Bias Removal for Goldstein Filtering Power Using a Second Kind Statistical Coherence Estimator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
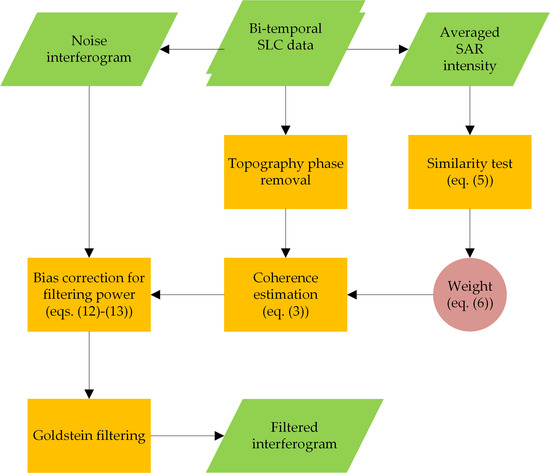
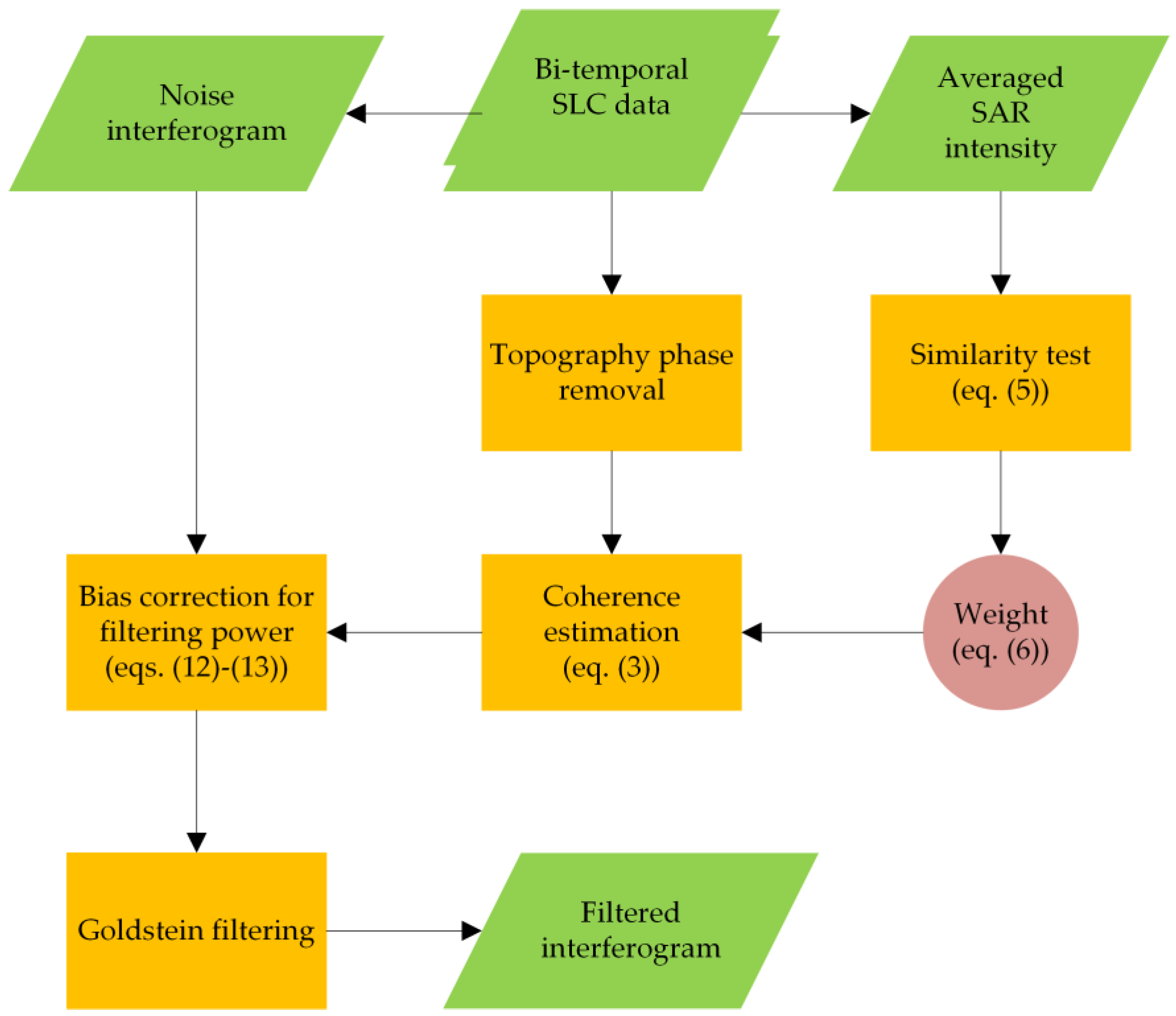
2. Methodology
2.1. Adaptive Goldstein Filtering
2.2. Coherence Estimation Based on the Second Kind Statistic
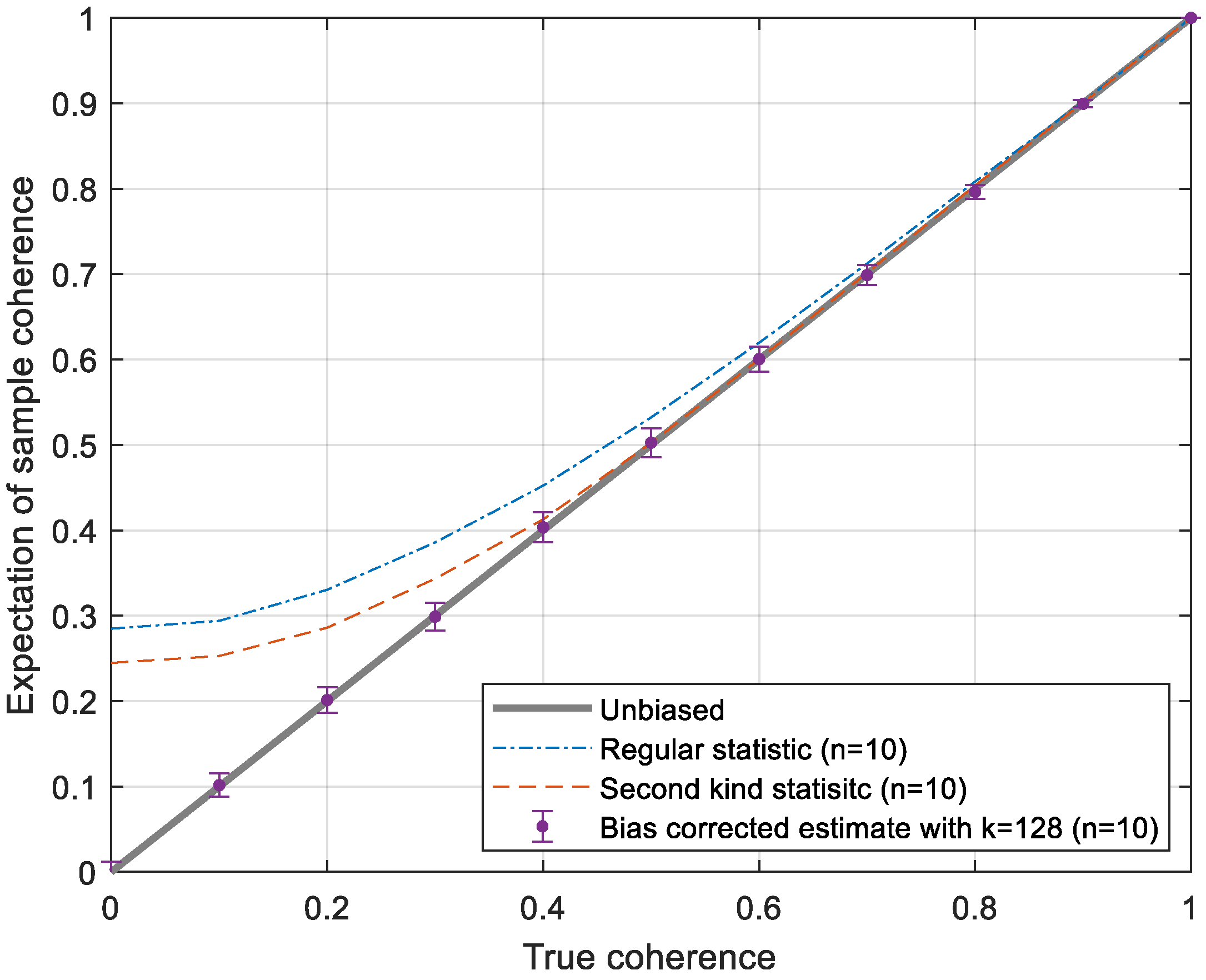
2.2.1. Definition of the Coherence Estimator
2.2.2. Weight Determination Weight
2.2.3. Bias Removal Using Second Kind Statistic Estimator
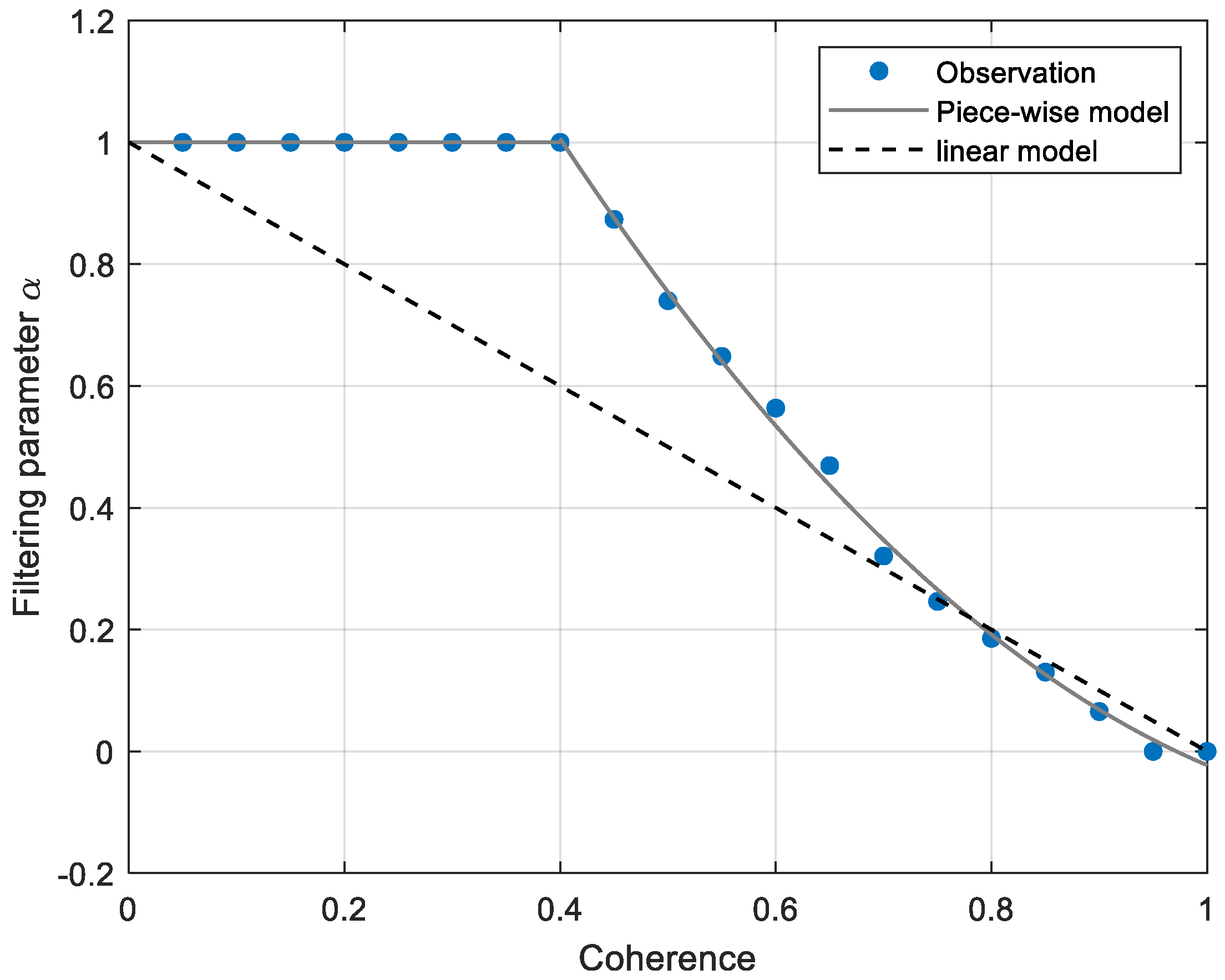
2.3. Modeling Filtering Power Using Unbiased Coherence
2.4. Filter Development
- (1)
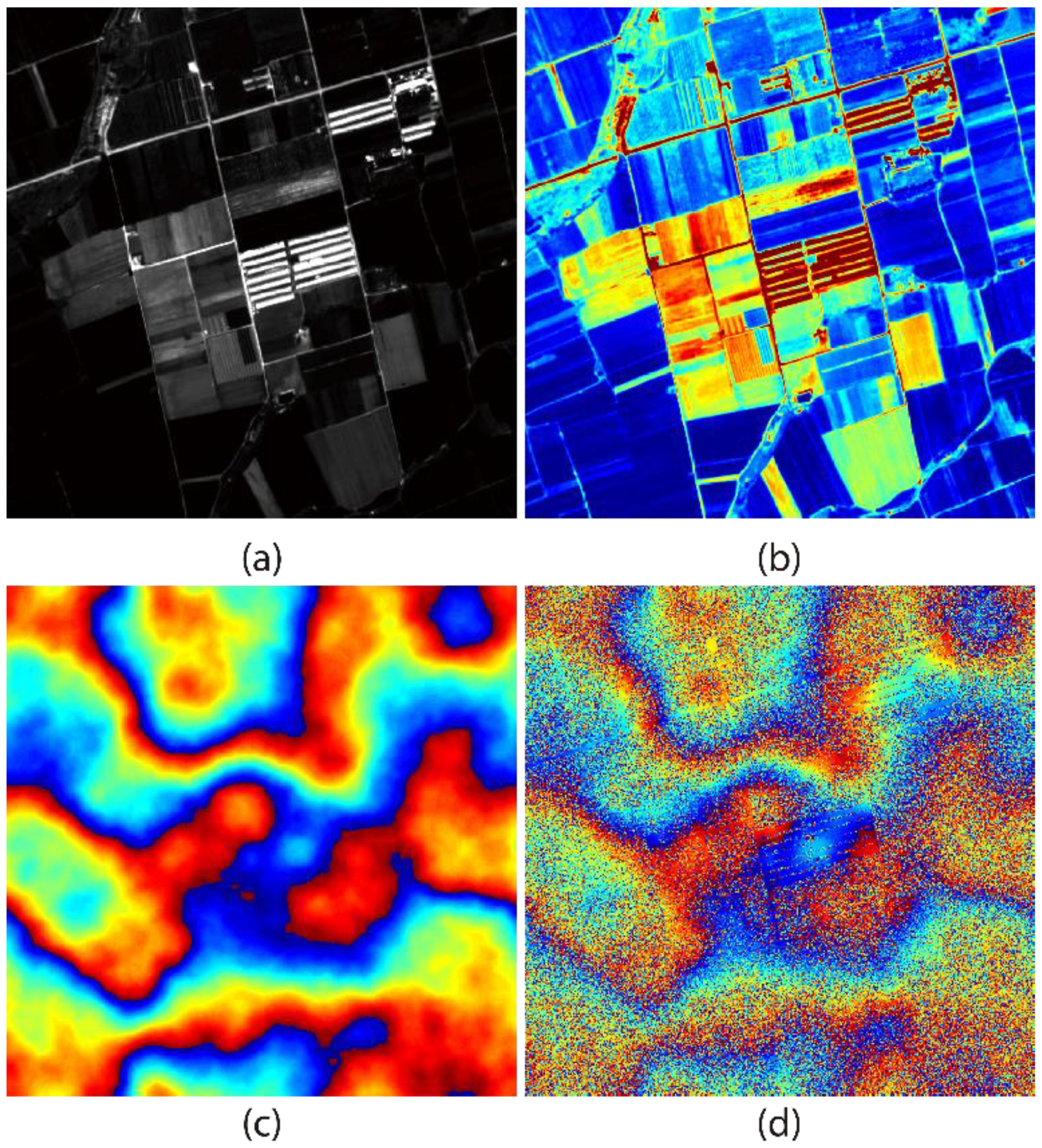
- For each image pixel P, a coherence estimate window of size n is defined. The similarity between P and its neighbors is compared individually on an average intensity SAR image with patch size m (Figure 1a), and the weight of the coherence estimate window is confirmed using Equation (6). The sample coherence for pixel P is then estimated using Equation (3).
- (2)
- The procedure is repeated until the sample coherence of the last pixel in the whole image is estimated and coherence map is generated.
- (3)
- Goldstein filtering is performed on the interferogram in which the coherence sample with size k in each filtering patch is first averaged to obtain using Equation (11), and is further corrected to unbiased coherence according to Equation (12).
- (4)
- The filtering power is adjusted according to Equation (13) and Goldstein filtering is performed on such patches.
- (5)
- Steps (3) and (4) are repeated until the whole interferogram has been filtered.
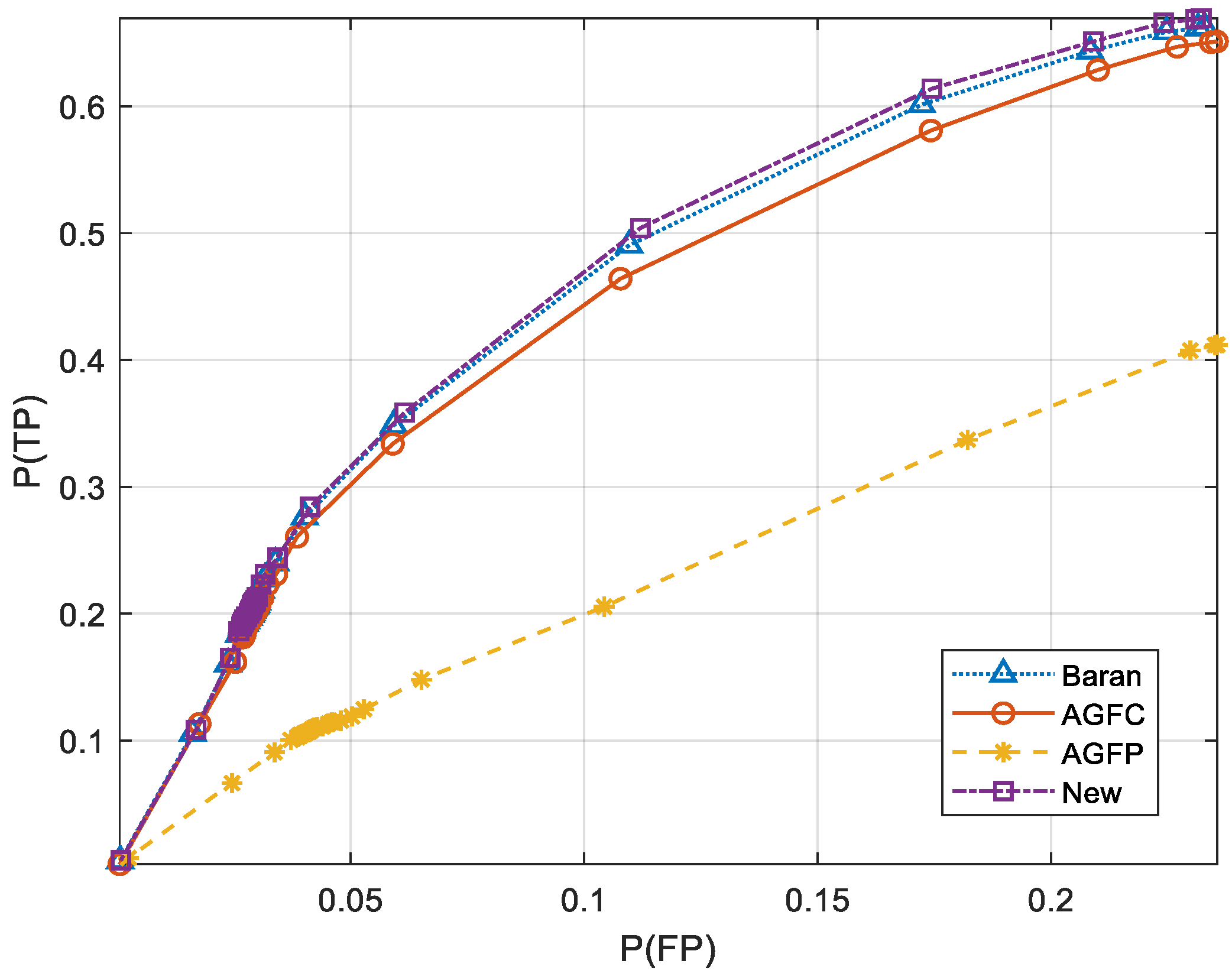
3. Results and Discussion
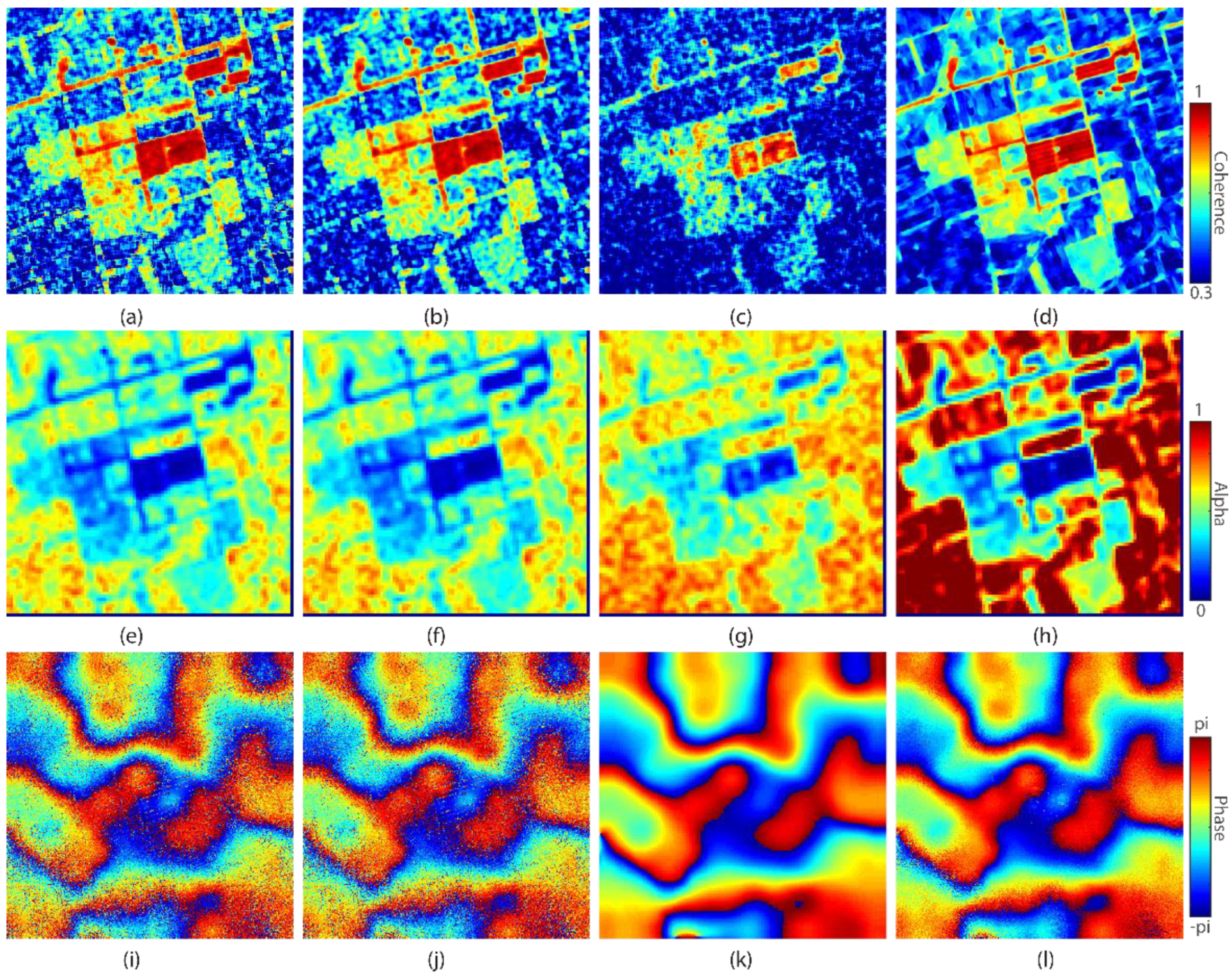
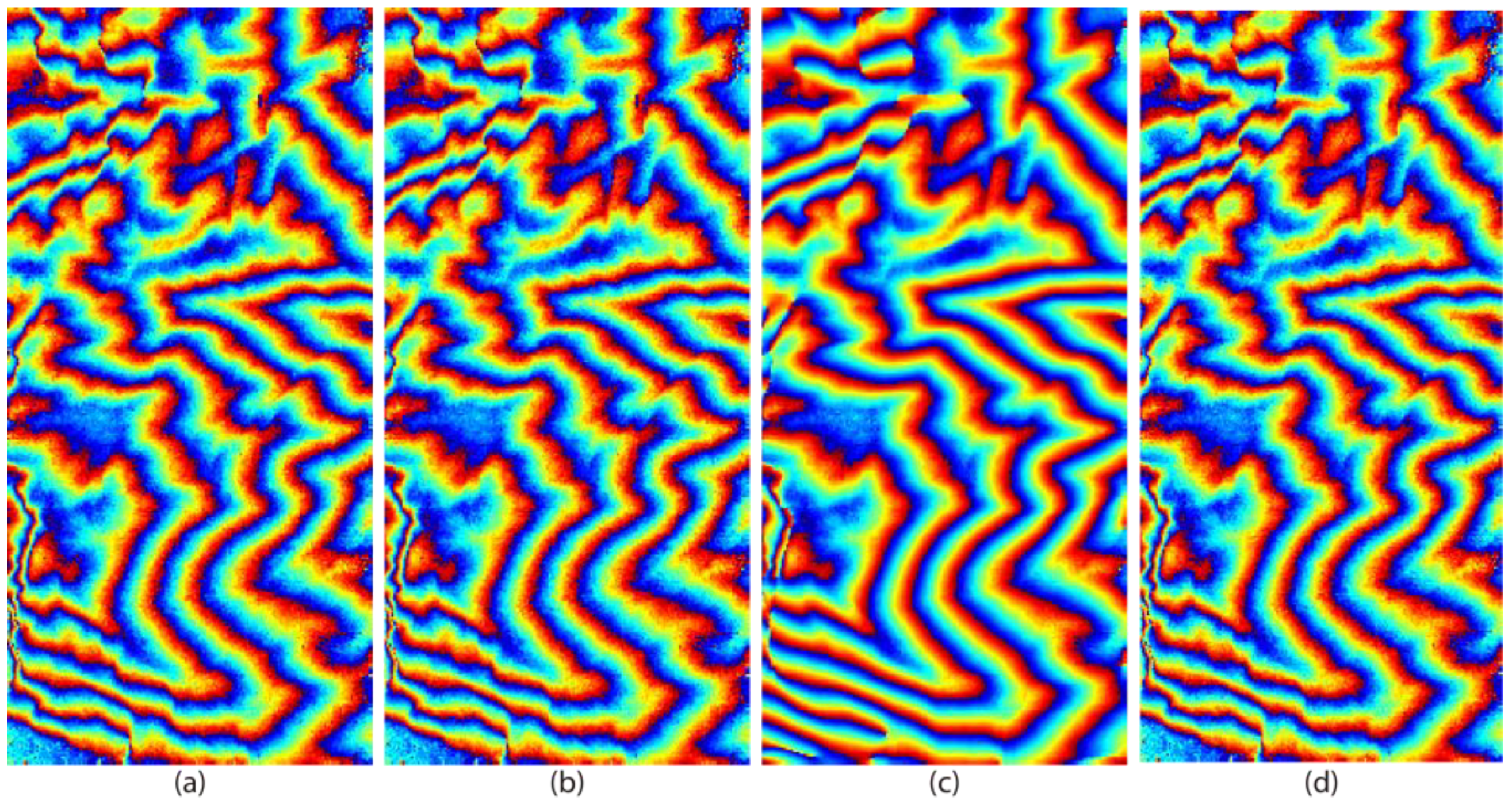
3.1. Synthetic Data
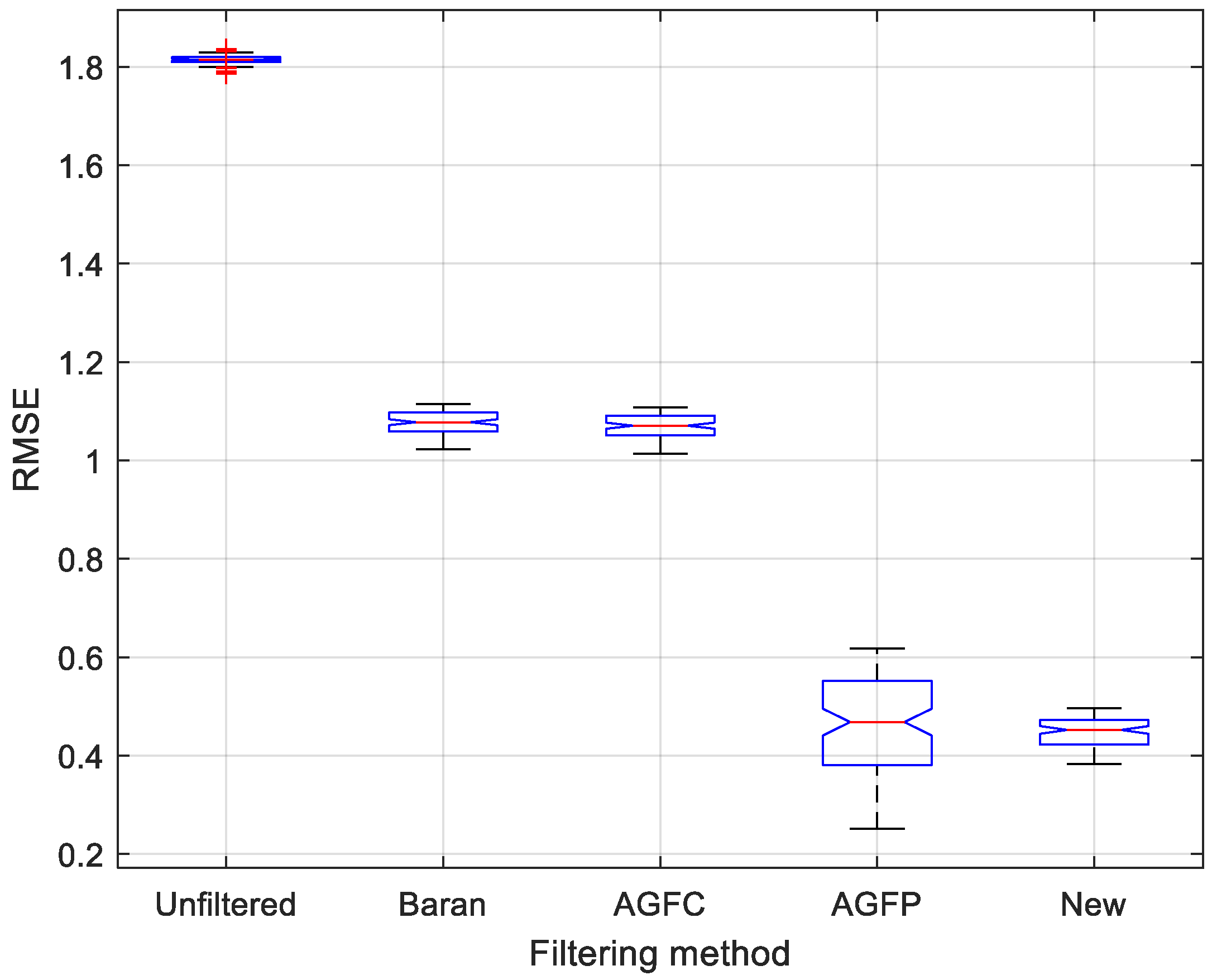
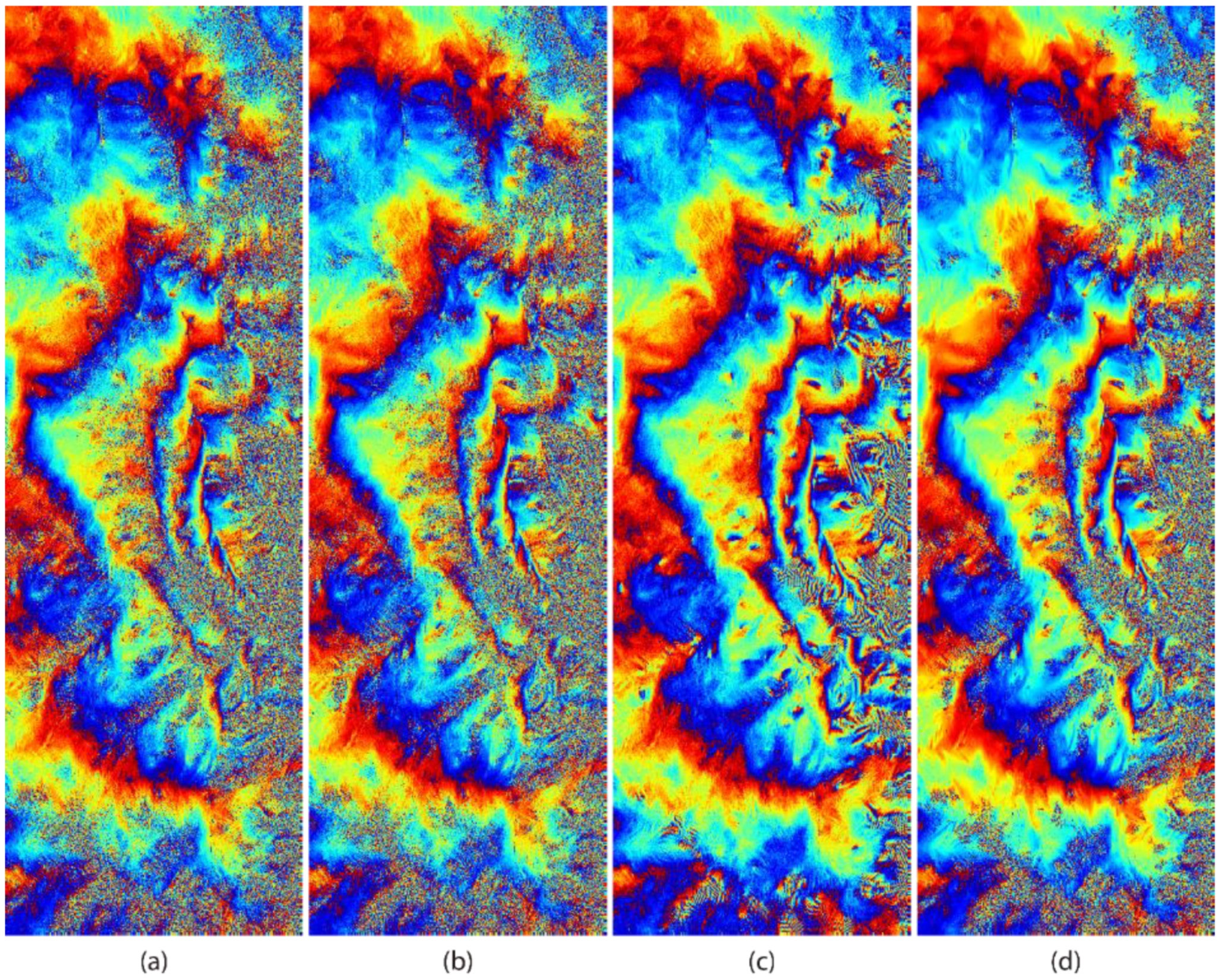
3.2. Real Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. Landslide displacement monitoring with split-bandwidth interferometry: A case study of the shuping landslide in the three gorges area. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Astrup, R.; Breidenbach, J.; Nilsen, B.; Weydahl, D. Monitoring spruce volume and biomass with insar data from tandem-x. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yong, B.; Tian, X.; Malhotra, R.; Hu, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X. The potential of more accurate insar covariance matrix estimation for land cover mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Runge, H. Theoretical evaluation of several possible along-track insar modes of terrasar-x for ocean current measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Thomas, M.Y.; Parsons, B.; Walker, R.T. Time-dependent postseismic slip following the 1978 m w 7.3 tabas-e-golshan, iran earthquake revealed by over 20 years of esa insar observations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 483, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.A. Phase unwrapping in three dimensions with application to insar time series. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2007, 24, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, I.; Stewart, M.P.; Kampes, B.M.; Perski, Z.; Lilly, P. A modification to the goldstein radar interferogram filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y. Improved filtering parameter determination for the goldstein radar interferogram filter. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, B. The improvement for baran phase filter derived from unbiased insar coherence. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-H.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Y. An improved sar interferogram denoising method based on principal component analysis and the goldstein filter. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J. An iterative goldstein sar interferogram filter. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3443–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre-Quereda, A.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Selva, J.; Gonzalez, P.J. An improved phase filter for differential sar interferometry based on an iterative method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4477–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P.W. Coherence estimation for sar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z. Hybrid approach for unbiased coherence estimation for multitemporal insar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2459–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Farmen, M.; Gijbels, I. Local maximum likelihood estimation and inference. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1998, 60, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettitt, A.N. A two-sample anderson-darling rank statistic. Biometrika 1976, 63, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, D. The kolmogorov-smirnov, cramer-von mises tests. Ann. Math. Stat. 1957, 28, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, C.; Kolmogorov, V.; Blake, A. Grabcut: Interactive Foreground Extraction Using Iterated Graph Cuts; ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG); ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: Squeesar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast statistically homogeneous pixel selection for covariance matrix estimation for multitemporal insar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, J.M. Introduction to second kind statistics: Application of log-moments and log-cumulants to sar image law analysis. Trait. Signal 2002, 19, 139–168. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfattah, R.; Nicolas, J.M. Interferometric sar coherence magnitude estimation using second kind statistics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecknold, S.; Lovejoy, S.; Schertzer, D.; Hooge, C.; Malouin, J. The simulation of universal multifractals. In Cellular Automata: Prospects in Astronomy and Astrophysics; Perdang, J.M., Lejeune, A., Eds.; World Scientific Pub Co Inc.: Singapore, 1993; pp. 228–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 142. [Google Scholar]
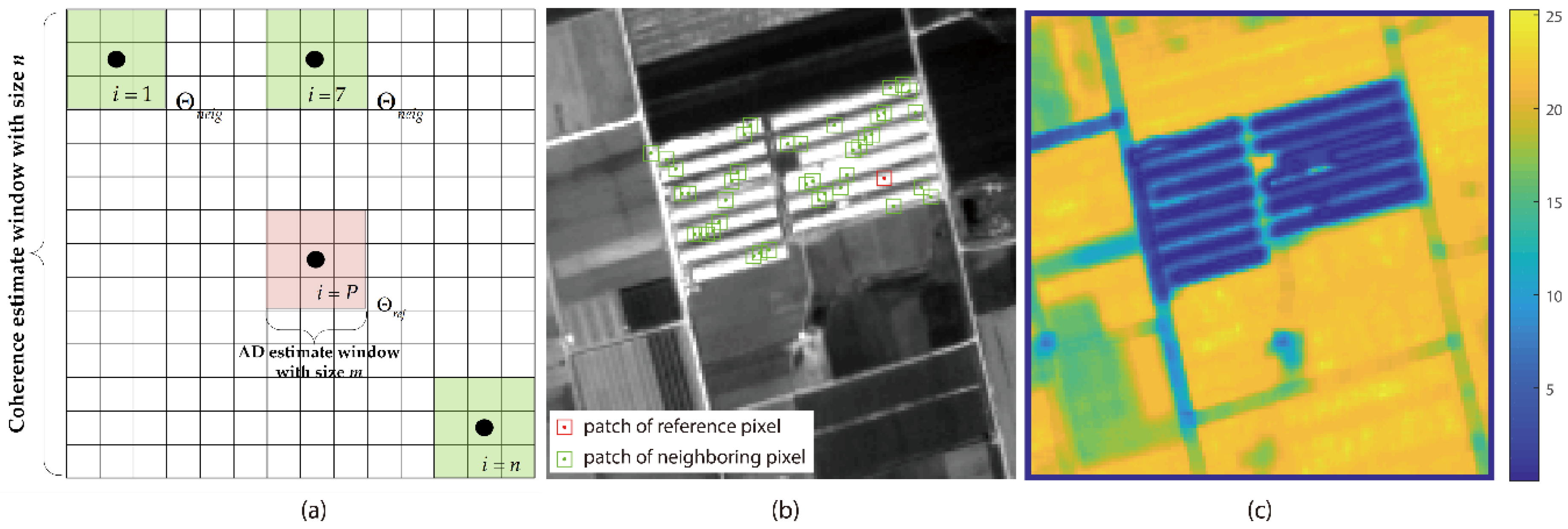
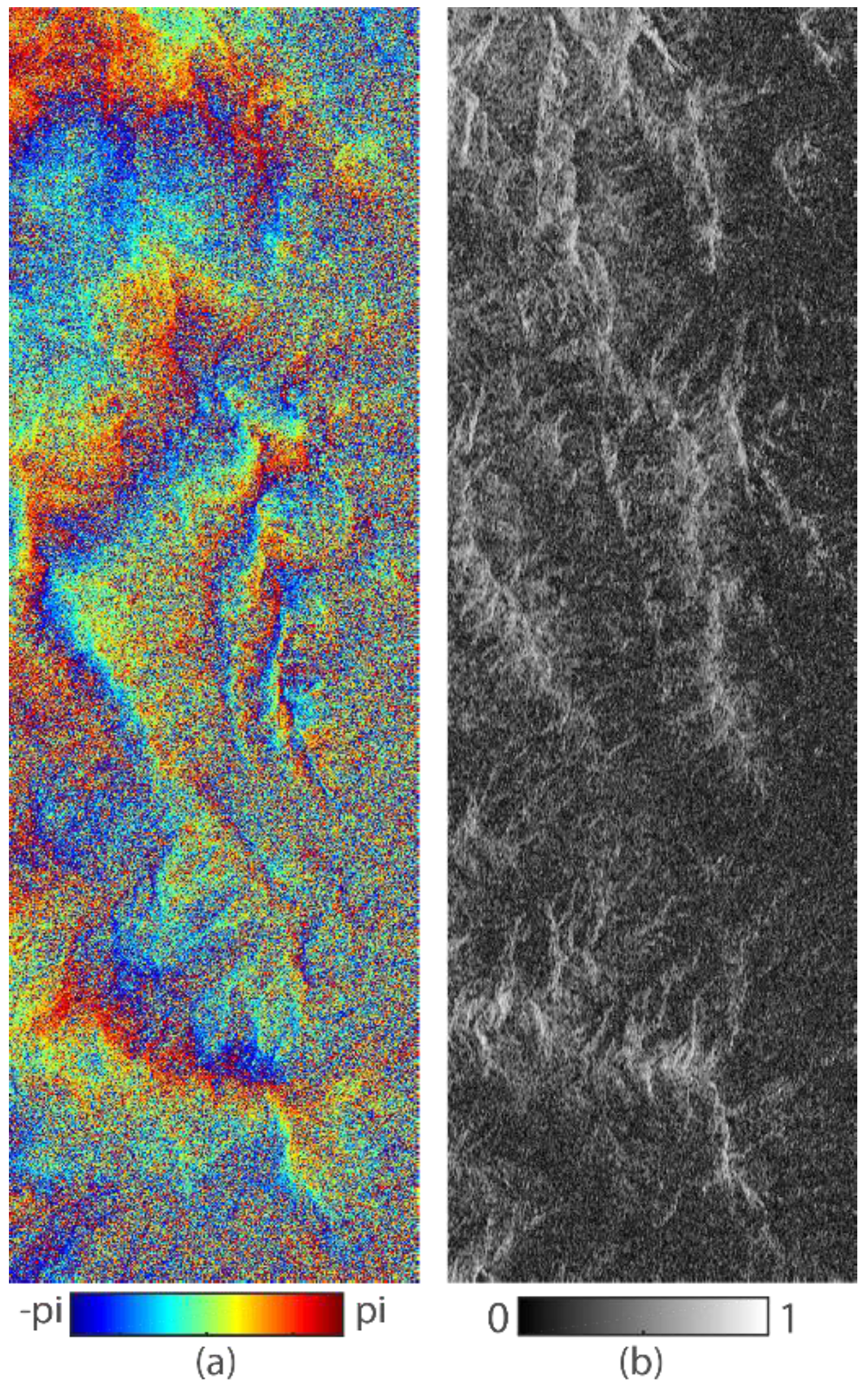
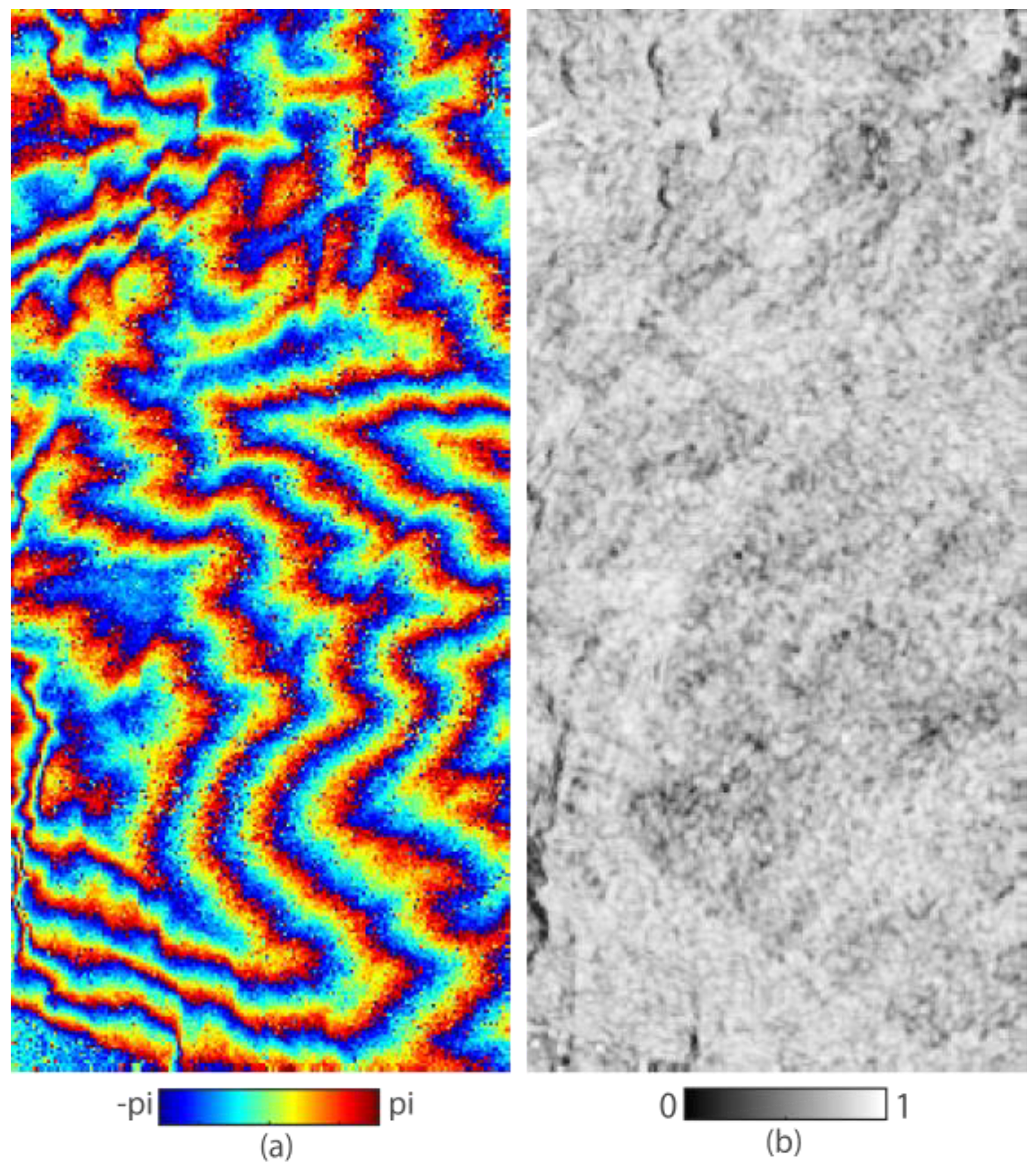
| Sensor | Track | Acquisition Date | Perp. Baseline | Imaging Area | Interferometric Feature | Mean Coherence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1A | 128 | 30 July 2017 | 35 m | Jiuzhaigou, China | Incoherent | 0.25 |
| 11 August 2017 | ||||||
| TanDEM-X | - | 1 January 2013 | 286 m | Hong Kong, China | Coherent | 0.76 |
| 1 January 2013 |
| Method | Residue Number | Residue Reduction (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unfiltered | 2.88 | 393,230 | - |
| Baran | 1.80 | 136,828 | 65.20 |
| AGFC | 1.72 | 125,197 | 68.16 |
| AGFP | 1.05 | 17,647 | 95.51 |
| New | 1.35 | 94,460 | 75.98 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Jiang, M.; Xiao, R.; Malhotra, R. Bias Removal for Goldstein Filtering Power Using a Second Kind Statistical Coherence Estimator. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101559
Tian X, Jiang M, Xiao R, Malhotra R. Bias Removal for Goldstein Filtering Power Using a Second Kind Statistical Coherence Estimator. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101559
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xin, Mi Jiang, Ruya Xiao, and Rakesh Malhotra. 2018. "Bias Removal for Goldstein Filtering Power Using a Second Kind Statistical Coherence Estimator" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101559
APA StyleTian, X., Jiang, M., Xiao, R., & Malhotra, R. (2018). Bias Removal for Goldstein Filtering Power Using a Second Kind Statistical Coherence Estimator. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101559