Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study provides a comprehensive spatial assessment of heavy metal (HM) contamination in both seawater and sediments along the RBSC, integrating data from 40 sampling stations across 12 transects;
- Unlike previous studies that focused on either seawater or sediments, this research combines both matrices to offer a more holistic view of contamination patterns and sources;
- The study evaluates compliance with Environmental Quality Standards (EQS), including maximum allowable concentrations (MAC) for seawater and effects range-low (ERL) thresholds for sediments, to assess potential environmental risks;
- PCA was applied to establish relationships between selected variables, i.e., HM concentrations and water depth, and identify contamination sources, distinguishing between natural inputs (e.g., Danube River, soil erosion) and anthropogenic sources (e.g., industrial discharges, maritime transport, wastewater outflows);
- The findings contribute to the understanding of heavy metal contamination dynamics in the northwestern Black Sea and offer scientific support for pollution mitigation and sustainable coastal management strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Seawater and Sediment Sampling and Characterization
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
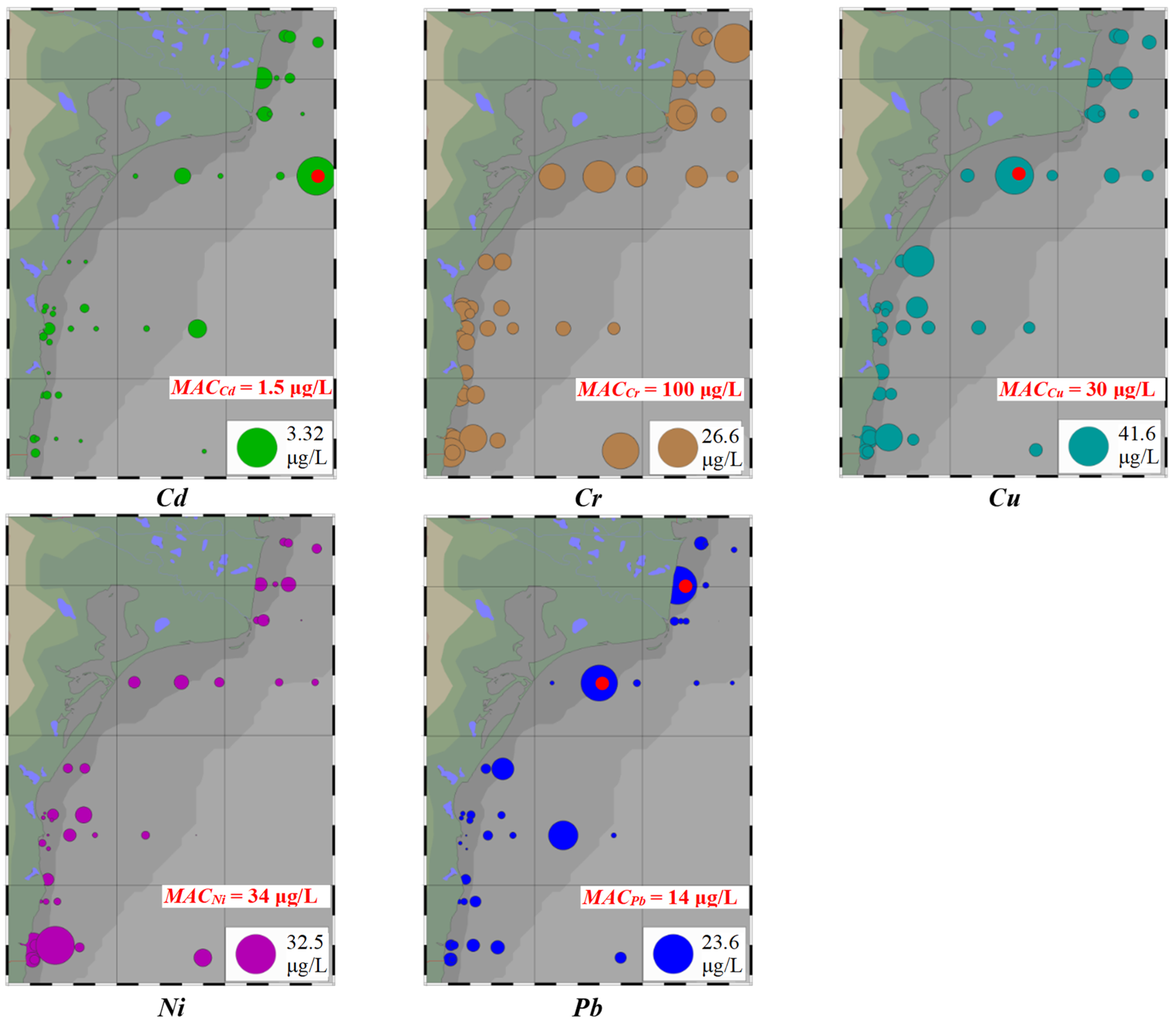
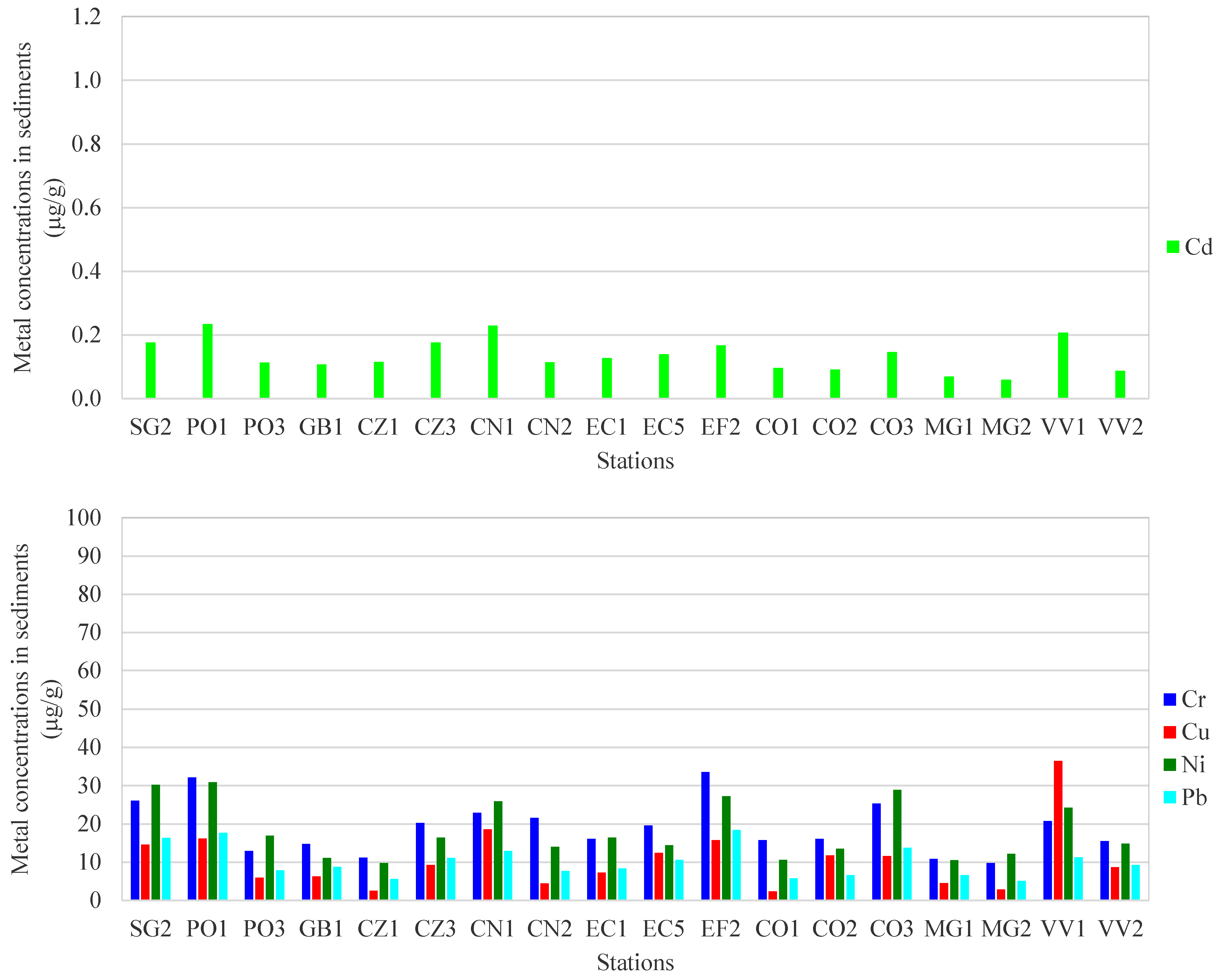
3.1. Metal Concentrations in Seawater
- (i)
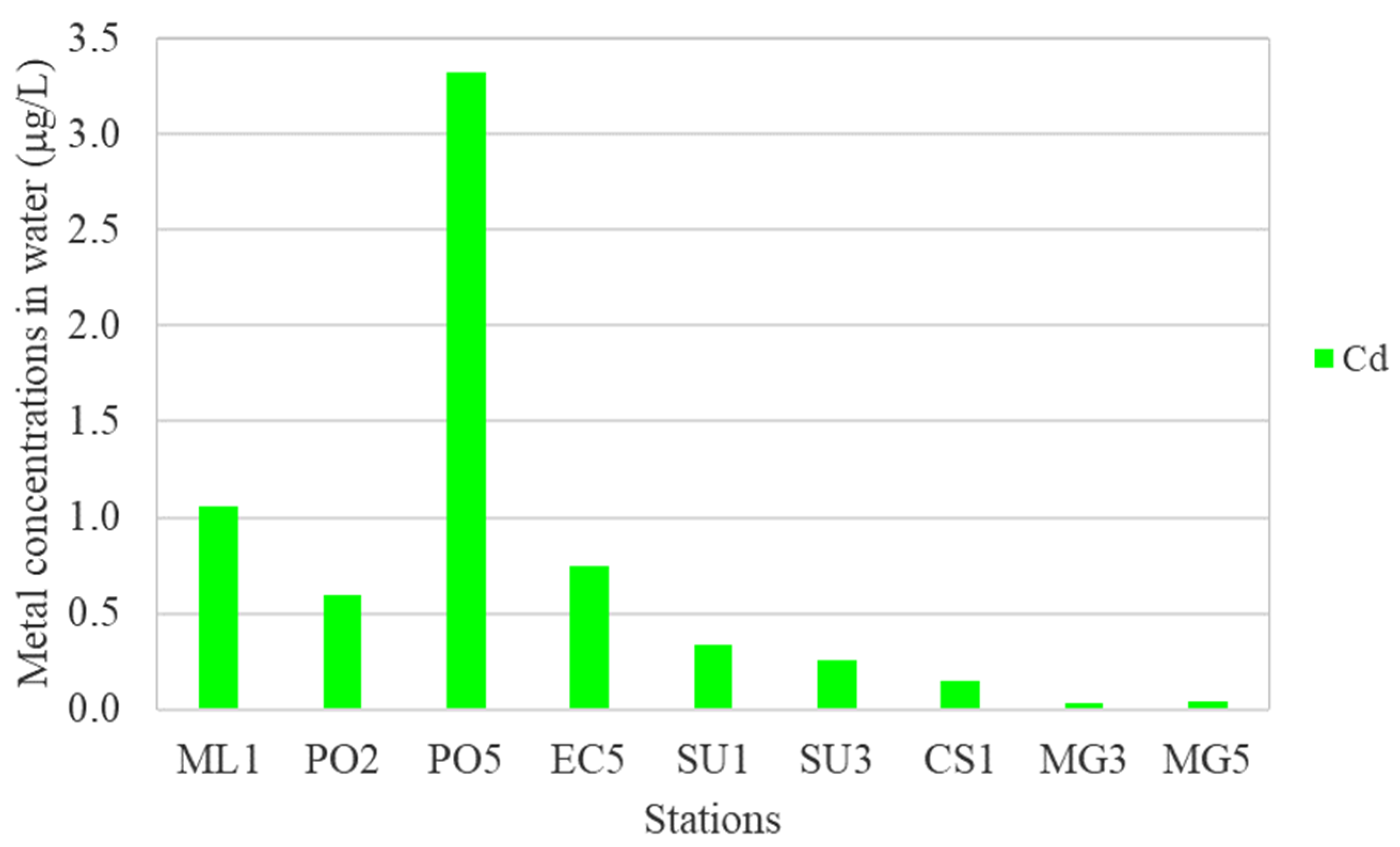
- Higher levels of Cd (0.495–3.320 μg/L) at stations ML1, SG2, PO2, PO5, and EC5; maximum level of Cd (found at PO5) was 2.2 times higher than MACCd (1.5 μg/L);
- (ii)
- Higher levels of Cr (13.12–26.60 μg/L) at stations SU3, SG2, PO2, MG3, MG5, and VV1; no level of Cr exceeded MACCr (100 μg/L);
- (iii)
- Higher levels of Cu (9.415–41.62 μg/L) at stations ML1, ML3, SG2, PO2, GB2, CZ3, MG1, and MG3; maximum level of Cu (found at PO2) was 1.4 times higher than MACCu (30 μg/L);
- (iv)
- Higher levels of Ni (14.20 μg/L and 32.48 μg/L) at stations MG1 and MG3; no level of Ni exceeded MACNi (34 μg/L);
- (v)
- Higher levels of Pb (7.751–23.58 μg/L) at stations ML1, PO2, GB2, and EC4; levels of Pb found at ML1 (23.58 μg/L) and PO2 (21.05 μg/L) were up to 1.7 times higher than MACPb (14 μg/L);
- (vi)
- Significant variability of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb (84.98% ≤ RSD ≤ 203.13%).
| Statistics | Metal Concentration in Water (μg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | |
| Minimum (MIN) | 0.011 | 1.174 | 1.120 | 0.027 | 0.001 |
| Maximum (MAX) | 3.320 | 26.60 | 41.62 | 32.48 | 23.58 |
| Mean (m) | 0.249 | 6.899 | 7.300 | 3.115 | 2.554 |
| Median | 0.082 | 4.704 | 5.016 | 1.782 | 0.763 |
| Quartile 25 | 0.051 | 3.821 | 3.713 | 0.621 | 0.391 |
| Quartile 75 | 0.192 | 7.173 | 6.757 | 3.336 | 1.974 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.061 | 5.863 | 7.819 | 5.428 | 5.188 |
| Relative standard deviation (RSD) (%) | 0.543 | 84.98 | 107.1 | 174.2 | 203.1 |
| Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) | 1.5 * | 100 ** | 30 ** | 34 * | 14 * |
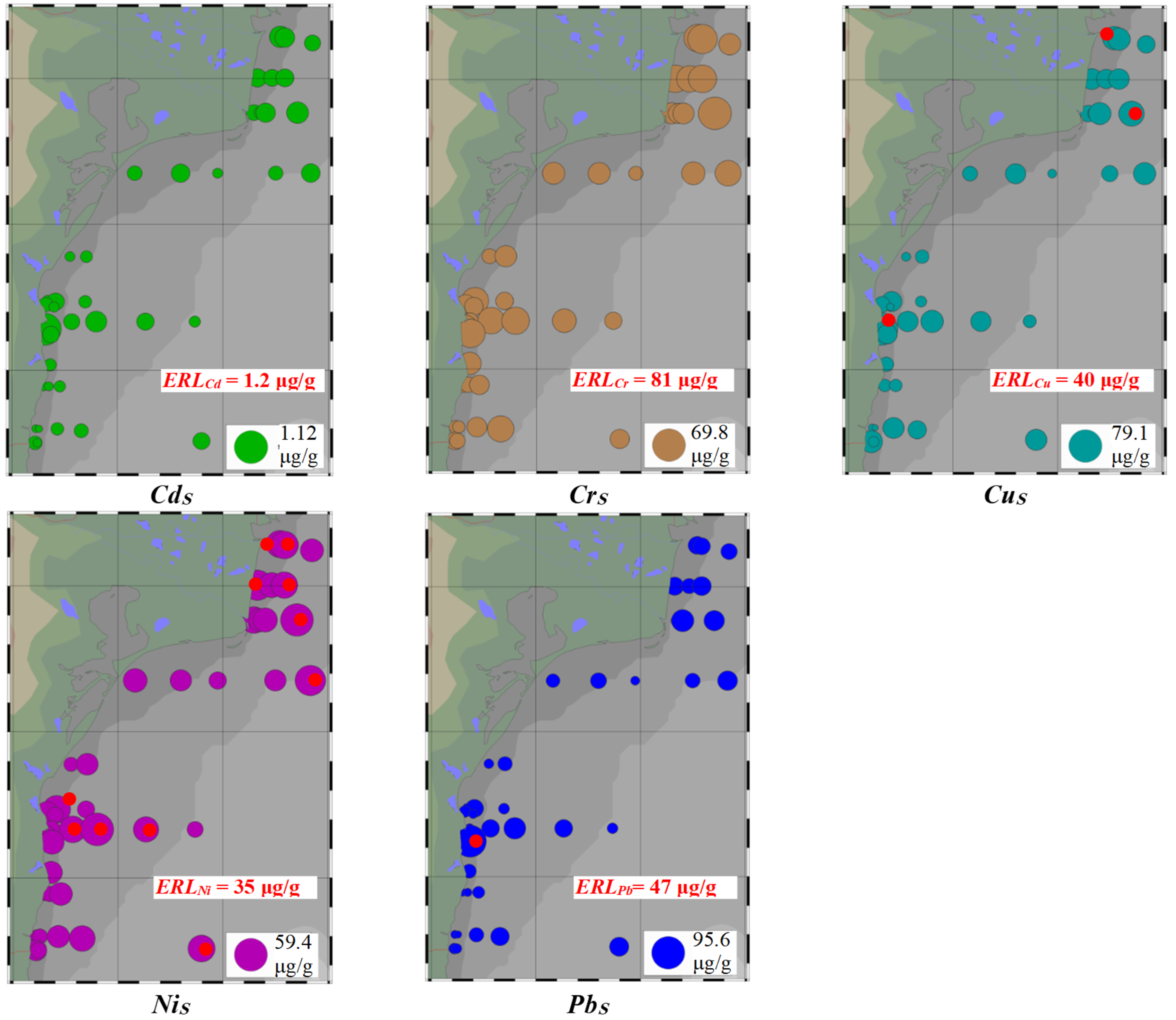
3.2. Metal Concentrations in Surface Sediments
- (i)
- All levels of CdS (0.059–1.124 μg/g) and CrS (9.760–69.77 μg/g) were lower than ERLCd (1.2 μg/g) and ERLCr (81 μg/g);
- (ii)
- The levels of CuS (2.362–79.14 μg/g) exceeded ERLCu (40 μg/g) at stations SU1 (by 4%), SG4 (by 19%), and CS1 (by 98%);
- (iii)
- The levels of NiS (9.693–59.35 μg/g) exceeded ERLNi (35 μg/g) at 11 stations (SU1, SU2, ML1, ML3, SG4, PO5, CZ2, EC2–4, and MG4) (by 1.0–70%), the values being higher by more than 20% at stations SU2, ML1, SG4, PO5, CZ2, and EC3;
- (iv)
- The levels of PbS (5.042–95.63 μg/g) exceeded ERLPb (47 μg/g) only at station CS2;
- (v)
- CdS, CrS, CuS, NiS, and PbS had a significant variability (45.91% ≤ RSD ≤ 72.80%).
| Statistics | Metal Concentration in Surface Sediments (μg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdS | CrS | CuS | NiS | PbS | |
| Minimum (MIN) | 0.059 | 9.760 | 2.362 | 9.693 | 5.042 |
| Maximum (MAX) | 1.124 | 69.77 | 79.14 | 59.35 | 95.63 |
| Mean (m) | 0.266 | 31.72 | 22.90 | 28.99 | 22.62 |
| Median | 0.226 | 29.85 | 21.81 | 28.15 | 20.34 |
| Quartile 25 | 0.137 | 20.04 | 11.00 | 16.39 | 10.24 |
| Quartile 75 | 0.342 | 45.67 | 32.74 | 38.74 | 30.42 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.188 | 14.98 | 15.61 | 13.31 | 16.47 |
| Relative standard deviation (RSD) (%) | 70.76 | 47.22 | 68.18 | 45.91 | 72.80 |
| Effects range-low (ERL) | 1.2 ** | 81 ** | 40 * | 35 * | 47 ** |
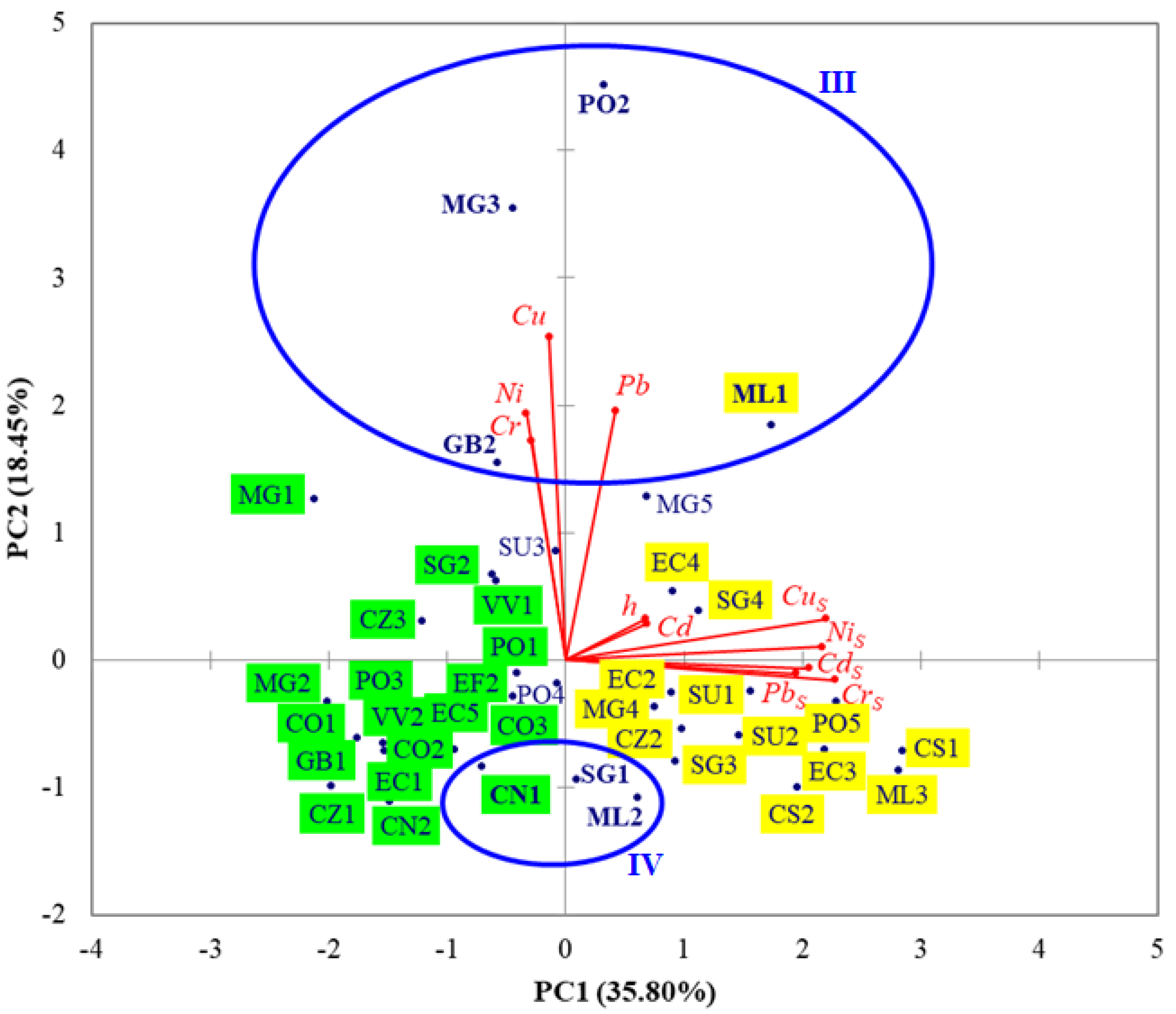
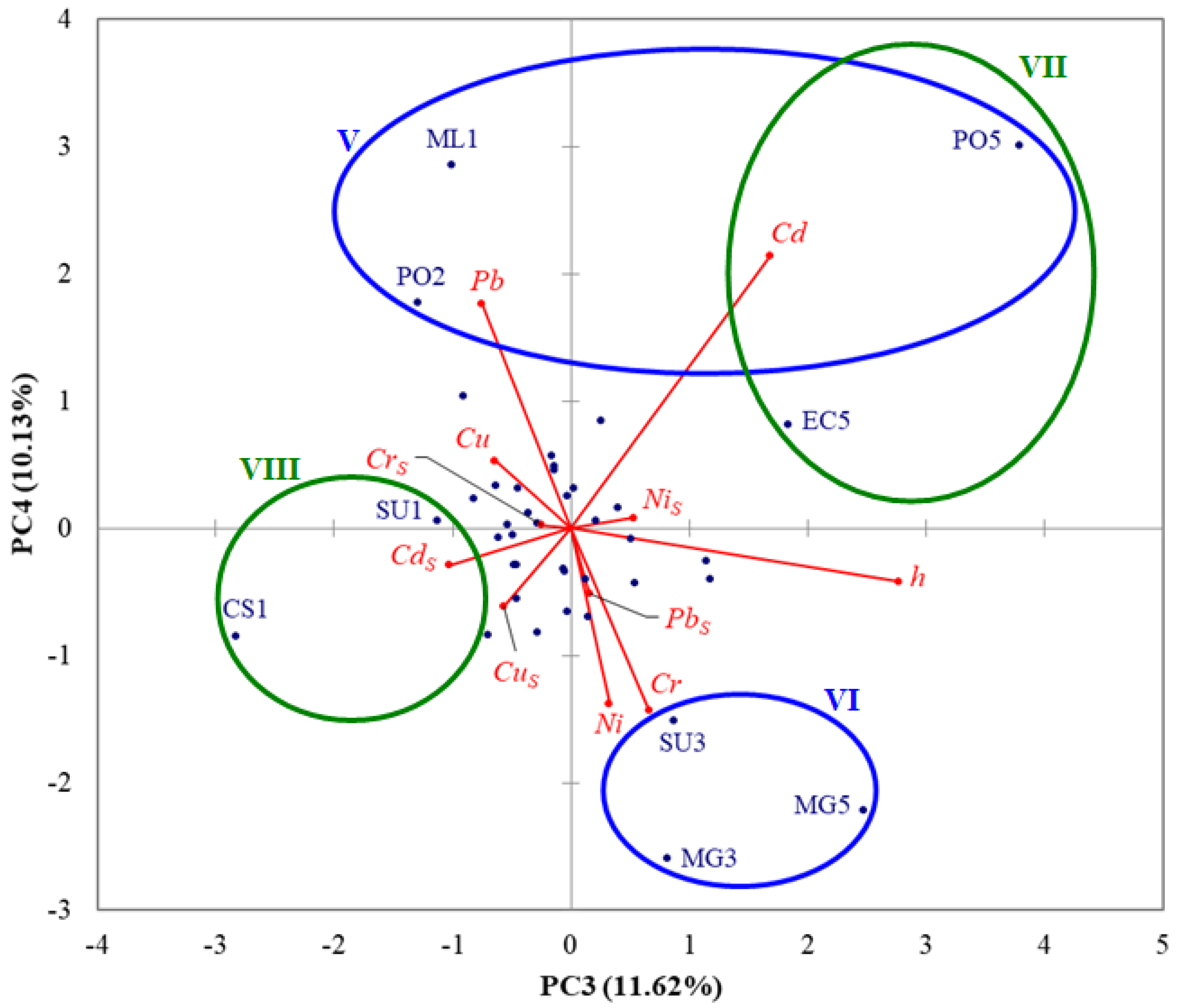
3.3. PCA Results
4. Discussion
- (i)
- Discrimination on PC1 and significant positive correlation coefficients between CdS, CrS, CuS, NiS, and PbS indicate that HMs in surface sediments likely came from common natural and anthropogenic sources, e.g., Danube River discharges, rock/soil weathering and erosion, agricultural runoff, port and construction activities, maritime and road transport, coastal tourism, petrochemical industry, wastewater discharges, offshore oil and gas extraction [36,38,39];
- (ii)
- The significant positive correlation coefficient between NiS and h highlights that Ni associated with finer carriers, including silt, clay, and organic matter, was transported offshore by currents and waves [36];
- (iii)
- Discrimination on PC2 and significant positive correlation coefficients between Cu and Cr, Cu and Ni, Cu and Pb emphasize common sources of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb in seawater at stations ML1, GB2, PO2, and MG3, e.g., port activities, maritime and road transport, urban and industrial discharges;
- (iv)
- Discrimination on PC3 indicates higher levels of Cd in seawater samples collected from deeper stations PO5 (h = 57 m) and EC5 (h = 54 m); a possible pathway of Cd contamination is the atmospheric deposition of airborne particles from industrial emissions, fossil fuel burning, and waste incineration [85];
- (v)
- Discrimination on PC4 reveals higher levels of Cd and Pb in seawater samples collected from stations ML1 and PO2, probably caused by the Danube discharges [4].
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krutov, A. (Ed.) BSC State of the Environment of the Black Sea (2009–2014/5); Publications of the Commission on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution (BSC): Istanbul, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Văidianu, N.; Tătui, F.; Ristea, M.; Stănică, A. Managing Coastal Protection through Multi-Scale Governance Structures in Romania. Mar. Policy 2020, 112, 103567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Ibáñez, C.; Lazar, L.; Raimbault, P.; Giani, M. Flow Regime and Nutrient-Loading Trends from the Largest South European Watersheds: Implications for the Productivity of Mediterranean and Black Sea’s Coastal Areas. Water 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L. (Ed.) ANEMONE Deliverable 2.1, 2021. Impact of the Rivers on the Black Sea Ecosystem; Editura CD Press: Bucharest, Romania, 2021; ISBN 978-606-528-528-6. [Google Scholar]
- Strokal, M.; Strokal, V.; Kroeze, C. The Future of the Black Sea: More Pollution in over Half of the Rivers. Ambio 2023, 52, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, L. (Ed.) ANEMONE Deliverable 2.2 “Anthropogenic Pressures and Impacts on the Black Sea Coastal Ecosystem”; Editura CD Press: Bucharest, Romania, 2021; ISBN 978-606-528-529-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bisinicu, E.; Abaza, V.; Boicenco, L.; Adrian, F.; Harcota, G.-E.; Marin, O.; Oros, A.; Pantea, E.; Spinu, A.; Timofte, F.; et al. Spatial Cumulative Assessment of Impact Risk-Implementing Ecosystem-Based Management for Enhanced Sustainability and Biodiversity in the Black Sea. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Spanu, A.; Boicenco, L.; Oros, A.; Damir, N.; Bisinicu, E.; Abaza, V.; Filimon, A.; Harcota, G.; Marin, O.; et al. Methodology for Prioritizing Marine Environmental Pressures under Various Management Scenarios in the Black Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1388877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, D.; Garrido-Pérez, M.C.; Nebot-Sanz, E.; Sales-Márquez, D. Source and Fate of Heavy Metals in Marine Sediments from a Semi-Enclosed Deep Embayment Subjected to Severe Anthropogenic Activities. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2011, 221, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asih, A.S.; Zamroni, A.; Alwi, W.; Sagala, S.T.; Putra, A.S. Assessment of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Seawater in the Coastal Areas around Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta Province, Indonesia. Iraqi Geol. J. 2022, 55, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Kuang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, H. Heavy Metals in Marine Surface Sediments of Daya Bay, Southern China: Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment, and Ecological Risk Assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 755873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, B.-S.; Liu, X.-L.; Li, C.-X. Spatial Variations and Potential Risks of Heavy Metals in Seawater, Sediments, and Living Organisms in Jiuzhen Bay, China. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 7971294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucşe, A.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Vasiliu, D.; Lupașcu, N.; Voica, C. Levels of Heavy Metal Concentration in M. Galloprovincialis Mollusc Species from NW Black Sea (Romania). U.P.B. Sci. Bull Ser. B 2021, 83, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pund, A.; Kurhe, A. A Review on Heavy Metals Impact and Marine Molluscs. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 2023, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajargah, M.F.; Azar, H. Investigating the Effects of Accumulation of Lead and Cadmium Metals in Fish and Its Impact on Human Health. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2023, 12, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morankar, N.H.; Kurhe, D.A.R. An Overview of the Impact of Heavy Metal Accumulation on Marine Molluscs. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 2023, 4, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bat, L. One Health: The Interface Between Fish and Human Health. Curr. World Environ. 2019, 14, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X. Heavy Metals in Seawater and Sediments from the Northern Liaodong Bay of China: Levels, Distribution and Potential Risks. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Du, D.; Mahmoud, E. Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Environments: Ecological Implications and Management Strategies: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, C.; Leitner, P.; Unfer, G.; Pulg, U.; Habersack, H.; Graf, W. The Role of Sediment and Sediment Dynamics in the Aquatic Environment. In Riverine Ecosystem Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- Özşeker, K.; Erüz, C.; Terzi, Y. Evaluation of Toxic Metals in Different Grain Size Fractions of Sediments of the Southeastern Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.W.; Langston, W.J. Bioavailability, Accumulation and Effects of Heavy Metals in Sediments with Special Reference to United Kingdom Estuaries: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1992, 76, 89–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, E.Y.; Buyukisik, B. Geochemical and Statistical Approach for Assessing Heavy Metal Accumulation in the Southern Black Sea Sediments. Ekoloji 2012, 21, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of Sediment Geochemical Properties on Heavy Metal Bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornero, V.; Hanke, G. Chemical Contaminants Entering the Marine Environment from Sea-Based Sources: A Review with a Focus on European Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negahdari, S.; Sabaghan, M.; Pirhadi, M.; Alikord, M.; Sadighara, P.; Darvishi, M.; Nazer, M. Potential Harmful Effects of Heavy Metals as a Toxic and Carcinogenic Agent in Marine Food-An Overview. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 52, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macken, A.; Giltrap, M.; Ryall, K.; Foley, B.; McGovern, E.; McHugh, B.; Davoren, M. A Test Battery Approach to the Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Cadmium and Copper Employing a Battery of Marine Bioassays. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, A.; Pantea, E.-D.; Ristea, E. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Wild Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819) during 2001–2023 and Potential Risks for Consumers: A Study on the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Science 2024, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damir, N.; Coatu, V.; Danilov, D.; Lazăr, L.; Oros, A. From Waters to Fish: A Multi-Faceted Analysis of Contaminants’ Pollution Sources, Distribution Patterns, and Ecological and Human Health Consequences. Fishes 2024, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaţchi, M.; Oros, A.; Coatu, V.; Costache, M.; Coprean, D.; Galaţchi, L.-D. Pollutant Bioaccumulation in Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Tissue, Fish Species of Commercial Interest at the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2017, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bat, L.; Şahin, F.; Öztekin, A. Heavy Metal Contamination of Pleuronectiformes Species from Sinop Coasts of the Black Sea. Sustain. Agri. Food Environ. Res. 2019, 7, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, E.; Öztekin, A.; Bat, L. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Black Sea: Evaluating Mussels. Curr. World Environ. 2018, 13, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-López, A.D.; Toniolo, M.A.; Colombo, C.V.; Rimondino, G.N.; Cuadrado, D.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Malanca, F.E. Marine Microdebris Pollution in Sediments from Three Environmental Coastal Areas in the Southwestern Argentine Atlantic. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, A.; Coatu, V.; Damir, N.; Danilov, D.; Ristea, E. Recent Findings on the Pollution Levels in the Romanian Black Sea Ecosystem: Implications for Achieving Good Environmental Status (GES) Under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (Directive 2008/56/EC). Sustainability 2024, 16, 9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucşe, A.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Vasiliu, D.; Rădulescu, F.; Lupaşcu, N.; Ispas, B.A. Spatial Distribution of Trace Elements and Potential Contamination Sources for Surface Sediments of the North-Western Black Sea, Romania. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1310164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secrieru, D.; Secrieru, A. Heavy Metal Enrichment of Man-Made Origin of Superficial Sediment on the Continental Shelf of the North-Western Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucse, A.; Vasiliu, D.; Balan, S.; Parvulescu, O.C.; Dobre, T. Heavy Metalspatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment in the Surface Sediments of the North—Western Black Sea Shelf. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, A. Monitoring and Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Romanian Black Sea Ecosystem during 2006-2018, in the Context of Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) 2008/56/EC Implementation. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2019, 49, 8–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Pan, Z.; Lin, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, K.; Lin, H. Integrated Insights into Potentially Hazardous Metals in Sediments of a Typical Bay under Long-Term Human Impacts: Implications for Coastal Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gâștescu, P. The Ecosystems of the Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve State-of the-Art. Risks Catastr. J. 2021, 28, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, N.; Jipa, D. Danube River Sediment Input and Its Interaction with the North-Western Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, A.M.; Tyler, A.N.; Stanica, A.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Catianis, I.; Panin, N. A Century of Human Interventions on Sediment Flux Variations in the Danube-Black Sea Transition Zone. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1068065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catianis, I.; Ungureanu, C.; Magagnini, L.; Ulazzi, E.; Campisi, T.; Stanica, A. Environmental Impact of the Midia Port—Black Sea (Romania), on the Coastal Sediment Quality. Open Geosci. 2016, 8, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, C.; Micu, A.-E.; Rusu, E. Multi-Criteria Analysis of the Mass Tourism Management Model Related to the Impact on the Local Community in Constanta City (Romania). Inventions 2021, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olteanu, A.C.; Dragan, C.; Stinga, V.G. Strategic Management of Constanta Port. Postmod. Open. 2022, 13, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucşe, A.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Vasiliu, D.; Mureșan, M. The Contents of Some Trace Elements (As, Br, Cu, Hg, Se, and Zn) in Mytilus Galloprovincialis Mussels From Agigea Port, Romania. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 899555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Vlas, O.; Pantea, E.; Boicenco, L.; Marin, O.; Abaza, V.; Filimon, A.; Bisinicu, E. Black Sea Eutrophication Comparative Analysis of Intensity between Coastal and Offshore Waters. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; ISBN 978-3-527-61399-1. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP/IOC/IAEA. UNEP/IOC/IAEA (1995). Manual for the Geochemical Analysis of Marine Sediments and Suspended Particulate Matter; Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies No. 63; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. Dissolved Trace Metal Distributions and Cu Speciation in the Southern Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Chem. 2015, 172, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, B.H.; Kamal, L.T.; Elbaz, R.M.; Khalifa, M.R.; Abdelnaser, A. From Contamination to Detection: The Growing Threat of Heavy Metals. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency, IAEA-MEL Training Manual on the Measurement of Heavy Metals in Environmental Samples; IAEA-MEL: Monaco-Ville, Monaco, 1999.
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. Available online: https://odv.awi.de (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- OJ L 327, 22.12.2000; Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- OJ L 226, 24.8.2013; Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- OJ L 164, 25.6.2008; Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Marine Environmental Policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- OFFICIAL GAZETTE no. 511 from June 13, 2006; Order No. 161/2006 for the Approval of the Regulation on the Classification of Surface Water Quality for Determining the Ecological Status of Water Bodies. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. (In Romanian)
- Panin, N.; Jipa, D.C.; Gomoiu, M.T.; Secrieru, D. Importance of Sedimentary Processes in Environmental Changes: Lower River Danube—Danube Delta—Western Black Sea System. In Environmental Degradation of the Black Sea: Challenges and Remedies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- ICPDR. Danube River Basin Management Plan Part A-Basin-Wide Overview Update 2021; ICPDR: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Simionov, I.-A.; Cristea, D.S.; Petrea, S.-M.; Mogodan, A.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G.; Baltag, E.S.; Jijie, R.; Strungaru, S.-A. Preliminary Investigation of Lower Danube Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Metals. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, E.O.; Solarte-Vasquez, M.C.; Inkinen, T. Smart Regulations in Maritime Governance: Efficacy, Gaps, and Stakeholder Perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 202, 116341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.J.; Berry, K.L.E.; Brinkman, D.L.; Kookana, R.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Melvin, S.D.; Neale, P.A.; Negri, A.P.; Puotinen, M.; Tsang, J.J.; et al. Sources, Presence and Potential Effects of Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the Marine Environments of the Great Barrier Reef and Torres Strait, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 135140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boicenco, L.; Abaza, V.; Anton, E.; Bisinicu, E.; Buga, L.; Coatu, V.; Damir, N.; Diaconeasa, D.; Dumitrache, C.; Filimon, A.; et al. Studiu Privind Elaborarea Raportului Privind Starea Ecologică a Ecosistemului Marin Marea Neagră Conform Cerintelor Art. 17 Ale Directivei Cadru Strategia Pentru Mediul Marin (2008/56/EC); European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- OSPAR Commission. 2019 Updated Audit Trail of OSPAR EACs and Other Assessment Criteria Used to Distinguish above and below Thresholds; Ospar Commission: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.; Morgan, L. The Potential for Biological Effects of Sediment-Sorbed Contaminants Tested in the National Status and Trends Program; US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Ocean Service: Silver Spring, MY, USA, 1991; Volume 52.
- Long, E.R.; Field, L.J.; MacDonald, D.D. Predicting Toxicity in Marine Sediments with Numerical Sediment Quality Guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of Adverse Biological Effects within Ranges of Chemical Concentrations in Marine and Estuarine Sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Riegl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Other Sediment Disturbances on Corals: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oros, A.; Coatu, V.; Secrieru, D.; Tiganus, D.; Vasiliu, D.; Atabay, H.; Beken, C.; Tolun, L.; Moncheva, S.; Bat, L. Results of the Assessment of the Western Black Sea Contamination Status in the Frame of the MISIS Joint Cruise. Cercet. Mar. 2016, 46, 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- Vignati, D.A.L.; Secrieru, D.; Bogatova, Y.I.; Dominik, J.; Céréghino, R.; Berlinsky, N.A.; Oaie, G.; Szobotka, S.; Stanica, A. Trace Element Contamination in the Arms of the Danube Delta (Romania/Ukraine): Current State of Knowledge and Future Needs. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 125, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, O.A.I.E.; Secrieru, D.; Bondar, C.; Szobotka, Ş.; Laura, D.U.Ţ.U.; Stănescu, I.; Opreanu, G.; Florin, D.U.Ţ.U.; Pojar, I.; Manta, T. Lower Danube River: Characterization of Sediments and Pollutants. Geo-Eco-Marina 2015, 21, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.B.; Mendiguchía, C.; Er-Raioui, H.; Marhraoui, M.; Lafraoui, G.; Oulad-Abdellah, M.K.; García-Vargas, M.; Moreno, C. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Marine Sediments of Tetouan Coast (North of Morocco): Natural and Anthropogenic Sources. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 4171–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbay, Ö. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Surface Sediments of the Mersin Bay, Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravisankar, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Kanagasabapathy, K.V.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Satapathy, K.K. Statistical Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments of East Coast of Tamilnadu Using Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (EDXRF). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 102, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Gao, Y.-P. An Unconstrained Ordination- and GIS-Based Approach for Identifying Anthropogenic Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Marine Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. Marine Pollution from Antifouling Paint Particles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lan, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, R.; Song, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, B. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Sediment from the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.M.; van Helmond, N.A.G.M.; Slomp, C.P.; Jilbert, T. Trace Metals in Coastal Marine Sediments: Natural and Anthropogenic Sources, Correlation Matrices, and Proxy Potentials. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, B.T. Uptake of Trace Metals by Sediments and Suspended Particulates: A Review. Hydrobiologia 1982, 91–92, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğiterhan, O.; Murray, J.W. Trace Metal Composition of Particulate Matter of the Danube River and Turkish Rivers Draining into the Black Sea. Mar. Chem. 2008, 111, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, A.E. Transportation of Pollutants of the Danube River into the (Western) Black Sea. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 5013–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The Pollution Conveyed by Urban Runoff: A Review of Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Shen, W. Effects of Industrial Land Conveyance on Coastal Marine Pollution: An Spatial Durbin Econometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; He, Q.; Liang, Y.; Peng, B.; Christie, P. Atmospheric Deposition of Cadmium in an Urbanized Region and the Effect of Simulated Wet Precipitation on the Uptake Performance of Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damir, N.; Danilov, D.; Oros, A.; Lazăr, L.; Coatu, V. Chemical Status Evaluation of the Romanian Black Sea Marine Environment Based on Benthic Organisms’ Contamination. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2022, 52, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadrami, H.A.; Mbadugha, L.; Paton, G.I. Hazard and Risk Assessment of Human Exposure to Toxic Metals Using in Vitro Digestion Assay. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2016, 28, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.L.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V. Ecological Effects of Contaminated Sediments Following a Decade of No Industrial Effluents Emissions: The Sediment Quality Triad Approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.; Palomares, M.L.D.; Lundquist, C.J. Safeguarding Seafood Security, Marine Biodiversity and Threatened Species: Can We Have Our Fish and Eat It Too? Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 826587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, S.; Costa, V.; Tramati, C.; Gianguzza, P.; Mazzola, A. Trophic Transfer of Trace Elements in an Isotopically Constructed Food Chain From a Semi-Enclosed Marine Coastal Area (Stagnone Di Marsala, Sicily, Mediterranean). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriil, A.M.; Angelidis, M.O. Metal and Organic Carbon Distribution in Water Column of a Shallow Enclosed Bay at the Aegean Sea Archipelago: Kalloni Bay, Island of Lesvos, Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Duca, F.; Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; De Simone, B.; Russo, I.; Nubi, R.; Triassi, M. Assessing Heavy Metals in the Sele River Estuary: An Overview of Pollution Indices in Southern Italy. Toxics 2024, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Bogalecka, M. The Baltic Sea under Anthropopressure—The Sea of Paradoxes. Water 2022, 14, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremling, K.; Tokos, J.J.S.; Brügmann, L.; Hansen, H.-P. Variability of Dissolved and Particulate Trace Metals in the Kiel and Mecklenburg Bights of the Baltic Sea, 1990–1992. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brügmann, L.; Hallberg, R.; Larsson, C.; Löffler, A. Trace Metal Speciation in Sea and Pore Water of the Gotland Deep, Baltic Sea, 1994. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlawatsch, S.; Neumann, T.; van den Berg, C.M.G.; Kersten, M.; Harff, J.; Suess, E. Fast-Growing, Shallow-Water Ferro-Manganese Nodules from the Western Baltic Sea: Origin and Modes of Trace Element Incorporation. Mar. Geol. 2002, 182, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozińska, N.; Bąkowska, M. Effects of Heavy Metals in Lake Water and Sediments on Bottom Invertebrates Inhabiting the Brackish Coastal Lake Łebsko on the Southern Baltic Coast. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, D.H.; Basiony, A.I.; El-Alfy, M.A. Mapping Heavy Metals Contamination and Eco-Risk along Mediterranean Sea Coast, Egypt. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 8645–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penezić, A.; Gašparović, B.; Cuculić, V.; Strmečki, S.; Djakovac, T.; Mlakar, M. Dissolved Trace Metals and Organic Matter Distribution in the Northern Adriatic, an Increasingly Oligotrophic Shallow Sea. Water 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migon, C.; Nicolas, E. The Trace Metal Recycling Component in the North-Western Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.M.; Soliman, N.F.; El-Saoud, A.A.; Okbah, M.A.; Abdelkhaleq, M.A. Temporal-Spatial Variations, Source Identification and Ecological Risks of Nutrients and Dissolved Metals in Seawater of the Southeastern Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Human. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2017, 23, 2097–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghani, S.; Hamdona, S.; Shakweer, L.; El Saharty, A. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface and Bottom Water along the Eastern Part of the Egyptian Mediterranean Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankéré, S.P.C.; Muller, F.L.L.; Burton, J.D.; Statham, P.J.; Guieu, C.; Martin, J.-M. Trace Metal Distributions in Shelf Waters of the Northwestern Black Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 1501–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remeikaitė-Nikienė, N.; Garnaga-Budrė, G.; Lujanienė, G.; Jokšas, K.; Stankevičius, A.; Malejevas, V.; Barisevičiūtė, R. Distribution of Metals and Extent of Contamination in Sediments from the South-Eastern Baltic sea (Lithuanian Zone). Oceanologia 2018, 60, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Luo, S.; Deng, S.; Huang, R.; Chen, B.; Deng, Z. Heavy Metal Pollution Status and Deposition History of Mangrove Sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 989584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.E.; Preda, M. Trace Metal Distribution Within Marine and Estuarine Sediments of Western Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia: Relation to Land Use and Setting. Geogr. Res. 2005, 43, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, A.P.; Priya, S.L.; Banerjee, K.; Hariharan, G.; Purvaja, R.; Ramesh, R. Heavy Metal Assessment Using Geochemical and Statistical Tools in the Surface Sediments of Vembanad Lake, Southwest Coast of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5899–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, E.Y. A New Assessment of Heavy Metal Contaminations in an eutrophicated Bay (Inner Izmir Bay, Turkey). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, D.; Bucse, A.; Lupascu, N.; Ispas, B.; Gheablau, C.; Stanescu, I. Assessment of the Metal Pollution in Surface Sediments of Coastal Tasaul Lake (Romania). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozebon, D.; Lima, E.C.; Maia, S.M.; Fachel, J.M.G. Heavy Metals Contribution of Non-Aqueous Fluids Used in Offshore Oil Drilling. Fuel 2005, 84, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, P.; Arienzo, M.; Imperato, M.; Naimo, D.; Nardi, G.; Stanzione, D. Distribution and Partition of Heavy Metals in Surface and Sub-Surface Sediments of Naples City Port. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of Heavy Metals on the Environment and Human Health: Novel Therapeutic Insights to Counter the Toxicity. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstner, U.; Wittmann, G.T.W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; ISBN 978-3-540-12856-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, B.; Pye, K.; Rae, J.E.; Rey, D. Sedimentological Characteristics, Heavy Metal Distribution and Magnetic Properties in Subtidal Sediments, Ria de Pontevedra, NW Spain. Sedimentology 2001, 48, 1277–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.-P.; Song, Z. Heavy Metal Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessments in Urban Mangrove Sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, South China. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21306–21316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richir, J. Trace Elements in Marine Environments: Occurrence, Threats and Monitoring with Special Focus on the Coastal Mediterranean. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 1000349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rabbi, A.H.M.F.; Anik, A.H.; Khan, R.; Al Masud, M.A.; Nedjoud, G.; Idris, A.M.; Rahman, M.N.; Senapathi, V. Source Distribution, Ecological Risks, and Controlling Factors of Heavy Metals in River Sediments: Receptor Model-Based Study in a Transboundary River Basin. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2025, 40, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Ali, M.; Hossain, D.; Al-Imran; Suzan Khan, M.; Begum, M.; Hasan Osman, M. Environmental Pollution with Heavy Metals: A Public Health Concern. In Heavy Metals—Their Environmental Impacts and Mitigation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Chi, G. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment from Bohai Bay, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A.; Johnston, E.L. Assessing Contaminated Sediments in the Context of Multiple Stressors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, K.; Chu, F.; Ge, Q.; Xu, D.; Han, X.; Ye, L. Sources and Spatial Variations of Heavy Metals in Offshore Sediments of the Western Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaune, R.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Roberts, H.H.; White, J.R. Trace Metal Concentrations in Marsh Profiles Under the Influence of an Emerging Delta (Atchafalaya River and Wax Lake Delta) Overlying a Several Thousand Year Old (Former)Mississippi River Delta Lobe. Soil. Sediment. Contam. Int. J. 2016, 25, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santschi, P.H.; Presley, B.J.; Wade, T.L.; Garcia-Romero, B.; Baskaran, M. Historical Contamination of PAHs, PCBs, DDTs, and Heavy Metals in Mississippi River Delta, Galveston Bay and Tampa Bay Sediment Cores. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 52, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Reza, A.H.M.S.; Hoyanagi, K. Anthropogenic and Natural Contribution of Potentially Toxic Elements in Southwestern Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna Delta, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, B.; Seddique, A.A.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, A.; Liu, J.; Shi, X. Distribution, Sources and Chemical Screening-Level Assessment of Toxic Metals in the Northern Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, G.; Dassenakis, M.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Lazogiannis, K. Sediment Quality Assessment in an Industrialized Greek Coastal Marine Area (Western Saronikos Gulf). Biogeosciences 2023, 20, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Xiong, Y. Heavy Metal Contamination in Surface Sediments: A Comprehensive, Large-Scale Evaluation for the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, D.; Liao, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z. Heavy Metals in Surficial Sediments of the Central Bohai Sea: Their Distribution, Speciation and Sources. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Rong, S.; Wu, J.; Yue, W.; Li, Q. Pollution Assessment and SSD-Based Ecological Assessment of Heavy Metals in Multimedia in the Coast of Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bing, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, L. Ecological Risk Assessment and Sources Identification of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a River–Reservoir System. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Nador Lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, G.F.; Draz, S.E.O.; El-Sadaawy, M.M.; Moneer, A.A. Sedimentology, Geochemistry, Pollution Status and Ecological Risk Assessment of Some Heavy Metals in Surficial Sediments of an Egyptian Lagoon Connecting to the Mediterranean Sea. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part. A 2014, 49, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L. (Ed.) ANEMONE Deliverable 2.3 “Black Sea State of Environment Based on ANEMONE Joint Cruise”; Editura CD Press: Bucharest, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Topa, C.; Murariu, G.; Calmuc, V.; Calmuc, M.; Arseni, M.; Serban, C.; Chitescu, C.; Georgescu, L. A Spatial–Seasonal Study on the Danube River in the Adjacent Danube Delta Area: Case Study—Monitored Heavy Metals. Water 2024, 16, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morina, A.; Morina, F.; Djikanović, V.; Spasić, S.; Krpo-Ćetković, J.; Lenhardt, M. Seasonal Variation in Element Concentrations in Surface Sediments of Three Rivers with Different Pollution Input in Serbia. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphanga, T.; Chidi, B.S.; Phungela, T.T.; Gqomfa, B.; Madonsela, B.S.; Malakane, K.C.; Lekata, S.; Shale, K. The Interplay between Temporal and Seasonal Distribution of Heavy Metals and Physiochemical Properties in Kaap River. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 6053–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devalloir, Q.; Fritsch, C.; Bangjord, G.; Bårdsen, B.-J.; Bourgeon, S.; Eulaers, I.; Bustnes, J.O. Long-Term Monitoring of Exposure to Toxic and Essential Metals and Metalloids in the Tawny Owl (Strix Aluco): Temporal Trends and Influence of Spatial Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, F.; Gu, Y.; Liang, R.; Wang, B.; Jordan, R.W.; Jiang, S. Anthropogenic Impacts on the Temporal Variation of Heavy Metals in Daya Bay (South China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, P.-F.; Salomon, M.; Assoumani, A.; Blard-Zakar, A. Multiyear and Seasonal Wide-Scale Indicators for French Surface Waters Contamination by WFD Substances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.K.; Miller, B.A.; Panigrahi, N.; Mishra, A. Exploring the Effect of Sampling Density on Spatial Prediction with Spatial Interpolation of Multiple Soil Nutrients at a Regional Scale. Land 2024, 13, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaenark, C.; Phankamolsil, Y.; Sawangproh, W. Ecological and Health Implications of Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Thai Fauna: A Systematic Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaynab, M.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Ameen, A.; Sharif, Y.; Ali, L.; Fatima, M.; Khan, K.A.; Li, S. Health and Environmental Effects of Heavy Metals. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidon, N.B.; Szabó, R.; Budai, P.; Lehel, J. Trophic Transfer and Biomagnification Potential of Environmental Contaminants (Heavy Metals) in Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, L.; Bao, R.; Hu, R.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Hydrodynamically–Driven Distribution and Remobilization of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments around the Coastal Area of Shandong Peninsula, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, K.; Guo, Z.; Pan, F. High Resolution Dissolved Heavy Metals in Sediment Porewater of a Small Estuary: Distribution, Mobilization and Migration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Xia, Y.; Li, D.; Bai, F.; Xu, C. Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metal and Its Fate in Intertidal Sediments: A Review. Processes 2024, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Wang, Z. Occurrence, Risk, and Source of Heavy Metals in Lake Water Columns and Sediment Cores in Jianghan Plain, Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, K.; Gao, S.; Liang, B.; Lu, J.; Fu, G. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in the Water, Sediment, and Organisms from The Sea Ranching Areas of Haizhou Bay in China. Water 2023, 15, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.; Williams, I.; Preston, J.; Clarke, N.; Odum, M.; O’Gorman, S. Ports in a Storm: Port-City Environmental Challenges and Solutions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Labianca, C.; Chen, L.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M.; Guo, B.; Sun, J.; Ding, S.; Wang, L. Sustainable Ex-Situ Remediation of Contaminated Sediment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Lee, D.K.; Choi, J. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Mitigation Measures in Environmental Impact Assessments: A Comprehensive Review of Development Projects in Korea. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olea-Olea, S.; Alcocer, J.; Armienta, M.A.; Oseguera, L.A. Geochemical Modeling Unravels the Water Chemical Changes along the Largest Mexican River. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 137, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R. The Marine Strategy Framework Directive: A New European Approach to the Regulation of the Marine Environment, Marine Natural Resources and Marine Ecological Services. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law. 2011, 29, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.M.; Harwell, M.C.; Jackson, C.A. Integrated Stakeholder Prioritization Criteria for Environmental Management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Area | Station | Water Depth, h (m) | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sulina | SU1 | 10 | 29.7717 | 45.1439 |
| 2 | Sulina | SU2 | 20 | 29.7934 | 45.1411 |
| 3 | Sulina | SU3 | 30 | 29.9242 | 45.1228 |
| 4 | Mila 9 | ML1 | 10 | 29.6630 | 45.0033 |
| 5 | Mila 9 | ML2 | 20 | 29.7333 | 45.0033 |
| 6 | Mila 9 | ML3 | 30 | 29.7928 | 45.0033 |
| 7 | Sf. Gheorghe | SG1 | 10 | 29.6475 | 44.8836 |
| 8 | Sf. Gheorghe | SG2 | 20 | 29.6783 | 44.8836 |
| 9 | Sf. Gheorghe | SG3 | 30 | 29.7017 | 44.8836 |
| 10 | Sf. Gheorghe | SG4 | 40 | 29.8529 | 44.8836 |
| 11 | Portita | PO1 | 10 | 29.0812 | 44.6767 |
| 12 | Portita | PO2 | 20 | 29.2992 | 44.6767 |
| 13 | Portita | PO3 | 30 | 29.4742 | 44.6767 |
| 14 | Portita | PO4 | 50 | 29.7500 | 44.6767 |
| 15 | Portita | PO5 | 57 | 29.9167 | 44.6767 |
| 16 | Gura Buhaz | GB1 | 10 | 28.7750 | 44.3897 |
| 17 | Gura Buhaz | GB2 | 20 | 28.8530 | 44.3897 |
| 18 | Cazino Mamaia | CZ1 | 10 | 28.6686 | 44.2396 |
| 19 | Cazino Mamaia | CZ2 | 20 | 28.7061 | 44.2350 |
| 20 | Cazino Mamaia | CZ3 | 30 | 28.8472 | 44.2347 |
| 21 | Constanta Nord | CN1 | 10 | 28.6607 | 44.2250 |
| 22 | Constanta Nord | CN2 | 20 | 28.7003 | 44.2167 |
| 23 | Constanta Est | EC1 | 14 | 28.6833 | 44.1667 |
| 24 | Constanta Est | EC2 | 28 | 28.7833 | 44.1667 |
| 25 | Constanta Est | EC3 | 36 | 28.9000 | 44.1667 |
| 26 | Constanta Est | EC4 | 47 | 29.1333 | 44.1667 |
| 27 | Constanta Est | EC5 | 54 | 29.3667 | 44.1667 |
| 28 | Constanta Sud | CS1 | 5 | 28.6561 | 44.1406 |
| 29 | Constanta Sud | CS2 | 20 | 28.6850 | 44.1217 |
| 30 | Eforie Sud | EF2 | 20 | 28.6816 | 44.0187 |
| 31 | Costinesti | CO1 | 10 | 28.6504 | 43.9450 |
| 32 | Costinesti | CO2 | 20 | 28.6739 | 43.9450 |
| 33 | Costinesti | CO3 | 30 | 28.7267 | 43.9450 |
| 34 | Mangalia | MG1 | 10 | 28.6133 | 43.7989 |
| 35 | Mangalia | MG2 | 20 | 28.6278 | 43.7989 |
| 36 | Mangalia | MG3 | 39 | 28.7156 | 43.7986 |
| 37 | Mangalia | MG4 | 53 | 28.8290 | 43.7921 |
| 38 | Mangalia | MG5 | 70 | 29.3983 | 43.7573 |
| 39 | Vama Veche | VV1 | 10 | 28.6105 | 43.7511 |
| 40 | Vama Veche | VV2 | 20 | 28.6211 | 43.7511 |
| No. | Variable | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | |||||
| 1 | Cd concentration in water | Cd | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.51 | 0.63 |
| 2 | Cr concentration in water | Cr | −0.11 | 0.59 | 0.20 | −0.42 |
| 3 | Cu concentration in water | Cu | −0.06 | 0.87 | −0.20 | 0.16 |
| 4 | Ni concentration in water | Ni | −0.13 | 0.66 | 0.10 | −0.41 |
| 5 | Pb concentration in water | Pb | 0.17 | 0.67 | −0.23 | 0.52 |
| 6 | Cd concentration in surface sediments | CdS | 0.83 | −0.02 | −0.31 | −0.09 |
| 7 | Cr concentration in surface sediments | CrS | 0.92 | −0.05 | −0.08 | 0.01 |
| 8 | Cu concentration in surface sediments | CuS | 0.89 | 0.11 | −0.17 | −0.18 |
| 9 | Ni concentration in surface sediments | NiS | 0.88 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.02 |
| 10 | Pb concentration in surface sediments | PbS | 0.79 | −0.04 | 0.05 | −0.15 |
| 11 | Water depth | h | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.84 | −0.12 |
| Variable | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | CdS | CrS | CuS | NiS | PbS | h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | −0.07 | 0.04 | −0.08 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.28 |
| Cr | −0.07 | 1 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.15 | −0.09 | −0.20 | 0.01 | −0.05 | −0.04 | 0.15 |
| Cu | 0.04 | 0.32 | 1 | 0.47 | 0.59 | −0.03 | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.07 | −0.07 | −0.05 |
| Ni | −0.08 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 1 | 0.11 | −0.14 | −0.15 | 0.04 | −0.07 | −0.10 | 0.11 |
| Pb | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.06 | −0.05 |
| CdS | 0.12 | −0.09 | −0.03 | −0.14 | 0.10 | 1 | 0.68 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 0.53 | −0.01 |
| CrS | 0.15 | −0.20 | −0.04 | −0.15 | 0.13 | 0.68 | 1 | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.18 |
| CuS | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.93 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.14 |
| NiS | 0.28 | −0.05 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.68 | 1 | 0.63 | 0.33 |
| PbS | 0.10 | −0.04 | −0.07 | −0.10 | 0.06 | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 1 | 0.24 |
| h | 0.28 | 0.15 | −0.05 | 0.11 | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ristea, E.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Lavric, V.; Oros, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062586
Ristea E, Pârvulescu OC, Lavric V, Oros A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062586
Chicago/Turabian StyleRistea, Elena, Oana Cristina Pârvulescu, Vasile Lavric, and Andra Oros. 2025. "Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062586
APA StyleRistea, E., Pârvulescu, O. C., Lavric, V., & Oros, A. (2025). Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Seawater and Sediments Along the Romanian Black Sea Coast: Spatial Distribution and Environmental Implications. Sustainability, 17(6), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062586










