An Innovative Approach Toward Enhancing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Resource Recovery from Hazardous Zn-Bearing Dusts from Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aims of the Investigation
- ▪
- Key metallic resources (Fe and Zn) are present jointly as ZnFe2O4 and are difficult to separate in a simple manner.
- ▪
- While H2 reduction could be used in principle to extract metallic values, with the advantages of lower operating temperatures and zero GHG emissions, there are supply issues with H2 and higher operating costs. Due to the large volumes of industrial wastes involved and the relatively low-grade quality of the resources recovered, the H2-based reduction of ZBDs may not be a cost-effective and economically viable approach.
- ▪
- The carbothermal reduction of ZBDs is associated with high levels of energy consumption and GHG emissions and is clearly not a desirable option as the steel industry is seriously trying to limit and reduce emissions from the sector.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Preparation of Briquettes
2.3. Experiments: Reduction Investigations
2.4. Analytical Instruments Used for Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Weight Loss of Briquettes
3.2. Elemental Composition of Briquettes After Reduction
3.3. Recovery of Zn-Based Powders from ZBDs
3.3.1. Elemental Composition
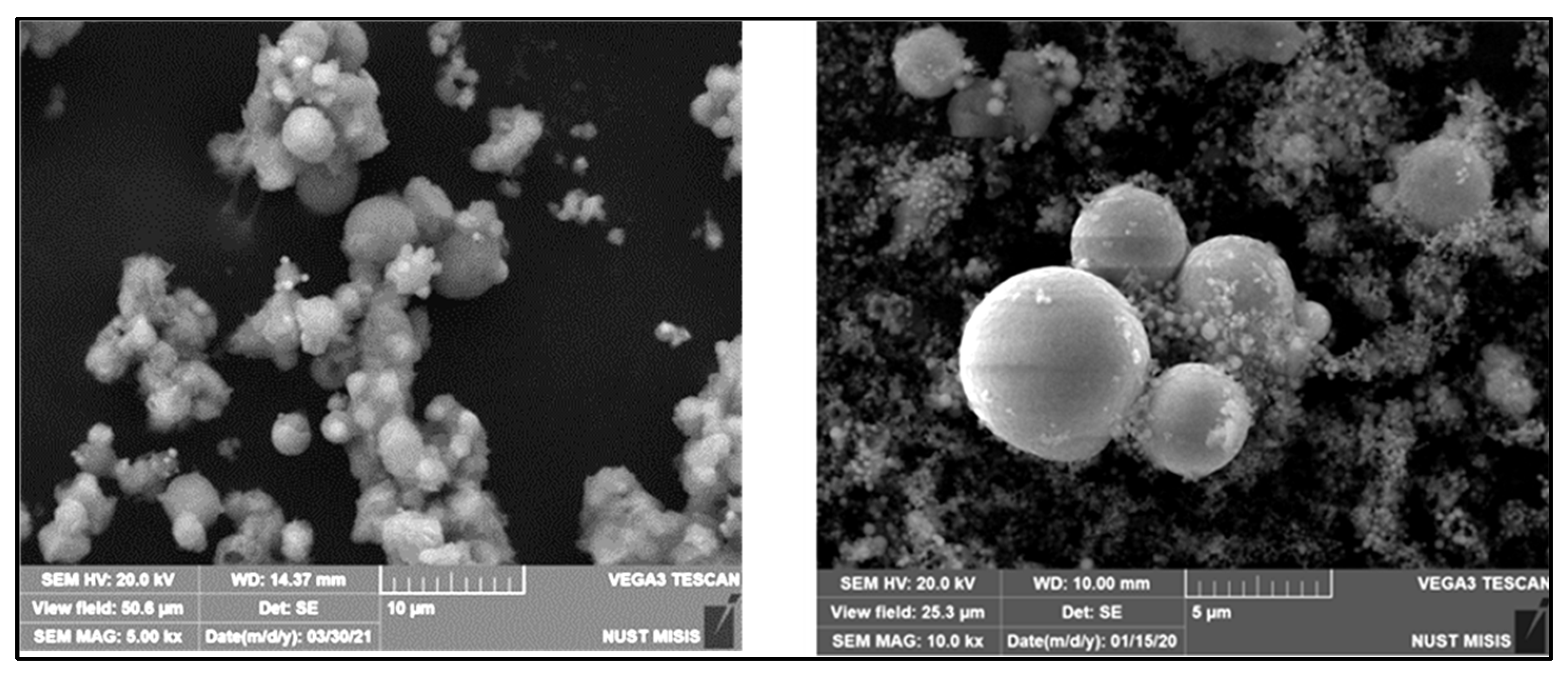
3.3.2. Electron Microscopic Investigations
3.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The World Steel Association. Total Production of Crude Steel. World Total. 2023. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/data/annual-production-steel. (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Gomes, H.I.; Mares, W.M.; Rogerson, M.; Stewart, D.I.; Burke, I.T. Alkaline residues and the environment: A review of impacts, management practices and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lin, L.L.; Yang, G.; Deng, S.H.; Li, L.; Yu, X.Y.; Qi, H.; et al. Sustainability evaluation of a steel production system in China based on energy. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Chu, M.S.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Z. Mechanism of zinc damaging to blast furnace tuyere refractory. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2009, 22, 454. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, H.; Ibaraki, T.; Abe, Y. Dust recycling system by the rotary hearth furnace. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2006, 94, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Peng, Z.; Yan, J. Pyrometallurgical recycling of electric arc furnace dust. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 1079–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, C.; Piehl, P.; Weingart, E.; Stolle, D.; Al-Sabbagh, D.; Ostermann, M.; Auer, G.; Adam, C. Selective removal of zinc and lead from electric arc furnace dust by chlorination–evaporation reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.X.; Li, H.M.; Wei, R.F. Present situation and prospect of iron and steel dust and sludge utilization technology. Iron Steel 2019, 54, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, T.; Nowacki, K.; Zelichowska, M.; Kania, H. Innovation in metallurgical waste management. Metalurgija 2015, 54, 283–285. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; Al-Nu’airat, J.; Al-Otoom, A.; Al-jabali, H.; Al-zoubi, M. Treatments of electric arc furnace dust and halogenated plastic wastes: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102856. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzerstorfer, C. Electric arc furnace (EAF) dust: Application of air classification for improved zinc enrichment in in-plant recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.S.; Xia, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.H. Research on Zn load control and utilization of ferrous dust in blast furnace of steel plant. Sinter. Pelletizing 2020, 45, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kongkarat, S.; Khanna, R.; Koshy, P.; O’kane, P.; Sahajwalla, V. Recycling waste polymers in EAF steelmaking: Influence of polymer composition on carbon/slag interactions. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, J.G.; Brehm, F.A.; Moraes, C.A.M.; Dos Santos, C.A.; Vilela, A.C.F.; Da Cunha, J.B.M. Chemical, physical, structural and morphological characterization of the electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 953–960. [Google Scholar]
- Hagni, A.M.; Hagni, R.D.; Demars, C. Mineralogical characteristics of electric arc furnace dusts. Jom 1991, 43, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.M.; dos Reis Neto, J.M.; da Cunha, C.J. Mineral phases of weathered and recent electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, K.; Fu, T.; Gao, J.; Hussain, S.; AlGarni, T.S. Pyrometallurgical recovery of zinc and valuable metals from electric arc furnace dust—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126788. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ju, D.; Mao, R.; Ma, H.; Peng, H.; Du, W. Carbothermic kinetics and reaction mechanism of carbon-containing pellets: A combined treatment of chromium-containing sludge and zinc-bearing dust. J. Sustain. Met. 2022, 8, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, L.M.; Alpatova, A.A.; Demidova, N.V. The EAF dust chemical and phase composition research techniques. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Gan, M.; Fan, X.; Ji, Z.; Chen, X. Mechanism of calcium oxide promoting the separation of zinc and iron in metallurgical dust under reducing atmosphere. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5745–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Niu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Han, M. Atmospheric sulfuric acid leaching thermodynamics from metallurgical zinc-bearing dust sludge. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2018, 36, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Tsai, M.S.; Chang, F.C. Removal of chloride from electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, G.; Martín, D.; Frías, C.; Sanchez, F. Emerging applications of ZINCEX and PLACID technologies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 53, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Marques, E. Some studies on the leaching behaviour of electric arc furnace steelmaking dusts with water and with acetic acid. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2001, 4, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hilber, T.; Marr, R.; Siebenhofer, M.; Simon, V. Extractive separation of zinc from oxidic solid bulk feed. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlík, T.; Turzakova, M.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Atmospheric leaching of EAF dust with diluted sulphuric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Cang, D. Zinc leaching from electric arc furnace dust in alkaline medium. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2010, 17, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oustadakis, P.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Katsiapi, A.; Agatzini-Leonardou, S. Hydrometallurgical process for zinc recovery from electric arc furnace dust (EAFD). Part I: Characterization and leaching by diluted sulphuric acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcai, Z.; Stanforth, R. Integrated hydrometallurgical process for production of zinc from electric arc furnace dust in alkaline medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 80, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments-A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Steenari, B.M. Leaching optimization of municipal solid waste incineration ash for resource recovery: A case study of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, P.; Kehagias, T.; Tsilika, I.; Kaimakamis, G.; Chrissafis, K.; Kokkou, S.; Papadopoulos, D.; Karakostas, T. Glass-ceramic materials from electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.F.; Rodríguez-Pinero, M.; Vale, J. Solidification/stabilization of electric arc furnace dust using coal fly ash. Analysis of the stabilization process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 82, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pickles, C.A. Thermodynamic modelling of the formation of zinc-manganese ferrite spinel in electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huaiwei, Z.; Xin, H. An overview for the utilization of wastes from stainless steel industries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Quijorna, N.; De Pedro, M.; Romero, M.; Andrés, A. Characterisation of the sintering behaviour of Waelz slag from electric arc furnace (EAF) dust recycling for use in the clay ceramics industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo Neto, A.P.; Sales, F.A.; Ramos, W.B.; Brito, R.P. Thermo-environmental evaluation of a modified Waelz process for hazardous waste treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhan, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Innovative and green utilization of zinc-bearing dust by hydrogen reduction: Recovery of zinc and lead, and synergetic preparation of Fe/C micro-electrolysis materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, X. Removal mechanism of Zn, Pb and alkalis from metallurgical dusts in direct reduction process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Chen, W.S.; Tsai, M.S.; Wang, Y.N. Reduction behaviour of zinc ferrite in EAF-dust recycling with CO gas as a reducing agent. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 143, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C.; Olivetti, E.A. Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature 2019, 575, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- McKinsey & Company. Decarbonization Challenge for Steel by Christian Hoffmann, Michel Van Hoey, and Benedikt Zeumer. 2020. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/metals-and-mining/our-insights/decarbonization-challenge-for-steel#/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- European Parliament, Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Country and Sector (Infographic). 2019. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/society/20180301STO98928/ (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Overview of Greenhouse Gases. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/overview-greenhouse-gases (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- SSAB; HYBRIT. A New Revolutionary Steel Making Technology. Available online: https://www.ssab.com/en/fossil-free-steel/hybrit-a-newrevolutionary-steelmakingtechnology (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Wang, R.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Babich, A.; Senk, D.; Fan, X.Y. Hydrogen direct reduction (H-DR) in steel industry—An overview of challenges and opportunities. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 329, 129797. [Google Scholar]
- Dr. Vincent Chevrier Presents in “Ironmaking with Alternative Reductants” Webinar by AIST. Available online: https://www.midrex.com/story/dr-vincent-chevrier-presents-in-ironmaking-with-alternative-reductants-webinar-by-aist/ (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Brandner, U.; Antrekowitsch, J.; Leuchtenmueller, M. A review on the fundamentals of hydrogen-based reduction and recycling concepts for electric arc furnace dust extended by a novel conceptualization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 31894–31902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junca, E.; Grillo, F.F.; Alves, J.O.; Oliveira, J.R.; Restivo, T.A.G.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Tenório, J.A.S. Reduction of electric arc furnace dust pellets by mixture containing hydrogen. REM Int. Eng. J. 2019, 72, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Polsilapa, S.; Sadedin, D.R.; Wangyao, P. Thermodynamics analysis for the zinc ferrite reduction by hydrogen. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2011, 30, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Yang, C. Hydrogen reduction process for zinc-bearing dust treatment: Reduction kinetic mechanism and microstructure transformations in a novel and environmentally friendly metallurgical technique. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Saini, R.; Park, M.; Ellamparuthy, G.; Biswal, S.K.; Mukherjee, P.S. Factors influencing the release of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) during thermal processing of electronic waste. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 414–424. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Peng, Z.; Ye, L.; Wang, L.; Augustine, R.; Lee, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Rao, M.; Jiang, T.; et al. Thermodynamic Analysis of Carbothermic Reduction of Electric Arc Furnace Dust. In 10th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing; Jiang, T., Hwang, J.-Y., Gregurek, D., Peng, Z., Downey, J.P., Zhao, B., Yücel, O., Keskinkilic, E., Padilla, R., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatova, A.A. Study of Dust Formation Processes During Arc Heating of Metal and Dust Properties for the Purpose of Its Utilization. Ph.D. Thesis, NUST MISIS, Moscow, Russia, 24 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, J.; Zglinicka, I.; Znak, L.; Kaszkur, Z. Reduction of Fe2O3 with hydrogen/Reduction of Fe2O3 with hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 381, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Kang, Y.; Gao, J.; Guo, Z. Promoted acid leaching of Zn from hazardous zinc-containing metallurgical dusts: Focusing on transformation of Zn phases in selective reduction roasting. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 163, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, D.; Pan, J.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y. A study on the zinc removal kinetics and mechanism of zinc-bearing dust pellets in direct reduction. Powder Technol. 2021, 380, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Khanna, R.; Dutta, R.K.; Cayumil, R.; Ikram-Ul-Haq, M.; Agarwala, V.; Ellamparuthy, G.; Jayasankar, K.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Sahajwalla, V. A novel approach for reducing toxic emissions during high temperature processing of electronic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ellamparuthy, G.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Khanna, R.; Jayasankar, K.; Cayumil, R.; Ikram-Ul-Haq, M.; Sahajwalla, V.; Mishra, B.K. Environmental impact of recycling electronic waste using thermal plasma: In-depth analysis of aerosol particulates captured in gas filters. Curr. Environ. Eng. 2017, 4, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, W.; Jiao, F.; Yang, C.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Qin, W. Separation and recovery of zinc, lead and iron from electric arc furnace dust by low temperature smelting. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 312, 123355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, R.; He, X.; Lv, X.; Zhu, R.; Jin, H.; Deng, X. Research for the recovery of Zn and Pb from electric arc furnace dust through vacuum carbothermal reduction. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 960–970. [Google Scholar]
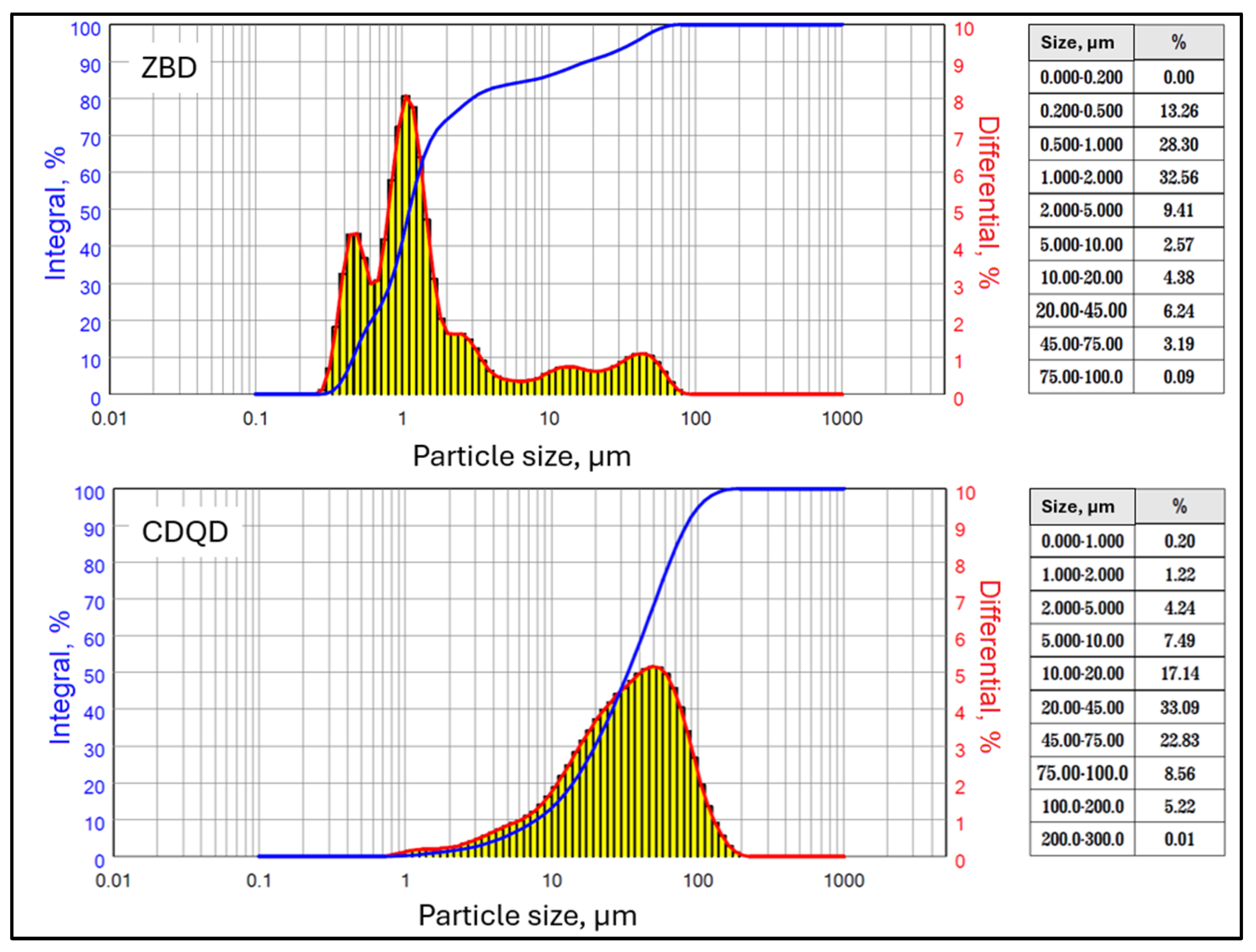

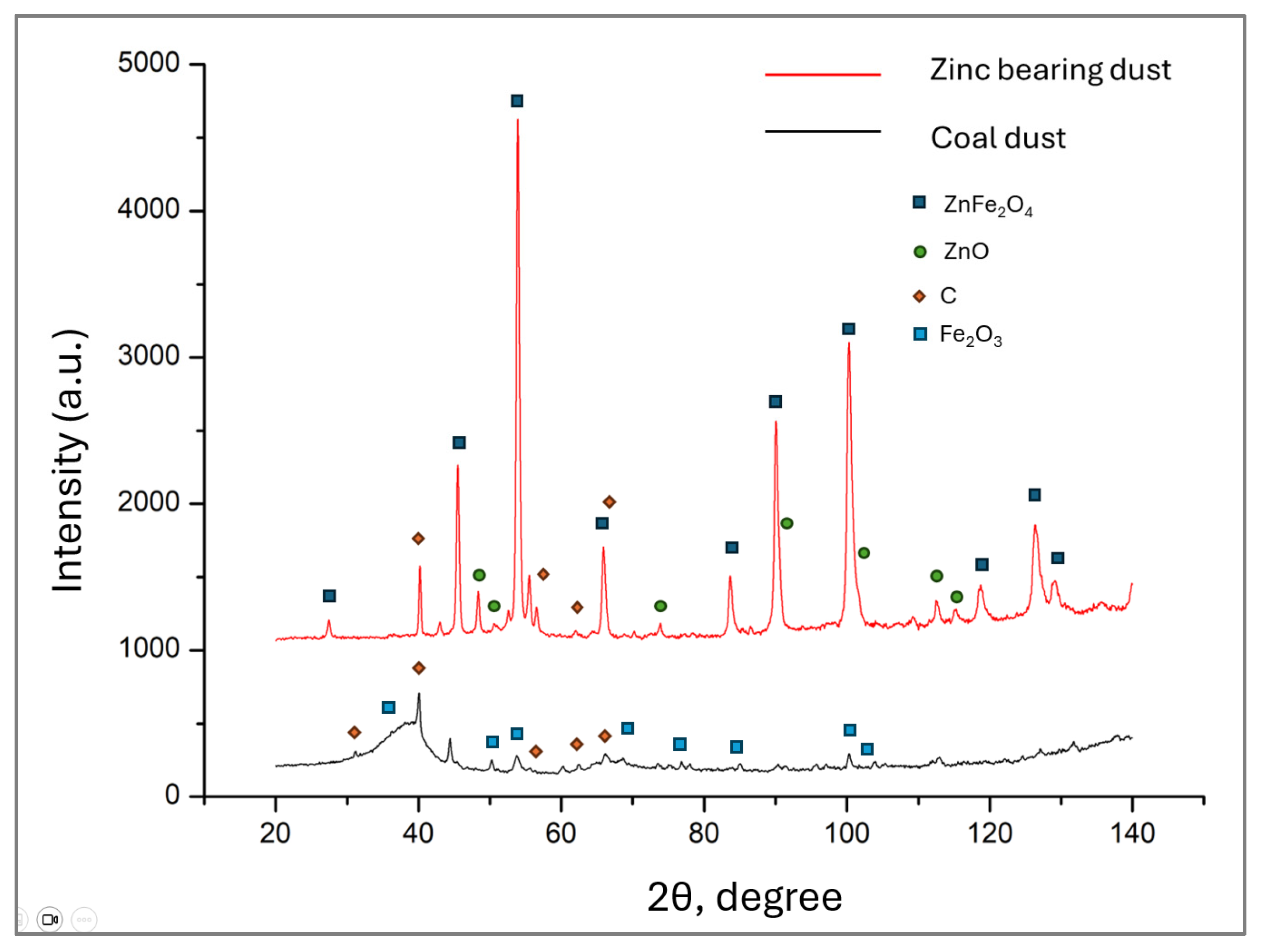
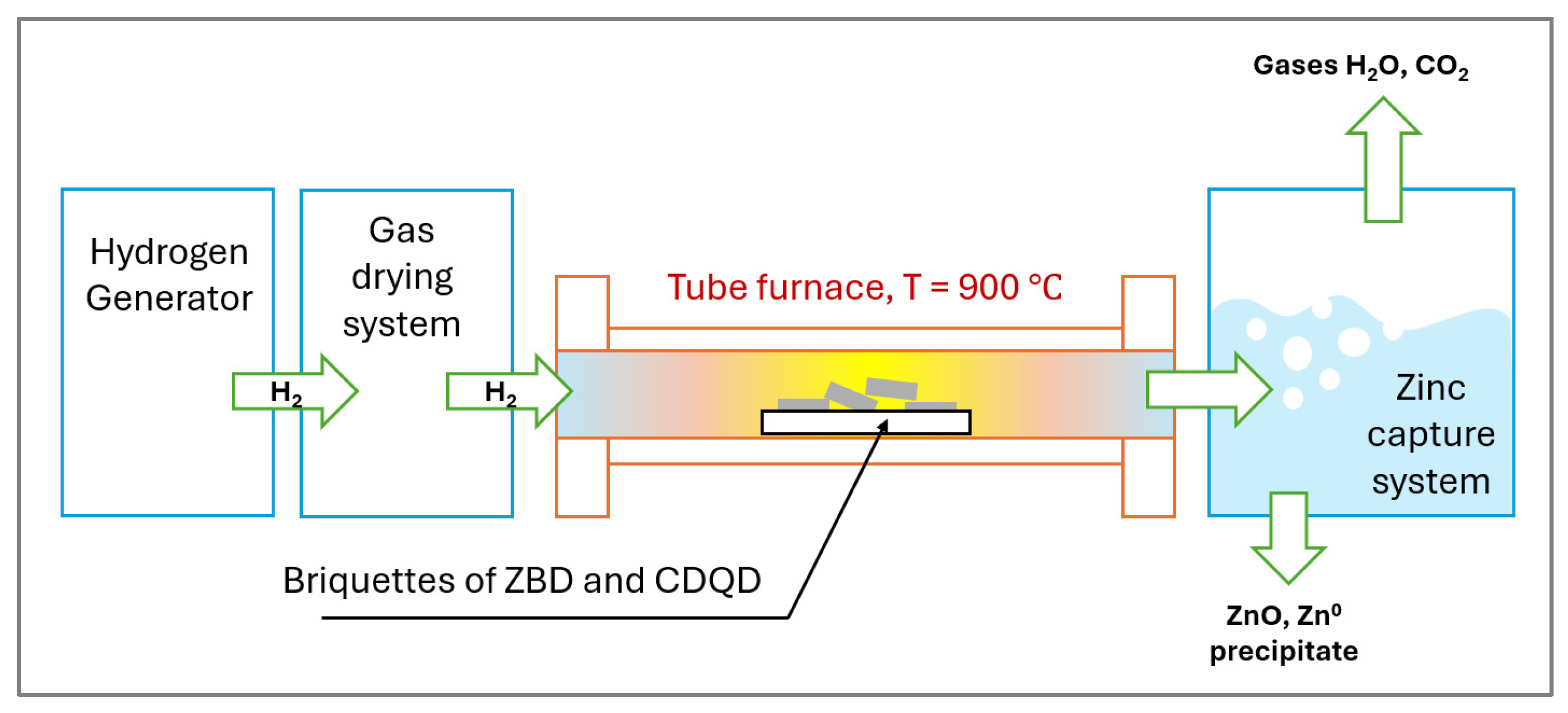
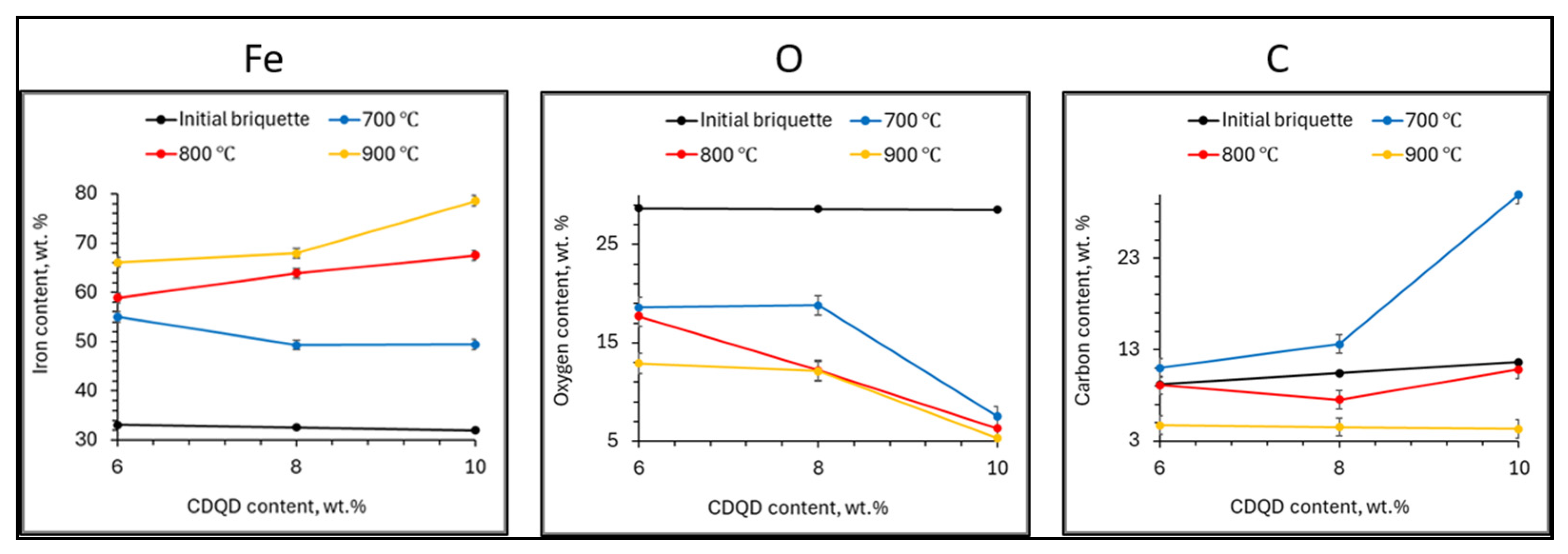



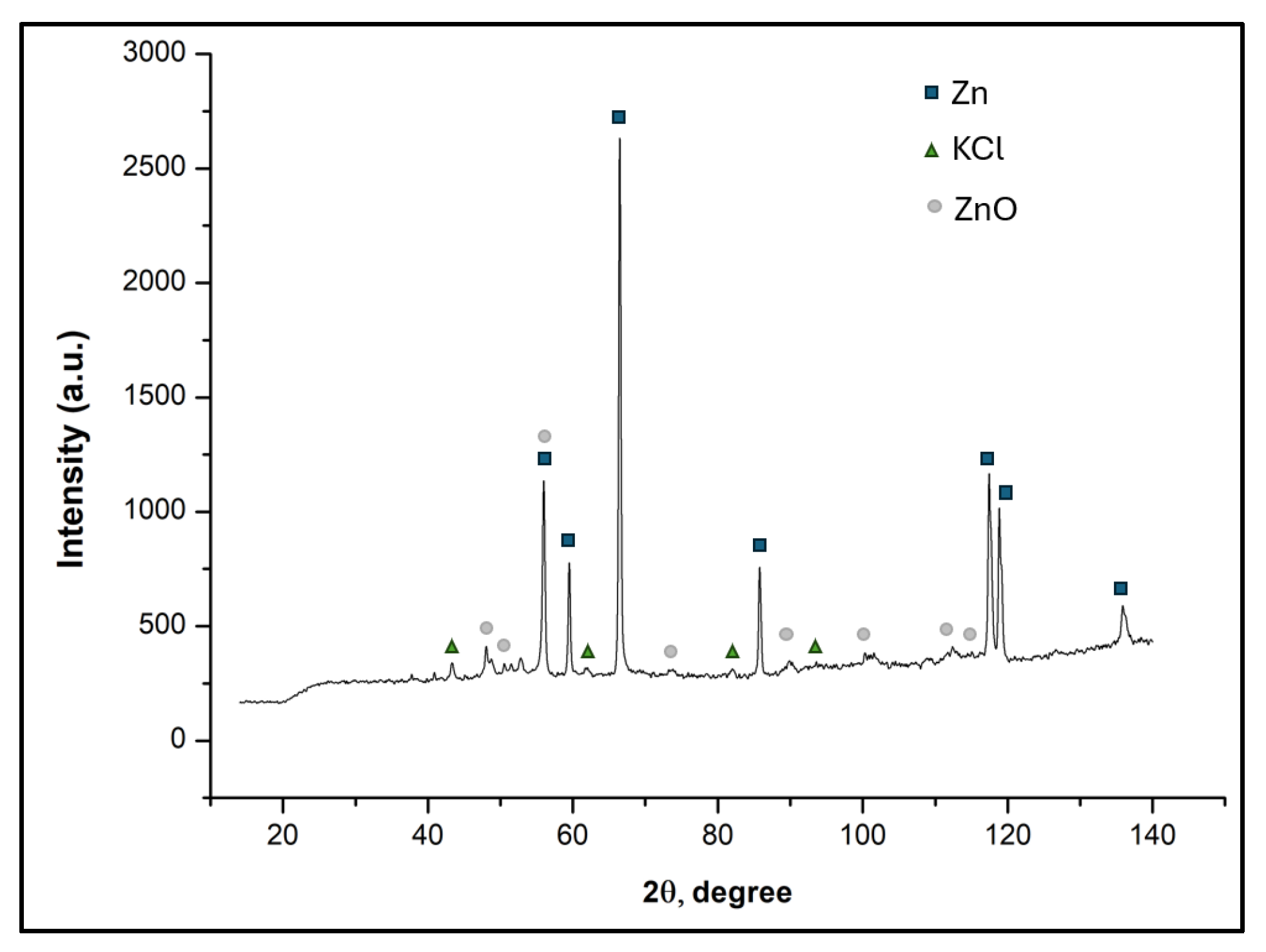
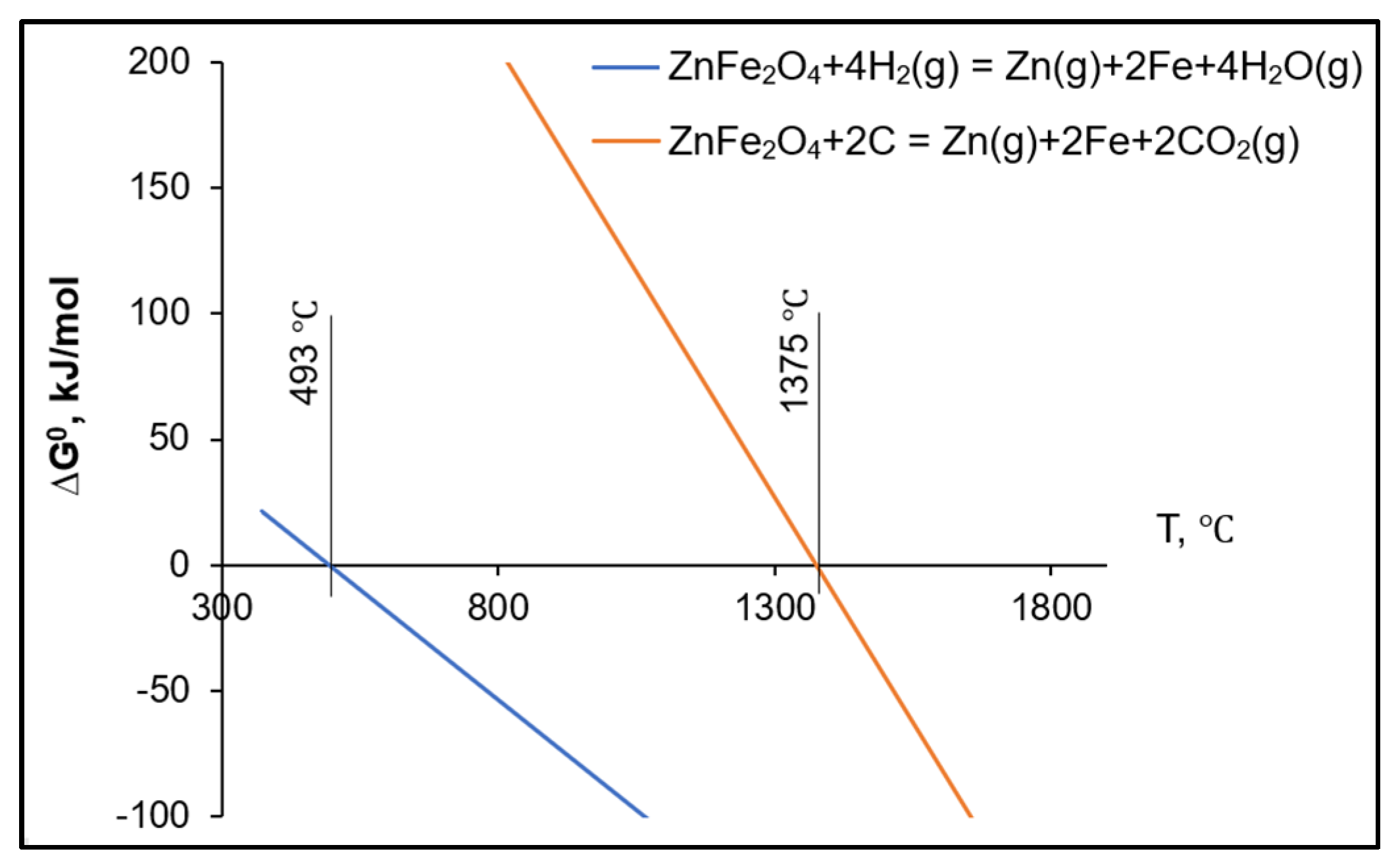
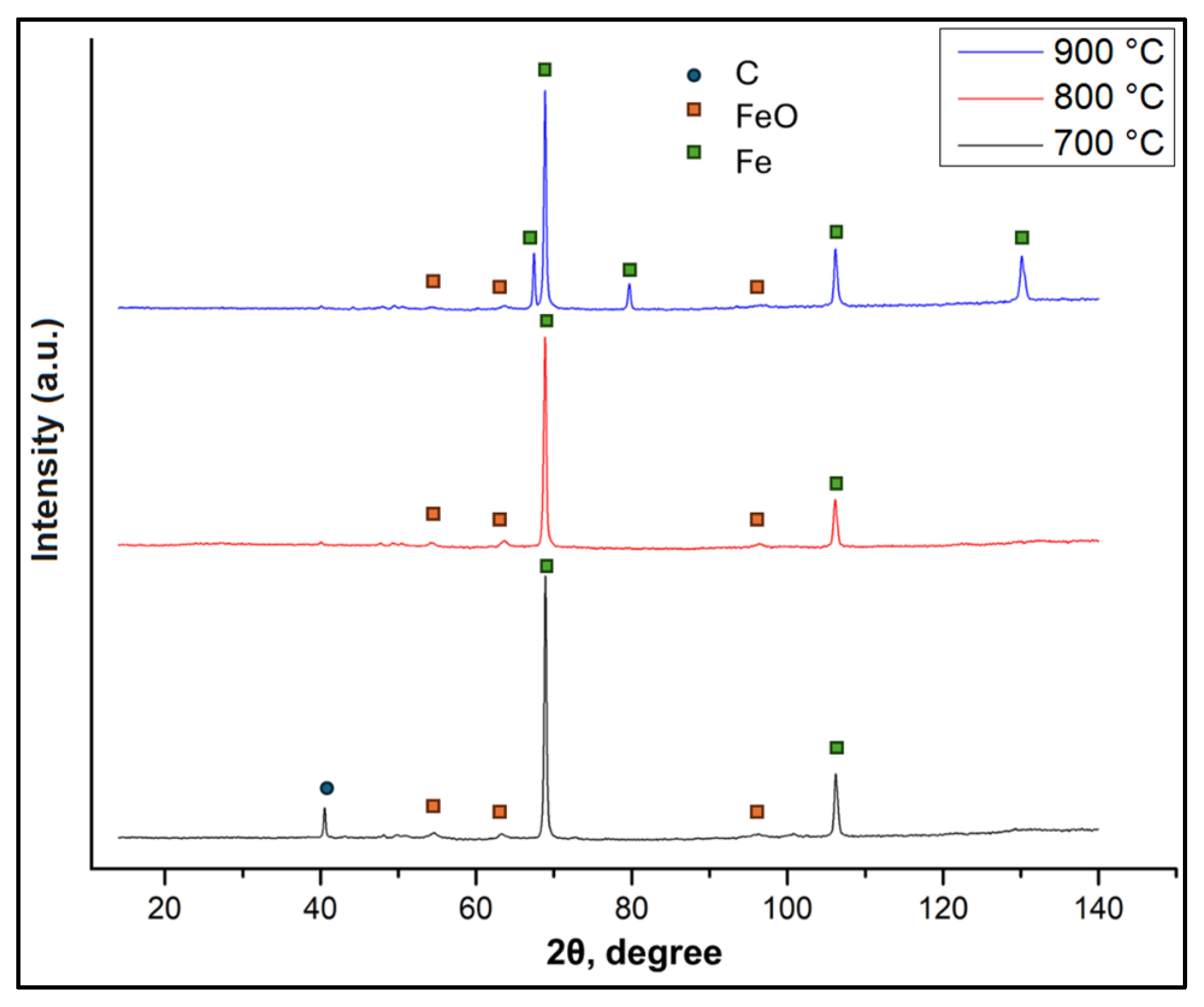
| Element | ZBD | CDQD | Briquette CDQD Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 wt.% | 8 wt.% | 10 wt.% | |||
| Fe | 35 | 5 | 33 | 33 | 32 |
| O | 29 | 25 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Zn | 18 | - | 17 | 16 | 16 |
| C | 6 | 67 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
| Na | 4 | - | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Mn | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Ca | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Cl | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Temperature (°C) | Weight Loss (%, ±0.5) CDQD Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 wt.% | 8 wt.% | 10 wt.% | |
| 700 | 31.3 | 31.1 | 34.9 |
| 800 | 31.4 | 33.3 | 38.4 |
| 900 | 40.3 | 40.4 | 42.1 |
| Temperature (°C) | Content (wt.%, ±1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 700 °C | 800 °C | 900 °C | |
| Fe | 33 | 55 | 59 | 66 |
| O | 29 | 19 | 18 | 13 |
| Zn | 17 | – | – | – |
| C | 9 | 11 | 9 | 5 |
| Temperature, (°C) | Content (wt.%, ±1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 700 °C | 800 °C | 900 °C | |
| Fe | 33 | 49 | 64 | 68 |
| O | 29 | 19 | 12 | 12 |
| Zn | 16 | – | – | – |
| C | 10 | 14 | 8 | 5 |
| Temperature, (°C) | Content (wt.%, ±1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 700 °C | 800 °C | 900 °C | |
| Fe | 32 | 49 | 68 | 79 |
| O | 29 | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| Zn | 16 | – | – | – |
| C | 12 | 30 | 11 | 4 |
| Element | Content (wt.%, ±1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 800 °C | 900 °C | ||
| Zn | 16 | 51 | |
| C | 65 | 24 | |
| O | 16 | 13 | |
| Na | 2 | 4 | |
| Pb | 5 | 14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaidarov, T.B.; Khanna, R.; Khaidarov, B.B.; Li, K.; Suvorov, D.S.; Metlenkin, D.A.; Burmistrov, I.N.; Gorokhovsky, A.V.; Volokhov, S.V.; Kuznetsov, D.V. An Innovative Approach Toward Enhancing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Resource Recovery from Hazardous Zn-Bearing Dusts from Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062773
Khaidarov TB, Khanna R, Khaidarov BB, Li K, Suvorov DS, Metlenkin DA, Burmistrov IN, Gorokhovsky AV, Volokhov SV, Kuznetsov DV. An Innovative Approach Toward Enhancing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Resource Recovery from Hazardous Zn-Bearing Dusts from Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062773
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaidarov, Timur B., Rita Khanna, Bekzod B. Khaidarov, Kejiang Li, Dmitrii S. Suvorov, Dmitrii A. Metlenkin, Igor N. Burmistrov, Alexander V. Gorokhovsky, Sergey V. Volokhov, and Denis V. Kuznetsov. 2025. "An Innovative Approach Toward Enhancing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Resource Recovery from Hazardous Zn-Bearing Dusts from Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062773
APA StyleKhaidarov, T. B., Khanna, R., Khaidarov, B. B., Li, K., Suvorov, D. S., Metlenkin, D. A., Burmistrov, I. N., Gorokhovsky, A. V., Volokhov, S. V., & Kuznetsov, D. V. (2025). An Innovative Approach Toward Enhancing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Resource Recovery from Hazardous Zn-Bearing Dusts from Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking. Sustainability, 17(6), 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062773









