Determinants of Green ICT Adoption in Organizations: A Theoretical Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition of the Topic
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Questions
- Q.1:
- What are the general and specific motivations in the adoption of green ICT?
- Q.2:
- How can the motivations in the adoption of green ICT be classified?
3.2. Research Method
4. Analysis, Findings and Discussion
4.1. Publications by Year
4.2. Overview of Factors Influencing the Adoption of Green ICT in Literature
- Eco-efficiency refers to a business’s desire to deliver “competitively priced goods and services […] while progressively reducing ecological impacts”.
- Eco-equity focuses on “equal rights of people to environmental resources” and a business’s “social responsibility for the future generations”.
- Eco-effectiveness “aims to stop contamination and depletion […] by directing individual and organizational attention to the underlying and fundamental factors of environmental problems […] through a fundamental redesign of the system”.
- implementation of environmental policy instruments: economic and regulatory;
- existence and anticipation of environmental regulations;
- regulatory design.
- cost savings and productivity improvements;
- organizational innovations;
- R&D activities;
- industrial relationships, supply chain pressure and networking activities.
- environmental consciousness and consumers’ preferences for ecological products;
- expected increase in market share or penetration of new market segments.
4.3. Classifications of the Determinants Influencing Green IT Adoption
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peattie, K. Green Consumption: Behavior and Norms. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 195–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, D. Eco-innovation and new product development: Understanding the influences on market performance. Technovation 2006, 26, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, F.; Hertin, J. Impacts of Information and Communication Technologies on Environmental Sustainability: Speculations and Evidence; Report to the OECD; OECD Publishing: Brighton, UK, 2001; Available online: http://www.oecd.org/sti/inno/1897156.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2015).
- Guster, D.; Hemminger, C.; Krzenski, S. Using Virtualization to Reduce Data Center Infrastructure and Promote Green Computing. Int. J. Bus. Res. 2009, 9, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, C. The Implications of New Information and Communication Technologies for Sustainability Environment. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2008, 10, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, S. Green It More Than a Three Percent Solution? Internet Comput. 2009, 13, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson Rivera, M.; Håkansson, C.; Svenfelt, T.; Finnveden, G. Including second order effects in environmental assessments of ICT. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 56, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, I.; Bara, A.; Popeangă, J. Measuring and Improving Energy Efficiency Indicators for a Greener Romania. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. Res. 2014, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Saravana Kumar, P. E-Waste in India—The Dark Side of Information Technology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2, 148–151. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Tian, B.G.; Liu, T.Z. Status quo of e-waste management in mainland China. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2006, 8, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanne, F.Z. Green IT—Why Developing Countries Should Care? Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 8, 424–427. [Google Scholar]
- Krikke, J. Recycling E-Waste: The Sky is the Limit. IT Prof. 2008, 10, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, W.J. ICT and the Environment in Developing Countries: A Review of Opportunities and Developments. In What Kind of Information Society? Governance, Virtually, Surveillance, Sustainability, Resilience; Berleur, J.J., Hercheui, M.D., Hilty, L.M., Eds.; (IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 328, pp. 236–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, H. The effect of ICT development on economic growth and energy consumption in Japan. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, R.E.A.; Rahman, A. Resource-based framework of green it capability toward firms’ competitive advantage. In Proceedings of the 17th Pacific Asia Conference on Information System, Jeju Island, Korea, 18–22 June 2013. Paper 280.
- Nanath, K.; Pillai, R.R. Green Information Technology: Literature Review and Research Domains. J. Manag. Syst. 2014, 24, 57–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tushi, B.T.; Sedera, D.; Recker, J. Green IT Segment Analysis: An Academic Literature Review. In Smart Sustainability: The Information Systems Opportunity, Proceedings of the 12th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Savannah, GA, USA, 7–9 August 2014; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014; pp. 2566–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis, J.; Koo, C.; Watson, R. Green information systems & technologies—This generation and beyond: Introduction to the special issue. Inf. Syst. Front. 2013, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, S. Harnessing Green IT: Principles and Practices. IT Prof. 2008, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, M.C.; Chen, A.; Huber, M. Green Is: Building Sustainable Business Practices. In Information Systems: A Global Text; Watson, T.R., Ed.; Global Text Project: Athens, Greece, 2008; pp. 1–17. Available online: http://www.ceport.com/files/file/Green%20IS%20CePORT%20Article.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- Molla, A. Organisational Motivations for Green IT: Exploring Green IT Matrix and Motivation Models. In Proceedings of the 13th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Hyderabad, India, 10–12 July 2009. Paper 13.
- Andreopoulou, Z. Green Informatics: ICT for Green and Sustainability. J. Agric. Inform. 2012, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingay, S. Green IT: The New Industry Shock Wave, 2007. Available online: http://www.ictliteracy.info/rf.pdf/Gartner_on_Green_IT.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2015).
- Hilty, L.M.; Aebischer, B. ICT for Sustainability: An Emerging Research Field. In ICT Innovations for Sustainability. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Hilty, L.M., Aebischer, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 310, pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bachour, N.; Chasteen, L. Optimizing the Value of Green IT Projects within Organisations. In Proceedings of the Green Technologies Conference, Grapevine, TX, USA, 15–16 April 2010; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkin, A.T.; Webster, J.; McShane, L. An agenda for Green information technology and systems research. Inf. Organ. 2011, 21, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, C.; Piattini, M. Introduction to Green in Software Engineering. In Green in Software Engineering; Calero, C., Piattini, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.T.; Boudreau, M.C.; Chen, A.J. Information Systems and Environmentally Sustainable Development: Energy Informatics and New Directions for the IS Community. MIS Quart. 2010, 34, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, A.; Pittayachawan, S.; Corbitt, B.; Deng, H. An International Comparison of Green IT Diffusion. Int. J. e-Bus. Manag. 2009, 3, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Han, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, C. The Influence of Environmental Management Practices and Supply Chain Integration on Technological Innovation Performance—Evidence from China’s Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15342–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unhelkar, B. Green IT: The Next Five Years. IT Prof. 2011, 13, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishant, R.; Thompson, T.; Goh, M. Sustainable Information Systems: Does It Matter? In Proceedings of the 17th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Jeju Island, Korea, 18–22 June 2013. Paper 88.
- Hankel, A. Understanding Higher Order Impacts of Green ICT. In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference of ICT for Sustainability, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–27 August 2014; Höjer, M., Lago, P., Wangel, J., Eds.; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Nanath, K.; Pillai, R.R. A Sustainability Model of Green IT Initiatives. In Proceedings of 33rd International Conference on Information Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 December 2012; pp. 1–22. Available online: http://aisel.aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1064&context=icis2012 (accessed on 10 July 2016).
- Nishant, R. Green Is and Organizational Performance. An Empirical Examination. In Proceedings of the 16th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Hochiminh City, Vietnam, 11–15 July 2012. Paper 185.
- Nedbal, D.; Wetzlinger, W.; Auinger, A.; Wagner, G. Sustainable Is Initialization through Outsourcing: A Theory-Based Approach. In Proceedings of 17th Americas Conference Information Systems, Detroit, MI, USA, 4–8 August 2011; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; pp. 2282–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Kassarjian, H.H. Content Analysis in Consumer Research. J. Consum. Res. 1977, 4, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. Content Analysis: An. Introduction to Its Methodology, 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Albertao, F. Sustainable Software Development. In Harnessing Green It: Principles and Practices; Murugesan, S., Gangadharan, G.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.A.; Watson, T.R.; Boudreau, M.C.; Karahanna, E. An Institutional Perspective on the Adoption of Green IS & IT. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2011, 17, 5–27. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, M.; Speir, C. Motivations for Proactive Environmental Management. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2664–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, R.S.; Fryxell, G.E. Are conglomerates less environmentally responsible? An empirical examination of diversification strategy and subsidiary pollution in the U.S. chemical industry. J. Bus. Ethics 1999, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 14000–Environmental Management, 2015. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/iso14000 (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Weng, H.H.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, P.C. Effects of Green Innovation on Environmental and Corporate Performance: A Stakeholder Perspective. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4997–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Design for the environment: A quality-based model for green product development. Manag. Sci. 2001, 47, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärling, T.; Fujii, S.; Gärling, A.; Jakobsson, C. Moderating effects of social value orientation on determinants of proenvironmental behavior intention. J. Environ. Psychol. 2003, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Abareshi, A. Green IT Adoption: A Motivational Perspective. In Proceedings of the 15th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, 7–11 July 2011. Paper 137.
- Mishra, D.; Akman, I.; Mishra, A. Theory of Reasoned Action Application for Green Information Technology Acceptance. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 36, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Abareshi, A. Organisational Green Motivations for Information Technology: Empirical Study. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2012, 52, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, A. GITAM: A Model for the Adoption of Green IT. In Proceedings of the 19th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Christchurch, New Zealand, 3–5 December 2008. Paper 64.
- Koo, C.; Chung, N.; Lee, Y.C. The Influential Motivations of Green It Device Use and the Role of Reference Group Perspective. In Proceedings of the 17th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Jeju Island, Korea, 18–22 June 2013. Paper 90.
- Molla, A.; Abareshi, A.; Cooper, V. Green IT beliefs and pro-environmental IT practices among IT professionals. Inf. Technol. People 2014, 27, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.J.; Boudreau, M.C.; Watson, R.T. Information systems and ecological sustainability. J. Syst. Inform. Tech. 2008, 3, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zailani, S.; Govindan, K.; Iranmanesh, M.; Shaharudin, M.R. Green Innovation Adoption in Automotive Supply Chain: The Malaysian case. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Towards a Dynamic Theory of Strategy. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, N.A.; Hall, P.R. The Importance of Regulation-Induced Innovation for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2011, 3, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, W.; Avital, M. From Green IT to Sustainable Innovation. In Proceedings of the 16th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Lima, Peru, 12–15 August 2010; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; pp. 3737–3746. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. For a Socially Responsible European ICT Sector, 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/ict4society-multi-stakeholder-platform (accessed on 2 June 2016).
- European Commission. Directive 2012/19/EU on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE), 2016. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/weee/index_en.htm (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- European Commission. A Digital Single Market for Europe: Commission sets out 16 Initiatives to Make it Happen, 2015. Available online: http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_IP-15-4919_en.htm (accessed on 21 June 2016).
- European Commission. Green Public Procurement a Collection of Good Practices, 2012. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/gpp/pdf/GPP_Good_Practices_Brochure.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2016).
- European Commission. Directive 2002/95/EC on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment, 2015. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/rohs_eee/legis_en.htm (accessed on 5 June 2016).
- Ozturk, A.; Umit, K.; Medeni, I.T.; Ucuncu, B.; Caylan, M.; Akba, F.; Medeni, T.D. Green ICT (Information and Communication Technologies): A Review of Academic and Practitioner Perspectives. Int. J. e-Bus. e-Government Stud. 2011, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, R.; Luo, X. Integrative Framework for Assessing Firms’ Potential to Undertake Green It Initiatives via Virtualization–a Theoretical Perspective. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2011, 20, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S.; Binney, D. Environmentally sustainable ICT: Developing Corporate Capabilities and an Industry-Relevant IS Research Agenda. In Proceedings of the 12th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Suzhou, China, 3–7 July 2008. Paper 209.
- Oltra, V. Environmental Innovation and Industrial Dynamics: The Contributions of Evolutionary Economics. In Paper presented at the 1st DIME (Dynamics of Institutions and Markets in Europe) Scientific Conference on Knowledge in space and time: economic and policy implications of the Knowledge-based economy, Strasbourg, France, 7–9 April 2008; Available online: http://www.dime-eu.org/files/active/0/DIME_WP_n7_oltra.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2015).
- Kuo, N.B. Organizational Green IT: It seems the bottom line rules. In Proceedings of the 16th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Lima, Peru, 12–15 August 2010; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; pp. 2716–2725. [Google Scholar]
- Loeser, F.; Erek, K.; Zarnekow, R.; Schmidt, N.H.; Kolbe, L.M. Aligning Green IT with Environmental Strategies: Development of a Conceptual Framework that Leverages Sustainability and Firm Competitiveness. In Proceedings of 17th Americas Conference Information Systems, Detroit, MI, USA, 4–8 August 2011; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; pp. 1991–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, V.; Langella, I.; Carbo, J. From green to sustainability: Information Technology and an integrated sustainability framework. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2011, 20, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Monitoring industrial research: The 2010 EU Industrial R&D Investment SCOREBOARD; Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg City, Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Green Peace. Make IT Green Cloud Computing and its Contribution to Climate Change, 2010. Available online: http://www.greenpeace.org/international/Global/international/planet-2/report/2010/3/make-it-green-cloud-computing.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2016).
- Bansal, P.; Roth, K. Why companies go green: A model of ecological responsiveness. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 13, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Funding Opportunities, 2016. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/funding/intro_en.htm (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Gu, Q.; Lago, P.; Bozzelli, P. A Decision-Making Model for Adopting Green ICT Strategies. In Green in Software Engineering; Calero, C., Piattini, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 285–300. [Google Scholar]
- Caia, F.; Năstase, P. Modeling a Business Intelligence System for Investment Projects. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. 2015, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. EUROPE 2020. A Strategy for Smart, Sustainable and Inclusive Growth, 2010. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A52010DC2020 (accessed on 5 June 2016).
- European Commission. Europe 2020 Indicators—Climate Change and Energy, 2016. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Europe_2020_indicators_-_climate_change_and_energy (accessed on 18 July 2015).
- Bayo-Morionesa, A.; Lera-Lópezb, F. A firm-level analysis of determinants of ICT adoption in Spain. Technovation 2007, 27, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.R.; Lubbe, S. Synthesis of Green IS Frameworks for Achieving Strong Environmental Sustainability in Organisations. In Proceedings of the South African Institute for Computer Scientists and Information Technologists Conference, Pretoria, South Africa, 1–3 October 2012; Machanick, P., Tsietsi, M., Eds.; ACM: New York, USA, 2013; pp. 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ashford, N.A. An innovation-based strategy for a sustainable environment. In Innovation-Oriented Environmental Regulation: Theoretical Approach and Empirical Analysis; Hemmelskamp, J., Rennings, K., Leone, F., Eds.; Physica-Verlag Heidelberg: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 67–107. [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum, D.S. Cloud Computing and SOA Convergence in Your Enterprise: A Step-by-Step Guide; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.R.; Chien, K.M.; Yang, T.N. Green Component Procurement Collaboration for Improving Supply Chain Management in the High Technology Industries: A Case Study from the Systems Perspective. Sustainability 2016, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unhelkar, B. Green IT Strategies and Applications: Using Environmental Intelligence (Advanced & Emerging Communications Technologies); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Ji, S. Organizational Green IT Adoption: Concept and Evidence. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16737–16755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, E.; Surti, C.; Searcy, C. A literature review and a case study of sustainable supply chains with a focus on metrics, Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Green information technology (IT)/ICT is… |
|---|---|
| [18] | …how “hardware and other infrastructure […] can be better managed and designed from an environmental perspective.” |
| [19] | …“the study and practice of designing, manufacturing, using, and disposing of computers, servers, and associated subsystems—such as monitors, printers, storage devices, and networking and communications systems—efficiently and effectively with minimal or no impact on the environment. Green IT also strives to achieve economic viability and improved system performance and use, while abiding by our social and ethical responsibilities.” |
| [20] | …“mainly focused on energy efficiency and equipment utilization.” |
| [21] | …“an organization’s ability to systematically apply environmental sustainability criteria (such as pollution prevention, product stewardship, use of clean technologies) to the design, production, sourcing, use and disposal of the IT technical infrastructure as well as within the human and managerial components of the IT infrastructure.” |
| [22] | … “design technique, construction technique, the function of the information diffusion technique to achieve optimal environmental governance, and the approach is also about optimization and improvement of the organization’s operational processes without hindering its progress in use of technology.” |
| Concept | Definition | Concept | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| green by IT | “the impact of IT on the environmental productivity of other sectors” [27] | green by hardware | Equipment and installation to help monitor and protect the environment; The use and disposal of hardware with minimum negative influences on the environment. |
| green by software | Software dedicated exclusively to environmental protection and monitoring; Software that provides efficient resources management for other applications. | ||
| green in IT | “the IT sector’s own activity and its impact on environmental efficiency” [27] | green in hardware | All ICT industry initiatives to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, pollution and waste efficient management. |
| green in software | Minimizing negative influences of software development on the environment and supporting the complete life cycle of sustainable software system engineering. |
| Database | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM Digital Library | - | 3 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 42 |
| Web of Science | 1 | 8 | 6 | 9 | 21 | 19 | 18 | 13 | 95 |
| Science Direct | - | - | 2 | 3 | 23 | 16 | 15 | 31 | 90 |
| IEEE Explorer | - | 6 | 4 | 10 | 19 | 47 | 9 | 113 | 208 |
| Total | 1 | 17 | 17 | 28 | 71 | 90 | 49 | 126 | 435 |
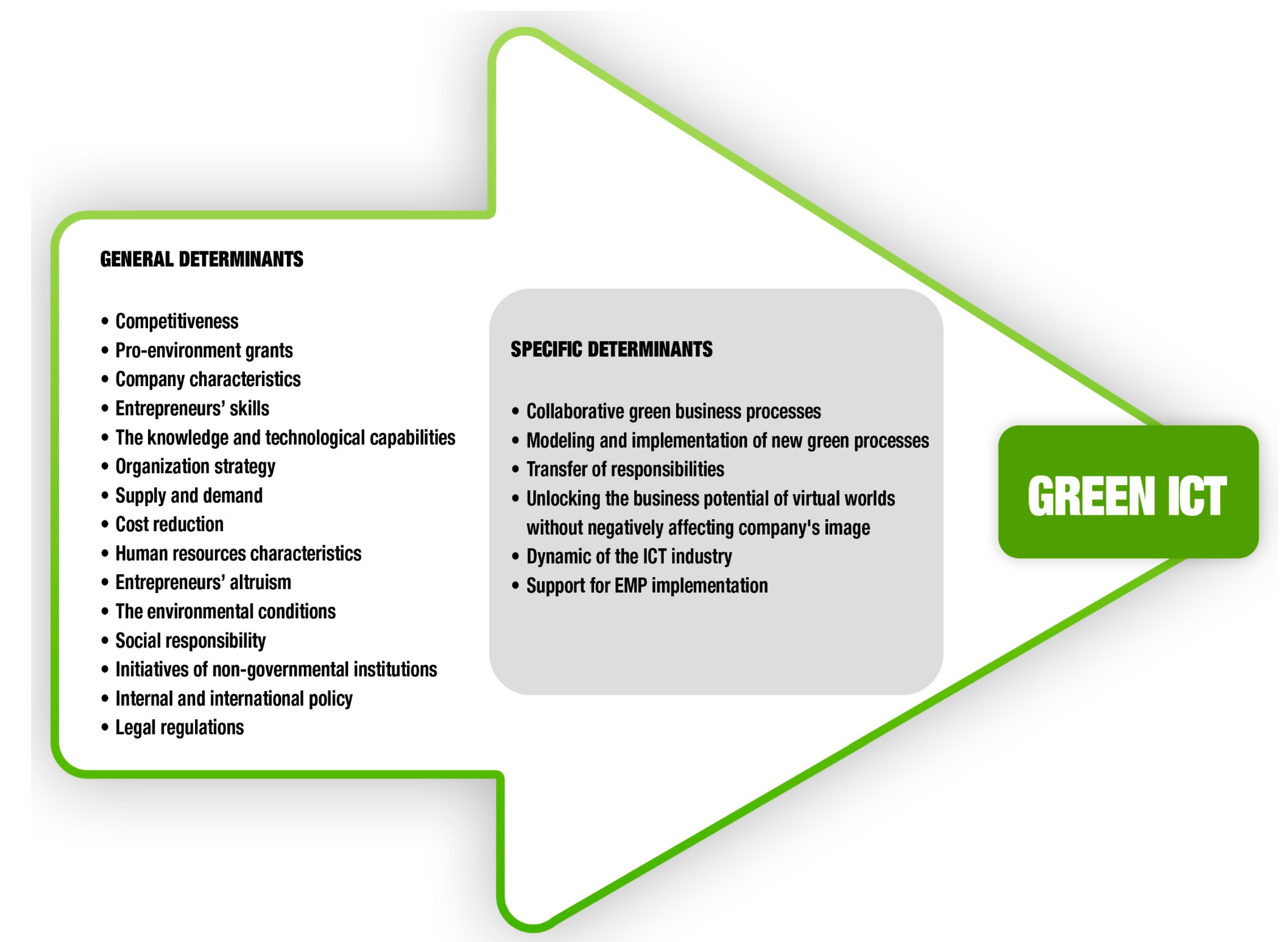
| Economic | Ethical | Regulatory |
|---|---|---|
| Competitiveness [40,44,67,68,69,72] | — | — |
| — | Social responsibility [44,49,53,65,67] | — |
| — | — | Initiatives of non-governmental institutions [71,84] |
| — | The environmental conditions: pollution, diminishing of exhaustible resources, global warming, etc. [40,46,47,66] | — |
| Pro-environment grants [70,73,74,75,76,77] | — | Pro-environment grants [70,73,74,75,76,77] |
| Company characteristics [25,54,56,79,80] | Company characteristics [25,54,56,79,80] | — |
| — | — | Internal and international policy [61,62,66,70,77] |
| Entrepreneurs’ skills [67,80,84] | Entrepreneurs’ skills [67,80,84] | — |
| — | Entrepreneurs’ altruism [21,52,72,84] | — |
| The knowledge and technological capabilities [67,80,84] | — | — |
| Organization strategy: eco-efficiency, eco-equity, eco-effectiveness [49,53] | Organization strategy: eco-efficiency, eco-equity, eco-effectiveness [49,53] | — |
| — | — | Legal regulations [11,40,44,53,54,55,56,57,63,64,66,67,84] |
| Supply and demand [29,44,66] | — | — |
| Cost reduction [29,42,44,45,55,56,57,64,66,72] | — | — |
| Human resources characteristics [42,44,67] | Human resources characteristics [42,44,67] | — |
| Economic | Ethical | Regulatory |
|---|---|---|
| Collaborative green business processes | — | Collaborative green business processes |
| Harnessing the potential of the presence in the virtual environment, without adversely affecting the company's image | Harnessing the potential of the presence in the virtual environment, without adversely affecting the company's image | — |
| Modelling and implementation of new green processes | — | — |
| The transfer of responsibilities | The transfer of responsibilities | — |
| The dynamic of the ICT industry | The dynamic of the ICT industry | The dynamic of the ICT industry |
| The support for implementation of EMPs | The support for implementation of EMPs | The support for implementation of EMPs |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radu, L.-D. Determinants of Green ICT Adoption in Organizations: A Theoretical Perspective. Sustainability 2016, 8, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080731
Radu L-D. Determinants of Green ICT Adoption in Organizations: A Theoretical Perspective. Sustainability. 2016; 8(8):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080731
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadu, Laura-Diana. 2016. "Determinants of Green ICT Adoption in Organizations: A Theoretical Perspective" Sustainability 8, no. 8: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080731
APA StyleRadu, L.-D. (2016). Determinants of Green ICT Adoption in Organizations: A Theoretical Perspective. Sustainability, 8(8), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080731






