Recycling of Spandex: Broadening the Way for a Complete Cycle of Textile Waste
Abstract
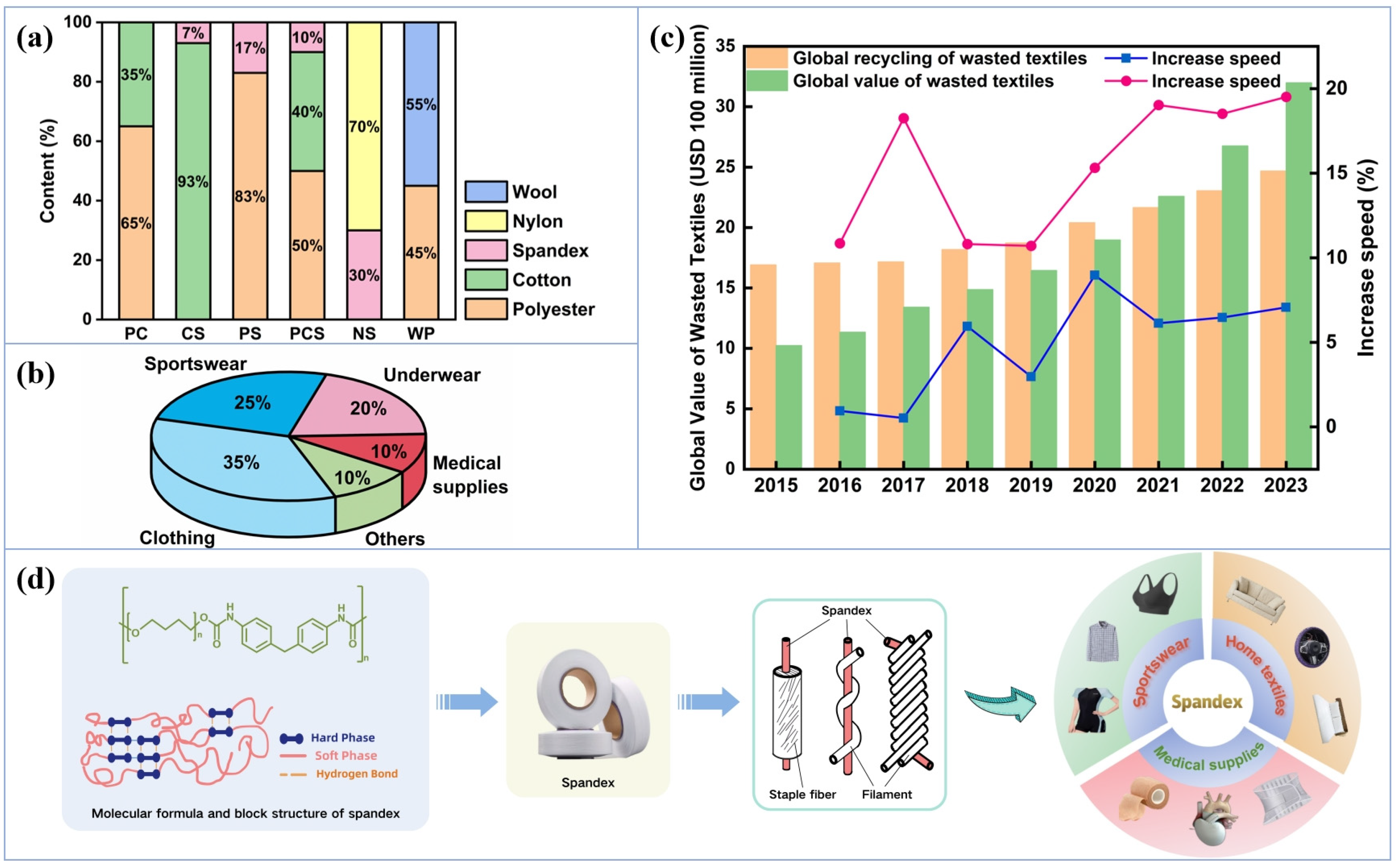
1. Introduction
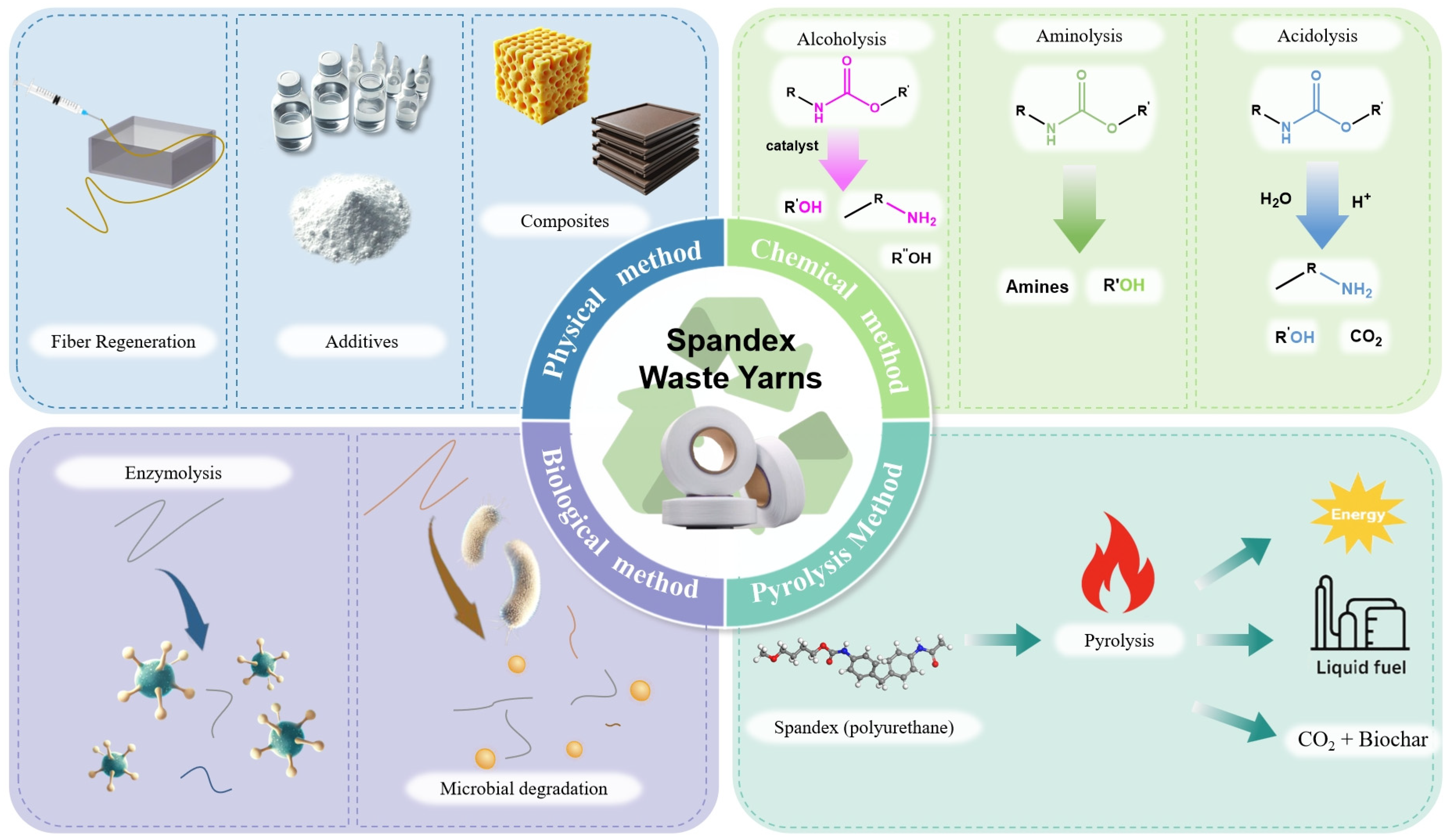
2. Recycling and Utilization of Spandex Waste Yarns
2.1. Physical Methods
2.2. Pyrolysis Methods
2.3. Chemical Methods

2.4. Biological Methods
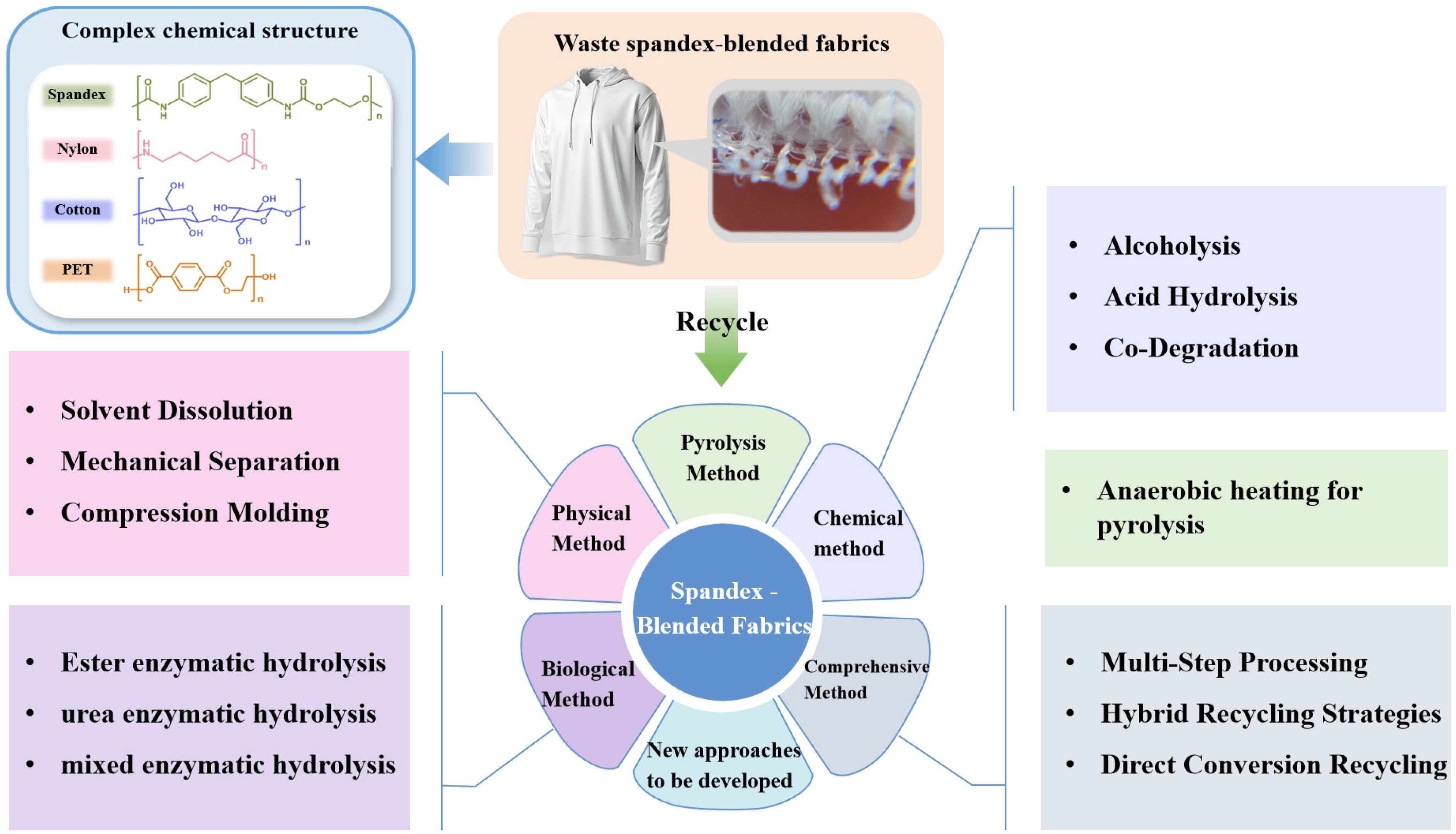
3. Recycling and Utilization of Spandex-Blended Fabrics
3.1. Physical Methods
3.2. Chemical Methods
3.3. Comprehensive Methods
4. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, F.; Akhtar, K.S.; Anam, W.; Mushtaq, B.; Rasheed, A.; Ahmad, S.; Azam, F.; Nawab, Y. Recent Developments in Materials and Manufacturing Techniques Used for Sports Textiles. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 2023, 2021622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarsolo, A.P. Plastics in Fashion: A Review of Plastic Materials in Modern and Contemporary Costume Collections and Their Conservation. Conserv. Patrim. 2023, 43, 113–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Yao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, P.; Hong, Y. Recycling of Waste Nylon 6/Spandex Blended Fabrics by Melt Processing. Compos. B Eng. 2015, 77, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Hao, B.; Li, D.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Large-Scale Production of Weavable, Dyeable and Durable Spandex/CNT/Cotton Core-Sheath Yarn for Wearable Strain Sensors. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, E.; Valls, C.; Roncero, M.B. Dissolving-Grade Pulp: A Sustainable Source for Fiber Production. Wood Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 23–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.B.; Khaliq, Z.; Tahir, R.; Javaid, A. Elastomeric Yarns. In Handbook of Stretchable and Elastomeric Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanga-Labayen, J.P.; Labayen, I.V.; Yuan, Q. A Review on Textile Recycling Practices and Challenges. Textiles 2022, 2, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Khan, I.; Alharthi, M.; Zafar, M.W.; Saeed, A. Sustainable Energy Policy, Socio-Economic Development, and Ecological Footprint: The Economic Significance of Natural Resources, Population Growth, and Industrial Development. Util. Policy 2023, 81, 101490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkar, A.; Pabba, M.; Sekhar, S.C.; Sridhar, S. Current Limitations and Challenges in the Global Textile Sector. In Fundamentals of Natural Fibres and Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 741–764. [Google Scholar]
- Patti, A.; Cicala, G.; Acierno, D. Eco-Sustainability of the Textile Production: Waste Recovery and Current Recycling in the Composites World. Polymers 2020, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Bartoli, F.; Bruni, C.; Fernandez-Avila, C.; Rodriguez-Turienzo, L.; Mellado-Carretero, J.; Spinelli, D.; Coltelli, M.-B. Opportunities and Limitations in Recycling Fossil Polymers from Textiles. Macromol 2023, 3, 120–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briga-Sá, A.; Gaibor, N.; Magalhaes, L.; Pinto, T.; Leitao, D. Thermal Performance Characterization of Cement-Based Lightweight Blocks Incorporating Textile Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, C.A.; Handoko, W.; Pahlevani, F.; Sahajwalla, V. Cascading Use of Textile Waste for the Advancement of Fibre Reinforced Composites for Building Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navone, L.; Moffitt, K.; Hansen, K.-A.; Blinco, J.; Payne, A.; Speight, R. Closing the Textile Loop: Enzymatic Fibre Separation and Recycling of Wool/Polyester Fabric Blends. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Motamed, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Naebe, M. Death by Waste: Fashion and Textile Circular Economy Case. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowska, P. Fibres and Textiles in the Circular Economy. In Fundamentals of Natural Fibres and Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 691–717. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas-Abadi, M.S.; Tomme, B.; Goshayeshi, B.; Mynko, O.; Wang, Y.; Roy, S.; Kumar, R.; Baruah, B.; De Clerck, K.; De Meester, S. Advancing Textile Waste Recycling: Challenges and Opportunities Across Polymer and Non-Polymer Fiber Types. Polymers 2025, 17, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndagano, U.N.; Cahill, L.; Smullen, C.; Gaughran, J.; Kelleher, S.M. The Current State-of-the-Art of the Processes Involved in the Chemical Recycling of Textile Waste. Molecules 2025, 30, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mashud, M.; Rahman, M.M. Advanced Technology in Textiles: Fibre to Apparel; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; ISBN 981-9921-42-2. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, S.-L.; Yu, E.; Hu, X. Tackling Critical Challenges in Textile Circularity: A Review on Strategies for Recycling Cellulose and Polyester from Blended Fabrics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloyi, R.B.; Gbadeyan, O.J.; Sithole, B.; Chunilall, V. Recent Advances in Recycling Technologies for Waste Textile Fabrics: A Review. Text. Res. J. 2024, 94, 508–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, K.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Recycling of Blended Fabrics for a Circular Economy of Textiles: Separation of Cotton, Polyester, and Elastane Fibers. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.T.; Sun, Y.; Shim, E. Progress of Recycled Polyester in Rheological Performance in Molding, and Economic Analysis of Recycled Fibers in Fashion and Textile Industry. In Next-Generation Textiles; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 1-80355-883-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, D.; Yue, J.; Wu, L.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, X. Progress of Air Flow Field and Fiber Motion Analysis in Textile Manufacturing Process: A Review. Text. Res. J. 2024, 94, 1581–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Du, R.-C.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. New Insights into Urethane Alcoholysis Enable Chemical Full Recycling of Blended Fabric Waste. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschmeier, E.; Archodoulaki, V.-M.; Schwaighofer, A.; Lendl, B.; Ipsmiller, W.; Bartl, A. New Separation Process for Elastane from Polyester/Elastane and Polyamide/Elastane Textile Waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Marrodan, C.; Brandi, F.; Barbaro, P.; Liguori, F. Advances in Catalytic Chemical Recycling of Synthetic Textiles. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 11832–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yao, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Removal of Spandex from Nylon/Spandex Blended Fabrics by Selective Polymer Degradation. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albitres, G.A.V.; Mendes, L.C.; Cestari, S.P. Polymer Blends of Polyamide-6/Spandex Fabric Scraps and Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, D.; Wulandari, L.A.; Bagaskoro, A.; Rianjanu, A.; Wu, H.-S. Possibility Routes for Textile Recycling Technology. Polymers 2021, 13, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, D.G.K.; Weerasinghe, D.U.; Wijesinghe, K.A.P.; Kalpage, K.M.D.M.P. Developing a Compression Moulded Thermal Insulation Panel Using Postindustrial Textile Waste. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.; Welle, F. Recycling of Post-Consumer Packaging Materials into New Food Packaging Applications—Critical Review of the European Approach and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuelli, M.A. Introduction of Fibre-Reinforced Polymers−Polymers and Composites: Concepts, Properties and Processes. In Fiber Reinforced Polymers—The Technology Applied for Concrete Repair; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 953-51-0938-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y.-C.; Gong, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Li, W.-T.; Gao, S. Formation of Nano- and Microplastics and Dissolved Chemicals During Photodegradation of Polyester Base Fabrics with Polyurethane Coating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1894–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, P.K. A Review of Textile Industry: Wet Processing, Environmental Impacts, and Effluent Treatment Methods. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2018, 27, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, S.A. Municipal Solid and Plastic Waste Derived High-Performance Biochar Production: A Comprehensive Review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 181, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-M.; Lee, T.; Jung, S.; Tsang, Y.F.; Bhatnagar, A.; Lee, S.S.; Song, H.; Park, W.-K.; Kwon, E.E. Control of the Fate of Toxic Pollutants from Catalytic Pyrolysis of Polyurethane by Oxidation Using CO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Cheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, P.; Cen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, B. A Review on Catalytic Pyrolysis of Textile Waste to High-Value Products: Catalytic Mechanisms, Products Application and Perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155120. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Analysis of the Influencing Factors of the Efficient Degradation of Waste Polyurethane and Its Scheme Optimization. Polymers 2023, 15, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, N.; Godinho, B.; Marques, G.; Silva, R.; Barros-Timmons, A.; Ferreira, A. Recycling of Polyurethane Scraps via Acidolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, T.B.; Donslund, B.S.; Kristensen, S.K.; Skrydstrup, T. Chemical Separation of Polyurethane via Acidolysis—Combining Acidolysis with Hydrolysis for Valorisation of Aromatic Amines. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 8395–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, S.; Van Der Voort, S.H.E.; Lange, J.-P.; Kersten, S.R.A.; Ruiz, M.P. Polyurethane Recycling: Thermal Decomposition of 1,3-Diphenyl Urea to Isocyanates. Polymers 2023, 15, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin, A.; Pollet, E.; Phalip, V.; Avérous, L. Evaluation of Biological Degradation of Polyurethanes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107457. [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson, C.; Wei, R.; Biundo, A.; Landberg, J.; Schwarz Bour, L.; Pezzotti, F.; Toca, A.; M. Jacques, L.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Syrén, P. Biocatalysis in the Recycling Landscape for Synthetic Polymers and Plastics towards Circular Textiles. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4028–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, M.; Molla, G.; Castellani, P.; Pirillo, V.; Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N. Microbial Enzyme Biotechnology to Reach Plastic Waste Circularity: Current Status, Problems and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Yaashikaa, P. A Review on Catalytic-Enzyme Degradation of Toxic Environmental Pollutants: Microbial Enzymes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergal, M.; Balaban, M. Synthesis and structure-property relationships of biodegradable polyurethanes. In Biodegradable Polymers: Recent Developments and Newperspectives; IAPC Publishing: Zagreb, Croatia, 2017; pp. 141–190. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/21.15107/rcub_cer_5768 (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Amjed, N.; Bhatti, I.A.; Simon, L.; Dal Castel, C.; Zia, K.M.; Zuber, M.; Hafiz, I.; Murtaza, M.A. Preparation and Characterization of Thermoplastic Polyurethanes Blended with Chitosan and Starch Processed through Extrusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oenema, J.; Liu, H.; De Coensel, N.; Eschenbacher, A.; Van de Vijver, R.; Weng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Van Geem, K.M. Review on the Pyrolysis Products and Thermal Decomposition Mechanisms of Polyurethanes. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharyan, E.; Maksimov, A. Pyrolysis of Polyurethanes. Process Features and Composition of Reaction Products. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2022, 95, 191–255. [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbacher, A.; Varghese, R.J.; Weng, J.; Van Geem, K.M. Fast Pyrolysis of Polyurethanes and Polyisocyanurate with and without Flame Retardant: Compounds of Interest for Chemical Recycling. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 160, 105374. [Google Scholar]
- Morado, E.G.; Paterson, M.L.; Ivanoff, D.G.; Wang, H.-C.; Johnson, A.; Daniels, D.; Rizvi, A.; Sottos, N.R.; Zimmerman, S.C. End-of-Life Upcycling of Polyurethanes Using a Room Temperature, Mechanism-Based Degradation. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
- Anceschi, A.; Trotta, F.; Zoccola, M.; Caldera, F.; Magnacca, G.; Patrucco, A. From Waste to Worth: Innovative Pyrolysis of Textile Waste into Microporous Carbons for Enhanced Environmental Sustainability. Polymers 2025, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doifode, C. Chemical Recycling of Elastane and Elastane Blends. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y. Recycling of Waste Cotton Textile Containing Elastane Fibers through Dissolution and Regeneration. Membranes 2022, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, N.V.; Ferreira, A.; Barros-Timmons, A. Polyurethane Foams: Past, Present, and Future. Materials 2018, 11, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liao, G. Transforming Waste Polyurethane Foam into High Value-Added Hyper-Crosslinked Polymer for Efficient Removal of Multiple Contaminants from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribul, M.; Lanot, A.; Tommencioni Pisapia, C.; Purnell, P.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Baurley, S. Mechanical, Chemical, Biological: Moving towards Closed-Loop Bio-Based Recycling in a Circular Economy of Sustainable Textiles. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katnic, S.P.; Gupta, R.K. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Commercial Enzymes for Polyurethane Biodegradation. J. Polym. Environ. 2025, 33, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes-Jaime, J.; Vargas-Suárez, M.; Cruz-Gómez, M.J.; Loza-Tavera, H. Concerted Action of Extracellular and Cytoplasmic Esterase and Urethane-Cleaving Activities during Impranil Biodegradation by Alicycliphilus Denitrificans BQ1. Biodegradation 2022, 33, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Bian, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Liang, Q.; Qi, Q. Biodegradation of Polyurethane by the Microbial Consortia Enriched from Landfill. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Duquesne, S.; Guillamot, F.; Cramail, H.; Taton, D.; Marty, A.; André, I. Enzymes’ Power for Plastics Degradation. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5612–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-L.; Kim, H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Tseng, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-P.; Chiang, P.-C. Implementation of Green Chemistry Principles in Circular Economy System towards Sustainable Development Goals: Challenges and Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasim, A.; More, V.S.; More, S.S. Large-Scale Production of Enzymes for Biotechnology Uses. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Raghunath, S.S.; Prasanna, D.V.; Venkat, P.; Shree, V.; Chithananthan, C.; Choudhary, S.; Surender, K.; Geetha, K. An Update on Overview of Cellulose, Its Structure and Applications. Cellulose 2019, 201, 84727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul Anuar, N.F.S.; Huyop, F.; Ur-Rehman, G.; Abdullah, F.; Normi, Y.M.; Sabullah, M.K.; Abdul Wahab, R. An Overview into Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Hydrolases and Efforts in Tailoring Enzymes for Improved Plastic Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, M.; Grinstaff, M.W. Beyond Nylon 6: Polyamides via Ring Opening Polymerization of Designer Lactam Monomers for Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 8258–8275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Solubility, Hansen Solubility Parameter, Molecular Simulation and Thermodynamic Analysis of N-Methyl-3, 4, 5-Trinitropyrazole at Various Temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.; Ügdüler, S.; Harinck, L.; Denolf, R.; Roosen, M.; O’Rourke, G.; De Vos, D.; Van Speybroeck, V.; De Clerck, K.; De Meester, S. Analysing the Potential of the Selective Dissolution of Elastane from Mixed Fiber Textile Waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 191, 106903. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, U.; Mundkur, S.; Athalye, A. Strategies for Separating and Recycling Textile Blends. Adv. Environ. Waste Manag. Recycl. 2023, 6, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
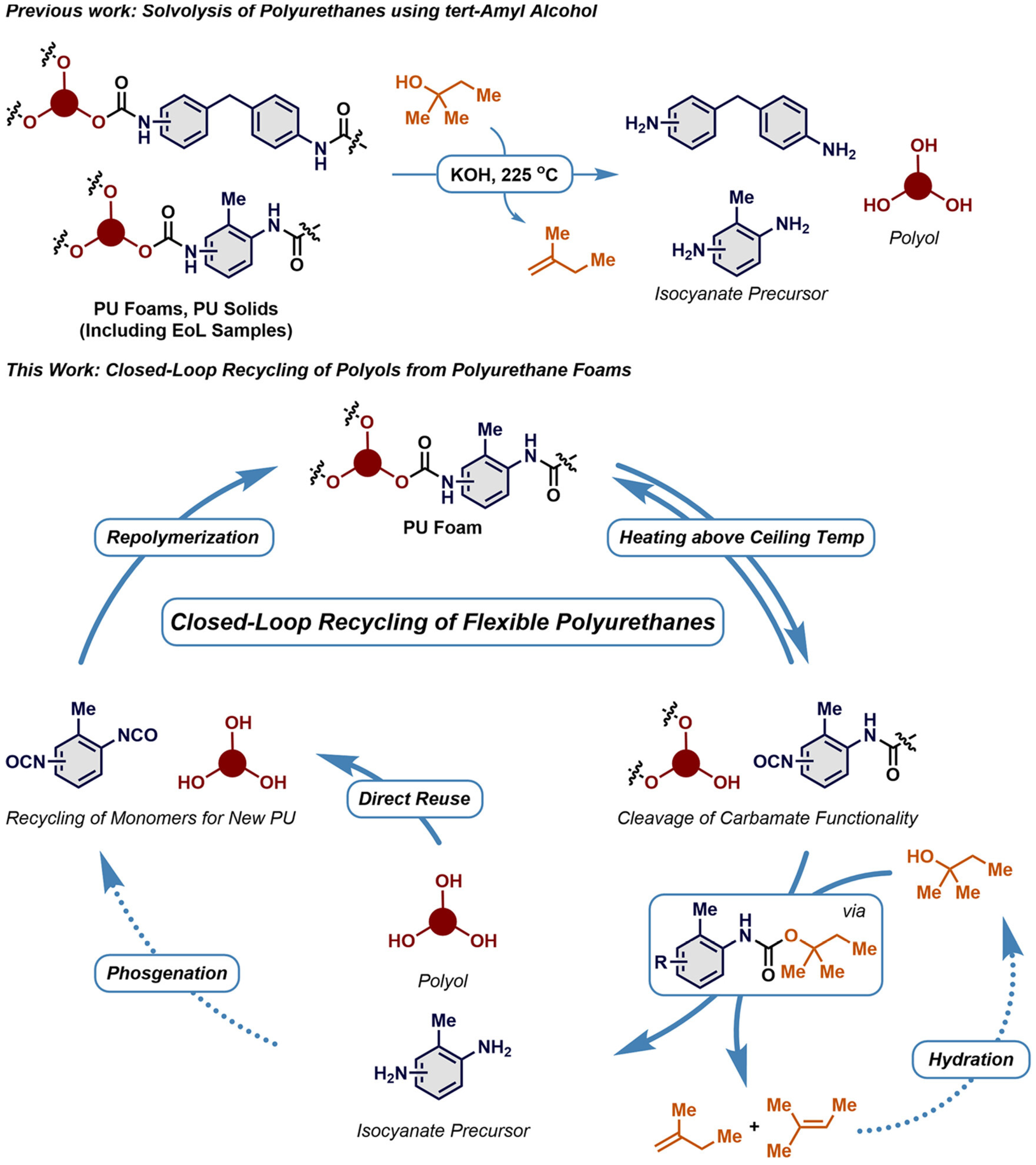
- Johansen, M.B.; Donslund, B.S.; Larsen, E.; Olsen, M.B.; Pedersen, J.A.; Boye, M.; Smedsgård, J.K.; Heck, R.; Kristensen, S.K.; Skrydstrup, T. Closed-Loop Recycling of Polyols from Thermoset Polyurethanes by Tert-Amyl Alcohol-Mediated Depolymerization of Flexible Foams. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 10737–10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.B.; Donslund, B.S.; Henriksen, M.L.; Kristensen, S.K.; Skrydstrup, T. Selective Chemical Disassembly of Elastane Fibres and Polyurethane Coatings in Textiles. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10622–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhave, R.V.; Srivastava, S.; Mahanwar, P.A.; Gadekar, P.T. Recycling and Disposal Methods for Polyurethane Wastes: A Review. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2019, 09, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Darai, T.; Ter-Halle, A.; Blanzat, M.; Despras, G.; Sartor, V.; Bordeau, G.; Lattes, A.; Franceschi, S.; Cassel, S.; Chouini-Lalanne, N.; et al. Chemical Recycling of Polyester Textile Wastes: Shifting towards Sustainability. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 6857–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Aguirre-Villegas, H.A.; Allen, R.D.; Bai, X.; Benson, C.H.; Beckham, G.T.; Bradshaw, S.L.; Brown, J.L.; Brown, R.C.; Cecon, V.S. Expanding Plastics Recycling Technologies: Chemical Aspects, Technology Status and Challenges. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8899–9002. [Google Scholar]
- Alaghemandi, M. Sustainable Solutions Through Innovative Plastic Waste Recycling Technologies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Quintana, R.A.; Chen, L.; Smiatek, J. Insights into Hildebrand Solubility Parameters–Contributions from Cohesive Energies or Electrophilicity Densities? ChemPhysChem 2024, 25, e202300566. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Quan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L. Effect of Chemical Penetration Enhancer-Adhesive Interaction on Drug Release from Transdermal Patch: Mechanism Study Based on FT-IR Spectroscopy, 13 C NMR Spectroscopy, and Molecular Simulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, C.F. Selectivity Evaluation of Extraction Systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1695, 463939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonbrül, L.; Cordin, M.; Manian, A.P.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Solvent Blends for Selective Elastane Dissolution and Recovery from Mixed Polyamide Fabrics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 200, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Ma, Y.; Jiao, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J. Complete Recycling and Valorization of Waste Cotton-Spandex Blended Fabrics into Value-Added UV-Blocking Cellulose/Graphene Films and Transparent Polyurethane Film. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2025, 43, e01234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. Dissolution and recycling of waste nylon/polyester/spandex composite fabrics. Synth. Fibres 2023, 52, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambyal, P.; Najmi, P.; Sharma, D.; Khoshbakhti, E.; Hosseini, H.; Milani, A.S.; Arjmand, M. Plastic Recycling: Challenges and Opportunities. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 1, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
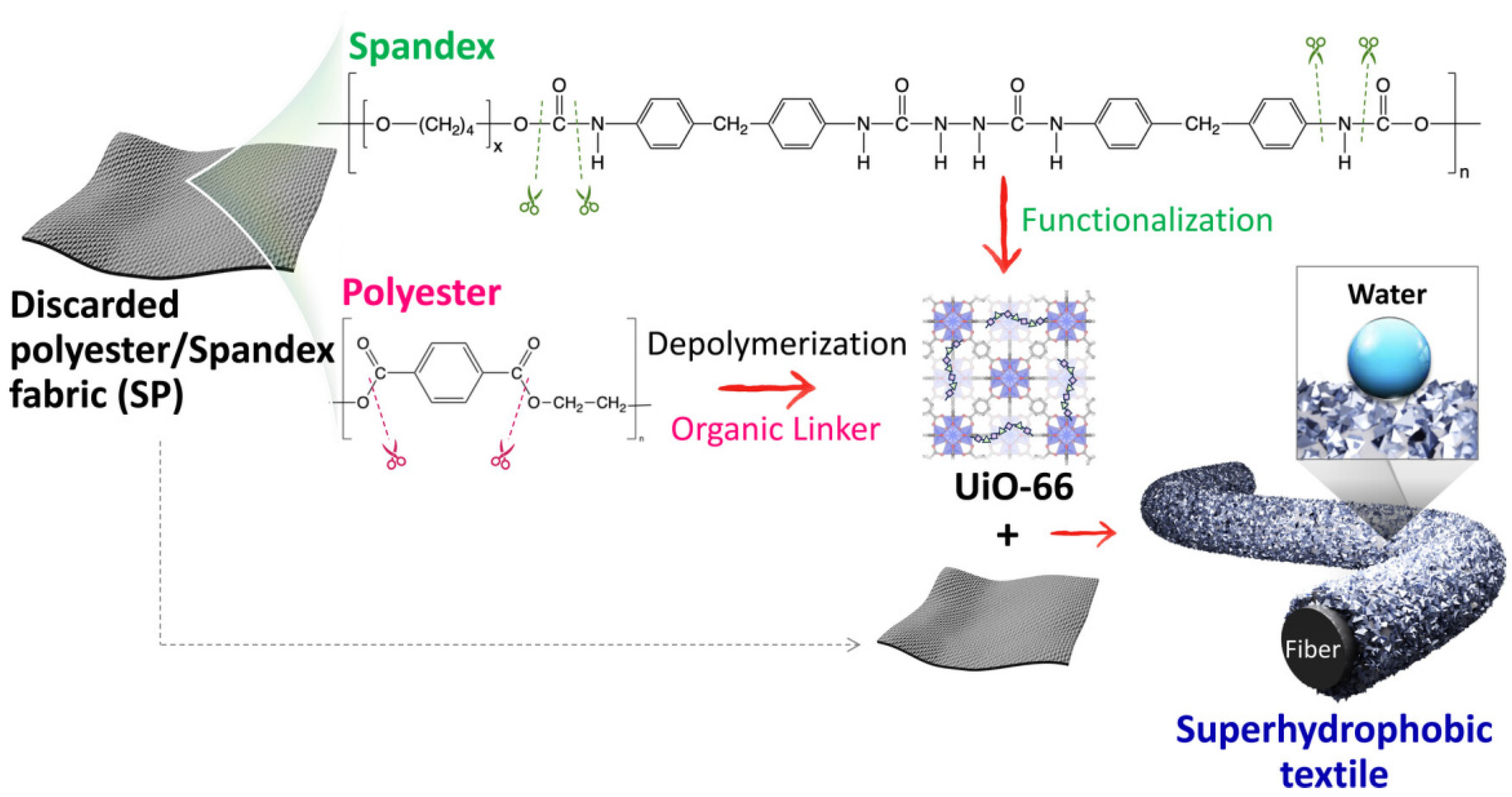
- Ko, Y.; Uyar, T.; Hinestroza, J.P. UiO-66 Inspired Superhydrophobic Coatings Fabricated from Discarded Polyester/Spandex Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 53163–53176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piribauer, B.; Bartl, A. Textile Recycling Processes, State of the Art and Current Developments: A Mini Review. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2019, 37, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, K. Analysis of Spandex/Cotton Elastomeric Properties: Spinning and Applications. Cell 2012, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorpas, A.A. The Hidden Concept and the Beauty of Multiple “R” in the Framework of Waste Strategies Development Reflecting to Circular Economy Principles. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andini, E.; Bhalode, P.; Gantert, E.; Sadula, S.; Vlachos, D.G. Chemical Recycling of Mixed Textile Waste. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Trentle, M.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, K.; Higgins, W.; Wang, Y.; Xue, B.; Yang, S. Polymer Complex Fiber: Property, Functionality, and Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 7639–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, P.; Jindal, M.; Jindal, T. A Review on Economically-Feasible and Environmental-Friendly Technologies Promising a Sustainable Environment. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannio, M.; Boccaccini, D.N.; Caporali, S.; Taurino, R. Superhydrophobic Materials from Waste: Innovative Approach. Clean Technol. 2024, 6, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S. Advances in the Application of Superhydrophobic Fabric Surfaces for Oil-Water Separation and Extension of Functionalization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undas, A.K.; Groenen, M.; Peters, R.J.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Safety of Recycled Plastics and Textiles: Review on the Detection, Identification and Safety Assessment of Contaminants. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Mofijur, M.; Nuzhat, S.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Rafa, N.; Uddin, M.A.; Inayat, A.; Mahlia, T.; Ong, H.C.; Chia, W.Y. Recent Developments in Physical, Biological, Chemical, and Hybrid Treatment Techniques for Removing Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Recycling Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages | Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Method | Fiber Regeneration | Low cost, high recycling efficiency, mature technology. | Relative molecular weight and solution viscosity decrease. | [19,22,23] |
| Additives | Low process requirements, high recovery rate. | The surface finish is poor, and the application scenarios are limited. | [32,33,34] | |
| Composites | Avoid the problem of uniformity of spinning liquid, and the product is widely used. | High cost of equipment and materials. | [35,36] | |
| Pyrolysis | High-temperature pyrolysis | Can be used to treat mixed waste, and the products (oil, carbon, gas) are widely used. | The separation and purification are difficult, and the energy consumption of the equipment is high. | [37,38] |
| Chemical Method | Alcoholysis | The decomposition conditions are mild, and the polyols can be recovered for recycled polyurethane synthesis. | Solvent recovery is costly, and the catalyst can introduce metal contamination. | [39] |
| Acidolysis | Efficient separation of soft segments (polyols) and hard segments (diamines) for rigid PU (polyurethane) foams. | strong acids (e.g., succinic acid) are required; corrosion equipment; after hydrolysis, it needs to be neutralized. | [40,41] | |
| Aminolysis | Selectively cleaves urethane bonds, and the product is of high purity. | Amine reagents are highly toxic (e.g., ethylenediamine); residual amines may contaminate the recovered product. | [42] | |
| Biological Method | Esterolytic Degradation | Has a fast degradation rate and is suitable for polyester PU; works well in a humid environment. | Polyether-type PU cannot be effectively processed. | [43,44] |
| Urethanolytic Degradation | Suitable for PU of urethane and amide bonds; degradable urethane urea. | The rate of hydrolysis is slow, and the effect on bonds embedded in deep layers is poor. | [45] | |
| Synergistic degradation | Some microorganisms are assisted by oxidase and peroxidase to break the chain and enhance the degradation efficiency. | The process is complex, and it is necessary to optimize the enzyme combination and reaction conditions. | [46] | |
| Recycling Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages | Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Method | Physical dissolution | Simple, economically viable. | Limited solvent options, many not environmentally friendly. | [22,26,68] |
| Mechanical separation | Suitable for initial fiber sorting, simple, eco-friendly. | Low fiber separation efficiency. | [69] | |
| Compression molding | No complex pretreatment, reduces solvent use, suitable for large-scale recovery. | Low economic value of recovered materials, potential fiber property loss. | [22,70] | |
| Pyrolysis | High-temperature pyrolysis | Can treat mixed waste, products (oil, carbon, gas) widely used. | Complex products, difficult separation and purification, high energy consumption. | [37,38] |
| Chemical Method | Alcoholysis | Complete spandex decomposition, polyols suitable for new materials. | High technology demand, harsh conditions, expensive catalysts. | [71,72] |
| Acidolysis | Effective for complex polyurethane degradation. | Requires high temperature, corrosive chemicals, potential environmental and equipment damage. | [73,74] | |
| Co-Degradation | Suitable for mixed textiles, improves fiber recovery rate. | Complex, requires optimization for different fibers. | [29] | |
| Comprehensive Method | Multi-Step Processing | Combines physical and chemical methods, enhances recycling efficiency, more product possibilities. | Complex, high technical and equipment requirements, increased costs. | [75,76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Gao, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.; Zhang, M.; Su, Q. Recycling of Spandex: Broadening the Way for a Complete Cycle of Textile Waste. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3319. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083319
Zhu M, Gao C, Wang S, Shi S, Zhang M, Su Q. Recycling of Spandex: Broadening the Way for a Complete Cycle of Textile Waste. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3319. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083319
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Mengxue, Chengyong Gao, Shuhua Wang, Sheng Shi, Meiling Zhang, and Qianyu Su. 2025. "Recycling of Spandex: Broadening the Way for a Complete Cycle of Textile Waste" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3319. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083319
APA StyleZhu, M., Gao, C., Wang, S., Shi, S., Zhang, M., & Su, Q. (2025). Recycling of Spandex: Broadening the Way for a Complete Cycle of Textile Waste. Sustainability, 17(8), 3319. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083319






