Implications of Pixel Quality Flags on the Observation Density of a Continental Landsat Archive
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Automated Cloud Screening Algorithms
1.2. Sensor Saturation
- Summarize clear observation count (no clouds, no saturation in any band detected) to identify areas where either saturation or errors of commission in the cloud screening algorithm are affecting the number of observations available for analysis.
- Identify areas of commission error by normalizing the count of Fmask cloud flags by the total number of observations.
- Identify areas of systematic sensor saturation by normalizing the count of sensor saturation flags by the total number of observations.
2. Materials and Methods
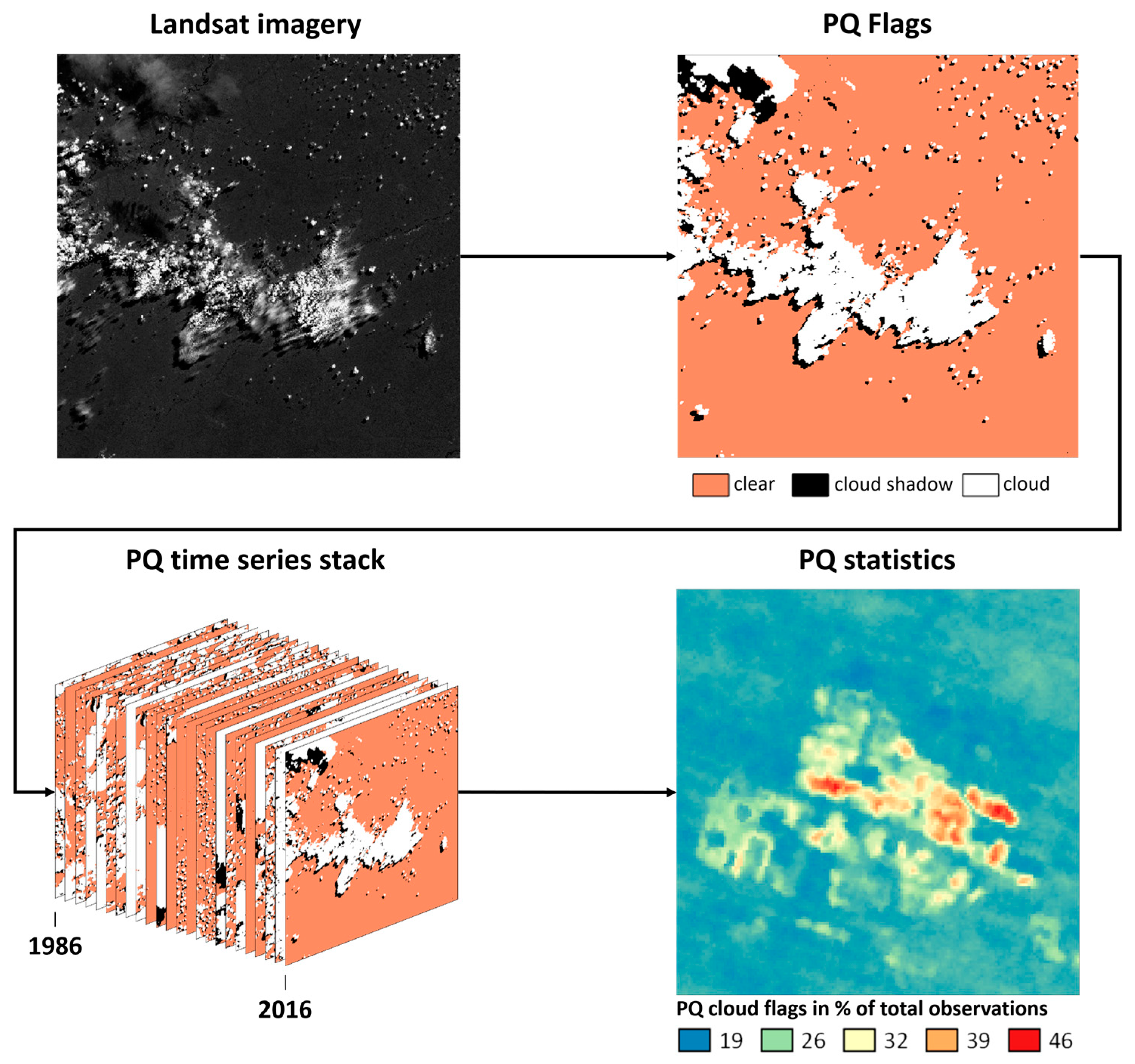
2.1. Image Processing
- Extracting total observation count (number of total Landsat scenes acquired between 1986 and 2016, per pixel);
- Extracting the number of observations either flagged as cloud by Fmask or saturated in each individual spectral band (BLUE, GREEN, RED, NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2);
- Normalizing PQ flag count by total observation count.
2.1.1. Fmask Cloud
2.1.2. Sensor Saturation
2.1.3. Experimental Design
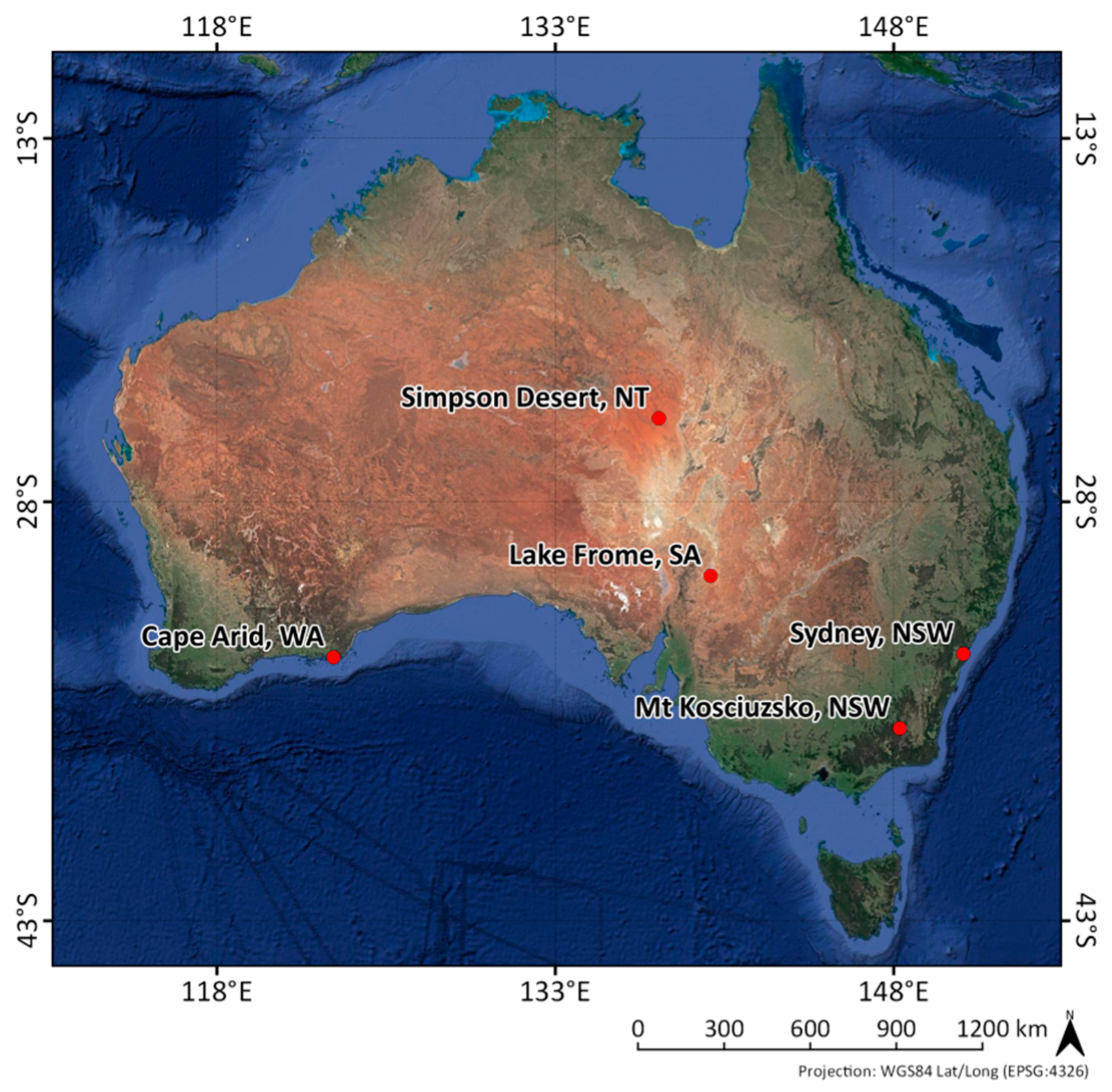
2.2. Location
3. Results
3.1. Cloud Commission
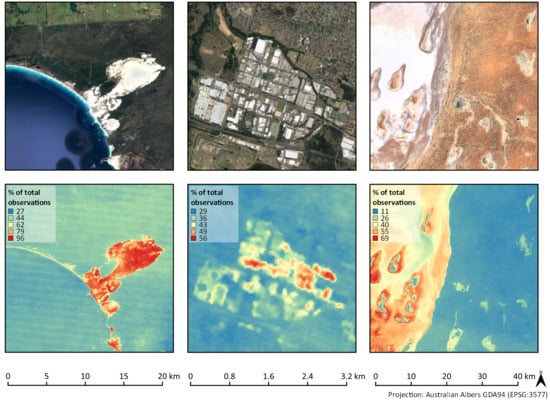
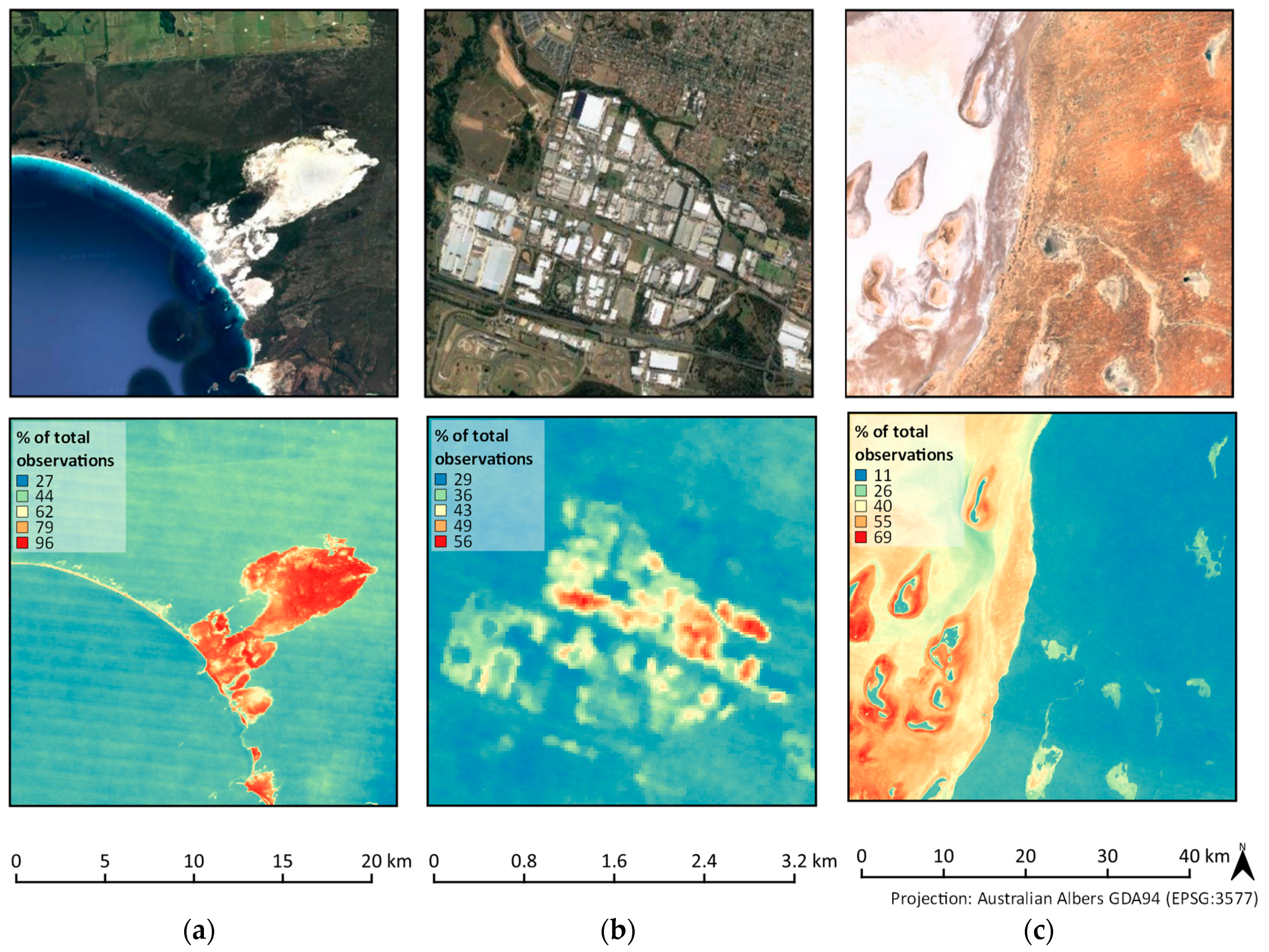
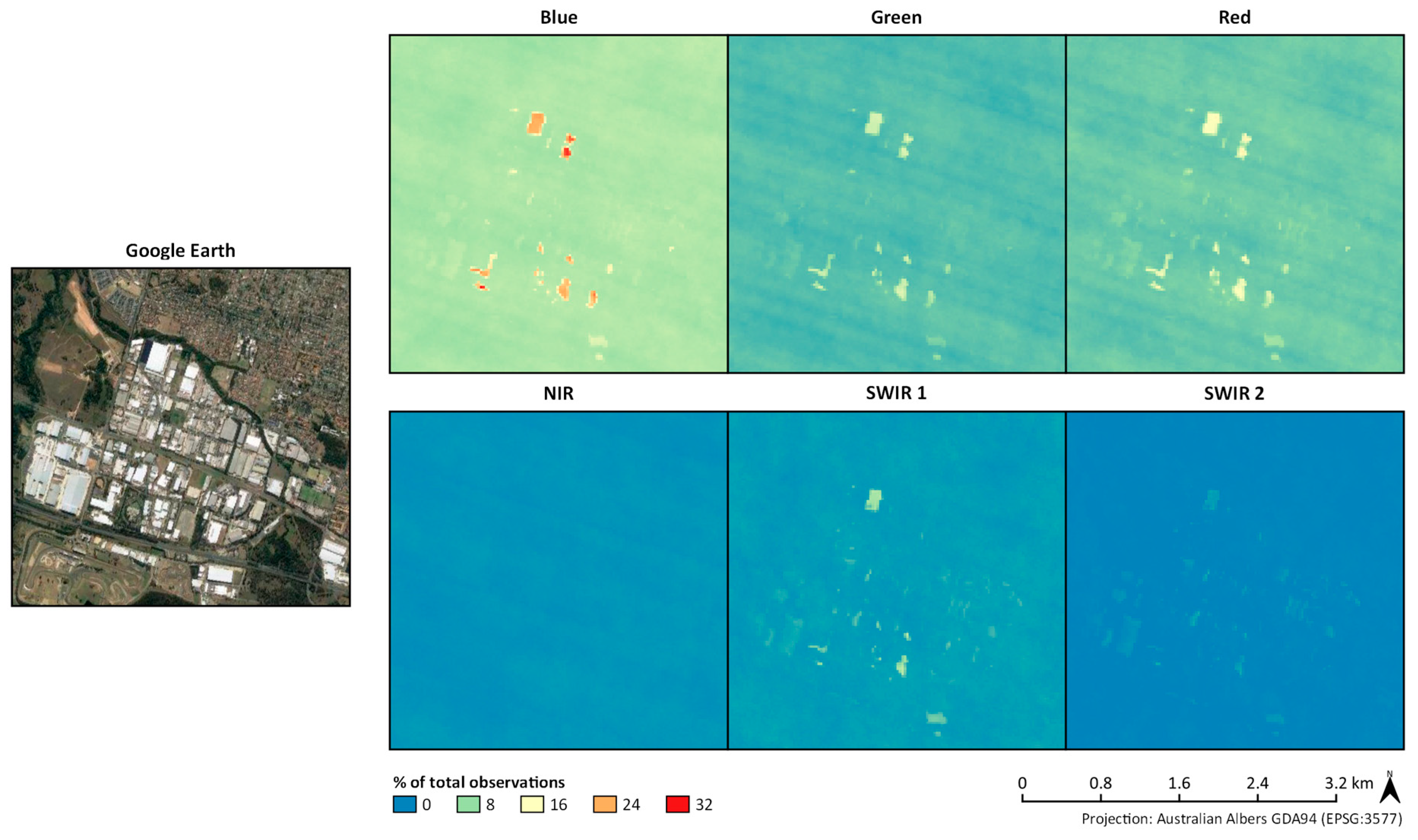
3.1.1. Coastal Areas, Urban Environments, and Salt Lakes
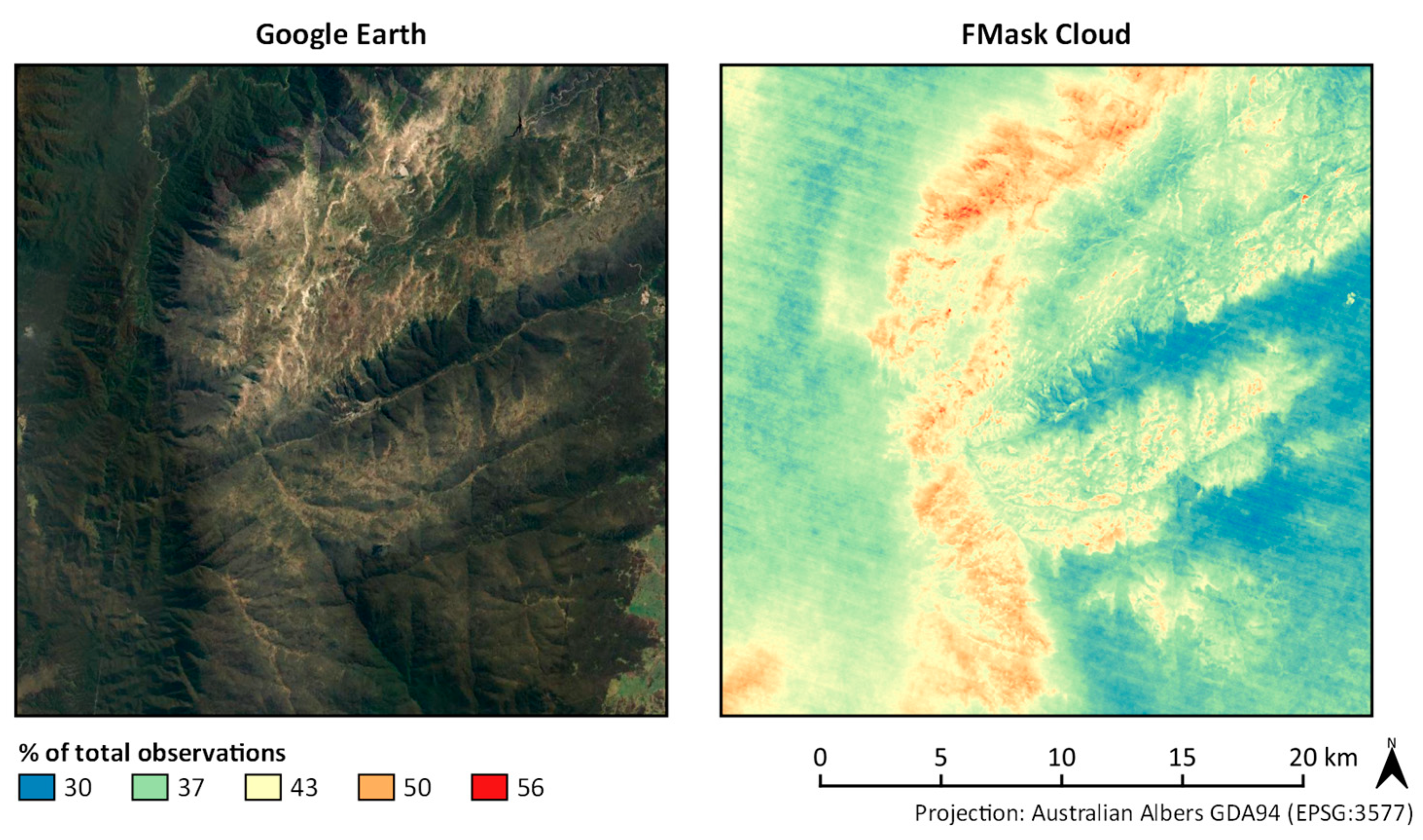
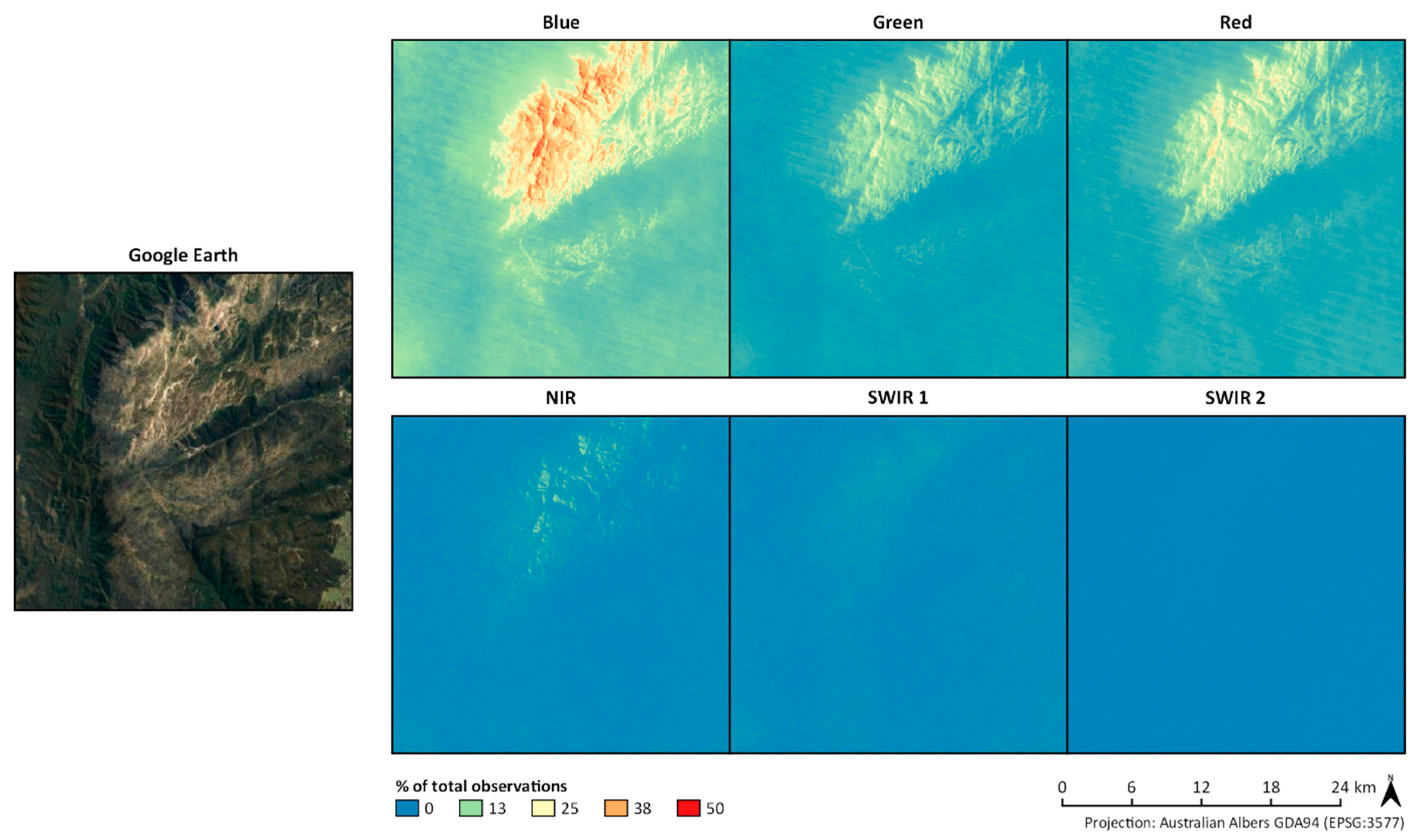
3.1.2. Mountainous/Alpine Environments
3.2. Saturation
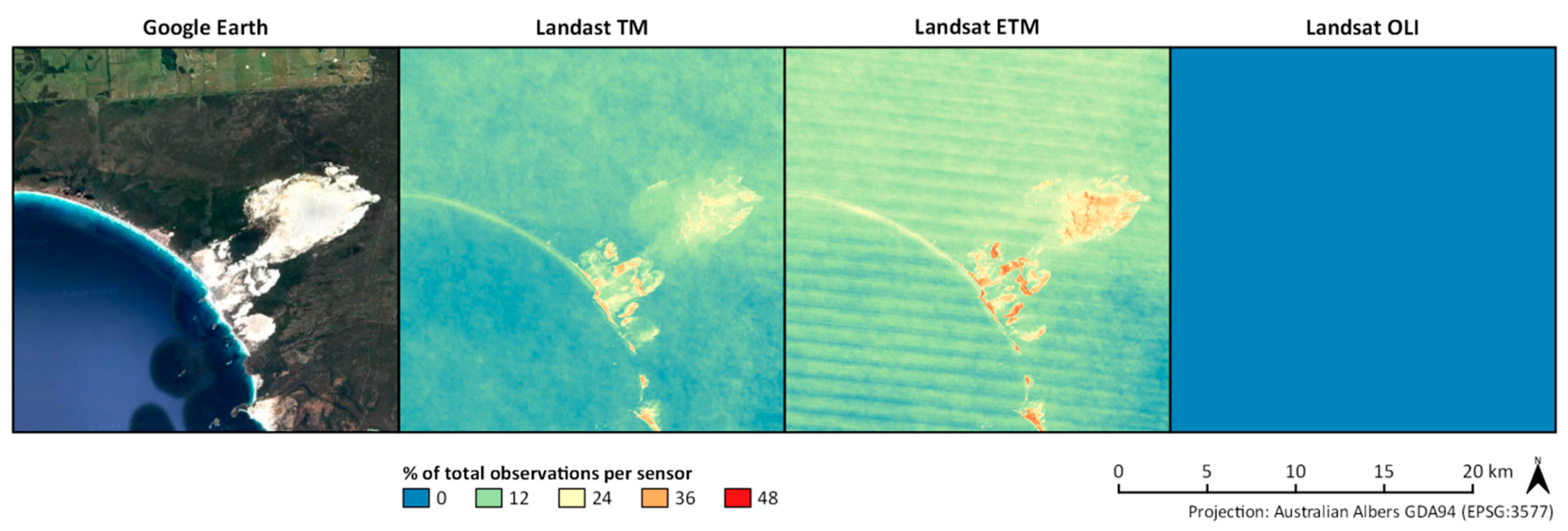
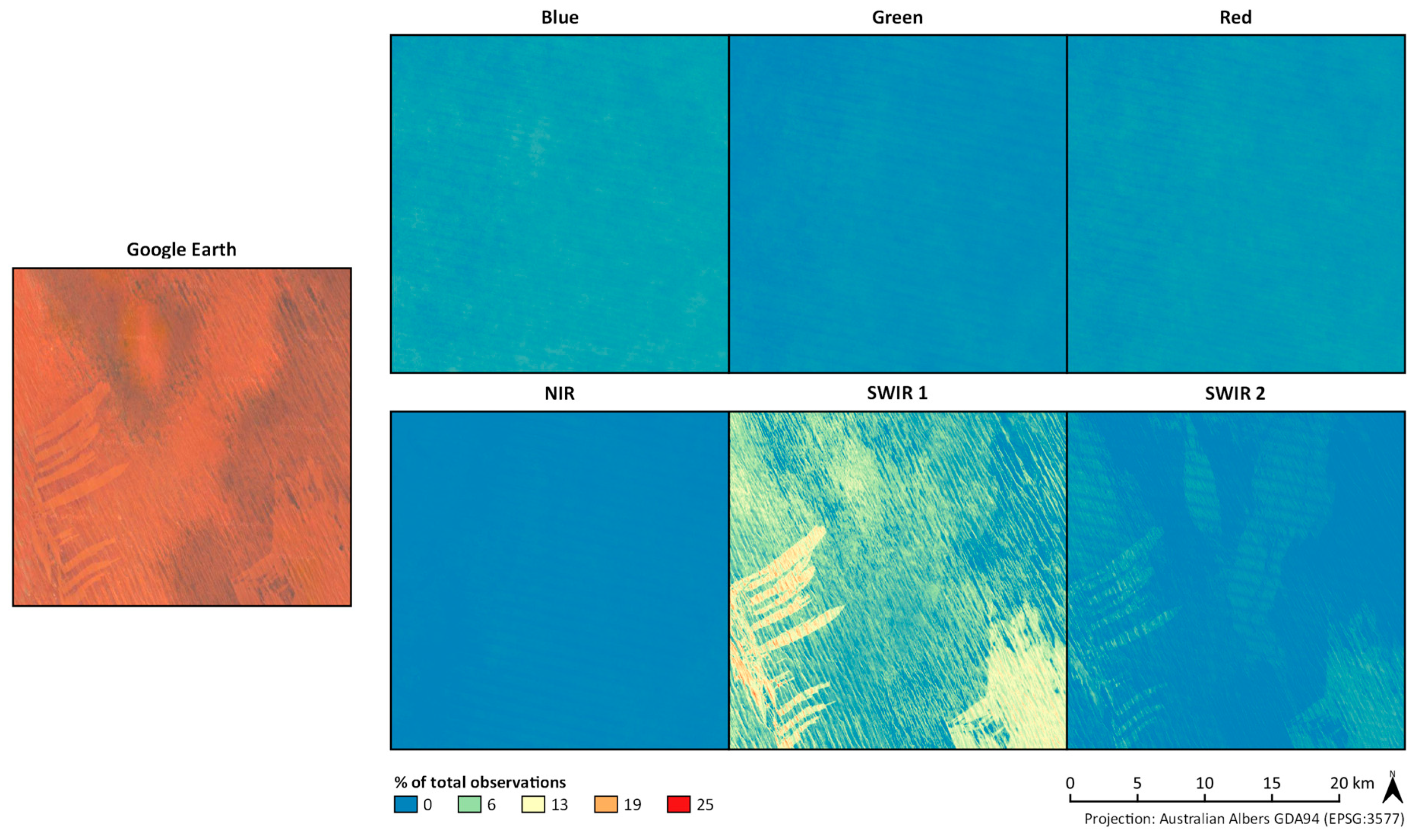
3.2.1. Coastal Environments
3.2.2. Urban Environments
3.2.3. Deserts
3.2.4. Salt Lakes
3.2.5. Mountainous/Alpine Environments
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Cloud Screening Algorithms
4.2. Sensor Saturation
4.3. Systematic Summary of ARD
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W.; Campbell, L.B. Mass data processing of time series Landsat imagery: Pixels to data products for forest monitoring. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Continuous change detection and classification of land cover using all available Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; van der Linden, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Hostert, P. A pixel-based Landsat compositing algorithm for large area land cover mapping. IEEE J-STARS 2013, 6, 2088–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.R.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C. Web-enabled Landsat Data (WELD): Landsat ETM+ composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Hobart, G.W.; Luther, J.E.; Hermosilla, T.; Griffiths, P.; Coops, N.C.; Hall, R.J.; Hostert, P.; Dyk, A.; et al. Pixel-based image compositing for large-area dense time series applications and science. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Röder, A.; Stellmes, M.; Hill, J. Phenology-adaptive pixel-based compositing using optical earth observation imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.; Lewis, A.; Roberts, D.; Ring, S.; Melrose, R.; Sixsmith, J.; Lymburner, L.; McIntyre, A.; Tan, P.; Curnow, S.; et al. Water observations from space: Mapping surface water from 25 years of Landsat imagery across Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Roberts, D.; Bala, B.; Lymburner, L. Extracting the intertidal extent and topography of the Australian coastline from a 28 year time series of Landsat observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, R.R. Landsat 7 Automatic Cloud Cover Assessment. Available online: https://bit.ly/2QQhiiy (accessed on 21 September 2018).
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Hayes, D. Automated detection of cloud and cloud shadow in single-date Landsat imagery using neural networks and spatial post-processing. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4907–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Yue, T.; Liu, Y. An optional threshold with SVM cloud detection algorithm and DSP implementation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B8, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, N.R.; Collett, L.J.; Denham, R.J.; Flood, N.; Tindall, D. Cloud and cloud shadow screening across Queensland, Australia: An automated method for Landsat TM/ETM+ time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Homer, C.; Yang, L.; Xian, G.; Fry, J.; Danielson, P.; Townsend, P.A. Automated cloud and shadow detection and filling using two-date Landsat imagery in the USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1540–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection in multitemporal Landsat data: An algorithm designed specifically for monitoring land cover change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Joseph Hughes, M.; Laue, B. Cloud detection algorithm comparison and validation for operational Landsat data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindschadler, R.; Vornberger, P.; Fleming, A.; Fox, A.; Mullins, J.; Binnie, D.; Paulsen, S.J.; Granneman, B.; Gorodetzky, D. The Landsat image mosaic of Antarctica. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4214–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Marks, D. Snow mapping and classification from Landsat Thematic Mapper data. Ann. Glaciol. 1987, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Chang, A.T.; Siddalingaiah, H. Reflectances of glaciers as calculated using Landsat-5 Thematic Mapper data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnieli, A.; Ben-Dor, E.; Bayarjargal, Y.; Lugasi, R. Radiometric saturation of Landsat-7 ETM+ data over the Negev Desert (Israel): Problems and solutions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2004, 5, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfitt, R.; Barsi, J.; Levy, R.; Markham, B.; Micijevic, E.; Ong, L.; Scaramuzza, P.; Vanderwerff, K. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) radiometric performance on-orbit. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2208–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixsmith, J.; Oliver, S.; Lymburner, L. A Hybrid Approach to Automated Landsat Pixel Quality. Available online: https://bit.ly/2zAGGm4 (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Loveland, T.R.; Dwyer, J.L. Landsat: Building a strong future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkowitz, D.; Forster, R. An Automated Approach for Mapping Persistent Ice and Snow Cover over High Latitude Regions. Remote Sens. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Röder, A.; Udelhoven, T.; Schmidt, M. Enhancing the detectability of clouds and their shadows in multitemporal dryland Landsat imagery: Extending Fmask. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; He, B.; Zhu, Z.; Liao, Z.; Quan, X. Improving Fmask cloud and cloud shadow detection in mountainous area for Landsats 4–8 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Pascual, D.V.; Dedieu, G. A multi-temporal method for cloud detection, applied to FORMOSAT-2, VENµS, LANDSAT and SENTINEL-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Chova, L.; Amoros-Lopez, J.; Ruiz-Verdu, A.; Munoz-Mari, J.; Camps-Vails, G. Operational Cloud Screening Service for Sentinel-2 Image Time Series. Available online: https://bit.ly/2zAQGvm (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Frantz, D.; Haß, E.; Uhl, A.; Stoffels, J.; Hill, J. Improvement of the Fmask algorithm for Sentinel-2 images: Separating clouds from bright surfaces based on parallax effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, A.; Roy, D.; Zhang, H.; Hansen, M.; Kommareddy, A. Demonstration of percent tree cover mapping using Landsat Analysis Ready Data (ARD) and sensitivity with respect to Landsat ARD processing level. Remote Sens. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Roy, D.P.; White, J.C.; Hermosilla, T. Land cover 2.0. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4254–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ernst, S.; Lymburner, L.; Sixsmith, J. Implications of Pixel Quality Flags on the Observation Density of a Continental Landsat Archive. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101570
Ernst S, Lymburner L, Sixsmith J. Implications of Pixel Quality Flags on the Observation Density of a Continental Landsat Archive. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101570
Chicago/Turabian StyleErnst, Stefan, Leo Lymburner, and Josh Sixsmith. 2018. "Implications of Pixel Quality Flags on the Observation Density of a Continental Landsat Archive" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101570
APA StyleErnst, S., Lymburner, L., & Sixsmith, J. (2018). Implications of Pixel Quality Flags on the Observation Density of a Continental Landsat Archive. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101570





