How Do Bird Population Trends Relate to Human Pressures Compared to Economic Growth?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Multi-Scale Approach
2.2. Bird Species Data
2.3. Anthropogenic Data
2.4. Estimation of Species Population Trends
2.5. Time Series Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bird Population Trends
3.2. Long-Run Relationship Between the Population Trends, HFI, and GDP
4. Discussion
4.1. Bird Population Trends at National and Sub-National Levels
4.2. Long-Term Response of Biodiversity to Economic Growth and Human Activity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDL | Autoregressive Distributed Lag |
| CAC | Common Birds Census |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| HFI | Human Footprint Index |
| MSI-Tool | Multi-Species Indicator Tool |
| SPEA | Portuguese Society for the Study of Birds |
| TRIM | TRends & Indices for Monitoring data |
| UTM | Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system |
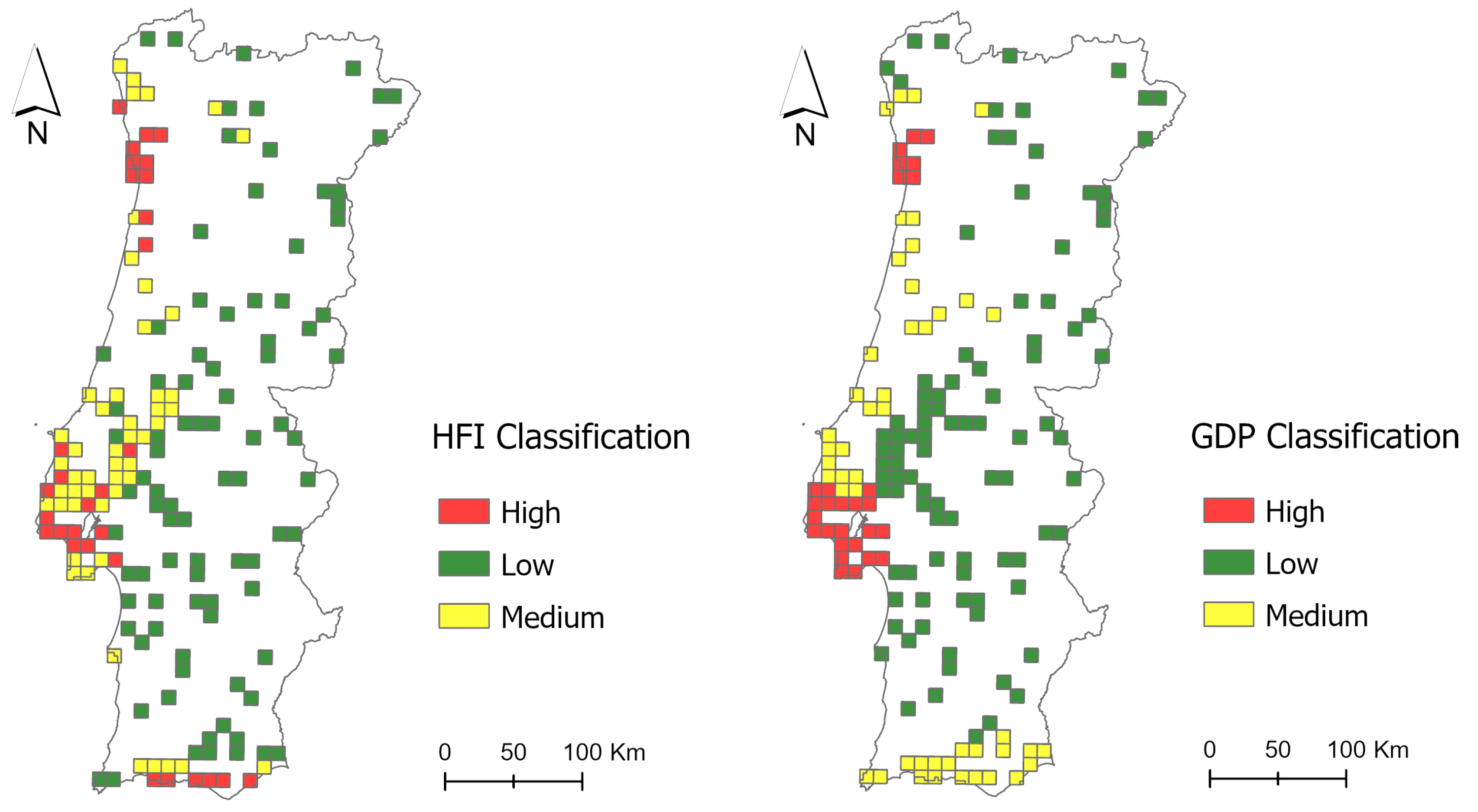
Appendix A. Bird Data Cell Information
| Bird Data Cell | UTM | NUTSII | Nº of Visits | HFI Category | GDP Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MC68 | Lisboa | 12 | High | High |
| 2 | MC69 | Lisboa | 15 | High | High |
| 3 | MC78 | Lisboa | 10 | High | High |
| 4 | MC85 | Lisboa | 4 | Medium | High |
| 5 | MC86 | Lisboa | 4 | Medium | High |
| 6 | MC87 | Lisboa | 5 | High | High |
| 7 | MC95 | Lisboa | 15 | Medium | High |
| 8 | MC97 | Lisboa | 9 | High | High |
| 9 | MD60 | Lisboa | 7 | Medium | High |
| 10 | MD61 | Lisboa | 3 | High | High |
| 11 | MD70 | Lisboa | 4 | Medium | High |
| 12 | MD71 | Lisboa | 5 | Medium | High |
| 13 | MD72 | Centro | 5 | High | Medium |
| 14 | MD73 | Centro | 6 | Medium | Medium |
| 15 | MD74 | Centro | 7 | High | Medium |
| 16 | MD75 | Centro | 5 | Medium | Medium |
| 17 | MD80 | Lisboa | 6 | Medium | High |
| 18 | MD81 | Centro | 11 | Medium | Medium |
| 19 | MD82 | Centro | 5 | Medium | Medium |
| 20 | MD84 | Centro | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 21 | MD90 | Lisboa | 9 | High | High |
| 22 | MD91 | Centro | 5 | Medium | Medium |
| 23 | MD98 | Centro | 7 | Medium | Medium |
| 24 | NB10 | Algarve | 7 | Low | Medium |
| 25 | NB19 | Alentejo | 6 | Medium | Low |
| 26 | NB31 | Algarve | 20 | Medium | Medium |
| 27 | NB35 | Alentejo | 6 | Low | Low |
| 28 | NB41 | Algarve | 3 | Medium | Medium |
| 29 | NB56 | Alentejo | 15 | Low | Low |
| 30 | NB61 | Algarve | 2 | Medium | Medium |
| 31 | NB68 | Alentejo | 10 | Low | Low |
| 32 | NB69 | Alentejo | 4 | Low | Low |
| 33 | NB70 | Algarve | 7 | High | Medium |
| 34 | NB72 | Algarve | 3 | Low | Medium |
| 35 | NB80 | Algarve | 1 | High | Medium |
| 36 | NB82 | Algarve | 5 | Low | Medium |
| 37 | NB83 | Alentejo | 2 | Low | Low |
| 38 | NB90 | Algarve | 11 | High | Medium |
| 39 | NB94 | Alentejo | 2 | Low | Low |
| 40 | NC06 | Lisboa | 14 | Medium | High |
| 41 | NC08 | Lisboa | 2 | High | High |
| 42 | NC16 | Lisboa | 5 | High | High |
| 43 | NC18 | Lisboa | 3 | Low | High |
| 44 | NC21 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 45 | NC23 | Alentejo | 9 | Low | Low |
| 46 | NC25 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 47 | NC30 | Alentejo | 19 | Low | Low |
| 48 | NC35 | Alentejo | 19 | Low | Low |
| 49 | NC41 | Alentejo | 11 | Low | Low |
| 50 | NC43 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 51 | NC56 | Alentejo | 9 | Low | Low |
| 52 | NC59 | Alentejo | 14 | Low | Low |
| 53 | NC69 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 54 | NC73 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 55 | NC75 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 56 | NC76 | Alentejo | 7 | Low | Low |
| 57 | NC82 | Alentejo | 8 | Low | Low |
| 58 | NC83 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 59 | ND00 | Lisboa | 5 | Medium | High |
| 60 | ND01 | Lisboa | 6 | High | High |
| 61 | ND07 | Centro | 20 | Medium | Medium |
| 62 | ND11 | Alentejo | 14 | Medium | Low |
| 63 | ND12 | Alentejo | 11 | Medium | Low |
| 64 | ND13 | Alentejo | 14 | Medium | Low |
| 65 | ND14 | Alentejo | 8 | Medium | Low |
| 66 | ND15 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 67 | ND17 | Centro | 9 | Low | Medium |
| 68 | ND18 | Centro | 7 | Medium | Medium |
| 69 | ND21 | Alentejo | 9 | Low | Low |
| 70 | ND22 | Alentejo | 4 | Medium | Low |
| 71 | ND23 | Alentejo | 1 | Medium | Low |
| 72 | ND24 | Alentejo | 20 | High | Low |
| 73 | ND25 | Alentejo | 12 | Medium | Low |
| 74 | ND26 | Centro | 5 | Medium | Low |
| 75 | ND32 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 76 | ND35 | Alentejo | 8 | Medium | Low |
| 77 | ND40 | Alentejo | 20 | Low | Low |
| 78 | ND41 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 79 | ND44 | Alentejo | 15 | Low | Low |
| 80 | ND45 | Alentejo | 8 | Low | Low |
| 81 | ND47 | Centro | 8 | Medium | Low |
| 82 | ND48 | Centro | 11 | Medium | Low |
| 83 | ND50 | Alentejo | 5 | Low | Low |
| 84 | ND57 | Centro | 1 | Medium | Low |
| 85 | ND58 | Centro | 3 | Medium | Low |
| 86 | ND66 | Centro | 2 | Low | Low |
| 87 | ND69 | Centro | 4 | Low | Low |
| 88 | ND76 | Centro | 12 | Low | Low |
| 89 | ND86 | Centro | 11 | Low | Low |
| 90 | ND92 | Alentejo | 4 | Low | Low |
| 91 | ND98 | Centro | 13 | Low | Low |
| 92 | NE01 | Centro | 5 | Low | Medium |
| 93 | NE28 | Centro | 3 | Medium | Medium |
| 94 | NE33 | Centro | 6 | Medium | Medium |
| 95 | NE36 | Centro | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 96 | NE39 | Centro | 9 | High | Medium |
| 97 | NE43 | Centro | 1 | Low | Medium |
| 98 | NE54 | Centro | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 99 | NE71 | Centro | 5 | Low | Low |
| 100 | NE75 | Centro | 7 | Low | Medium |
| 101 | NE80 | Centro | 8 | Low | Low |
| 102 | NE94 | Centro | 3 | Low | Medium |
| 103 | NF21 | Centro | 5 | Medium | Medium |
| 104 | NF25 | Norte | 3 | High | High |
| 105 | NF26 | Norte | 4 | High | High |
| 106 | NF31 | Centro | 9 | High | Medium |
| 107 | NF35 | Norte | 2 | High | High |
| 108 | NF37 | Norte | 2 | High | High |
| 109 | NF47 | Norte | 2 | High | High |
| 110 | NF70 | Centro | 2 | Low | Low |
| 111 | NF89 | Norte | 2 | Medium | Medium |
| 112 | NF97 | Norte | 2 | Low | Low |
| 113 | NG12 | Norte | 3 | Medium | Low |
| 114 | NG20 | Norte | 2 | Medium | Medium |
| 115 | NG21 | Norte | 1 | Medium | Low |
| 116 | NG30 | Norte | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 117 | NG34 | Norte | 1 | Low | Low |
| 118 | NG54 | Norte | 4 | Low | Low |
| 119 | PB02 | Algarve | 2 | Low | Medium |
| 120 | PB03 | Algarve | 9 | Low | Medium |
| 121 | PB07 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 122 | PB10 | Algarve | 4 | High | Medium |
| 123 | PB16 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 124 | PB21 | Algarve | 6 | Medium | Medium |
| 125 | PB22 | Algarve | 9 | Low | Medium |
| 126 | PB29 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
| 127 | PC06 | Alentejo | 14 | Low | Low |
| 128 | PC14 | Alentejo | 7 | Low | Low |
| 129 | PC16 | Alentejo | 11 | Low | Low |
| 130 | PC48 | Alentejo | 5 | Low | Low |
| 131 | PD02 | Alentejo | 2 | Low | Low |
| 132 | PD15 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 133 | PD36 | Alentejo | 3 | Low | Low |
| 134 | PD45 | Alentejo | 5 | Low | Low |
| 135 | PD52 | Alentejo | 18 | Low | Low |
| 136 | PE15 | Centro | 2 | Low | Low |
| 137 | PE21 | Centro | 9 | Low | Low |
| 138 | PE22 | Centro | 4 | Low | Low |
| 139 | PE35 | Centro | 7 | Low | Low |
| 140 | PE49 | Centro | 1 | Low | Low |
| 141 | PE53 | Centro | 3 | Low | Low |
| 142 | PE64 | Centro | 4 | Low | Low |
| 143 | PE71 | Centro | 5 | Low | Low |
| 144 | PF07 | Norte | 2 | Medium | Low |
| 145 | PF13 | Norte | 1 | Low | Low |
| 146 | PF19 | Norte | 9 | Low | Low |
| 147 | PF26 | Norte | 1 | Low | Low |
| 148 | PF63 | Centro | 2 | Low | Low |
| 149 | PF71 | Centro | 1 | Low | Low |
| 150 | PF72 | Centro | 14 | Low | Low |
| 151 | PF73 | Centro | 1 | Low | Low |
| 152 | PG03 | Norte | 3 | Low | Low |
| 153 | PG82 | Norte | 1 | Low | Low |
| 154 | QF07 | Norte | 20 | Low | Low |
| 155 | QG00 | Norte | 9 | Low | Low |
| 156 | NB00 | Algarve | 1 | Low | Medium |
| 157 | PB32 | Algarve | 4 | Low | Medium |
| 158 | QG10 | Norte | 3 | Low | Low |
| 159 | MC88 | Lisboa | 1 | High | High |
| 160 | MD92 | Centro | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 161 | NF19 | Norte | 3 | High | Medium |
| 162 | NF99 | Norte | 2 | Low | Low |
| 163 | NB40 | Algarve | 1 | High | Medium |
| 164 | NB50 | Algarve | 3 | High | Medium |
| 165 | NB51 | Algarve | 1 | Medium | Medium |
| 166 | ND46 | Alentejo | 2 | Medium | Low |
| 167 | ND49 | Centro | 1 | Low | Low |
| 168 | NF24 | Norte | 1 | High | High |
| 169 | NF34 | Norte | 1 | High | High |
| 170 | PC38 | Alentejo | 1 | Low | Low |
Appendix B. Bird Species and Habitat
| Euring | Scientific Name | Habitat | MSI Population Trend | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | HFI Clusters | GDP Clusters | |||||||
| HighHFI | MediumHFI | LowHFI | HighGDP | MediumGDP | LowGDP | ||||
| 14,370 | Aegithalos caudatus | forest | ↔ | ⇓ | ↑ | ↔ | ⇑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| 1860 | Anas platyrhynchos | other | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ |
| 7950 | Apus apus | other | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 1220 | Ardea cinerea | other | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 7570 | Athene noctua | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 1110 | Bubulcus ibis | agricultural | ↓ | ↔ | ↑ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 2870 | Buteo buteo | other | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 16,530 | Carduelis carduelis | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 9950 | Cecropis daurica | other | ↑ | ↔ | ⇑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 14,870 | Certhia brachydactyla | forest | ↑ | ↑ | ⇑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 12,200 | Cettia cetti | other | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ |
| 16,490 | Chloris chloris | agricultural | ↔ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ |
| 1340 | Ciconia ciconia | agricultural | ↑ | ⇑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ⇑ | ↑ |
| 12,260 | Cisticola juncidis | agricultural | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 6650 | Columba livia | other | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ |
| 6700 | Columba palumbus | forest | ⇑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↑ | ⇑ |
| 15,670 | Corvus corone | other | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ⇑ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 3700 | Coturnix coturnix | agricultural | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ |
| 7240 | Cuculus canorus | forest | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ |
| 14,620 | Cyanistes caeruleus | forest | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 15,470 | Cyanopica cyanus | other | ↑ | ↑ | ⇑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 10,010 | Delichon urbicum | agricultural | ↔ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 8760 | Dendrocopos major | forest | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ |
| 1190 | Egretta garzetta | other | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 2350 | Elanus caeruleus | other | ↔ | - | ↔ | ↓ | - | ⇑ | ↓ |
| 18,820 | Emberiza calandra | agricultural | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| 18,580 | Emberiza cirlus | agricultural | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 10,990 | Erithacus rubecula | forest | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 3040 | Falco tinnunculus | agricultural | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 16,360 | Fringilla coelebs | forest | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| 9720 | Galerida cristata | agricultural | ↔ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ |
| 4240 | Gallinula chloropus | other | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 15,390 | Garrulus glandarius | forest | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 2980 | Hieraaetus pennatus | other | ↔ | - | ↑ | ↓ | - | - | ↓ |
| 12,600 | Hippolais polyglotta | other | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↔ | ⇓ | ⇓ | ↔ |
| 9920 | Hirundo rustica | agricultural | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 32,910 | Lanius meridionalis | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 15,230 | Lanius senator | forest | ↓ | - | ⇓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ |
| 16,600 | Linaria cannabina | agricultural | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 14,540 | Lophophanes cristatus | forest | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 9740 | Lullula arborea | forest | ↓ | - | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 11,040 | Luscinia megarhynchos | other | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ |
| 8400 | Merops apiaster | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↑ | ⇓ | ↓ |
| 2380 | Milvus migrans | agricultural | ↑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↔ | ⇑ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 10,200 | Motacilla alba | other | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ |
| 10,190 | Motacilla cinerea | other | ↔ | - | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ |
| 15,080 | Oriolus oriolus | forest | ↔ | - | ↔ | ↑ | - | ↔ | ↑ |
| 14,640 | Parus major | forest | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 15,910 | Passer domesticus | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 15,980 | Passer montanus | other | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | ↓ | ⇓ | ↔ | ↔ |
| 14,610 | Periparus ater | forest | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ | ↑ | ↓ |
| 11,210 | Phoenicurus ochruros | other | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ⇑ | ↔ | ↔ |
| 15,490 | Pica pica | agricultural | ↑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 8560 | Picus sharpei | forest | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ⇑ | ↔ |
| 11,390 | Saxicola torquatus | agricultural | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 16,400 | Serinus serinus | agricultural | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 14,790 | Sitta europaea | forest | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ |
| 6840 | Streptopelia decaocto | other | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 6870 | Streptopelia turtur | forest | ↓ | ⇓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 15,830 | Sturnus unicolor | agricultural | ↑ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↓ | ⇑ | ⇑ | ↔ |
| 12,770 | Sylvia atricapilla | forest | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 12,670 | Sylvia melanocephala | other | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| 10,660 | Troglodytes troglodytes | forest | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ | ↑ | ↑ | ↔ |
| 11,870 | Turdus merula | other | ↔ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↔ | ↓ |
| 8460 | Upupa epops | agricultural | ↔ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ | ↓ | ↔ | ↔ |
Appendix C. HFI and GDP Time Series at the National Scale
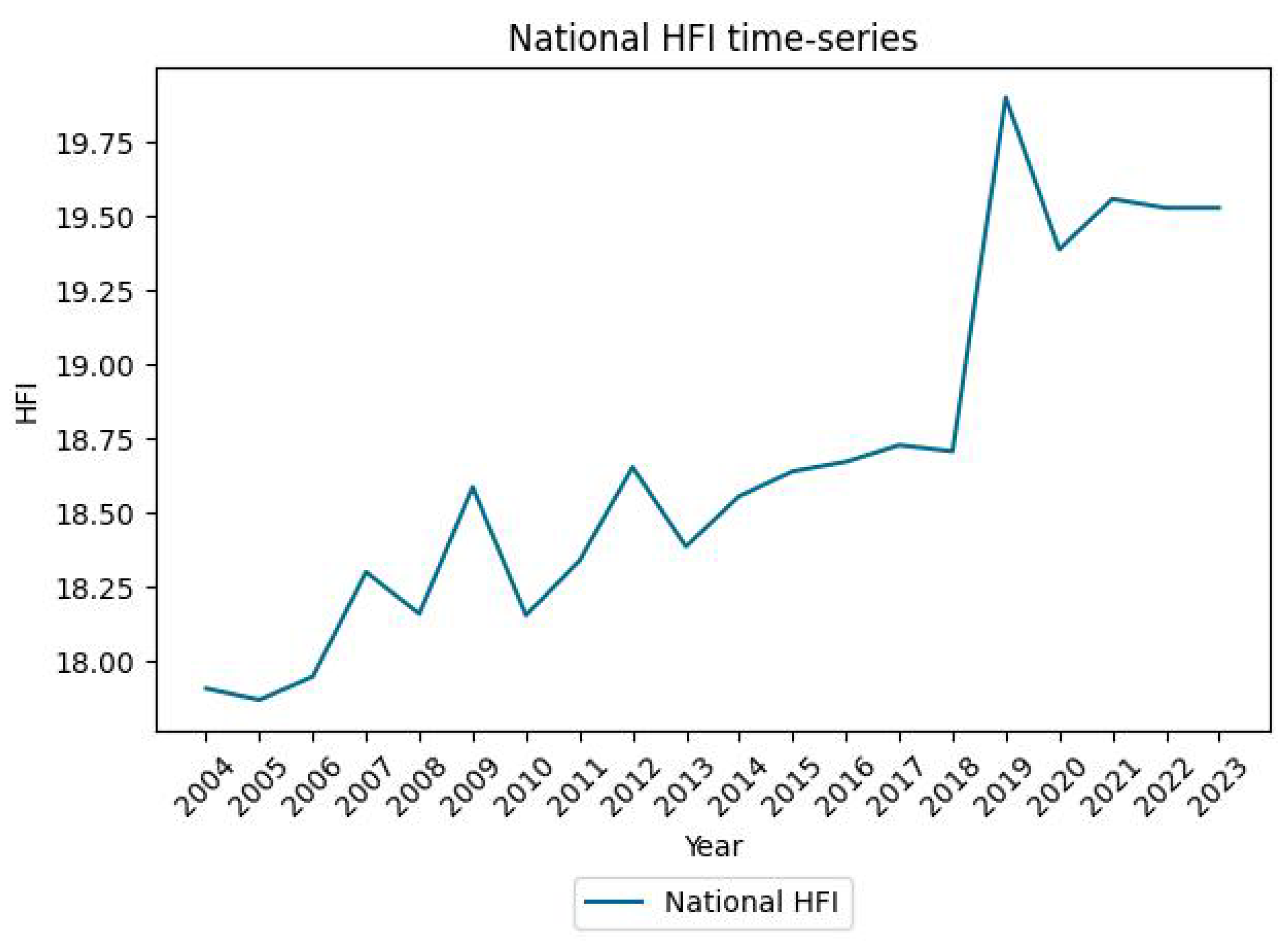
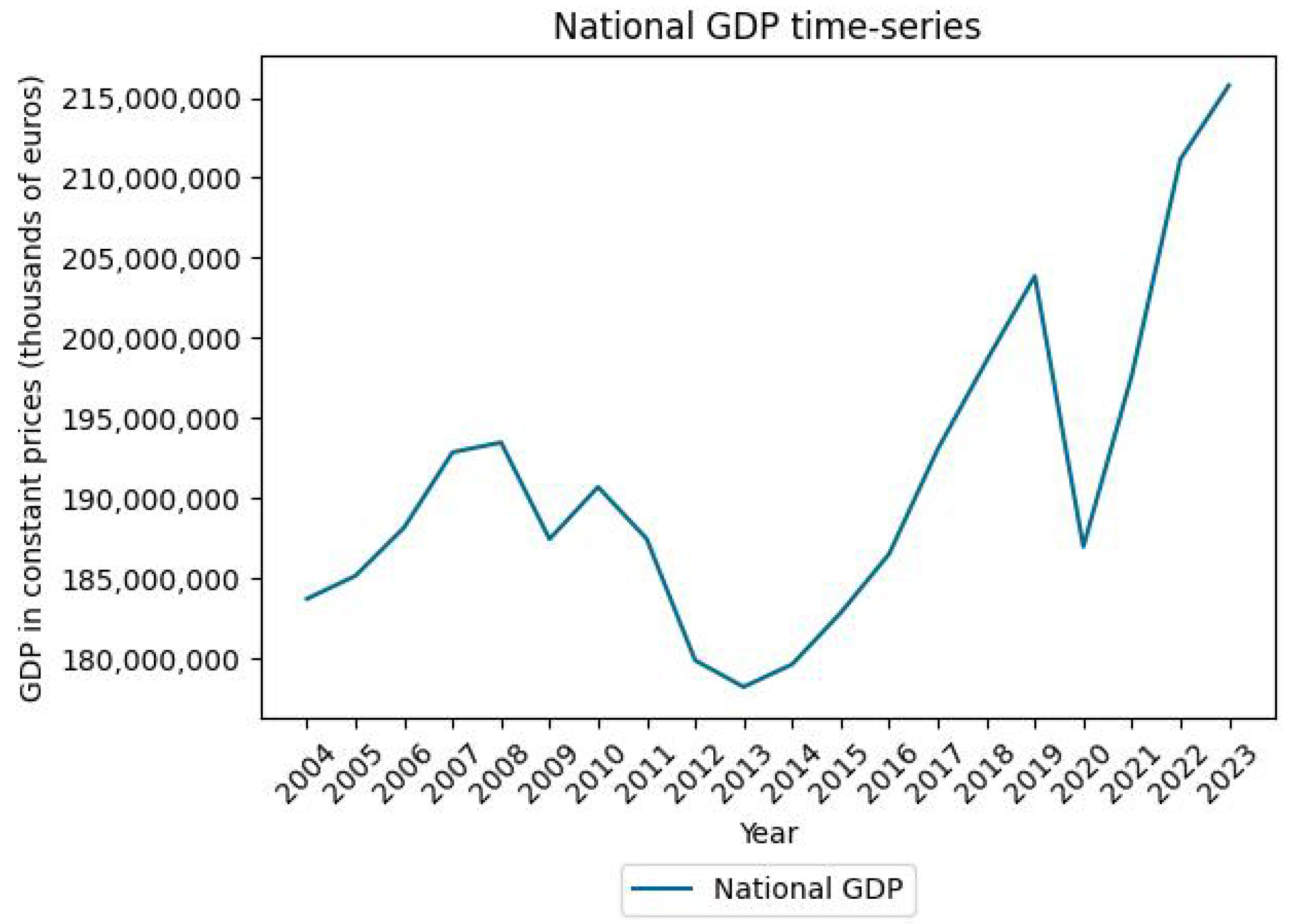
References
- Steffen, W.; Broadgate, W.; Deutsch, L.; Gaffney, O.; Ludwig, C. The trajectory of the Anthropocene: The great acceleration. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Putting people in the map: Anthropogenic biomes of the world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, R.; Grooten, M.; Juffe Bignoli, D.; Petersen, T. Living Planet Report 2022—Building a Nature Positive Society; Technical Report; WWF: Gland, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, S.; Fargione, J.; Chapin, F.S., III; Tilman, D. Biodiversity loss threatens human well-being. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, S.; Demissew, S.; Carabias, J.; Joly, C.; Lonsdale, M.; Ash, N.; Larigauderie, A.; Adhikari, J.R.; Arico, S.; Báldi, A.; et al. The IPBES Conceptual Framework—Connecting nature and people. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin, M. The links between biodiversity, ecosystem services and human well-being. In Ecosystem Ecology: A New Synthesis; Raffaelli, D.G., Frid, C.L.J., Eds.; Ecological Reviews; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 110–139. [Google Scholar]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin, M. Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services; Centre for Environmental Management, University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D., Jr.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.J.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-offs across space, time, and ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmqvist, T.; Tuvendal, M.; Krishnaswamy, J.; Hylander, K. Managing trade-offs in ecosystem services. In Values, Payments and Institutions for Ecosystem Management; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2013; pp. 70–89. [Google Scholar]
- Trauger, D.L.; Czech, B.; Erickson, J.D.; Garrettson, P.R.; Kernohan, B.J.; Miller, C.A. The Relationship of Economic Growth to Wildlife Conservation; Vol. 03-1, The Wildlife Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Jaiteh, M.; Levy, M.A.; Redford, K.H.; Wannebo, A.V.; Woolmer, G. The human footprint and the last of the wild. BioScience 2002, 52, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Fisher, K.; Robinson, N.; Sampson, D.; Duncan, A.; Royte, L. The March of the Human Footprint. 2022. Available online: https://ecoevorxiv.org/repository/view/3641/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.R.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.; Fekete, B.M.; et al. Global terrestrial Human Footprint maps for 1993 and 2009. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynan, K.; Sheiner, L.; GDP as a Measure of Economic Well-Being. Technical Report, Hutchins Center Working Paper. 2018. Available online: https://www.degruyterbrill.com/document/doi/10.7208/chicago/9780226836348-002/pdf (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.L.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W. The Limits to Growth: A Report for the Club of Rome’s Project on the Predicament of Mankind; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Asafu-Adjaye, J. Biodiversity loss and economic growth: A cross-country analysis. Contemp. Econ. Policy 2003, 21, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, I.M.; Campos, M.; Gustafsson, L. Economic development, institutions, and biodiversity loss at the global scale. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alier, J.; Pascual, U.; Vivien, F.D.; Zaccai, E. Sustainable de-growth: Mapping the context, criticisms and future prospects of an emergent paradigm. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Kallis, G.; Martinez-Alier, J. Crisis or opportunity? Economic degrowth for social equity and ecological sustainability. Introduction to this special issue. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Decoupling Natural Resource Use and Environmental Impacts from Economic Growth. A Report of the Working Group on Decoupling to the International Resource Panel; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenhofer, D.; Virág, D.; Kalt, G.; Plank, B.; Streeck, J.; Pichler, M.; Mayer, A.; Krausmann, F.; Brockway, P.; Schaffartzik, A.; et al. A systematic review of the evidence on decoupling of GDP, resource use and GHG emissions, part I: Bibliometric and conceptual mapping. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, S.; Adger, W. Economic growth, biodiversity loss and conservation effort. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 68, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitic, P.; Kojic, M.; Minović, J. A Literature Survey of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Econ. Anal. 2019, 52, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.D.; Van Strien, A.; Vorisek, P.; Gmelig Meyling, A.W.; Noble, D.G.; Foppen, R.P.; Gibbons, D.W. Developing indicators for European birds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.M.; Cooper, H.D. Towards the global monitoring of biodiversity change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, F.; Eaton, M.A.; Burfield, I.J.; Klvaňová, A.; Šilarová, E.; Staneva, A.; Gregory, R.D. Abundance decline in the avifauna of the European Union reveals cross-continental similarities in biodiversity change. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 16647–16660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, H.; Coelho, R.; Gouveia, C.; Rethoré, G.; Teodósio, J. Relatório do Censo de Aves Comuns 2004–2023; Technical Report; Sociedade Portuguesa para o Estudo das Aves: Lisboa, Portugal, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, P.; Su, W.; Miao, S.; Geng, M. A global record of annual terrestrial Human Footprint dataset from 2000 to 2018. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMECO Database. Available online: https://economy-finance.ec.europa.eu/economic-research-and-databases/economic-databases/ameco-database_en (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Statistics Portugal. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_cnacionais2010b2016&menuBOUI=13707095&contexto=cr&selTab=tab3&perfil=392023561&INST=391966542 (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Pannekoek, J.; Van Strien, A. TRIM 3 Manual (TRends & Indices for Monitoring Data); Statistics Netherlands: Voorburg, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Soldaat, L.L.; Pannekoek, J.; Verweij, R.J.; van Turnhout, C.A.; van Strien, A.J. A Monte Carlo method to account for sampling error in multi-species indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannekoek, J.; Bogaart, P.; van der Loo, M. Models and Statistical Methods in Rtrim; Statistics Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaran, H.; Shin, Y. An Autoregressive Distributed Lag Modeling Approach to Co-integration Analysis. In Econometncs and Economic Theory in the 20st Century: The Ragnar Frisch Centennial Symposium; Department of Applied Economics, University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 1995; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, R.J.; Reyers, B.; Biggs, R.; Spierenburg, M.; Duriappah, A. Multi-scale and cross-scale assessments of social–ecological systems and their ecosystem services. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Isbell, F.; Cadotte, M.W. Assessing the importance of species and their assemblages for the biodiversity-ecosystem multifunctionality relationship. Ecology 2023, 104, e4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigal, S.; Dakos, V.; Alonso, H.; Auniņš, A.; Benko, Z.; Brotons, L.; Chodkiewicz, T.; Chylarecki, P.; De Carli, E.; Del Moral, J.C.; et al. Farmland practices are driving bird population decline across Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216573120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.D.; Skorpilova, J.; Vorisek, P.; Butler, S. An analysis of trends, uncertainty and species selection shows contrasting trends of widespread forest and farmland birds in Europe. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.D.; Eaton, M.A.; Burfield, I.J.; Grice, P.V.; Howard, C.; Klvaňová, A.; Noble, D.; Šilarová, E.; Staneva, A.; Stephens, P.A.; et al. Drivers of the changing abundance of European birds at two spatial scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2023, 378, 20220198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J. Long-term trends in bird populations: A review of patterns and potential drivers in North America and Europe. Acta Ornithol. 2013, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Gamero, A.; Hološková, A.; Aunins, A.; Chodkiewicz, T.; Hristov, I.; Kurlavičius, P.; Leivits, M.; Szép, T.; Voříšek, P. Accelerated farmland bird population declines in European countries after their recent EU accession. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.T.; Currie, D.J. Effects of human activity on global extinction risk. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozumder, P.; Berrens, R.P.; Bohara, A.K. Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for the risk of biodiversity loss? J. Dev. Areas 2006, 39, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelson, G.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Peterson, G.D. Economic inequality predicts biodiversity loss. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Strong increase | Lower CL > 1.05 (significant increase of more than 5% per year) |
| Moderate increase | 1.00 < lower CL < 1.05 (significant increase, but not significantly more than 5% per year) |
| Stable | CI includes 1.00 and 0.95 ≤ lower CL and upper CL ≤ 1.05 (no significant increase or decline, likely that changes are smaller than 5% per year) |
| Moderate decline | 0.95 < upper CL < 1.00 (significant decline, but not significantly more than 5% per year) |
| Steep decline | upper CL < 0.95 (significant decline of more than 5% per year) |
| Uncertain | lower CL < 0.95 and 1.05 < upper CL (no significant increase or decline, unlikely that changes are smaller than 5% per year) |
| Approach | Sub-National Level | Group | MSI Classification | Independent Variable: HFI | Independent Variable: GDP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | R-Squared | Coefficient | R-Squared | ||||
| National | Common | ↔ | ns | ||||
| Agricultural | ↓ | ns | |||||
| Forest | ↑ | ns | ns | ||||
| Clusters HFI | High HFI | Common | ↔ | ||||
| Agricultural | ↔ | ||||||
| Forest | ↓ | ns | |||||
| Medium HFI | Common | ↑ | |||||
| Agricultural | ↑ | ns | ns | ||||
| Forest | ↑ | ||||||
| Low HFI | Common | ↓ | ns | ns | |||
| Agricultural | ↓ | ||||||
| Forest | ↑ | ns | |||||
| Clusters GDP | High GDP | Common | ↑ | ns | ns | ||
| Agricultural | ↔ | ||||||
| Forest | ↑ | ns | |||||
| Medium GDP | Common | ↑ | ns | ||||
| Agricultural | ↔ | ||||||
| Forest | ↔ | ns | ns | ns | |||
| Low GDP | Common | ↓ | ns | ||||
| Agricultural | ↓ | ns | |||||
| Forest | ↑ | ns | ns | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baptista, L.; Domingos, T.; Santos, J.; Proença, V. How Do Bird Population Trends Relate to Human Pressures Compared to Economic Growth? Sustainability 2025, 17, 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083506
Baptista L, Domingos T, Santos J, Proença V. How Do Bird Population Trends Relate to Human Pressures Compared to Economic Growth? Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083506
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaptista, Leonor, Tiago Domingos, João Santos, and Vânia Proença. 2025. "How Do Bird Population Trends Relate to Human Pressures Compared to Economic Growth?" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083506
APA StyleBaptista, L., Domingos, T., Santos, J., & Proença, V. (2025). How Do Bird Population Trends Relate to Human Pressures Compared to Economic Growth? Sustainability, 17(8), 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083506







