Abstract
Combining pre-disaster optical and post-disaster synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite data is essential for the timely damage investigation because the availability of data in a disaster area is usually limited. This article proposes a novel method to assess damage in urban areas by analyzing combined pre-disaster very high resolution (VHR) optical data and post-disaster polarimetric SAR (PolSAR) data, which has rarely been used in previous research because the two data have extremely different characteristics. To overcome these differences and effectively compare VHR optical data and PolSAR data, a technique to simulate polarization orientation angles (POAs) in built-up areas was developed using building orientations extracted from VHR optical data. The POA is an intrinsic parameter of PolSAR data and has a physical relationship with building orientation. A damage level indicator was also proposed, based on the consideration of diminished homogeneity of POA values by damaged buildings. The indicator is the difference between directional dispersions of the pre and post-disaster POA values. Damage assessment in urban areas was conducted by using the indicator calculated with the simulated pre-disaster POAs from VHR optical data and the derived post-disaster PolSAR POAs. The proposed method was validated on the case study of the 2011 tsunami in Japan using pre-disaster KOMPSAT-2 data and post-disaster ALOS/PALSAR-1 data. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method accurately simulated the POAs with a root mean square error (RMSE) value of 2.761° and successfully measured the level of damage in built-up areas. The proposed method can facilitate efficient and fast damage assessment in built-up areas by comparing pre-disaster VHR optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data.
1. Introduction
Remote sensing techniques have been developed during the past few decades to detect damage induced by natural disasters. Numerous studies have successfully mapped such damage using spaceborne data, particularly optical data and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data, due to its broad sensing ability. The common method to detect disaster-induced damage is based on the change detection technique whereby the data remotely sensed, before and after the disaster, are compared.
Disaster-induced damage should be immediately assessed in order to initiate a prompt rescue operation. Therefore, it is necessary to acquire data shortly after a disaster. In this situation, a SAR is superior to an optical sensor due to its relative insensitivity to the weather and illumination conditions. Several studies have investigated disaster-induced damage using pre and post-disaster SAR data [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Recently, damage investigation has been improved using fully polarimetric SAR (PolSAR) data because it allows more efficient results with its additional polarization scattering mechanism compared to a single polarization mode [5,6].
However, pre-disaster SAR data is less abundant than pre-disaster optical data because optical sensors have traditionally been used. Therefore, the combination of pre-disaster optical data and post-disaster SAR data is regarded as desirable for rapid damage assessment [7]. Due to the significant radiometric and geometric differences between optical and SAR data, it is practically impossible to directly compare the two data. The previous studies using both data have been focused on well integrating different types of information derived from each data for land cover and land use mapping [8,9,10,11]. The research comparing the two data, particularly the pre-disaster optical data and the post-disaster SAR data, for damage mapping has been relatively less conducted [7,12].
To overcome the differences and to enable direct comparison between them, simulation methods have been suggested [7,12]. In these studies, the authors numerically simulated a SAR backscattering signal of an individual building using its geometric parameters estimated from pre-disaster optical data and assessed building damage by comparing the simulated SAR image to an actual post-disaster SAR image. These alternative methods of rapidly detecting disaster-induced damage have been used effectively to assess damage; however, they use very high resolution (VHR) SAR data to detect damage from individual buildings. Consequently, it is difficult to apply these previous methods to the combination of pre-disaster optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data because the fully PolSAR data is relatively coarse.
Considering the advantages of PolSAR data revealed in many applications [5,6,13,14,15], it is worth analyzing the potential of combining pre-disaster optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data for damage detection, but very few studies have used such data combination. Plank et al. [16] used such data combination for landslide mapping. The areas with a high vegetation index value in pre-disaster optical data and a low entropy value in post-disaster PolSAR data were extracted as landslides. The work in Reference [16] showed that combining optical data and PolSAR data is an efficient way to map damage, but it is limited to landslides. Damage detection methods for urban areas, where there can be huge loss of human life and property, are necessary to be developed. Therefore, in this article, we propose a novel method of assessing disaster-induced damage in built-up areas by comparing pre-disaster optical data with post-disaster PolSAR data.
Similar to the previous methods using pre-disaster optical data and post-disaster SAR data [7,12], the proposed method is based on a simulation approach to deal with the extreme differences and to effectively compare the pre-disaster optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data. Numerous polarimetric parameters are derived from PolSAR data [6,17,18,19], and each one relates to different characteristics of ground scatterers. Of the parameters, we focused on the polarization orientation angle (POA) because it has a physical relationship with building orientation [20,21,22], which can be estimated using VHR optical data. Therefore, the proposed method first simulates the pre-disaster POA using pre-disaster VHR optical data. The simulated pre-disaster POA is compared to the estimated post-disaster PolSAR POA to investigate disaster-induced damage. Particularly, the proposed method uses an index, which is the difference between directional dispersions of the pre- and the post-disaster POAs in a small built-up area, to measure the damage level.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows. In Section 2, we briefly review POA shifts in built-up areas. In Section 3, we describe the three steps of the proposed method in detail: (1) Post-disaster PolSAR POA estimation, (2) pre-disaster POA simulation using VHR optical data, and (3) damage assessment. In Section 4, we evaluate the performance of the proposed method using KOMPSAT-2 data and ALOS/PALSAR-1 data acquired before and after the 2011 tsunami in Japan, respectively. In Section 5, we provide the conclusion.
2. POA in Built-Up Areas
A POA is an inherent parameter of PolSAR data and one of three parameters of the polarization ellipse describing the wave polarization of a scatterer—amplitude A, orientation angle , and ellipticity angle , as depicted in Figure 1a [23]. The POA is defined by the angle between the major axis of the polarization ellipse and the horizontal axis. The received POA from a scatterer is changed if the surface of the scatter is not horizontal. The shift of the POA is affected by the slopes of the tilted surface and radar look angles, as in Equation (1):
where is the radar incidence angle, and tanω and tan are the slopes of the surface in the azimuth (i.e., flight) direction and the ground range directions, respectively [24,25].
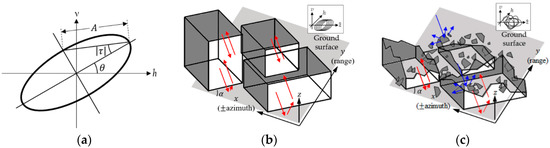
Figure 1.
(a) Polarization ellipse; (b) Illustration of the polarization orientation angle (POA) in a built-up area for oriented buildings; and (c) Illustration of the POA changes in a built-up area for damaged buildings. Red lines indicate the reflections from the walls with the rotation angle along the azimuth direction. Blue lines indicate the reflections from damaged parts of buildings.
When analyzing the received signal of PolSAR data, the neighboring pixels are usually spatially averaged (i.e., multi-looked) to reduce speckle noise or to make a nearly square azimuth and range pixel size. In built-up areas, numerous complicated features are spread out, and the size of the averaged pixel is enough to cover several features. The observed POA is therefore a mixture of different POA shifts induced by the surfaces of various urban features. Buildings, which are the most dominant scatterers in built-up areas, induce deterministic POA shifts because they are uniformly distributed in a certain scale of area. On the contrary, other built-up features, such as vehicles or trees on a street, randomly induce POA shifts. Consequently, the observed POA of a built-up area is usually affected by the buildings.
Kimura [22] established a scattering model for built-up areas where there are three surfaces of the two major scatterers, the surrounding ground and the roof and the wall of a building. As the surface of the surrounding ground in built-up areas is commonly horizontal (i.e., and are zero), there are no POA shifts due to the ground. In addition, the roofs do not induce POA shifts as they are almost flat. The amount of POA shift induced by a vertical wall is defined as Equation (2) because and tan in Equation (1) are converted to (π/2 − ) and zero, respectively. In:
α is the rotation angle of the vertical walls along the azimuth direction, as described in Figure 1b. The relationship between the POA and the building direction has been demonstrated by the experimental results in References [20,21,22]. The relationship between POAs and building directions has been expected to enable various applications for built-up areas, including building detection and characterization [23], a process to retrieve building parameters such as shape and height [26].
A group of parallel buildings induces similar POA shifts determined by Equation (2), and the neighboring POAs therefore appear homogeneous. When the buildings partially or entirely collapse as the result of a disaster, the remaining buildings and surrounding debris randomly induce POA shifts, and the POAs in built-up areas appear as random values (Figure 1c). The damaged areas are detectable by comparing two estimated POAs. The study in Reference [5] verified that the POA became fluctuated after the tsunami and proposed an efficient index for damage investigation in built-up areas. The index in Reference [5] is the standard deviation of the differences between pre and post-tsunami POAs sorted in descending order.
3. The Proposed Method
Figure 2 shows a block diagram of the proposed method, which consists of a preprocessing step and three main steps. The preprocessing step of PolSAR data is required for registration, as described in Section 3.3.1. The three main steps are: (1) Post-disaster PolSAR POA estimation; (2) pre-disaster POA simulation using VHR optical data; and (3) damage assessment. A detailed explanation of each step is as follows.
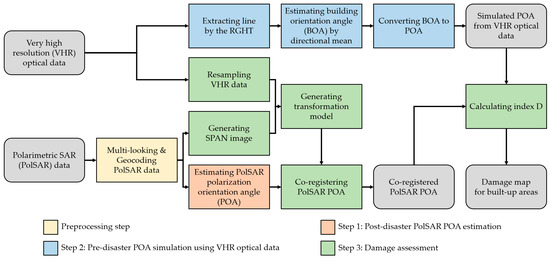
Figure 2.
Block diagram of the proposed method. The regular grid-based Hough transform (RGHT) is the line extraction method proposed by Yeom and Kim [27]. A SPAN image represents the total scattering power of PolSAR data as Equation (9). An index D is the damage level indicator proposed in this article as Equation (13).
3.1. Step 1: Post-Disaster PolSAR POA Estimation
PolSAR data is represented using the scattering matrix S in Equation (3), as follows:
where Shv indicates the backscattering of the horizontal transmitting and vertical receiving polarizations; the other terms are defined in a similar way. The multi-looked PolSAR data can be represented by the covariance matrix or the coherency matrix [28]. The coherency matrix T based on the reciprocity condition (Shv≈Svh) is defined as:
where indicates averaging and k = [Shh + Svv Shh − Svv Shv]T is a Pauli scattering vector. The superscripts * and T denote the complex conjugate and the transpose, respectively.
There are several methods to estimate POA from PolSAR data [24,29,30,31]. The most efficient method was proposed by Lee et al. [24]. They modified and refined the POA estimation method based on the circular polarization proposed in [31] and investigated why their method worked well [25]. According to the method in [24], the POA is calculated using the components of the coherence matrix, as follows:
where Re(T23) is the real part of T23 and nπ (n = 0, 1) is necessary to prevent the coherency matrix from being rotated toward the wrong axis [24,32]. The range of the estimated POA is limited from −45 to 45.
3.2. Step 2: Pre-Disaster POA Simulation Using VHR Optical Data
The purpose of this step is to simulate pre-disaster POAs as accurately as possible to assess disaster-induced damage instead of perhaps absent pre-disaster PolSAR POAs. According to Equation (2), two factors are necessary for simulating POAs in built-up areas—the rotation angle of the vertical walls along the azimuth direction α and the radar incidence angle ϕ. The latter is determined by the geometry of the PolSAR platform. Therefore, the major challenge in this step is to estimate accurate building orientations. Fortunately, the building orientations can be accurately estimated using VHR optical data because they are appropriate for building characterization based on the excellent visibility of the optical data.
The building orientations are estimated using a simple new technique proposed in this article instead of building detection techniques already proposed in References [33,34,35,36,37]. Such previous techniques are not suitable to estimate the building orientations because they cannot automatically detect all buildings, which has been constantly argued in References [33,35,36]. Furthermore, the spatial resolution of post-disaster multi-looked PolSAR POAs is generally sufficient to cover multiple small buildings in one pixel; therefore, estimating dominant orientation of a group of buildings is appropriate for pre-disaster POA simulation. The orientation of an individual building detected by the previously developed building detection technique incurs additional computational costs. Therefore, the proposed technique is optimized for estimating the major orientation of a group of buildings. The spatial resolution of the estimated building orientations is the same as that of the post-disaster multi-looked PolSAR data to be compared.
In general, multiple buildings are uniformly distributed and parallel to neighboring roads. Consequently, they exhibit noticeable lines, and the building orientation of a group of buildings is determined using those lines. The proposed estimation technique of building orientation using VHR optical data is based on the lines and consists of three steps: (1) Line extraction using the regular grid-based Hough transform (RGHT) [27]; (2) building orientation angle (BOA) estimation using directional mean; and (3) converting the estimated BOA to POA. A BOA is an angle between a building wall and the x-axis direction of the VHR optical image. These three steps are described in detail in the subsequent sections.
3.2.1. Line Extraction Using the RGHT
Lines are representative features in the built-up areas; therefore, many urban applications have used them [35,36,37,38,39]. The Hough transform (HT) [40] is the common line extraction method in such applications. The HT was originally developed in the computer vision field, and numerous applications have demonstrated its advantages [41,42]. However, it has some limitations when applied to remote sensing data. One is that the HT has a high computational cost because remote sensing data includes numerous edges [43,44]. The HT also neglects the connectivity among edges [45] and extracted inappropriate lines from built-up areas where objects are complexly concentrated. Therefore, Yeom and Kim [27] proposed a RGHT to solve such problems. The RGHT extracts the HT lines from each grid and extends them between neighboring grids. The RGHT is a simple, bottom-up method that efficiently extracts lines at buildings and roads without omission [27].
Most of the VHR optical satellites acquire data via not only the panchromatic (Pan) band, but also via several multi-spectral (MS) bands. As the spatial resolution of the Pan image is generally four times better than that of the MS images, the dominant lines in built-up areas are extracted from the Pan image. The popular Canny edge operator [46] generates an edge image that the line extraction method will be applied to. To extract sufficient noticeable lines in built-up areas, the size of the regular grid is set to 10 pixels (i.e., 10 m in the KOMPSAT-2 Pan image), which is appropriate for the detection of most urban features, and the peak number parameter is four. These parameters were the same as those in Reference [27], which efficiently extracted lines from urban objects. Figure 3 shows the line extracted by the RGHT with the above-mentioned parameters. As expected, the lines well delineate the major objects in built-up areas.
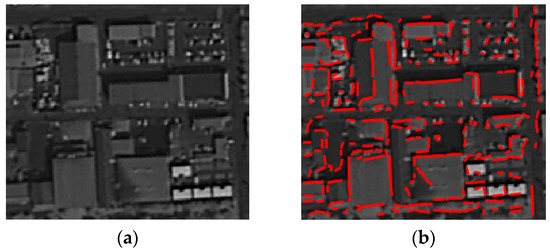
Figure 3.
(a) Original very high-resolution (VHR) panchromatic (Pan) image; and (b) Lines extracted by the regular grid-based Hough transform (RGHT) (red lines).
3.2.2. BOA Estimation Using Directional Mean
As mentioned, we estimate a BOA in a certain area, called the window in this article, as wide as the spatial resolution of post-disaster PolSAR data. Because of the complicated objects in built-up areas, there are several broken lines extracted by the RGHT in the window. As they well delineate built-up objects parallel to buildings, as shown in Figure 3b, their directions are relevant to the building directions. The mean angle of the disconnected lines in the window is considered a BOA. It is obvious that the simple mean generally used is inappropriate for angular data. For example, the simple mean of two angular values 1 and 359 is 180; however, the ideal mean should be 0. To solve this problem, we apply the directional statistic technique to calculate the mean angle.
Suppose there are n angular observations, , , , …; the directional mean is given by [47]:
where and . n is zero if and , n is 1 if , and n is 2 if , and . v’ is defined as:
where the range of an angular data is [a, b), as Equation (6) is defined as assuming the angular observations range [0, 360). The angles of line direction have a range from 0 to 180. Furthermore, the original formulas and do not consider the lengths of the lines that can be used as the weights. We modified them to include the length of each line l to be and .
Unfortunately, some of the lines could be irrelevant to building direction because the RGHT extracts sufficient lines in built-up areas without omission. Such false lines are generally extracted from randomly distributed objects such as vehicles in parking lots as presented in Figure 3b. Even though these lines are usually short and have low weights, they distort the mean angle calculated by Equation (6) and should be eliminated to improve the accuracy of the estimated BOAs.
To reduce the effects of the false lines, the directional mean angle is calculated twice. First, a directional mean angle of all the extracted lines in a window is calculated. Due to the low weights of some incorrect lines, the calculated value tends to be close to the major building direction in the window. The incorrect lines are far from the first mean value. Therefore, the BOA is determined by the second directional mean angle calculated with the selected lines, the angles of which are ±15 from the first mean value.
It is found that the RGHT extracts lines from the boundaries of shadows, as shown in Figure 3b. These lines can be a problem when a number of high-rise buildings are located in a built-up area. The false lines from the shadows of the high-rise buildings are normally long and parallel to the sun azimuth angle. Thus, the first directional mean value from such area can be dissimilar to the major building direction. The VHR optical data with a high sun elevation angle can reduce the errors by the shadows of the high-rise buildings. When such optical data is not available, the false lines from the shadows of the high-rise buildings can be removed using the sun azimuth angle of optical data before calculating the first mean value.
3.2.3. Converting BOA to POA
POAs in built-up areas are calculated using Equation (2) with the accurately estimated BOAs from the previous step. However, the estimated BOAs are oriented angles along the x-axis direction of the VHR optical Pan image, which does not correspond to the azimuth direction of the PolSAR image. As the numerator of Equation (2) is a BOA along the azimuth direction of PolSAR data, the estimated BOA should be adjusted considering the difference in angles between the x-axis direction of the VHR optical data and the azimuth direction of the PolSAR data. The adjusted BOA is denominated as BOAaz in this article.
The incidence angle is another factor in POA simulation. Due the geometry between the PolSAR platform and the earth surface, the incidence angle changes along the range direction. Fortunately, the incidence angle of spaceborne PolSAR data, which is very suitable for investigating disaster-induced damage, does not dramatically change along the range direction. Therefore, the fixed value, particularly the approximate incidence angle at the center of post-disaster PolSAR image, can be used in the denominator of Equation (2). Additionally, the incidence angle should be changed if the airborne PolSAR data, the incidence angle of which varies significantly, is used. The POA using VHR optical data is simulated using Equation (8), defined as:
where (n = 0, 1) is necessary for the simulated POA value and has a range from −45 to 45 the same as the PolSAR POA in Equation (5).
3.3. Step 3: Damage Assessment
3.3.1. Image Registration
To accurately investigate disaster-induced damage, the simulated pre-disaster POA and the estimated post-disaster PolSAR POA must be well registered. Image registration refers to aligning two images to have the corresponding coordinates through a geometric transformation performed on one of the images [48]. The transformed image is the sensed image, and the other is the reference image. Unfortunately, the derived POAs are inappropriate for finding the optimal geometric transformation between the data covering diverse land cover because their physical relationship is restricted to the built-up areas. Therefore, the transformation model is optimized using the Pan image of VHR optical data and the SPAN image of the PolSAR data instead of using the POAs. The optimized transformation model is then applied to a POA.
Methods for image registration are generally classified into two categories, area and feature-based techniques. The former use pixel intensity values of two images to find optimal geometric transformation. The latter uses reliable features, such as lines and points. Considering the difficulties in extracting common features between optical and SAR data, we adopt the area-based method to register the Pan and SPAN images. The SPAN image represents the total scattering power of the PolSAR data, as follows:
where Tij is the ijth component of the coherency matrix in Equation (4).
SPAN = T11 + T22 + T33,
If two images are well registered, the similarity between their pixel intensity values is high. The normalized mutual information (MI), which is the modified version of the MI in Reference [49], is used to measure the similarity. The MI is an extensively used measurement and is robust to nonlinear radiometric differences, which is the typical relationship existing between optical and SAR data [50]. The normalized MI is less sensitive to changes in image overlap than the original MI. The normalized MI of two images A and B can be described as:
where H(A) and H(B) are the marginal entropies of A and B, respectively, and H(A, B) is their joint entropy [49].
To simplify the registration process, all the PolSAR data are geocoded to the same map projection of the VHR optical data using the metadata after the multi-looking process. The Pan image is down-sampled to the same resolution of the geocoded SPAN image that is relatively coarse. In this way, the rotation and scale differences between the images are eliminated, and only differences in the translation of the x- and y- directions remain. There are usually dozens of pixels between the down-sampled Pan image and the geocoded SPAN image. Consequently, the final transformation of the sensed image can be described as:
where (x’, y’) is the transformed coordinate of a pixel in the sensed image, and (x, y) is the original coordinate. p and q are the offsets in the x- and y- directions, respectively. The reference image is fixed, and the sensed image is moved over the reference image from [−20, 20] pixels in both the x- and y- directions at one pixel spacing. The MI value is calculated with every movement. The parameters at the maximum MI value are assumed as the optimum offset, p and q, in Equation (11). In this article, the offsets are estimated using the down-sampled Pan image as the reference image and the geocoded SPAN image as the sensed image. The PolSAR POA is transformed according to Equation (11) with the optimum offsets. The transformed PolSAR POA is expected to be well aligned with the simulated POA from VHR optical data.
3.3.2. Index for the Damage Assessment
The POA values are homogeneous in a small built-up area where the buildings are regularly orientated. After those buildings are physically damaged, the destroyed buildings and the surrounding debris induce random POA values, as depicted in Figure 1c. As the damage level increases, the reflections from the damaged parts become stronger and they overwhelm the homogeneous reflections from the undestroyed parts of the buildings. Therefore, the homogeneous POA values in the small built-up area become heterogeneous. The usefulness of this change between pre and post-disaster POA distributions for damage assessment on a city block scale was demonstrated in Reference [5] using the standard deviation of the differences between pre and post-disaster POAs.
Considering that the POA is angular data, we use a directional dispersion , defined as Equation (12), instead of the common standard deviation. The directional dispersion is similar to the standard deviation.
and are defined in Equation (6). The range of is from 0 to 1. A value of 0 means that the angular observations are uniformly dispersed. On the contrary, a value of 1 means that they are completely concentrated [47]. The relatively homogeneous pre-disaster POAs show higher value than the post-disaster POAs.
As the reduction of homogeneity in POAs in the small built-up area due to the disaster, the value of post-disaster POAs decreases. Consequently, the difference between the values of pre and post-disaster POAs is a good index for damage assessment. The proposed index D using the directional dispersion is defined as:
where and are the directional dispersions of pre- and post-disaster POAs in the small area. The size of the small area is set at 5 by 5 pixels in this article, which is determined by considering the average block size of the study site. A positive value of D is only considered for damage assessment and ranges from 0 to 1. The index D value represents the damage level in built-up areas since the higher the D value is, the more severe the damage induced by the disaster.
The objective of this study is to investigate disaster-induced damage using a combination of pre-disaster VHR optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data, which enables fast investigation of the damage. Therefore, the index D is calculated with the simulated pre-disaster POAs from VHR optical data and the post-disaster POAs from PolSAR data, which have the corresponding coordinates through the previous registration process.
4. Study Site and Data Description
An earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred off the Northern Pacific coast of Japan in the Tohoku region and induced a catastrophic tsunami with a maximum height up to 40 m on 11 March 2011. The study site is located in the city of Ishinomaki, Miyagi prefecture, reported as the most severely damaged prefecture, with 83,003 completely collapsed buildings and 155,130 partially destroyed buildings [51].
Table 1 shows the remotely sensed data used for mapping damage caused by the 2011 Japan tsunami in built-up areas by comparing the simulated pre-tsunami POA using VHR optical data to the estimated post-tsunami POA from PolSAR data. The VHR optical data for the pre-tsunami was acquired on 1 October 2009 by KOMPSAT-2, of which the spatial resolutions for the Pan and MS images are one m and four m, respectively. Figure 4 shows the false color image of KOMPSAT-2 data as replacing the red channel of the RGB composition by the near infrared (NIR) band. The vegetated areas, such as forests and croplands, are distinctly red compared with the built-up areas. There is no high-rise building in built-up areas.

Table 1.
Description of the remote sensing data.
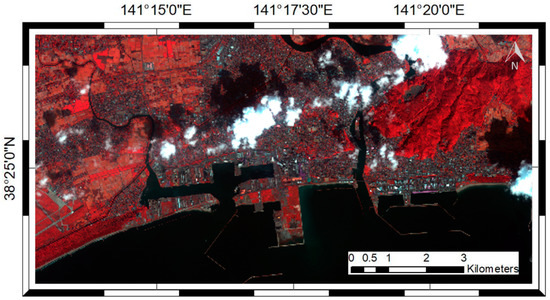
Figure 4.
False color image of KOMPAT-2 data on 1 October 2009. NIR, green, blue images are assigned to the RGB channel.
The post-tsunami SAR data in fully polarimetric mode was acquired by the ALOS/PALSAR-1 on April 8. As the L-band PolSAR data is in better agreement with Equation (2) than X-band [22], ALOS/PALSAR-1 data is thought appropriate to investigate damage in built-up areas using the POA shifts. To verify the usefulness of the pre-tsunami POA simulation step described in Section 3.2, the pre-tsunami fully polarimetric ALOS/PALSAR-1 data acquired on April 2, 2009 was used. The spatial resolutions of the two single-look PolSAR data are very similar since they have the almost same acquisition parameters with the nearly identical viewing configuration (Table 1). There was a light rainfall with the total precipitation of 0.5 mm during the 12 h before the pre-tsunami data acquisition. In addition, there was no rainfall during the 12 h before the post-tsunami data acquisition [52].
To register the KOMPSAT-2 data and the ALOS/PALSAR-1 data, the single-look ALOS/PALSAR data were preprocessed, as aforementioned in Section 3.3.1. A seven-look multi-looking process in the azimuth direction was first performed on both single-look PolSAR data in order to make their azimuth and range pixel size nearly square. The multi-looking process also reduces inevitable speckle noise of PolSAR data. The coordinates of the multi-looked PolSAR data do not correspond with that of the VHR optical data. Therefore, the multi-looked PolSAR data were geocoded to the map projection of KOMPSAT-2 data, Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) 54N with the World Geodetic System (WGS)-84 datum using the ALOS/PALSAR-1 metadata. The spatial resolution of the geocoded PolSAR data is 25 m using the nearest neighboring approach.
Figure 5a,b shows the pre and the post-tsunami Pauli RGB images of ALOS/PALSAR-1, respectively. The noticeable changes between the two images are mainly located in croplands. Tsunami-induced damage in built-up areas is difficult to be delineated by comparing two Pauli images. Consequently, various polarimetric parameters derived from fully PolSAR data have been alternatively used for the damage mapping [5,6,16]. The extreme differences between KOMPSAT-2 and ALOS/PALSAR-1 data found between Figure 4 and Figure 5b indicate that damage assessment using the pre-disaster VHR optical data and the post-disaster PolSAR data is problematic. Therefore, we proposed the novel method based on the simulation approach to facilitate comparing the two data.
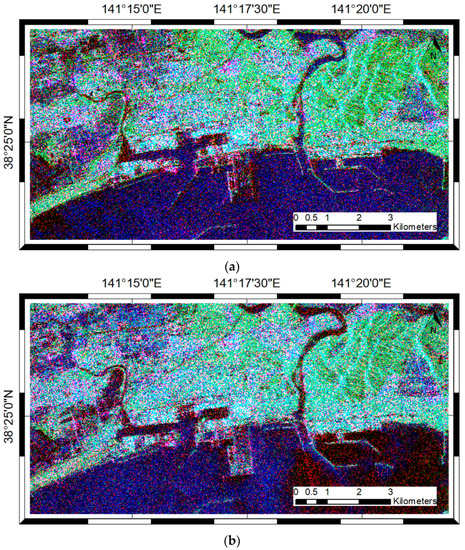

Figure 5.
Pauli RGB images of (a) ALOS/PALSAR-1 on April 2, 2009; and (b) ALOS/PALSAR-1 on 8 April 2011. , , and are assigned to the Pauli RGB channel.
The performance of the proposed index D for the damage assessment defined as Equation (13) was examined using the reference data. The reference data is the building damage map of the 2011 tsunami occurred in Japan and the building damage was interpreted using aerial photos [53]. As shown in Figure 6, the reference map does not cover the entire area of the study site. The building damage types at the study site were classified into five categories—high, low, and inundated damaged, undamaged, and unknown. It is found that the buildings near the seashore were severely damaged by the tsunami, as expected. Even though some clouds cover several areas in the KOMPSAT-2 image, they do not affect the performance validation of the proposed method because they do not cover the areas near the seashore, which are mainly damaged by the tsunami.
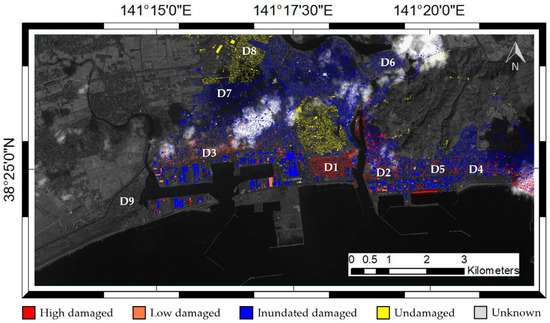
Figure 6.
Map of building damage [53]. The building damage is categorized into five classes: High, low, and inundated-damaged, undamaged, and unknown. The locations of the nine selected districts for the validation, described in Section 5.2, are labeled as D1 to D9. The base image is the panchromatic image of the KOMPSAT-2 data.
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. POAs from ALOS/PALSAR-1 and KOMPSAT-2 Data
Figure 7 shows the PolSAR POAs derived from the pre- and the post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data using Equation (5). The built-up areas manually delineated using the VHR optical data are highlighted with black lines. It is found that the POA values of the built-up areas are relatively homogeneous compared to areas with other types of landcover, such as forests and croplands. The homogeneous values are caused by the groups of parallel buildings, as mentioned in Section 2. The built-up areas can be divided into several homogeneous patches according to their dominant POA values. Some of them in Figure 7a near the seashore have fluctuated POA values in the post-tsunami POAs, as shown in Figure 7b. It is expected that the damaged areas can be distinguished, based on the difference between the POA distributions.
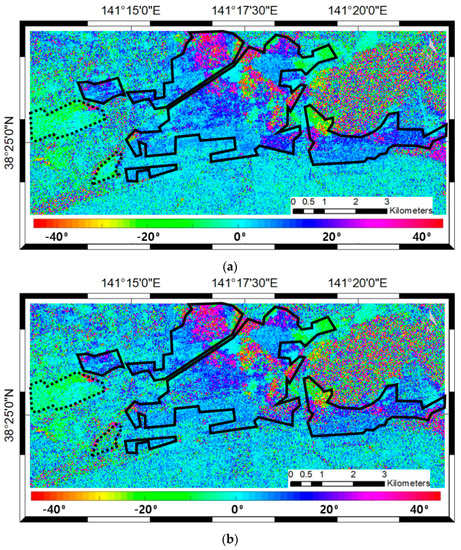
Figure 7.
Estimated POAs using PolSAR data: (a) POAs from ALOS/PALSAR-1 on 2 April 2009;and (b) POAs from ALOS/PALSAR-1 on April 8, 2011. The range of the PolSAR POAs is from −45° to 45°. The densely built-up areas are highlighted with black solid lines. The areas highlighted with black dotted lines are the sparsely built-up areas.
Figure 8a shows the estimated BOA using the proposed approach based on the RGHT and the directional means. The built-up areas at the study site can be divided into similar small patches of the pre-tsunami PolSAR data in Figure 7a. It shows that the POA values in built-up areas were affected by building directions defined as the theoretical model in Equation (2). To simulate POA from the estimated BOA, the incidence angle was assumed to be 23.836, which corresponded to the incidence angle of post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data (Table 1). The azimuth direction angle to the North was assumed to be 22, which was an estimated value because the azimuth direction was omitted in the metadata of the ALOS/PALSAR-1 data.
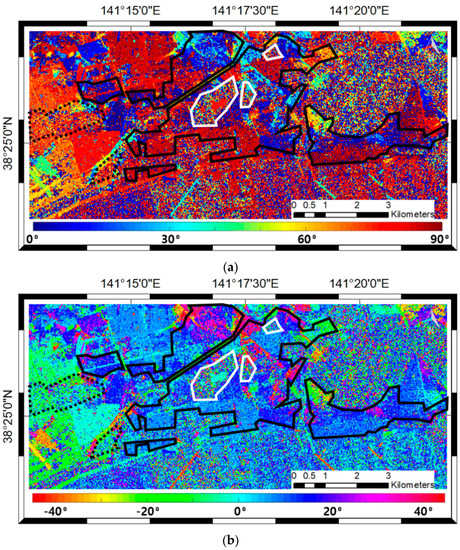
Figure 8.
Results from the POA simulation step using KOMPSAT-2 data: (a) The estimated BOAs. The range of the BOAs is adjusted from 0° to 90° considering that the typical shape of urban buildings is rectangular; and (b) the simulated POAs with 23.836° of the incidence angle from post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data and 20° of the azimuth direction angle to the North. The range of the simulated POAs is from −45° to 45°. The densely built-up areas are highlighted with solid black lines, while the sparse built-up areas are highlighted with dotted black lines. The clouds are highlighted with white lines.
Figure 8b shows the simulated POAs using the KOMPSAT-2 data. As the geometry of the ALOS/PALSAR-1 sensor and the earth’s surface is almost consistent, the simulated POAs can be compared to the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs in Figure 7a, assuming there were no serious changes in built-up areas between the acquisition dates of the pre-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data and the KOMPSAT-2 data.
The simulated POAs in Figure 8b are similar to the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs in Figure 7a in built-up areas. The slight differences between them are inevitable. The simulated POAs are mainly determined by the lines; therefore, the small randomly distributed scatterers, such as small vegetation, cannot affect the simulation results. On the contrary, the PolSAR POAs are a mixture of the signals reflected by all the scatterers in each resolution cell. Furthermore, the simulated POAs are distorted where the line features are vague or particularly distinct. The vague lines are found in suburban areas where the sparse buildings cannot form continuous lines. These areas are highlighted with black dotted lines in Figure 7 and Figure 8. The pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs are homogeneous in these areas, whereas the simulated POAs are not. The particularly distinct lines are found near an artery, such as a highway, where there are numerous line features, although few vertical surfaces exist. Moreover, these distinct lines are sometimes irrelevant to building orientations. Consequently, the proposed simulation approach is specialized for densely built-up areas.
To validate the accuracy of the proposed simulation method, we quantitatively compared the simulated POA and the estimated pre-tsunami PolSAR POA. The comparison was restricted to densely built-up areas. The 15 small regions where neighboring buildings were uniformly oriented were selected from the KOMPSAT-2 Pan image. The selected regions have various actual BOAs that are manually measured.
As the simulated POAs are highly correlated with the estimated BOAsaz, the accuracy of BOAsaz was first evaluated (Table 2). The root mean square error (RMSE) of the estimated BOAsaz for the 15 selected areas is 2.956°. The minimum difference between them is −3.055°, and the maximum is 6.522°. These values indicate that the building orientation in a window was accurately estimated by the simple approach using the RGHT and the directional means. Furthermore, Table 2 shows the directional means and dispersions of the simulated POA values and the pre-disaster PolSAR POA values for the 15 selected areas. The RMSE between the directional means is 2.761°. The scatter plot in Figure 9 shows the directional means of the simulated POAs versus the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs for each selected region. The scatter plot with a R2 value of 0.986 confirms that the simulated POAs are in good agreement with the PolSAR POAs. The quantitative comparison demonstrated that the PolSAR POAs in built-up areas can be accurately simulated from the VHR optical data using the proposed approach. This implies the simulated POAs can be alternatively used when the pre-tsunami PolSAR data is unavailable.

Table 2.
Comparison of the simulated polarization orientation angles (POAs) and the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs ().
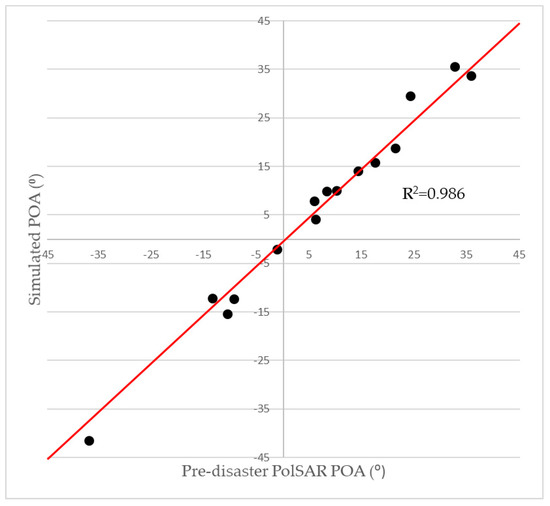
Figure 9.
The directional means of the simulated POA versus the pre-tsunami PolSAR POA for the 15 selected regions. The red line indicates that the two POAs are corresponding.
5.2. Tsunami-Induced Damage Investigation
In this section, we validate the performance of the proposed index D for damage assessment in built-up areas and the possibility of replacing the pre-tsunami PolSAR POA with the simulated POA from VHR optical data. Three index D maps representing the tsunami-induced damage level were generated using the different pairs of the extracted POAs, as shown in Figure 10. The densely built-up areas focused on in this article are highlighted with solid red lines. The sparsely built-up areas and the clouds are referentially highlighted with dotted red lines and white lines, respectively.
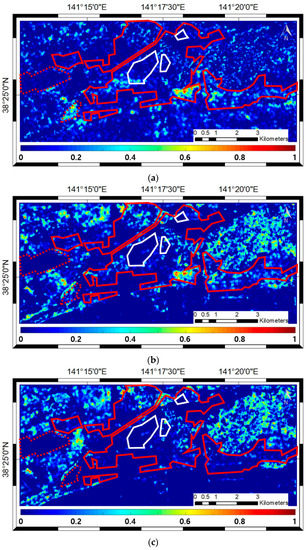
Figure 10.
Damage level map by the index D using: (a) The pair of pre- and post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data (P1); (b) the pair of pre-tsunami KOMPSAT-2 data and post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data (P2); and (c) the pair of pre-tsunami KOMPSAT-2 data and pre-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data (P3). The index D values range from 0 to 1. The higher the D value is, the higher the damage level is. The built-up areas with high and low density are highlighted with red solid and dotted lines, respectively. The clouds are highlighted with white lines.
We first visually compared the damage level map produced using the pair of pre and post-tsunami PolSAR POAs (called P1 for convenience) in Figure 10a with the reference building damage map in Figure 6. The high and low damaged buildings in the reference data were considered because only physical damage affects the distribution of POA values, which determines the index D values. It is observed that physically damaged areas are distinguishable by the index D values. The noticeable small areas with the high index D values in Figure 10a are the areas where the high and low damaged buildings are concentrated according to the reference map in Figure 6.
These small areas in Figure 10a also have high index D values in Figure 10b, which is the damage level map generated using the pair of simulated pre-tsunami POAs from KOMPSAT-2 data and post-tsunami PolSAR POAs (P2). It indicates that the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs can be substituted with the simulated POAs for damage assessment. For further validation, the map is produced using the pair of simulated POAs and PolSAR POAs for the pre-tsunami case (P3), as shown in Figure 10c. The index D values seem lower than those of the maps using P1 and P2, and the areas determined to be physically damaged according to the other maps are not conspicuous in Figure 10c.
For a quantitative evaluation, nine built-up districts with different damage levels are manually delineated. The location of each district is labeled on the reference map (Figure 6). The damage level was approximately estimated by referring not only to the reference map, but also to the images from Google Earth because the reference map does not cover the entire study site. There are four categories of the damage level, as in Reference [5]: 80–100% (D1, D9), 50–80% (D2, D3), 20–50% (D4, D5), and 0–20% (D6-D8). The high damage level indicates a severely damaged area. D9, where buildings are sparse, was referentially selected.
The means of the index D values of each district from the damage maps produced by three different pairs, P1, P2, and P3, were calculated, as shown in Table 3. It is observed that the mean values of the index D from P1 successfully distinguishes the level of damage in built-up areas. The value in D1 is 0.383, while in D7 it is 0.020. The other values of D2 to D6 from P1 increase as the damage level increases. The tendency of the values in P1 continues in the mean values of P2, although the mean values of each district in P1 and P2 are not exactly same. The values from P2 are 0.443, 0.276, 0.151, and 0.023 for D1, D2, D4, and D6, respectively. Figure 11 diagrammatically represents the increase in the mean values of D1 to D7 in P1 and P2 as the damage level increases. The quantitative evaluation shows that the index D values can assess the damage level in built-up areas and the simulated pre-disaster POAs from VHR optical data can replace pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs. The mean values of D8 relatively high compared to the mean values of D6 and D7, which have the same damage level of D8. A possible reason is discussed in Section 5.3.

Table 3.
The mean value of the index D of districts with various levels of damage.
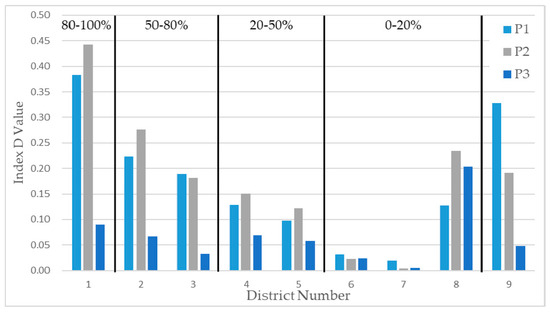
Figure 11.
The mean values of the index D values in each selected district from P1, P2, and P3. The damage level is annotated in the graph. The locations of the nine districts are labeled in Figure 6.
The index D values from P3 should be low because there was no physical damage in built-up areas between the simulated pre-tsunami POAs and the pre-tsunami PolSAR POAs. Table 3 and Figure 11 show that the mean values from P3 are low and not related to the damage level. The values of D1 to D5 from P3 are relatively low compared to those from P1 and P2. No districts among D1 to D5 are determined as considerably damaged based on the values from P3. The highest value among them, 0.090 of D1, is lower than the any values of D1 to D5 from P2 and D1 is determined as almost undamaged. Furthermore, the values of D6 and D7, the damage levels of which are 0–20%, from P3 are similar to the values from the other pairs.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to establish an exact quantitative relationship between the index D values and the damage level due to the limited data, and the index D values, therefore, cannot determine the specific damage level in this article. The damage level in this article is divided into the four categories, and the damage level of each district was approximately estimated based on the reference data and the images from Google Earth. Moreover, there is an insufficient number of districts in the study site for estimating the quantitative relationship. Nonetheless, it is obvious that the damage level map presented by the index D values in Figure 10b, which is generated using the pre-tsunami KOMPSAT-2 data and the post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data, can offer sufficient and important information of disaster-induced damage to initiate a rapid rescue operation.
5.3. Limitations of the Proposed Approach
The values of D8 and D9 in Table 3 show the limitations of the proposed method for investigating disaster-induced damage. One limitation is that an area with POA values close to 45° or -45° is possibly classified as damaged, according to the index D value. For instance, the mean of the index D values of D8 for P2, 0.234, is as high as those of the districts such as D1 to D3 that are more than 50% damaged (Table 3). It is caused by the low directional dispersions in areas with PolSAR POAs around 45° or −45°. The index D was designed based on the assumption that a directional dispersion of POAs in a small built-up area is reduced after damage occurs. However, the areas with PolSAR POAs around 45° or −45° is already low before damage occurs. In practice, Table 2 shows that the directional dispersions in areas with PolSAR POAs around 0 are high, and those around 45° or −45° are low.
A possible reason for the low directional dispersion values is the unstableness of arctangent induced by the denominator of Equation (5), as discussed in detail in Reference [21]. This certain problem with Equation (5) is that the results have a small area with a directional mean of POAs around 45 or −45 and have a low directional dispersion value of PolSAR POAs, even though buildings are physically intact. In contrast, the directional dispersions of the simulated POAs are independent of their directional mean values, as shown in Table 2. Consequently, the damage levels in such areas tend to be overestimated by the index D values from P2. The unstableness of arctangent further affects the damage assessment using P1, the pair of the pre and the post-tsunami PolSAR POA. The mean value of D8 from P1, 0.127, is high, although the estimated damage level is 0–20%. This limitation is manifested in Figure 10, as the areas with high index D values, where the buildings are physically intact, are located in the areas with POAs around 45° or −45°, according to Figure 7a.
A possible solution to this limitation is to use multiple post-disaster POAs with various azimuth directions. If there are two PolSAR data with 45° differences between the azimuth directions, the proposed method can effectively assess damage in any oriented built-up areas. In this respect, the airborne PolSAR data are advantageous because an azimuth direction of spaceborne SAR is restricted. Furthermore, using airborne data may enable assessment of individual building damage due to its fine resolution. However, the incidence angle of the airborne PolSAR data dramatically varies along the range direction, and PolSAR POA tends to be overestimated with a large incidence angle [21]. For accurate damage assessment using pre-disaster VHR optical data and multiple post-disaster airborne PolSAR, the proposed method should be modified based on the characteristics of airborne PolSAR data.
In addition, the proposed method failed to assess the damage level of a suburban area, D9. According to the value of D9 from P2, D9 is regarded as 50–80% damaged compared to the values of D1–D7 from P2. However, the actual damage level of D9 is 80–100%, manually determined using the Google Earth images. According to the value of D9 from P1, the damage level of D9 can be correctly determined. It is reasonable because the proposed simulation technique cannot precisely simulate POAs from VHR optical data in suburban areas, where buildings were sparsely distributed, as mentioned in Section 5.1. Since the proposed approach in this article is specialized at the densely built-up areas, damage in areas with other types of landcover cannot be investigated. To improve the damage assessment results, the proposed method can be refined using other advanced methods, such as in References [16,54], which are available for other land cover types.
6. Conclusions
A novel method of assessing disaster-induced damage using pre-event VHR optical data and post-event PolSAR data has been developed and evaluated. To achieve this, an approach to simulate POAs in built-up areas was proposed based on the relationship between POAs and building orientations. An index D was also proposed to present the damage level as considered that damaged buildings induce changes in the distributions of POA values. The index was calculated by subtracting the directional dispersion of the post-disaster POAs from that of the pre-disaster POAs at a certain scale of the built-up area. The experimental results demonstrated the usefulness of the proposed method. First, it well simulated the intrinsic parameter of PolSAR data, POA, using VHR optical data. Second, the proposed damage assessment method based on the index D can measure the level of damage. Finally, damage in built-up areas induced by the 2011 tsunami in Japan was successfully assessed using pre-tsunami KOMPSAT-2 data and post-tsunami ALOS/PALSAR-1 data.
The achievement in this article is expected to facilitate efficient and fast disaster-induced damage assessment, as the combination of pre-disaster VHR optical data and post-disaster PolSAR data is desirable for timely damage assessment. Furthermore, our approach is meaningful because it is the first to simulate a polarimetric parameter using optical data. The simulation approach can be used not only in damage assessment, but also in other applications related to built-up areas.
The two limitations of our approach will be overcome in the near future. One is that damage in the areas with PolSAR POAs around 45 or −45 tends to be overestimated. The other is that the method is concentrated on densely built-up areas, as a POA is quantitatively correlated with a building orientation. These problems can be resolved by using multiple PolSAR data with various azimuth directions and by combining the proposed method with other methods available for other land cover types.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.; Data curation, M.J. and J.Y.; Formal analysis, M.J.; Funding acquisition, Y.K.; Investigation, M.J. and J.Y.; Methodology, M.J. and J.Y.; Project administration, Y.K.; Resources, Y.K.; Software, M.J. and J.Y.; Supervision, Y.K.; Validation, M.J.; Visualization, M.J.; Writing—original draft, M.J.; Writing—review & editing, J.Y. and Y.K.
Funding
This work was supported by Global Surveillance Research Center (GSRC) program funded by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) and Agency for Defense Development (ADD).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yonezawa, C.; Takeuchi, S. Decorrelation of SAR data by urban damages caused by the 1995 Hyogoken-nanbu earthquake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, G.A.; Bijker, W.; Kerle, N.; Tolpekin, V.A. Coherence-and amplitude-based analysis of seismogenic damage in Bam, Iran, using ENVISAT ASAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Pierdicca, N.; Emery, W.J. Exploiting SAR and VHR optical images to quantify damage caused by the 2003 Bam earthquake. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Wang, D. Automatic detection of terrain surface changes after Wenchuan earthquake, May 2008, from ALOS SAR images using 2EM-MRF method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-W.; Sato, M. Tsunami damage investigation of built-up areas using multitemporal spaceborne full polarimetric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kim, D. Polarimetric SAR remote sensing of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake using ALOS/PALSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Lemoine, G.; Bruzzone, L. Earthquake damage assessment of buildings using VHR optical and SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 48, 2403–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Ticehurst, C.J.; Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Donald, G.E.; Henry, D. Integration of optical and radar classifications for mapping pasture type in Western Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1665–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarsaikhan, D.; Blotevogel, H.H.; Van Genderen, J.L.; Ganzorig, M.; Gantuya, R.; Nergui, B. Fusing high-resolution SAR and optical imagery for improved urban land cover study and classification. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, G.V.; Liesenberg, V.; Chen, Q.; Guerriero, L.; Frate, F.D.; Bartolini, A.; Coomes, D.; Wilebore, B.; Lidsell, J.; Valentini, R. Optical and SAR sensor synergies for forest and land cover mapping in a tropical site in West Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapoğlu, N.G.; Eltoft, T. Decision fusion of classifiers for multifrequency PolSAR and optical data classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), Istanbul, Turkey, 12–14 June 2013; pp. 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-L.; Jin, Y.-Q. Postearthquake building damage assessment using multi-mutual information from pre-event optical image and postevent SAR image. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Schon, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Potential of estimating soil moisture under vegetation cover by means of PolSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yeh, A.G.O.; Li, X.; Lin, Z. A novel algorithm for land use and land cover classification using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, M.; Susaki, J. Urban-area extraction from polarimetric SAR images using polarization orientation angle. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, S.; Twele, A.; Martinis, S. Landslide mapping in vegetated areas using change detection based on optical and polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ishido, M.; Yamada, H. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Polarization orientation effects in urban areas on SAR data. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 4863–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribe, K.; Sato, M. Analysis of polarization orientation angle shifts by artificial structures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Radar polarization orientation shifts in built-up areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Imaging: From Basics to Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781420054989. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Schuler, D.L.; Ainsworth, T.L. Polarimetric SAR data compensation for terrain azimuth slope variation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2153–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Schuler, D.L.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Krogager, E.; Kasilingam, D.; Boerner, W.-M. On the estimation of radar polarization orientation shifts induced by terrain slopes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaso, S.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A.; Pottier, E. Building characterization using L-band polarimetric interferometric SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-I. A regular gird-based Hough transform for the extraction of urban features using high-resolution satellite images. Remote Sen. Lett. 2015, 6, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; De Grandi, G. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, D.L.; Lee, J.-S.; De Grandi, G. Measurement of topography using polarimetric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, E.; Schuler, D.L.; Lee, J.S.; Ainsworth, T.L. Estimation of the terrain surface azimuthal/range slopes using polarimetric decomposition of POLSAR data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 2212–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, D.L.; Lee, J.S.; Ainsworth, T.L. Compensation of terrain azimuthal slope effects in geophysical parameter studies using polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-W.; Ohki, M.; Shimada, M.; Sato, M. Deorientation effect investigation for model-based decomposition over orientated built-up areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Optimisation of building detection in satellite images by combining multispectral classification and texture filtering. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Morphological building/shadow index for building extraction from high-resolution imagery over urban areas. IEEE J. STARS 2012, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yan, Q.; Reinartz, P. Complex building description and extraction based on Hough transformation and cycle detection. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigillo, D.; Fras, M.K.; Petrovič, D. Automated building extraction from IKONOS images in suburban areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5149–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, M.; Koc-San, D. Building extraction from high-resolution optical spaceborne images using the integration of support vector machine (SVM) classification, Hough transformation and perceptual grouping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poullis, C.; You, S. Delineation and geometric modeling of road networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Couloigner, I. Accurate centerline detection and line width estimation of thick lines using the radon transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, P.V.C. Method and Means for Recognizing Complex Patterns. US Patent 3,609,654, 25 March 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth, J.; Kittler, J. A survey of the Hough transform. Comput. Gr. Image Process. 1988, 44, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.; Yao, A.; Razavi, N.; Gool, L.V.; Lempitsky, V. Hough forests for object detection, tracking and action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2188–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryati, N.; Eldar, Y.; Bruckstein, A.M. A probabilistic Hough transform. Pattern Recognit. 1991, 24, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, V.; Destain, M.F. Line cluster detection using a variant of the Hough transform for culture row localization. Image Vis. Comput. 2006, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, R.F.C.; Aguiar, P.M.Q. Connectivity-enforcing Hough transform for the robust extraction of line segments. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4819–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaile, G.L.; Burt, J.E. Directional Statistics; Geo Abstracts: Birmingham, UK, 1980; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Huo, C.; Pan, C.; Kong, Q. Registration of optical and SAR satellite images by exploring the spatial relationship of the improved SIFT. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studholme, C.; Hill, D.L.; Hawkes, D.J. An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recognit. 1999, 32, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shan, J.; Bruzzone, L.; Shen, L. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2941–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Police Agency. Available online: http://www.npa.go.jp/news/other/earthquake2011/pdf/higaijok yo_e.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php (accessed on 6 November 2018).
- WorldMap—Ishinomaki Building Inundation. Available online: https://worldmap.harvard.edu/data/geo node:ishinomakimerge_063 (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- Zhang, F.; Xie, C.; Li, K.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Xia, Z. Forest and deforestation identification based on multitemporal polarimetric RADARSAT-2 images in Southwestern China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).