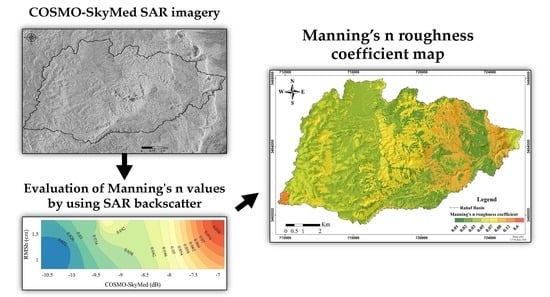
Evaluation of Manning’s n Roughness Coefficient in Arid Environments by Using SAR Backscatter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SAR Data and Processing for Roughness Extraction
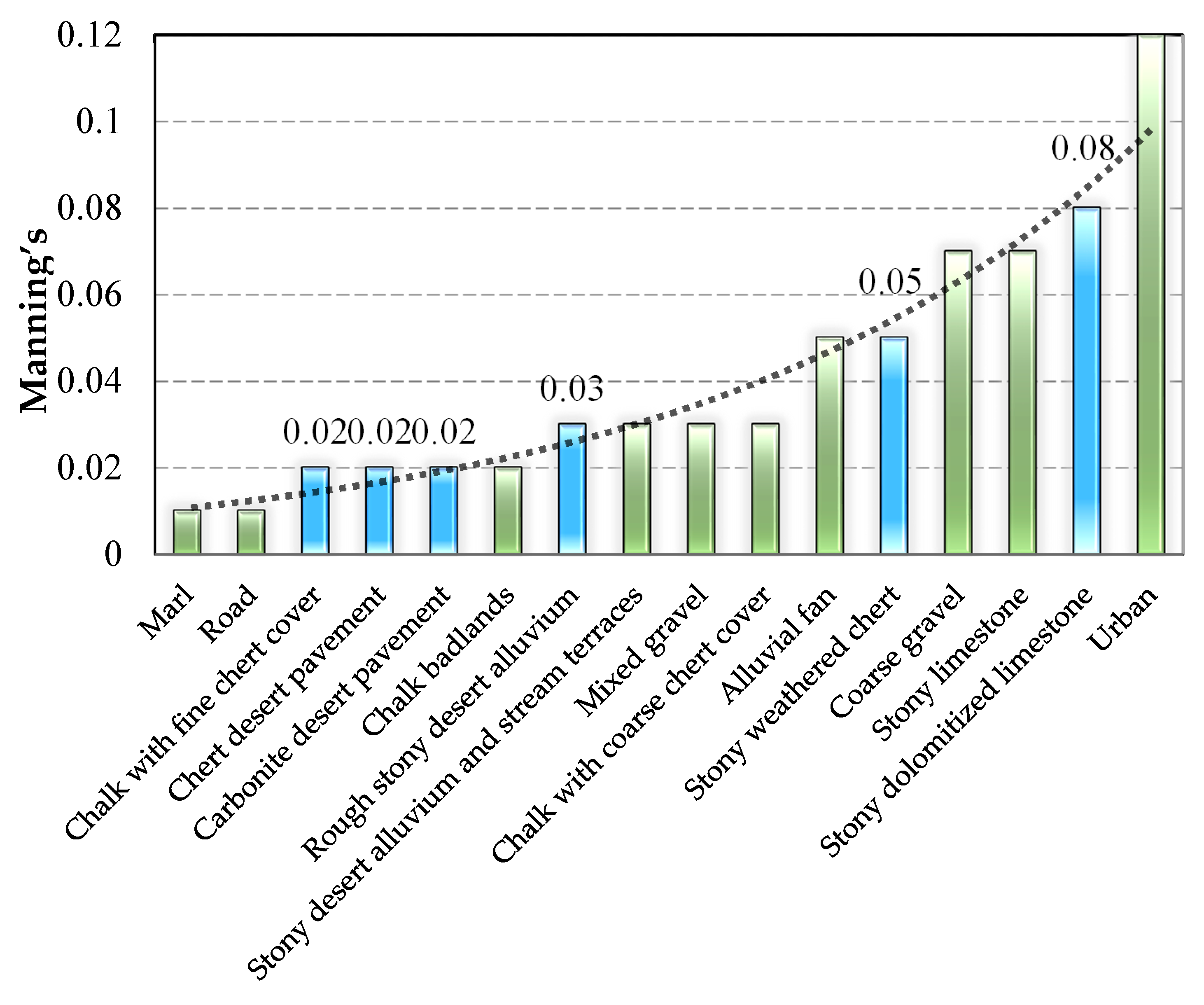
2.3. Field Roughness Measurements
3. Results
3.1. COSMO-SkyMed Imagery Analysis
3.2. Surface Roughness-Field Measurements
3.3. Correlation between the SAR Backscatter and Surface Roughness
3.4. Using SAR Backscatter for the Evaluation of Manning’s n
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.; Chen, B.; Fang, J. Flood-Induced Mortality Across the Globe: Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprotny, D.; Sebastian, A.; Morales-Nápoles, O.; Jonkman, S.N. Trends in Flood Losses in Europe over the Past 150 Years. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K. Flood Risk and Climate Change: Global and Regional Perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Fan, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Liu, C. Floods and Associated Socioeconomic Damages in China Over the Last Century. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, A.; Raz-Yassif, N. Hydrological Processes in a Small Arid Catchment: Scale Effects of Rainfall and Slope Length. Geomorphology 2004, 61, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Real Time Flood Forecasting-Indian Experiences. In Hydrological Modelling in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas; Wheater, H., Sorooshian, S., Sharma, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M.; Ghoneim, E.M.; Arnell, N.W. Predicting Locations Sensitive to Flash Flooding in an Arid Environment. J. Hydrol. 2004, 292, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Erosional Development of Streams and their Drainage Basins; Hydrophysical Approach to Quantitative Morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1945, 56, 275–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.; Sorooshian, S. Comparison of Simple versus Complex Distributed Runoff Models on a Midsized Semiarid Watershed. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, E.T. Roughness Coefficients for Routing Surface Runoff. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1986, 112, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.; Miller, S.N.; Goodrich, D.C.; Goff, B.F.; Kepner, W.G.; Edmonds, C.M.; Jones, K.B. Modeling runoff response to land cover and rainfall spatial variability in semi-arid watersheds. In Monitoring Ecological Condition in the Western United States; Anonymous; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum, N.; Margalit, A.; Schick, A.P.; Sharon, D.; Baker, V.R. A High Magnitude Storm and Flood in a Hyperarid Catchment, Nahal Zin, Negev Desert, Israel. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, A.; Kossovsky, A. Climate and Surface Properties: Hydrological Response of Small Arid and Semi-Arid Watersheds. Geomorphology 2002, 42, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J. Dynamics of Transmission Losses in a Large Arid Stream Channel. J. Hydrol. 2005, 306, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Laronne, J.B. High Rates of Sediment Transport by Flashfloods in the Southern Judean Desert, Israel. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, B.E. Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Using GIS, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Forzieri, G.; Castelli, F.; Preti, F. Advances in Remote Sensing of Hydraulic Roughness. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 630–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcement, G.J.; Schneider, V.R. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains; United States Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2339; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1989.
- El Bastawesy, M.; White, K.; Nasr, A. Integration of Remote Sensing and GIS for Modelling Flash Floods in Wadi Hudain Catchment, Egypt. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, D.; Goodrich, D.; Unkrich, C.; Smith, R.; Woolhiser, D.; Miller, S. KINEROS2 and the AGWA modelling framework. In Hydrological Modelling in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas; Wheater, H., Sorooshian, S., Sharma, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Woolhiser, D.A.; Smith, R.; Goodrich, D.C. KINEROS: A Kinematic Runoff and Erosion Model; Documentation and User Manual; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Hagemann, M.; Gleason, C.; Durand, M. BAM: Bayesian AMHG-Manning Inference of Discharge using Remotely Sensed Stream Width, Slope, and Height. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9692–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Wang, C.; Xi, X. Constructing River Stage-Discharge Rating Curves using Remotely Sensed River Cross-Sectional Inundation Areas and River Bathymetry. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 670–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.K.; Aggarwal, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Jain, S. One-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Modeling of GLOF and Impact on Hydropower Projects in Dhauliganga River using Remote Sensing and GIS Applications. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 1057–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Farooq, M.; Sarwar, T.; Tareen, M.J.; Wahid, M.A. Flood Modeling and Simulations using Hydrodynamic Model and ASTER DEM—A Case Study of Kalpani River. Arabian J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Sensitivity Analysis of the Surface Runoff Coefficient of HiPIMS in Simulating Flood Processes in a Large Basin. Water 2018, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzieri, G.; Degetto, M.; Righetti, M.; Castelli, F.; Preti, F. Satellite Multispectral Data for Improved Floodplain Roughness Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Moran, M.; Thoma, D.; Bryant, R.; Holifield Collins, C.; Jackson, T.; Orr, B.; Tischler, M. Mapping Surface Roughness and Soil Moisture using Multi-Angle Radar Imagery without Ancillary Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.L.; Farr, T.G.; Van Zyl, J.J. Estimates of Surface Roughness Derived from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoest, N.E.; Lievens, H.; Wagner, W.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Moran, M.S.; Mattia, F. On the Soil Roughness Parameterization Problem in Soil Moisture Retrieval of Bare Surfaces from Synthetic Aperture Radar. Sensors 2008, 8, 4213–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzahn, P.; Ludwig, R. On the Derivation of Soil Surface Roughness from Multi Parametric PolSAR Data and its Potential for Hydrological Modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Paillou, P.; Grandjean, G.; Dubois, P.; Davidson, M. Relationship between Profile Length and Roughness Variables for Natural Surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3375–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, G.; Mushkin, A.; Blumberg, D.G.; Baer, G.; Ginat, H. Estimating the Age of Desert Alluvial Surfaces with Spaceborne Radar Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Robinson, C.; El-Baz, F.; Stern, R.J. Applications of Orbital Imaging Radar for Geologic Studies in Arid Regions: The Saharan Testimony. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 717–726. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, D.G.; Greeley, R. Field Studies of Aerodynamic Roughness Length. J. Arid Environ. 1993, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Henderson, F.M. Understanding the Relationships between Radar Response Patterns and the Bio-and Geophysical Parameters of Urban Areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, D.G.; Freilikher, V. Soil Water-Content and Surface Roughness Retrieval using ERS-2 SAR Data in the Negev Desert, Israel. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 49, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, R.; Smith, M.; Pak, K.; Li, W.; Gillespie, A.; Gustafson, B. Surface Roughness, Radar Backscatter, and Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance in Death Valley, California. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 23077–23090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, R.; Smith, M.; Pak, K.; Gillespie, A. Inversions of SIR-C and AIRSAR Data for the Roughness of Geological Surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.A.; Campbell, D.B. Analysis of Volcanic Surface Morphology on Venus from Comparison of Arecibo, Magellan, and Terrestrial Airborne Radar Data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1992, 97, 16293–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroin, J.; Simonin, A. An Empirical Model for Interpreting the Relationship between Backscattering and Arid Land Surface Roughness as seen with the SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H. Floods and Sediment Transport in Dryland Rivers. Ph.D. Thesis, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheba, Israel, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, H.; Laronne, B.J. Rainfall-Runoff Relations in Arid Environment and Applications for Floods and Sediment Transport Forecast; Department of Geography and Environmental Development, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev: Beer-Sheva, Israel, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G. Guide to Magellan Image Interpretation; Chapter 5: Radar Interactions with Geologic Surfaces; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Z.; Wilby, R.L. An Evaluation of the Impacts of Land Surface Modification, Storm Sewer Development, and Rainfall Variation on Waterlogging Risk in Shanghai. Nat. Hazards 2012, 63, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.; Moran, M.S.; Thoma, D.P.; Holifield Collins, C.D.; Skirvin, S.; Rahman, M.; Slocum, K.; Starks, P.; Bosch, D.; Gonzalez Dugo, M.P. Measuring Surface Roughness Height to Parameterize Radar Backscatter Models for Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Ulaby, F.T. An Empirical Model and an Inversion Technique for Radar Scattering from Bare Soil Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushkin, A.; Sagy, A.; Trabelci, E.; Amit, R.; Porat, N. Measuring the Time and Scale-Dependency of Subaerial Rock Weathering Rates Over Geologic Time Scales with Ground-Based Lidar. Geology 2014, 42, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Panciera, R.; Tanase, M.A.; Lowell, K.; Hacker, J.M.; Walker, J.P. Estimation of Soil Surface Roughness of Agricultural Soils using Airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, F.; Le Toan, T.; Souyris, J.; De Carolis, C.; Floury, N.; Posa, F.; Pasquariello, N. The Effect of Surface Roughness on Multifrequency Polarimetric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Mozos, J.; Gonzalez-Audicana, M.; Casali, J.; Larranaga, A. Effective Versus Measured Correlation Length for Radar-Based Surface Soil Moisture Retrieval. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5397–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, E. The Geology of the Judean Desert. Master’s Thesis, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.; Asal, F.; Priestnall, G. The use of Photogrammetry and Lidar for Landscape Roughness Estimation in Hydrodynamic Studies. ISPRS XXXB Part B 2004, 3, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Horritt, M.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Bates, P.; Brath, A. Comparing the Performance of a 2-D Finite Element and a 2-D Finite Volume Model of Floodplain Inundation using Airborne SAR Imagery. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2745–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T. Hydraulic Modelling Calibration in Small Rivers by using Coarse Resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtamba, J.; van der Velde, R.; Ndomba, P.; Zoltán, V.; Mtalo, F. Use of Radarsat-2 and Landsat TM Images for Spatial Parameterization of Manning’s Roughness Coefficient in Hydraulic Modeling. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 836–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simoes, N.E.d.C. Urban Pluvial Flood Forecasting. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, D.; Werrity, A.; Bassett, D.; Geddes, A.; Hoolachan, A.; McMillan, M. Pluvial (Rain-Related) Flooding in Urban Areas: The Invisible Hazard; Joseph Rowntree Foundation: York, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zevenbergen, C.; Ma, Y. Urban Pluvial Flooding and Stormwater Management: A Contemporary Review of China’s Challenges and “sponge Cities” Strategy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Coll, M.; Ballester-Merelo, F.; Martinez-Peiro, M.; De la Hoz-Franco, E. Real-Time Early Warning System Design for Pluvial Flash Floods-A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadeh, Y.; Cohen, H.; Maman, S.; Blumberg, D.G. Evaluation of Manning’s n Roughness Coefficient in Arid Environments by Using SAR Backscatter. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101505
Sadeh Y, Cohen H, Maman S, Blumberg DG. Evaluation of Manning’s n Roughness Coefficient in Arid Environments by Using SAR Backscatter. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101505
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadeh, Yuval, Hai Cohen, Shimrit Maman, and Dan G. Blumberg. 2018. "Evaluation of Manning’s n Roughness Coefficient in Arid Environments by Using SAR Backscatter" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101505
APA StyleSadeh, Y., Cohen, H., Maman, S., & Blumberg, D. G. (2018). Evaluation of Manning’s n Roughness Coefficient in Arid Environments by Using SAR Backscatter. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101505