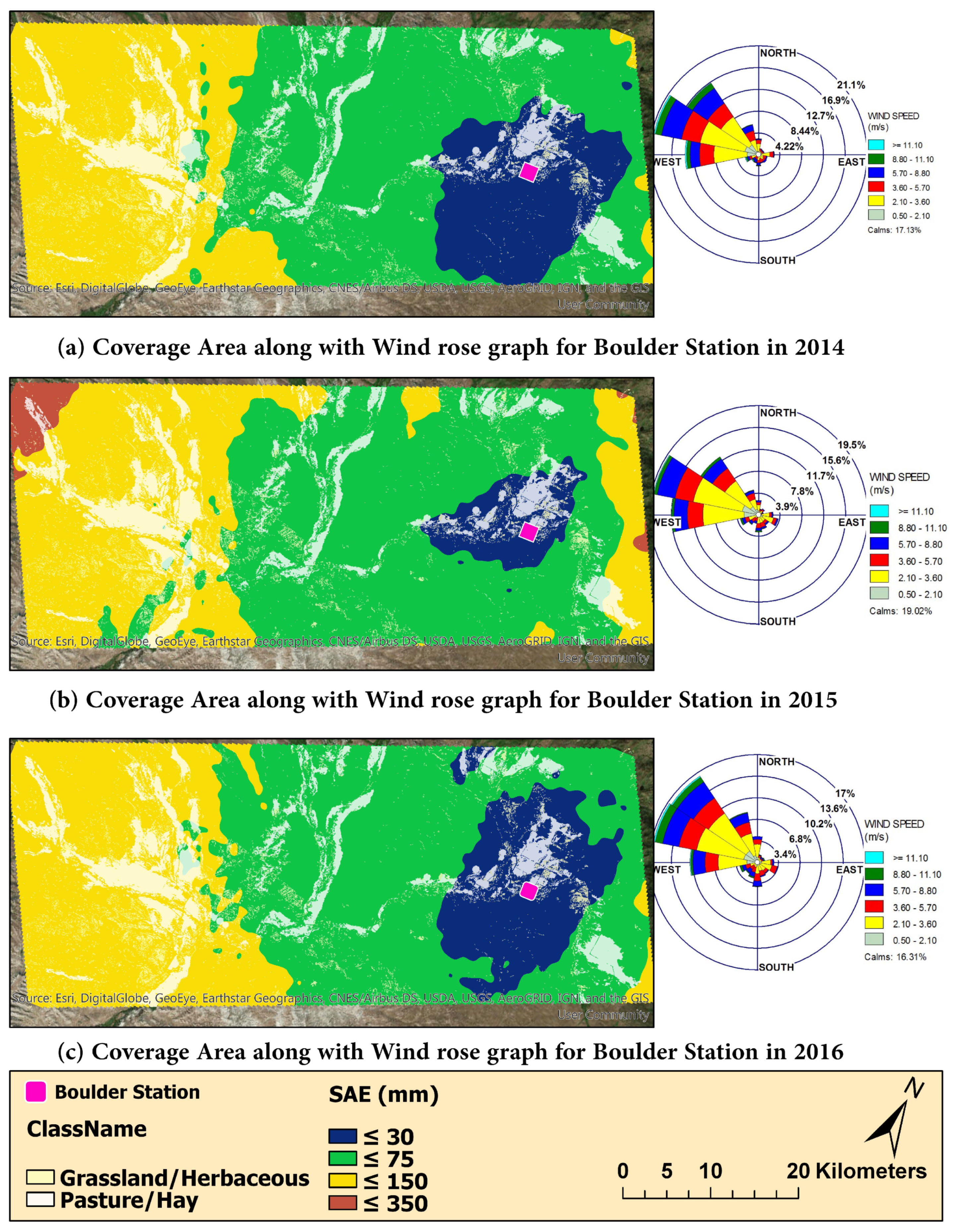
3.4. Weather Station Coverage Area for Rainfall
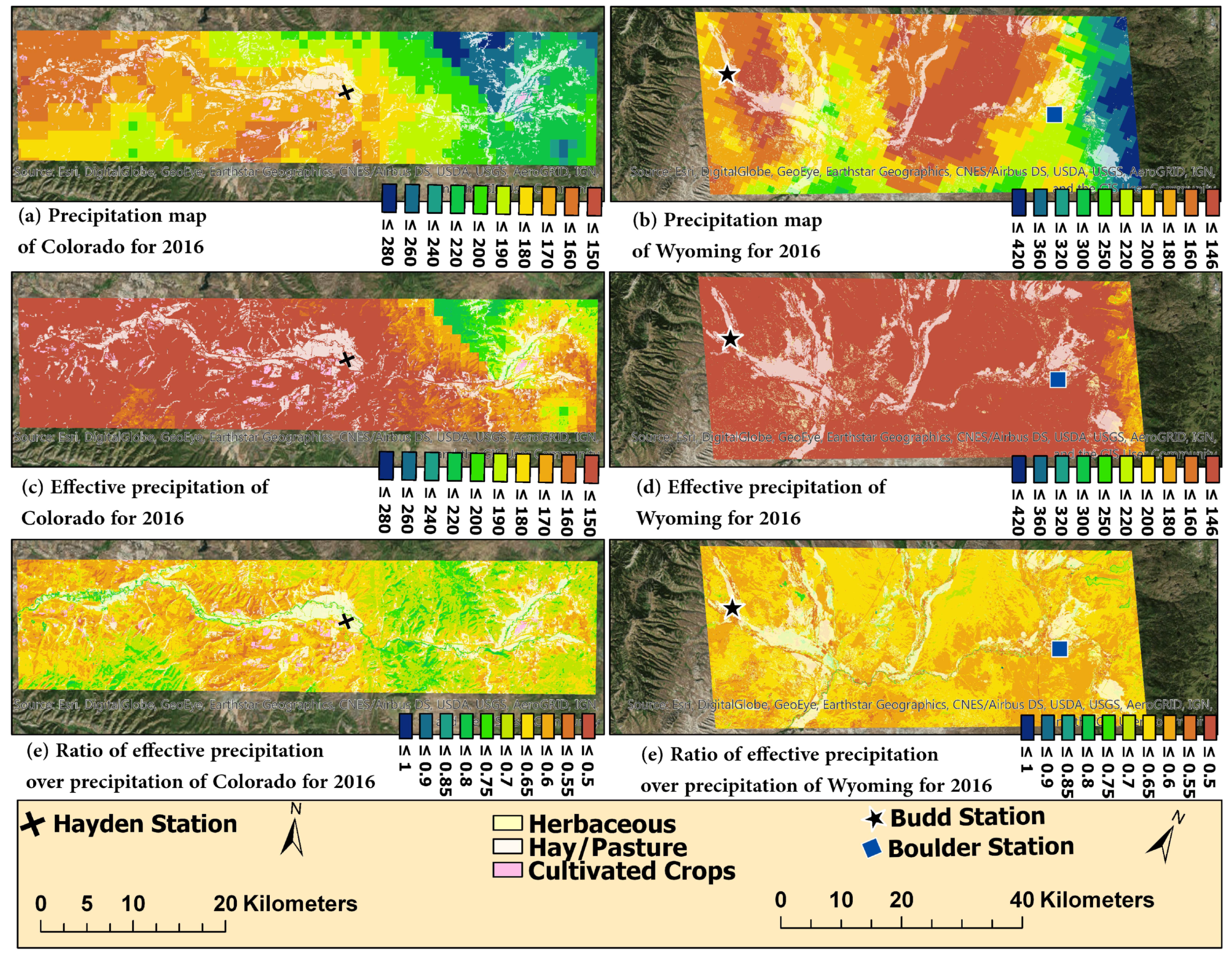
3.5. Spatial Effective Rainfall Estimates
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SGM | Satellite-Gauge-Model |
| GPCC | Global Precipitation Climatology Center |
| 1DD | One-Degree Daily |
| GPCP | Global Precipitation Climatology Project |
| TRMM | Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission |
| CONUS | Contiguous United States |
| GHCN-D | Global Historical Climatology Network-Daily |
| PRISM | Parameter-Elevation Regression on Independent Slopes Model |
| PERSIANN | Precipitation Estimation from Remotely-Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| IDW | Inverse Square Distance Weighting |
| KED | Kriging with the External Drift |
| ET | Evapotranspiration |
| TMI | TRMM microwave imager |
| SSM/I | Special Sensor Microwave Imager |
| AMSU | Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit |
| AMSR-E | Advanced Microwave Sounding Radiometer-Earth Observing System |
| PM | Passive Microwave |
| TIR | Thermal Infrared |
| NLCD | National Land Cover Database |
| SAE | Summation of Absolute Error |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Squared Error |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe model Efficiency |
| USDA | U.S. Department of Agriculture |
| SCS | Soil Conservation Service |
| MRLC | Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics |
| CMAP | The Climate Prediction Center Merged Analysis of Precipitation |
| REP | The Ratio of Effective precipitation over Precipitation |
References
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, F.R.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Keehn, P.R. Global precipitation estimates based on a technique for combining satellite-based estimates, rain gauge analysis, and NWP model precipitation information. J. Clim. 1994, 8, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P. Analyses of global monthly precipitation using gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model predictions. J. Clim. 1995, 9, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, F.R.; Morrissey, M.M.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Joyce, R.; McGavock, B.; Susskind, J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, F.R.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Nelkin, E.J. Tropical Rainfall Distributions Determined Using TRMM Combined with Other Satellite and Rain Gauge Information. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2000, 39, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Arakawa, O.; Kamiguchi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Nodzu, M.I.; Hamada, A. A 44-year daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. 2009, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Kamiguchi, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hamada, A.; Yasutomi, N.; Kitoh, A. APHRODITE: Constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, O.P.; Nelson, B.P. Evaluation of precipitation estimates over CONUS derived from satellite, radar, and rain gauge datasets at daily to annual scales (2002–2012). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2037–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.M. Relation between measured radar reflectivity and surface rainfall. Mon. Weather Rev. 1987, 115, 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, J.; Lee, R. The application of radar-gauge comparison to operational profile corrections. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 2612–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite-based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Grover-Kopec, E.; Lemma, M.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of satellite rainfall products over East Africa’s complex topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1503–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and Its Utility in Hydrologic Prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, P.; Hobouchian, M.P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates over southern South America using a dense rain gauge network. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.C.; Liu, M.F. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products using rain gauge observation over Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xu, X.; Sun, A.Y.; Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Tong, X.; Liu, W. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products using rain gauge data over complex terrain in southwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, H.; You, Y.; Mullens, E.; Hu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, M.; He, L.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, X. Evaluation of high-resolution precipitation estimates from satellites during July 2012 Beijing flood event using dense rain gauge observations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolli, S.; D’Adderio, L.; Campbell, J.R.; Sicard, M.; Welton, E.J.; Binci, A.; Rea, A.; Tokay, A.; Comerón, A.; Barragan, R.; et al. Vertically resolved precipitation intensity retrieved through a synergy between the ground-based NASA MPLNET Lidar network measurements, surface disdrometer datasets and an analytical model solution. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; Bievre, B.; Wyseure, G. Spatial and temporal rainfall variability in mountainous areas: A case study from the south Ecuadorian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberlandt, U. Geostatistical interpolation of hourly precipitation from rain gauges and radar for a large-scale extreme rainfall event. J. Hydrol. 2007, 332, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, J.; Frei, C. Trends of heavy precipitation and wet and dry spells in Switzerland during the 20th century. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Water Requirements, Technical Release; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 21.
- Homer, C.G.; Dewitz, J.A.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.D.; Wickham, J.D.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the conterminous United States-Representing a decade of land cover change information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://mesowest.utah.edu/ (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Available online: https://coagmet.colostate.edu/ (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis: Quasi-Global, Multi-Year, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.A. Physiographically-sensitive mapping of temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Smith, J.I.; Olson, K.V. Mapping atmospheric moisture climatologies across the conterminous United States. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, P.E.; Thornton, M.M.; Mayer, B.W.; Wei, Y.; Devarakonda, R.; Vose, R.S.; Cook, R.B. Daymet: Daily Surface Weather Data on a 1-km Grid for North America; Version 3; ORNL DAAC: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://mrcc.illinois.edu/CLIMATE/ (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Yang, D.; Goodison, B.E.; Ishida, B.; Benson, C.S. Adjustment of daily precipitation data at 10 climate stations in Alaska: Application of World Meteorological Organization intercomparison results. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Mubarak, S. Effective rainfall calculation methods for field crops: An Overview, Analysis and New Formulation. Asian Res. J. Agric. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.G.; Kselik, R.A.L.; Allen, R.G.; Molden, D.J. Water Requirements for Irrigation and the Environment; Springer Science and Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Chapter 3; pp. 81–102. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.L.; Gilley, J.R. National Engineering Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Part 623, Chapter 2; pp. 142–154.
- Brouwer, C.; Prins, K.; Heibloem, M. Irrigation Water Management: Irrigation Scheduling; Training Manual No. 4; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.; Torres-rua, A. Verification of Water Conservation from Deficit Irrigation Pilot Project in the Upper Colorado River Basin; Walton Family Foundation: Sacramento, CA, USA, May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- USDA NASS. Census of Agriculture; USDA NASS: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Ghajarnia, N.; Liaghat, A.; Arasteh, P.D. Comparison and evaluation of high resolution precipitation estimation products in Urmia Basin-Iran. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Li, J.; Feng, P.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Q. Evaluation of multiple satellite precipitation products and their use in hydrological modelling over the Luanhe River basin, China. Water 2018, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Evaluation and hydrologic validation of three satellite-based precipitation products in the upper catchment of the Red River basin, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakes Environmental Software. WRPLOT View—Air Dispersion Modelling; Lakes Environmental Software: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2014; Available online: http://www.WebLakes.com/ (accessed on 18 December 2018).
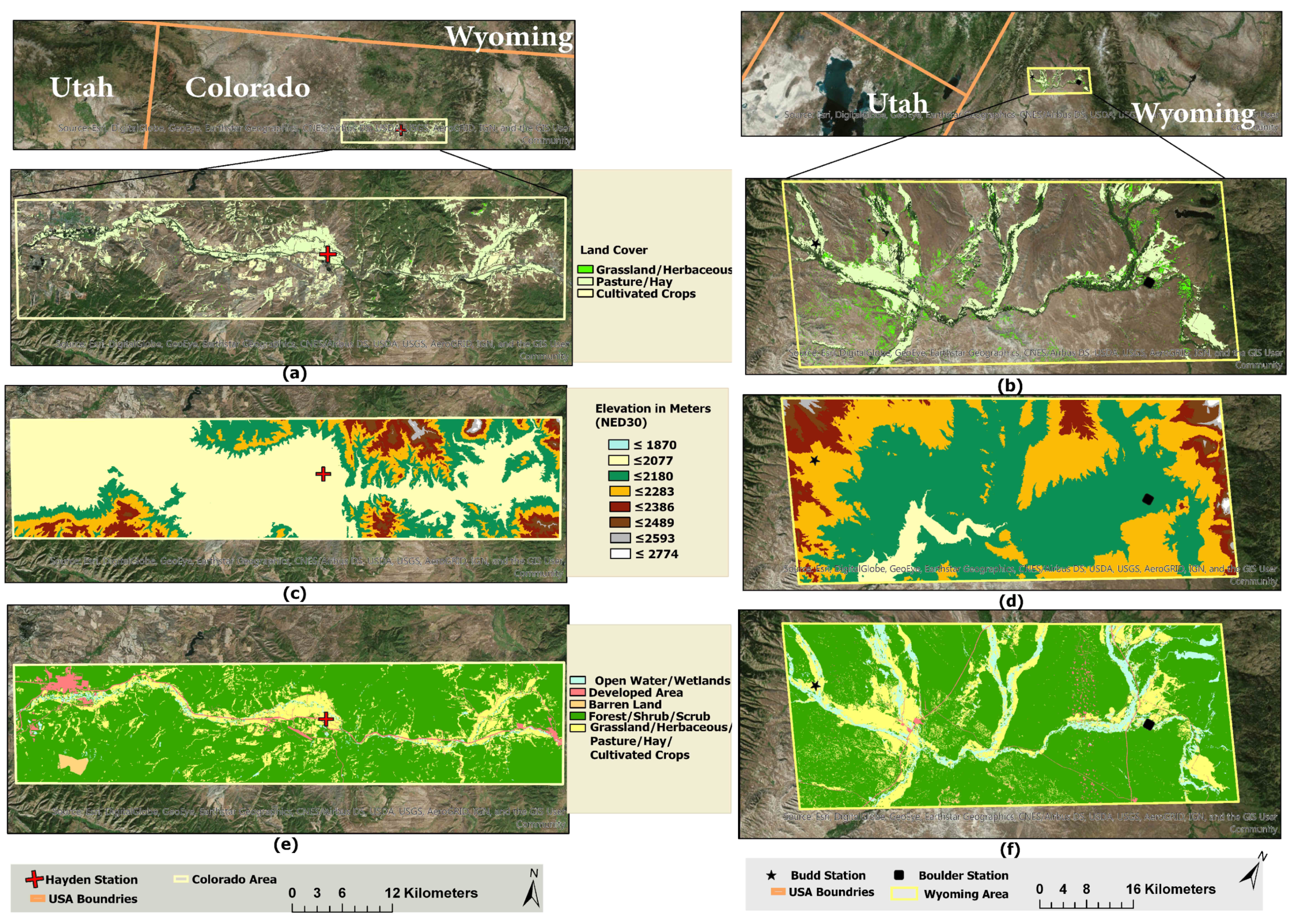
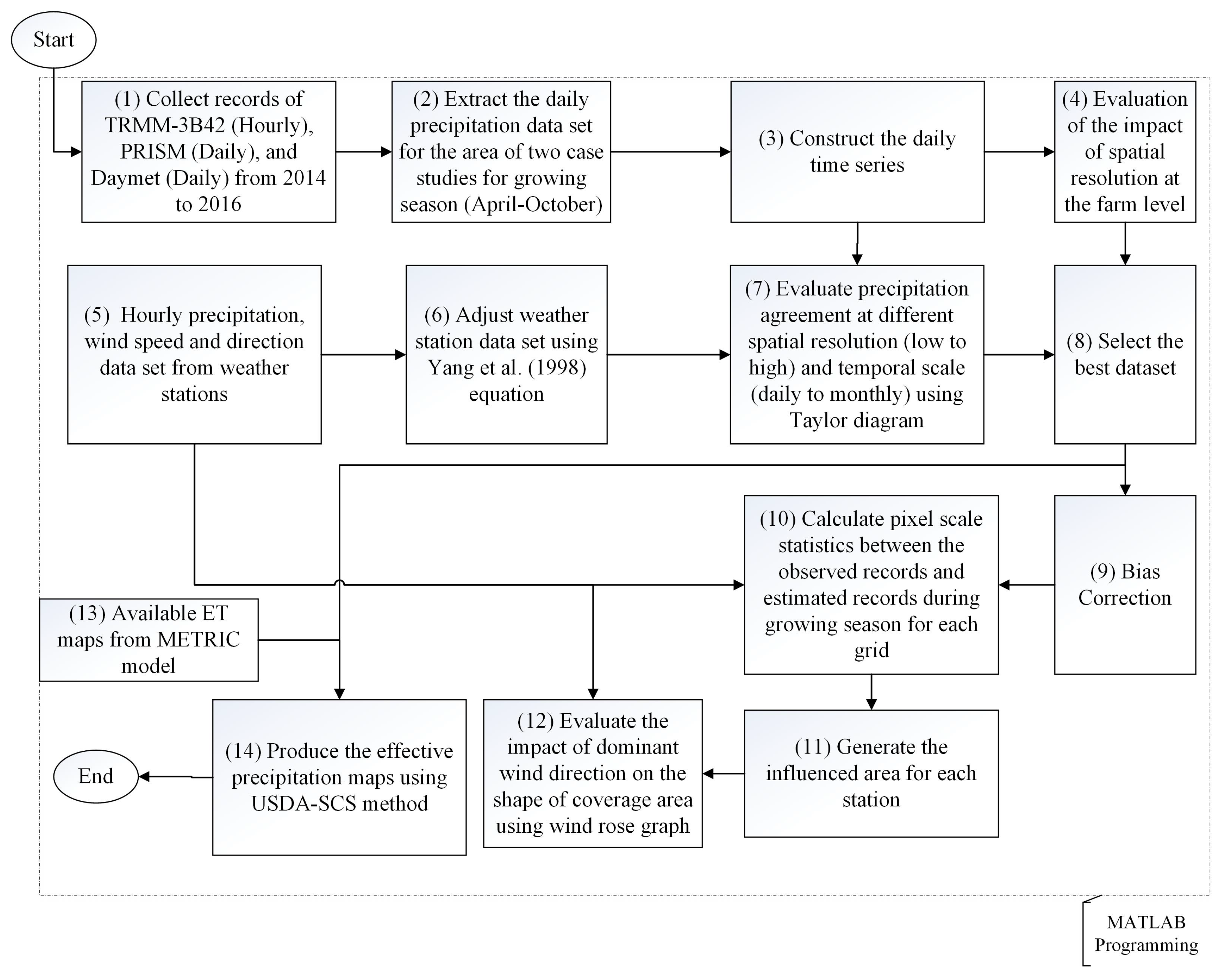

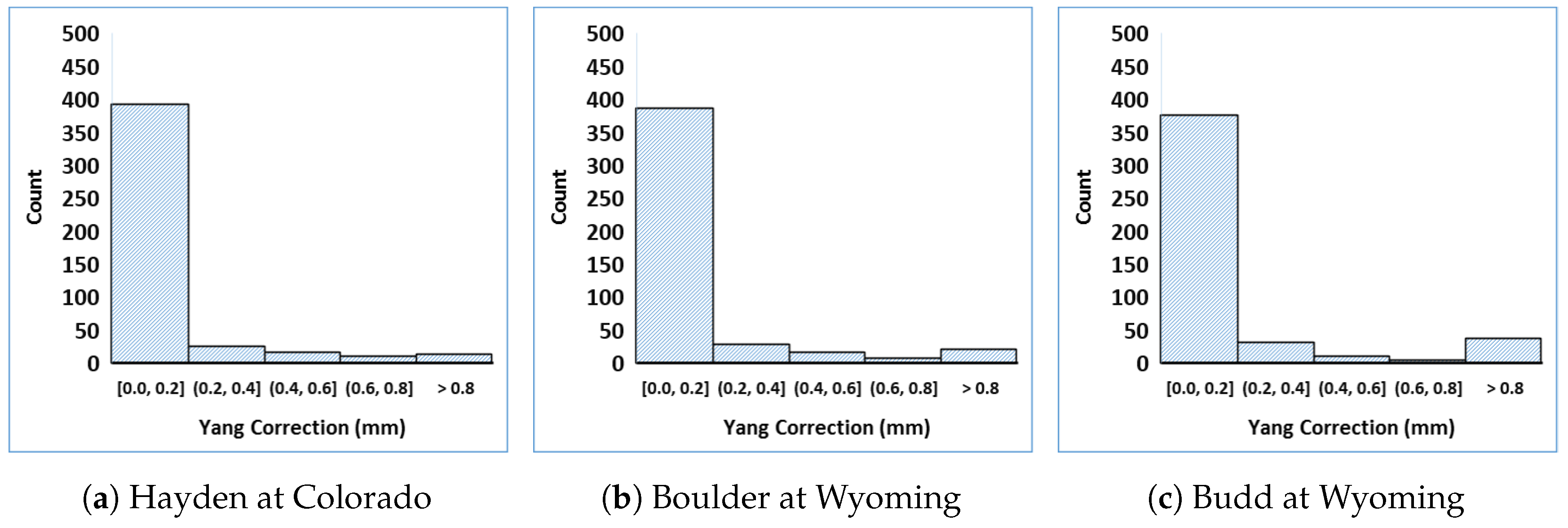
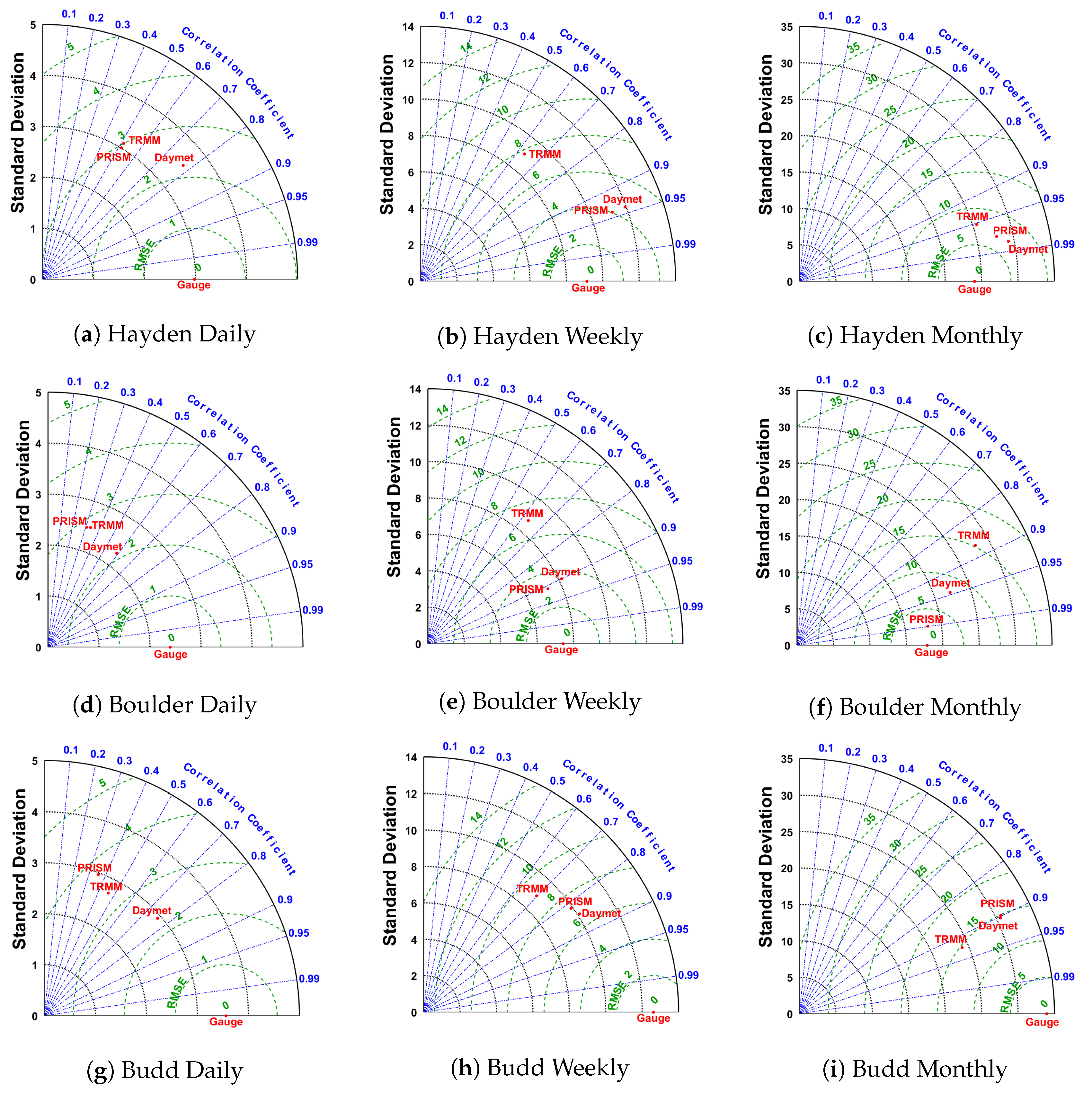
| Precipitation Products | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Latency | Spatial Coverage | Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRMM-3B42 | 0.25° | 3 h | Real time | 50 S–50 N 180 W–180 E | 1998–2018 |
| PRISM | 4 km | Daily | 6 months later | United Sates | 1981–2018 |
| Daymet | 1 km | Daily | 1 year later | United States, Mexico, Canada, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico | 1980–2017 |
| Soil Type | Shallow Rooting Crops | Medium Rooting Crops | Deep Rooting Crops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow and/or sandy soil | 15 | 30 | 40 |
| Loamy soil | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| Clayey soil | 30 | 50 | 70 |
| Station | Datasets | Nash Coeff | SAE (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Weekly | Monthly | Daily | Weekly | Monthly | ||
| Daymet | 0.42 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 411 | 219 | 125 | |
| Hayden | PRISM | 0.01 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 606 | 192 | 102 |
| TRMM | −0.02 | 0.27 | 0.87 | 571 | 346 | 95 | |
| Daymet | 0.21 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 408 | 179 | 86 | |
| Boulder | PRISM | −0.43 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 549 | 145 | 33 |
| TRMM | −0.39 | 0.23 | 0.48 | 624 | 346 | 181 | |
| Daymet | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 408 | 288 | 160 | |
| Budd | PRISM | −0.1 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 749 | 307 | 181 |
| TRMM | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0.76 | 609 | 394 | 183 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboutalebi, M.; Torres-Rua, A.F.; Allen, N. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation and Effective Rainfall Using Gauge Observations, Satellite, and Gridded Climate Data for Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Colorado River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122058
Aboutalebi M, Torres-Rua AF, Allen N. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation and Effective Rainfall Using Gauge Observations, Satellite, and Gridded Climate Data for Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Colorado River Basin. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122058
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboutalebi, Mahyar, Alfonso F. Torres-Rua, and Niel Allen. 2018. "Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation and Effective Rainfall Using Gauge Observations, Satellite, and Gridded Climate Data for Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Colorado River Basin" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122058
APA StyleAboutalebi, M., Torres-Rua, A. F., & Allen, N. (2018). Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation and Effective Rainfall Using Gauge Observations, Satellite, and Gridded Climate Data for Agricultural Water Management in the Upper Colorado River Basin. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122058







